Comparison of Deepfake Detection Techniques through Deep Learning
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Deepfake Detection Datasets
2.2. Deepfake Detection Algorithms
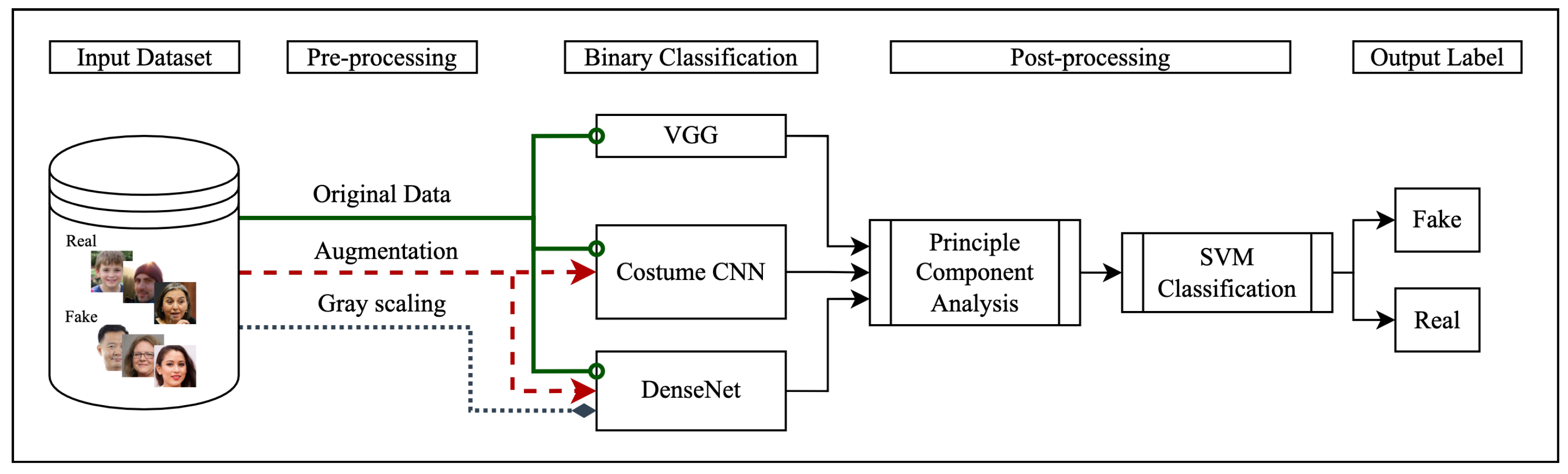
3. Approach
3.1. Implementation
- Rotation range of 20 for DenseNET and no rotation on Custom CNN
- Scaling factor of 1/255 was used for coefficient reduction
- Shear range of 0.2 to randomly apply shearing transformations
- Zoom range of 0.2 to randomly zoom inside pictures
- Randomized images using horizontal and vertical flipping
3.2. Evaluation
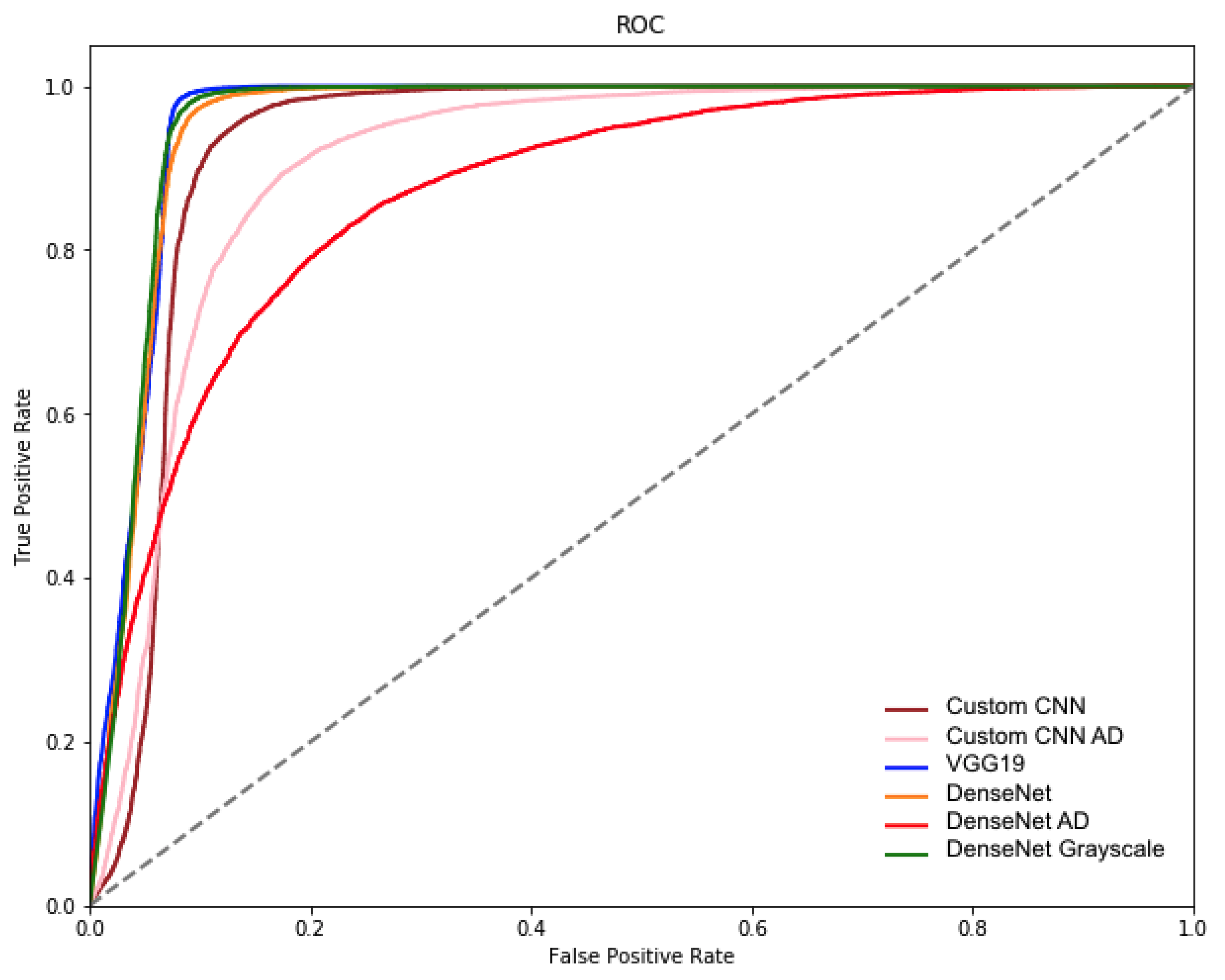
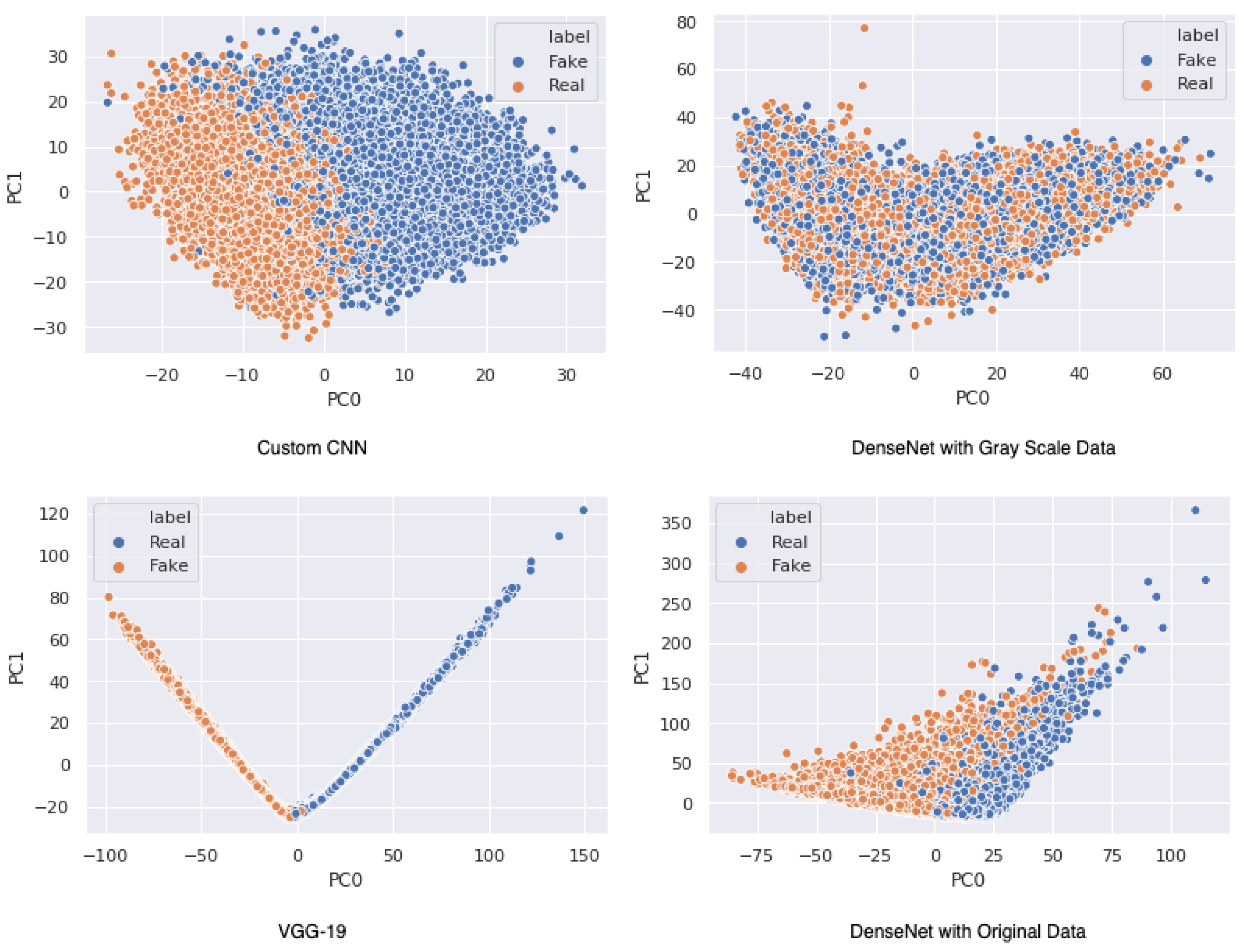
4. Preliminary Results
4.1. Dataset
4.2. Algorithms
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferreira, S.; Antunes, M.; Correia, M.E. Exposing Manipulated Photos and Videos in Digital Forensics Analysis. J. Imaging 2021, 7, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harwell, D. Fake-Porn Videos are Being Weaponized to Harass and Humiliate Women: ‘Everybody is a Potential Target’. 2018. Available online: https://www.defenseone.com/technology/2019/03/next-phase-ai-deep-faking-whole-world-and-china-ahead/155944/ (accessed on 28 November 2021).
- Tucker, P. The Newest AI-Enabled Weapon: ’Deep-Faking’ Photos of the Earth. 2021. Available online: https://www.washingtonpost.com/technology/2018/12/30/fake-porn-videos-are-being-weaponized-harass-humiliate-women-everybody-is-potential-target/ (accessed on 28 November 2021).
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative adversarial nets. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2014, 2. Available online: https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper/2014/hash/5ca3e9b122f61f8f06494c97b1afccf3-Abstract.html (accessed on 28 November 2021).
- Sajjadi, M.S.; Scholkopf, B.; Hirsch, M. Enhancenet: Single image super-resolution through automated texture synthesis. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 4491–4500. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, P.; Xia, Z.; Fei, J.; Lu, Y. A Survey on Deepfake Video Detection. IET Biom. 2021, 10, 607–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, S.; Antunes, M.; Correia, M.E. A Dataset of Photos and Videos for Digital Forensics Analysis Using Machine Learning Processing. Data 2021, 6, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durall, R.; Keuper, M.; Pfreundt, F.J.; Keuper, J. Unmasking deepfakes with simple features. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1911.00686. [Google Scholar]
- De keersmaecker, J.; Roets, A. ‘Fake news’: Incorrect, but hard to correct. The role of cognitive ability on the impact of false information on social impressions. Intelligence 2017, 65, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zhou, W.; Chen, D.; Wei, T.; Zhang, W.; Yu, N. Multi-attentional deepfake detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 2185–2194. [Google Scholar]
- Bonettini, N.; Cannas, E.D.; Mandelli, S.; Bondi, L.; Bestagini, P.; Tubaro, S. Video face manipulation detection through ensemble of cnns. In Proceedings of the 2020 25th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Milan, Italy, 10–15 January 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 5012–5019. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, S.H.; Bethany, M.; Votto, A.M.; Scarff, I.H.; Beebe, N.; Najafirad, P. Deepfake forensics analysis: An explainable hierarchical ensemble of weakly supervised models. Forensic. Sci. Int. Synerg. 2022, 4, 100217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerlund, M. The emergence of deepfake technology: A review. Technol. Innov. Manag. Rev. 2019, 9, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, A.; Elpeltagy, M.; Zaki, M.; ElDahshan, K.A. Deepfake video detection: YOLO-Face convolution recurrent approach. Peerj Comput. Sci. 2021, 7, e730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coccomini, D.; Messina, N.; Gennaro, C.; Falchi, F. Combining efficientnet and vision transformers for video deepfake detection. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.02612. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Bhavsar, A.; Verma, R. Detecting deepfakes with metric learning. In Proceedings of the 2020 8th International Workshop on Biometrics and Forensics (IWBF), Porto, Portugal, 29–30 April 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Lyu, S. Exposing deepfake videos by detecting face warping artifacts. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1811.00656. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Bao, J.; Zhang, T.; Yang, H.; Chen, D.; Wen, F.; Guo, B. Face X-ray for more general face forgery detection. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.H.; Yamagishi, J.; Echizen, I. Capsule-forensics: Using capsule networks to detect forged images and videos. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2019–2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Brighton, UK, 12–17 May 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 2307–2311. [Google Scholar]
- Albanesius, C. Deepfake Videos Are Here, and We’re Not Ready. 2019. Available online: https://www.pcmag.com/news/deepfake-videos-are-here-and-were-not-ready (accessed on 5 December 2021).
- Yang, X.; Li, Y.; Lyu, S. Exposing deep fakes using inconsistent head poses. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2019–2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Brighton, UK, 12–17 May 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 8261–8265. [Google Scholar]
- Korshunov, P.; Marcel, S. Deepfakes: A new threat to face recognition? assessment and detection. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1812.08685. [Google Scholar]
- Rössler, A.; Cozzolino, D.; Verdoliva, L.; Riess, C.; Thies, J.; Nießner, M. FaceForensics++: Learning to Detect Manipulated Facial Images. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Dolhansky, B.; Bitton, J.; Pflaum, B.; Lu, J.; Howes, R.; Wang, M.; Ferrer, C.C. The DeepFake Detection Challenge Dataset. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.07397. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Sun, P.; Qi, H.; Lyu, S. Celeb-DF: A Large-scale Challenging Dataset for DeepFake Forensics. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Patten Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 3207–3216. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L.; Li, R.; Wu, W.; Qian, C.; Loy, C.C. Deeperforensics-1.0: A large-scale dataset for real-world face forgery detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 2889–2898. [Google Scholar]
- Yonsei University. Real and Fake Face Detection. 2019. Available online: https://archive.org/details/real-and-fake-face-detection (accessed on 30 August 2021).
- NVlabs. NVlabs/ffhq-Dataset: Flickr-Faces-HQ Dataset (FFHQ). 2019. Available online: https://archive.org/details/ffhq-dataset (accessed on 29 August 2021).
- Nguyen, T.T.; Nguyen, C.M.; Nguyen, D.T.; Nguyen, D.T.; Nahavandi, S. Deep learning for deepfakes creation and detection: A survey. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1909.11573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Juefei-Xu, F.; Guo, Q.; Xie, X.; Ma, L.; Miao, W.; Liu, Y.; Pu, G. FakeRetouch: Evading deepfakes detection via the guidance of deliberate noise. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2009.09213. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.; Chellappa, R.; Phillips, P.J.; Rosenfeld, A. Face recognition: A literature survey. Acm Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 2003, 35, 399–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maksutov, A.A.; Morozov, V.O.; Lavrenov, A.A.; Smirnov, A.S. Methods of deepfake detection based on machine learning. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Conference of Russian Young Researchers in Electrical and Electronic Engineering (EIConRus), St. Petersburg, Russia, 27–30 January 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 408–411. [Google Scholar]
- Tariq, S.; Lee, S.; Kim, H.; Shin, Y.; Woo, S.S. Gan is a friend or foe? a framework to detect various fake face images. In Proceedings of the 34th ACM/SIGAPP Symposium on Applied Computing, Limassol, Cyprus, 8–12 April 2019; pp. 1296–1303. [Google Scholar]
- Cozzolino, D.; Thies, J.; Rössler, A.; Riess, C.; Nießner, M.; Verdoliva, L. Forensictransfer: Weakly-supervised domain adaptation for forgery detection. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1812.02510. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.Y.; Wang, O.; Zhang, R.; Owens, A.; Efros, A.A. CNN-generated images are surprisingly easy to spot … for now. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 8695–8704. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Chang, M.; Lyu, S. Exposing AI Created Fake Videos by Detecting Eye Blinking. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE InterG National Workshop on Information Forensics and Security (WIFS), Hong Kong, China, 11–13 December 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Afchar, D.; Nozick, V.; Yamagishi, J.; Echizen, I. Mesonet: A compact facial video forgery detection network. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Workshop on Information Forensics and Security (WIFS 2018), Hong Kong, China, 11–13 December 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, X.; Wu, J.; Yang, T.; Feng, G. Deepfake face image detection based on improved VGG convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the 2020 39th Chinese Control Conference (CCC), Shenyang, China, 27–30 July 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 7252–7256. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Han, S.; Woo, S.S. Classifying Genuine Face images from Disguised Face Images. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data), Los Angelas, CA, USA, 9–12 December 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 6248–6250. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Van Der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely connected convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 4700–4708. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, C.C.; Zhuang, Y.X.; Lee, C.Y. Deep fake image detection based on pairwise learning. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matern, F.; Riess, C.; Stamminger, M. Exploiting visual artifacts to expose deepfakes and face manipulations. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Winter Applications of Computer Vision Workshops (WACVW), Waikoloa Village, HI, USA, 1–7 January 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, T.; Kim, S.; Kim, K. DeepVision: Deepfakes detection using human eye blinking pattern. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 83144–83154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chang, M.C.; Lyu, S. In ictu oculi: Exposing ai created fake videos by detecting eye blinking. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Workshop on Information Forensics and Security (WIFS 2018), Hong Kong, China, 11–13 December 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Korshunov, P.; Marcel, S. Speaker inconsistency detection in tampered video. In Proceedings of the 2018 26th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO), Rome, Italy, 3–7 September 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 2375–2379. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, S.; Farid, H.; Gu, Y.; He, M.; Nagano, K.; Li, H. Protecting World Leaders Against Deep Fakes. In Proceedings of the CVPR Workshops, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Chollet, F. Xception: Deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1251–1258. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, M.; Le, Q. Efficientnet: Rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Long Beach, CA, USA, 9–15 June 2019; pp. 6105–6114. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Yu, K.; Ji, S.; Wang, Y.; Wu, C.; Xue, H. Fighting against deepfake: Patch&pair convolutional neural networks (PPCNN). In Proceedings of the Companion Proceedings of the Web Conference, Taipei, Taiwan, 20–24 April 2020; pp. 88–89.
- Pokroy, A.A.; Egorov, A.D. EfficientNets for deepfake detection: Comparison of pretrained models. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Conference of Russian Young Researchers in Electrical and Electronic Engineering (EIConRus), St. Petersburg, Russia, 26–29 January 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 598–600. [Google Scholar]
- Mitra, A.; Mohanty, S.P.; Corcoran, P.; Kougianos, E. A novel machine learning based method for deepfake video detection in social media. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Symposium on Smart Electronic Systems (iSES) (Formerly iNiS), Chennai, India, 14–16 December 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 91–96. [Google Scholar]
- Dolecki, M.; Karczmarek, P.; Kiersztyn, A.; Pedrycz, W. Utility functions as aggregation functions in face recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Symposium Series on Computational Intelligence (SSCI), Athens, Greece, 6–9 December 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.X.T.; Duong, L.H.; Trung, H.T.; Tam, P.M.; Hung, N.Q.V.; Jo, J. Efficient-frequency: A hybrid visual forensic framework for facial forgery detection. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Symposium Series on Computational Intelligence (IEEE SSCI), Canberra, Australia, 1–4 December 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 707–712. [Google Scholar]
- Tjon, E.; Moh, M.; Moh, T.S. Eff-YNet: A Dual Task Network for DeepFake Detection and Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2021 15th International Conference on Ubiquitous Information Management and Communication (IMCOM), Seoul, Korea, 4–6 January 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Do, N.T.; Na, I.S.; Kim, S.H. Forensics face detection from GANs using convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Symposium on Information Technology Convergence (ISITC 2018), Jeonju, Korea, 24–27 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Goel, R.; Mehmood, I.; Ugail, H. A Study of Deep Learning-Based Face Recognition Models for Sibling Identification. Sensors 2021, 21, 5068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varoquaux, G.; Buitinck, L.; Louppe, G.; Grisel, O.; Pedregosa, F.; Mueller, A. Scikit-learn: Machine learning without learning the machinery. Getmobile: Mob. Comput. Commun. 2015, 19, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, S.B.; Park, S.H.; Lee, Y.K. A Measurement Study on Gray Channel-based Deepfake Detection. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Information and Communication Technology Convergence (ICTC), Jeju Island, Korea, 20–22 October 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 428–430. [Google Scholar]
- Amerini, I.; Galteri, L.; Caldelli, R.; Del Bimbo, A. Deepfake video detection through optical flow based cnn. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; p. 2. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Yang, X.; Wu, B.; Lyu, S. Hiding faces in plain sight: Disrupting ai face synthesis with adversarial perturbations. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1906.09288. [Google Scholar]
- Tolosana, R.; Romero-Tapiador, S.; Fierrez, J.; Vera-Rodriguez, R. Deepfakes evolution: Analysis of facial regions and fake detection performance. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Virtual Event, 10–15 January 2021; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 442–456. [Google Scholar]
- Corcoran, K.; Ressler, J.; Zhu, Y. Countermeasure against Deepfake Using Steganography and Facial Detection. J. Comput. Commun. 2021, 9, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Jiao, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, S.; Liu, F. Fuzzy sparse autoencoder framework for single image per person face recognition. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2017, 48, 2402–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Type of Media | Examples | Intention to Mislead | Level of Truth |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hoax | Tampering evidence Scam and Fraud Harming Credibility | High | Low |
| Entertainment | Altering movies Editing Special effects Art Demonstration | Low | Low |
| Propaganda | Misdirection Political Warfare Corruption | High | High |
| Trusted | Authentic Content | Low | High |
| Real | Fake | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dataset | Video | Frame | Video | Frame | Generation Method | Release Date | Generation Group |
| UADFV | 49 | 17.3K | 49 | 17.3K | FakeAPP | 11/2018 | 1st |
| DF-TIMIT | 320 | 34K | 320 | 34K | Faceswap-GAN | 12/2018 | 1st |
| *Real & Fake Face Detection | 1081 | 405.2K | 960 | 399.8K | Expert-generated high-quality photoshopped | 01/2019 | 2st |
| FaceForensics++ | 1000 | 509.9k | 1000 | 509.9K | DeepFakes, Face2Face, FaceSwap, NeuralTextures | 01/2019 | 2nd |
| DeepFakeDetection | 363 | 315.4K | 3068 | 2242.7K | Similar to FaceForensics++ | 09/2019 | 2nd |
| DFDC | 1131 | 488.4K | 4113 | 1783.3K | Deepfake, GAN-based, and non-learned methods | 10/2019 | 2nd |
| Celeb-DF | 590 | 225.4K | 5639 | 2116.8K | Improved DeepFake synthesis algorithm | 11/2019 | 2nd |
| *140K Real & Fake Faces | 70K | 15.8M | 70K | 15.8M | StyleGAN | 12/2019 | 2nd |
| DeeperForensics | 50,000 | 12.6M | 10,000 | 2.3M | Newly proposed end-to-end face swapping framework | 06/2020 | 2nd |
| Dataset | Drawbacks | Improvements |
|---|---|---|
| UADF DFTMIT | Lack of quantity and Diversity | Suitable baseline |
| DFD | Limited size and methods | Extension to FaceForensics dataset |
| DFDC | Distinguishable visual artifacts | Large number of clips of varying quality |
| Celeb-DF | Low realness score Biased: impractical for face Forgery detection | Fixed color mismatch Accurate face masks |
| Deeper Forensics-1.0 | Challenging as a test database | High realness score |
| Generation Method | Fake | Real |
|---|---|---|
| GAN | 70K | 70K |
| Human Expert | 960 | 1081 |
| Model Performance | PCA-SVM Performance | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Architecture | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | Accuracy | Precision | Recall |
| VGG-19 | 95 | 93 | 97 | 99 | 99 | 99 |
| DenseNet OD | 94 | 92 | 96 | 98 | 98 | 98 |
| DenseNet AD | 73 | 66 | 95 | 86 | 86 | 86 |
| DenseNet GS | 94 | 91 | 99 | 50 | 50 | 47 |
| Custom CNN OD | 89 | 91 | 87 | 97 | 97 | 97 |
| Custom CNN AD | 84 | 87 | 79 | 91 | 90 | 91 |
| Architecture | F-1 | ROC-AUC | AP |
|---|---|---|---|
| VGG-19 | 95 | 96 | 93 |
| DenseNet OD | 92 | 99 | 99 |
| DenseNet AD | 92 | 97 | 97 |
| DenseNet GS | 97 | 99 | 99 |
| Custom CNN OD | 91 | 98 | 98 |
| Custom CNN AD | 85 | 95 | 95 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Taeb, M.; Chi, H. Comparison of Deepfake Detection Techniques through Deep Learning. J. Cybersecur. Priv. 2022, 2, 89-106. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcp2010007
Taeb M, Chi H. Comparison of Deepfake Detection Techniques through Deep Learning. Journal of Cybersecurity and Privacy. 2022; 2(1):89-106. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcp2010007
Chicago/Turabian StyleTaeb, Maryam, and Hongmei Chi. 2022. "Comparison of Deepfake Detection Techniques through Deep Learning" Journal of Cybersecurity and Privacy 2, no. 1: 89-106. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcp2010007
APA StyleTaeb, M., & Chi, H. (2022). Comparison of Deepfake Detection Techniques through Deep Learning. Journal of Cybersecurity and Privacy, 2(1), 89-106. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcp2010007







