Insight into the Physicochemical Properties of Co-Based Catalysts in Fischer–Tropsch Synthesis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
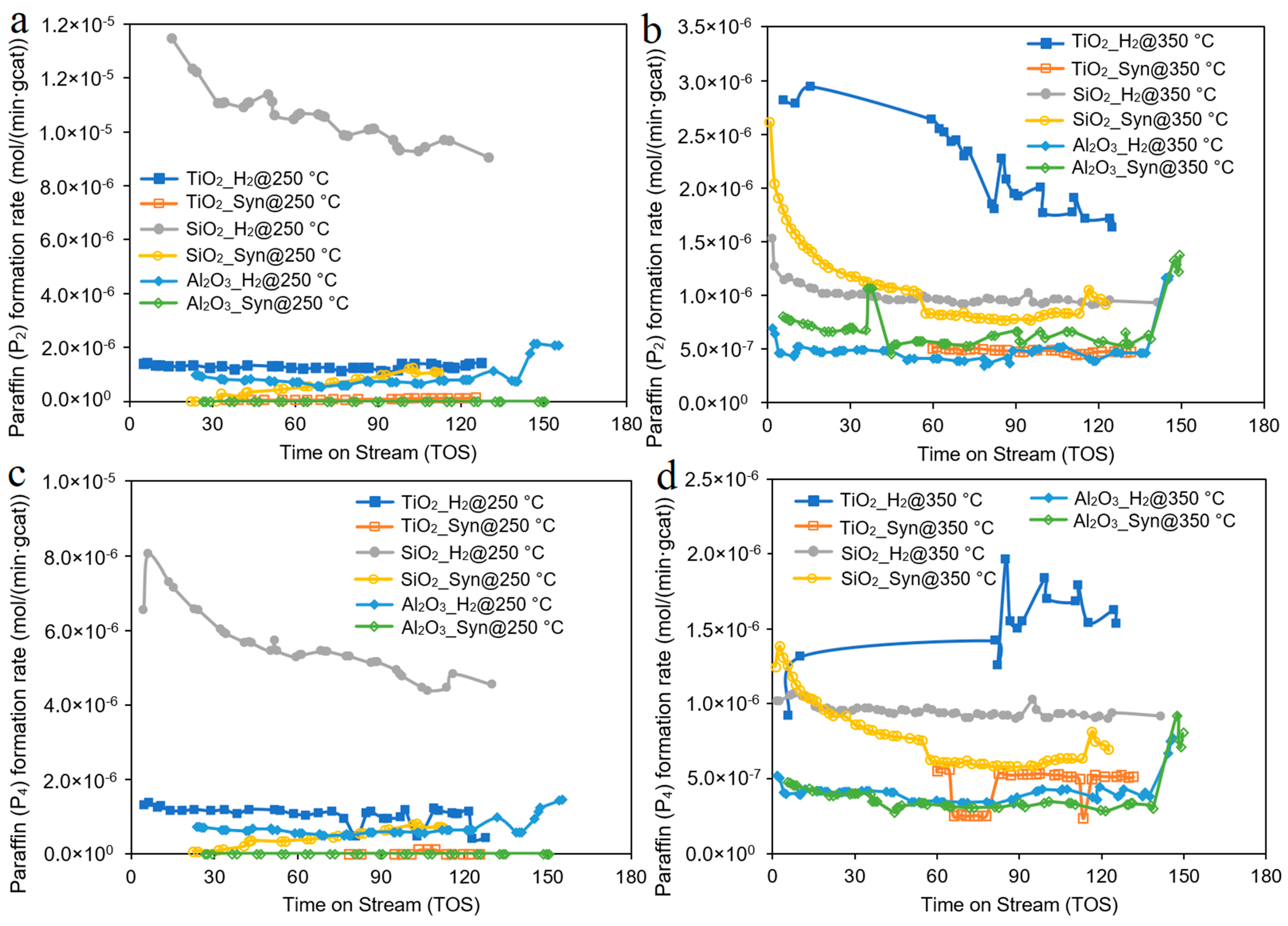
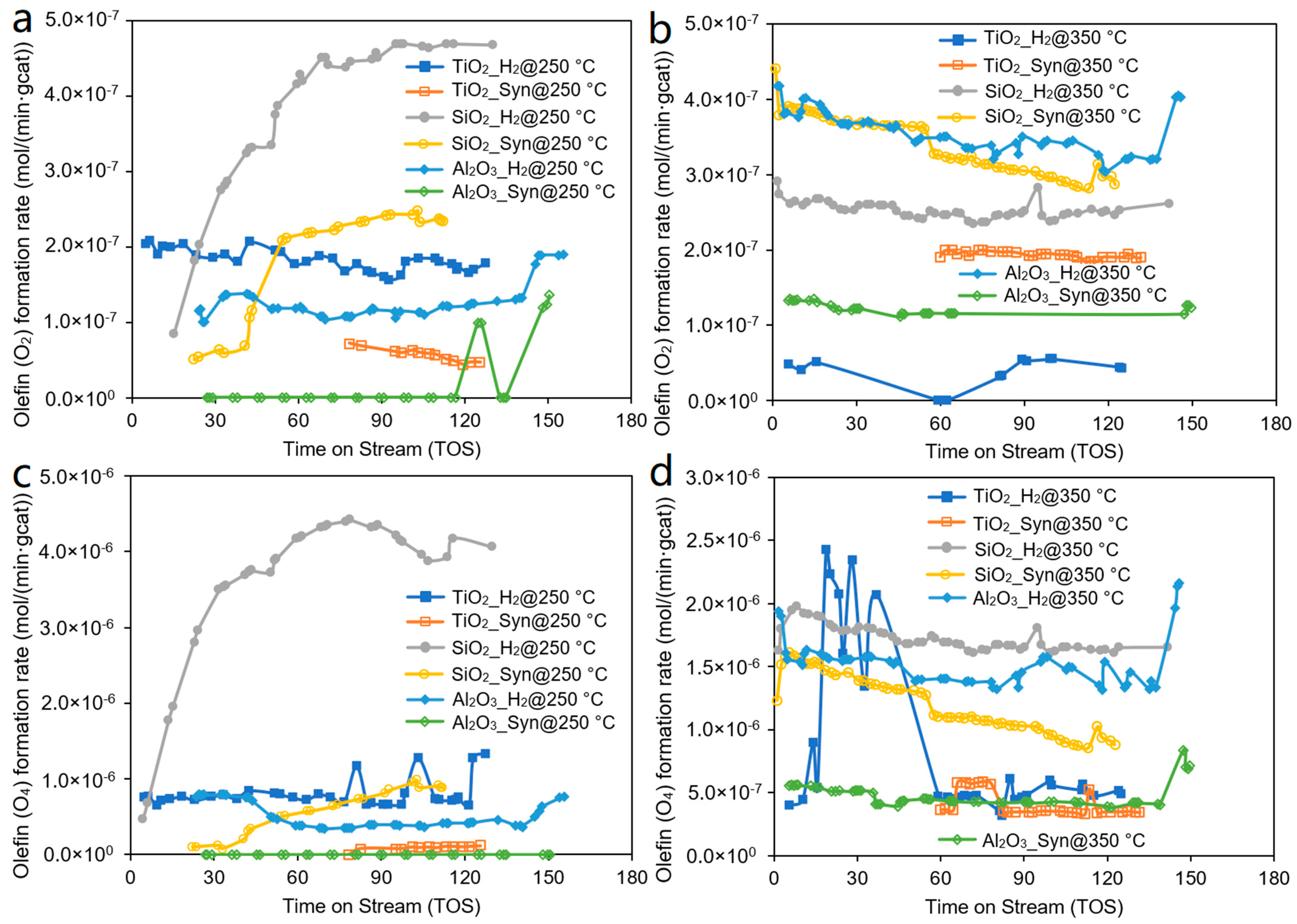
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sage, V.; Sun, Y.; Hazewinkel, P.; Bhatelia, T.; Braconnier, L.; Tang, L.; Chiang, K.; Batten, M.; Burke, N. Modified product selectivity in Fischer–Tropsch synthesis by catalyst pre-treatment. Fuel Process. Technol. 2017, 167, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vosoughi, V.; Badoga, S.; Dalai, A.K.; Abatzoglou, N. Effect of pretreatment on physicochemical properties and performance of multiwalled carbon nanotube supported cobalt catalyst for Fischer–Tropsch Synthesis. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 6049–6059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, R.W.; Lloyd, D.C.; van de Water, L.G.A.; Ellis, P.R.E.; Metcalfe, K.A.; Sibbald, C.; Davies, L.H.; Enache, D.I.; Kelly, G.J.; Boyes, E.D.; et al. Effect of pretreatment method on the nanostructure and performance of supported Co catalysts in Fischer–Tropsch synthesis. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 8816–8829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiba, N.C.; Yao, Y.; Liu, X.; Hildebrandt, D. Recent developments in catalyst pretreatment technologies for cobalt based Fisher–Tropsch synthesis. Rev. Chem. Eng. 2022, 38, 503–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Q.; Li, K.; Zhang, C.; Cheruvathur, A.V.; Zheng, L.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y. XAFS Studies of Fe−SiO2 Fischer–Tropsch Catalyst during activation in CO, H2, and Synthesis Gas. ChemCatChem 2019, 11, 2206–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Wang, B.; Xiao, G.; Wang, N.; Zhang, Y.; Khodakov, A.Y.; Li, J. Tuning the metal–support interaction and enhancing the stability of titania-supported cobalt Fischer–Tropsch catalysts via carbon nitride coating. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 5554–5566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, H.; Wu, B.; Xiang, H.; Li, Y. Fischer–Tropsch synthesis: Influence of support incorporation manner on metal dispersion, metal–support interaction, and activities of iron catalysts. ACS Catal. 2012, 2, 1877–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Liu, Y.; Lyu, S.; Tian, Y.; Ma, Q.; Li, X. Manipulating metal-support interactions of metal catalysts for Fischer-Tropsch synthesis. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2021, 35, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowker, M.; Stone, P.; Morrall, P.; Smith, R.; Bennett, R.; Perkins, N.; Kvon, R.; Pang, C.; Fourre, E.; Hall, M. Model catalyst studies of the strong metal–support interaction: Surface structure identified by STM on Pd nanoparticles on TiO2 (110). J. Catal. 2005, 234, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Su, X.; Li, L.; Qi, H.; Yang, C.; Liu, W.; Pan, X.; Liu, X.; Yang, X.; Huang, Y.; et al. Ru/TiO2 catalysts with size-dependent metal/support interaction for tunable reactivity in Fischer–Tropsch synthesis. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 12967–12975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kliewer, C.E.; Soled, S.L.; Kiss, G. Morphological transformations during Fischer-Tropsch synthesis on a titania-supported cobalt catalyst. Catal. Today 2019, 323, 233–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo-Tarifa, F.; Cabrera, S.; Sanchez-Dominguez, M.; Boutonnet, M. Ce-promoted Co/Al2O3 catalysts for Fischer–Tropsch synthesis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 9754–9765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jia, L.; Hou, B.; Sun, D.; Li, D. Cobalt aluminate-modified alumina as a carrier for cobalt in Fischer–Tropsch synthesis. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2017, 530, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, M.; Fischer, N.; Claeys, M. Formation of metal-support compounds in cobalt-based Fischer-Tropsch synthesis: A review. Chem. Catal. 2021, 1, 1014–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavasoli, A.; Abbaslou, R.M.M.; Dalai, A.K. Deactivation behavior of ruthenium promoted Co/γ-Al2O3 catalysts in Fischer–Tropsch synthesis. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2008, 346, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsakoumis, N.E.; Walmsley, J.C.; Rønning, M.; van Beek, W.; Rytter, E.; Holmen, A. Evaluation of reoxidation thresholds for γ-Al2O3-supported cobalt catalysts under Fischer–Tropsch synthesis conditions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 3706–3715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melaet, G.; Ralston, W.T.; Li, C.S.; Alayoglu, S.; An, K.; Musselwhite, N.; Kalkan, B.; Somorjai, G.A. Evidence of highly active cobalt oxide catalyst for the Fischer–Tropsch synthesis and CO2 hydrogenation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 2260–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiba, N.C.; Yao, Y.; Forbes, R.P.; Okoye-Chine, C.G.; Liu, X.; Hildebrandt, D. Role of CoO-Co nanoparticles supported on SiO2 in Fischer–Tropsch synthesis: Evidence for enhanced CO dissociation and olefin hydrogenation. Fuel Process. Technol. 2021, 216, 106781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Yu, F.; Li, X.; Lin, T.; An, Y.; Zhong, L.; Sun, Y. Fischer-Tropsch to olefins over Co2C-based catalysts: Effect of thermal pretreatment of SiO2 support. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2021, 623, 118283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, G.; Das, T.K.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Racoillet, G.; Davis, B.H. Fischer–Tropsch synthesis: Support, loading, and promoter effects on the reducibility of cobalt catalysts. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2002, 233, 263–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiba, N.C.; Liu, X.; Hildebrandt, D.; Yao, Y. Effect of pre-treatment conditions on the activity and selectivity of cobalt-based catalysts for CO hydrogenation. Reactions 2021, 2, 258–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Hamasaki, A.; Honma, T.; Tokunaga, M. Anti-ASF distribution in Fischer–Tropsch synthesis over unsupported cobalt catalysts in a batch slurry phase reactor. Catal. Today 2011, 175, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiba, N.C.; Liu, X.; Yao, Y. Advances in lower olefin production over cobalt-based catalysts via the Fischer–Tropsch process. Fuel Process. Technol. 2022, 238, 107489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojeda, M.; Nabar, R.; Nilekar, A.U.; Ishikawa, A.; Mavrikakis, M.; Iglesia, E. CO activation pathways and the mechanism of Fischer–Tropsch synthesis. J. Catal. 2010, 272, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Parvari, M.; Bukur, D.B. Fischer–Tropsch synthesis on Co/ZnO–Two step activation procedure for improved performance. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2014, 480, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xu, L.; Keogh, R.; Davis, B. Fischer–Tropsch synthesis: Effect of CO pretreatment on a ruthenium promoted Co/TiO2. Catal. Lett. 2000, 70, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Jacobs, G.; Jermwongratanachai, T.; Pendyala, V.R.; Ma, W.; Chen, D.; Holmen, A.; Davis, B.H. Fischer–Tropsch synthesis: Impact of H2 or CO activation on methane selectivity. Catal. Lett. 2014, 144, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanudin, H.; Asri, W.R.; Fanani, Z.; Adisti, S.J.; Hadiah, F.; Maryana, R.; Al Muttaqii, M.; Zhu, Z.; Machado, N.T. Facile fabrication of SiO2/Zr Assisted with EDTA complexed-impregnation and templated methods for crude palm oil to biofuels conversion via catalytic hydrocracking. Catalysts 2022, 12, 1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kababji, A.H.; Joseph, B.; Wolan, J.T. Silica-supported cobalt catalysts for Fischer–Tropsch synthesis: Effects of calcination temperature and support surface area on cobalt silicate formation. Catal. Lett. 2009, 130, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alothman, Z.A. A review: Fundamental aspects of silicate mesoporous materials. Material 2012, 5, 2874–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claeys, M. Cobalt gets in shape. Nature 2016, 538, 44–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rytter, E.; Holmen, A. On the support in cobalt Fischer–Tropsch synthesis—Emphasis on alumina and aluminates. Catal. Today 2016, 275, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saib, A.M.; Claeys, M.; Van Steen, E. Silica supported cobalt Fischer–Tropsch catalysts: Effect of pore diameter of support. Catal. Today 2002, 71, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diehl, F.; Khodakov, A.Y. Promotion of cobalt Fischer-Tropsch catalysts with noble metals: A review. Oil Gas Sci. Technol. 2009, 64, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalama, K.; Kabuba, J.; Xiong, H.; Jewell, L.L. Co/TiO2 Fischer–Tropsch catalyst activation by synthesis gas. Catal. Commun. 2012, 17, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.Y.; Lee, Y.J.; Karandikar, P.R.; Jun, K.W.; Ha, K.S.; Park, H.G. Fischer–Tropsch catalysts deposited with size-controlled Co3O4 nanocrystals: Effect of Co particle size on catalytic activity and stability. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2012, 411, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
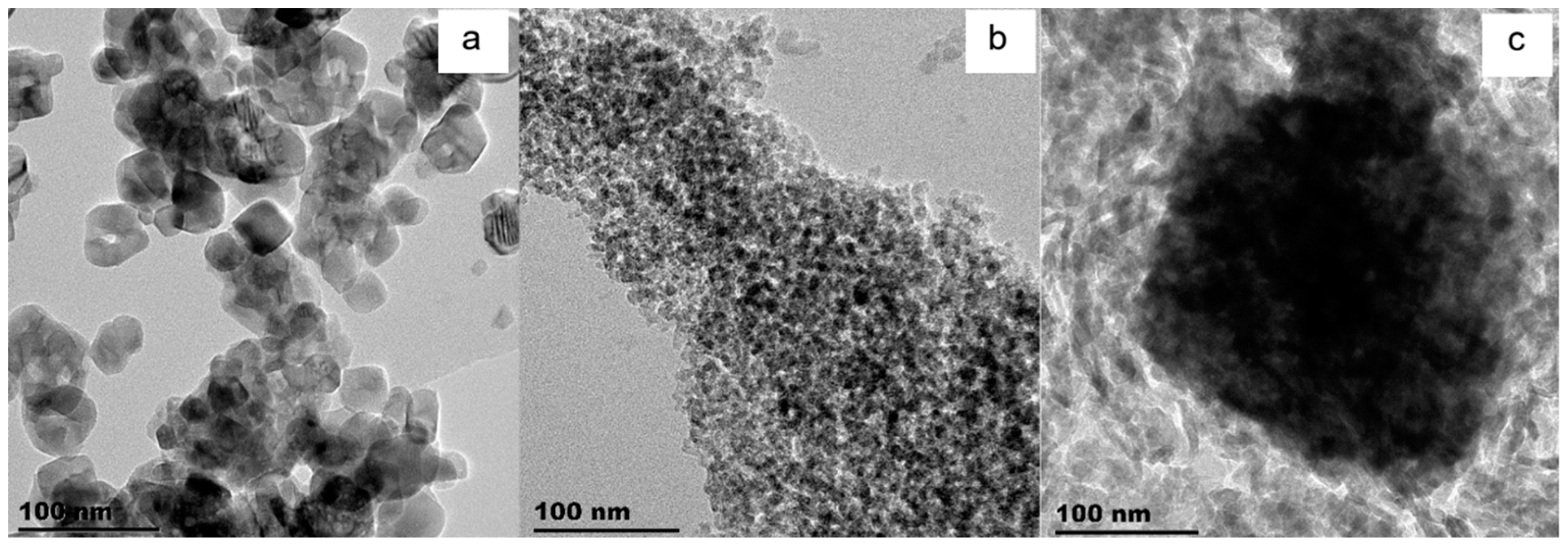
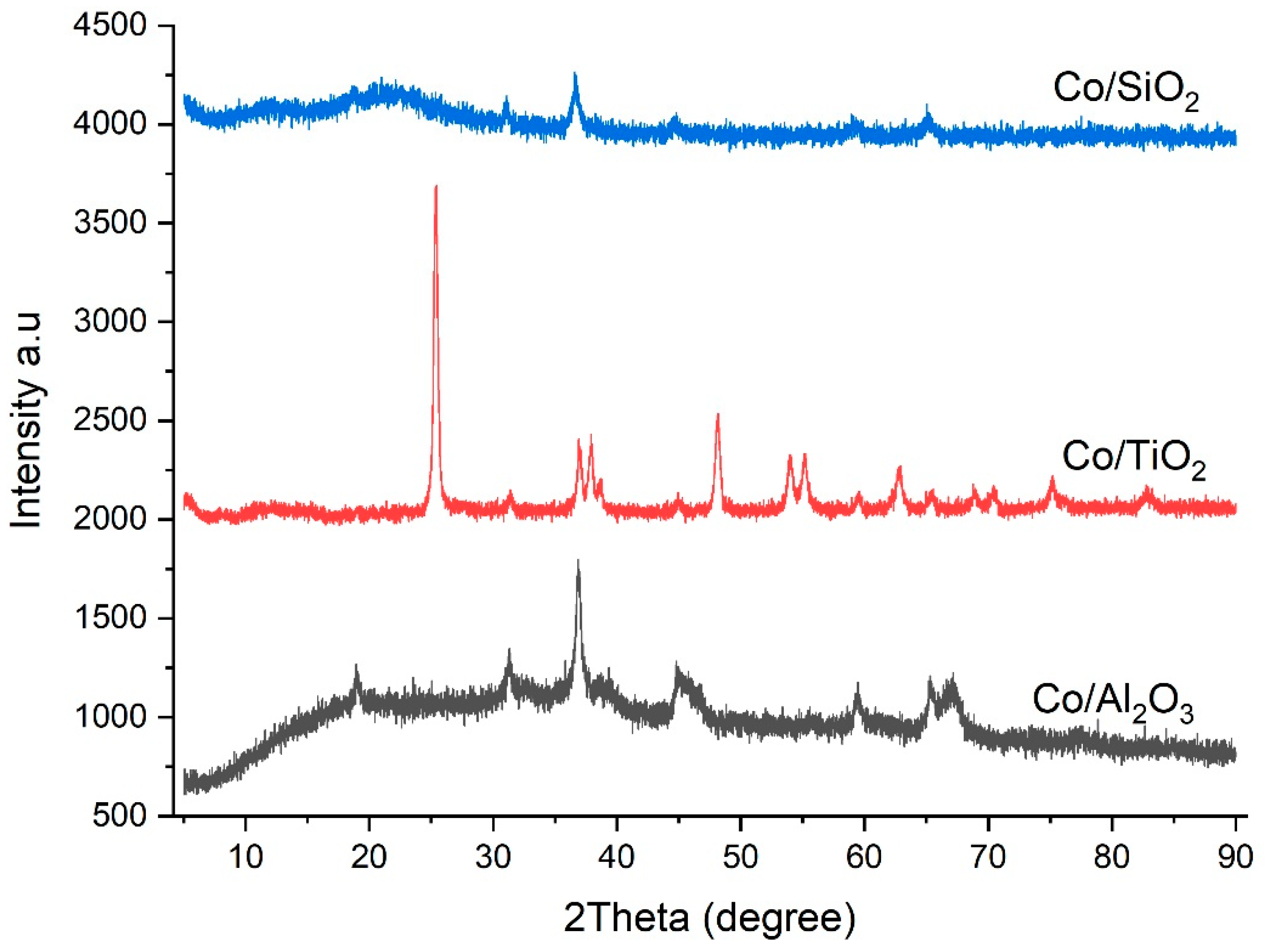
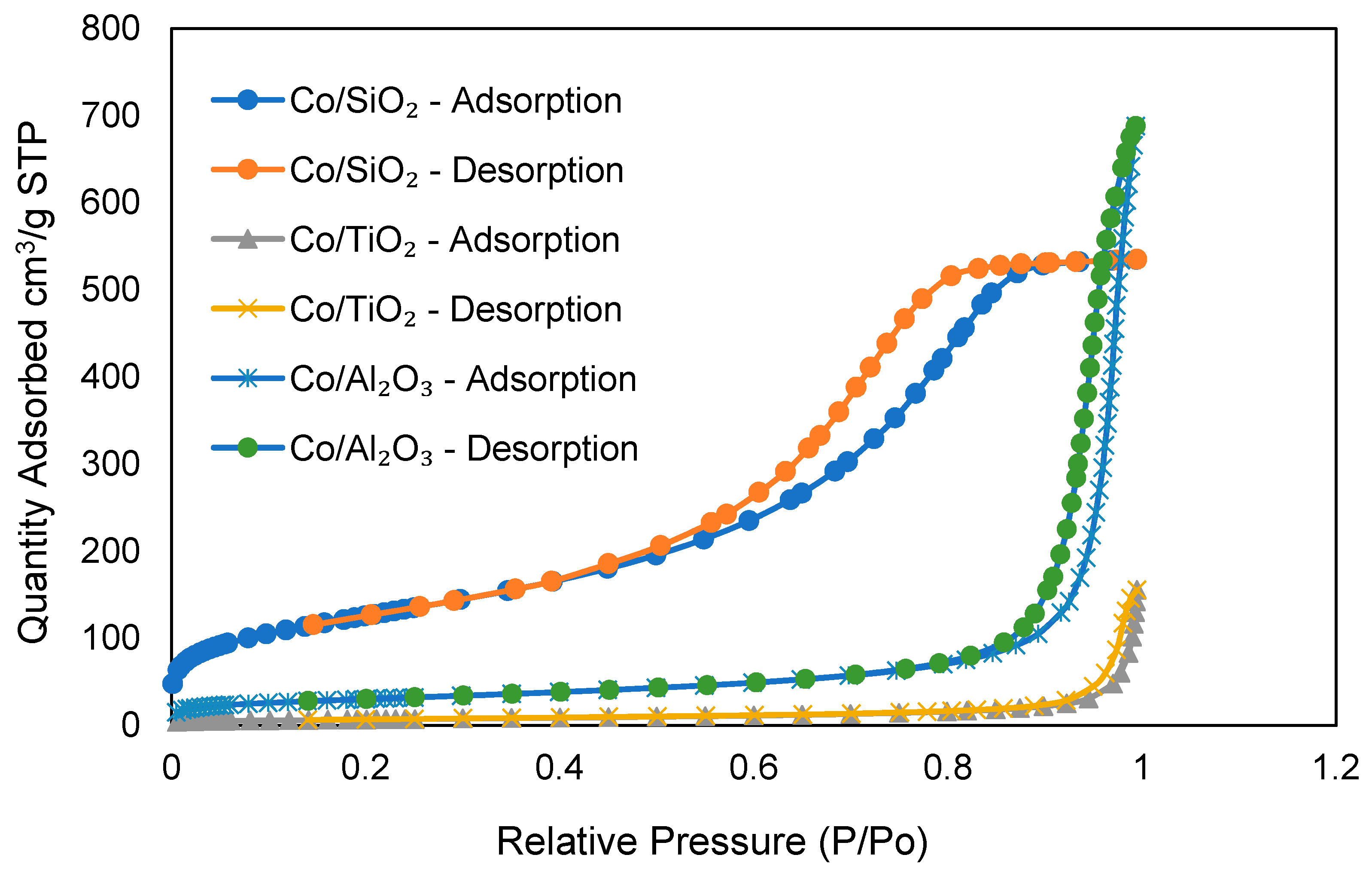
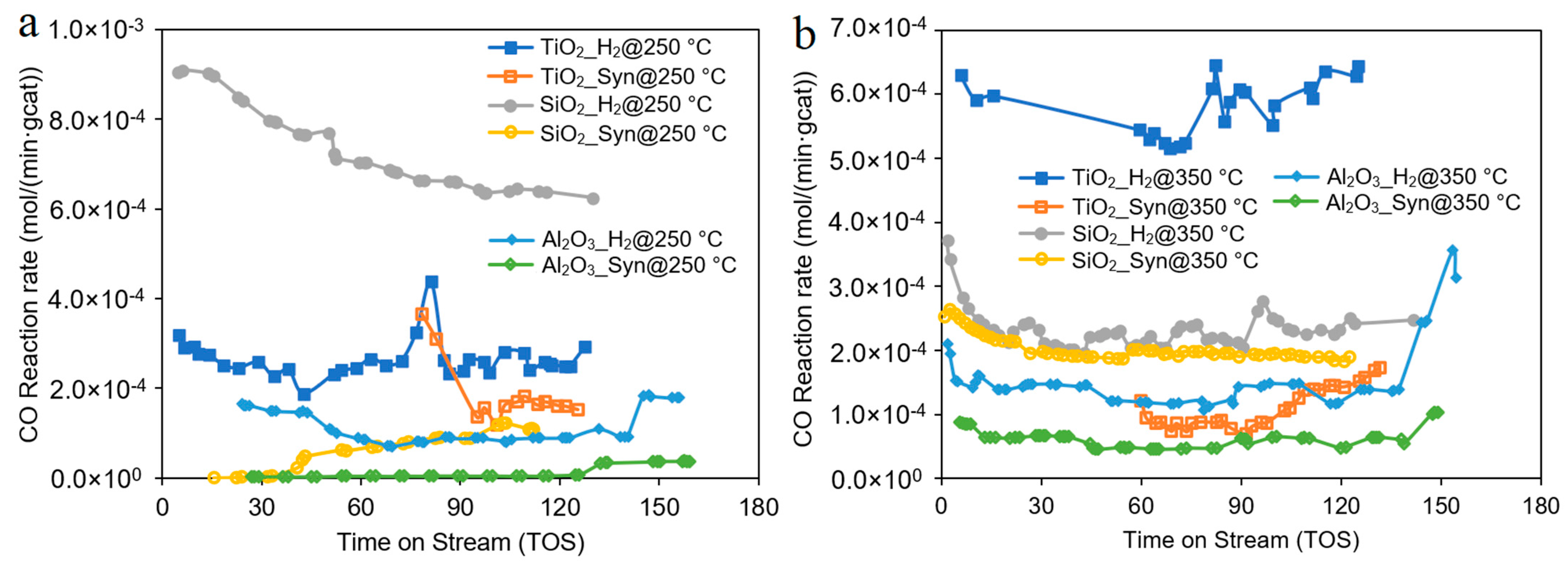
| Catalyst | Co/SiO2 | Co/TiO2 | Co/Al2O3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Catalyst Characterization Data | |||
| BET surface area for the support [m2/g] | 456.5 | 24.15 | 107.5 |
| BET surface area after calcination [m2/g] | 407.0 | 88.4 | 115.8 |
| TEM Co3O4 particle size [nm] | 26 | 28 | 38 |
| XRD Co3O4 particle size [nm] b | 17 | 22 | 33 |
| XRD Co0 crystallite size [nm] c | 12.8 | 16.5 | 24.8 |
| BET pore size [nm] | 6.78 | 38.1 | 43.1 |
| Catalyst reduction conditions | |||
| Temperature (°C) | 250 or 350 | ||
| Reduction agents | H2 or syngas (H2/CO/N2 = 60/30/10) | ||
| FTS reaction conditions | |||
| Feed gas | syngas (H2/CO/N2 = 60/30/10) | ||
| Temperature (°C) | 220 | ||
| Pressure (bar) | 20 | ||
| Flowrate (Nml/min) | 60 | ||
| Catalyst | Reducing T | CO% | CH4% | CH2–4% | C5+% | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co/SiO2 | 250 °C | 69 | 23 | 14.9 | 62 | This work. |
| 350 °C | 26 | 9 | 8.8 | 82 | This work. | |
| 350 °C | 44 | 12 | ___ | 71 | Data from Ref [33], reaction conditions: 220 °C, 15 bar, and GHSV = 1 (NTP)/h.g with 20% Co loading. | |
| Co/TiO2 | 250 °C | 31 | 12 | 6.9 | 81 | This work. |
| 350 °C | 72 | 8 | 3.3 | 89 | This work. | |
| 350 °C | 42.6 | 8.9 | ___ | 84.8 | Data from Ref [34], reaction conditions: 210 °C, 15 bar and GHSV = 3595 mL/g/h with 10% Co loading with 0.5% Re promotion. | |
| 250 °C | 15 | 3.9 | ___ | 92.2 | Data from Ref [35], reaction conditions: 220 °C, 15 bar and GHSV = 3 NL/gCat/h with 10% Co loading. | |
| Co/Al2O3 | 250 °C | 23 | 25 | 12.5 | 62 | This work. |
| 350 °C | 42 | 14 | 11.2 | 77 | This work. | |
| 350 °C | 4.7 | 14.5 | 16.8 | 68.5 | Data from Ref [36], reaction T was 240 °C, 9.8 bar and GHSV = 3600 L/kgCat/h with 5% Co loading. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shiba, N.C.; Liu, X.; Yao, Y. Insight into the Physicochemical Properties of Co-Based Catalysts in Fischer–Tropsch Synthesis. Reactions 2023, 4, 420-431. https://doi.org/10.3390/reactions4030025
Shiba NC, Liu X, Yao Y. Insight into the Physicochemical Properties of Co-Based Catalysts in Fischer–Tropsch Synthesis. Reactions. 2023; 4(3):420-431. https://doi.org/10.3390/reactions4030025
Chicago/Turabian StyleShiba, Nothando C., Xinying Liu, and Yali Yao. 2023. "Insight into the Physicochemical Properties of Co-Based Catalysts in Fischer–Tropsch Synthesis" Reactions 4, no. 3: 420-431. https://doi.org/10.3390/reactions4030025
APA StyleShiba, N. C., Liu, X., & Yao, Y. (2023). Insight into the Physicochemical Properties of Co-Based Catalysts in Fischer–Tropsch Synthesis. Reactions, 4(3), 420-431. https://doi.org/10.3390/reactions4030025






