The Barbero–Immirzi Parameter: An Enigmatic Parameter of Loop Quantum Gravity
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Ashtekar’s Formalism
1.2. Why the BI Parameter Was Introduced in LQG?
1.3. The Holst Action and the BI Parameter
2. Various Proposals on the Physical Significance of the BI Parameter
2.1. Historical Timeline
2.2. The Area Operator and the BI Parameter
Pros and Cons of the Area Operator and the BI Parameter
2.3. The BI Parameter and Black Hole Entropy Calculation in LQG
Pros and Cons of the BI Parameter and Black Hole Entropy Calculation in LQG
2.4. The BI Parameter as Immirzi Ambiguity
Pros and Cons of the BI Parameter as Immirzi Ambiguity
2.5. Origin of the BI Parameter
Pros and Cons of Origin of the BI Parameter
2.6. On a Covariant Formulation of the BI Connection
Pros and Cons of a Covariant Formulation of the BI Connection
2.7. The BI Parameter as a Scalar Field
Pros and Cons of the BI Parameter as a Scalar Field
2.8. Topological Interpretation of the BI Parameter
Pros and Cons of Topological Interpretation of the BI Parameter
2.9. The Peccei–Quinn Mechanism in Gravity and the Nature of the BI Parameter
Pros and Cons of the Peccei–Quinn Mechanism in Gravity and the Nature of the BI Parameter
2.10. The Kodama State and the BI Parameter
Pros and Cons of the Kodama State and the BI Parameter
2.11. The Quantum Gravity BI Parameter—A General Physical and Topological Interpretation
Pros and Cons of the Quantum Gravity BI Parameter—A General Physical and Topological Interpretation
2.12. A Correction to the BI Parameter of SU(2) Spin Networks
Pros and Cons of a Correction to the BI Parameter of Spin Networks
2.13. Physical Effect of the Immirzi Parameter in LQG
Pros and Cons of Physical Effect of the Immirzi Parameter in LQG
2.14. A Relation between the BI Parameter and the Standard Model
Pros and Cons of a Relationship between the BIParameter and the Standard Model
2.15. The Holographic Principle and the BI Parameter of LQG
Pros and Cons of the Holographic Principle and the BI Parameter of LQG
2.16. Discussion
3. Concluding Remarks
- In this paper, initially, a short introduction of the Barbero–Immirzi (BI) parameter, , along with the introduction to the Ashtekar formalism, the origin of the BI parameter, the Holst action and a historical timeline of research on the physical significance of the in LQG are given.
- The value of the and its implication are very important, especially in the area operator spectrum and the black hole entropy calculation in LQG; afterwards, these are elaborated on.
- Thereafter, various proposals on the physical significance of the in LQG are given in brief with their pros and cons.
- Most of the proposals advocate the real valued BI parameter , since the significance of the complex valued BI parameter is not yet clear. However, the complex valued is also important, as it removes mathematical complexities from the LQG framework. Research on the complex valued BI parameter will shed light on its physical significance in future.
- Hence, the , whether it is complex valued or the real valued, is a crucial free parameter of LQG.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thiemann, T. Modern Canonical Quantum General Relativity; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovelli, C. Quantum Gravity; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashtekar, A.; Pullin, J. Loop Quantum Gravity. The First 30 Years; World Scientific Publishing: Singapore, Singapore, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovelli, C.; Vidotto, F. Covariant Loop Quantum Gravity; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, Cambridge, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovelli, C. Loop quantum gravity. Living Rev. Relat. 2008, 11, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gambini, R.; Pullin, J. Loops, Knots, Gauge Theories and Quantum Gravity; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashtekar, A. Lectures on Non-Perturbative Canonical Gravity; World Scientific: Singapore, 1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojowald, M. Quantum Cosmology; Springer Science+Business Media, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojowald, M. Canonical Gravity and Applications; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambini, R.; Pullin, J. A First Course in Loop Quantum Gravity; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovelli, C.; Gaul, M. Loop Quantum Gravity and the Meaning of Diffeomorphism Invariance. In Towards Quantum Gravity: Proceed. XXXV Intern. Winter School on Theoretical Physics, Polanica, Poland, 2–11 February 1999; Kowalski-Glikman, J., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2000; pp. 277–324. Available online: https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/3-540-46634-7_11 (accessed on 30 August 2022).
- Ashtekar, A.; Lewandowski, J. Background independent quantum gravity: A status report. Class. Quant. Grav. 2004, 21, R53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandrov, S.; Roche, P. Critical overview of loops and foams. Phys. Rep. 2011, 506, 41–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercuri, S. Introduction to loop quantum gravity. PoS ISFTG 2009, 81, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doná, P.; Speziale, S. Introductory lectures to loop quantum gravity. arXiv 2010, arXiv:1007.0402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, G. An introduction to quantum gravity. arXiv 2011, arXiv:1108.3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovelli, C. Zakopane Lectures on loop gravity. arXiv 2011, arXiv:1102.3660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, A. The new spin foam models and quantum gravity. Papers Phys. 2012, 4, 040004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovelli, C. Notes for a brief history of quantum gravity. arXiv 2001, arXiv:gr-qc/0006061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovelli, C. Loop quantum gravity: The first 25 years. Class. Quant. Grav. 2011, 28, 153002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashtekar, A.; Bianchi, E. A short review of loop quantum gravity. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2021, 84, 042001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corichi, A.; Hauser, A. Bibliography of publications related to classical self-dual variables and loop quantum gravity. arXiv 2005, arXiv:gr-qc/0509039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyas, R.P.; Joshi, M.J. Loop quantum gravity: A demystified view. Gravit. Cosmol. 2022, 28, 228–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashtekar, A. New variables for classical and quantum gravity. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1986, 57, 2244–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbero G., J.F. Real Ashtekar variables for Lorentzian signature space-times. Phys. Rev. D 1995, 51, 5507–5510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbero G., J.F. From Euclidean to Lorentzian general relativity: The real way. Phys. Rev. D 1996, 54, 1492–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immirzi, G. Real and complex connections for canonical gravity. Class. Quant. Grav. 1997, 14, L177–L181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immirzi, G. Quantum gravity and Regge calculus. Nucl. Phys. B Proc. Suppl. 1997, 57, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holst, S. Barbero’s Hamiltonian derived from a generalized Hilbert–Palatini action. Phys. Rev. D 1996, 53, 5966–5969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penrose, R. On the Nature of Quantum Geometry. In Magic Without Magic; Klauder, J., Ed.; Freeman: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1972; pp. 333–354. Available online: https://math.ucr.edu/home/baez/penrose/Penrose-OnTheNatureOfQuantumGeometry.pdf (accessed on 30 August 2022).
- Penrose, R. Angular Momentum: An Approach to Combinatorial Space-Time. In Quantum Theory and Beyond; Bastin, T., Ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1971; pp. 151–180. Available online: https://math.ucr.edu/home/baez/penrose/Penrose-AngularMomentum.pdf (accessed on 30 August 2022).
- Krasnov, K. On the constant that fixes the area spectrum in canonical quantum gravity. Class. Quant. Grav. 1998, 15, L1–L4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovelli, C. Black hole entropy from loop quantum gravity. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 3288–3291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashtekar, A.; Baez, J.; Corichi, A.; Krasnov, K. Quantum geometry and black hole entropy. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1998, 80, 904–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreyer, O. Quasinormal modes, the area spectrum, and black hole entropy. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003, 90, 081301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meissner, K. Black-hole entropy in loop quantum gravity. Class. Quant. Grav. 2004, 21, 5245–5252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domagala, M.; Lewandowski, J. Black hole entropy from quantum geometry. Class. Quant. Grav. 2004, 21, 5233–5244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, T. Renormalization and black hole entropy in loop quantum gravity. Class. Quant. Grav. 2007, 24, 4875–4879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frodden, E.; Geiller, M.; Noui, K.; Perez, A. Black-hole entropy from complex Ashtekar variables. Europhys. Lett. 2014, 107, 10005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasnov, K.V. Counting surface states in the loop quantum gravity. Phys. Rev. D 1997, 55, 3505–3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pranzetti, D. Geometric temperature and entropy of quantum isolated horizons. Phys. Rev. D 2014, 89, 104046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majhi, A. The microcanonical entropy of quantum isolated horizon, ‘quantum hair’ N and the Barbero–Immirzi parameter fixation. Class. Quant. Grav. 2014, 31, 095002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magueijo, J.; Benincasa, D.M.T. Chiral vacuum fluctuations in quantum gravity. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 106, 121302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engle, J.; Noui, K.; Perez, A.; Pranzetti, D. Black hole entropy from an SU(2)-invariant formulation of Type I isolated horizons. Phys. Rev. D 2010, 82, 044050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engle, J.; Noui, K.; Perez, A. Black hole entropy and SU(2) Chern–Simons theory. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 105, 031302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majumdar, P. Quantum black hole entropy. arXiv 1998, arXiv:gr-qc/9807045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaul, R.K.; Majumdar, P. Logarithmic correction to the Bekenstein-Hawking entropy. Phys. Lett. B 1998, 439, 267–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pranzetti, D.; Sahlmann, H. Horizon entropy with loop quantum gravity methods. Phys. Lett. B 2015, 746, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rovelli, C.; Thiemann, T. Immirzi parameter in quantum general relativity. Phys. Rev. D 1997, 57, 1009–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, J. Comment on “Immirzi parameter in quantum general relativity“. Phys. Rev. D 2001, 64, 048501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veraguth, O.J.; Wang, C.H.-T. Immirzi parameter without Immirzi ambiguity: Conformal loop quantization of scalar-tensor gravity. Phys. Rev. D 2017, 96, 084011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, C.-H.; Tung, R.-S.; Yu, H.-L. Origin of the Immirzi parameter. Phys. Rev. D 2005, 72, 064016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatibene, L.; Francaviglia, M.; Rovelli, C. On a covariant formulation of the Barbero–Immirzi connection. Class. Quant. Grav. 2007, 24, 3055–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taveras, V.; Yunes, N. Barbero–Immirzi parameter as a scalar field: K-inflation from loop quantum gravity? Phys. Rev. D 2008, 78, 064070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calcagni, G.; Mercuri, S. Barbero–Immirzi parameter field in canonical formalism of pure gravity. Phys. Rev. D 2009, 79, 084004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Date, G.; Kaul, R.K.; Sengupta, S. Topological interpretation of Barbero–Immirzi parameter. Phys. Rev. D 2008, 79, 044008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercuri, S. Peccei-Quinn mechanism in gravity and the nature of the Barbero–Immirzi parameter. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 103, 081302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randono, A. Generalizing the Kodama state. I: Construction. arXiv 2006, arXiv:gr-qc/0611073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randono, A. Generalizing the Kodama state. II: Properties and physical interpretation. arXiv 2006, arXiv:gr-qc/0611074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieland, W. Complex Ashtekar variables, the Kodama state and spinfoam gravity. arXiv 2011, arXiv:1105.2330. [Google Scholar]
- El Naschie, M.S. The quantum gravity Immirzi parameter—A general physical and topological interpretation. Gravit. Cosmol. 2013, 19, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadiq, M. A correction to the Immirizi parameter of SU(2) spin networks. Phys. Lett. B 2015, 741, 280–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, A.; Rovelli, C. Physical effects of the Immirzi parameter in loop quantum gravity. Phys. Rev. D 2006, 73, 044013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broda, B.; Szanecki, M. A relation between the Barbero–Immirzi parameter and the standard model. Phys. Lett. B 2010, 690, 87–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sadiq, M. The holographic principle and the Immirzi parameter of loop quantum gravity. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1510.04243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
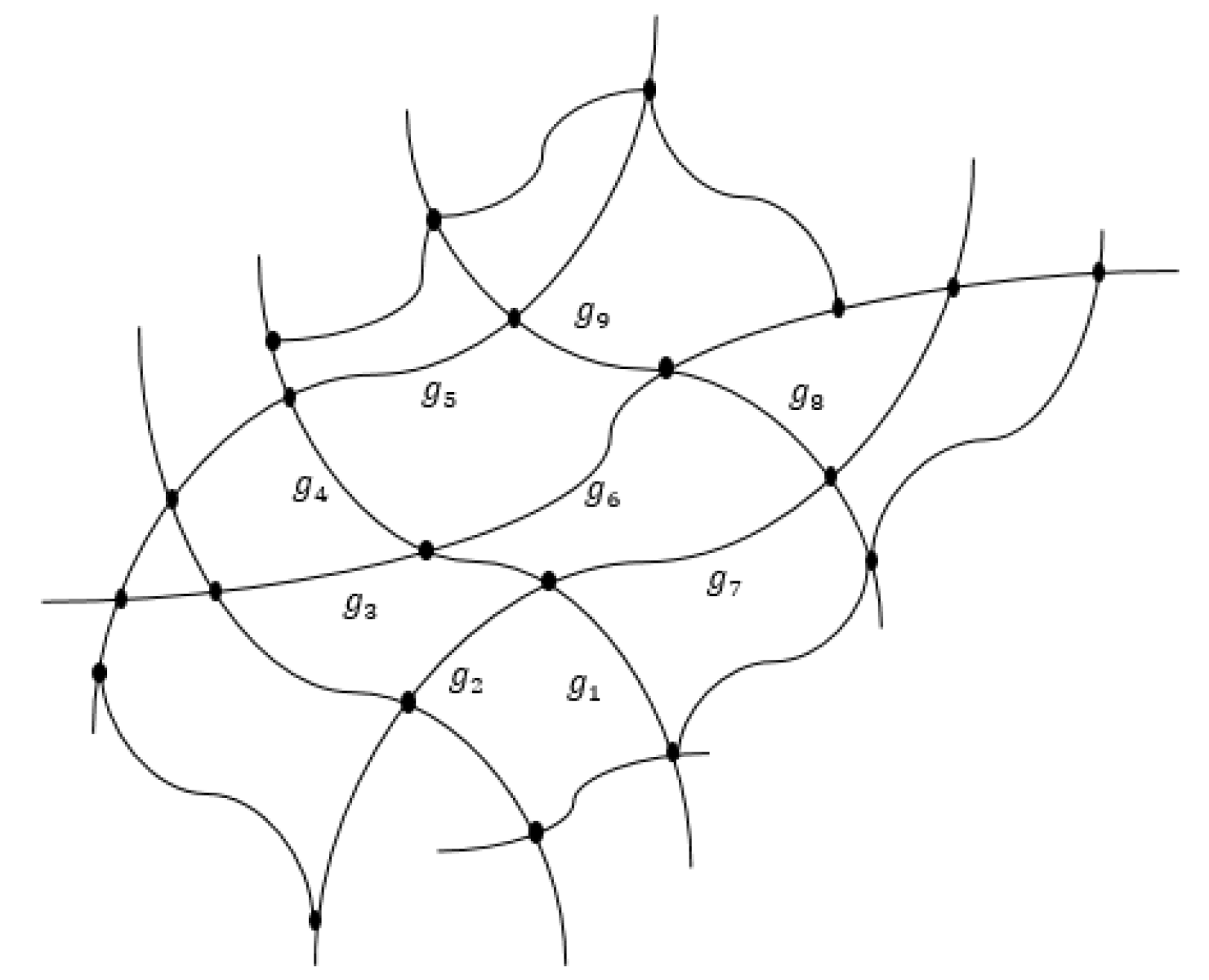
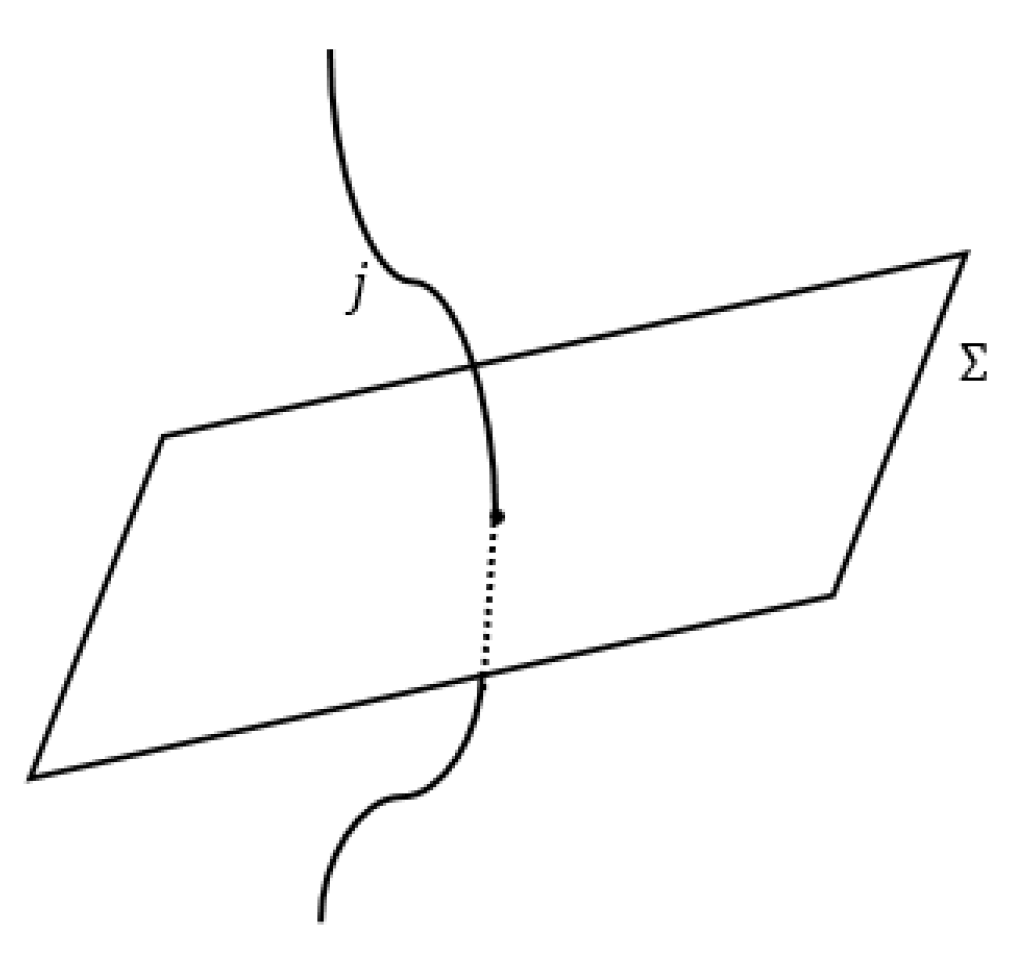
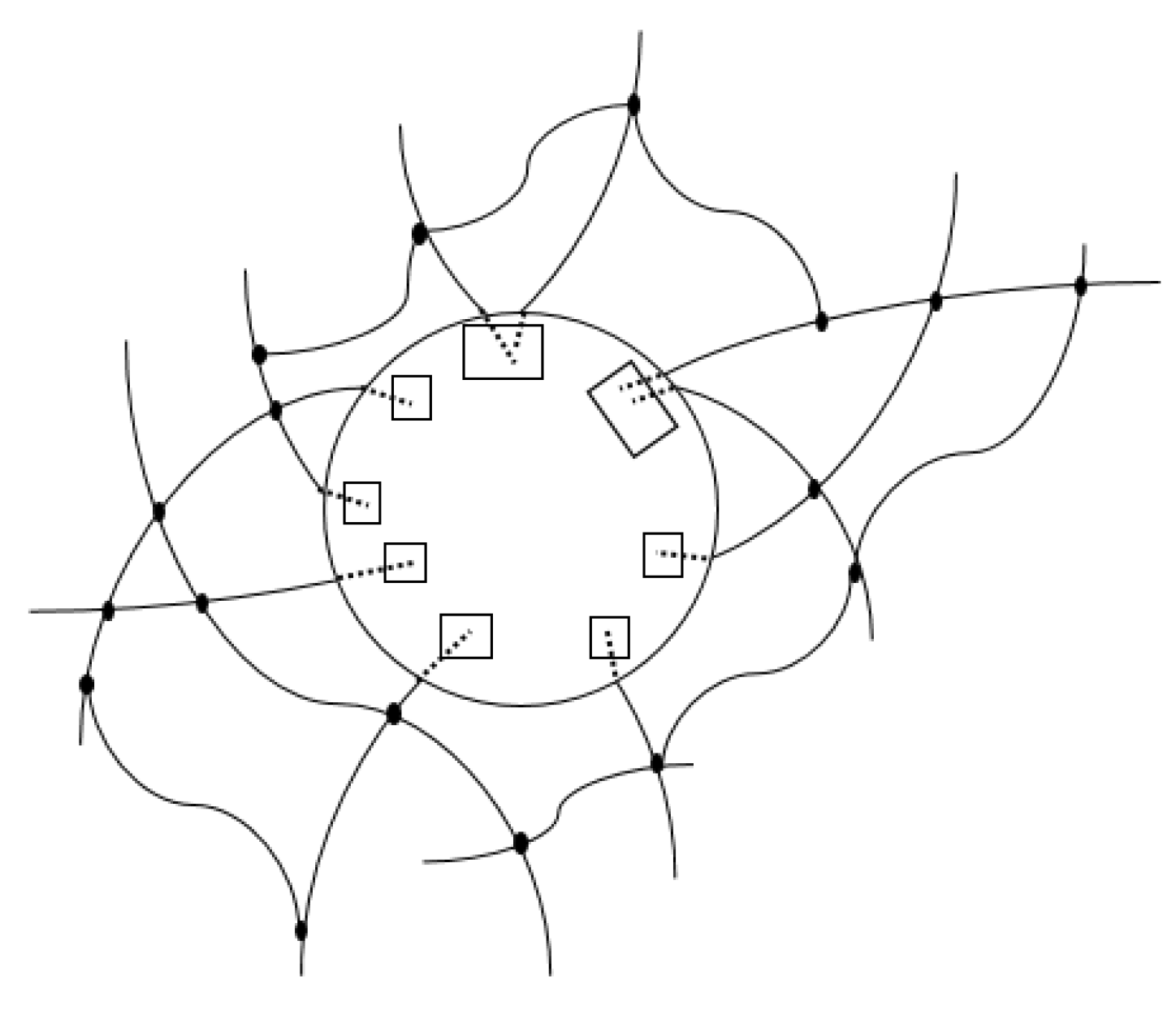
| Year | Research on the BI Parameter and Its Significance |
|---|---|
| 1986 | Discovery of the Ashtekar variables |
| 1995 | Real Ashtekar variables for Lorentzian signature space–times |
| 1996 | Barbero’s Hamiltonian derived from a generalized Hilbert–Palatini action |
| 1996 | Black hole entropy from loop quantum gravity |
| 1996 | From Euclidean to Lorentzian general relativity: the real way |
| 1996 | Real and complex connections for canonical gravity |
| 1997 | Quantum gravity and Regge calculus |
| 1997 | Counting surface states in loop quantum gravity (LQG) |
| 1997 | Immirzi parameter in quantum general relativity |
| 1997 | On the constant that fixes the area spectrum in canonical quantum gravity |
| 1998 | Quantum geometry and black hole entropy |
| 2000 | Is Barbero’s Hamiltonian formulation a gauge theory of Lorentzian gravity? |
| 2001 | Comment on “Immirzi parameter in quantum general relativity“ |
| 2003 | Quasinormal modes, the area spectrum, and black hole entropy |
| 2004 | Black-hole entropy in loop quantum gravity |
| 2004 | Black-hole entropy from quantum geometry |
| 2005 | Origin of the Immirzi parameter |
| 2005 | Physical effects of the Immirzi parameter |
| 2005 | On choice of connection in LQG |
| 2007 | On a covariant formulation of the Barbero–Immirzi connection |
| 2007 | Renormalization and black hole entropy in Loop Quantum Gravity |
| 2008 | From the Einstein–Cartan to the Ashtekar–Barbero canonical constraints, passing through the Nieh–Yan functional |
| 2008 | The Barbero–Immirzi parameter as a scalar field: K-inflation from LQG? |
| 2008 | Topological interpretation of Barbero–Immirzi parameter |
| 2009 | Peccei–Quinn mechanism in gravity and the nature of the Barbero–Immirzi parameter |
| 2010 | A relation between the Barbero–Immirzi parameter and the standard model |
| 2011 | Complex Ashtekar variables, the Kodama state and spinfoam gravity |
| 2012 | The quantum gravity Immirzi parameter—A general physical and topological interpretation |
| 2012 | Complex Ashtekar variables and realitycConditions for Holst’s action |
| 2013 | Black Hole Entropy from complex Ashtekar variables |
| 2014 | Geometric temperature and entropy of quantum isolated horizons |
| 2014 | A Correction to the Immirizi Parameter of SU(2) Spin Networks |
| 2014 | The Microcanonical Entropy of quantum isolated horizon, “quantum hair” N and the Barbero–Immirzi parameter fixation |
| 2015 | The holographic principle and the Immirzi parameter of loop quantum gravity |
| 2017 | Immirzi parameter without Immirzi ambiguity: conformal loop quantization of scalar-tensor gravity |
| 2018 | Horizon entropy with loop quantum gravity methods |
| 2018 | Generalizing the Kodama state. I: construction |
| 2018 | Generalizing the Kodama state. II: properties and physical interpretation |
| 2018 | Chiral vacuum fluctuations in quantum gravity |
| 2018 | Black hole entropy from the SU(2)-invariant formulation of Type I isolated horizons |
| 2018 | Black hole entropy and SU(2) Chern–Simons theory |
| 2020 | On the value of the Immirzi parameter and the horizon entropy |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vyas, R.P.; Joshi, M.J. The Barbero–Immirzi Parameter: An Enigmatic Parameter of Loop Quantum Gravity. Physics 2022, 4, 1094-1116. https://doi.org/10.3390/physics4040072
Vyas RP, Joshi MJ. The Barbero–Immirzi Parameter: An Enigmatic Parameter of Loop Quantum Gravity. Physics. 2022; 4(4):1094-1116. https://doi.org/10.3390/physics4040072
Chicago/Turabian StyleVyas, Rakshit P., and Mihir J. Joshi. 2022. "The Barbero–Immirzi Parameter: An Enigmatic Parameter of Loop Quantum Gravity" Physics 4, no. 4: 1094-1116. https://doi.org/10.3390/physics4040072
APA StyleVyas, R. P., & Joshi, M. J. (2022). The Barbero–Immirzi Parameter: An Enigmatic Parameter of Loop Quantum Gravity. Physics, 4(4), 1094-1116. https://doi.org/10.3390/physics4040072





