A New Hydrotalcite-Like Absorbent OSA-LDH and Its Adsorption Capacity for Pb2+ Ions in Water
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of OSA-LDH
2.3. Characterization Method of OSA-LDH
2.4. Adsorption Experiments
3. Results
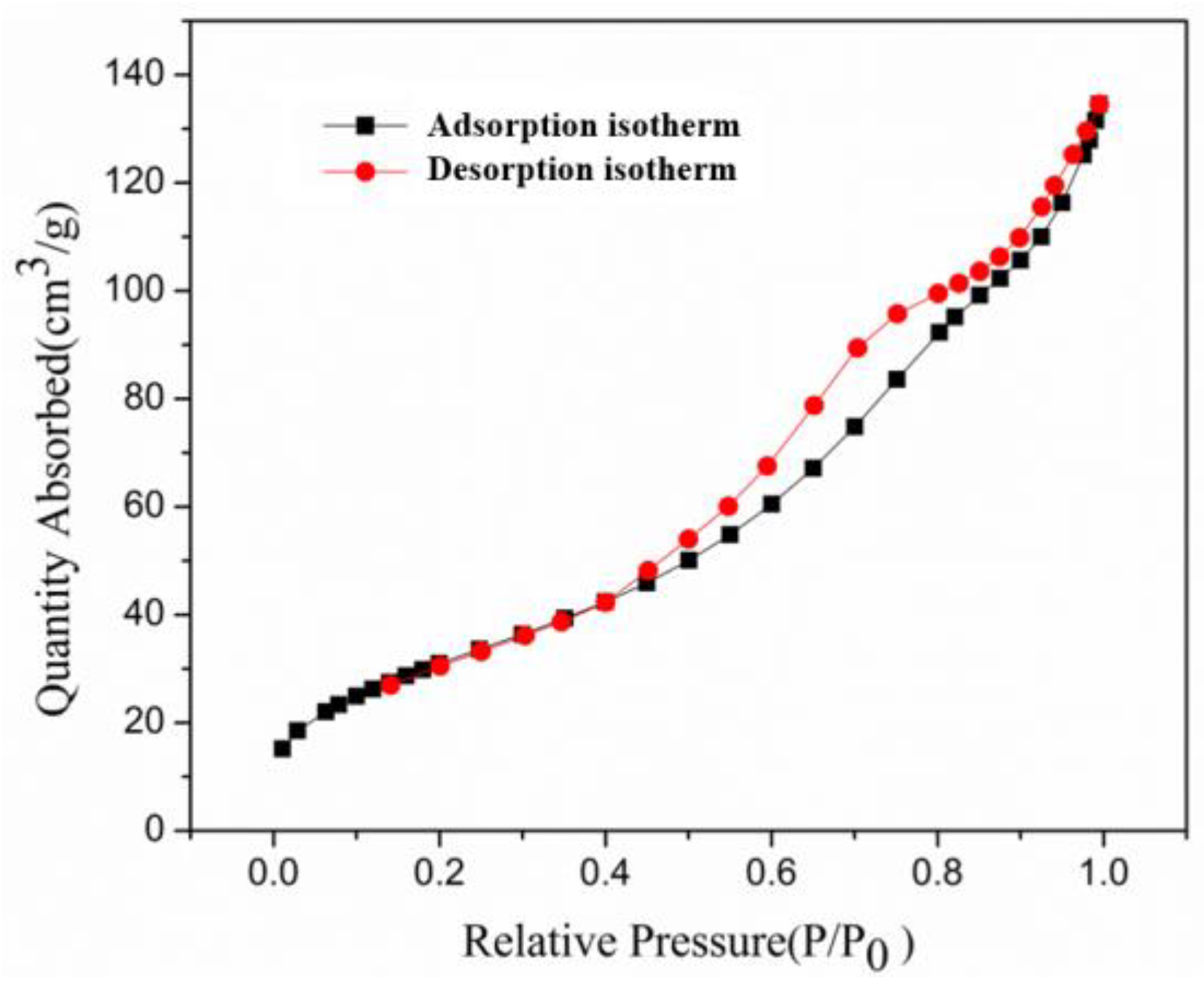
3.1. Characterization of OSA-LDH
3.2. Optimization of the Batch Adsorption Conditions
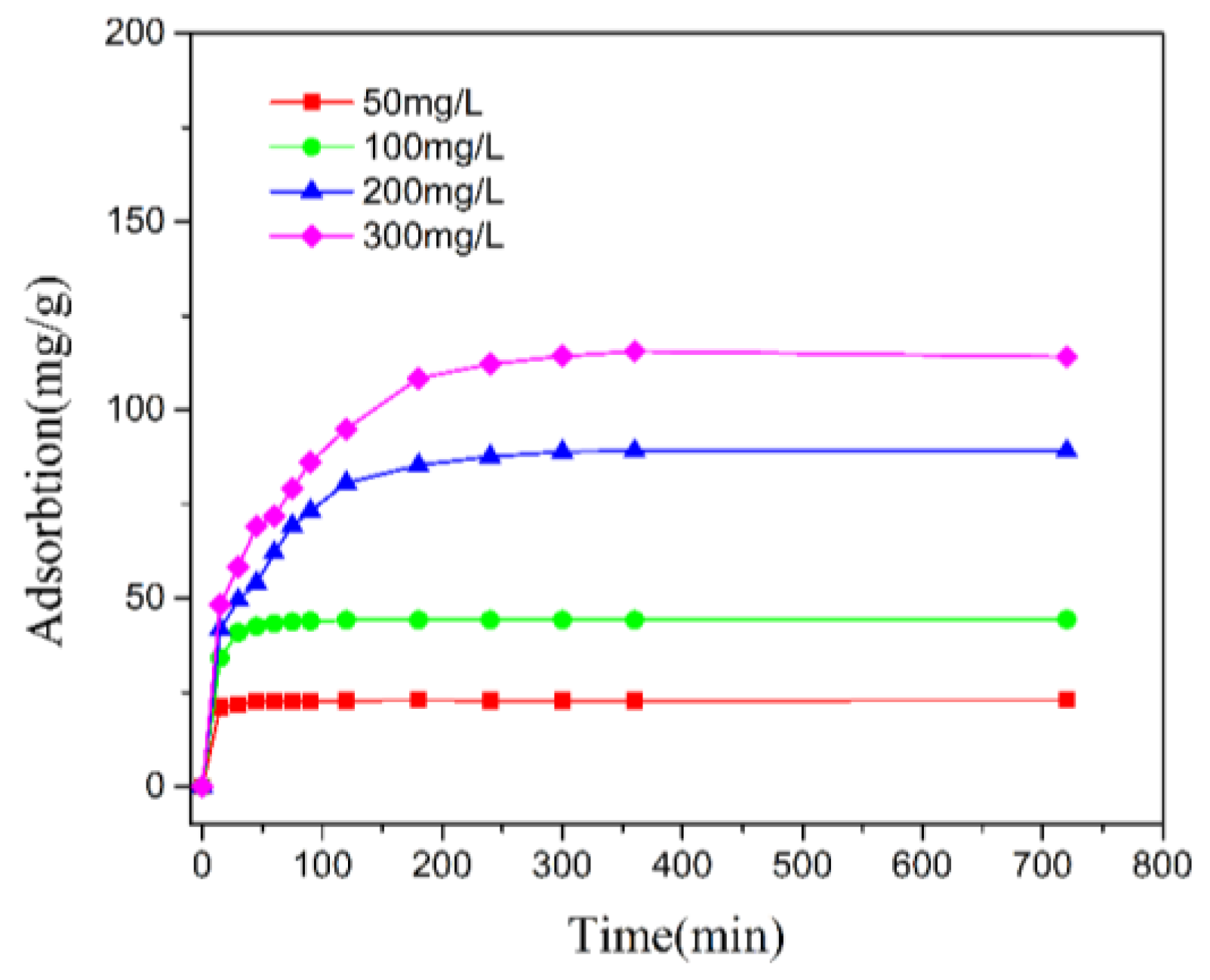
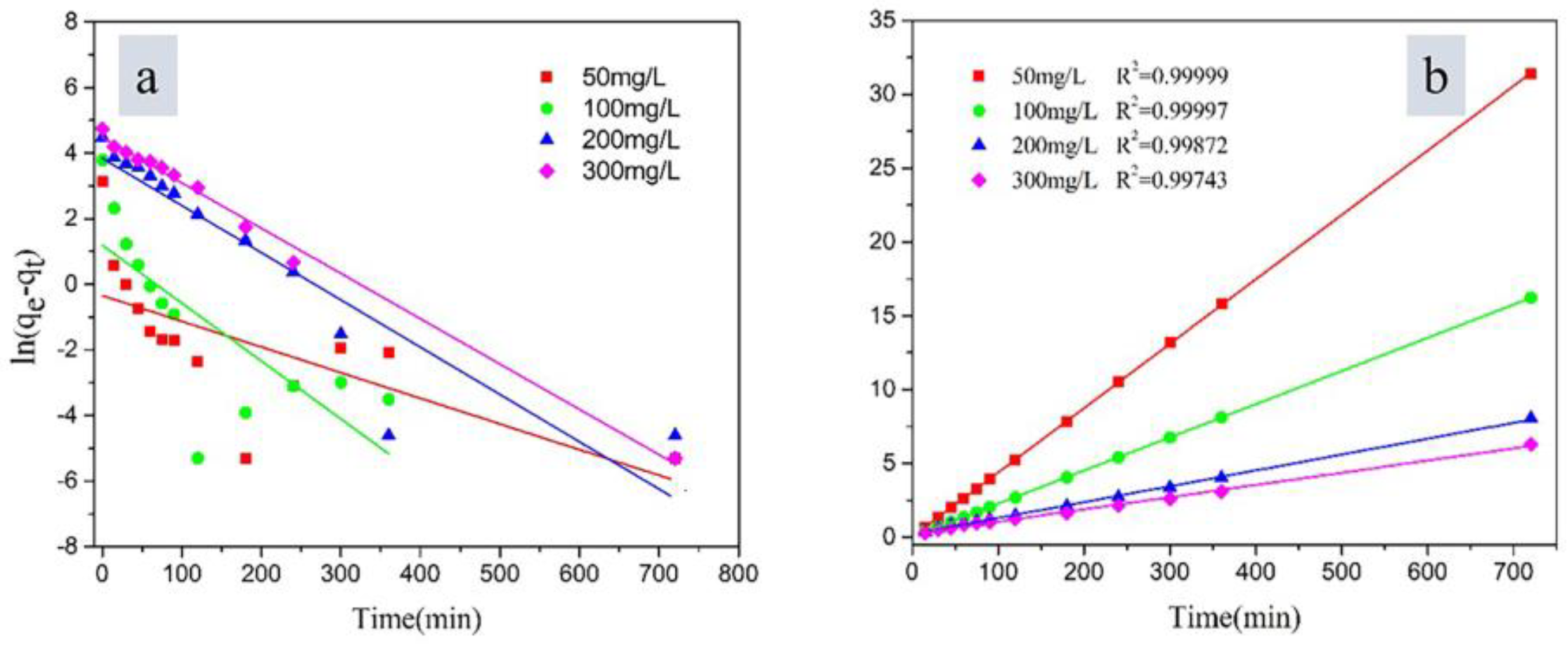
3.3. Adsorption Kinetics
3.4. Adsorption Isotherms
3.5. Adsorption Mechanisms
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moyo, A.; Parbhakar-Fox, A.; Meffre, S.; Cooke, D.R. Alkaline industrial wastes–Characteristics, environmental risks, and potential for mine waste management. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 323, 121292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramasamy, R.; Aragaw, T.A.; Balasaraswathi Subramanian, R. Wastewater treatment plant effluent and microfiber pollution: Focus on industry-specific wastewater. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 51211–51233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, A.K.; Satyanarayanan, M.; Govil, P.K. Assessment of heavy metal pollution in water using multivariate statistical techniques in an industrial area: A case study fromPatancheru, Medak District, Andhra Pradesh, India. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 167, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiyadh, S.S.; Alardhi, S.M.; Al Omar, M.; Aljumaily, M.M.; Al Saadi, M.A.; Fayaed, S.S.; Ahmed, S.N.; Salman, A.D.; Abdalsaim, A.H.; Jabbar, N.M.; et al. A comprehensive review on modelling the adsorption process for heavy metal removal from waste water using artificial neural network technique. Heliyon 2023, 9, e15455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danziger, J.; Mukamal, K.J.; Weinhandl, E. Associations of community water lead concentrations with hemoglobin concentrations and erythropoietin-stimulating agent use among patients with advanced CKD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2021, 32, 2425–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alyüz, B.; Veli, S. Kinetics and equilibrium studies for the removal of nickel and zinc from aqueous solutions by ion exchange resins. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 167, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Ge, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J. A mild one-step method to fabricate graphene oxide cross-linked with dopamine/polyethyleneimine (GO@DA/PEI) composite membranes with an ultrahigh flux for heavy metal ion removal. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 339, 126618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.-K.; Chiu, K.-F.; Lin, C.-Y.; Leu, H.-J. Electrochemical treatment of wastewater: Selectivity of the heavy metals removal process. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 27741–27748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Fu, P.; Ni, W.; Zhang, S.; Li, S.; Deng, W.; Hu, W.; Li, J.; Pei, F.; Du, L.; et al. A review of solid wastes-based stabilizers for remediating heavy metals co-contaminated soil: Applications and challenges. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 920, 170667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, Y.; Hu, Y. Design, synthesis, and performance of adsorbents for heavy metal removal from wastewater: A review. J. Mater. Chem. A 2022, 10, 1047–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hmtshirazi, R.; Mohammadi, T.; Asadi, A.A. Incorporation of amine-grafted halloysite nanotube to electrospun nanofibrous membranes of chitosan/poly (vinyl alcohol) for Cd (II) and Pb (II) removal. Appl. Clay Sci. 2022, 220, 106460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panja, S.; Hanson, S.; Wang, C. EDTA-inspired polydentate hydrogels with exceptionally high heavy metal adsorption capacity as reusable adsorbents for wastewater purification. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 25276–25285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Song, S.; Xia, L.; Yin, H.; Meza JV, G.; Ju, W. Enhanced Pb(II) removal by algal-based biosorbent cultivated in high-phosphorus cultures. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 361, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Gong, Z.; Zhuo, Z.; Zhong, X.; Zhou, M.; Xiang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y. Tunning the defects in lignin-derived-carbon and trimetallic layered double hydroxides composites (LDH@LDC) for efficient removal of U(VI) and Cr(VI) in aquatic environment. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 428, 132113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Li, C.; Zhang, C. Recent progress of hydrogenation and hydrogenolysis catalysts derived from layered double hydroxides. Catalysts 2022, 12, 1125–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano-Lunar, A.; Álvarez, J.I.; Navarro-Blasco, Í.; Jiménez, J.R.; Fernandez-Rodriguez, J.M. Optimization of mortar with Mg-Al-Hydrotalcite as sustainable management strategy lead waste. Appl. Clay Sci. 2021, 212, 336–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Hou, W.; Xu, Y.; Sun, G.; Wang, L.; Sun, Y.; Qin, X. Sorption of lead ion by layered double hydroxide intercalated with diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid. Colloid Surf. A 2010, 366, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Chen, Y.; Yu, H.; Yan, L.; Du, B.; Pei, Z. Removal of Cu2+, Cd2+ and Pb2+ from aqueous solutions by magnetic alginate microsphere based on Fe3O4/MgAl-layered double hydroxide. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 532, 474–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foo, K.Y.; Hameed, B.H. Value-added utilization of oil palm ash: A superior recycling of the industrial agricultural waste. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 172, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shawabkeh, R. Equilibrium study and kinetics of Cu2+ removal from water by zeolite prepared from oil shale ash. Process Saf. Environ. 2009, 87, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shawabkeh, R.; Al-Harahsheh, A.; Hami, M.; Khlaifat, A. Conversion of oil shale ash into zeolite for cadmium and lead removal from wastewater. Fuel 2004, 83, 981–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.; Chu, M.; Zhou, L.; Chang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Guo, H.; Liu, B.; Wang, S. Modified oil shale ash and oil shale ash zeolite for the removal of Cd2+ ion from aqueous solutions. Environ. Technol. 2019, 40, 1485–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Wang, J.; Evans, D.G.; Li, D. Layered and intercalated hydrotalcite-like materials as thermal stabilizers in PVC resin. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2006, 67, 998–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhen, W.; Li, J. Structure, properties and applications of LDHs. Chem. Ind. Eng. Prog. 2013, 32, 610–616. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Shen, L.; Gao, B.; Hao, L.; Lu, X.; Zhanh, F.; Ding, B.; Yuan, C. Enhanced high-current capacitive behavior of graphene/CoAl-layered double hydroxide composites as electrode material for supercapacitors Yuan. J. Power Sources 2012, 199, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagergren, S. About the theory of so-called adsorption of soluble substances. K. Sven. Vetenskapsakademiens Handl. 1898, 24, 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G. Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem. 1999, 34, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limousin, G.; Gaudet, J.P.; Charlet, L. Sorption isotherms: A review on physical bases, modeling and measurement. Appl. Geochem. 2007, 22, 249–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Xu, Y.; Sun, G.; Wang, L.; Sun, Y.; Qin, X. Preparation, characterization of thiol-functionalized silica and applicationfor sorptionof Pb2+ and Cd2+. Colloids Surf. A 2009, 349, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Hou, W.; Xu, J. Sorption of Pb(II) on Mg–Fe layered double hydroxide. Chin. J. Chem. 2009, 27, 1981–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

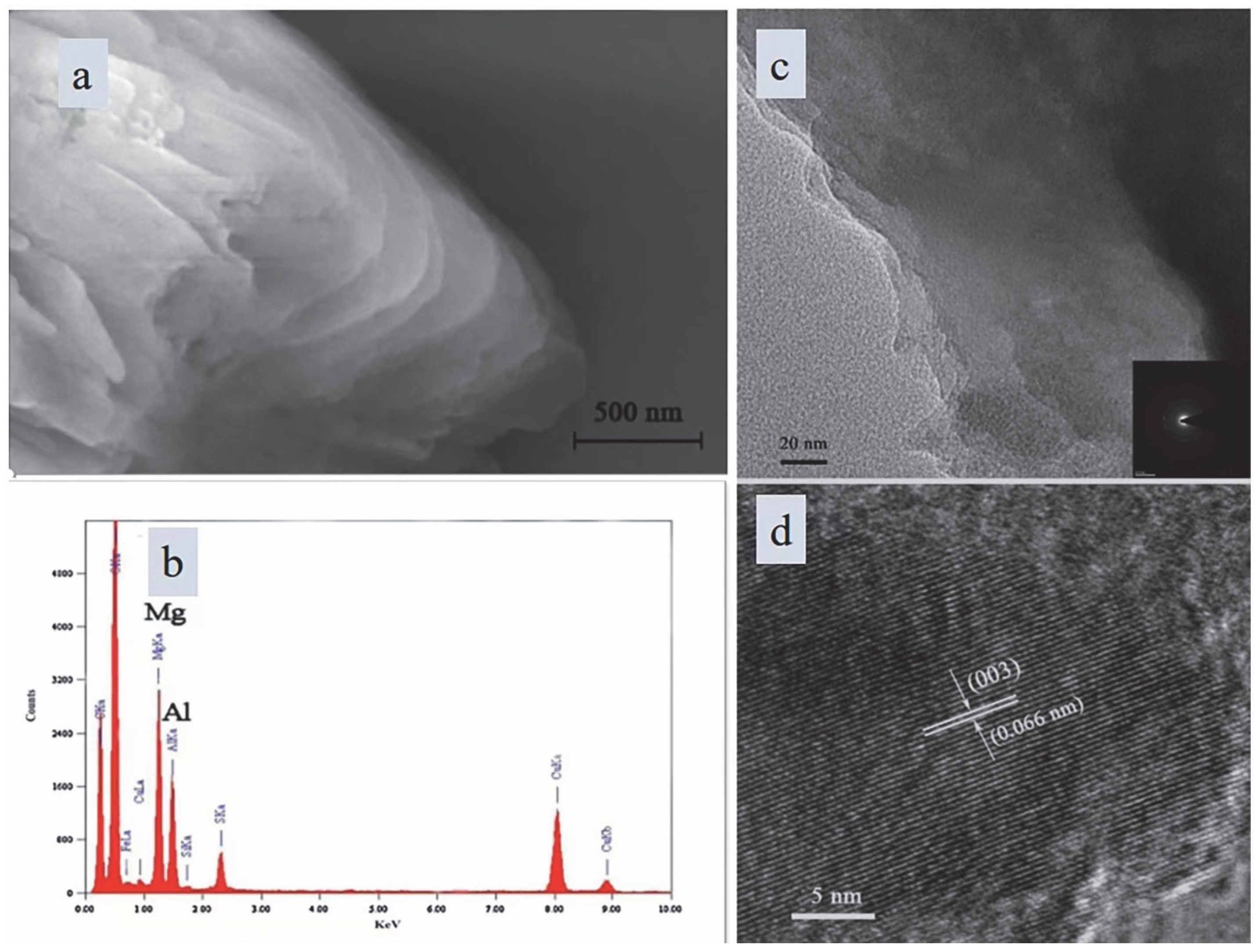





| Component | O | Na | Mg | Al | Si | Ca | Fe | K | Ti |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ratio (%) | 47.245 | 0.906 | 1.075 | 9.539 | 30.120 | 4.444 | 4.048 | 1.501 | 0.547 |
| Transition Temperature (°C) | Weight Loss (wt%) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1st | 57.7 | 0.7 |
| 2nd | 270.9 | 6.0 |
| qe,exp mg·g−1 | Pseudo-First-Order | Pseudo-Second-Order | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qe,cal mg·g−1 | k1 min−1 | R12 | qe,cal mg·g−1 | k2 g·(mg min)−1 | R22 | ||
| 50 | 22.92 | 0.7090 | 0.0078 | 0.4351 | 22.93 | 0.0465 | 0.9999 |
| 100 | 44.34 | 3.301 | 0.0177 | 0.5248 | 44.50 | 0.0126 | 0.9999 |
| 200 | 89.13 | 46.67 | 0.0144 | 0.8462 | 93.11 | 0.0005 | 0.9987 |
| 300 | 114.13 | 87.62 | 0.0138 | 0.9636 | 120.92 | 0.0003 | 0.9974 |
| Model | Freundlich | Langmuir | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Kf (mg·g−1) | 1/n | R2 | qmax (mg·g−1) | A (mg·L−1) | R2 |
| Pb2+ | 0.027702 | 1.582 | 0.8845 | 147.93 | 20.47 | 0.9916 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Z.-L.; Yu, H.; Chen, Y.-N.; Feng, W. A New Hydrotalcite-Like Absorbent OSA-LDH and Its Adsorption Capacity for Pb2+ Ions in Water. Chemistry 2024, 6, 1523-1534. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry6060092
Liu Z-L, Yu H, Chen Y-N, Feng W. A New Hydrotalcite-Like Absorbent OSA-LDH and Its Adsorption Capacity for Pb2+ Ions in Water. Chemistry. 2024; 6(6):1523-1534. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry6060092
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Zong-Lai, Hao Yu, Ya-Nan Chen, and Wei Feng. 2024. "A New Hydrotalcite-Like Absorbent OSA-LDH and Its Adsorption Capacity for Pb2+ Ions in Water" Chemistry 6, no. 6: 1523-1534. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry6060092
APA StyleLiu, Z.-L., Yu, H., Chen, Y.-N., & Feng, W. (2024). A New Hydrotalcite-Like Absorbent OSA-LDH and Its Adsorption Capacity for Pb2+ Ions in Water. Chemistry, 6(6), 1523-1534. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry6060092






