Abstract
Traditional barcode encoding methods are constrained by the inability to dynamically control crystal orientations, thereby limiting their applications. In this work, we investigate the dynamic magnetic control of lanthanide metal–organic framework crystals and their potential for advancing photonic barcode technology. A paramagnetic fluorescent Eu-MOF microcrystal with sizes ranging from 30 to 40 μm in length and 5 to 10 μm in width was synthesized, and its magnetic orientation and polarized emission were systematically investigated. Eu-MOF crystallizes in an orthorhombic space group, growing along the crystallographic b-axis and ultimately forming an anisotropic cuboid shape. Eu-MOF microcrystals exhibit significant magnetic anisotropy, causing the crystallographic c-axis of the crystal to align with the magnetic field when a uniaxial magnetic field of ~10 mT is applied. Furthermore, the Eu-MOF microcrystal exhibited characteristic Eu emissions with peaks at 594 nm, 616 nm, and 695 nm, and showed a high degree of polarization (DOP), reaching 0.904 at 616 nm. Therefore, the utilization of a rotating magnetic field not only enables precise and dynamic control over the crystal orientations but also results in a significant variation in the luminescence intensity. This capability enabled us to propose an innovative encryption barcode scheme in which the emission intensities of different luminescence peaks are converted into barcode widths, with the sequence of magnetic field directions serving as the encryption key. This approach presents a novel method for data storage and anti-counterfeiting, significantly enhancing the versatility and capacity of photonic barcodes.
1. Introduction
Photonic barcodes have attracted considerable attention for their promising applications in material tracking and information security [1,2,3,4,5,6]. Luminescent lanthanide metal–organic framework (Ln-MOF) crystals possess combined advantages in outstanding material design and processability, narrow and efficient light emission as well as high capability of assembly into diverse microstructures [7,8]. The photoluminescence (PL) characteristics of Ln-MOFs can be converted into specific recognition codes for spectroscopic encoding, serving as a fundamental principle for designing novel microscale photonic barcodes [9]. Additionally, Ln-MOFs with unique anisotropic shapes and orientations are believed to possess higher degrees of polarization (DOP), a feature that enhances their information capacity and spectral encodability in polarized modes [7,8,10,11]. Zhang et al. achieved polarized emission in Ln-MOFs, demonstrating high-capacity photonic barcodes for advanced encoding and security applications [9]. Wen et al. demonstrated polarized upconversion luminescence in Er3+-doped single nanorods, showing reconfigurable dual anti-counterfeiting capabilities [12]. However, owing to the lack of effective dynamic control over crystal orientations, current methods for barcode encoding rely primarily on the precontrol of crystal orientations or the construction of specific microstructures. This reliance complicates the construction process and limits it to a single-use barcode. Therefore, achieving dynamic control of the orientation of luminescent Ln-MOFs would present significant opportunities for the construction and reuse of photonic barcodes.
Since Professor George Whitesides pioneered the use of diamagnetic levitation to manipulate the assembly of diamagnetic objects, researchers have recognized the numerous advantages of magnetic fields as a means of control, including contactless operation, non-destructive handling, and dynamic adjustability [13,14,15,16,17]. To date, significant progress has been made in the dynamic manipulation of materials with weak susceptibility (usually < 10−3) with the assistance of magnetic media [18,19,20,21,22]. Recently, we discovered that paramagnetic Ln-MOFs, which also exhibit weak susceptibility (10−5–10−3), can achieve compass-like magnetic orientations in weak magnetic fields in the order of mT without magnetic media [23,24]. These magnetic orientations can be attributed to the intrinsic magnetic anisotropy of lanthanide ions originating from the 4f electrons and the highly ordered crystal structure of MOF materials. Combined with the fact that the luminescence intensity of these Ln-MOFs is also orientation-related due to the DOP [9,11], it is promising to use magnetic fields to dynamically control the crystal orientation and thereby adjust the luminescence intensity.
In this work, we successfully synthesized a paramagnetic fluorescent Eu-MOF microcrystal and investigated its magnetic orientation and linearly polarized emission. Eu-MOF microcrystals in an orthorhombic space group grow along the crystallographic b-axis and ultimately form an anisotropic cuboid shape. Under a uniaxial magnetic field of ~10 mT, Eu-MOF microcrystal rapidly aligns perpendicularly to the field direction within a few seconds. Optical magnetometry measurements revealed that the magnetic anisotropy of Eu-MOF microcrystals is along the crystallographic c-axis. Additionally, Eu-MOF microcrystals exhibited linear emission with a strong DOP, achieving a polarization intensity of 0.904 at 616 nm. These features enable us to design a novel barcode encryption strategy by using a magnetic field to dynamically control the magnetic orientation of Eu-MOF microcrystals and consequently alter their emission intensity. This magnetic field-dependent barcode enhances anti-counterfeiting authentication and shows substantial potential for data recording and information encryption.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Analytically pure Eu(NO3)3‧nH2O and pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylic acid (DPA) were purchased from Macklin (Shanghai, China) for the preparation of Eu-MOF. N,N-Dimethylformamide (DMF), and deionized water was purchased from Aladdin (Shanghai, China) and used without further purification. NaOH and HNO3 were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany) and used to control the size of Eu-MOF crystals.
2.2. Preparation
Eu-MOF microcrystals were prepared via solvothermal synthesis. In a typical preparation, a mixture of 0.01 mmol Eu(NO3)3‧nH2O, 0.04 mmol PDA, DMF (9 mL), and H2O (6 mL) was sealed in a 20 mL glass bottle at room temperature. After heating at 60 °C for 2 days to allow the Eu ions to coordinate with DPA, Eu-MOF microcrystals (approximately 30–40 μm in length and 5–10 μm in width) were obtained. The microcrystals were subsequently centrifuged and washed 3 times with DMF and subsequently dispersed in DMF. The large crystals (approximately 3–4 mm in length, and 1–1.5 mm in width) were prepared by additionally adding 1 mL of 1.6 M HNO3 solution before heating.
2.3. Characterization
All Eu-MOF samples used in our characterization were handled at room temperature. Bright-field optical images of Eu-MOF microcrystals were taken via an optical microscope (Ti-U, Nikon Corporation, Tokyo, Japan). The selected area electron diffraction (SAED) pattern of Eu-MOF microcrystals was characterized via transmission electron microscopy (TEM, JEM-2100, JEOL Ltd., Tokyo, Japan). Powder X-Ray diffraction (PXRD) patterns were recorded via a PANalytical B.V. Empyrean diffractometer (Almelo, The Netherlands) with Cu Kα (1.54 Å) radiation. Single crystal X-Ray diffraction data were collected using a cube approximately 0.2 × 0.2 × 0.2 mm3 in size, cut from a large Eu-MOF crystal, at 150 K on an X-Ray single crystal diffractometer (MM007HF Saturn724+, Rigaku Corporation, Tokyo, Japan). The UV-Vis diffuse reflection data were recorded at room temperature using a powdered BaSO4 sample as a standard (100% reflectance) on a PerkinElmer Lamda-950 UV/Vis/NIR spectrophotometer (PerkinElmer, Inc., Waltham, MA, USA). Steady-state photoluminescence spectra and time-resolved PL (TRPL) spectra of Eu-MOF microcrystals were obtained with Edinburgh Instruments FLS 1000 (Livingston, UK). The magnetic hysteresis (M-H) loops of Eu-MOF microcrystals were measured with a vibrating sample magnetometer in a physical property measurement system (DynaCool-9T, Quantum Design, San Diego, CA, USA). The Kerr rotations of single Eu-MOF microcrystals were measured via a magneto-optical Kerr effect (MOKE) microscope (NanoMOKE3, Durham, UK). Under 365 nm excitation, photoluminescence imaging of the microcrystals at different depths of field was performed using a Nikon confocal laser scanning microscope (Nikon Corporation, Tokyo, Japan).
2.4. Magnetic Alignment Experiments
Eu-MOF microcrystals were placed under an optical microscope for in situ observation of their magnetic alignment. Helmholtz coils were used to supply a uniform magnetic field with variable in-plane directions. For the reproducibility and reliability of our experiments, Eu-MOF microcrystals were immersed in a liquid film (pure DMF) confined between a coverslip and a glass substrate after surface treatment to minimize the resistance to motion. The glass substrates were first cleaned with ethanol and acetone and then processed with oxygen plasma. Finally, the glass substrates and a drop of OTS were placed in a vacuum dryer and heated at 90 °C for 3 h.
3. Results and Discussion
The novel Eu-MOF crystals were synthesized from Eu(NO3)3 and the organic ligand pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylic acid via a simple hydrothermal method [25]. The synthesis of microcrystals (30–40 μm in length, 5–10 μm in width, Figure S1) or macroscopic crystals (3–4 mm in length, 1–1.5 mm in width) can be controlled by adjusting the pH of the synthetic mixture through the addition of HNO3 [26]. As shown in Figure 1a, the as-prepared large Eu-MOF crystal has a high degree of crystallinity and a cuboid shape, emitting red fluorescence emission under ultraviolet light. Further photoluminescence imaging in Figure S2 was performed using a Nikon confocal laser scanning microscope at different depths of field, proving the cuboid shape of the microcrystals. Single crystal X-Ray diffraction data were collected using a cube approximately 0.2 × 0.2 × 0.2 mm, cut from a large Eu-MOF crystal, at 150 K on an X-Ray single crystal diffractometer. As shown in Table 1 and Table S1, Eu-MOF crystallizes in the orthorhombic space group Pbcn with unit cell parameters of a = 16.8322(3) Å, b = 10.6273(2) Å, c = 18.4369(4) Å, and a unit cell volume of 3298.01(11) Å3. Figure 1b shows the bc-plane view of the three-dimensional framework, where each Eu ion is coordinated by six oxygen atoms and three nitrogen atoms, forming a [EuO6N3] polyhedron unit (Figure S3). There are four polyhedral units of different orientations in a unit cell, with two-by-two symmetry between them, corresponding exactly to the three secondary rotational symmetry axes of the Pbcn space group (Figure S4). The microcrystals have a crystal structure consistent with that of the larger crystals. This is demonstrated by the powder XRD pattern in Figure S5, where the XRD patterns are nearly identical and closely match the XRD pattern simulated from the single crystal data. All subsequent discussions correspond to the Eu-MOF microcrystal samples. The growth morphology predicted via the Bravais–Friedel-Donnay–Harker (BFDH) method [27] shows that the unit cells are stacked along the crystallographic b-axis and that the dominant exposure facet corresponds to the (200) crystal facet (Figure 1c). These results are in good agreement with the powder XRD data and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) image of Eu-MOF. As shown in Figure 1d, the XRD patterns of the ground microcrystals matched well with the simulated data, whereas only the (200) diffraction peak was observed before grinding. The TEM image and selected-area electron diffraction (SAED) pattern in Figure 1e also indicate that Eu-MOF is grown along the crystallographic b-axis, with the (200) crystal facet as the dominant exposure facet.
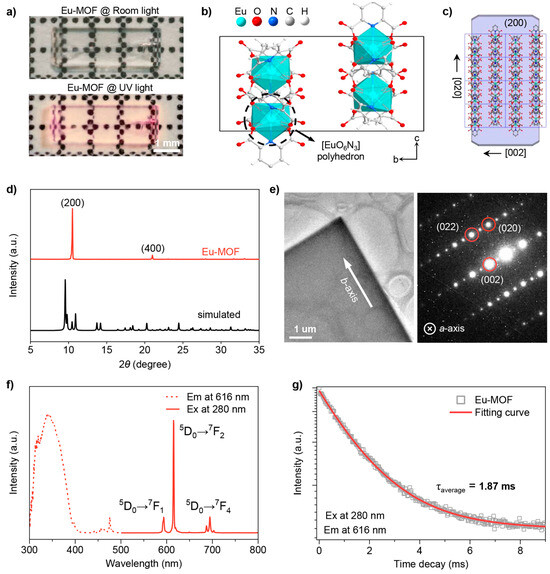
Figure 1.
(a) Optical photos of large Eu-MOF crystal under room light (top) and UV light (bottom). The scale bar is 1 mm; (b) view of a unit cell in the Pbcn space group along the crystallographic a-axis, where the dashed circle indicates a [EuO6N3] polyhedron unit; (c) theoretically predicted growth morphology of Eu-MOF microcrystal; (d) powder X-Ray diffraction (PXRD) spectra of Eu-MOF microcrystal before and after grinding; (e) transmission electron microscopy (TEM) image (left) and corresponding selected-area electron diffraction (SAED) pattern (right) of Eu-MOF microcrystal. The scale bar is 1 μm; (f) excitation (dashed, λex = 616 nm) and emission (solid, λex = 280 nm) spectra of Eu-MOF microcrystals; (g) PL decay lifetime of Eu-MOF microcrystal (λex = 616 nm and λex = 280 nm). The squares and lines represent the experimental data and fitting results, respectively.

Table 1.
Single crystal data of Eu-MOF.
The optical properties of Eu-MOF were then systematically investigated. As shown in Figure S6, UV-Vis diffuse reflectance spectroscopy reveals that Eu-MOF strongly absorbs in the UV region, with a band gap energy of 3.80 eV determined from the Tauc plot. As depicted in Figure 1f, an extensive band spanning from 300 to 400 nm is evident in the excitation spectra of Eu-MOF. Upon excitation at 280 nm, the Eu-MOF exhibits three characteristic emission bands at 594 nm, 616 nm, and 695 nm, corresponding to the 5D0→7F1, 5D0→7F2 and 5D0→7F4 transitions, respectively. These characteristic luminescence properties of Eu originate from the shielding effect of the 4f electron layer [28,29,30,31,32,33]. Among these peaks, the emission at 616 nm is the most intense one that causes the red emission by Eu-MOF. The distinct luminescent properties of Eu-MOF are further corroborated by luminescence lifetime measurements and temperature-dependent photoluminescence tests. As shown in Figure 1g, the fitted luminescence lifetime of Eu-MOF is 1.87 ms, which is consistent with the forbidden nature of the 4f-4f electronic transitions, which typically results in long-lived excited states. Moreover, within the temperature range of 80–300 K, there is no significant shift in the emission peaks of Eu-MOF crystals. This stability is attributed to the inner-shell nature of the 4f electron orbitals, rendering them less sensitive to thermal perturbations (Figure S7).
Magnetic hysteresis (M-H) loops were measured over the temperature range of 2–298 K to investigate the magnetic properties of Eu-MOF. As shown in Figure 2a, Eu-MOF exhibits typical paramagnetic behavior, with its magnetization (M) increasing linearly with the applied magnetic field (H) up to 7 T at room temperature. Notably, as the temperature decreases from 298 K to 2 K, no magnetic hysteresis is observed in the M-H loops of Eu-MOF, indicating that there are no magnetic interactions between the neighboring Eu-ions [34]. To further assess the magnetic anisotropy of Eu-MOF, angle-resolved magneto-optical Kerr effect (MOKE) measurements were conducted [35]. As shown in Figure 2b, a single Eu-MOF microcrystal was placed in a uniaxial magnetic field, and the polarized laser reflected from it would generate a rotation of the polarization plane, namely, Kerr rotation. The intensity of the Kerr rotation is proportional to the magnetization along the field direction, i.e., the maximum Kerr rotation will be obtained when the crystal possesses the maximum magnetic susceptibility χmax. Therefore, by rotating the Eu-MOF crystals, their magnetic anisotropy can be reflected in the angle-dependent Kerr rotations. As shown in Figure 2c, the maximum Kerr rotation occurs at 90°, indicating that the χmax of Eu-MOF aligns along the crystallographic c-axes, underscoring the anisotropic magnetic behavior of the material.
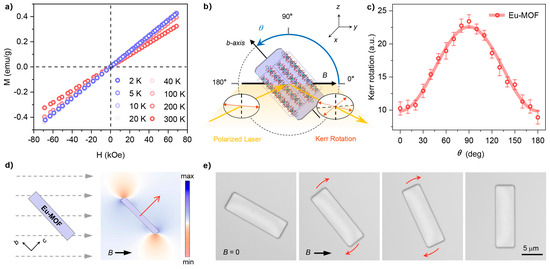
Figure 2.
(a) Magnetic hysteresis (M-H) loops of Eu-MOF microcrystals measured by a vibrating sample magnetometer at several temperatures within the field range from −70 to 70 kOe. The sweep rate is 200 Oe·s−1; (b) schematic illustration of the configuration for the angle-resolved magneto-optical Kerr effect (MOKE) measurement used to characterize the macroscopic magnetic anisotropy of the Eu-MOF microcrystal. The Eu-MOF microcrystal rotates along the x-axis with an angle φ to the applied uniaxial magnetic field; (c) Kerr rotations measured at a 0.8 kOe field as a function of the angle θ for the Eu-MOF microcrystal. (d) Simulated distribution of the magnetic energy of the Eu-MOF microcrystal under a uniform uniaxial magnetic field. The red arrows represent the directions of χmax. (e) Sequences of optical images of the Eu-MOF microcrystal showing its perpendicular magnetic orientations under a uniaxial magnetic field.
In principle, a magnetically anisotropic Eu-MOF produces an inhomogeneous magnetic potential energy in a uniform field, which can be expressed as [36]:
where V is the crystal volume, μ0 is the vacuum permeability, and θ is the angle between B and the direction of χmax. Therefore, without considering resistance, the Eu-MOF rotates until the direction of χmax is parallel to the B field since E reaches a minimum when θ = 0°. We simulated the magnetic energy distribution of Eu-MOF via the finite element method. As shown in Figure 2d, under a uniform uniaxial magnetic field, the low magnetic energy regions of Eu-MOF, with χmax aligned along the crystal’s short axis (i.e., the crystallographic c-axis), are located on the upper and lower sides of the crystal ends. Consequently, the crystal tends to rotate clockwise until its long axis is perpendicular to the magnetic field. To investigate this behavior, we conducted magnetic orientation experiments by immersing microscopic Eu-MOF crystals in a liquid film (pure DMF) to minimize motion resistance [23]. The in situ recorded images of the magnetic orientation processes for Eu-MOF crystals are shown in Figure 2e. Under a field strength of ~10 mT, the long axis of Eu-MOF rapidly aligns perpendicularly to the magnetic field direction, with this process completing within a few seconds. Notably, the magnetic orientation behavior observed in the experiment aligns very closely with the simulation results. These results indicate that the magnetic anisotropy of Eu-MOF allows for simple and precise control of its orientation via a magnetic field.
Considering that Eu-MOFs possess a regular crystal shape, highly ordered crystal structure, and characteristic luminescence originating from the 4f–4f electronic transitions, their luminescence should be polarized [9,11]. We further investigated the DOP of Eu-MOF via a conventional reflective imaging system. As shown in Figure 3a, a polarized 375 nm continuous wave laser was used as the pumping source, which initially passes through a polarizer to purify the polarization state and further passes through a quarter-wave plate to become circularly polarized. Therefore, the excitation light reaching the Eu-MOF through a microscope objective is isotropic. The emission signals are collected by the spectrometer after passing through a polarizer (LP2), which can be rotated counterclockwise to record the polarization characteristics of Eu-MOF luminescence. Note that the Eu-MOF crystal is fixed with its b-axis parallel to the y-axis, and the polarization direction of LP2 is parallel to the z axis at φ = 0°. As shown in Figure 3b, the luminescence intensities of Eu-MOF change dramatically when the LP2 rotates from 0° to 360°, suggesting a high DOP. Notably, the intensity of each emission peak exhibits a periodic variation with a period of 180°. Simultaneously, the intensities of different emission peaks tend to change reciprocally, with some peaks intensifying while others diminish.
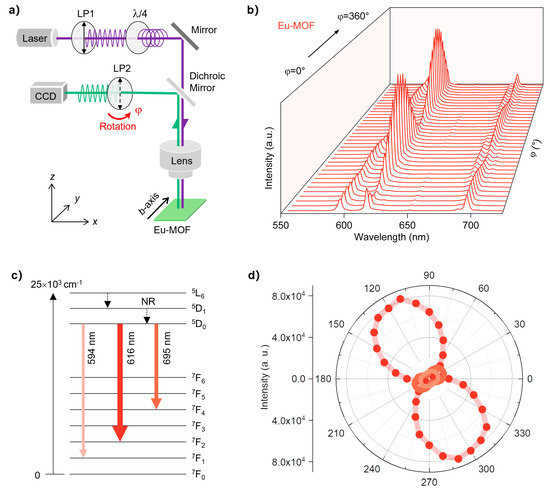
Figure 3.
(a) Schematic illustration of the experimental setup for polarized emission measurements. The excitation wavelength is 375 nm, and some shortpass filters are omitted for the sake of simplicity. An Ocean Optics QE Pro spectrometer was used to capture the signals, and the X-factor of the objective lens was 10; (b) photoluminescence spectra of the Eu-MOF microcrystal as a function of rotation angle; (c) energy level diagrams of Eu-MOF; (d) polarization diagrams collected at various emission wavelengths of the Eu-MOF microcrystal.
Therefore, we extracted the emission intensities of the characteristic peaks of Eu-MOF (594, 616, and 695 nm) and plotted them in polar coordinates, as shown in Figure 3c,d. The intensities of all the peaks clearly exhibit a twofold symmetric pattern, with a 90-degree difference between the axes of symmetry. Specifically, the luminescence intensity at 616 nm is maximized at 120/300°, whereas the luminescence intensities of the other two peaks are maximized at 30/210°. This difference is attributed to the distinct energy level transitions corresponding to each luminescent peak. We further quantitatively evaluate the polarization state of these luminescent peaks by the DOP, which is given as DOP = (Imax − Imin)/(Imax + Imin), where Imax and I min are the maximum and minimum luminescence intensities, respectively. The calculated DOP values at different characteristic peaks significantly vary, with DOP values of 0.201, 0.904, and 0.596 observed at 594, 616, and 695 nm, respectively. Notably, the DOP value at 616 nm surpasses that of most luminescent metal–organic complex crystals [9,37,38], which we attribute to its highly ordered crystal structure and well-regularized crystal shape.
Typical barcodes encode information by varying the widths and spacings of a series of black parallel lines [9]. In contrast, lanthanide metal–organic frameworks exhibit narrow-band emission characteristics and exceptional DOP, enabling the conversion of emission intensities at different spectral peaks into variable barcode widths for data storage applications. The above experimental data indicate that our synthesized Eu-MOF crystals have unique emission fingerprints characterized by their distinct and sharp emission peaks, which can be precisely distinguished through their luminescence spectra. Moreover, the remarkable DOP value in Eu-MOF allows significant modulation of luminescence intensity by rotating the crystal under fixed polarization conditions, thereby greatly enhancing its capacity for information embedding. To develop highly secure data-storage applications based on Eu-MOF, we first investigated the relationship between their magnetic orientation behavior and luminescence intensity. As shown in Figure 4a, under an in-plane rotating magnetic field provided by a set of Helmholtz coils, Eu-MOF exhibited continuous rotational behavior due to its persistent magnetic orientation response. Simultaneously, when excited with circularly polarized light and with a fixed polarization angle during collection, Eu-MOFs display significant variations in fluorescence intensity, manifesting as distinct bright and dark differences. Specifically, when the magnetic field is oriented at 120°, the luminescence is notably bright, whereas at 30°, the luminescence is nearly undetectable. In other words, the precisely controllable magnetic rotation behavior of Eu-MOFs directly correlates the field direction with the luminescence intensity.
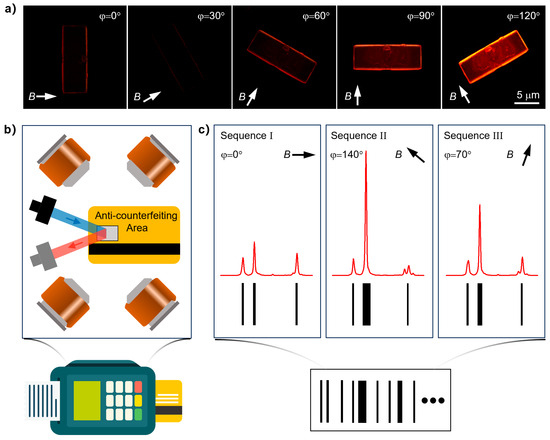
Figure 4.
(a) Sequences of the fluorescence microscopy images of Eu-MOF microcrystals showing the changes in their luminescence intensities during the continuous magnetic orientation response; (b) schematic diagram of the internal structure of the card reader. The anti-counterfeiting area is placed at the center of the Helmholtz coils and the polarization spectra are read after the magnetic field is applied; (c) illustration of the encoding strategy. A barcode is obtained by combining a series of spectral data under different magnetic field directions.
On the basis of the dynamic control of Eu-MOF’s luminescence intensity by the magnetic field, we propose a conceptual demonstration of an innovative encryption barcode reading scheme, as illustrated in Figure 4b. The encoding strategy for these photonic barcodes involves the use of multiple magnetic field directions and their specific sequences as encryption keys. These key-specific magnetic fields, generated by Helmholtz coils embedded within the barcode reader, induce linearly polarized spectra corresponding to the different magnetic field orientations. By concatenating the collected spectral data and systematically analyzing the emission peak intensities, each black parallel line in the barcode is positioned at the location of an emission peak, with the line width directly proportional to the relative integrated intensity of that peak. This method allows for the decryption of the barcode. Additionally, applying a magnetic field at any angle can theoretically generate a unique barcode, thereby introducing a new dimension to data storage and significantly enhancing the storage capacity, as shown in Figure 4c. The integration of magnetic field-controlled luminescence with polarized emission characteristics facilitates the development of dynamic, multi-dimensional barcodes, offering enhanced security and substantial potential for high-capacity data storage and anti-counterfeiting applications [39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46]. This underscores the transformative potential of Ln-MOFs in the fields of secure data storage and advanced encryption technologies.
4. Conclusions
In summary, the dynamic magnetic control of Eu-MOFs is demonstrated to show their polarized emission for advancing photonic barcode technology. Eu-MOFs are crystalline in orthorhombic space groups and exhibit significant magnetic anisotropy. Under a uniaxial magnetic field of ~10 mT, the crystallographic c-axis of an Eu-MOF aligns with the magnetic field, which is consistent with its magnetic anisotropy. The Eu-MOF microcrystal exhibited characteristic Eu emissions with peaks at 594 nm, 616 nm, and 695 nm, and show impressive DOP of 0.904 at 616 nm. A rotating magnetic field enables precise and dynamic control over the orientations as well as the luminescence intensities of Eu-MOF. This further allows us to develop a novel barcode encryption strategy by using a magnetic field to dynamically control the behavior of Eu-MOF, which represents a promising approach to advanced techniques for data recording and information encryption.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/chemistry6060084/s1, Figure S1: Optical images of a Eu-MOF microcrystal under bright field microscopy; Figure S2: Microcrystal, large single crystal and simulated powder XRD patterns of Eu-MOF; Figure S3: View of the polyhedron unit structure of Eu-MOF along the c-axis; Figure S4: Views of the unit cell structure of Eu-MOF along the c-, a- and b-axes; Figure S5 cuboid shape of the microcrystals was revealed by adjusting the imaging depth of field in the laser confocal microscopy; Figure S6: UV-Vis optical diffuse reflectance spectrum of Eu-MOF; Figure S7: Pseudocolor map from temperature-dependent PL spectra of Eu-MOF at 594, 616 and 695 nm wavelengths during cooling; Table S1: Fractional atomic coordinates and equivalent isotropic displacement parameters for Eu-MOF; Table S2: Bond lengths for Eu-MOF.
Author Contributions
C.Z. and H.J. supervised the project. B.S. and H.J. synthesized the Eu-MOF. H.J. carried out the morphological, crystallographic and magnetic characterization measurements. B.S. and S.Z. carried out the optical and magneto-optical measurements. B.S. and H.J. analyzed the data and wrote the draft. L.C., Y.Z., B.Y. and S.B. assisted with the writing and revision of the manuscript. All authors discussed and contributed to the manuscript preparation. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (2018YFA0704802 and 2022YFA1505400) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (22090021 and 22203098).
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge Ye Zou and Tongling Liang from the Institute of Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences for technical support.
Conflicts of Interest
Author H.J. was employed by National Engineering Research Center for Rare Earth, Grirem Advanced Materials Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Lee, J.; Bisso, P.W.; Srinivas, R.L.; Kim, J.J.; Swiston, A.J.; Doyle, P.S. Universal process-inert encoding architecture for polymer microparticles. Nat. Mater. 2014, 13, 524–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Deng, R.; Tian, J.; Zong, Y.; Jin, D.; Liu, X. Multicolor Barcoding in a Single Upconversion Crystal. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 4893–4896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillou, O.; Daiguebonne, C.; Calvez, G.; Bernot, K. A Long Journey in Lanthanide Chemistry: From Fundamental Crystallogenesis Studies to Commercial Anticounterfeiting Taggants. Acc. Chem. Res. 2016, 49, 844–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, C.; He, J.; Cao, Y.; Fang, X.; Chi, X.; Yi, J.; Wu, J.; Guo, Q.; Masoomi, H.; et al. Precisely Encoded Barcodes through the Structure-Fluorescence Combinational Strategy: A Flexible, Robust, and Versatile Multiplexed Biodetection Platform with Ultrahigh Encoding Capacities. Small 2021, 17, 2100315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shikha, S.; Salafi, T.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, Y. Versatile design and synthesis of nano-barcodes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 7054–7093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Hua, D.; Huang, C.; Samal, S.K.; Xiong, R.; Sauvage, F.; Braeckmans, K.; Remaut, K.; De Smedt, S.C. Materials and Technologies to Combat Counterfeiting of Pharmaceuticals: Current and Future Problem Tackling. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1905486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Yue, Y.; Qian, G.; Chen, B. Luminescent Functional Metal–Organic Frameworks. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 1126–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, J.; Carlos, L.D.; Paz, F.A.A.; Ananias, D. Luminescent multifunctional lanthanides-based metal–organic frameworks. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 926–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, K.; Wu, J.; Zhao, M.; Feng, X.; Li, Y.; Ma, Y.; Li, H.; Zhai, T. Polarized Emission of Lanthanide Metal–Organic Framework (Ln-MOF) Crystals for High-Capacity Photonic Barcodes. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2022, 10, 2102143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Zhang, J.; Gan, J.; Tang, Y.; Cui, Y.; Yu, Y.; Qian, G. Controlled dye release from a metal–organic framework: A new luminescent sensor for water. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 2722–2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Lin, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, Y.S.; Yan, D. Lanthanide Metal–Organic Framework Microrods: Colored Optical Waveguides and Chiral Polarized Emission. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 7853–7857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, D.; Zuo, S.; Huang, C.; Tan, Z.; Lu, F.; Liang, Y.; Mo, X.; Lin, T.; Cao, S.; Qiu, J.; et al. Tunable Excitation Polarized Upconversion Luminescence and Reconfigurable Double Anti-Counterfeiting from Er3+ Doped Single Nanorods. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2023, 11, 2301126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirica, K.A.; Shevkoplyas, S.S.; Phillips, S.T.; Gupta, M.; Whitesides, G.M. Measuring Densities of Solids and Liquids Using Magnetic Levitation: Fundamentals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 10049–10058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, S.C.; Nemiroski, A.; Mirica, K.A.; Mace, C.R.; Hennek, J.W.; Kumar, A.A.; Whitesides, G.M. Magnetic Levitation in Chemistry, Materials Science, and Biochemistry. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 17810–17855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemiroski, A.; Soh, S.; Kwok, S.W.; Yu, H.D.; Whitesides, G.M. Tilted Magnetic Levitation Enables Measurement of the Complete Range of Densities of Materials with Low Magnetic Permeability. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 1252–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, S.; Whitesides, G.M. “Axial” Magnetic Levitation Using Ring Magnets Enables Simple Density-Based Analysis, Separation, and Manipulation. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 12239–12245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennek, J.W.; Nemiroski, A.; Subramaniam, A.B.; Bwambok, D.K.; Yang, D.; Harburg, D.V.; Tricard, S.; Ellerbee, A.K.; Whitesides, G.M. Using Magnetic Levitation for Non-Destructive Quality Control of Plastic Parts. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 1587–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, B.; Jia, H.; Wang, H.; Chen, R.; Xu, L.; Zhao, Y.S.; Zhang, C.; Yao, J. Magnetic-Field-Driven Reconfigurable Microsphere Arrays for Laser Display Pixels. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 1187–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, B.; Jia, H.; Chen, R.; Chang, Q.; Feng, J.; Gao, H.; Wu, Y.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, C. Magnetic Domain Confined Printing of Programmable Organic Microcrystal Assemblies for Information Encryption. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2108279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharti, B.; Fameau, A.-L.; Rubinstein, M.; Velev, O.D. Nanocapillarity-mediated magnetic assembly of nanoparticles into ultraflexible filaments and reconfigurable networks. Nat. Mater. 2015, 14, 1104–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirörs, A.F.; Pillai, P.P.; Kowalczyk, B.; Grzybowski, B.A. Colloidal assembly directed by virtual magnetic moulds. Nature 2013, 503, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Lau, G.C.; Yuan, H.; Aggarwal, A.; Dominguez, V.L.; Liu, S.; Sai, H.; Palmer, L.C.; Sather, N.A.; Pearson, T.J.; et al. Fast and programmable locomotion of hydrogel-metal hybrids under light and magnetic fields. Sci. Robot. 2020, 5, eabb9822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, H.; Yin, B.; Chen, J.; Zou, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, T.; Shi, Q.; Yao, J.; Bai, S.; et al. A Paramagnetic Compass Based on Lanthanide Metal-Organic Framework. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202309073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, H.; Chen, L.; Yang, D.; Zou, Y.; Wang, H.; Yin, B.; Bai, S.; Zhang, C.; Yao, J. Magnetic Switching of Second-Harmonic Generation from Single Cerium-Based Coordination Polymer Microcrystals. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2024, 15, 6728–6735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Zhu, G.; Li, Z.; Sun, F.; Yang, Z.; Qiu, S. A lanthanide metal–organic framework with high thermal stability and available Lewis-acid metal sites. Chem. Commun. 2006, 14, 3172–3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, S.; Su, S.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, H. Combining Coordination Modulation with Acid–Base Adjustment for the Control over Size of Metal–Organic Frameworks. Chem. Mater. 2012, 24, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnay, J.D.H.; Harker, D. A new law of crystal morphology extending the law of Bravais. Am. Mineral. 1937, 22, 446–467. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, Y.; Chen, D.; Chen, W.; Zhang, W.; Su, X.; Deng, R.; An, Z.; Chen, H.; Xie, R.-J. X-Ray-charged bright persistent luminescence in NaYF4:Ln3+@NaYF4 nanoparticles for multidimensional optical information storage. Light Sci. Appl. 2021, 10, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhuang, Y.; Li, X.; Lin, F.; Peng, D.; Tu, D.; Xie, A.; Xie, R.-J. Achieving Remote Stress and Temperature Dual-Modal Imaging by Double-Lanthanide-Activated Mechanoluminescent Materials. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2101567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zhou, W.; Li, X.; Li, Z.; Lu, S.; Shang, X.; Tan, C.; Hu, P.; Chen, Z.; Chen, X. AIEgen-sensitized lanthanide nanocrystals as luminescent probes for intracellular Fe3+ monitoring. Talanta 2023, 262, 124729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Huang, P.; Zheng, W.; Song, X.; Shang, X.; Zhang, W.; Yang, D.; Yi, X.; Chen, X. Lanthanide-Doped KMgF3 Upconversion Nanoparticles for Photon Avalanche Luminescence with Giant Nonlinearities. Nano Lett. 2023, 23, 8576–8584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, K.; Ren, Y.; Wan, S.; Yang, C.; Li, J.; Wang, F.; Chen, C.; Su, J.; Chen, D.; et al. Highly Plasticized Lanthanide Luminescence for Information Storage and Encryption Applications. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2105108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Chen, L.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y. Lanthanide Luminescence Supramolecular Switch Based on Photoreactive Ammonium Molybdate. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 59126–59131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mugiraneza, S.; Hallas, A.M. Tutorial: A beginner’s guide to interpreting magnetic susceptibility data with the Curie-Weiss law. Commun. Phys. 2022, 5, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansuripur, M. Classical Optics and Its Applications; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, T.B. Electromechanics of Particles; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, S.; Sun, L.-D.; Xue, Y.-X.; Dong, H.; Wu, K.; Guo, S.-C.; Wu, B.-T.; Yan, C.-H. Scalable Direct Writing of Lanthanide-Doped KMnF3 Perovskite Nanowires into Aligned Arrays with Polarized Up-Conversion Emission. Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 2964–2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.K.; Zhang, W.; Schneider, J.; Rogach, A.L.; Chigrinov, V.G.; Kwok, H.-S. Photoaligned Nanorod Enhancement Films with Polarized Emission for Liquid-Crystal-Display Applications. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1701091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Yang, S.; Xu, B.; Zhang, T.; Chen, S.; Zhang, W.; Sun, X.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Meng, X.; et al. Laterally Engineering Lanthanide-MOFs Epitaxial Heterostructures for Spatially Resolved Planar 2D Photonic Barcoding. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 24519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Feng, X.; Xu, B.; Lin, R.; Xu, Y.; Chen, S.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Meng, X.; Gao, Z. Directional Self-Assembly of Facet-Aligned Organic Hierarchical Super-Heterostructures for Spatially Resolved Photonic Barcodes. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 6341–6349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, M.; He, G.-P.; Wang, X.; Liao, L. Organic superstructure microwires with hierarchical spatial organisation. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Xu, C.-F.; Mao, X.-R.; Wu, Y.; Yang, J.; Xu, L.; Zhuo, M.; Lin, H.; Zhuo, S.; Wang, X.-D. Oriented Self-Assembly of Hierarchical Branch Organic Crystals for Asymmetric Photonics. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 9285–9291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucinotta, G.; Perfetti, M.; Luzon, J.; Etienne, M.; Car, P.-E.; Caneschi, A.; Calvez, G.; Bernot, K.; Sessoli, R. Magnetic Anisotropy in a Dysprosium/DOTA Single-Molecule Magnet: Beyond Simple Magneto-Structural Correlations. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 1606–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briganti, M.; Lucaccini, E.; Chelazzi, L.; Ciattini, S.; Sorace, L.; Sessoli, R.; Totti, F.; Perfetti, M. Magnetic Anisotropy Trends along a Full 4f-Series: The fn+7 Effect. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 8108–8115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Fan, Q.; Wu, W.; Liang, T.; Liu, Y.; Yu, H.; Yin, Y. Magnetically Tunable One-Dimensional Plasmonic Photonic Crystals. Nano Lett. 2023, 23, 1981–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Kim, J.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, H.; Nam, K.T.; Kim, D.H. Block Copolymer Enabled Synthesis and Assembly of Chiral Metal Oxide Nanoparticle. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 7611–7623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).