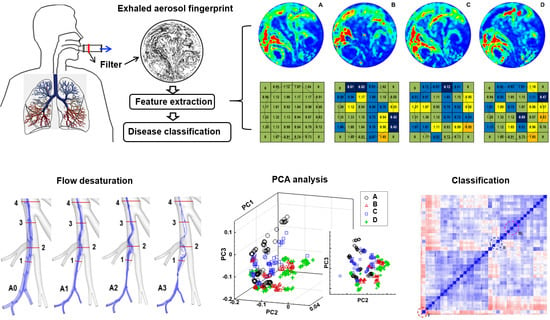
Deciphering Exhaled Aerosol Fingerprints for Early Diagnosis and Personalized Therapeutics of Obstructive Respiratory Diseases in Small Airways
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Healthy and Diseased Airway Models

2.2. Acquisition of Exhaled Aerosol Images
2.3. Feature Extraction of Exhaled Aerosol Images
2.3.1. Relative Concentration
2.3.2. Fractal Dimension and Multifractal Spectrum Analysis
2.3.3. Dynamic Mode Decomposition (DMD)
2.4. Image Classification of Exhaled Aerosol Images
3. Results
3.1. Proof-of-Concept Study in Upper Airway Models
3.1.1. Image Acquisition from Physiology-Based Modeling
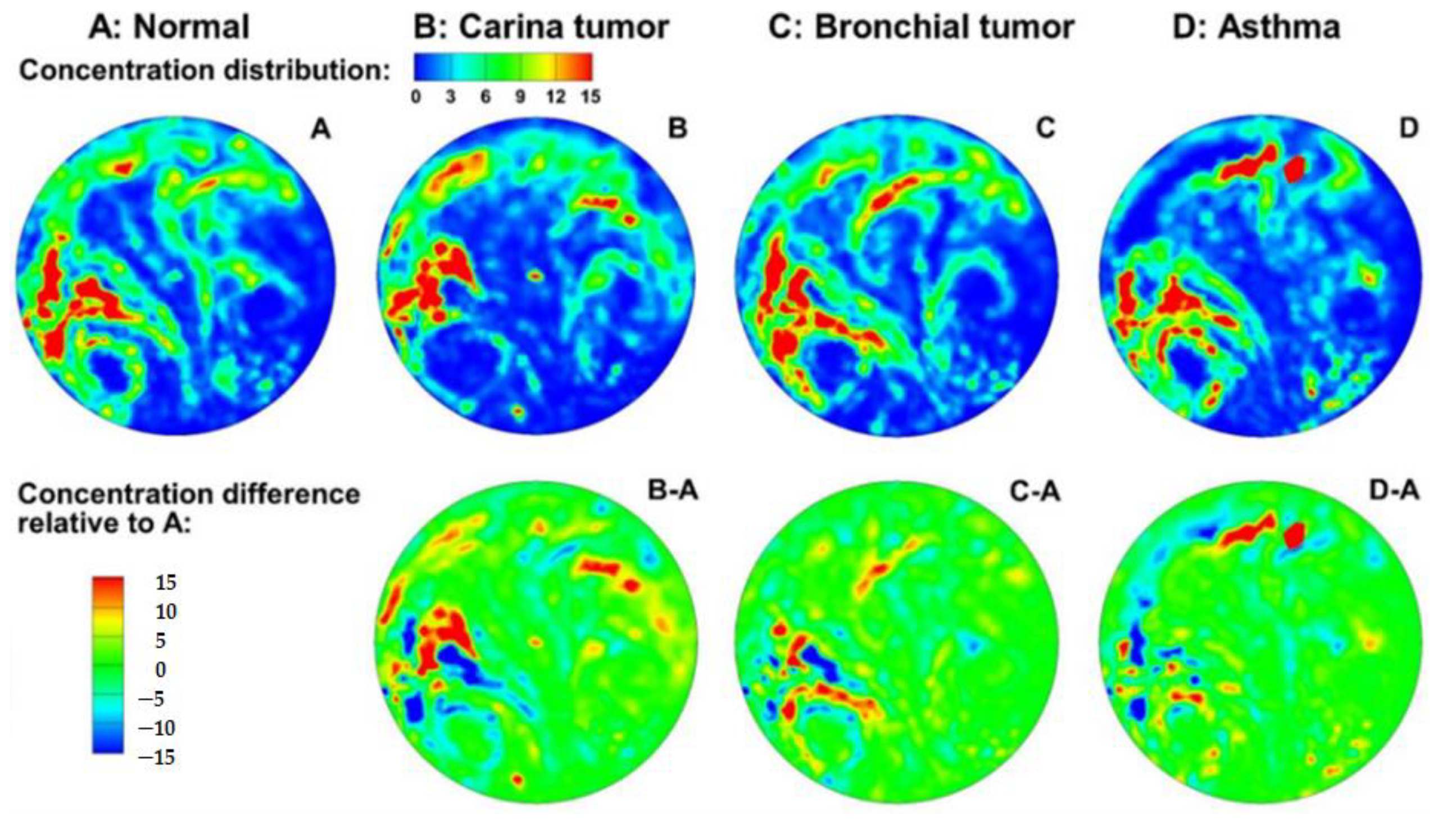
3.1.2. Relative Concentration
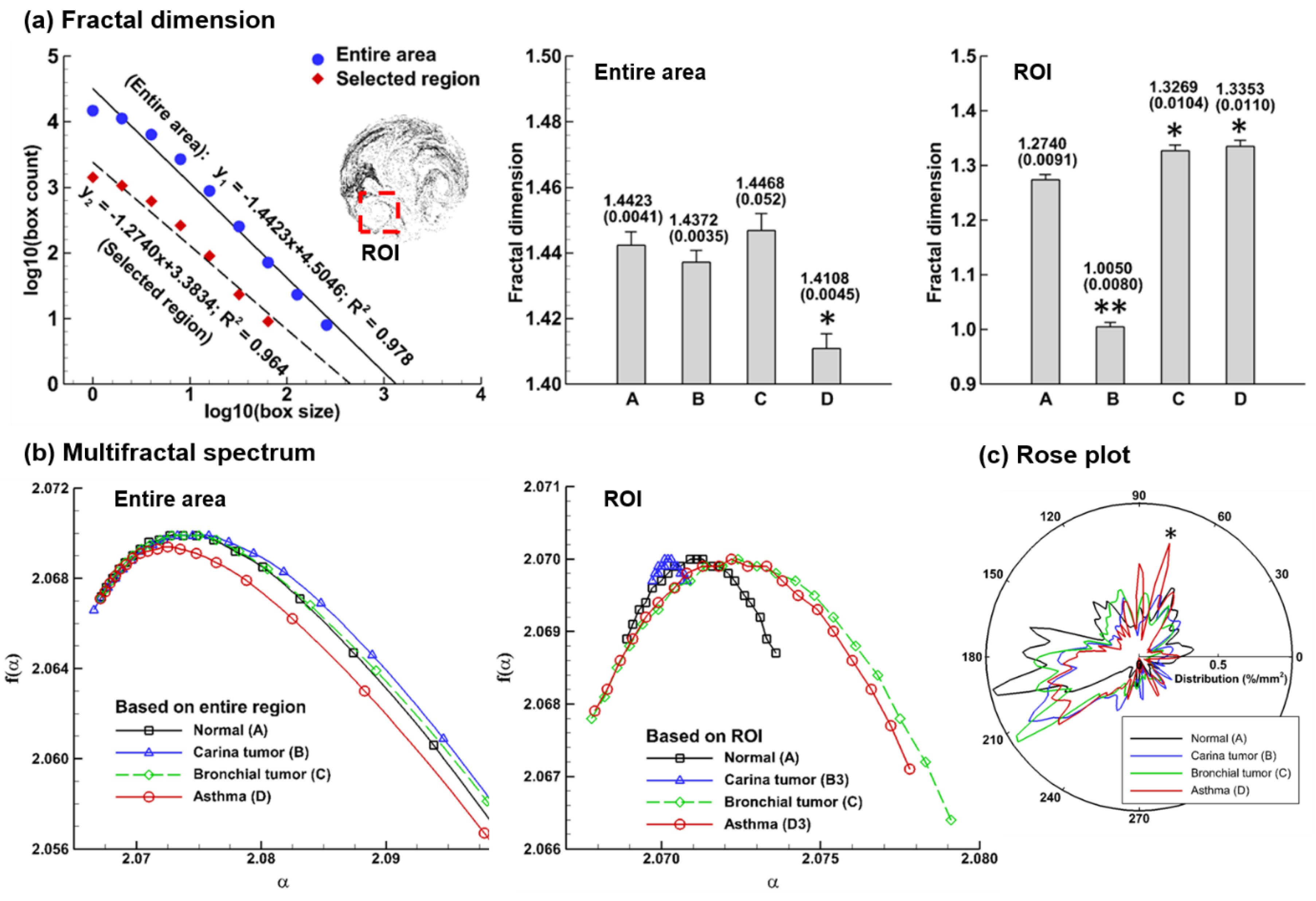
3.1.3. Fractal and Multifractal Feature Extraction
3.2. Growing Bronchial Tumor
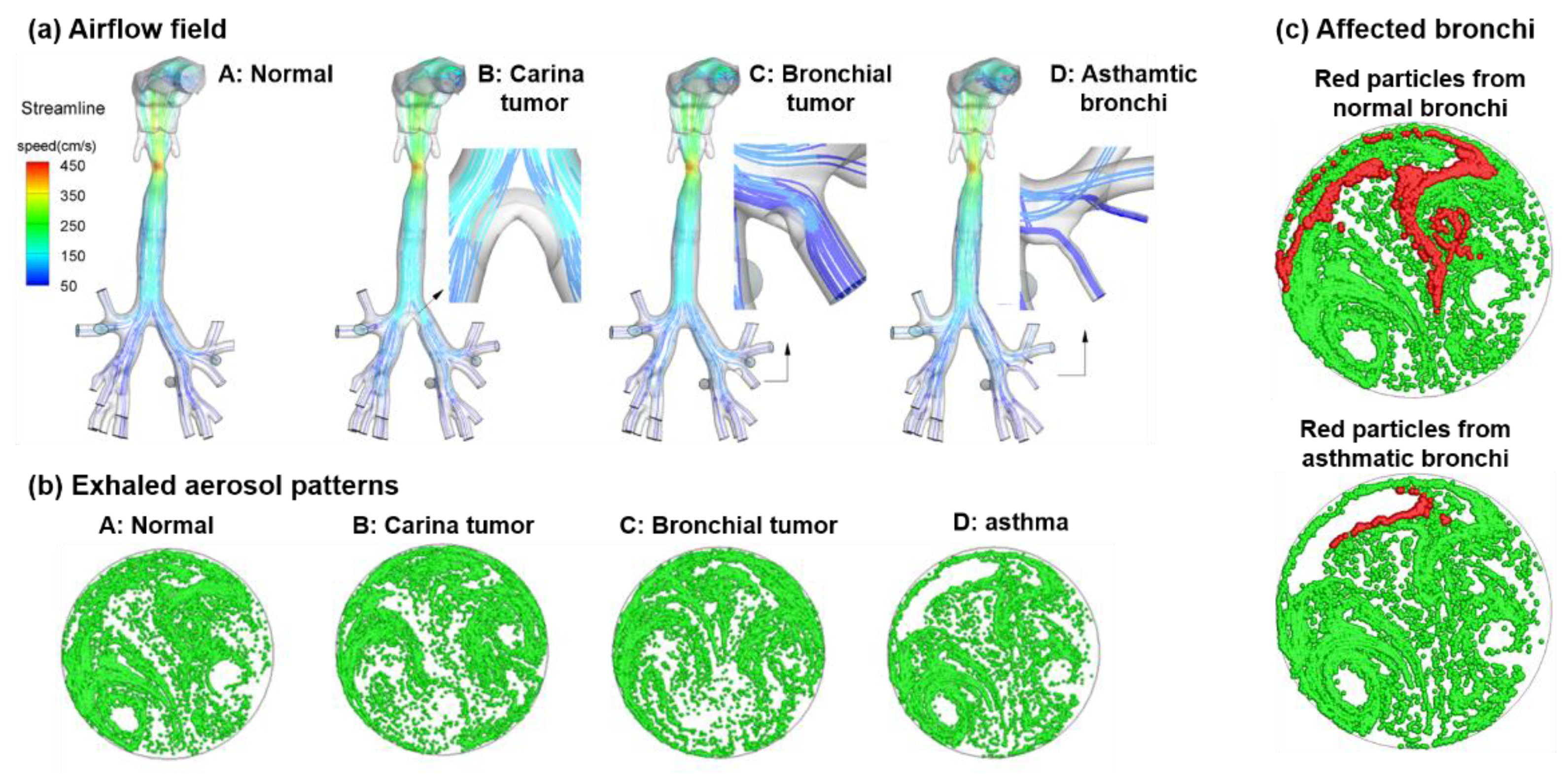
3.2.1. Perturbed Airflow Field
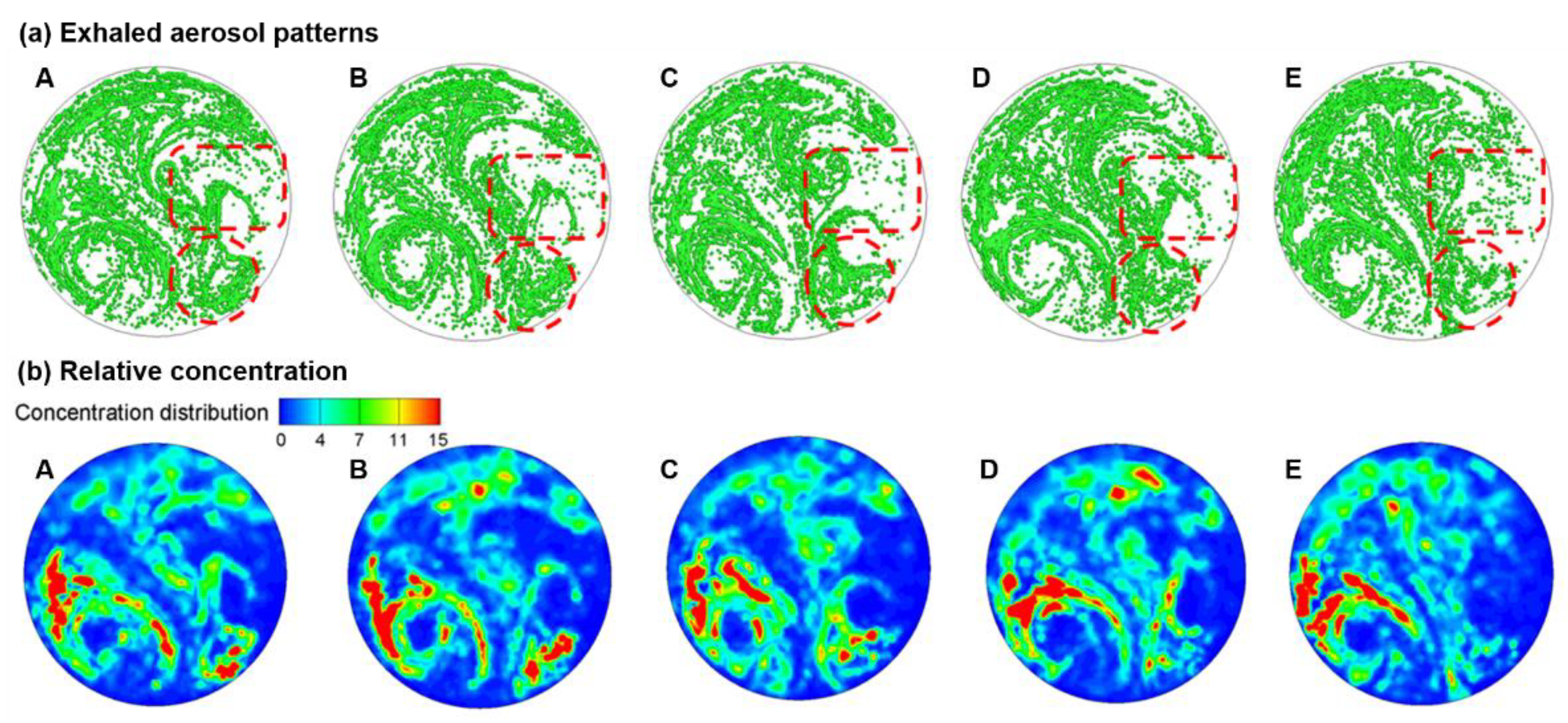
3.2.2. Patterns of Exhaled Aerosol Fingerprints
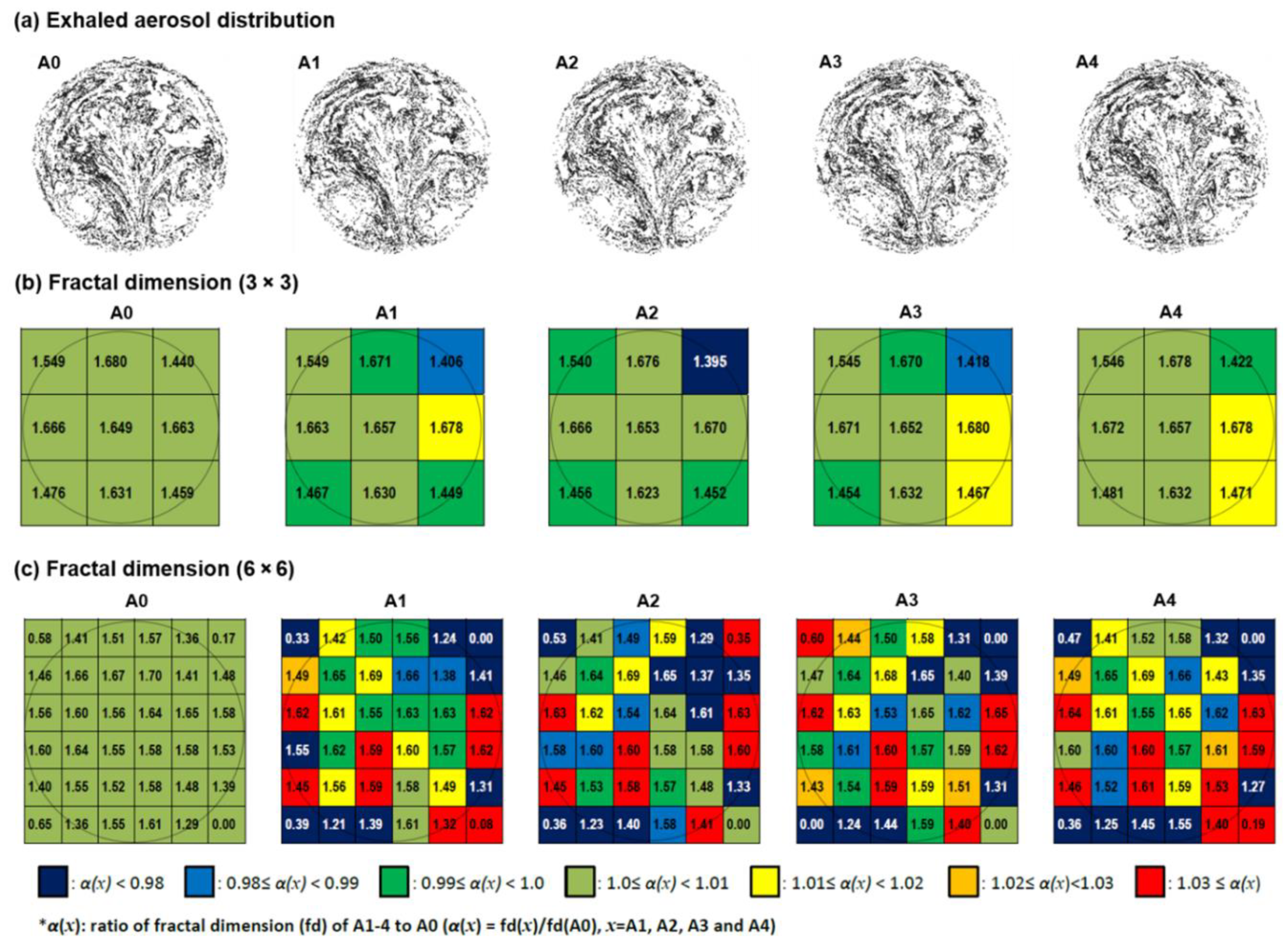
3.2.3. Fractal Dimension
3.2.4. Multifractal Spectrum Analysis
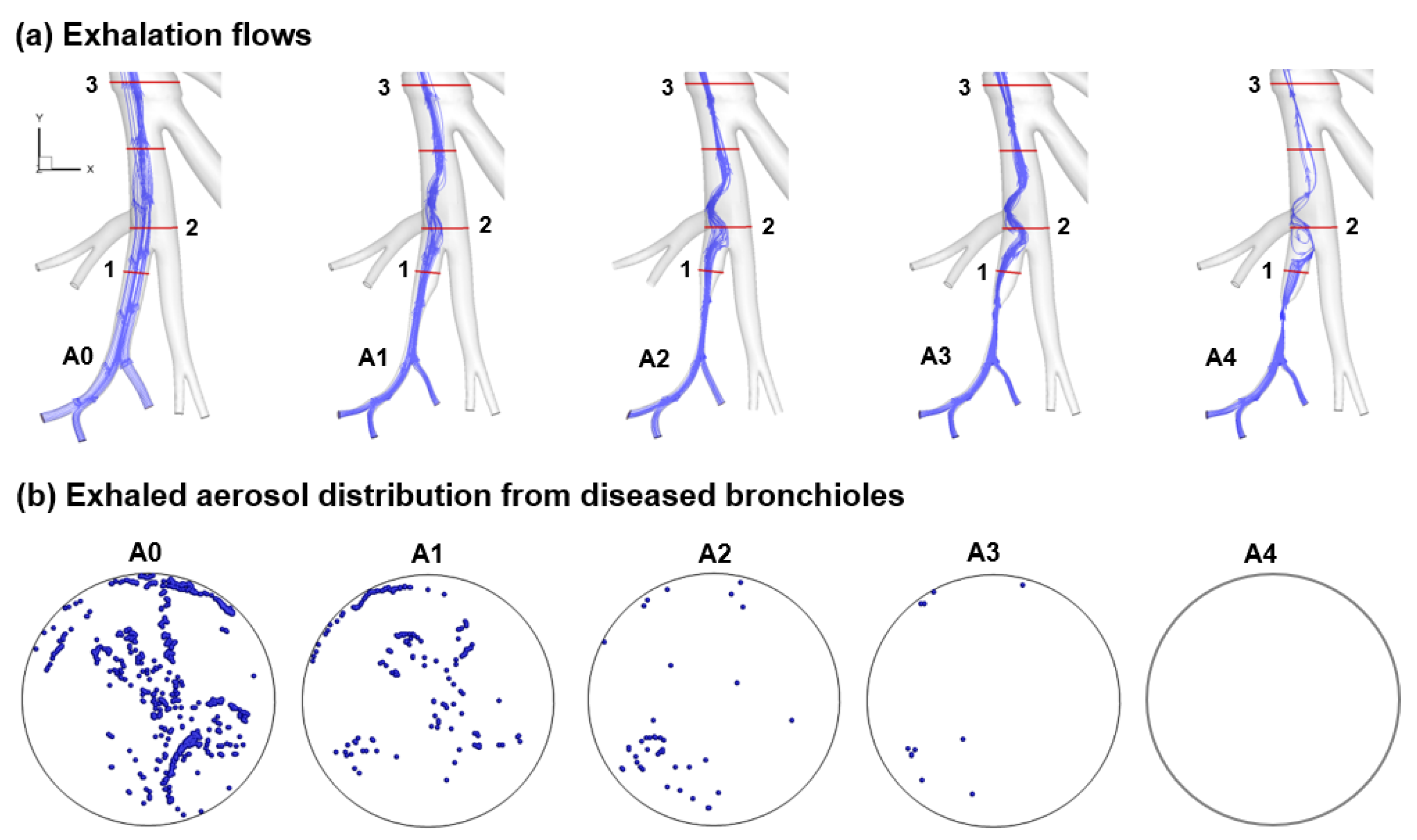
3.3. Asthmatic Bronchioles in Small Airways
3.3.1. Airflow Field and Exhaled Aerosol Images
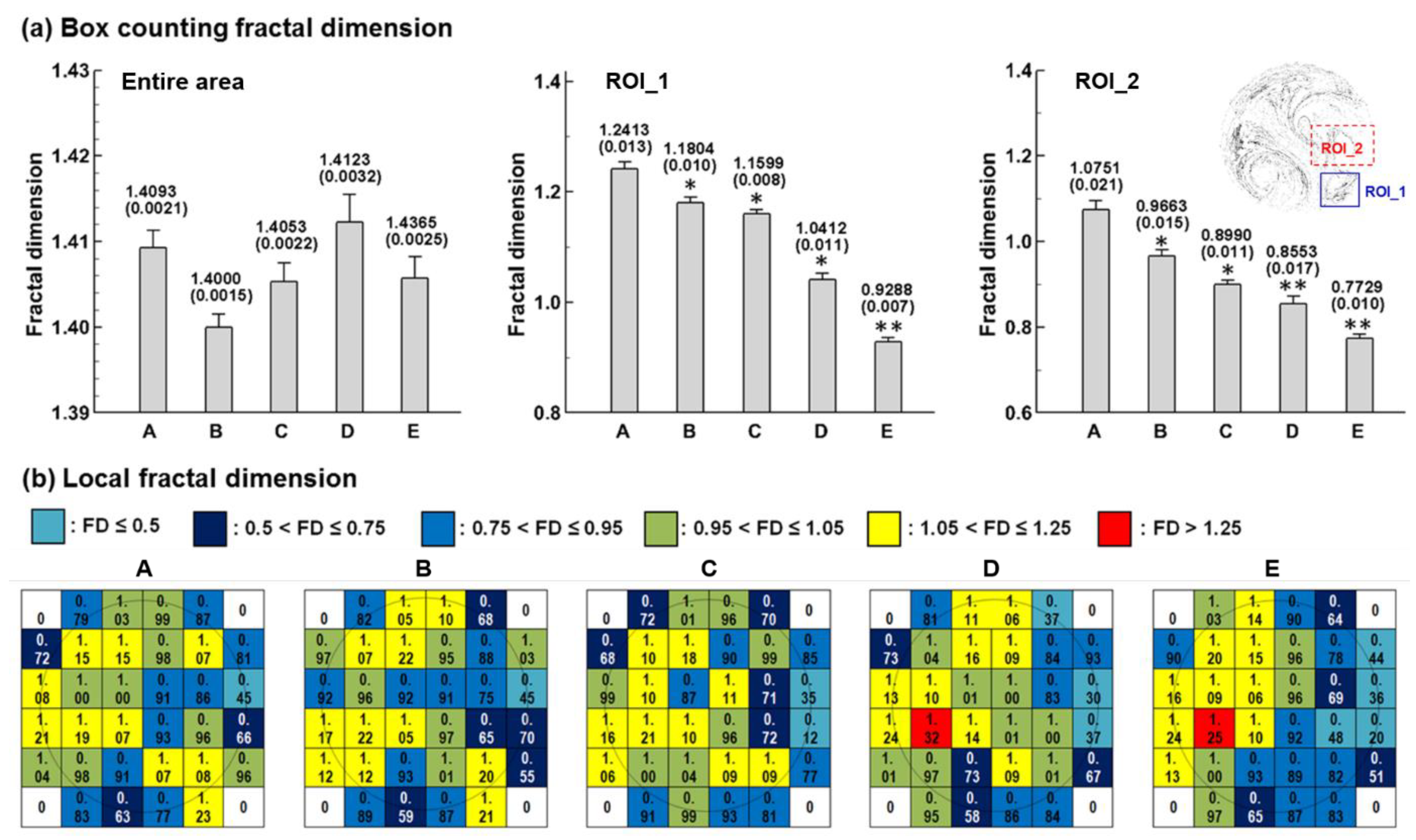
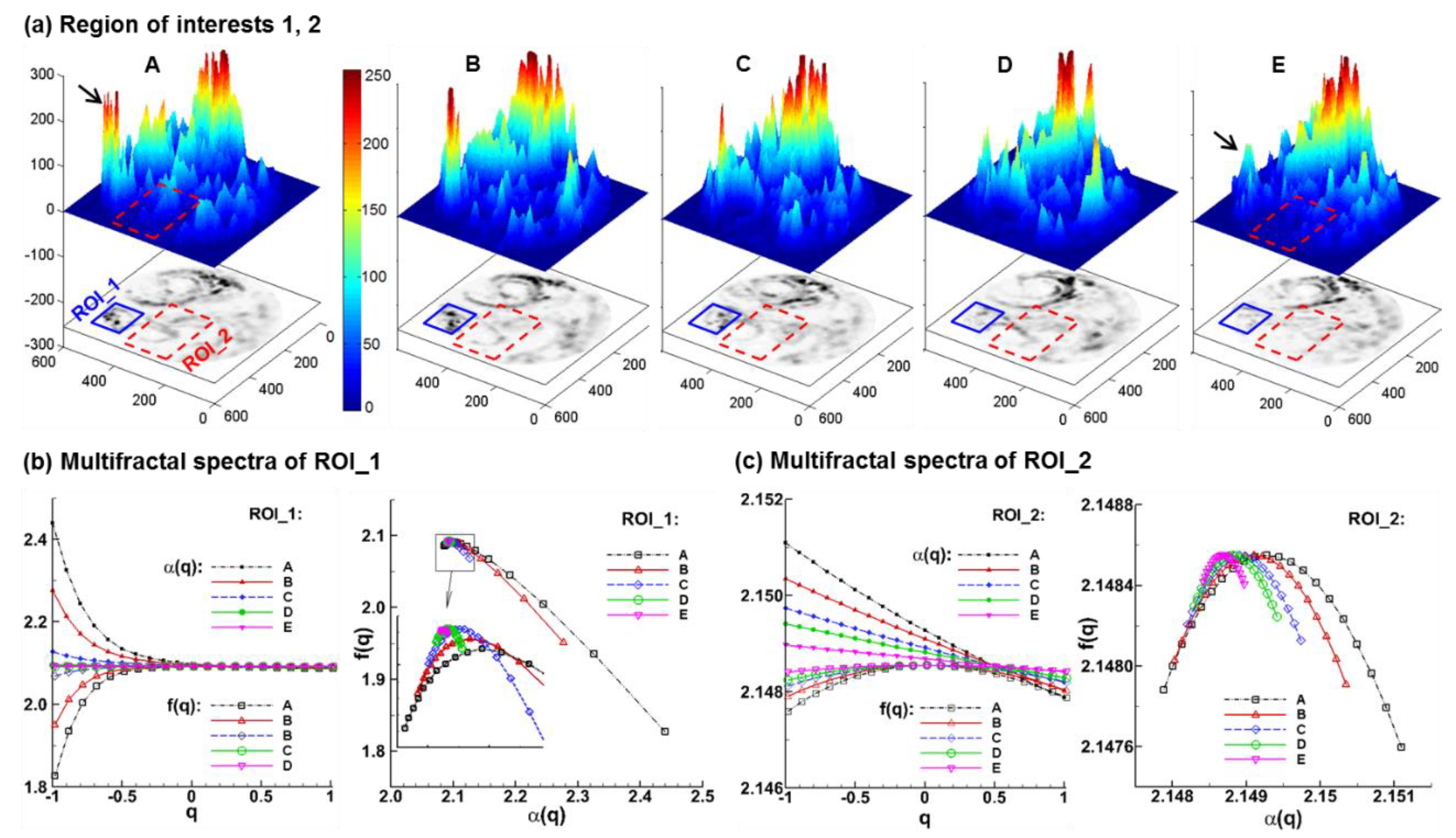
3.3.2. Fractal-Feature Extraction
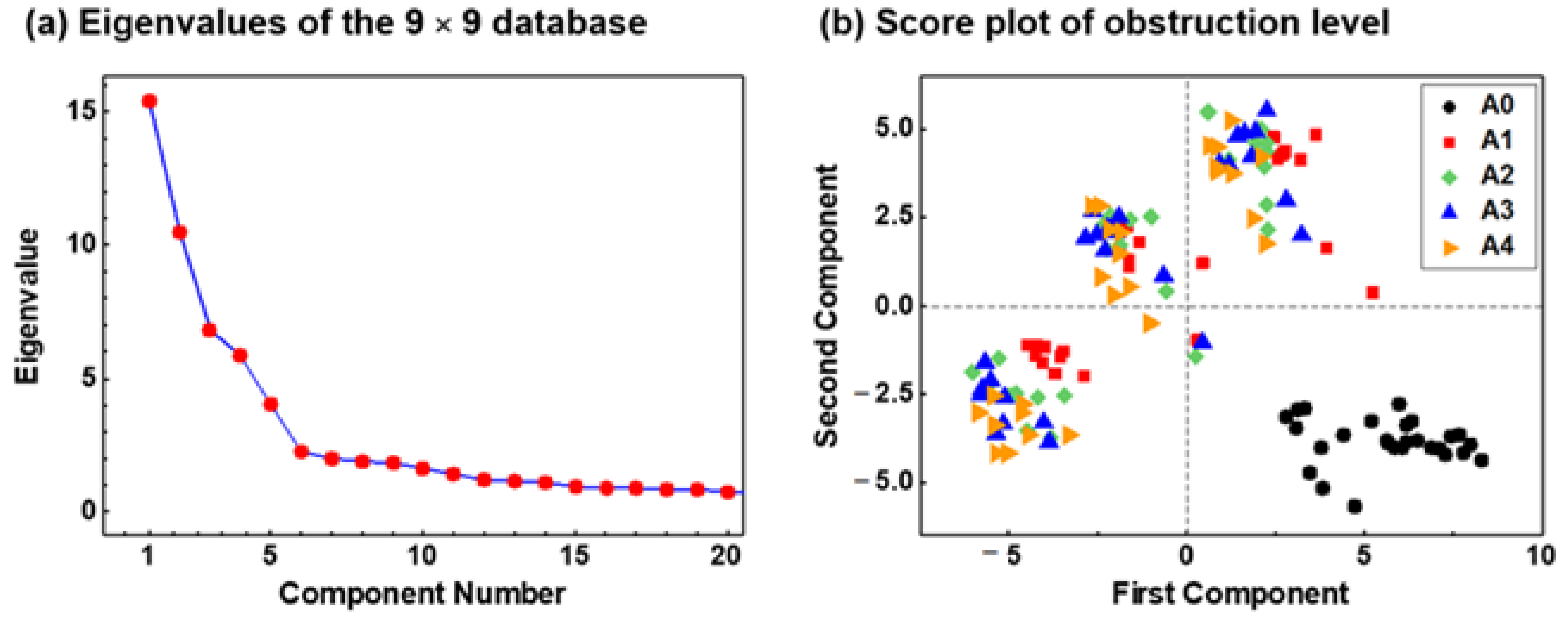
3.3.3. Database Quality Check
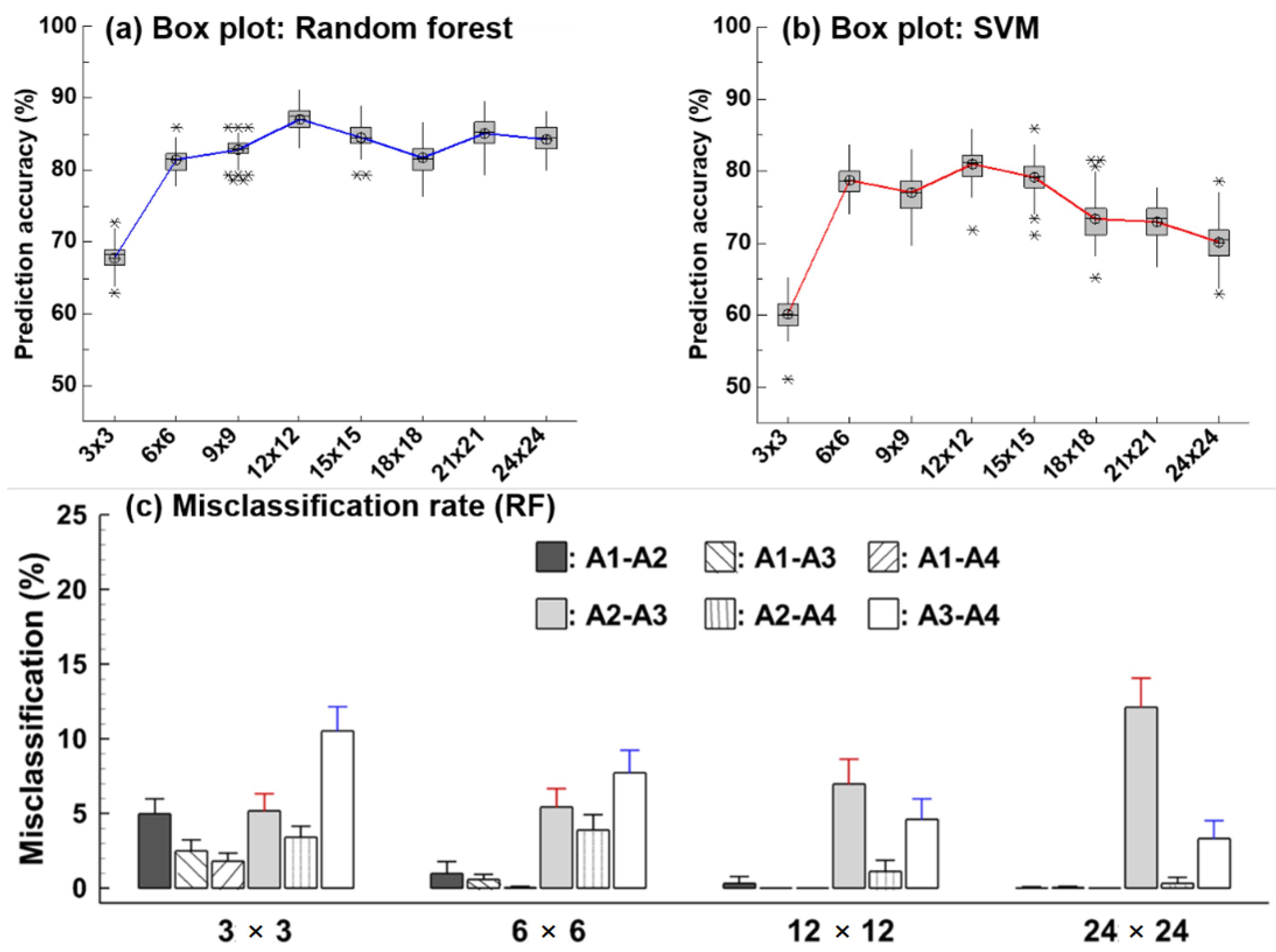
3.3.4. Classification Using SVM and Random Forest (RF) Algorithms
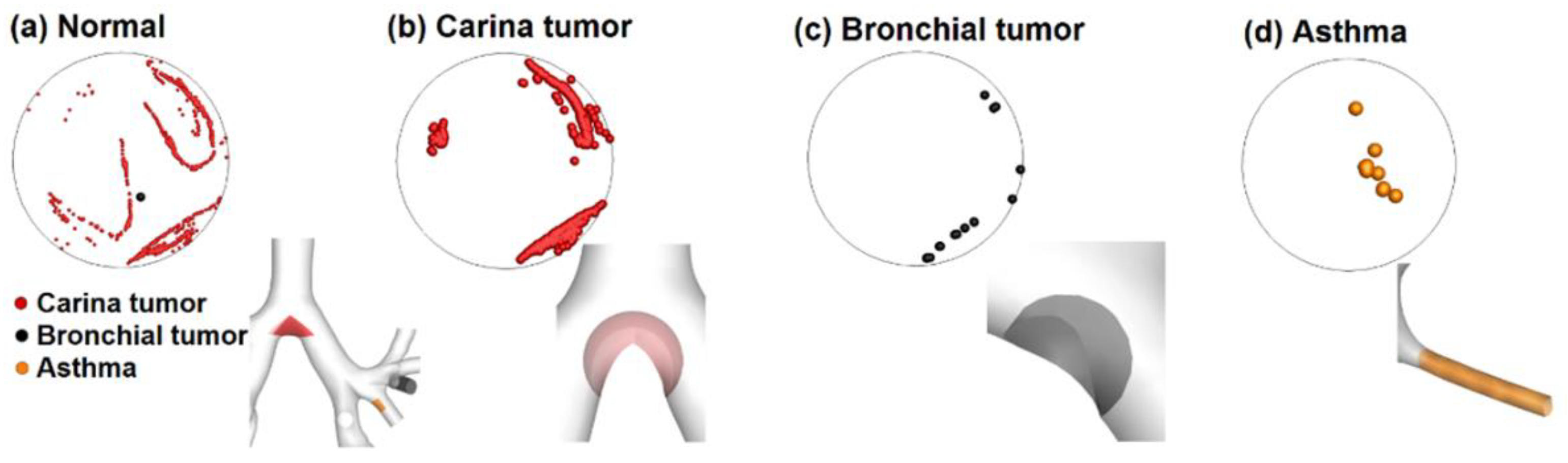
3.3.5. Misclassification Analysis
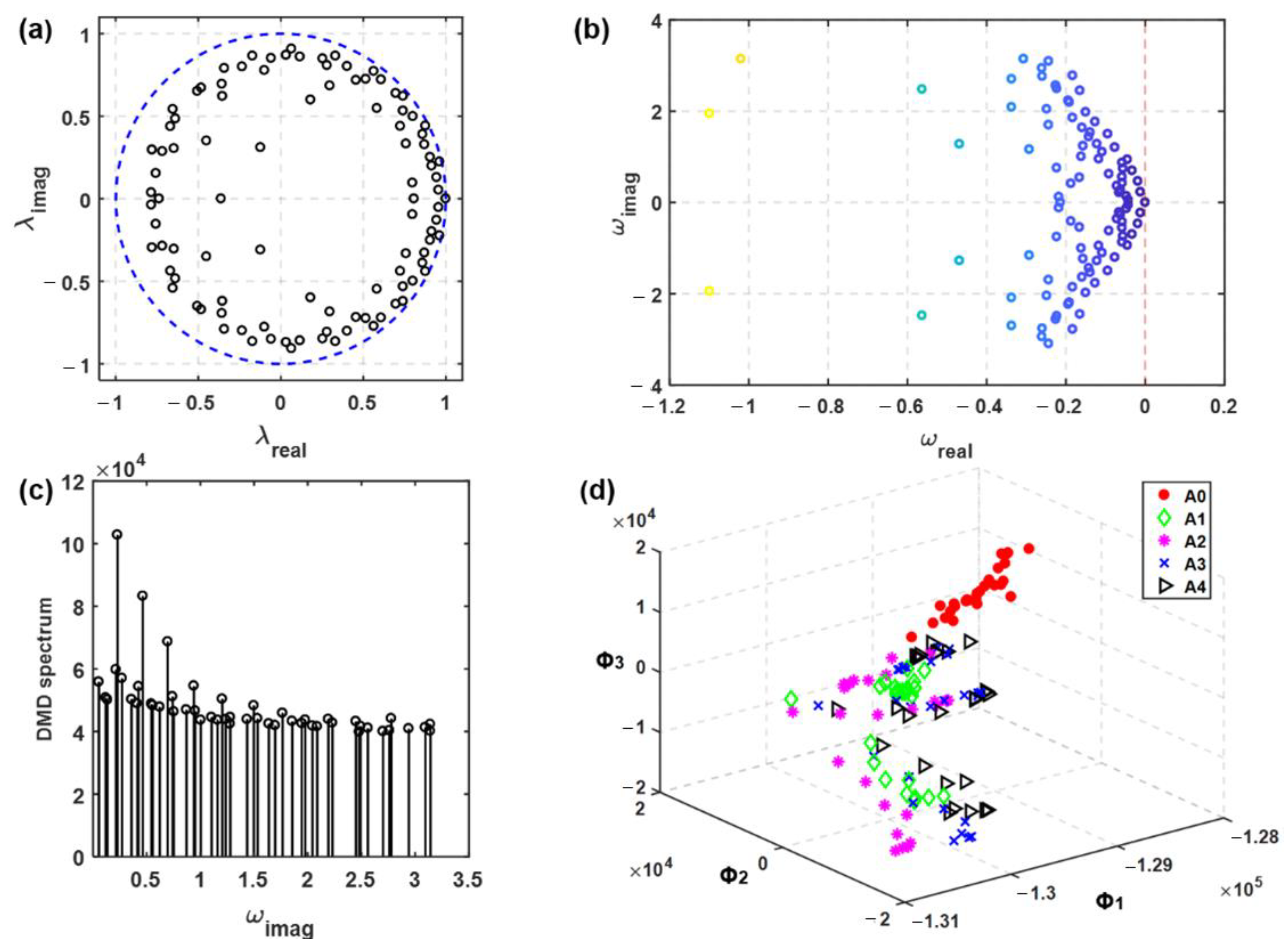
3.4. Dynamic Mode Decomposition (DMD) to Catch Disease Growth
3.4.1. DMD vs. Conventional Algorithms
3.4.2. DMD Feature Extraction of Exhaled AFP Images
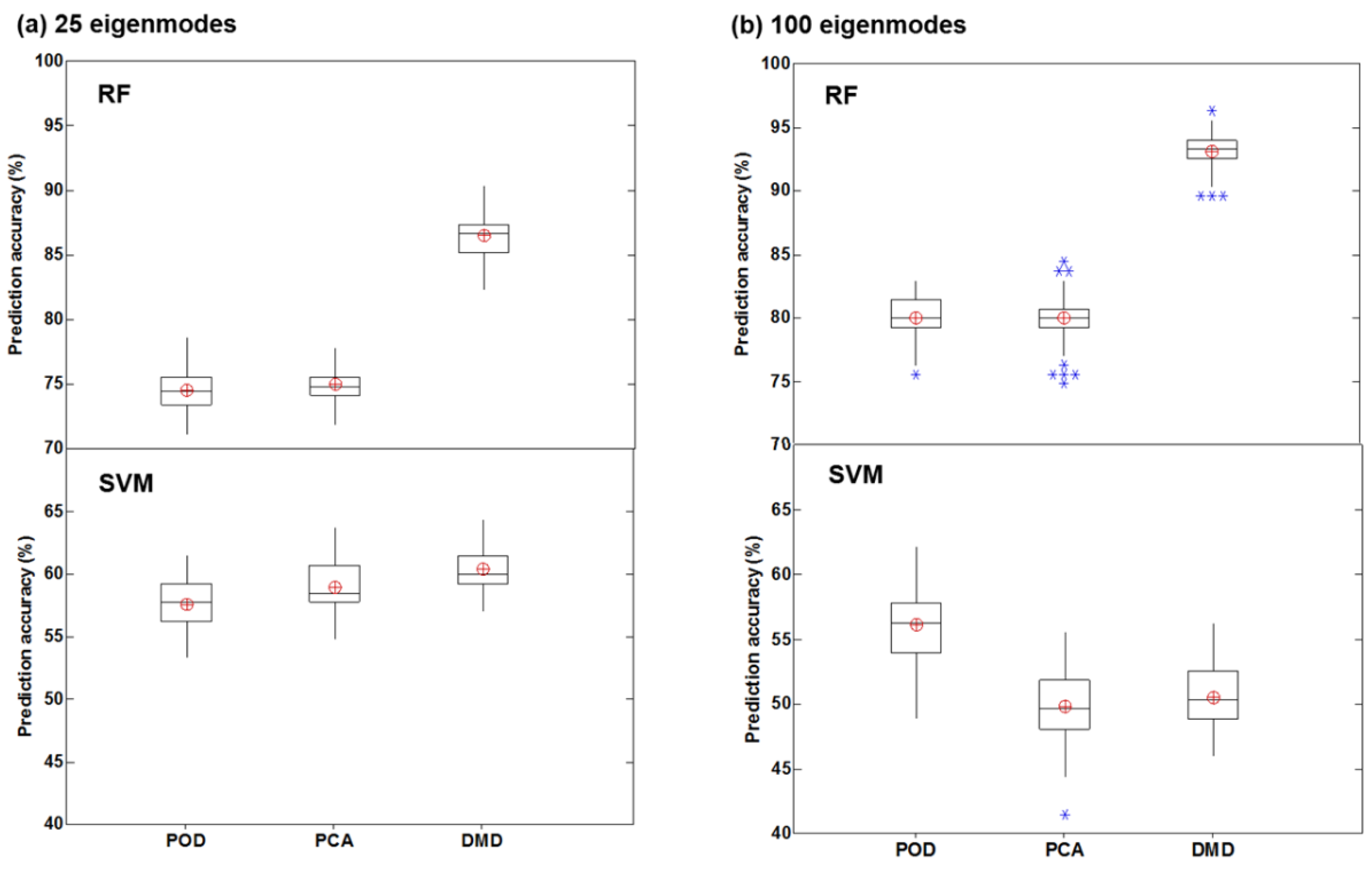
3.4.3. SVM and RF Classification Based on DMD Features
4. Discussion
4.1. DMD vs. Other Feature Extraction Algorithms
4.2. Future Directions
4.3. Assumptions and Limitations
4.4. Potential Roadblocks and Solutions
4.4.1. How the Proposed Breath Test Can Be Implemented in Clinical Settings?
4.4.2. How Can a Classifier Be Developed when There Is No Record of Aerosol Images at the Patient’s First Visit?
4.4.3. There Is Significant Intersubject Variability in Upper Airway Morphology and Breathing Habit. How Can These Compounding Effects Be Minimized?
4.4.4. What Effects on the Breath Test Results Are Expected from Turbulent Flows?
4.4.5. Diseases Can Occur Anywhere in the Lung. How to Tell the Location of the Disease from an Aerosol Image?
5. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wong, J.; Magun, B.E.; Wood, L.J. Lung inflammation caused by inhaled toxicants: A review. Int. J. Chron. Obstruct. Pulmon. Dis. 2016, 11, 1391–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sheehan, W.J.; Gaffin, J.M.; Peden, D.B.; Bush, R.K.; Phipatanakul, W. Advances in environmental and occupational disorders in 2016. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 140, 1683–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Castranova, V.; Vallyathan, V. Silicosis and coal workers’ pneumoconiosis. Environ. Health Perspect. 2000, 108, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stewart, J.I.; Criner, G.J. The small airways in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: Pathology and effects on disease progression and survival. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2013, 19, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martonen, T.B.; Hoffmann, W.; Lowe, J.E. Cigarette smoke and lung cancer. Health Phys. 1987, 52, 213–217. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, J.; Meng, Y.; Adcock, I.M.; Yao, X. Role of inflammatory cells in airway remodeling in COPD. Int. J. Chron. Obstruct. Pulmon. Dis. 2018, 13, 3341–3348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boulet, L.P. Airway remodeling in asthma: Update on mechanisms and therapeutic approaches. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2018, 24, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, C.A.; Lee, K.S.; Shin, M.H.; Cho, Y.Y.; Choi, Y.H.; Kwon, O.J.; Shin, K.E. Low-dose CT screening in an Asian population with diverse risk for lung cancer: A retrospective cohort study. Eur. Radiol. 2015, 25, 2335–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inage, T.; Nakajima, T.; Yoshino, I.; Yasufuku, K. Early lung cancer detection. Clin. Chest. Med. 2018, 39, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roointan, A.; Ahmad Mir, T.; Ibrahim Wani, S.; Mati Ur, R.; Hussain, K.K.; Ahmed, B.; Abrahim, S.; Savardashtaki, A.; Gandomani, G.; Gandomani, M.; et al. Early detection of lung cancer biomarkers through biosensor technology: A review. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2019, 164, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sears, C.R.; Mazzone, P.J. Biomarkers in lung cancer. Clin. Chest. Med. 2020, 41, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coate, L.E.; Massey, C.; Hope, A.; Sacher, A.; Barrett, K.; Pierre, A.; Leighl, N.; Brade, A.; de Perrot, M.; Waddell, T.; et al. Treatment of the elderly when cure is the goal: The influence of age on treatment selection and efficacy for stage III non-small cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2011, 6, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hubbard, M.O.; Fu, P.; Margevicius, S.; Dowlati, A.; Linden, P.A. Five-year survival does not equal cure in non-small cell lung cancer: A Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results-based analysis of variables affecting 10-to 18-year survival. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2012, 143, 1307–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krause, A. Diagnosis of interstitial Lung diseases. Z Rheumatol. 2012, 71, 542–543. [Google Scholar]
- McCunney, R.J.; Morfeld, P.; Payne, S. What component of coal causes coal workers’ pneumoconiosis? J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2009, 51, 462–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miller, B.G.; Jacobsen, M. Dust exposure, pneumoconiosis and mortality of coalminers. Br. J. Ind. Med. 1985, 42, 723–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cox, C.W.; Rose, C.S.; Lynch, D.A. State of the art: Imaging of occupational lung disease. Radiology 2014, 270, 681–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimura, N. Pathology and pathophysiology of pneumoconiosis. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2000, 6, 140–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjunatha, Y.C.; Seith, A.; Kandpal, H.; Das, C.J. Rheumatoid arthritis: Spectrum of computed tomographic findings in pulmonary diseases. Curr. Probl. Diagn. Radiol. 2010, 39, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amann, A.; Miekisch, W.; Schubert, J.; Buszewski, B.; Ligor, T.; Jezierski, T.; Pleil, J.; Risby, T. Analysis of exhaled breath for disease detection. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2014, 7, 455–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krilaviciute, A.; Heiss, J.A.; Leja, M.; Kupcinskas, J.; Haick, H.; Brenner, H. Detection of cancer through exhaled breath: A systematic review. Oncotargeting 2015, 6, 38643–38657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hayes, S.A.; Haefliger, S.; Harris, B.; Pavlakis, N.; Clarke, S.J.; Molloy, M.P.; Howell, V.M. Exhaled breath condensate for lung cancer protein analysis: A review of methods and biomarkers. J. Breath. Res. 2016, 10, 034001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvath, I.; Lazar, Z.; Gyulai, N.; Kollai, M.; Losonczy, G. Exhaled biomarkers in lung cancer. Eur. Respir. J. 2009, 34, 261–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miekisch, W.; Schubert, J.K.; Noeldge-Schomburg, G.F.E. Diagnostic potential of breath analysis—focus on volatile organic compounds. Clinica Chimica Acta 2004, 347, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostikas, K.; Koutsokera, A.; Papiris, S.; Gourgoulianis, K.I.; Loukides, S. Exhaled breath condensate in patients with asthma: Implications for application in clinical practice. Clin. Exp. Allergy. 2008, 38, 557–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, C.; Faelli, N.; Tirelli, A.S.; Fortunato, F.; Biffi, A.; Claut, L.; Cariani, L.; Dacco, V.; Prato, R.; Conese, M. Analysis of inflammatory and immune response biomarkers in sputum and exhaled breath condensate by a multi-parametric biochip array in cystic fibrosis. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2011, 24, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loukides, S.; Bakakos, P.; Kostikas, K. Oxidative stress in patients with COPD. Curr. Drug Targets 2011, 12, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, H.P.; Tran, V.; Lewis, C.; Thomas, P.S. Elevated levels of oxidative stress markers in exhaled breath condensate. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2009, 4, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Poli, D.; Carbognani, P.; Corradi, M.; Goldoni, M.; Acampa, O.; Balbi, B.; Bianchi, L.; Rusca, M.; Mutti, A. Exhaled volatile organic compounds in patients with non-small cell lung cancer: Cross sectional and nested short-term follow-up study. Respir. Res. 2005, 6, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vijverberg, S.J.H.; Koenderman, L.; Koster, E.S.; van der Ent, C.K.; Raaijmakers, J.A.M.; Maitland-van der Zee, A.H. Biomarkers of therapy responsiveness in asthma: Pitfalls and promises. Clin. Exp. Allergy. 2011, 41, 615–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzone, P.J. Analysis of volatile organic compounds in the exhaled breath for the diagnosis of lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2008, 3, 774–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Buszewski, B.; Kesy, M.; Ligor, T.; Amann, A. Human exhaled air analytics: Biomarkers of diseases. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2007, 21, 553–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, M.; Cataneo, R.N.; Cummin, A.R.C.; Gagliardi, A.J.; Gleeson, K.; Greenberg, J.; Maxfield, R.A.; Rom, W.N. Detection of lung cancer with volatile markers in the breath. Chest 2003, 123, 2115–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Talaat, K.; Xi, J.; Baldez, P.; Hecht, A. Radiation dosimetry of inhaled radioactive aerosols: CFPD and MCNP transport simulations of radionuclides in the lung. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talaat, K.; Hecht, A.; Xi, J. A comparison of CFPD, compartment, and uniform distribution models for radiation dosimetry of radionuclides in the lung. J. Radiol. Prot. 2021, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, J.; Longest, P.W. Transport and deposition of micro-aerosols in realistic and simplified models of the oral airway. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2007, 35, 560–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, J.; Longest, P.W. Characterization of submicrometer aerosol deposition in extrathoracic airways during nasal exhalation. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 808–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, J.; Longest, P.W.; Martonen, T.B. Effects of the laryngeal jet on nano- and microparticle transport and deposition in an approximate model of the upper tracheobronchial airways. J. Appl. Physiol. 2008, 104, 1761–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, J.; Si, X.; Kim, J.W.; Berlinski, A. Simulation of airflow and aerosol deposition in the nasal cavity of a 5-year-old child. J. Aerosol Sci. 2011, 42, 156–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, X.; Xi, J.; Kim, J. Effect of laryngopharyngeal anatomy on expiratory airflow and submicrometer particle deposition in human extrathoracic airways. Open J. Fluid Dyn. 2013, 3, 40441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Si, X.A.; Xi, J.; Kim, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhong, H. Modeling of release position and ventilation effects on olfactory aerosol drug delivery. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2013, 186, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, J.; Si, X.; Longest, P.W. Electrostatic charge effects on pharmaceutical aerosol deposition in human nasal-laryngeal airways. Pharmaceutics 2013, 6, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xi, J.; Si, X.A.; Gaide, R. Electrophoretic particle guidance significantly enhances olfactory drug delivery: A feasibility study. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, J.D. Aerosol bolus dispersion and aerosol-derived airway morphometry: Assessment of lung pathology and response to therapy. 1. J. Aerosol Med. Depos. Clear. Eff. Lung 1996, 9, 183–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goo, J.; Kim, C.S. Analysis of aerosol bolus dispersion in a cyclic tube flow by finite element method. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2001, 34, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Lee, J. Dispersion of aerosol bolus during one respiratory cycle in a model lung airway. J. Aerosol Sci. 2002, 33, 1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, P.J.; Dolovich, M.B. Aerosols as diagnostic tools. J. Aerosol Med. Depos. Clear. Eff. Lung 1994, 7, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, J.D. Aerosol bolus dispersion and aerosol-derived airway morphometry: Assessment of lung pathology and response to therapy. 2. J. Aerosol Med. Depos. Clear. Eff. Lung 1996, 9, 453–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, H.C.; Schum, G.M. Models of human lung airways and their application to inhaled particle deposition. Bull. Math. Biology 1980, 42, 461–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICRP. Human Respiratory Tract Model. for Radiological Protection; Elsevier Science: New York, NY, USA, 1994; Volume 66. [Google Scholar]
- Heistracher, T.; Hofmann, W. Physiologically realistic models of bronchial airway bifurcations. J. Aerosol Sci. 1995, 26, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segal, R.A.; Guan, X.; Shearer, M.; Martonen, T.B. Mathematical model of airflow in the lungs of children I: Effects of tumor sizes and locations. J. Theor. Med. 2000, 2, 199–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daisne, J.F.; Duprez, T.; Weynand, B.; Lonneux, M.; Hamoir, M.; Reychler, H.; Gregoire, V. Tumor volume in pharyngolaryngeal squamous cell carcinoma: Comparison at CT, MR imaging, and FDG PET and validation with surgical specimen. Radiology 2004, 233, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, J.; Kim, J.; Si, X.A.; Mckee, E.; Corley, R.A.; Kabilan, S.; Wang, S. CFD modeling and image analysis of exhaled aerosols due to a growing bronchial tumor: Towards non-invasive diagnosis and treatment of respiratory obstructive diseases. Theranostics 2015, 5, 443–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, J.; Yuan, J.E.; Si, X.; Zhou, Y.; Cheng, Y.S. Parametric study on mouth-throat geometrical factors on depositions of orally inhaled aerosols. J. Aerosol Sci. 2015, 99, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, J.; Zhao, W.; Yuan, J.E.; Cao, B.; Zhao, L. Multi-resolution classification of exhaled aerosol images to detect obstructive lung diseases in small airways. Comput. Biol. Med. 2017, 87, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, J.; Kim, J.; Si, X.A.; Zhou, Y. Diagnosing obstructive respiratory diseases using exhaled aerosol fingerprints: A feasibility study. J. Aerosol Sci. 2013, 64, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.W.; Xi, J.; Si, X.A. Dynamic growth and deposition of hygroscopic aerosols in the nasal airway of a 5-year-old child. Int. J. Numer. Method. Biomed. Eng. 2013, 29, 17–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, D.C. Formulation of the k-w turbulence model revisited. AIAA J. 2008, 46, 2823–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Longest, P.W.; Xi, J. Computational investigation of particle inertia effects on submicron aerosol deposition in the respiratory tract. J. Aerosol Sci. 2007, 38, 111–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morsi, S.A.; Alexander, A.J. An investigation of particle trajectories in two-phase flow systems. J. Fluid Mech. 1972, 55, 193–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, M.D.; Raabe, O.G. Slip correction measurements of spherical solid aerosol particles in an improved Millikan apparatus. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 1985, 4, 269–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longest, P.W.; Xi, J. Effectiveness of direct Lagrangian tracking models for simulating nanoparticle deposition in the upper airways. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 380–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, J.; Longest, P.W. Evaluation of a drift flux model for simulating submicrometer aerosol dynamics in human upper tracheobronchial airways. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2008, 36, 1714–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, J.; Si, X.A.; Kim, J.; Mckee, E.; Lin, E.B. Exhaled aerosol pattern discloses lung structural abnormality: A sensitivity study using computational modeling and fractal analysis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karperien, A.; Ahammer, H.; Jelinek, H.F. Quantitating the subtleties of microglial morphology with fractal analysis. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karperien, A. Fractal Dimension and Lacunarity. 2013; ImageJ. Available online: https://imagej.nih.gov/ij/plugins/fraclac/fraclac.html (accessed on 6 May 2021).
- Cortes, C.; Vapnik, V. Support-vector networks. Mach. Learn. 1995, 20, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramaswamy, S.; Tamayo, P.; Rifkin, R.; Mukherjee, S.; Yeang, C.H.; Angelo, M.; Ladd, C.; Reich, M.; Latulippe, E.; Mesirov, J.P.; et al. Multiclass cancer diagnosis using tumor gene expression signatures. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 15149–15154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noble, W.S. What is a support vector machine? Nat. Biotechnol. 2006, 24, 1565–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boser, S.R.; Park, H.; Perry, S.F.; Ménache, M.G.; Green, F.H.Y. Fractal geometry of airway remodeling in human asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 172, 817–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posadas, A.N.D.; Giménez, D.; Quiroz, R.; Protz, R. Multifractal characterization of soil pore systems. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2003, 67, 1361–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, D.J.; Vadakkan, T.J.; PochÉ, R.A.; Dickinson, M.E. Multifractal and lacunarity analysis of microvascular morphology and remodeling. Microcirculation 2011, 18, 136–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, S.; Nie, F.; Zhang, C. Learning a Mahalanobis distance metric for data clustering and classification. Pattern Recogn. 2008, 41, 3600–3612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, J.; Zhao, W. Correlating exhaled aerosol images to small airway obstructive diseases: A study with dynamic mode decomposition and machine learning. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0211413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hémon, P.; Santi, F. Simulation of a spatially correlated turbulent velocity field using biorthogonal decomposition. J. Wind. Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2007, 95, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, J.; Zhao, W.; Yuan, J.E.; Kim, J.; Si, X.; Xu, X. Detecting lung diseases from exhaled aerosols: Non-Invasive lung diagnosis using fractal analysis and SVM classification. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0139511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Litjens, G.; Kooi, T.; Bejnordi, B.E.; Setio, A.A.A.; Ciompi, F.; Ghafoorian, M.; van der Laak, J.; van Ginneken, B.; Sanchez, C.I. A survey on deep learning in medical image analysis. Med. Image Anal. 2017, 42, 60–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suzuki, K. Overview of deep learning in medical imaging. Radiol. Phys. Technol. 2017, 10, 257–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, H.; Zerbe, N.; Klempert, I.; Hellwich, O.; Hufnagl, P. Deep convolutional neural networks for automatic classification of gastric carcinoma using whole slide images in digital histopathology. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. Off. J. Comput. Med. Imaging Soc. 2017, 61, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, R.; Nishio, M.; Do, R.K.G.; Togashi, K. Convolutional neural networks: An overview and application in radiology. Insights Imaging 2018, 9, 911–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Talaat, M.; Si, X.A.; Dong, H.; Xi, J. Leveraging statistical shape modeling in computational respiratory dynamics: Nanomedicine delivery in remodeled airways. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2021, 204, 106079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, X.A.; Talaat, M.; Su, W.C.; Xi, J. Inhalation dosimetry of nasally inhaled respiratory aerosols in the human respiratory tract with locally remodeled conducting lungs. Inhal. Toxicol. 2021, 33, 143–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, J.; Talaat, M.; Si, X.A.; Chandra, S. The application of statistical shape modeling for lung morphology in aerosol inhalation dosimetry. J. Aerosol Sci. 2021, 151, 105623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou-Suckow, Z.; Duerr, J.; Hagner, M.; Agrawal, R.; Mall, M.A. Airway mucus, inflammation and remodeling: Emerging links in the pathogenesis of chronic lung diseases. Cell Tissue Res. 2017, 367, 537–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, J.; Yang, T. Variability in oropharyngeal airflow and aerosol deposition due to changing tongue positions. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 49, 674–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iltis, P.W.; Frahm, J.; Altenmüller, E.; Voit, D.; Joseph, A.; Kozakowski, K. Tongue position variability during sustained notes in healthy vs dystonic horn players using real-time MRI. Med. Probl. Perform. Art. 2019, 34, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, E.J.; Weisman, J.L.; Oldham, M.J.; Robinson, R.J. Flow field analysis in a compliant acinus replica model using particle image velocimetry (PIV). J. Biomech. 2010, 43, 1039–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oakes, J.M.; Marsden, A.L.; Grandmont, C.; Shadden, S.C.; Darquenne, C.; Vignon-Clementel, I.E. Airflow and particle deposition simulations in health and emphysema: From in vivo to in silico animal experiments. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2014, 42, 899–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oakes, J.M.; Marsden, A.L.; Grandmont, C.; Darquenne, C.; Vignon-Clementel, I.E. Distribution of aerosolized particles in healthy and emphysematous rat lungs: Comparison between experimental and numerical studies. J. Biomech. 2015, 48, 1147–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, J.; Xi, J.; Langenderfer, J.E. Sensitivity analysis and uncertainty quantification in pulmonary drug delivery of orally inhaled pharmaceuticals. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 106, 3303–3315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Si, X.A.; Xi, J. Deciphering Exhaled Aerosol Fingerprints for Early Diagnosis and Personalized Therapeutics of Obstructive Respiratory Diseases in Small Airways. J. Nanotheranostics 2021, 2, 94-117. https://doi.org/10.3390/jnt2030007
Si XA, Xi J. Deciphering Exhaled Aerosol Fingerprints for Early Diagnosis and Personalized Therapeutics of Obstructive Respiratory Diseases in Small Airways. Journal of Nanotheranostics. 2021; 2(3):94-117. https://doi.org/10.3390/jnt2030007
Chicago/Turabian StyleSi, Xiuhua April, and Jinxiang Xi. 2021. "Deciphering Exhaled Aerosol Fingerprints for Early Diagnosis and Personalized Therapeutics of Obstructive Respiratory Diseases in Small Airways" Journal of Nanotheranostics 2, no. 3: 94-117. https://doi.org/10.3390/jnt2030007
APA StyleSi, X. A., & Xi, J. (2021). Deciphering Exhaled Aerosol Fingerprints for Early Diagnosis and Personalized Therapeutics of Obstructive Respiratory Diseases in Small Airways. Journal of Nanotheranostics, 2(3), 94-117. https://doi.org/10.3390/jnt2030007