Gastrointestinal Involvement in Primary Antibody Deficiencies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Epidemiology
2.1. Epidemiology of Selective IgA Deficiency (sIgAD)
2.2. Epidemiology of Common Variable Immunodeficiency (CVID)
2.3. Epidemiology of X-Linked Agammaglobulinemia (XLA)
3. Genetic Background
3.1. Monogenic Causes of sIgAD
3.2. Monogenic Causes of CVID
3.3. Genetic Background of XLA
4. Mechanisms of Immune Dysregulation
4.1. Immune System Dysregulation in sIgAD
4.2. Immune System Dysregulation in CVID
5. GI Infections
6. The Role of Microbiome
7. Non-Infectious Manifestation
7.1. Non-Infectious Complications of sIgAD
7.2. Non-Infectious Complications of CVID
7.3. GI Malignancies
8. Therapy of GI Complications
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abolhassani, H.; Azizi, G.; Sharifi, L.; Yazdani, R.; Mohsenzadegan, M.; Delavari, S.; Sohani, M.; Shirmast, P.; Chavoshzadeh, Z.; Mahdaviani, S.A.; et al. Global systematic review of primary immunodeficiency registries. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2020, 16, 717–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousfiha, A.; Moundir, A.; Tangye, S.G.; Picard, C.; Jeddane, L.; Al-Herz, W.; Rundles, C.C.; Franco, J.L.; Holland, S.M.; Klein, C.; et al. The 2022 Update of IUIS Phenotypical Classification for Human Inborn Errors of Immunity. J. Clin. Immunol. 2022, 42, 1508–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fried, A.J.; Bonilla, F.A. Pathogenesis, diagnosis, and management of primary antibody deficiencies and infections. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2009, 22, 396–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Demirdag, Y.Y.; Gupta, S. Update on infections in primary antibody deficiencies. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 634181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballow, M. Primary immunodeficiency disorders: Antibody deficiency. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2002, 109, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brandtzaeg, P. Update on mucosal immunoglobulin A in gastrointestinal disease. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2010, 26, 554–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, H.E.; Cunningham-Rundles, C. Non-infectious complications of common variable immunodeficiency: Updated clinical spectrum, sequelae, and insights to pathogenesis. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Resnick, E.S.; Moshier, E.L.; Godbold, J.H.; Cunningham-Rundles, C. Morbidity and mortality in common variable immune deficiency over 4 decades. Blood 2012, 119, 1650–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tak Manesh, A.; Azizi, G.; Heydari, A.; Kiaee, F.; Shaghaghi, M.; Hossein-Khannazer, N.; Yazdani, R.; Abolhassani, H.; Aghamohammadi, A. Epidemiology and pathophysiology of malignancy in common variable immunodeficiency? Allergol. Immunopathol 2017, 45, 602–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Więsik-Szewczyk, E.; Jahnz-Różyk, K. From infections to autoimmunity: Diagnostic challenges in common variable immunodeficiency. World J. Clin. Cases. 2020, 8, 3942–3955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Shen, N.; Vyse, T.J.; Anand, V.; Gunnarson, I.; Sturfelt, G.; Rantapää-Dahlqvist, S.; Elvin, K.; Truedsson, L.; Andersson, B.A.; et al. Selective IgA deficiency in autoimmune diseases. Mol. Med. 2011, 17, 1383–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rider, N.L.; Kutac, C.; Hajjar, J.; Scalchunes, C.; Seeborg, F.O.; Boyle, M.; Orange, J.S. Health-related quality of life in adult patients with common variable immunodeficiency disorders and impact of treatment. J. Clin. Immunol. 2017, 37, 461–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Andersen, J.B.; Midttun, K.; Feragen, K.J.B. Measuring quality of life of primary antibody deficiency patients using a disease-specific health-related quality of life questionnaire for common variable immunodeficiency (CVID_QoL). J. Patient Rep. Outcomes. 2019, 3, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasparyan, A.Y.; Ayvazyan, L.; Blackmore, H.; Kitas, G.D. Writing a narrative biomedical review: Considerations for authors, peer reviewers, and editors. Rheumatol. Int. 2011, 31, 1409–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdani, R.; Azizi, G.; Abolhassani, H.; Aghamohammadi, A. Selective IgA deficiency: Epidemiology, pathogenesis, clinical phenotype, diagnosis, prognosis and management. Scand. J. Immunol. 2017, 85, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yel, L. Selective IgA deficiency. J. Clin. Immunol. 2010, 30, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weifenbach, N.; Schneckenburger, A.A.C.; Lötters, S. Global Distribution of Common Variable Immunodeficiency (CVID) in the Light of the UNDP Human Development Index (HDI): A Preliminary Perspective of a Rare Disease. J. Immunol. Res. 2020, 2020, 8416124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardenas-Morales, M.; Hernandez-Trujillo, V.P. Agammaglobulinemia: From X-linked to autosomal forms of disease. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2022, 63, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdani, R.; Latif, A.; Tabassomi, F.; Abolhassani, H.; Azizi, G.; Rezaei, N.; Aghamohammadi, A. Clinical phenotype classification for selective immunoglobulin A deficiency. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2015, 11, 1245–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, M.A.; Lebwohl, B.; Reilly, N.R.; Green, P.H.R. Immunoglobulin A deficiency in celiac disease. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2012, 46, 850–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumar, V.; Jarzabek-Chorzelska, M.; Sulej, J.; Karnewska, K.; Farrell, T.; Jablonska, S. Celiac disease and immunoglobulin A deficiency: How effective are the serological methods of diagnosis? Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 2002, 9, 1295–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ludvigsson, J.F.; Neovius, M.; Hammarström, L. Association between IgA deficiency & other autoimmune conditions: A population-based matched cohort study. J. Clin. Immunol. 2014, 34, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pikkarainen, S.; Martelius, T.; Ristimäki, A.; Siitonen, S.; Seppänen, M.R.J.; Färkkilä, M. A high prevalence of gastrointestinal manifestations in common variable immunodeficiency. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 114, 648–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Janssen, L.M.A.; van der Flier, M.; de Vries, E. Lessons learned from the clinical presentation of common variable immunodeficiency disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 620709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawat, A.; Jindal, A.K.; Suri, D.; Vignesh, P.; Gupta, A.; Saikia, B.; Minz, R.W.; Banday, A.Z.; Tyagi, R.; Arora, K.; et al. Clinical and genetic profile of X-linked agammaglobulinemia: A multicenter experience from India. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 612323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winkelstein, J.A.; Marino, M.C.; Lederman, H.M.; Jones, S.M.; Sullivan, K.; Burks, A.W.; Conley, M.E.; Cunningham-Rundles, C.; Ochs, H.D. X-linked agammaglobulinemia: Report on a United States registry of 201 patients. Medicine 2006, 85, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lougaris, V.; Soresina, A.; Baronio, M.; Montin, D.; Martino, S.; Signa, S.; Volpi, S.; Zecca, M.; Marinoni, M.; Baselli, L.A.; et al. Long-term follow-up of 168 patients with X-linked agammaglobulinemia reveals increased morbidity and mortality. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 146, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.-S.; Lee, H.-C.; Lee, K.-M.; Gong, Y.-N.; Shih, S.-R. Enterovirus and Encephalitis. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliday, E.; Winkelstein, J.; Webster, A.D.B. Enteroviral infections in primary immunodeficiency (PID): A survey of morbidity and mortality. J. Infect. 2003, 46, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, Z.A.; Abramova, I.; Aldave, J.C.; Al-Herz, W.; Bezrodnik, L.; Boukari, R.; Bousfiha, A.A.; Cancrini, C.; Condino-Neto, A.; Dbaibo, G.; et al. X-linked agammaglobulinemia (XLA):phenotype, diagnosis, and therapeutic challenges around the world. World Allergy Organ. J. 2019, 12, 100018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hernandez-Trujillo, V.P.; Scalchunes, C.; Cunningham-Rundles, C.; Ochs, H.D.; Bonilla, F.A.; Paris, K.; Yel, L.; Sullivan, K.E. Autoimmunity and inflammation in X-linked agammaglobulinemia. J. Clin. Immunol. 2014, 34, 627–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tangye, S.G.; Al-Herz, W.; Bousfiha, A.; Cunningham-Rundles, C.; Franco, J.L.; Holland, S.M.; Klein, C.; Morio, T.; Oksenhendler, E.; Picard, C.; et al. Human Inborn Errors of Immunity: 2022 Update on the Classification from the International Union of Immunological Societies Expert Committee. J. Clin. Immunol. 2022, 42, 1473–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abolhassani, H.; Aghamohammadi, A.; Hammarström, L. Monogenic mutations associated with IgA deficiency. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2016, 12, 1321–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lázár-Molnár, E.; Snyder, M. The role of human leukocyte antigen in celiac disease diagnostics. Clin. Lab. Med. 2018, 38, 655–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghamohammadi, A.; Mohammadi, J.; Parvaneh, N.; Rezaei, N.; Moin, M.; Espanol, T.; Hammarstrom, L. Progression of selective IgA deficiency to common variable immunodeficiency. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2008, 147, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lougaris, V.; Sorlini, A.; Monfredini, C.; Ingrasciotta, G.; Caravaggio, A.; Lorenzini, T.; Baronio, M.; Cattalini, M.; Meini, A.; Ruggeri, L.; et al. Clinical and laboratory features of 184 Italian pediatric patients affected with selective IgA deficiency (SIgAD): A longitudinal single-center study. J. Clin. Immunol. 2019, 39, 470–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogaert, D.J.A.; Dullaers, M.; Lambrecht, B.N.; Vermaelen, K.Y.; de Baere, E.; Haerynck, F. Genes associated with common variable immunodeficiency: One diagnosis to rule them all? J. Med. Genet. 2016, 53, 575–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aggarwal, V.; Banday, A.Z.; Jindal, A.K.; Das, J.; Rawat, A. Recent advances in elucidating the genetics of common variable immunodeficiency. Genes Dis. 2020, 7, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Valles-Ibáñez, G.; Esteve-Solé, A.; Piquer, M.; González-Navarro, E.A.; Hernandez-Rodriguez, J.; Laayouni, H.; González-Roca, E.; Plaza-Martin, A.M.; Deyà-Martínez, Á.; Martín-Nalda, A.; et al. Evaluating the genetics of common variable immunodeficiency: Monogenetic model and beyond. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimall, J.R.; Hagin, D.; Hajjar, J.; Henrickson, S.E.; Hernandez-Trujillo, H.S.; Tan, Y.; Kobrynski, L.; Paris, K.; Torgerson, T.R.; Verbsky, J.W.; et al. Use of genetic testing for primary immunodeficiency patients. J. Clin. Immunol. 2018, 38, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.M.; Patterson, S.J.; Levings, M.K. The role of the PI3K signaling pathway in CD4(+) T cell differentiation and function. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Limon, J.J.; Fruman, D.A. Akt and mTOR in B cell activation and differentiation. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Buchbinder, E.I.; Desai, A. CTLA-4 and PD-1 pathways: Similarities, differences, and implications of their inhibition. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 39, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oyewole-Said, D.; Konduri, V.; Vazquez-Perez, J.; Weldon, S.A.; Levitt, J.M.; Decker, W.K. Beyond T-cells: Functional characterization of CTLA-4 expression in immune and non-immune cell types. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 608024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broderick, L.; Yost, S.; Li, D.; McGeough, M.D.; Booshehri, L.M.; Guaderrama, M.; Brydges, S.D.; Kucharova, K.; Patel, N.C.; Harr, M.; et al. Mutations in topoisomerase IIβ result in a B cell immunodeficiency. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Conley, M.E.; Broides, A.; Hernandez-Trujillo, V.; Howard, V.; Kanegane, H.; Miyawaki, T.; Shurtleff, S.A. Genetic analysis of patients with defects in early B-cell development. Immunol. Rev. 2005, 203, 216–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middendorp, S.; Dingjan, G.M.; Maas, A.; Dahlenborg, K.; Hendriks, R.W. Function of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase during B cell development is partially independent of its catalytic activity. J. Immunol. 2003, 171, 5988–5996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sawada, A.; Takihara, Y.; Kim, J.Y.; Matsuda-Hashii, Y.; Tokimasa, S.; Fujisaki, H.; Kubota, K.; Endo, H.; Onodera, T.; Ohta, H.; et al. A congenital mutation of the novel gene LRRC8 causes agammaglobulinemia in humans. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 1707–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Warnatz, K.; Schlesier, M. Flowcytometric phenotyping of common variable immunodeficiency. Cytometry B Clin. Cytom. 2008, 74, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nechvatalova, J.; Pikulova, Z.; Stikarovska, D.; Pesak, S.; Vlkova, M.; Litzman, J. B-lymphocyte subpopulations in patients with selective IgA deficiency. J. Clin. Immunol. 2012, 32, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemarquis, A.L.; Einarsdottir, H.K.; Kristjansdottir, R.N.; Jonsdottir, I.; Ludviksson, B.R. Transitional B cells and TLR9 responses are defective in selective IgA deficiency. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nagaishi, T.; Watabe, T.; Kotake, K.; Kumazawa, T.; Aida, T.; Tanaka, K.; Ono, R.; Ishino, F.; Usami, T.; Miura, T.; et al. Immunoglobulin A-specific deficiency induces spontaneous inflammation specifically in the ileum. Gut 2022, 71, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aghamohammadi, A.; Abolhassani, H.; Biglari, M.; Abolmaali, S.; Moazzami, K.; Tabatabaeiyan, M.; Asgarian-Omran, H.; Parvaneh, N.; Mirahmadian, M.; Rezaei, N. Analysis of switched memory B cells in patients with IgA deficiency. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2011, 156, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosserichter-Wagener, C.; Franco-Gallego, A.; Ahmadi, F.; Moncada-Vélez, M.; Dalm, V.A.; Rojas, J.L.; Orrego, J.C.; Correa Vargas, N.; Hammarström, L.; Schreurs, M.W.; et al. Defective formation of IgA memory B cells, Th1 and Th17 cells in symptomatic patients with selective IgA deficiency. Clin. Transl. Immunology 2020, 9, e1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, F.B.; Saulep-Easton, D.; Figgett, W.A.; Fairfax, K.A.; Mackay, F. The BAFF/APRIL system: Emerging functions beyond B cell biology and autoimmunity. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2013, 24, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fodor, I.; Serban, O.; Serban, D.E.; Farcau, D.; Man, S.C.; Dumitrascu, D.L. B cell-activating factor (BAFF) in children with inflammatory bowel disease. Pediatr. Res. 2021, 89, 1798–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Liu, X.; Guo, A.; Xiong, J.; Fu, Y.; Zou, K. B cell-activating factor as a new potential marker in inflammatory bowel disease. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2016, 61, 2608–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumric, M.; Zivkovic, P.M.; Ticinovic Kurir, T.; Vrdoljak, J.; Vilovic, M.; Martinovic, D.; Bratanic, A.; Lizatovic, I.K.; Bozic, J. Role of B-cell activating factor (BAFF) in inflammatory bowel disease. Diagnostics 2021, 12, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreou, N.P.; Legaki, E.; Dovrolis, N.; Boyanov, N.; Georgiou, K.; Gkouskou, K.; Gazouli, M. B-cell activating factor (BAFF) expression is associated with Crohn’s disease and can serve as a potential prognostic indicator of disease response to infliximab treatment. Dig. Liver Dis. 2021, 53, 574–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Th Thorarinsdottir, K.; Camponeschi, A.; Gjertsson, I.; Mårtensson, I.-L. CD21 -/low B cells: A Snapshot of a Unique B Cell Subset in Health and Disease. Scand. J. Immunol. 2015, 82, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reincke, M.E.; Payne, K.J.; Harder, I.; Strohmeier, V.; Voll, R.E.; Warnatz, K.; Keller, B. The Antigen Presenting Potential of CD21low B Cells. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 535784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unger, S.; Seidl, M.; van Schouwenburg, P.; Rakhmanov, M.; Bulashevska, A.; Frede, N.; Grimbacher, B.; Pfeiffer, J.; Schrenk, K.; Munoz, L.; et al. The TH1 phenotype of follicular helper T cells indicates an IFN-γ-associated immune dysregulation in patients with CD21low common variable immunodeficiency. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 730–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Isnardi, I.; Ng, Y.-S.; Menard, L.; Meyers, G.; Saadoun, D.; Srdanovic, I.; Samuels, J.; Berman, J.; Buckner, J.H.; Cunningham-Rundles, C.; et al. Complement receptor 2/CD21- human naive B cells contain mostly autoreactive unresponsive clones. Blood 2010, 115, 5026–5036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Freudenhammer, M.; Voll, R.E.; Binder, S.C.; Keller, B.; Warnatz, K. Naive- and Memory-like CD21low B Cell Subsets Share Core Phenotypic and Signaling Characteristics in Systemic Autoimmune Disorders. J. Immunol. 2020, 205, 2016–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrón-Ruiz, L.; López-Herrera, G.; Vargas-Hernández, A.; Mogica-Martínez, D.; García-Latorre, E.; Blancas-Galicia, L.; Espinosa-Rosales, F.J.; Santos-Argumedo, L. Lymphocytes and B-cell abnormalities in patients with common variable immunodeficiency (CVID). Allergol. Immunopathol. 2014, 42, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehr, C.; Kivioja, T.; Schmitt, C.; Ferry, B.; Witte, T.; Eren, E.; Vlkova, M.; Hernandez, M.; Detkova, D.; Bos, P.R.; et al. The EUROclass trial: Defining subgroups in common variable immunodeficiency. Blood 2008, 111, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsotti, N.S.; Almeida, R.R.; Costa, P.R.; Barros, M.T.; Kalil, J.; Kokron, C.M. IL-10-producing regulatory B cells are decreased in patients with common variable immunodeficiency. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlkova, M.; Ticha, O.; Nechvatalova, J.; Kalina, T.; Litzman, J.; Mauri, C.; Blair, P.A. Regulatory B cells in CVID patients fail to suppress multifunctional IFN-γ+ TNF-α+ CD4+ T cells differentiation. Clin. Immunol. 2015, 160, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannon, P.J.; Fuss, I.J.; Dill, S.; Friend, J.; Groden, C.; Hornung, R.; Yang, Z.; Yi, C.; Quezado, M.; Brown, M.; et al. Excess IL-12 but not IL-23 accompanies the inflammatory bowel disease associated with common variable immunodeficiency. Gastroenterology 2006, 131, 748–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, G.; Abolhassani, H.; Kiaee, F.; Tavakolinia, N.; Rafiemanesh, H.; Yazdani, R.; Mahdaviani, S.A.; Mohammadikhajehdehi, S.; Tavakol, M.; Ziaee, V.; et al. Autoimmunity and its association with regulatory T cells and B cell subsets in patients with common variable immunodeficiency. Allergol. Immunopathol. 2018, 46, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azizi, G.; Hafezi, N.; Mohammadi, H.; Yazdani, R.; Alinia, T.; Tavakol, M.; Aghamohammadi, A.; Mirshafiey, A. Abnormality of regulatory T cells in common variable immunodeficiency. Cell Immunol. 2017, 315, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Shi, T.; Zhong, C.; Wang, Y.; Chang, M.; Liu, X. IL-10 and IL-10 receptor mutations in very early onset inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology Res. 2017, 10, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, G.K.; Huissoon, A.P. T-cell abnormalities in common variable immunodeficiency: The hidden defect. J. Clin. Pathol. 2016, 69, 672–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Azizi, G.; Rezaei, N.; Kiaee, F.; Tavakolinia, N.; Yazdani, R.; Mirshafiey, A.; Aghamohammadi, A. T-cell abnormalities in common variable immunodeficiency. J. Investig. Allergol Clin. Immunol. 2016, 26, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malphettes, M.; Gérard, L.; Carmagnat, M.; Mouillot, G.; Vince, N.; Boutboul, D.; Bérezné, A.; Nove-Josserand, R.; Lemoing, V.; Tetu, L.; et al. Late-onset combined immune deficiency: A subset of common variable immunodeficiency with severe T cell defect. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 49, 1329–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameratunga, R. Assessing disease severity in common variable immunodeficiency disorders (CVID) and CVID-like disorders. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aytekin, C.; Tuygun, N.; Gokce, S.; Dogu, F.; Ikinciogullari, A. Selective IgA deficiency: Clinical and laboratory features of 118 children in Turkey. J. Clin. Immunol. 2012, 32, 961–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludvigsson, J.F.; Neovius, M.; Ye, W.; Hammarström, L. IgA deficiency and risk of cancer: A population-based matched cohort study. J. Clin. Immunol. 2015, 35, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magen, E.; Waitman, D.A.; Goldstein, N.; Schlesinger, M.; Dickstein, Y.; Kahan, N.R. Helicobacter pylori infection in patients with selective immunoglobulin A deficiency. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2016, 184, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motta-Raymundo, A.; Rosmaninho, P.; Santos, D.F.; Ferreira, R.D.; Silva, S.P.; Ferreira, C.; Sousa, A.E.; Silva, S.L. Contribution of Helicobacter pylori to the inflammatory complications of common variable immunodeficiency. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 834137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhalla, F.; Da Silva, S.P.; Lucas, M.; Travis, S.; Chapel, H. Review of gastric cancer risk factors in patients with common variable immunodeficiency disorders, resulting in a proposal for a surveillance programme. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2011, 165, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ammann, A.J.; Hong, R. Selective IgA deficiency: Presentation of 30 cases and a review of the literature. Medicine 1971, 50, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zinneman, H.H.; Kaplan, A.P. The association of giardiasis with reduced intestinal secretory immunoglobulin A. Am. J. Dig. Dis. 1972, 17, 793–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyworth, M.F.; Carlson, J.R.; Ermak, T.H. Clearance of Giardia muris infection requires helper/inducer T lymphocytes. J. Exp. Med. 1987, 165, 1743–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agarwal, S.; Mayer, L. Pathogenesis and treatment of gastrointestinal disease in antibody deficiency syndromes. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009, 124, 658–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oksenhendler, E.; Gérard, L.; Fieschi, C.; Malphettes, M.; Mouillot, G.; Jaussaud, R.; Viallard, J.F.; Gardembas, M.; Galicier, L.; Schleinitz, N.; et al. Infections in 252 patients with common variable immunodeficiency. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 46, 1547–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Ven, A.A.J.M.; Janssen, W.J.M.; Schulz, L.S.; van Loon, A.M.; Voorkamp, K.; Sanders, E.A.M.; Kusters, J.G.; Nierkens, S.; Boes, M.; Wensing, A.M.; et al. Increased prevalence of gastrointestinal viruses and diminished secretory immunoglobulin A levels in antibody deficiencies. J. Clin. Immunol. 2014, 34, 962–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodward, J.; Gkrania-Klotsas, E.; Kumararatne, D. Chronic Norovirus infection and common variable immunodeficiency. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2017, 188, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Woodward, J.M.; Gkrania-Klotsas, E.; Cordero-Ng, A.Y.; Aravinthan, A.; Bandoh, B.N.; Liu, H.; Davies, S.; Zhang, H.; Stevenson, P.; Curran, M.D.; et al. The role of chronic Norovirus infection in the enteropathy associated with common variable immunodeficiency. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 110, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanitsch, L.; Baumann, U.; Boztug, K.; Burkhard-Meier, U.; Fasshauer, M.; Habermehl, P.; Hauck, F.; Klock, G.; Liese, J.; Meyer, O.; et al. Treatment and management of primary antibody deficiency: German interdisciplinary evidence-based consensus guideline. Eur. J. Immunol. 2020, 50, 1432–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catanzaro, J.R.; Strauss, J.D.; Bielecka, A.; Porto, A.F.; Lobo, F.M.; Urban, A.; Schofield, W.B.; Palm, N.W. IgA-deficient humans exhibit gut microbiota dysbiosis despite secretion of compensatory IgM. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moll, J.M.; Myers, P.N.; Zhang, C.; Eriksen, C.; Wolf, J.; Appelberg, K.S.; Lindberg, G.; Bahl, M.I.; Zhao, H.; Pan-Hammarström, Q.; et al. Gut microbiota perturbation in IgA deficiency is influenced by IgA-autoantibody status. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 2423–2434.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosák, J.; Lexa, M.; Fiedorová, K.; Gadara, D.C.; Micenková, L.; Spacil, Z.; Litzman, J.; Freiberger, T.; Šmajs, D. Patients with common variable immunodeficiency (CVID) show higher gut bacterial diversity and levels of low-abundance genes than the healthy housemates. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 671239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiedorová, K.; Radvanský, M.; Bosák, J.; Grombiříková, H.; Němcová, E.; Králíčková, P.; Černochová, M.; Kotásková, I.; Lexa, M.; Litzman, J.; et al. Bacterial but not fungal gut microbiota alterations are associated with common variable immunodeficiency (CVID) phenotype. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shulzhenko, N.; Dong, X.; Vyshenska, D.; Greer, R.L.; Gurung, M.; Vasquez-Perez, S.; Peremyslova, E.; Sosnovtsev, S.; Quezado, M.; Yao, M.; et al. CVID enteropathy is characterized by exceeding low mucosal IgA levels and interferon-driven inflammation possibly related to the presence of a pathobiont. Clin. Immunol. 2018, 197, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, S.F.; Trøseid, M.; Kummen, M.; Anmarkrud, J.A.; Michelsen, A.E.; Osnes, L.T.; Holm, K.; Høivik, M.L.; Rashidi, A.; Dahl, C.P.; et al. Altered gut microbiota profile in common variable immunodeficiency associates with levels of lipopolysaccharide and markers of systemic immune activation. Mucosal. Immunol. 2016, 9, 1455–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seidel, M.G.; Kindle, G.; Gathmann, B.; Quinti, I.; Buckland, M.; van Montfrans, J.; Scheible, R.; Rusch, S.; Gasteiger, L.M.; Grimbacher, B.; et al. The European Society for Immunodeficiencies (ESID) Registry Working Definitions for the Clinical Diagnosis of Inborn Errors of Immunity. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2019, 7, 1763–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.; Chang, C.; Gershwin, M.E. IgA deficiency and autoimmunity. Autoimmun. Rev. 2014, 13, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Tola, M.; Bizzaro, N.; Gaudio, M.; Maida, C.; Villalta, D.; Alessio, M.G.; Previtali, G.; Fabris, M.; Deleonardi, G.; Tampoia, M.; et al. Diagnosing and monitoring celiac patients with selective IgA deficiency: Still an open issue. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2021, 66, 3234–3241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGowan, K.E.; Lyon, M.E.; Butzner, J.D. Celiac disease and IgA deficiency: Complications of serological testing approaches encountered in the clinic. Clin. Chem. 2008, 54, 1203–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asada, Y.; Isomoto, H.; Shikuwa, S.; Wen, C.Y.; Fukuda, E.; Miyazato, M.; Okamoto, K.; Nakamura, T.; Nishiyama, H.; Mizuta, Y.; et al. Development of ulcerative colitis during the course of rheumatoid arthritis: Association with selective IgA deficiency. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 5240–5243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodgson, H.J.; Jewell, D.P. Selective IgA deficiency and Crohn’s disease: Report of two cases. Gut 1977, 18, 644–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Manfredi, R.; Coronado, O.V.; Marinacci, G.; Righi, M.; Calza, L. Chron’s disease, rare association with selective IgA immunodeficiency, and development of life-threatening bacterial infections. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 2004, 36, 523–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iizuka, M.; Itou, H.; Sato, M.; Yukawa, M.; Shirasaka, T.; Chiba, M.; Watanabe, S. Crohn’s disease associated with selective immunoglobulin A deficiency. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2001, 16, 951–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joo, M.; Shim, S.H.; Chang, S.H.; Kim, H.; Chi, J.G.; Kim, N.H. Nodular lymphoid hyperplasia and histologic changes mimicking celiac disease, collagenous sprue, and lymphocytic colitis in a patient with selective IgA deficiency. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2009, 205, 876–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkholy, S.; Mogawer, S.; Farag, A. Nodular Lymphoid Hyperplasia of the Gastrointestinal Tract: A comprehensive review. Acta Gastroenterol. Belg. 2017, 80, 405–410. [Google Scholar]
- Gathmann, B.; Mahlaoui, N.; Gérard, L.; Oksenhendler, E.; Warnatz, K.; Schulze, I.; Kindle, G.; Kuijpers, T.W.; van Beem, R.T.; Guzman, D.; et al. Clinical picture and treatment of 2212 patients with common variable immunodeficiency. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 134, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Odnoletkova, I.; Kindle, G.; Quinti, I.; Grimbacher, B.; Knerr, V.; Gathmann, B.; Ehl, S.; Mahlaoui, N.; van Wilder, P.; Bogaerts, K.; et al. The burden of common variable immunodeficiency disorders: A retrospective analysis of the European Society for Immunodeficiency (ESID) registry data. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2018, 13, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Schewick, C.M.; Nöltner, C.; Abel, S.; Burns, S.O.; Workman, S.; Symes, A.; Guzman, D.; Proietti, M.; Bulashevska, A.; Moreira, F.; et al. Altered microbiota, impaired quality of life, malabsorption, infection, and inflammation in CVID patients with diarrhoea. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostel Bal, S.; Haskologlu, S.; Serwas, N.K.; Islamoglu, C.; Aytekin, C.; Kendirli, T.; Kuloglu, Z.; Yavuz, G.; Dalgic, B.; Siklar, Z.; et al. Multiple presentations of LRBA deficiency: A single-center experience. J. Clin. Immunol. 2017, 37, 790–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, N.; Burns, S.O.; Walker, L.S.K.; Sansom, D.M. Immune deficiency and autoimmunity in patients with CTLA-4 (CD152) mutations. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2017, 190, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coulter, T.I.; Chandra, A.; Bacon, C.M.; Babar, J.; Curtis, J.; Screaton, N.; Goodlad, J.R.; Farmer, G.; Steele, C.L.; Leahy, T.R.; et al. Clinical spectrum and features of activated phosphoinositide 3-kinase δ syndrome: A large patient cohort study. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 139, 597–606.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maarschalk-Ellerbroek, L.J.; Oldenburg, B.; Mombers, I.M.H.; Hoepelman, A.I.M.; Brosens, L.A.A.; Offerhaus, G.J.A.; Ellerbroek, P.M. Outcome of screening endoscopy in common variable immunodeficiency disorder and X-linked agammaglobulinemia. Endoscopy 2013, 45, 320–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, R.S. Malignancies in the setting of primary immunodeficiency: Implications for hematologists/oncologists. Am. J. Hematol. 2011, 86, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulvirenti, F.; Pecoraro, A.; Cinetto, F.; Milito, C.; Valente, M.; Santangeli, E.; Crescenzi, L.; Rizzo, F.; Tabolli, S.; Spadaro, G.; et al. Gastric Cancer Is the Leading Cause of Death in Italian Adult Patients with Common Variable Immunodeficiency. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiaee, F.; Azizi, G.; Rafiemanesh, H.; Zainaldain, H.; Sadaat Rizvi, F.; Alizadeh, M.; Jamee, M.; Mohammadi, S.; Habibi, S.; Sharifi, L.; et al. Malignancy in common variable immunodeficiency: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2019, 15, 1105–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruns, L.; Panagiota, V.; von Hardenberg, S.; Schmidt, G.; Adriawan, I.R.; Sogka, E.; Hirsch, S.; Ahrenstorf, G.; Witte, T.; Schmidt, R.E.; et al. Common Variable Immunodeficiency-Associated Cancers: The Role of Clinical Phenotypes, Immunological and Genetic Factors. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 742530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kralickova, P.; Milota, T.; Litzman, J.; Malkusova, I.; Jilek, D.; Petanova, J.; Vydlakova, J.; Zimulova, A.; Fronkova, E.; Svaton, M.; et al. CVID-Associated Tumors: Czech Nationwide Study Focused on Epidemiology, Immunology, and Genetic Background in a Cohort of Patients with CVID. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Both, T.; Dalm, V.A.S.H.; Richardson, S.A.; van Schie, N.; van den Broek, L.M.; de Vries, A.C.; van Hagen, P.M.; Rombach, S.M. Inflammatory bowel disease in primary immunodeficiency disorders is a heterogeneous clinical entity requiring an individualized treatment strategy: A systematic review. Autoimmun. Rev. 2021, 20, 102872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz de Morales, J.G.; Muñoz, F.; Hernando, M. Successful Treatment of Common Variable Immunodeficiency-associated Inflammatory Bowel Disease with Ustekinumab. J. Crohns Colitis. 2017, 11, 1154–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uzzan, M.; Ko, H.M.; Mehandru, S.; Cunningham-Rundles, C. Gastrointestinal Disorders Associated with Common Variable Immune Deficiency (CVID) and Chronic Granulomatous Disease (CGD). Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2016, 18, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Egg, D.; Rump, I.C.; Mitsuiki, N.; Rojas-Restrepo, J.; Maccari, M.E.; Schwab, C.; Gabrysch, A.; Warnatz, K.; Goldacker, S.; Patiño, V.; et al. Therapeutic options for CTLA-4 insufficiency. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2022, 149, 736–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiykim, A.; Ogulur, I.; Dursun, E.; Charbonnier, L.M.; Nain, E.; Cekic, S.; Dogruel, D.; Karaca, N.E.; Cogurlu, M.T.; Bilir, O.A.; et al. Abatacept as a Long-Term Targeted Therapy for LRBA Deficiency. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2019, 7, 2790–2800.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulter, T.I.; Cant, A.J. The Treatment of Activated PI3Kδ Syndrome. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maccari, M.E.; Abolhassani, H.; Aghamohammadi, A.; Aiuti, A.; Aleinikova, O.; Bangs, C.; Baris, S.; Barzaghi, F.; Baxendale, H.; Buckland, M.; et al. Disease Evolution and Response to Rapamycin in Activated Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase δ Syndrome: The European Society for Immunodeficiencies-Activated Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase δ Syndrome Registry. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leone, P.; Vacca, A.; Dammacco, F.; Racanelli, V. Common Variable Immunodeficiency and Gastric Malignancies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- dos Santos-Valente, E.C.; Da Silva, R.; de Moraes-Pinto, M.I.; Sarni, R.O.S.; Costa-Carvalho, B.T. Assessment of nutritional status: Vitamin A and zinc in patients with common variable immunodeficiency. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2012, 22, 427–431. [Google Scholar]
- Baris, S.; Ozen, A.; Ercan, H.; Karakoc-Aydiner, E.; Cagan, H.; Ozdemir, C.; Barlan, M.; Bahceciler, N.N.; Barlan, I.B. Osteoporosis: An ignored complication of CVID. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2011, 22, 676–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohebbi, A.; Azizi, G.; Tavakolinia, N.; Abbasi, F.; Sayarifard, F.; Karimipour, M.; Kiaee, F.; Yazdani, R.; Ebrahimi, S.S.; Ebrahimi, M.; et al. Comparison of Bone Mineral Density in Common Variable Immunodeficiency and X-Linked Agammaglobulinaemia Patients. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets. 2017, 17, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, J.R.S.; Silva, R.; Andrade, I.G.A.; Fonseca, F.L.A.; Costa-Carvalho, B.T.; Sarni, R.O.S. Assessment of vitamin D status in common variable immunodeficiency or ataxia-telangiectasia patients. Allergol. Immunopathol. 2019, 47, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade, I.G.A.; de Souza, F.I.S.; Fonseca, F.L.A.; Aranda, C.S.; Sarni, R.O.S. Selenium-related nutritional status in patients with common variable immunodeficiency: Association with oxidative stress and atherosclerosis risk. BMC Immunol. 2021, 22, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, D.G.; Costa-Carvalho, B.T.; Hix, S.; Da Silva, R.; Correia, M.S.; Sarni, R.O.S. Higher Cardiovascular Risk in Common Variable Immunodeficiency and X-Linked Agammaglobulinaemia Patients. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2015, 66, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Infections | |
|---|---|
| Helicobacter pylori | Campylobacter spp. |
| Salmonella spp. | Gardia lamblia |
| Noroviruses | Enteroviruses |
| Non-infectious manifestation | |
| Chronic gastritis (gastropathy) | Pernicious anemia |
| Celiac (-like) disease | Inflammatory bowel (-like) disease |
| Nodular lymphoid hyperplasia | |
| Malignancy | |
| Gastric metaplasia (precancerous lesion) | Gastric cancer |
| Lymphoma | |
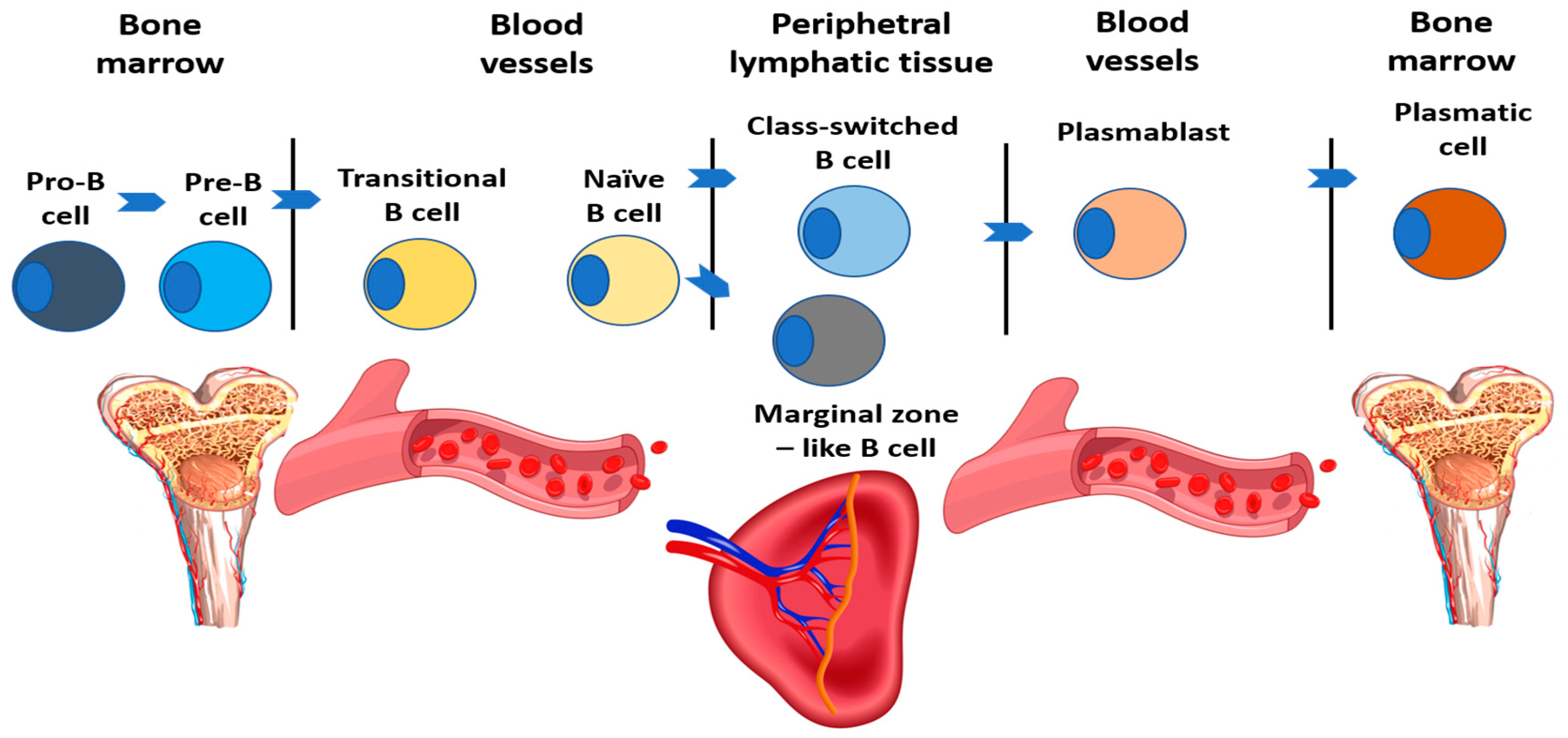
| Subpopulation | Characteristics | Relative Count (%) | Absolute Count (E9/l) |
|---|---|---|---|
| B cells (total) | CD19+ | 6–22 | 0.1–0.53 |
| Transitional B cells | CD19 + IgM + IgD + CD24 + CD38 + CD27- | 0.9–5.7 | 0–0.03 |
| Naїve B cells | CD19 + IgD + CD27- | 48.4–79.7 | 0.06–0.47 |
| Class-switched B cells | CD19 + CD27 + IgD-IgM- | 8.3–27.8 | 0.02–0.09 |
| Plasmablasts | CD19 + CD27 + CD38 + IgM-IgD-CD24- | 0.4–2.4 | 0–0.01 |
| Marginal zone-like B cells | CD19 + IgD + CD27+ | 7–23.8 | 0.01–0.08 |
| CD21(low)CD38(low) B cells | CD19 + CD21lowCD38low | 1.6–10 | 0.01–0.02 |
| Agammaglobulinemia |
|---|
| <2% of circulating B cells |
| normal number of T cells |
| <200 mg/dL in infants aged < 12 months or <500 mg/dL in children aged > 12 months or normal IgG levels with IgA and IgM below 2SD |
| onset of recurrent infections before 5 years of age |
| Common variable immunodeficiency |
| increased susceptibility to infection |
| autoimmune, granulomatous, lymphoproliferative manifestations |
| affected family member with antibody deficiency |
| marked decrease in IgG and marked decrease in IgA with or without low IgM levels (<2SD for specific age) |
| poor antibody response to vaccines and/or absent isohemagglutinins |
| secondary causes of hypogammaglobulinemia have been excluded |
| diagnosis is established after the 4th year of life |
| no evidence of profound T-cell deficiency |
| Selective IgA deficiency |
| increased susceptibility to infection |
| autoimmune manifestations |
| affected family member |
| undetectable serum IgA (<0.07 g/L) but normal serum IgG and IgM |
| normal IgG antibody response to all vaccinations |
| diagnosis after 4th year of life |
| secondary causes of hypogammaglobulinemia have been excluded |
| exclusion of T-cell defect |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Milota, T.; Smetanova, J.; Klojdova, I. Gastrointestinal Involvement in Primary Antibody Deficiencies. Gastrointest. Disord. 2023, 5, 52-67. https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord5010006
Milota T, Smetanova J, Klojdova I. Gastrointestinal Involvement in Primary Antibody Deficiencies. Gastrointestinal Disorders. 2023; 5(1):52-67. https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord5010006
Chicago/Turabian StyleMilota, Tomas, Jitka Smetanova, and Iveta Klojdova. 2023. "Gastrointestinal Involvement in Primary Antibody Deficiencies" Gastrointestinal Disorders 5, no. 1: 52-67. https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord5010006
APA StyleMilota, T., Smetanova, J., & Klojdova, I. (2023). Gastrointestinal Involvement in Primary Antibody Deficiencies. Gastrointestinal Disorders, 5(1), 52-67. https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord5010006






