Three-Photon Pulse Interference in a Tritter: A Novel Approach for a Three-Party Quantum Key Distribution Protocol
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Three Coherent Photons’ Interference at a Tritter
2.1. Unitary Matrices of the Tritter and Phase Modulator
2.2. Input Photon States
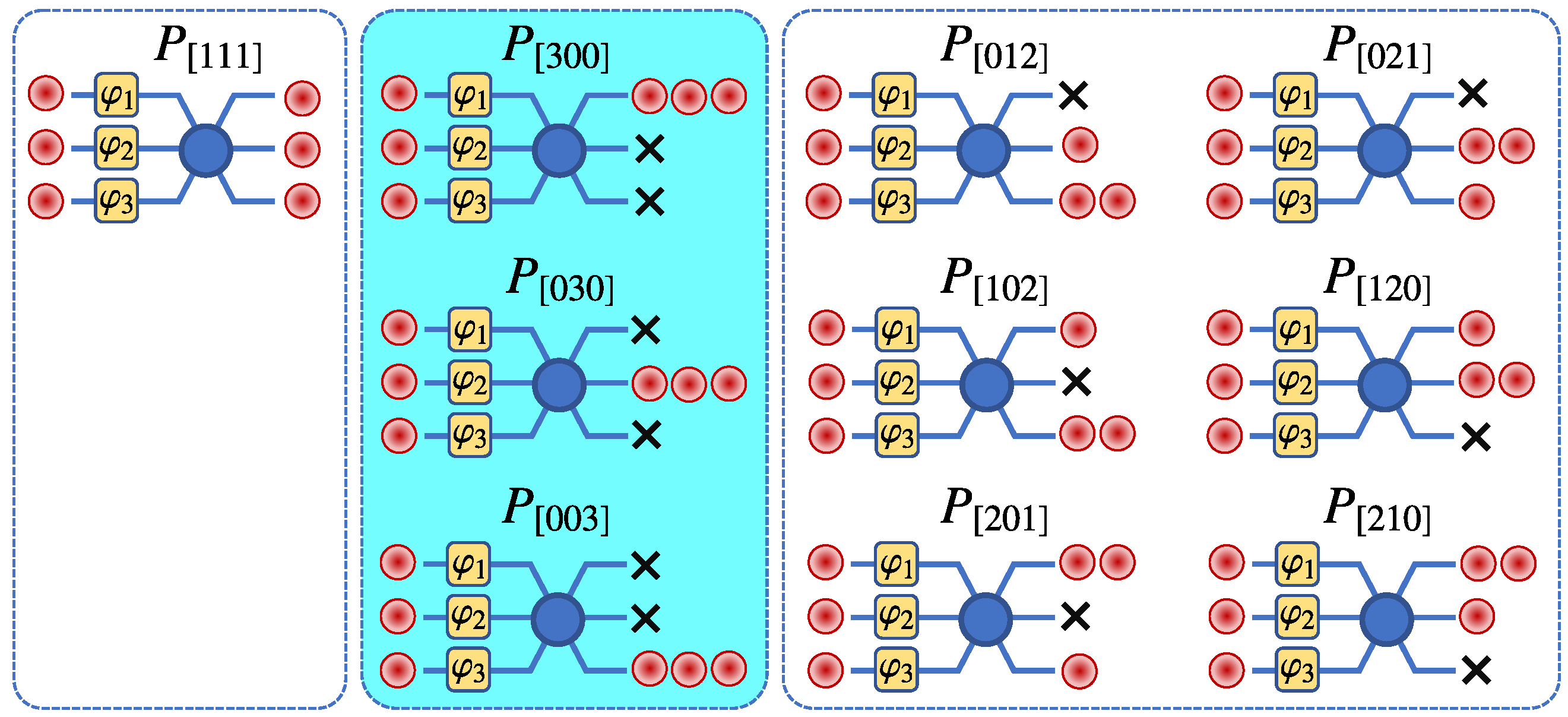
2.3. Output Photon States
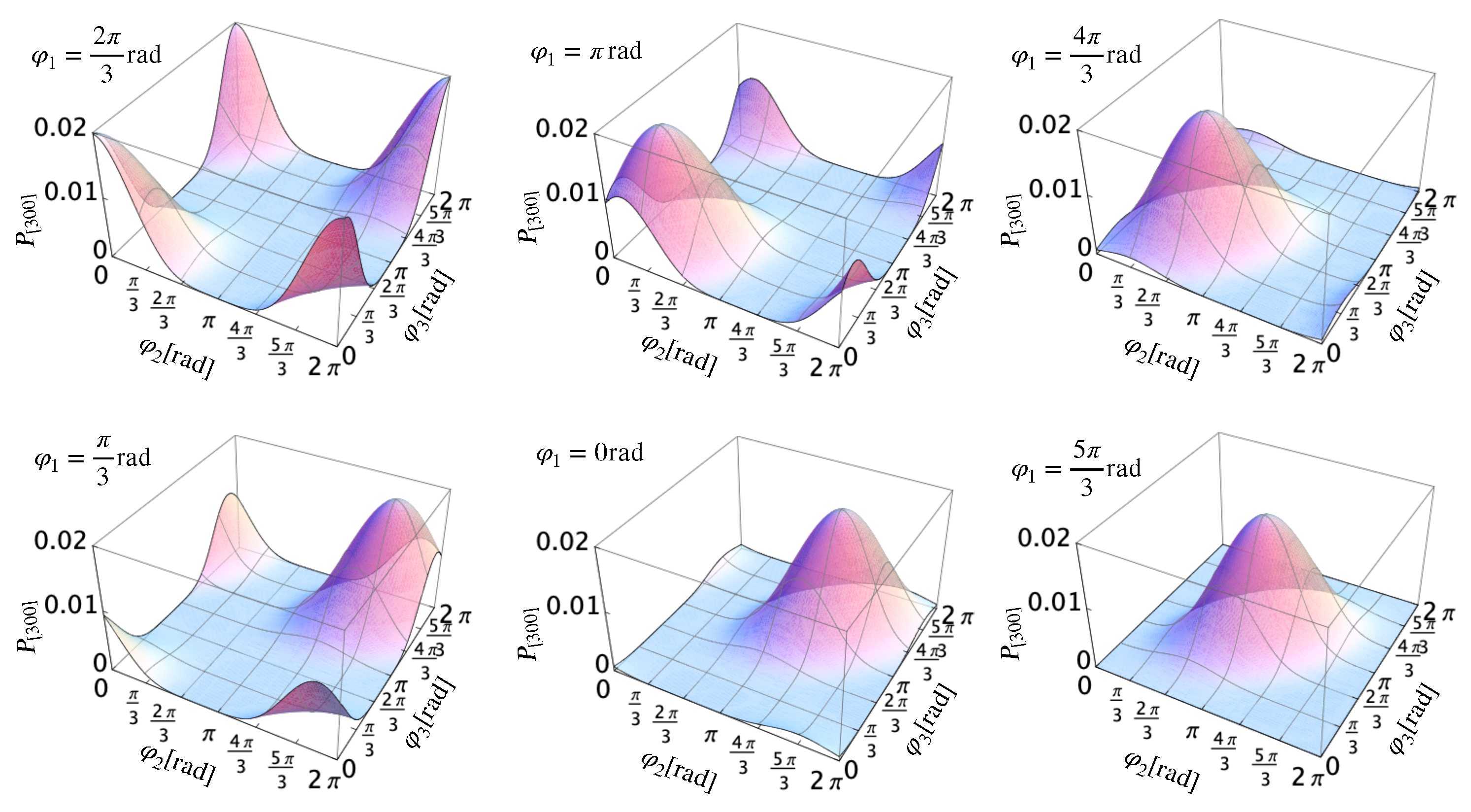
2.4. Probability Distribution Output Photons
2.5. Interference Fringes
3. Possible Applications for a Three-Party Quantum Key Distribution Protocol
- Alice, Bob, and Charlie independently generate weak coherent states using their respective laser sources (LSs), represented as , , and , respectively, where are randomly chosen by Alice, Bob, and Charlie. Here, to ensure that the combined random phases adhere to the rule outlined in Table 2, the phases chosen by Alice, Bob, and Charlie are discretized in increments of , where N is an integer.
- Alice, Bob, and Charlie simultaneously send their quantum states to an untrusted measurement station, Dave. Dave performs three-photon interference measurements using a tritter (a six-port optical beam splitter) and single-photon detectors , , and . For each trial, the following six outcomes are possible: “Only clicks”, “Only clicks”, “Only clicks”, “All detectors click”, “Two detectors click”, and “No detectors click”. By considering the cases where “All detectors click”, “Two detectors click”, or “No detectors click” as “No clicks”, Dave announces one of four possible outcomes.
- Following the detection and announcement session, Alice, Bob, and Charlie can identify the successful detection outcomes (“Only clicks”, “Only clicks”, and “Only clicks”,) that correlate with their randomly selected phase values x, y, and z. These outcomes are classified according to the following conditions: “Only clicks” when , “Only clicks” when , and “Only clicks” when . Based on these distinctive detection pattern characteristics in conjunction with their random phase combinations, one expects that raw keys can be established through further exploration.
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hong, C.K.; Ou, Z.Y.; Mandel, L. Measurement of subpicosecond time intervals between two photons by interference. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1987, 59, 2044–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchard, F.; Sit, A.; Zhang, Y.; Fickler, R.; Miatto, F.M.; Yao, Y.; Sciarrino, F.; Karimi, E. Two-photon interference: The Hong–Ou–Mandel effect. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2020, 84, 012402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mährlein, S.; von Zanthier, J.; Agarwal, G.S. Complete three photon Hong–Ou–Mandel interference at a three port device. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 15833–15847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Feng, X. Three-path interference of a photon and reexamination of the nested Mach–Zehnder interferometer. Phys. Rev. A 2019, 99, 053805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spagnolo, N.; Vitelli, C.; Aparo, L.; Mataloni, P.; Sciarrino, F.; Crespi, A.; Ramponi, R.; Osellame, R. Three-photon bosonic coalescence in an integrated tritter. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ripala, D.P.; Rohedi, A.Y.; Suryadi. Coalescence Phenomenon in the three photon quantum interferences. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1821, 012046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, H.-K.; Curty, M.; Qi, B. Measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 108, 130503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucamarini, M.; Yuan, Z.L.; Dynes, J.F.; Shields, A.J. Overcoming the rate–distance limit of quantum key distribution without quantum repeaters. Nature 2018, 557, 400–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Yin, H.-L.; Chen, T.-Y.; Chen, Z.-B. Long-distance measurement-device-independent multiparty quantum communication. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2015, 114, 090501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.-L.; Chen, T.-Y.; Yu, Z.-W.; Liu, H.; You, L.-X.; Zhou, Y.-H.; Chen, S.-J.; Mao, Y.; Huang, M.-Q.; Zhang, W.-J.; et al. Measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution over a 404 km optical fiber. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2016, 117, 190501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.-X.; Zhong, W.; Zhou, L.; Sheng, Y.-B. Measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution with hyper-encoding. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 2019, 62, 110311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.-W.; Zhang, C.-M.; Li, H.-W. Practical measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution with advantage distillation. Quant. Inform. Process. 2023, 22, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lu, F.-Y.; Wang, Z.-H.; Yin, Z.-Q.; Wang, S.; Geng, J.-Q.; Chen, W.; He, D.-Y.; Guo, G.-C.; Han, Z.-F. Fully passive measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2024, 21, 064067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.-M.; Bai, J.-L.; Lu, Y.-S.; Weng, C.-X.; Yin, H.-L.; Chen, Z.-B. Advantages of asynchronous measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution in intercity networks. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2023, 19, 054070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Liu, J.; Ding, H.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Q. Asymmetric measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution through advantage distillation. Entropy 2023, 25, 1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, G.-D.; Liu, J.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, Q.-P.; Fang, M.-F. Fully measurement-device-independent two-way quantum key distribution with finite single-photon sources. Quant. Inform. Process. 2024, 23, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-B.; Yu, Z.-W.; Hu, X.-L. Twin-field quantum key distribution with large misalignment error. Phys. Rev. A 2018, 98, 062323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curty, M.; Azuma, K.; Lo, H.-K. Simple security proof of twin-field type quantum key distribution protocol. npj Quant. Inform. 2019, 5, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Zhang, C.; Yuan, H.; Zhou, X.; Li, J.; Wang, Q. Passive light source monitoring for sending or not sending twin-field quantum key distribution. Entropy 2022, 24, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, K.; Shen, Z.; Zhao, S.; Mao, Q. Sending-or-not-sending twin-field quantum key distribution with a passive decoy-state method. Entropy 2022, 24, 662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krawec, W.O. A New security proof for twin-field quantum key distribution (QKD). Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.-L.; Fu, Y. Measurement-device-independent twin-field quantum key distribution. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertaina, G.; Clivati, C.; Donadello, S.; Liorni, C.; Meda, A.; Virzì, S.; Gramegna, M.; Genovese, M.; Levi, F.; Calonico, D.; et al. Phase noise in real-world twin-field quantum key distribution. Adv. Quant. Technol. 2024, 7, 2400032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-P.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, C.; Zhang, W.-J.; Han, Z.-Y.; Ma, S.-Z.; Hu, X.-L.; Li, Y.-H.; Liu, H.; et al. Twin-field quantum key distribution over a 511 km optical fibre linking two distant metropolitan areas. Nat. Photonics 2021, 15, 570–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittaluga, M.; Minder, M.; Lucamarini, M.; Sanzaro, M.; Woodward, R.I.; Li, M.-J.; Yuan, Z.; Shields, A.J. 600-km repeater-like quantum communications with dual-band stabilization. Nat. Photonics 2021, 15, 530–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.P.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, C.; Zhang, W.; Hu, X.L.; Guan, J.-Y.; Yu, Z.-W.; Xu, H.; Lin, J.; et al. Sending-or-not-sending with independent lasers: Secure twin-field quantum key distribution over 509 km. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2020, 124, 070501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Jiang, C.; Zhu, H.-T.; Zou, M.; Yu, Z.W.; Hu, X.-L.; Xu, H.; Ma, S.; Han, Z.; Chen, J.P.; et al. Field test of twin-field quantum key distribution through sending-or-not-sending over 428 km. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2021, 126, 250502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillery, M.; Bužek, V.; Berthiaume, A. Quantum secret sharing. Phys. Rev. A 1999, 59, 1829–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.-G.; Huo, M.; Hu, W.; Zhao, Y. Dynamic multiparty quantum secret sharing with a trusted party based on generalized GHZ state. IEEE Access 2021, 19, 22986–22995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.-L.; Fu, Y.; Liu, W.-B.; Xie, Y.-M.; Li, B.-H.; Zhou, M.-G.; Yin, H.-L.; Chen, Z.-B. Breaking the rate-distance limitation of measurement-device-independent quantum secret sharing. Phys. Rev. Res. 2023, 5, 033077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.-Q.; Li, S.; Liu, Z.-F.; Wang, T.-Y. Measurement-device-independent quantum secret sharing. Adv. Quant. Technol. 2024, 7, 2400060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Ying, J.-W.; Wang, Z.-J.; Zhong, W.; Du, M.-M.; Shen, S.-T.; Li, X.-Y.; Zhang, A.-L.; Gu, S.-P.; Wang, X.-F.; et al. Device-independent quantum secret sharing with advanced random key generation basis. Phys. Rev. A 2025, 111, 012603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Lu, Z.; Wang, P.; Tian, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, Y. Experimental demonstration of multiparty quantum secret sharing and conference key agreement. npj Quant. Inform. 2023, 9, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhong, W.; Du, M.-M.; Shen, S.-T.; Li, X.-Y.; Zhang, A.-L.; Zhou, L.; Sheng, Y.-B. Device-independent quantum secret sharing with noise preprocessing and postselection. Phys. Rev. A 2024, 110, 042403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeilinger, A.; Bernstein, H.J.; Greenberger, D.M.; Horne, M.A.; Zukowski, M. Controlling entanglement in quantum optics. In Quantum Control and Measurement; Ezawa, H., Murayama, Y., Eds.; North-Holland/Elsevier Science Publishers B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1993; pp. 9–23. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/253722501_Controlling_entanglement_in_quantum_optics (accessed on 4 April 2025).
- Osawa, S.; Simon, D.S.; Sergienko, A.V. Directionally-unbiased unitary optical devices in discrete-time quantum walks. Entropy 2019, 21, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reck, M.; Zeilinger, A.; Bernstein, H.J.; Bertani, P. Experimental realization of any discrete unitary operator. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1994, 73, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clements, W.R.; Humphreys, P.C.; Metcalf, B.J.; Kolthammer, W.S.; Walmsley, I.A. Optimal design for universal multiport interferometers. Optica 2016, 3, 1460–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meany, T.; Delanty, M.; Gross, S.; Marshall, G.D.; Steel, M.J.; Withford, M.J. Non-classical interference in integrated 3D multiports. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 26895–26905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spagnolo, N.; Aparo, L.; Vitelli, C.; Crespi, A.; Ramponi, R.; Osellame, R.; Mataloni, P.; Sciarrino, F. Quantum interferometry with three-dimensional geometry. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glauber, R.J. Coherent and incoherent states of the radiation field. Phys. Rev. 1963, 131, 2766–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walls, D.F.; Milburn, G.J. Quantum Optics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| 0 | ||||||
| 0 | ||||||
| 0 |
| Probability | Phase | Phase | Phase | ‡ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ( † + ) | 1.98% | |||
| † | 1.98% | |||
| † | 1.98% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Suryadi; Amadi, P.O.; Ali, N. Three-Photon Pulse Interference in a Tritter: A Novel Approach for a Three-Party Quantum Key Distribution Protocol. Physics 2025, 7, 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/physics7020014
Suryadi, Amadi PO, Ali N. Three-Photon Pulse Interference in a Tritter: A Novel Approach for a Three-Party Quantum Key Distribution Protocol. Physics. 2025; 7(2):14. https://doi.org/10.3390/physics7020014
Chicago/Turabian StyleSuryadi, Precious O. Amadi, and Norshamsuri Ali. 2025. "Three-Photon Pulse Interference in a Tritter: A Novel Approach for a Three-Party Quantum Key Distribution Protocol" Physics 7, no. 2: 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/physics7020014
APA StyleSuryadi, Amadi, P. O., & Ali, N. (2025). Three-Photon Pulse Interference in a Tritter: A Novel Approach for a Three-Party Quantum Key Distribution Protocol. Physics, 7(2), 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/physics7020014






