3D Computer-Aided Design Reconstructions and 3D Multi-Material Polymer Replica Printings of the First “Iron Hand” of Franconian Knight Gottfried (Götz) von Berlichingen (1480–1562): An Overview
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- http://www.landesarchiv-bw.de/plink/?f=4-1081856-1 (hand closed);
- http://www.landesarchiv-bw.de/plink/?f=4-1081855-1 (hand open).
- http://www.landesarchiv-bw.de/plink/?f=4-1078548-1 (hand closed);
- http://www.landesarchiv-bw.de/plink/?f=4-1078549-1 (hand open).
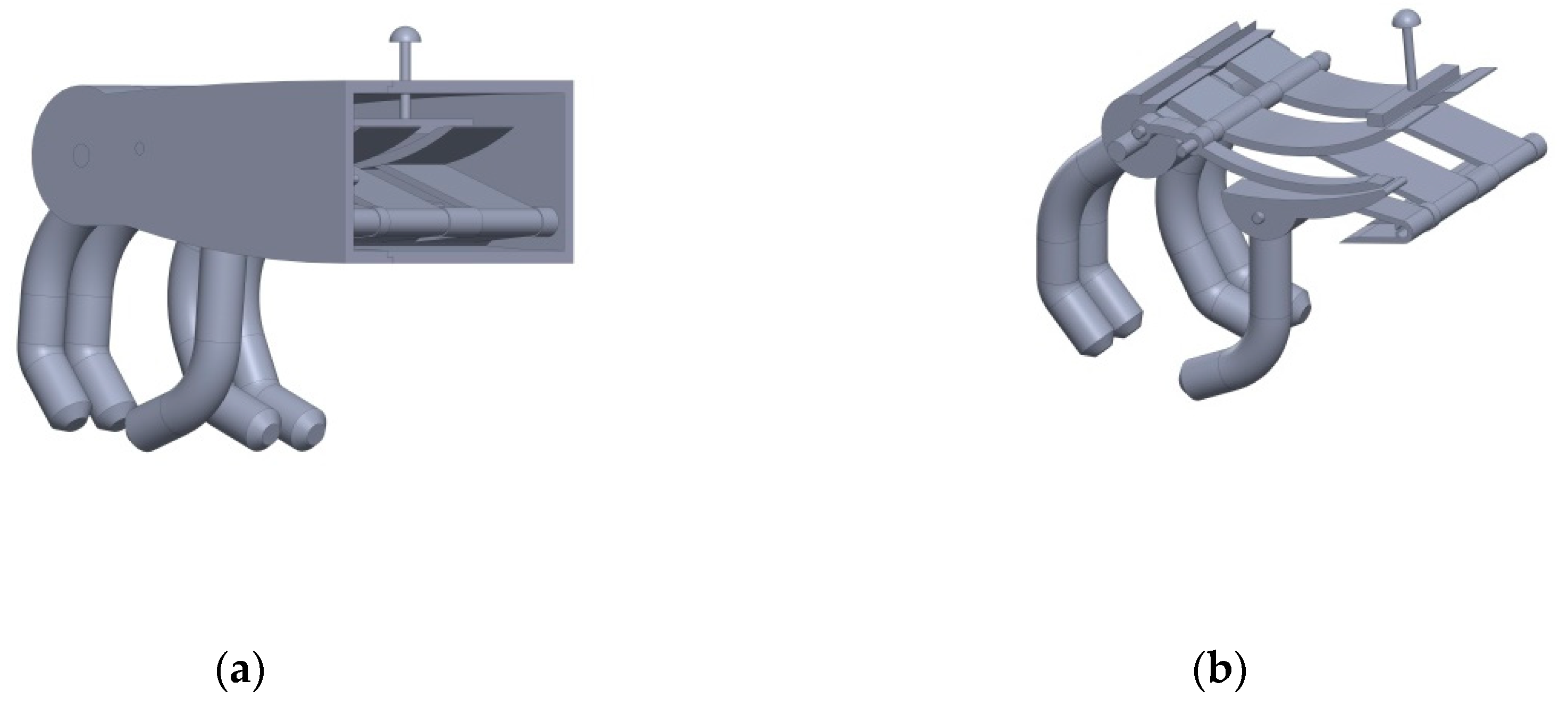
2. Reconstructions
2.1. The First 3D CAD Reconstruction
2.2. The Second 3D CAD Reconstruction with an Improved Thumb Lever Mechanism
2.3. The Third 3D CAD Reconstruction with an Opening Mechanism by a Torsion Spring
3. Further Developments
Conversion of the Götz Hand to A Sensorimotor, Controller-Controlled Intelligent Finger System
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A




References
- Quasigroch, G. Die Handprothesen des fränkischen Reichsritters Götz von Berlichingen—Der Landshuter Unfall [The hand prostheses of the Franconian imperial knight Götz von Berlichingen–The Landshut accident]. Z. der Ges. für Hist. Waffen-und Kostümkunde 1980, 22, 108–112. [Google Scholar]
- Von Berlichingen, G. Lebensbeschreibung des Ritters Götz von Berlichingen [Autobiography of the Knight Götz von Berlichingen]; Reclam: Stuttgart, Germany, 2014; p. 30, transl. by the author. [Google Scholar]
- Von Mechel, C. Die eiserne Hand des tapfern deutschen Ritters Götz von Berlichingen [The Iron Hand of the Brave German Knight Götz von Berlichingen]; Georg Decker: Berlin, Germany, 1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quasigroch, G. Die Handprothesen des fränkischen Reichsritters Götz von Berlichingen. 1. Fortsetzung: Die Ersthand [The hand prostheses of the Franconian imperial knight Götz von Berlichingen. 1st continuation: The first hand]. Z. der Ges. für Hist. Waffen-und Kostümkunde 1982, 24, 17–33. [Google Scholar]
- Quasigroch, G. Die Handprothesen des fränkischen Reichsritters Götz von Berlichingen. 2. Fortsetzung: Die Zweithand [The hand prostheses of the Franconian imperial knight Götz von Berlichingen. 2nd continuation: The second hand]. Z. der Ges. für Hist. Waffen-und Kostümkunde 1983, 25, 103–120. [Google Scholar]
- Weinert, O.; Otte, A. 3-D CAD-Rekonstruktion der ersten “Eisernen Hand” des Reichsritters Gottfried von Berlichingen (1480-1562) [3D CAD reconstruction of the first “Iron Hand” of German knight Gottfried von Berlichingen (1480-1562)]. Arch. Kriminol. 2017, 240, 50–58. [Google Scholar]
- Otte, A.; Weinert, O.; Junk, S. 3D-multimaterial printing–Knight Götz von Berlichingen’s trendsetting “iron hand”. Science 2017. Available online: http://science.sciencemag.org/content/353/6307/aaf2093/tab-e-letters (accessed on 2 December 2017). [CrossRef]
- Otte, A.; Weinert, O.; Junk, S. 3-D CAD-Rekonstruktion der ersten “Eisernen Hand“ des Reichsritters Gottfried von Berlichingen (1480–1562): 1. Fortsetzung: Funktionsprüfung mittels 3-D Druck. [3D CAD reconstruction of the first “Iron Hand” of German knight Gottfried von Berlichingen (1480–1562)—First continuation: Function test by means of 3D print]. Arch. Kriminol. 2017, 240, 185–192. [Google Scholar]
- Otte, A. Invasive versus non-invasive neuroprosthetics of the upper limb: Which way to go? Prosthesis 2020, 2, 237–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brezo, K. 3-D-CAD-Konstruktion Eines Neuen Doppelgelenks für den Daumenhebel bei der rekonstruierten ersten “Eisernen Hand“ des Götz von Berlichingen [3-D CAD Design of a New Double Joint for the Thumb Lever in the Reconstructed First “Iron Hand” of Götz von Berlichingen]. Bachelor’s Thesis, Offenburg University, Offenburg, Germany, 30 August 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Sadrija, A. 3D-unterstützte Optimierung der Mechanik der Fingerblöcke bei der ersten “Eisernen Hand“ des Götz von Berlichingen [3D-Supported Optimization of the Mechanics of the Finger Blocks in the First “Iron Hand” of Götz von Berlichingen]. Bachelor’s Thesis, Offenburg University, Offenburg, Germany, 17 April 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Löffler, L. Der Ersatz für die obere Extermität: Die Entwicklung von den ersten Zeugnissen bis heute [The Replacement of the Upper Extremity: The Development from the First Testimonies Until Today]; Enke: Stuttgart, Germany, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Hazubski, S.; Hoppe, H.; Otte, A. Electrode-free visual prosthesis/exoskeleton control using augmented reality glasses in a first proof-of-technical-concept study. Sci. Rep. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinert, O.; Otte, A. 3-D CAD-Rekonstruktion der ersten “Eisernen Hand” des Reichsritters Gottfried von Berlichingen (1480–1562)—2. Fortsetzung: Funktionsprüfung eines Umbaus zu einem sensomotorischen, controllergesteuerten intelligenten Fingersystem. [3D CAD reconstruction of the first “Iron Hand” of German knight Gottfried von Berlichingen (1480–1562)—Second continuation: Functional test of a conversion to a sensorimotor, controller-controlled intelligent finger system]. Arch. Kriminol. 2019, 243, 126–132. [Google Scholar]
- Ohnemus, D.; Otte, A. Medizinhistorische Fundstücke aus der (Neuro-)Prothetik: Eine Online-Analyse [Medico-historical findings of (neuro-) prosthetics: An online survey]. Arch. Kriminol. 2014, 234, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Finch, J. The ancient origins of prosthetic medicine. Lancet 2011, 377, 548–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otte, A.; Weinert, O. Die eiserne Hand des römischen Offiziers Marcus Sergius Silus (Ende des 3. Jahrhunderts v. Chr.)—Eine 3-D Computer-Aided Design (CAD)-Simulation [The iron hand of the Roman officer Marcus Sergius Silus (late 3rd century BC)—A 3-D computer-aided design (CAD) simulation]. Arch. Kriminol. 2018, 242, 184–192. [Google Scholar]
- Otte, A. Smart neuroprosthetics becoming smarter, but not for everyone? EClinicalMedicine 2018, 2–3, 11–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Otte, A. 3D Computer-Aided Design Reconstructions and 3D Multi-Material Polymer Replica Printings of the First “Iron Hand” of Franconian Knight Gottfried (Götz) von Berlichingen (1480–1562): An Overview. Prosthesis 2020, 2, 304-312. https://doi.org/10.3390/prosthesis2040027
Otte A. 3D Computer-Aided Design Reconstructions and 3D Multi-Material Polymer Replica Printings of the First “Iron Hand” of Franconian Knight Gottfried (Götz) von Berlichingen (1480–1562): An Overview. Prosthesis. 2020; 2(4):304-312. https://doi.org/10.3390/prosthesis2040027
Chicago/Turabian StyleOtte, Andreas. 2020. "3D Computer-Aided Design Reconstructions and 3D Multi-Material Polymer Replica Printings of the First “Iron Hand” of Franconian Knight Gottfried (Götz) von Berlichingen (1480–1562): An Overview" Prosthesis 2, no. 4: 304-312. https://doi.org/10.3390/prosthesis2040027
APA StyleOtte, A. (2020). 3D Computer-Aided Design Reconstructions and 3D Multi-Material Polymer Replica Printings of the First “Iron Hand” of Franconian Knight Gottfried (Götz) von Berlichingen (1480–1562): An Overview. Prosthesis, 2(4), 304-312. https://doi.org/10.3390/prosthesis2040027




