Sex Differences and Bmal1/Acetylcholine- or Bmal1/Noradrenaline-Mediated Effects of Blue Light Irradiation on Dextran-Sodium-Sulfate-Induced Ulcerative Colitis Model Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effects of Blue Light Irradiation on DSS-Treated Male and Female Mice
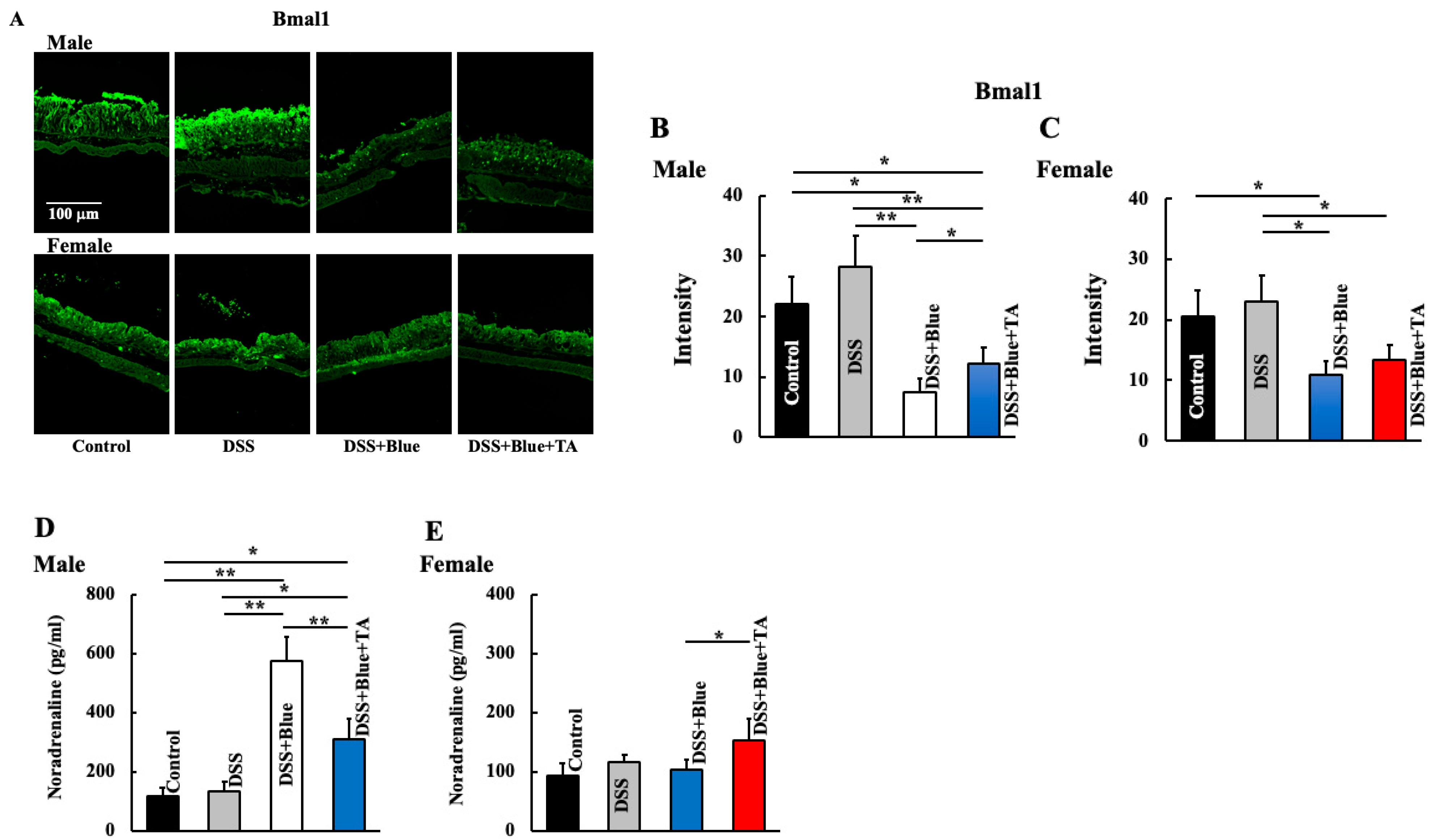
2.2. Effect of Blue Light Irradiation on the Expression of Bmal1 and Noradrenaline Levels in DSS-Treated Male and Female Mice
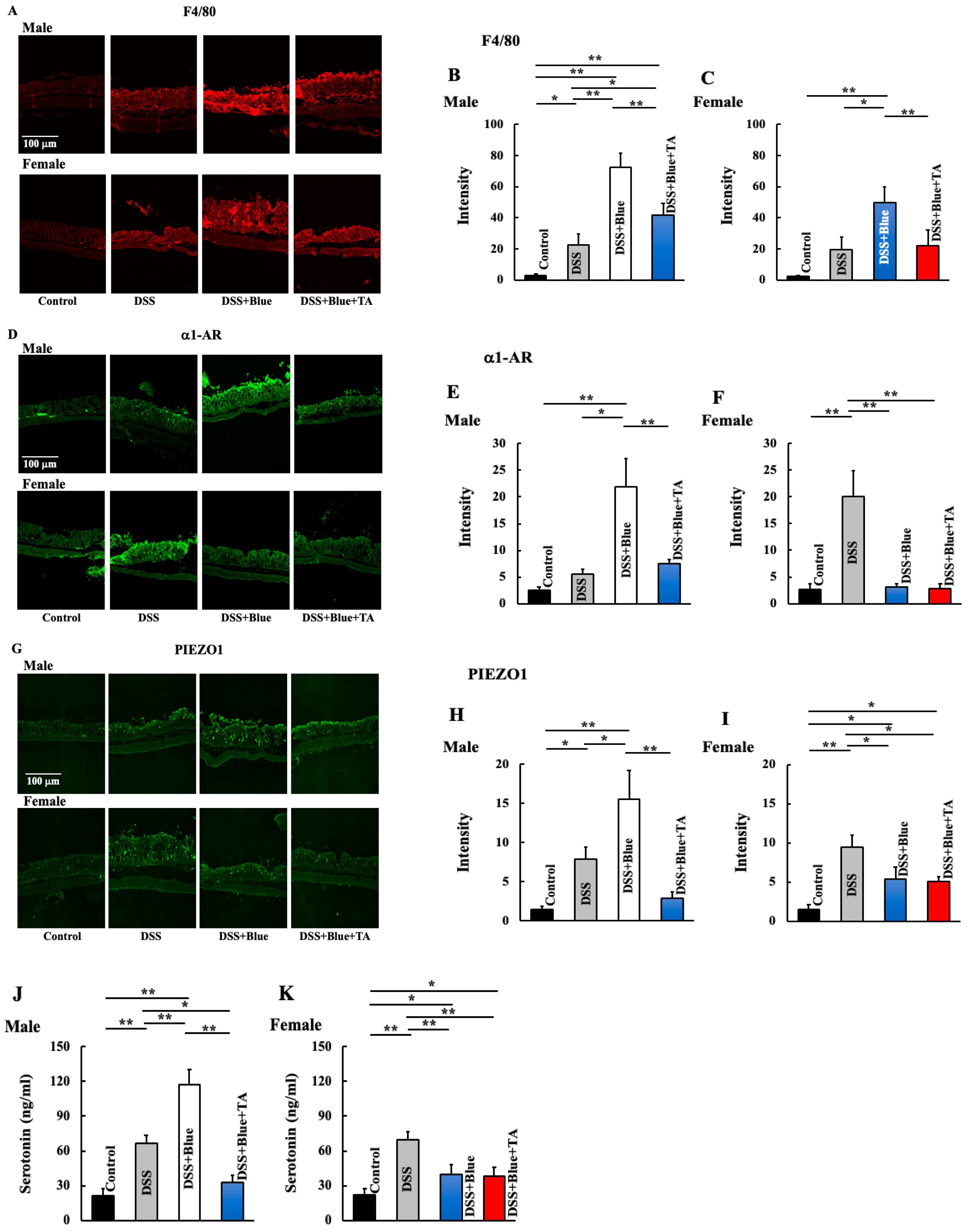
2.3. Effects of Blue Light Irradiation on the Expression of Macrophages, Piezo-Type Mechanosensitive Ion Channel Component 1 (PIEZO1), Alpha-1 Adrenergic Receptor (a1-AR), and Plasma Serotonin Levels in DSS-Treated Male and Female Mice
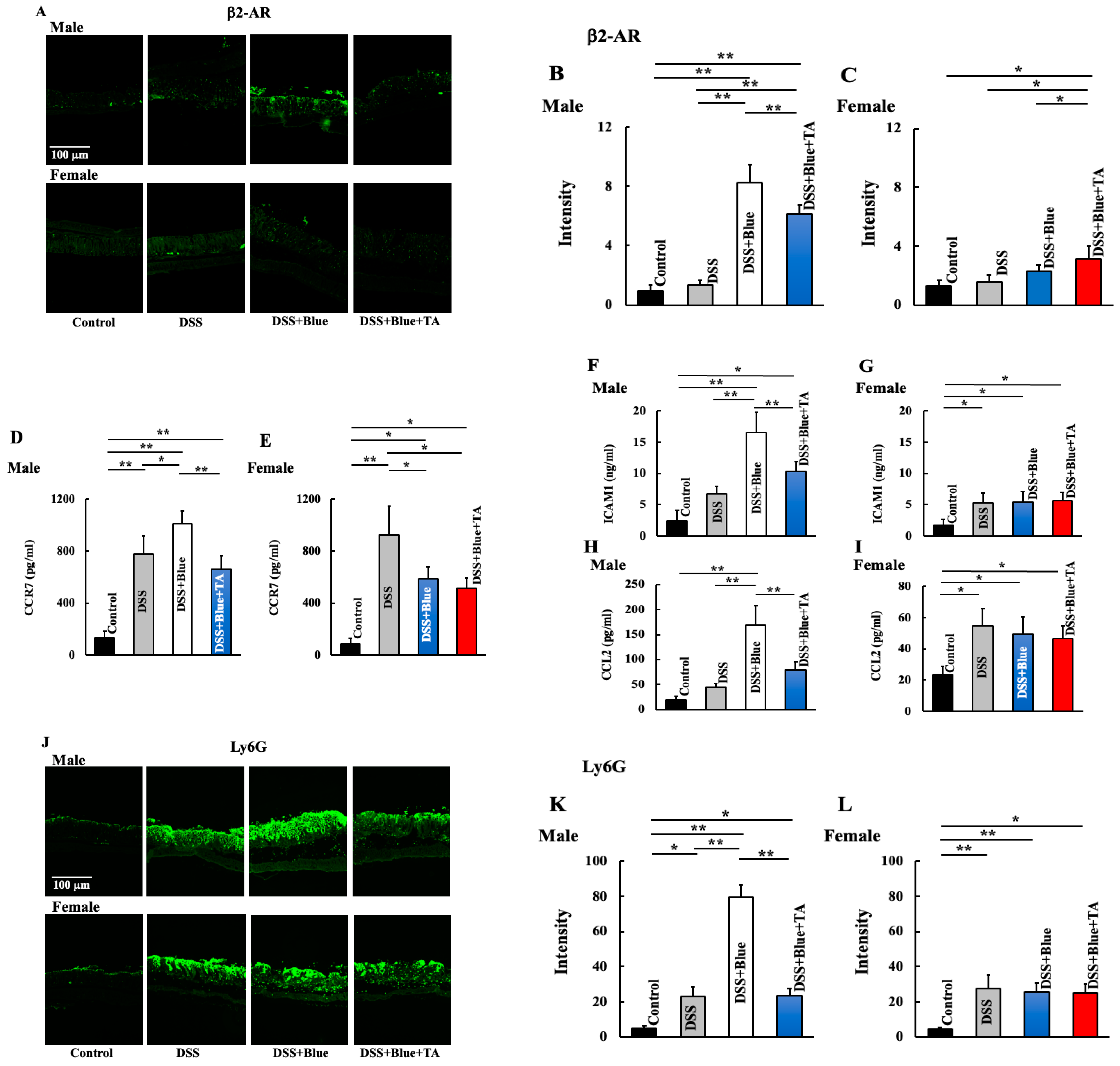
2.4. Effect of Blue Light Irradiation on the Expression of Beta 2 Adrenergic Receptor (β2-AR), Neutrophils, and Plasma Levels of C-C Motif Chemokine Receptor (CCR7), Intercellular Adhesion Molecule 1 (ICAM1), and C-C Motif Chemokine Ligand (CCL2) in DSS-Treated Male and Female Mice
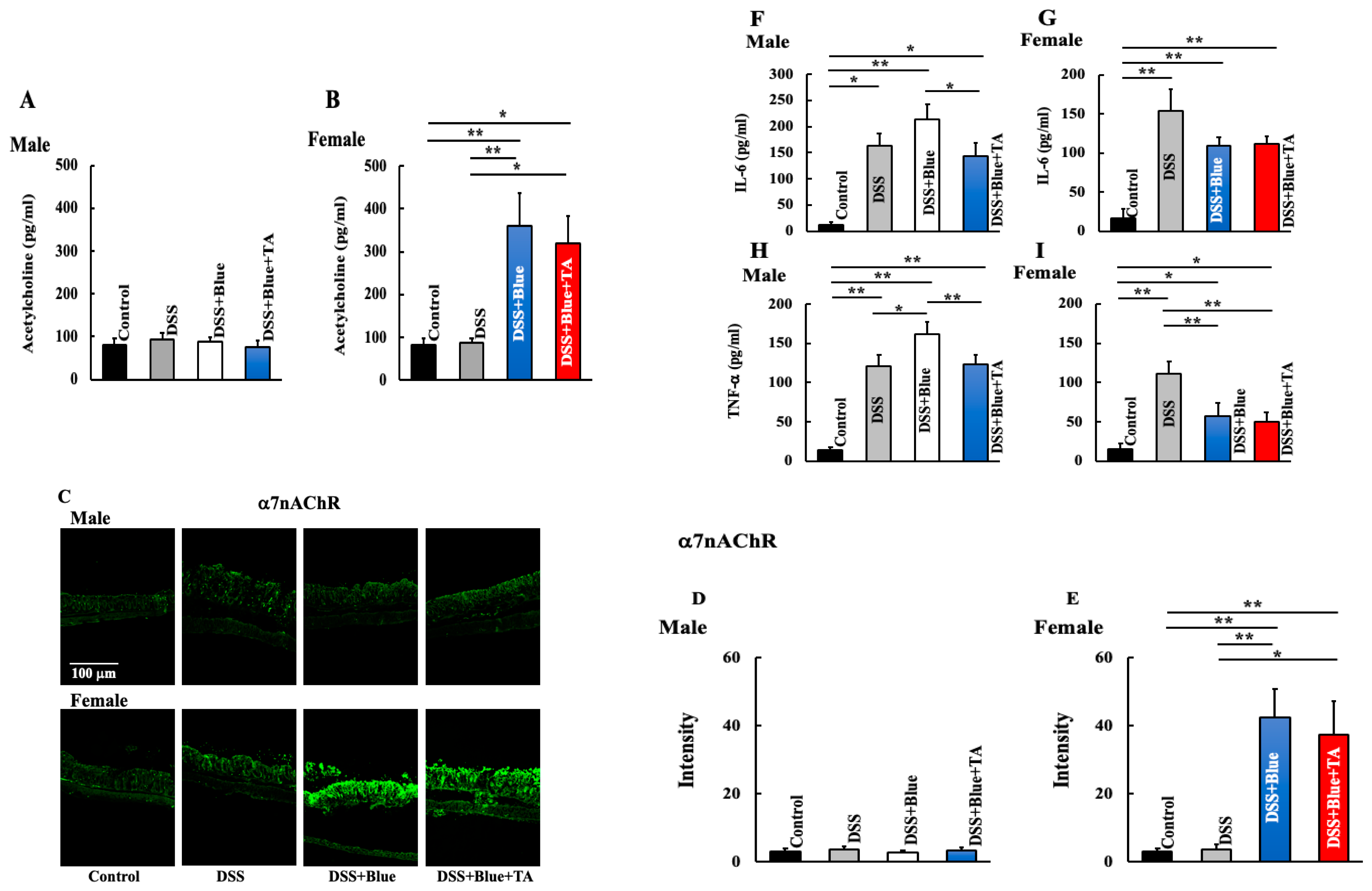
2.5. Effect of Blue Light Irradiation on the Expression of Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Alpha 7 (α7nAChR) and Plasma Levels of Interleukin (IL)-6 and TNF-α in DSS-Treated Male and Female Mice
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animal Experiments
4.2. DSS-Induced Colitis
4.3. TA Treatment
4.4. Preparation and Staining of the Colon
4.5. Measurement of Noradrenaline, CCR7, ICAM1, Serotonin, IL-6, TNF-a α, and CCL2 Levels in the Colon
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hirmatsu, T. Recent advances in the diagnosis and management of inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterol. Endosc. 2019, 61, 1523–1537. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, T.; Hibi, T. Concept, definition and epidemiology of inflammatory bowel diseases. Nihon Naika Gakkai Zasshi 2009, 98, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakiuchi, N.; Yoshida, K.; Uchino, M.; Kihara, T.; Akaki, K.; Inoue, Y.; Ogawa, S. Frequent mutations that converge on the NFKBIZ pathway n ulcerative colitis. Nature 2020, 577, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, N.; Watanabe, M.; Sato, T.; Okazawa, A.; Yamazaki, M.; Kanai, T.; Hibi, T. Restricted VH)gene usage in lamina propria B cells producing anticolon antibody from patients with ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology 2001, 121, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakazawa, A.; Watanabe, M.; Kanai, T.; Yajima, T.; Yamazaki, M.; Ogata, H.; Hibi, T. Functional expression of costimulatory molecule CD86 on epithelial cells in the inflamed colonic mucosa. Gastroenterology 1999, 117, 536–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M.; Ueno, Y.; Yajima, T.; Okamoto, S.; Hayashi, T.; Yamazaki, M.; Hibi, T. Interleukin 7 transgenic mice develop chronic colitis with decreased interleukin 7 protein accumulation in the colonic mucosa. J. Exp. Med. 1998, 187, 389–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogata, H.; Hibi, T. Inflammatory bowel disease: Current progress and future aspect. Nihon Shokakibyo Gakkai Zasshi 2007, 104, 1155–1164. [Google Scholar]
- Derkx, B.; Taminiau, J.; Rdema, S.; Stronkhorst, A.; Wortel, C.; Tytgat, G.; van Deventer, S. Tumour-necrosis-factor antibody treatment in Crohn’s disease. Lancet 1993, 342, 173–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.; Motoya, S.; Hanai, H.; Matsumoto, T.; Hibi, T.; Robinson, A.M.; Watanabe, M. Efficacy and safety of adalimumab in Japanese patients with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis. J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 49, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandborn, W.J.; Feagan, B.G.; Marano, C.; Zhang, H.; Strauss, R.; Johanns, J.; PURSUIT-SC Study Group. Subcutaneous golimumab induces clinical response and remission in patients with moderate-to-severe ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology 2014, 146, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandborn, W.J.; Gasink, C.; Gao, L.L.; Blank, M.A.; Johanns, J.; Guzzo, C.; Feagan, B.G. Ustekinumab induction and maintenance therapy in refractory Crohn’s disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 1519–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiramoto, K.; Yamate, Y.; Kasahara, E.; Sato, E.F. An inhibitor of casein kinase 1e/d (PF670462) prevents the deterioration of dextran sodium sulfate-induced ulcerative colitis caused by UVB eye irradiation. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 14, 992–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Touitou, Y.; Touitou, D.; Reinberg, A. Disruption of adolescents’ circadian clock: The vicious circle of media use, exposure to light at night, sleep loss and risk behaviors. J. Physiol. Paris 2016, 110, 467–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neubert, E.; Bach, K.M.; Busse, J.; Bogeski, I.; Schon, M.P.; Kruss, S.; Erpenbeck, L. Blue and long-wave ultraviolet light induce in vitro neutrophil extracellular trap (NET) formation. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 476466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Q.; Guo, X.; Su, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Peng, X.; Qiu, C.H. Blue light irradiation alleviated dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis mediated by the Bmal1 pathway in macrophages. J. Photochem. Photobiol. 2022, 12, 100156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiramoto, K.; Yamate, Y.; Sato, E.F. The effects of ultraviolet eye irradiation on dextran sodium sulfate-induced ulcerative colitis in mice. Photochem. Photobiol. 2016, 92, 728–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiramoto, K.; Yamate, Y.; Sugiyama, D.; Matsuda, K.; Iizuka, Y.; Yamaguchi, T. Ameriolative effect of tranexamic acid on physiological skin aging and its sex difference in mice. Ach. Dermatol. Res. 2019, 311, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiramoto, K.; Yamate, Y.; Sugiyama, D.; Matsuda, K.; Iizuka, Y.; Yamaguchi, T. Tranexamic acid ameliorates nonmelanoma skin cancer induced by long-term ultraviolet A irradiation. Photochem. Photobiol. 2019, 95, 612–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiyama, A.; Yujiri, T.; Tanaka, M.; Tanaka, Y.; Nakamura, Y.; Tanizawa, Y. Altered expression of circadian clock genes during peripheral blood stem cell mobilization induced by granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. Chronobiol. Int. 2015, 32, 934–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheiermann, C.; Kunisaki, Y.; Frenette, P.S. Circadian control of the immune system. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheiermann, C.; Kunisaki, Y.; Lucas, D.; Chow, A.; Jang, J.E.; Zhang, D.; Frenette, P.S. Adrenergic nerves govern circadian leukocyte recruitment to tissues. Immunity 2012, 37, 290–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaked, I.; Hanna, R.N.; Shaked, H.; Chodaczek, G.; Nowyhed, H.N.; Tweet, G.; Hedrick, C.C. Transcription factor Nr4a1 couples sympathetic and inflammatory cues in CNS-recruited macrophages to limit neuroinflammation. Nat. Immunol. 2015, 16, 1228–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flierl, M.A.; Rittirsch, D.; Nadeau, B.A.; Chen, A.J.; Sarma, J.V.; Zetoune, F.S.; Ward, P.A. Phagocyte-derived catecholamines enhance acute inflammatory injury. Nature 2007, 449, 721–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugisawa, E.; Takayama, Y.; Takemura, N.; Kondo, T.; Hatakeyama, S.; Kumagai, Y.; Maruyama, K. RNA sensing by gut piezo1 is essential for systemic serotonin synthesis. Cell 2020, 182, 609–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coste, B.; Mathur, J.; Schmidt, M.; Early, T.J.; Ranada, S.; Petrus, M.J.; Patapoutian, A. Piezo1 and piezo2 are essential components of distinct mechanically activated cation channels. Science 2010, 330, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atcha, H.; Jairaman, A.; Holt, J.R.; Meli, V.S.; Nagalla, R.R.; Veerasubramanian, P.K.; Liu, W.F. Mechanically activated ion channel Piezo1 modulates macrophage polarization and stiffness sensing. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, E.R. PIEZO1 promotes inflammation. Sci. Signal. 2019, 12, 4154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talley, N.J. Serotoninergic neuroenteric modulators. Lancet 2001, 358, 2061–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coates, M.D.; Mahoney, C.R.; Linden, D.R.; Sampson, J.E.; Chen, J.; Blaszyk, H.; Moses, P.L. Molecular defects in mucosal serotonin content and decreased serotonin reuptake transporter in ulcerative colitis and irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology 2004, 126, 1657–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Salhy, M.; Danielsson, A.; Stenling, R.; Grimelius, L. Colonic endocrine cells in inflammatory bowel disease. J. Intern. Med. 1997, 242, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yu, M.; Ochani, M.; Amella, C.A.; Tanovic, M.; Susarla, S.; Tracey, K.J. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor α7 subunit is an essential regulator of inflammation. Nature 2003, 421, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, U.; Tracey, K.J. Reflex principles of immunological homeostasis. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 30, 313–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tracey, K.J. Reflex control of immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 418–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosas-Ballina, M.; Olofsson, P.S.; Ochani, M.; Valdes-Ferrer, S.I.; Levine, Y.A.; Reardon, C.; Tracey, K.J. Acetylcholine-synthesizing T cells relay neural signals in a vagus nerve circuit. Science 2011, 334, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimura, T.; Andoh, A.; Hashimoto, T.; Kobori, A.; Tsujikawa, T.; Fujiyama, Y. Cellobiose prevents the development of dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced experimental colitis. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2010, 46, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudreau, R.M.; Johnson, M.; Veile, R.; Friend, L.A.; Goetzman, H.; Pritts, T.A.; Goodman, M.D. Impact of tranexamic acid on coagulation and inflammation in murine models of traumatic brain injury and hemorrhage. J. Surg. Res. 2017, 215, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, S.; Hiramoto, K.; Koyama, M.; Ooi, K. Skin disruption is associated with indomethacin-induced small intestine injury in mice. Exp. Dermatol. 2014, 23, 659–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hiramoto, K.; Kubo, S.; Tsuji, K.; Sugiyama, D.; Hamano, H. Sex Differences and Bmal1/Acetylcholine- or Bmal1/Noradrenaline-Mediated Effects of Blue Light Irradiation on Dextran-Sodium-Sulfate-Induced Ulcerative Colitis Model Mice. Gastrointest. Disord. 2024, 6, 720-732. https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord6030048
Hiramoto K, Kubo S, Tsuji K, Sugiyama D, Hamano H. Sex Differences and Bmal1/Acetylcholine- or Bmal1/Noradrenaline-Mediated Effects of Blue Light Irradiation on Dextran-Sodium-Sulfate-Induced Ulcerative Colitis Model Mice. Gastrointestinal Disorders. 2024; 6(3):720-732. https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord6030048
Chicago/Turabian StyleHiramoto, Keiichi, Sayaka Kubo, Keiko Tsuji, Daijiro Sugiyama, and Hideo Hamano. 2024. "Sex Differences and Bmal1/Acetylcholine- or Bmal1/Noradrenaline-Mediated Effects of Blue Light Irradiation on Dextran-Sodium-Sulfate-Induced Ulcerative Colitis Model Mice" Gastrointestinal Disorders 6, no. 3: 720-732. https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord6030048
APA StyleHiramoto, K., Kubo, S., Tsuji, K., Sugiyama, D., & Hamano, H. (2024). Sex Differences and Bmal1/Acetylcholine- or Bmal1/Noradrenaline-Mediated Effects of Blue Light Irradiation on Dextran-Sodium-Sulfate-Induced Ulcerative Colitis Model Mice. Gastrointestinal Disorders, 6(3), 720-732. https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord6030048





