Abstract
Ulcerative colitis is a chronic disease characterized by bleeding and ulcers in the colon. Disease severity assessment via colonoscopy videos is time-consuming and only focuses on the most severe lesions. Automated detection methods enable fine-grained assessment but depend on the training set quality. To suit the local clinical setup, an internal training dataset containing only rough bounding box annotations around lesions was utilized. Following previous works, we propose to use linear models in suitable color spaces to detect lesions. We introduce an efficient sampling scheme for exploring the set of linear classifiers and removing trivial models i.e., those showing zero false negative or positive ratios. Bounding boxes lead to exaggerated false detection ratios due to mislabeled pixels, especially in the corners, resulting in decreased model accuracy. Therefore, we propose to evaluate the model sensitivity on the annotation level instead of the pixel level. Our sampling strategy can eliminate up to 25% of trivial models. Despite the limited quality of annotations, the detectors achieved better performance in comparison with the state-of-the-art methods. When tested on a small subset of endoscopic images, the best models exhibit low variability. However, the inter-patient model performance was variable suggesting that appearance normalization is critical in this context.
1. Introduction
Inflammatory bowel diseases (IBDs) are chronic inflammatory illnesses associated with considerable healthcare costs [1]. Patients experience serious discomfort and long-term complications. The two main subtypes are Crohn’s disease (CD) and Ulcerative colitis (UC) distinguished by disease location and histology findings [2,3]. Diagnosis of IBDs is challenging [4] and involves a multifaceted approach, including clinical examination and specialized tests such as histology and radiology [5]. Advanced imaging techniques, blood tests and biopsies play an important role in confirming IBD and distinguishing CD from UC. The need for repeated testing and ongoing monitoring highlights the ongoing challenges of managing these diseases.
Gastroenterologists often use endoscopic procedures such as endoscopy to visually examine the gastrointestinal tract for signs of inflammation, bleeding, ulcers, or any mucosal damage. In medical practice, colonoscopy [6] and Wireless Capsule Endoscopy (WCE) [7] are the methods of reference for evaluating and monitoring IBD severity in order to make treatment decisions and assess treatment response. Colonoscopy, performed by an experienced clinician for UC, uses a flexible thin hose equipped with a mini-video camera, while WCE, suited for CD, uses an embedded, pill-sized, camera that can be swallowed.
Bleeding and ulcers are common lesions associated with both diseases, UC and CD [8]. Color information is the primary indicator used by specialists to distinguish between mucosal lesions and the surrounding normal or healthy mucosa. Bleeding shows up as dark red areas whereas ulcers appear as white spots on the gut wall, both distributed with diverse shapes and sizes. Currently, experts review manually colonoscopy or WCE videos consisting of 50 k to 120 k frames [9]. This process is a difficult and time-consuming task leading to only considering the characteristics of the most severe lesions.
Automated lesion detection offers significant benefits by improving the severity assessment reproducibility and decreasing the physicians’ burden. Various methods have been proposed to automatically detect bleeding and ulcer lesions, primarily tackling binary classification and segmentation challenges. Some of these methods use color features [10,11,12,13,14], while others combine them with texture information to enhance detection performance [15,16,17]. Recent studies have shown a growing interest in artificial intelligence (AI) offering a universally applicable approach to clinical diagnosis. Specifically, deep learning methods show promise in detecting and localizing endoscopic lesions [9,18].
The presented work focuses on detecting bleeding and ulcers from colonoscopy videos obtained in the context of UC disease during an ongoing collaboration with Bichat-Beaujon Hospital in Paris, France. Although the lesions’ appearance is similar between UC and CD, existing methods are biased to their training set, i.e., to well-delineated video-capsule images ([19,20,21,22,23]) rather than complete colonoscopy videos obtained on the local instruments. Consequently, we built a custom dataset of colonoscopy videos of real patients, called Vatic specific to this collaboration. To streamline the annotation process, we propose a user interface inspired by Vatic software (https://github.com/cvondrick/vatic, accessed on 15 November 2023) [24] allowing the doctors to delineate lesions by bounding boxes instead of precise boundaries.
Classical machine learning or Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) [9,18] approaches heavily depend on the quality of the training dataset affecting the accuracy of the detector. To address potential shortcomings, we opted for linear models due to their simplicity and ability to provide interpretable results. Following [13,14,19,25,26], we used linear models in convenient color spaces for bleeding and ulcer detection. We also proposed an efficient sampling scheme to explore the set of linear models and reject trivial classifiers, i.e., models that classify all the pixels into the same class. Given the imprecise delimitation of bleeding and ulcer lesions by bounding boxes, we take into account the annotation errors in computing detector sensitivity. Specifically, mislabeled pixels within the bounding box annotations were considered correctly identified abnormal pixels rather than false negatives.
In this paper, we have three main contributions:
- -
- We first propose a sampling strategy to effectively explore the set of linear models by only considering nontrivial models. This will be done in Section 3.2.3.
- -
- Then, we introduce performance criteria that can deal with bounding box annotation problems. In Section 3.2.4, we show its effectiveness with the help of some examples.
- -
- Finally, we study the variability of the detectors across the patients using small subsets of endoscopic images. Our study shows that the models used are not universal and personalized models should be developed for each patient. We illustrate the results in Section 5.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows: in Section 2, we present an overview of the current state-of-the-art methods proposed for UC lesions detection. Then, in Section 3, we describe our proposed sampling scheme to explore the set of linear models. Next, we introduce performance criteria that can deal with bounding box annotation problems. In Section 4, we discuss the results of our proposed approach. Finally, in Section 5 we study the variability of the models among the patients. Some limitations of the study will be provided in Section 6.
2. Related Work
2.1. Automatic Detection of Bleeding
Most of the current methods perform classification in a color space with maximum contrast between bleeding and nonbleeding regions. As bleeding pixels are red, it is natural to consider detection and classification in the RGB colorspace, or direct transformations of RGB [12,13,25,27,28,29].
In 2011, Fu et al. [27] trained a 3-layer perceptron on the ratios (R/G, R/B, R/G + B + R) for each pixel and applied morphological erosion. Later in 2014, the authors extended their approach by working with superpixel regions, and a Support-Vector Machine (SVM) classifier trained on 60,000 pixels [12]. In the same year, Ghosh et al. [25] applied a K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN) classifier to statistical parameters extracted from the R/G histogram. The authors reported that the combination of only three parameters, namely {median, variance, kurtosis} was sufficient to identify bleeding frames with an accuracy of 98.5%. This work was later extended by working on 7 pixels × 7 pixels blocks [13].
Some bleeding detection algorithms work on the histogram bin levels instead of the pixel values [25,28]. Kundu et al. [28] computed Regions of Interest (ROIs) defined by the color ratios and computed in the normalized RGB color space, denoted by rgb and applied a KNN classifier to 64 histogram bins in the green channel. The parameters and are chosen according to the maximal accuracy of pixel detection compared to the ground truth provided for 65 endoscopic images. In [29], the authors combined the RGB values into a single number with bit concatenation and applied an SVM classifier on the bins of the resulting histogram. In [19], the authors used a similar technique before PCA dimension reduction and classification with KNN.
Other color spaces were also considered in [11,30,31]. In [30], the authors used an SVM classifier with statistical features computed in Luma In-phase Quadrature (YIQ) color space. Deeba et al. [11] merged two SVM classifiers built from statistical features extracted from RGB and Hue-Saturation-Value (HSV) color histograms, respectively. In [31], the authors trained a three-layer probabilistic neural network on statistical features from RGB and Hue-Saturation-Intensity (HSI) pixel intensities. Recently, Pogorelov et al. [15] proposed to consider image texture combined with color information. They used RGB color features and 22 texture parameters extracted from the grey-level co-occurrence matrix. The authors tested many classification methods and found that the SVM classifier performed best.
2.2. Automatic Detection of Ulcers
Ulcers show as pinkish white, which explains why most methods focus on detecting bright pixels [14,32]. In [32], the authors trained an SVM classifier on statistical features in RGB and CIElab (Lab) spaces and concluded that (L, a, G) channels give the best detection performance. The authors later extended their work in [14] with more colorspaces (RGB, HSV, YCbCr, CMYK, YUV, CIElab, XYZ) and found that (Cr,Y,B) is the best features combination.
Ulcers also appear as rough surfaces which can be detected based on texture features [16,17,26]. In [17], the authors proposed to combine color (S from HSV and M from CMYK) and Leung-Malik filters [33] with an SVM classifier. In [26], the authors applied an SVM classifier to statistical moments of the Contourlet transform and Log Gabor filter in HSV and YCbCr color spaces. In Yeh et al. [16], the textural features were obtained from the Grey Level Co-occurrence Matrix. Different combinations of the number of features, feature selection algorithm, and classification algorithm were compared, and the best combination was obtained with decision trees, with 40 features selected by the ReliefF method.
3. Materials and Method
3.1. Colonoscopy Videos Dataset
From Vatic dataset [34], we used 5 videos (768 pixels × 576 pixels) containing both bleeding (1629 frames) and ulcer (1760 frames) annotations for training, for a total of 4349 frames (see Table 1). Each video was annotated by gastroenterologists with the help of the Vatic software [24]. For further information on the annotation process, please refer to [34].

Table 1.
Number of frames used for training: number of frames with bleeding annotations, number of frames with ulcer annotations, and total number in the video.
3.2. Proposed Method
Our proposed method involves several steps outlined in Figure 1. First of all, we remove all black pixels surrounding the informative pixels. Next, we compute the color histograms of healthy pixels. We thus propose an effective sampling method to explore the linear models. We also adjust the computation of the sensitivity criteria to encounter mislabeled pixels occurring during the annotation process using bounding boxes. Finally, we optimize the performance of the detectors utilizing the Youden index [35]. In what follows, we detail the process by showing some examples.

Figure 1.
Flowchart of the proposed method.
3.2.1. Image Preprocessing
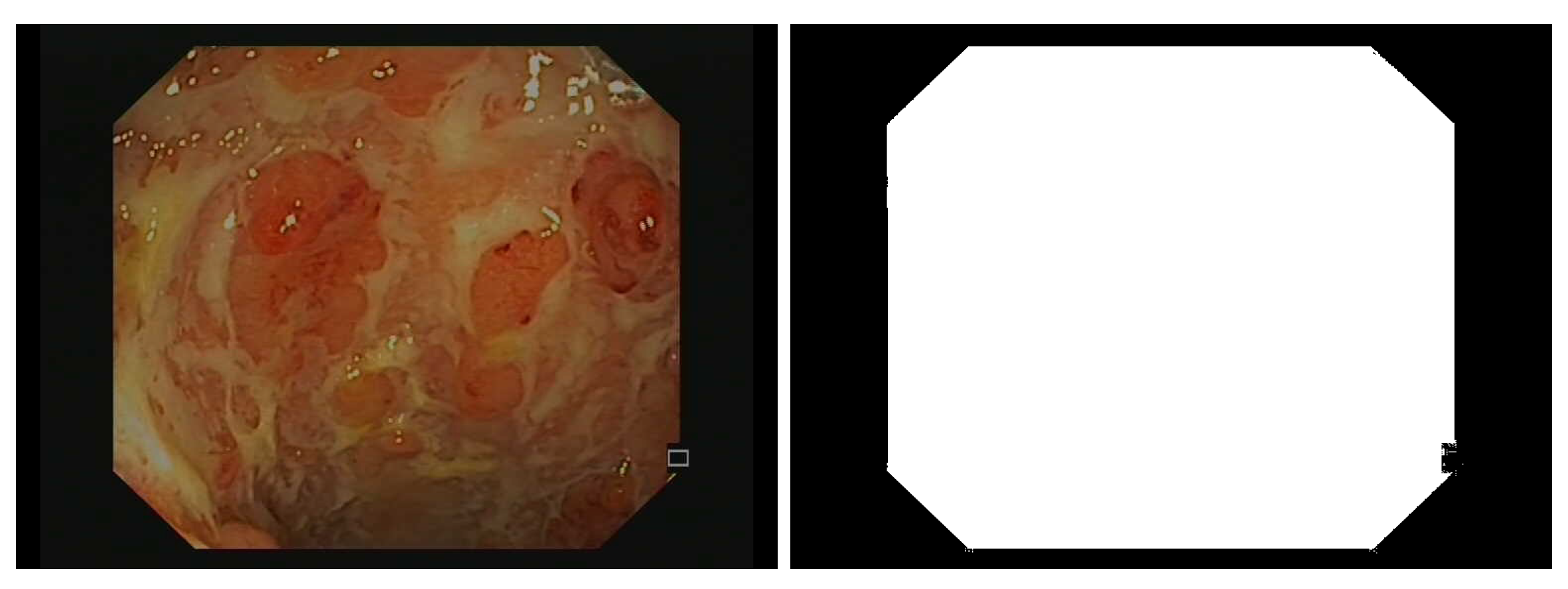
Due to the camera’s field of view, only an octagonal portion of the image is actually recorded in the endoscopic video, and the outer portions are set to black (see Figure 2). Additionally, some embedded textual information should be removed prior to bleeding or ulcer detection. Therefore, we detect pixels with small grey-level variance and grow the detected region with morphological dilation (5 × 5 square structuring element). Additionally, some unannotated areas are bright because of light shining on wet spots (specular reflection), so we remove the pixels , with chosen by visual inspection.
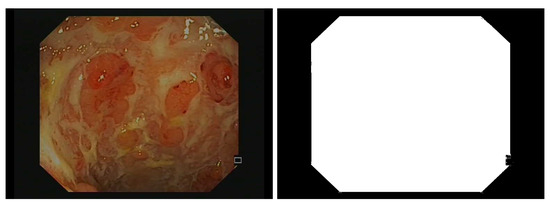
Figure 2.
Example of an endoscopic frame (on the left) and corresponding binary mask (on the right) used later to remove pixels that do not correspond to the colon wall during the training stage of the detectors.
3.2.2. Definition of Bleeding and Ulcer Detectors
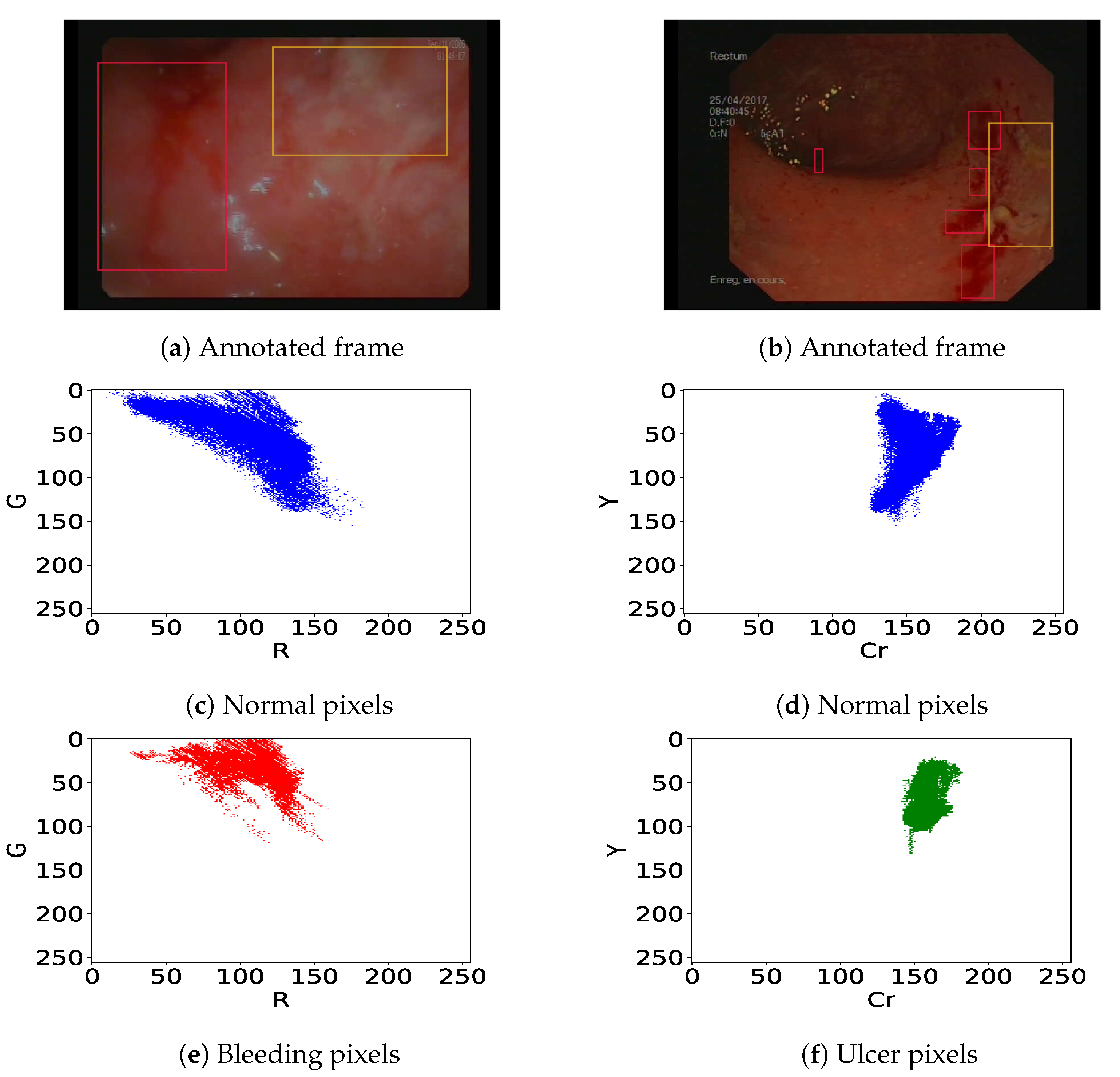
We previously pointed out that in colonoscopy videos, bleeding shows up as red patches and ulcers as pinkish-white patches on the gut wall (Figure 3). As previous authors [13,19,25] have shown that the R/G ratio is relevant (it leads to 11% overlap in [13]) to detect bleeding, we consider linear classifiers in the (R,G) subspace, i.e., . Similarly, following [14,26], we consider linear classifiers in the (Cr,Y) subspace obtained using Cr and Y channels from YCbCr and CMYK color spaces respectively, i.e., to detect ulcer lesions. This corresponds to finding a straight separation line between the histograms of normal and lesion pixels. Let’s take the example of endoscopic figures in Figure 3. The best bleeding detector should lead to a minimum overlap ratio between normal (Figure 3c) and bleeding pixels (Figure 3e) in the (R, G) color space. On the other hand, the best ulcer detector should lead to a minimum overlap ratio between normal (Figure 3d) and ulcer pixels (Figure 3f) within the (Cr, Y) color space.
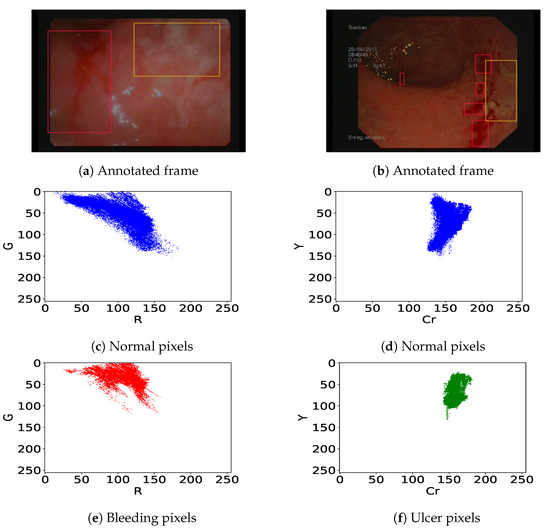
Figure 3.
(a,b) Annotated frames with bleeding (red bounding box) and ulcers (orange bounding box). Corresponding histograms of the normal pixels i.e., all pixels out of the bounding boxes (c,d), bleeding pixels (e), and ulcer pixels (f).
3.2.3. Proposed Sampling Strategy
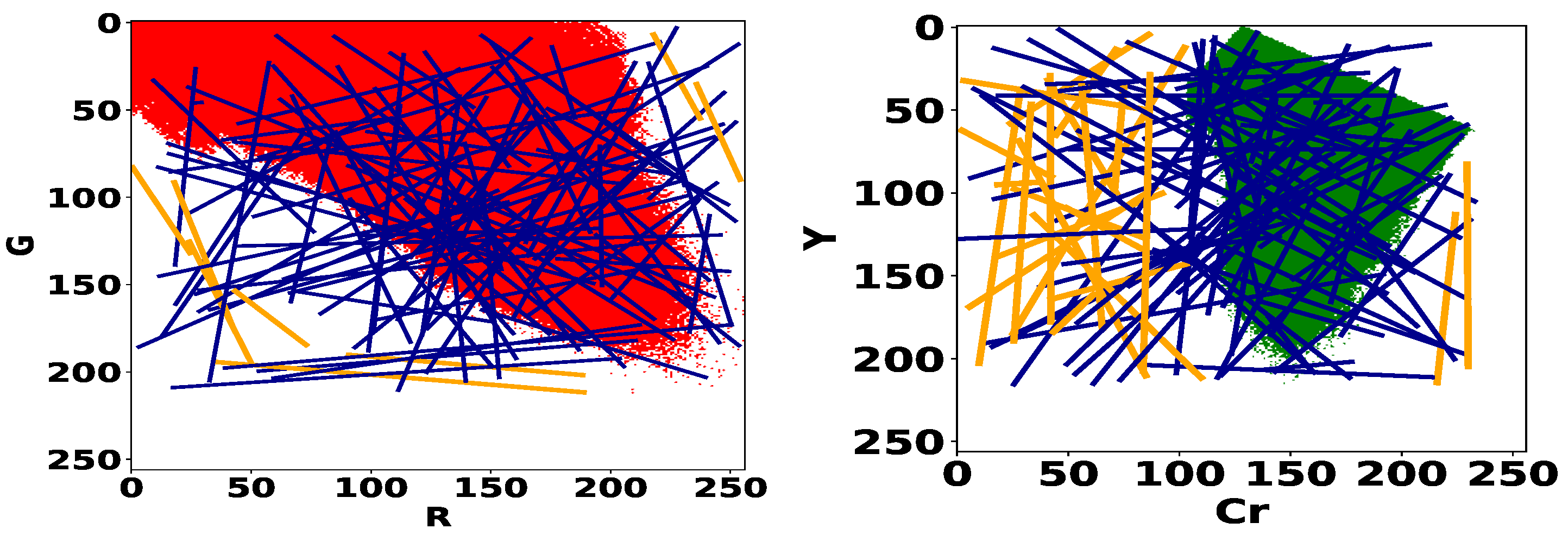
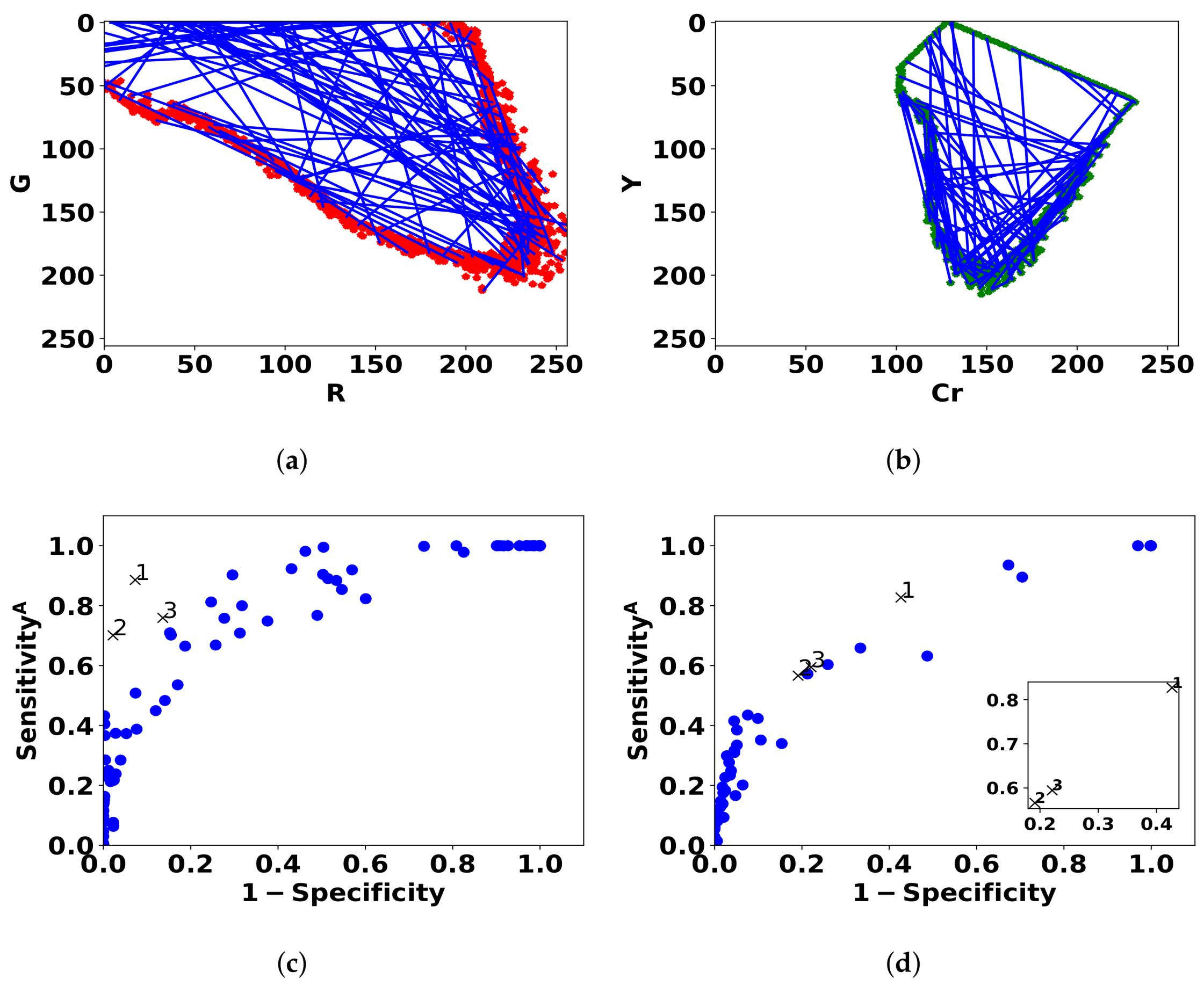
The model search process consists in exploring all the linear models of the color spaces (R, G) and (Cr, Y) for bleeding and ulcer detection respectively. In Figure 4, we give the histograms of normal pixels of the training dataset (Table 1). For each histogram, we plot a set of 100 random linear models. We can remark that classifiers that do not “cross” the histograms, herein highlighted in orange color, are trivial because they give the same label to all pixels. In particular, no normal pixel will be correctly identified by the detector and consequently, the true negative rate of this detector will be zero. Therefore, we decide to eliminate these models and restrict the optimization space to the set of random linear classifiers that go through the interior of the histogram. Additionally, if a line goes through the interior, it must cross the boundary of the set. We can avoid sampling redundant linear classifiers by focusing on the contour of the histogram instead of its interior. To sample the set of lines, we will thus draw two points in the contour of the RG and CrY histograms and consider the associated linear classifiers.
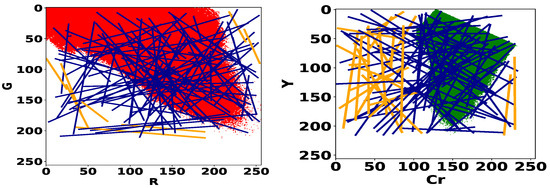
Figure 4.
Histograms of normal pixels for the training dataset (cf. Table 1) in the RG space (on the left) and CrY space (on the right). Trivial models are represented in orange color.
3.2.4. Proposed Performance Metric of the Detectors
In textbook statistics, the specificity or true negative (TN) rate measures the proportion of normal pixels correctly identified as such, and sensitivity or true positive (TP) rate measures the correctness of abnormal pixels detection. However, evaluating specificity and sensitivity hinges on reliable pixel annotations by gastroenterologists. Unfortunately, as previously discussed, the gastroenterologists’ annotations in our dataset contain many errors because the regions of interest are provided as bounding boxes, whereas bleeding and ulcers have more complex shapes (see Figure 3). Direct observation also suggests that many dark red pixels were not labeled as bleeding, and white pixels were not labeled as ulcers. Consequently, we expect over-inflated levels of FP and FN based on the dataset annotations. This will hide the correct classifier, and decrease the confidence in our results.
To overcome these problems, we modify the definition of sensitivity to take the labeling problems into account. The pixels inside an annotation and not detected as such should not count as false negatives when assessing the algorithm’s performance. Consequently, we count all pixels belonging to an annotation as TP, as soon as one pixel is detected inside. As pixels inside an annotation are either true positives or false negatives, this corresponds to counting “detected annotations” instead of “detected pixels”. More precisely, we count in terms of “area”, and define the sensitivity criteria as follows:
In comparison with the standard sensitivity criteria, may provide a compromise between bounding box annotations and the detector’s ability to correctly identify them. Specificity is not modified, as we expect missing annotations to represent a small number of pixels relative to nonannotated pixels .
Finally, the detector performance is measured in a sensitivity vs. (1-specificity) plot or Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) space. As we are only interested in single detectors, each detector’s performance is represented by a point. The ideal classifier corresponds to the upper left corner. Other good models are a compromise between sensitivity and specificity and are close to (0,1). We select the classifier that maximizes the Youden index [35]:
4. Results
4.1. Computation of the Proportion of Trivial Models
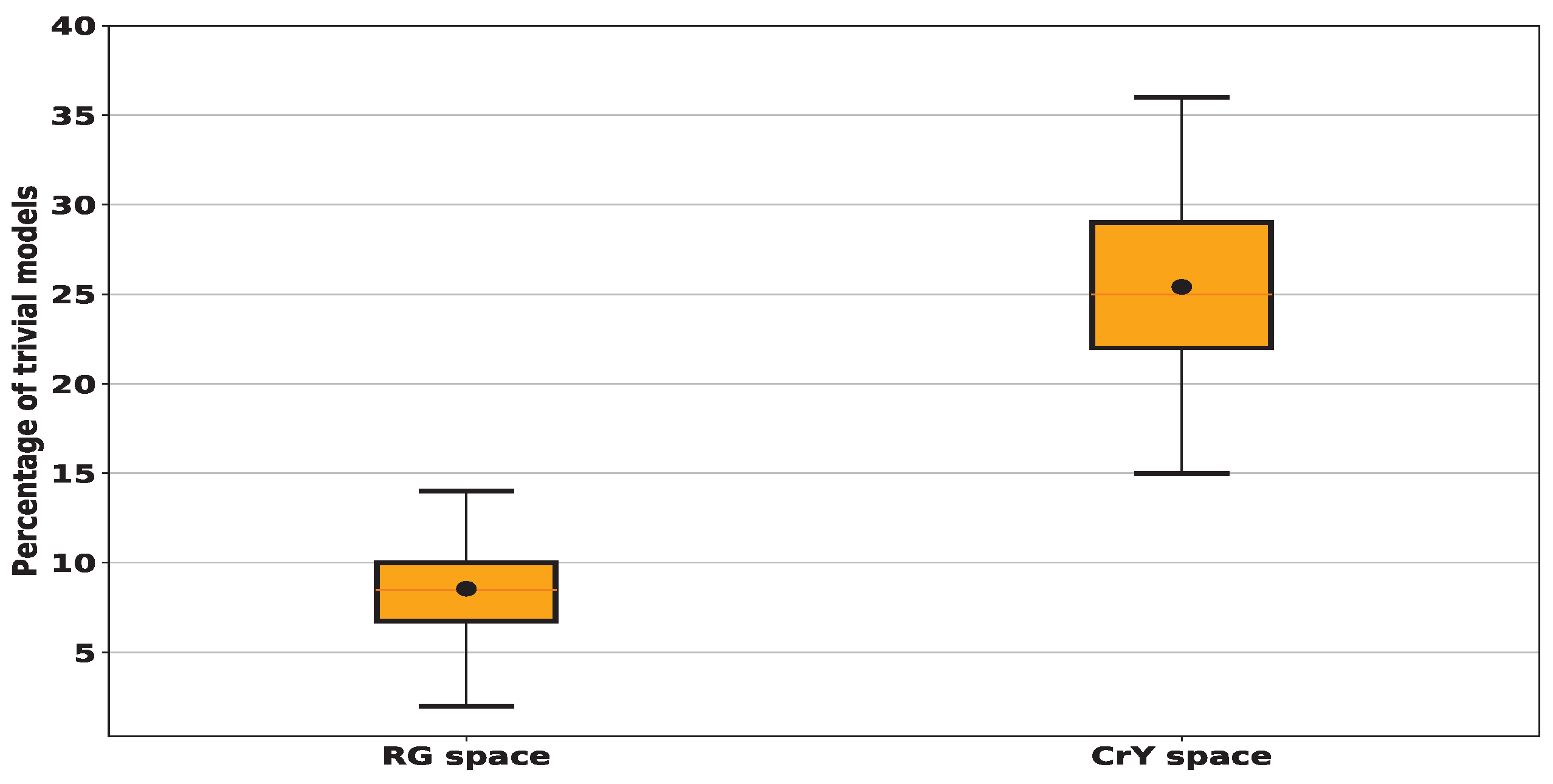
To study the amount of these trivial models, we ran a series of 100 trials, each involving 100 randomly generated lines. In Figure 5, we show the total amount of "trivial” models across 100 random tests. The results show that when sampling linear models in (R,G), also denoted by RG, color space, an average of 9% of these models is “trivial” with a standard deviation (std) of around 3%. In contrast, for the (Cr,Y), also denoted by CrY, space this amount increases significantly to achieve an average of 25% with a std of about 4%. When sampling the RG space using 10,000 random models, among them 9.41% are trivial whereas this number increases to 25.62% in the case of sampling CrY space. Since the number of trivial models remains almost the same when testing more than one hundred models, we decided to restrict the search for lesion detectors by testing only one hundred random linear models.
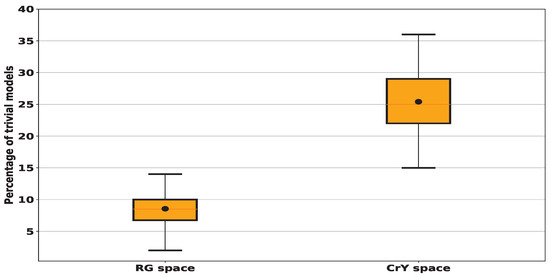
Figure 5.
We compute the percentage of trivial models, i.e. those non-crossing the histogram and consequently having a zero true positive or a zero true negative ratio for 100 random trials each of 100 lines for every histogram given in Figure 4. In black dots, we denote the mean values: for RG space, we find that around 9% of tested models fall outside the histogram and consequently are considered trivial while for CrY space, we find the average proportion of tested models identified as trivial is 25%.
4.2. Is Better Than Standard Sensitivity in the Context of Bounding Box Annotations
In Figure 6, we illustrate the results of bleeding detection (in red) using a chosen random linear model, and ulcer detection (in orange) using the linear model . We report the performance metrics of the models in terms of TP, TN, FP, and FN computed on the pixel level in Table 2. It can be seen that the model can correctly identify most of the annotated pixels (see the last row). However, as gastroenterologist annotations are usually wider than the actual lesion, some annotated pixels are not detected by our algorithm and therefore the false negative ratio is very high resulting in decreased sensitivity values (cf. Table 2).
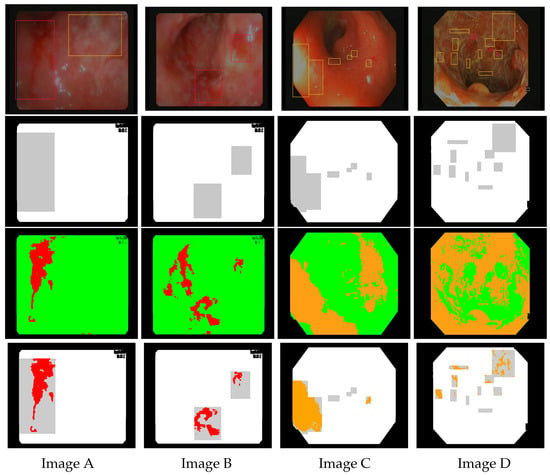
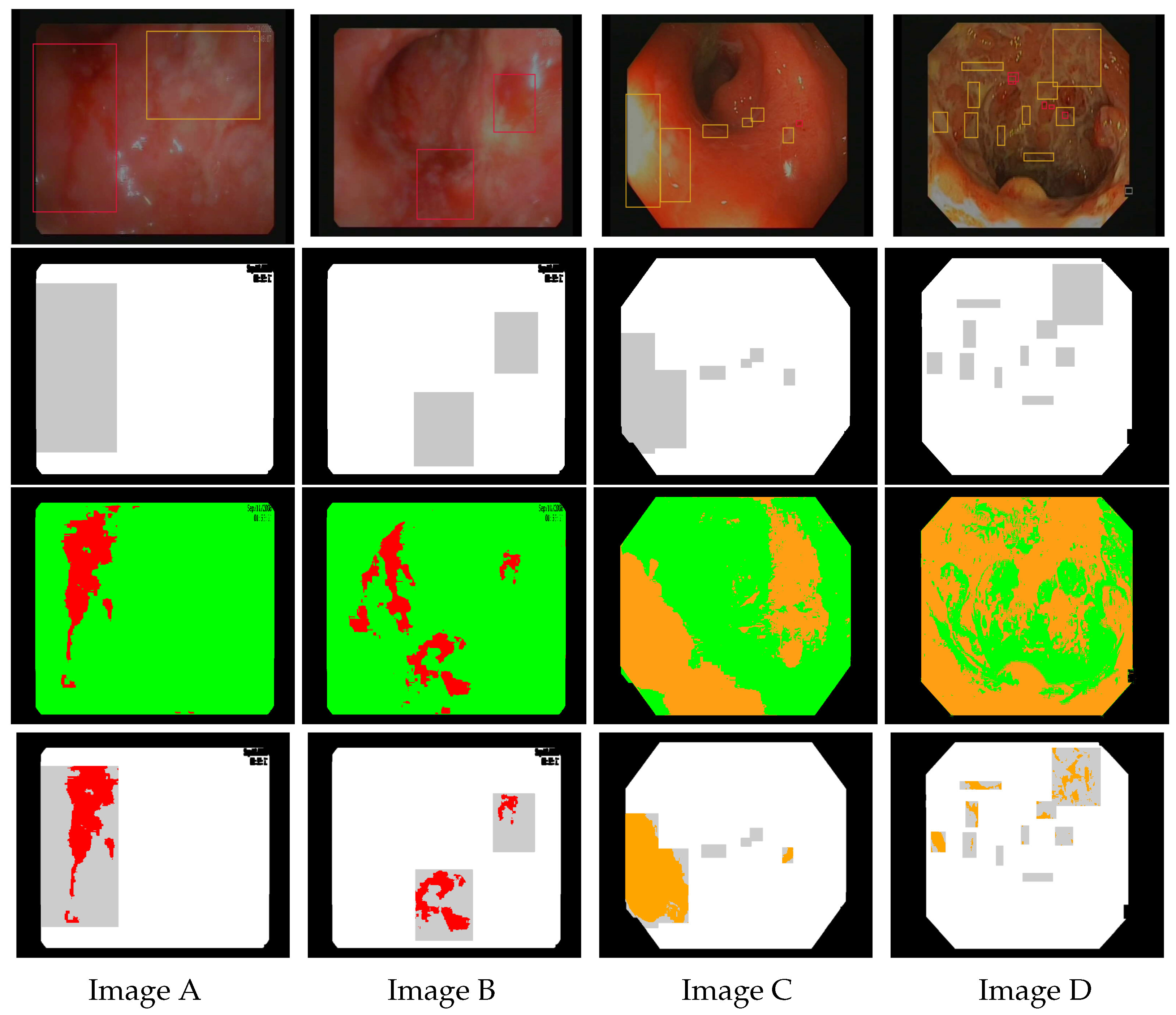
Figure 6.
Images (A–D) are endoscopic images extracted from Vatic dataset. The first row shows corresponding annotations for bleeding (red boxes) and ulcers (orange boxes). The second row represents the mask highlighting the ground truth obtained by bounding box annotations (in gray). The third row shows the results of bleeding detection (in red) using the linear model and ulcer detection (in orange) using the linear model . The last row shows the intersection between the models’ detection and the ground truth.

Table 2.
Performance results for endoscopic images given in Figure 6. TPA represents the number of pixels within the detected annotations and PA denotes the total number of pixels of all the annotations presented in the frame.
4.3. Best Lesions Detectors
As explained previously in Section 4.1, we take a random sample of size 100 from the set of linear models that cross the contour of the histogram of normal pixels. Figure 7 shows the sampled models in histogram space and in ROC space. Table 3 shows the performance of the three best linear models in terms of specificity, and standard sensitivity.
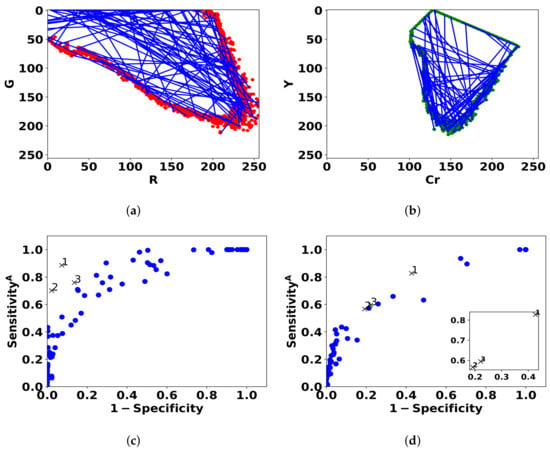
Figure 7.
Blue lines represent the 100 linear classifiers that are sampled by drawing two points from the contour of the (R,G) histogram of normal pixels (a) and (Cr,Y) histogram (b). The performance of the models for bleeding (c) and ulcer (d) is shown in ROC space by blue dots. The three best models are denoted by black cross markers.

Table 3.
Performance of the best linear models for bleeding and ulcer detection. Good performance is obtained based on , but standard sensitivity is low due to annotation errors.
As shown in Figure 7, the models achieve good performance results in ROC space, i.e., specificity and . Figure 8 (in the 2nd and 4th row) shows that there is a good visual agreement between the colors of detected lesions and the expert annotations. The best linear models can focus on the relevant areas rather than the entire annotation, and select candidate ROIs that were not annotated. As expected, the detected areas do not overlap “fully” with the annotations, which is the reason for the low standard sensitivity levels. Based on the 3 best models, we estimate that around 90% of bleeding annotations are incorrect, and 80% of ulcer annotations (see Table 3). As a result, training with the standard sensitivity would provide nonsensical models, whereas we can achieve good performance with .
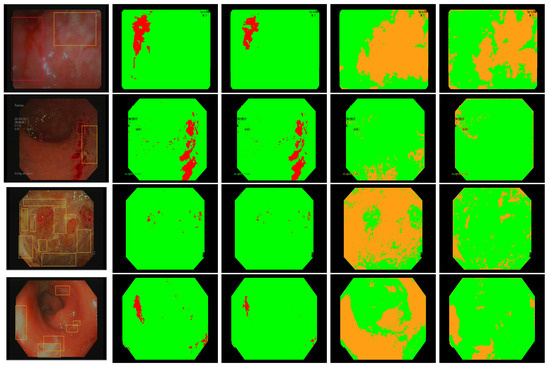
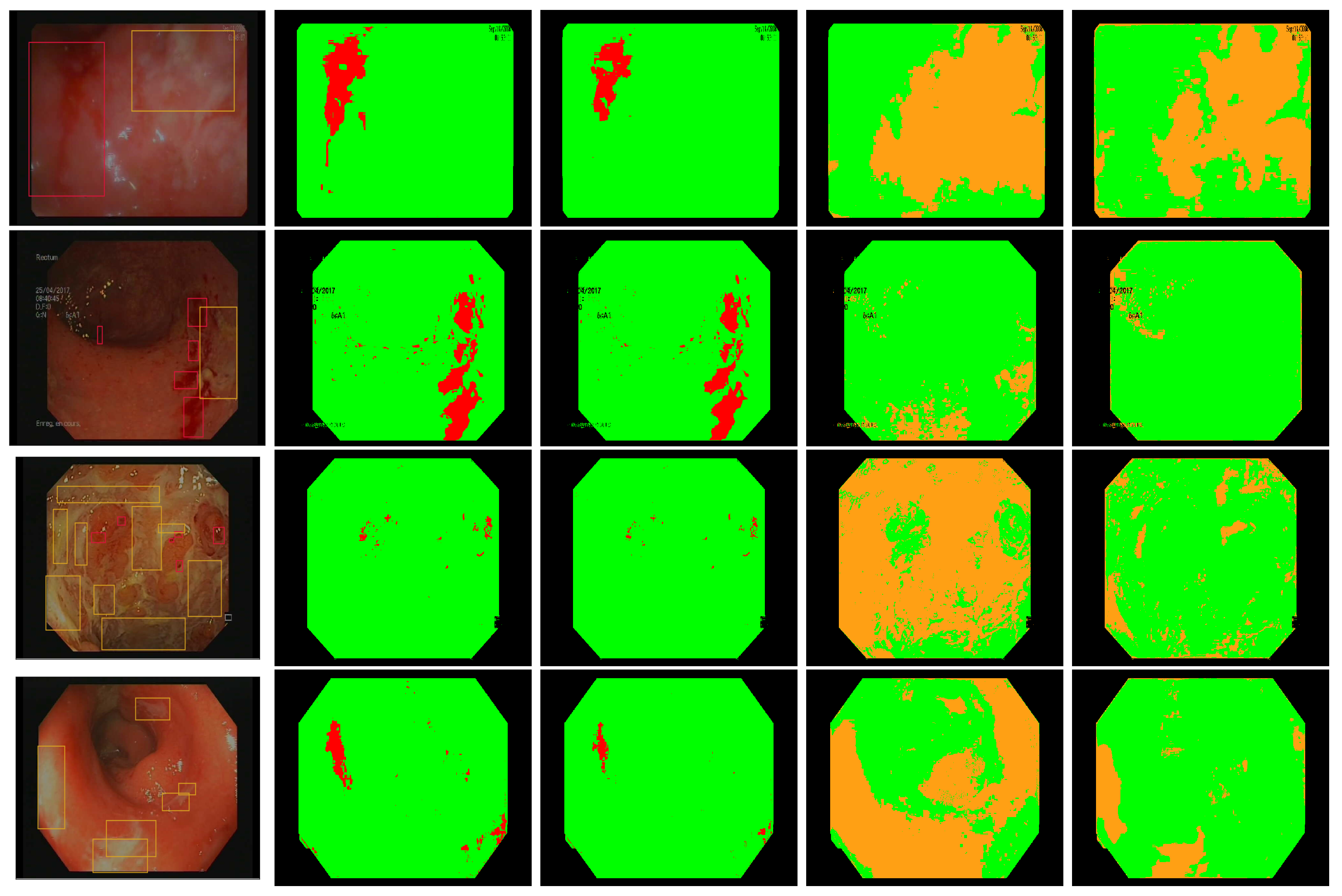
Figure 8.
Annotated frames from Vatic dataset (first column), bleeding detection with our best linear model (second column), bleeding detection by two simultaneous linear models [28] (third column), ulcer detection with our best linear model (fourth column), ulcer detection using SVM [14] (last column).
In Table 4, we summarize the results of our models compared to two methods found in the literature. As we are interested in detecting annotations, we apply two simultaneous color ratios as done in [28] and find the optimal parameters and to detect bleeding ROIs. We don’t further apply the KNN algorithm as the authors have done. On the other hand, for ulcer detection, an SVM model with a Radial basis function (RBF) kernel [36] and 10-fold cross-validation was trained on our dataset using two color bands and Y as done in [14]. Using a grid search within the values range , we find that the optimal parameters are in terms of regularization constant and in terms of kernel hyper-parameter. We then computed the detection performance for both resulted models on our training dataset (cf. Table 1) using the standard specificity and the proposed (cf. Section 3.2.4). Reported results show that linear models exhibit better compromise between specificity and compared with [14,28]. The SVM model fails on abnormality detection, here the ulcers found in Vatic dataset. We thus tried to make data augmentation on the ulcer pixels to maintain a balance in the training dataset, but remained low.

Table 4.
Performance of the best lesions detectors compared to the literature. Significant results are highlighted in bold.
In Figure 8, we present some annotated frames with the corresponding detection using our models as well as the models computed based on [14,28]. We find that our best linear models show better compromise between the detection of healthy pixels and lesions pixels than the other methods using similar color features.
5. Discussion
As discussed in Section 2.1, the RGB color space, and especially the Red and Green channels, have previously been used successfully for bleeding detection, whereas the YCbCr color space was used for ulcer detection. The information present in the pixel color is not altered by a change of color space, but a suitable color space presents this information more straightforwardly, and dimension reduction methods such as PCA can automatically perform this. In this manuscript, choosing the right colorspace based on the previous literature (see [11,15,20,29] for bleeding and [14,17,26] for ulcers) enables us to work with 2D linear models instead of 3D models.
The use of bounding box annotations in our dataset (see Figure 3) entails a considerable quantity of ground truth errors because annotations do not match the arbitrary and complicated shapes of the lesions. This is a major difficulty in our context, regardless of the type of model or machine-learning approach. To ease the annotation burden, semi-automatic region selection algorithms have been proposed. In the work of Sainju et al. [37], the authors use the growing region algorithm [38] to create homogeneous bleeding regions from consecutive capsule endoscopy frames. A seed is manually selected by the user and then enlarged by adding 8-connected neighbors, and the new centroid is taken as the seed for the following frame. This method extracts only one region per lesion, which can unbalance the normal and bleeding regions in the training dataset. In addition, it does not perform well in the absence of lesions due to forward and backward camera movements or in patients with mild forms of UC. In [11], the authors use a similar method to extract the bleeding regions but keep only a single frame rather than the complete sequence.
In this paper, we propose to adjust the performance criterion of lesion detection rather than automatically annotate the dataset. We chose to work with linear models instead of more sophisticated approaches in order to provide results that are easy to interpret and use in clinical practice. In addition, the good performance obtained in this and previous studies [11,13,14,17,25,26] suggests that clinical validation of the approach is the critical step, as opposed to more sophisticated approaches such as SVM or neural networks.
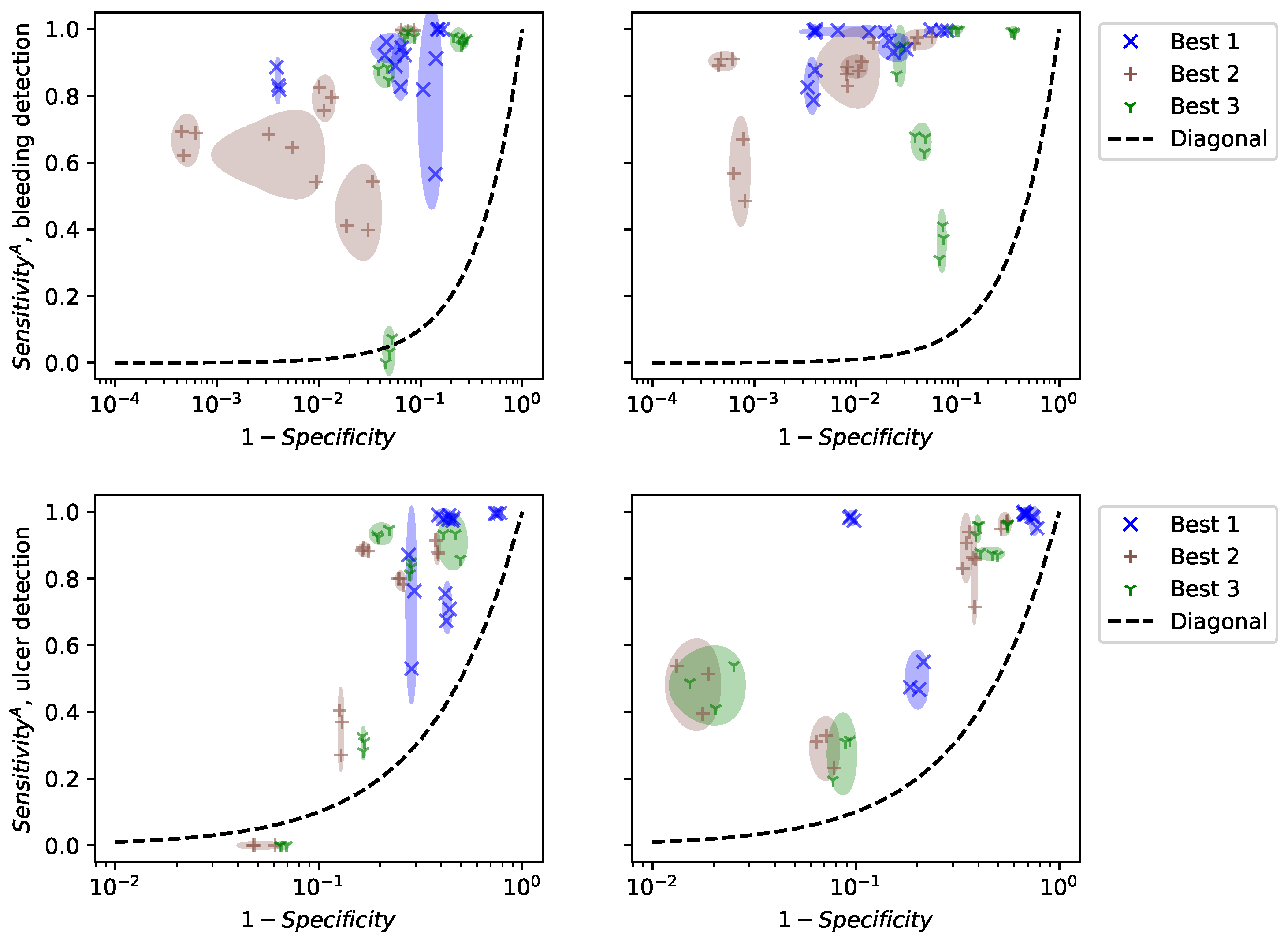
To evaluate the validity of our results, we did not perform cross-validation, but show the results of computing specificity and on a random subset of frames in each video in Figure 9. Cross-validation selects random subsets and finds the best model for each subset. Consequently, it selects different models at each run and evaluates the performance of the optimization algorithm. For clinical practice, we are interested in the performance of specific models, their reliability, and their generalization to new patients. Figure 9 shows the performance of the 3 best models for the patients in the training dataset (left) and 5 new patients (right). For each patient, we estimated specificity and on 20 random subsets of a video, each containing 10% of the frames. Only three points are drawn, but the size of the ellipses is computed from the standard deviations of the 20 subsets.
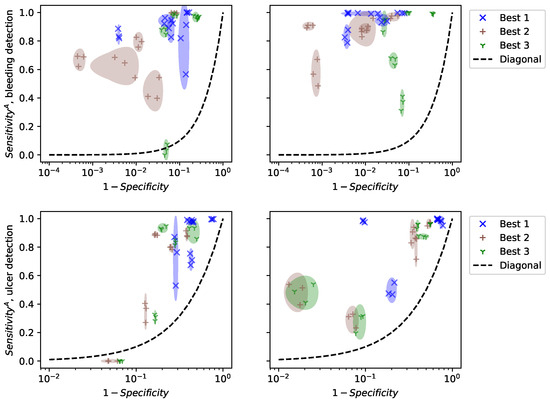
Figure 9.
Performance of the 3 best linear models depending on the patient, 5 training videos (left), and 5 test patients (right).
Figure 9 shows that specificity and are estimated precisely, even on a fraction of the frames. This suggests that computational time can be reduced by using only a small subset of the video. However, the performance varies a lot between patients, even inside the training set. This means that the selected models are not universal and that specific models should be trained for each patient. This observation was not reported in previous works because the datasets used contain frames that are not organized “by patient”. Consequently, methodological advances are necessary to make colonoscopy videos comparable, in order to apply trained models to new patients.
The application of AI in the detection of endoscopic lesions from colonoscopy videos marks a significant advancement in medical technology. With the capability to analyze vast amounts of visual data swiftly and accurately, AI algorithms contribute to the early identification of lesions, such as polyps or abnormalities, during colonoscopy procedures [9,18]. By leveraging machine learning and computer vision techniques, these AI systems can discern subtle changes in tissue patterns, helping clinicians in the timely diagnosis and intervention for patients. The integration of AI in endoscopic lesion detection not only enhances the efficiency of medical practitioners but also holds promise in improving overall patient outcomes by facilitating early detection and treatment of potentially concerning conditions. This technological synergy between AI and endoscopy stands poised to revolutionize the landscape of gastrointestinal healthcare.
6. Limitations of the Study
This study has several limitations. The first is the imprecision of lesion delineation using bounding boxes. Although the annotation process [24,34] employed in this study allowed an easy and fast ground truth construction, it does not permit accurate identification of all the pixels within the lesion contours. Several solutions could be further investigated on the bounding boxes: application of an automatic pixel-level annotation algorithm to encounter more precisely the lesion areas [11,37], use of semantic segmentation process [39,40] or application of a partial differential equation, i.e., non-linear diffusion types such as Malik and Perona equation to enhance contour identification and subsequently the abnormal pixels [41,42]. Another solution would be to use only an internal part of the available annotations. These areas of the image contain almost all the pixels of the lesion which may lead to better ground truth identification and consequently a performance enhancement of the detectors. The second limitation is the lack of a video processing stage. Given that the same lesions can be seen several times in a sequence of the colonoscopy video images [34], a processing step aimed at excluding redundancy in these images could contribute to more accurate identification of normal and abnormal pixels. The third limitation is the hand-crafted features employed in this study to identify the lesions in the colonoscopy videos. Investigation of more parameters and complex models of type deep learning could bring a potential improvement to the study. The visual interpretation of gastroenterologists during a colonoscopy examination is often affected by several artifacts such as motion, specularities, low contrast, and bubbles [43]. An appropriate video processing is desirable to eliminate such artifacts. Finally, although a large pool of videos was reviewed for Vatic dataset, the number of colonoscopy videos included in the study was small which may have restricted the performance of the proposed method. This could be overcome by considering a larger dataset.
7. Conclusions
This paper studies the automatic detection of bleeding and ulcers in colonoscopy videos for UC severity assessment based on a training dataset containing many annotation errors. Using bounding boxes, the annotation of bleeding and ulcers erroneously includes many healthy pixels. Thus, the ground truth accounts for many errors. We decided to deal with the annotation problem rather than proposing a sophisticated machine learning algorithm to improve detection performance as done by current studies. As in previous studies, we explore the set of linear classifiers and propose an efficient optimization method based on sampling the contour of the color histogram. The proposed strategy allows us to eliminate up to 25% trivial models which leads to focusing only on interesting models i.e., those giving nonzero true negative and true positive ratios. By adjusting the definition of sensitivity from pixel-level to annotation level, we can circumvent the effect of the annotation errors using bounding boxes, and select good pixel-level lesion detectors. The best linear models obtain 92.29 ± 0.443% specificity/88.59 ± 2.984% sensitivity for bleeding detection and 58.22 ± 0.393% specificity/81.68 ± 4.173% sensitivity for ulcer detection. Our results show better compromise between performance assessment in comparison with studies using similar models features. We also demonstrate that our models show reliable performance estimates from random subsets of the dataset. Our analysis shows that the best detectors achieve good performance, however, we notice that the performance results vary significantly from patient to patient, highlighting the need for a sort of normalization of the images from different patients for any method to work properly.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.A.-A., S.L.-T.-T. and H.Z.; methodology, S.A.-A. and S.L.-T.-T.; validation, X.T. and É.O.-D.; formal analysis, J.C.; investigation, S.A.-A.; resources, X.T. and A.P.-d.-S.; data curation, S.A.-A.; writing—original draft preparation, S.A.-A.; writing—review and editing, S.L.-T.-T. and H.Z.; visualization, S.A.-A.; supervision, S.L.-T.-T. and H.Z.; project administration, S.L.-T.-T. and H.Z.; funding acquisition, S.A.-A., S.L.-T.-T. and H.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was performed in the context of the Investissements d’Avenir programme ANR-11-IDEX-0005-02 and 10-LABX-0017, Sorbonne Paris Cité, Laboratoire d’excellence INFLAMEX. Safaa Al-Ali received funding from the Paris Region Fellowship Programme, attributed by the DIM MathInnov.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Institutional Review Board of Comité d’Evaluation de l’Ethique des projets de Recherche Biomédicale (CEERB) Paris Nord and the approval code is IRB 00006477.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study. Indeed, the patients’ videos were anonymous, and analyzed after obtaining their consent. The 340 study was approved by the local research study committee.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to warmly thank the anonymous reviewers for taking the time to read and comment on this manuscript. Their insightful comments and suggestions have significantly improved the overall quality of the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| IBD | Inflammatory bowel disease |
| CD | Crohn’s disease |
| UC | Ulcerative Colitis |
| WCE | Wireless Capsule Endoscopy |
| ROI | Region Of Interest |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| ROC | Receiver Operating Characteristic space |
| RGB | (Red, Green, Blue) color space |
| SVM | Directory of open access journals |
| KNN | K-Nearest Neighbors |
| YIQ | Luma In-phase Quadrature color space |
| HSV | Hue-Saturation-Value color space |
| HSI | Hue-Saturation-Intensity |
| CIElab, CMYK, YUV, CIElab, XYZ | diverse color spaces |
| TN | True Negative |
| TP | True Positive |
| FN | False Negative |
| FP | False Positive |
| TPA | Total number of pixels within the detected annotations |
| PA | Total number of pixels of all the annotations |
| RBF | Radial Basis Function |
| CrY | (Cr,Y) color space |
| RG | (R,G) color space |
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
References
- Popa, D.; Neamtu, B.; Mihalache, M.; Boicean, A.; Banciu, A.; Banciu, D.D.; Moga, D.F.; Birlutiu, V. Fecal Microbiota Transplant in Severe and Non-Severe Clostridioides difficile Infection. Is There a Role of FMT in Primary Severe CDI? J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popa, D.; Neamtu, B.; Mihalache, M.; Boicean, A.; Banciu, A.; Banciu, D.D.; Moga, D.F.; Birlutiu, V. The microbiome and inflammatory bowel disease: Is there a therapeutic role for fecal microbiota transplantation? Off. J. Am. Coll. Gastroenterol. ACG 2012, 107, 1452–1459. [Google Scholar]
- Boicean, A.; Birlutiu, V.; Ichim, C.; Anderco, P.; Birsan, S. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jäger, S.; Stange, E.F.; Wehkamp, J. Inflammatory bowel disease: An impaired barrier disease. Langenbeck’s Arch. Surg. 2013, 39, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamb, C.A.; Kennedy, N.A.; Raine, T.; Hendy, P.A.; Smith, P.J.; Limdi, J.K.; Hayee, B.; Lomer, M.C.E.; Parkes, G.C.; Selinger, C.; et al. British Society of Gastroenterology consensus guidelines on the management of inflammatory bowel disease in adults. Gut 2019, 68, s1–s106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Probert, F.; Walsh, A.; Jagielowicz, M.; Yeo, T.; Claridge, T.D.; Simmons, A.; Travis, S.; Anthony, D.C. Plasma nuclear magnetic resonance metabolomics discriminates between high and low endoscopic activity and predicts progression in a prospective cohort of patients with ulcerative colitis. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2018, 12, 1326–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iddan, G.; Meron, G.; Glukhovsky, A.; Swain, P. Wireless capsule endoscopy. Nature 2000, 405, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panaccione, R. Mechanisms of inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 9, 29–32. [Google Scholar]
- Du, W.; Rao, N.; Liu, D.; Jiang, H.; Luo, C.; Li, Z.; Gan, T.; Zeng, B. Review on the Applications of Deep Learning in the Analysis of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy Images. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 142053–142069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achanta, R.; Shaji, A.; Smith, K.; Lucchi, A.; Fua, P.; Süsstrunk, S. SLIC superpixels compared to state-of-the-art superpixel methods. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2012, 34, 2274–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeba, F.; Islam, M.; Bui, F.M.; Wahid, K.A. Performance assessment of a bleeding detection algorithm for endoscopic video based on classifier fusion method and exhaustive feature selection. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2018, 40, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Mandal, M.; Meng, M.Q. Computer-Aided Bleeding Detection in WCE Video. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2014, 18, 636–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, T.; Fattah, S.A.; Wahid, K.A.; Zhu, W.P.; Ahmad, M.O. Cluster based statistical feature extraction method for automatic bleeding detection in wireless capsule endoscopy video. Comput. Biol. Med. 2018, 94, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suman, S.; Hussin, F.A.; Malik, A.S.; Ho, S.H.; Hilmi, I.; Leow, A.H.R.; Goh, K.L. Feature selection and classification of ulcerated lesions using statistical analysis for WCE images. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogorelov, K.; Suman, S.; Azmadi Hussin, F.; Saeed Malik, A.; Ostroukhova, O.; Riegler, M.; Halvorsen, P.; Hooi Ho, S.; Goh, K.L. Bleeding detection in wireless capsule endoscopy videos—Color versus texture features. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2019, 20, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.Y.; Wu, T.H.; Tsai, W.J. Bleeding and ulcer detection using wireless capsule endoscopy images. J. Softw. Eng. Appl. 2014, 7, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, B.; Meng, M.Q.H. Saliency based ulcer detection for wireless capsule endoscopy diagnosis. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2015, 34, 2046–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jheng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lin, H.; Sung, K.; Chu, Y.; Wang, H.; Jiang, J.; Hou, M.; Lee, F.; Lu, C. A novel machine learning-based algorithm to identify and classify lesions and anatomical landmarks in colonoscopy images. Surg. Endosc. 2022, 36, 640–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, T.; Fattah, S.A.; Wahid, K.A. CHOBS: Color histogram of block statistics for automatic bleeding detection in wireless capsule endoscopy video. IEEE J. Transl. Eng. Health Med. 2018, 6, 1800112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, A.R.; Haque, M.A. Computer-aided gastrointestinal hemorrhage detection in wireless capsule endoscopy videos. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2015, 122, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.Y.; Gan, T.; Rao, N.N.; Xing, Y.W.; Zheng, J.; Li, S.; Luo, C.S.; Zhou, Z.J.; Wan, Y.L. Identification of lesion images from gastrointestinal endoscope based on feature extraction of combinational methods with and without learning process. Med. Image Anal. 2016, 32, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawarathna, R.; Oh, J.; Muthukudage, J.; Tavanapong, W.; Wong, J.; De Groen, P.C.; Tang, S.J. Abnormal image detection in endoscopy videos using a filter bank and local binary patterns. Neurocomputing 2014, 144, 70–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasilakakis, M.D.; Iakovidis, D.K.; Spyrou, E.; Koulaouzidis, A. DINOSARC: Color features based on selective aggregation of chromatic image components for wireless capsule endoscopy. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2018, 2018, 2026962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vondrick, C.; Patterson, D.; Ramanan, D. Efficiently scaling up crowdsourced video annotation. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2013, 101, 184–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, T.; Bashar, S.K.; Alam, M.S.; Wahid, K.; Fattah, S.A. A statistical feature-based novel method to detect bleeding in wireless capsule endoscopy images. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Informatics, Electronics & Vision (ICIEV), Dhaka, Bangladesh, 23–24 May 2014; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Koshy, N.E.; Gopi, V.P. A new method for ulcer detection in endoscopic images. In Proceedings of the 2015 2nd International Conference on Electronics and Communication Systems (ICECS), Coimbatore, India, 26–27 February 2015; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 1725–1729. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Y.; Mandal, M.; Guo, G. Bleeding region detection in WCE images based on color features and neural network. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE 54th International Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems (MWSCAS), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 7–10 August 2011; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Kundu, A.K.; Fattah, S.A.; Rizve, M.N. An automatic bleeding frame and region detection scheme for wireless capsule endoscopy videos based on interplane intensity variation profile in normalized RGB color space. J. Healthc. Eng. 2018, 2018, 9423062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, T.; Fattah, S.A.; Shahnaz, C.; Wahid, K.A. An automatic bleeding detection scheme in wireless capsule endoscopy based on histogram of an RGB-indexed image. In Proceedings of the 2014 36th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Chicago, IL, USA, 26–30 August 2014; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 4683–4686. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, T.; Fattah, S.A.; Bashar, S.; Shahnaz, C.; Wahid, K.A.; Zhu, W.P.; Ahmad, M.O. An automatic bleeding detection technique in wireless capsule endoscopy from region of interest. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Digital Signal Processing (DSP), Singapore, 21–24 July 2015; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 1293–1297. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, G.; Yan, G.; Qiu, X.; Cui, J. Bleeding detection in wireless capsule endoscopy based on probabilistic neural network. J. Med. Syst. 2011, 35, 1477–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suman, S.; Walter, N.; Hussin, F.A.; Malik, A.S.; Ho, S.H.; Goh, K.L.; Hilmi, I. Optimum colour space selection for ulcerated regions using statistical analysis and classification of ulcerated frames from wce video footage. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Neural Information Processing, Istanbul, Turkey, 9–12 November 2015; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 373–381. [Google Scholar]
- Leung, T.; Malik, J. Representing and recognizing the visual appearance of materials using three-dimensional textons. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2001, 43, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Ali, S. Mathematical Modelling of Chronic Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Ph.D. Thesis, Université Paris-Nord-Paris XIII, Villetaneuse, France, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Youden, W.J. Index for rating diagnostic tests. Cancer 1950, 3, 32–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.W.; Hsieh, C.J.; Chang, K.W.; Ringgaard, M.; Lin, C.J. Training and Testing Low-degree Polynomial Data Mappings via Linear SVM. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2010, 11, 1471–1490. [Google Scholar]
- Sainju, S.; Bui, F.M.; Wahid, K.A. Automated bleeding detection in capsule endoscopy videos using statistical features and region growing. J. Med. Syst. 2014, 38, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, D.C.; Chang, C.H. Color segmentation using perceptual attributes. In Proceedings of the 11th IAPR International Conference on Pattern Recognition, The Hague, The Netherlands, 30 August–1 September 1992; Volume III. Conference C: Image, Speech and Signal Analysis. IEEE Computer Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1992; pp. 228–231. [Google Scholar]
- Badrinarayanan, V.; Kendall, A.; Cipolla, R. SegNet: A deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 2481–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.-C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets atrous convolution and fully connected CRFs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2018, 40, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Ali, S.; Shahin, A.; Chakik, F. Influence of Ambiguity Cluster on Quality Improvement in Image Compression. Int. J. Comput. Inf. Eng. 2013, 7, 232–236. [Google Scholar]
- Shahin, A.; Chakik, F.; Al-Ali, S. Complexity Reduction and Quality Enhancement in Image Coding. Int. J. Future Comput. Commun. 2013, 2, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Zhou, F.; Braden, B.; Bailey, A.; Yang, S.; Cheng, G.; Zhang, P.; Li, X.; Kayser, M.; Soberanis-Mukul, R.D.; et al. An objective comparison of detection and segmentation algorithms for artefacts in clinical endoscopy. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).