Infection of Vascular Prostheses: A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
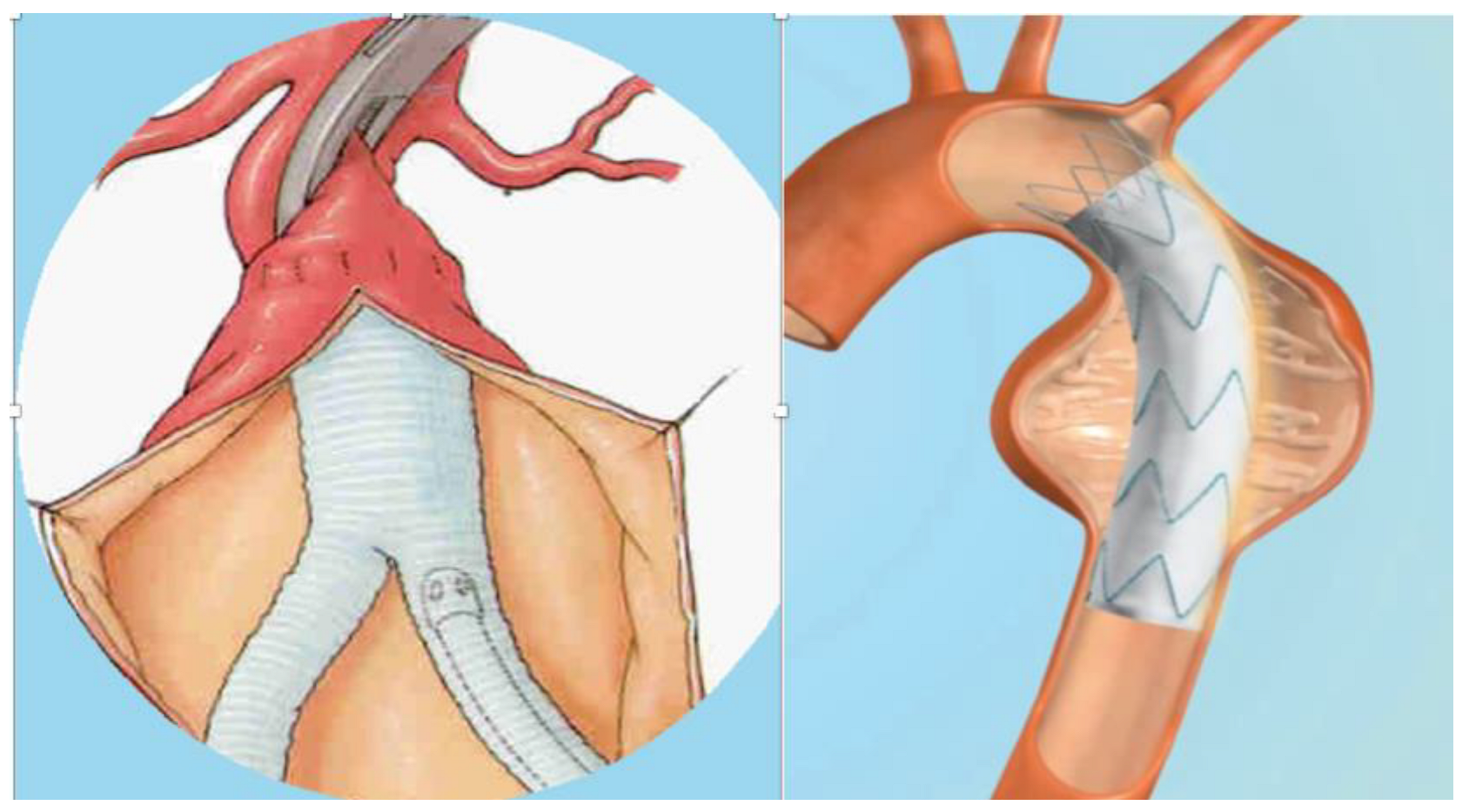
:1. Introduction
2. Pathogenesis
3. Diagnosis
4. Specific Aspects and Clinical Presentation According to Location of VGEI
5. Prevention of VGEI
6. Treatment of VGEI
7. Future Perspectives
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pennel, T.; Zilla, P. Clinical Applications and Limitations of Vascular Grafts. In Tissue-Engineered Vascular Grafts; Reference Series in Biomedical Engineering; Walpoth, B., Bergmeister, H., Bowlin, G., Kong, D., Rotmans, J., Zilla, P., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 1–32. [Google Scholar]
- Abbott, W.M.; Callow, A.; Moore, W.; Rutherford, R.; Veith, F.; Weinberg, S. Evaluation and performance standards for arterial prostheses. J. Vasc. Surg. 1993, 17, 746–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fazal, F.; Raghav, S.; Callanan, A.; Koutsos, V.; Radacsi, N. Recent advancements in the bioprinting of vascular grafts. Biofabrication 2021, 13, 032003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahl, S.L.; Blum, J.L.; Niklason, L.E. Bioengineered vascular grafts: Can we make them off-the-shelf? Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2011, 21, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonyshyn, J.A.; D’Costa, K.A.; Santerre, J.P. Advancing tissue-engineered vascular grafts via their endothelialization and mechanical conditioning. J. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2020, 61, 555–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafarihaghighi, F.; Ardjmand, M.; Mirzadeh, A.; Hassani, M.S.; Parizi, S.S. Current challenges and future trends in manufacturing small diameter artificial vascular grafts in bioreactors. Cell Tissue Bank. 2020, 21, 377–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, M.; Eaton-Evans, J.; Hillery, C.; Bakhshi, R.; You, Z.; Lu, J.; Hamilton, G.; Seifalian, A.M. AAA stent-grafts: Past problems and future prospects. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2010, 38, 1259–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, B.B.J.; Wakabayashi, N.; Oyama, K.; Kamiya, H.; Braghirolli, D.I.; Pranke, P. Vascular Tissue Engineering: Polymers and Methodologies for Small Caliber Vascular Grafts. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 7, 592361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obiweluozor, F.O.; Emechebe, G.A.; Kim, D.W.; Cho, H.J.; Park, C.H.; Kim, C.S.; Jeong, I.S. Considerations in the Development of Small-Diameter Vascular Graft as an Alternative for Bypass and Reconstructive Surgeries: A Review. Cardiovasc. Eng. Technol. 2020, 11, 495–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliason, J.L.; Upchurch, G.R., Jr. Endovascular treatment of aortic aneurysms: State of the art. Curr. Treat. Options Cardiovasc. Med. 2009, 11, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, R.; Bhandare, D.; St Louis, M.; Ruchi, R. Think before you leap: Cutaneous hypersensitivity to polytetrafluoroethylene arteriovenous graft masquerading as infection. BMJ Case Rep. 2019, 12, e230401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Xu, Y.; Ma, S.; Wang, L.; Liu, C.; Xu, W.; Shi, J.; Qiao, W.; Yang, H. Small-diameter polyurethane vascular graft with high strength and excellent compliance. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2021, 121, 104614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Zhou, F.; Ouyang, C.; Ye, W.; Yao, M.; Xu, B. Mechanical properties of small-diameter polyurethane vascular grafts reinforced by weft-knitted tubular fabric. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2010, 92, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.B.; Hwang, S.W.; Kim, M.S. Techniques and Outcomes of the No-Touch Vein Conduit as a Y-Composite Graft. Braz. J. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2022, 37, 38–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betz, T.; Neuwerth, D.; Steinbauer, M.; Uhl, C.; Pfister, K.; Töpel, I. Biosynthetic vascular graft: A valuable alternative to traditional replacement materials for treatment of prosthetic aortic graft infection? Scand. J. Surg. SJS Off. Organ Finn. Surg. Soc. Scand. Surg. Soc. 2019, 108, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keschenau, P.R.; Gombert, A.; Barbati, M.E.; Jalaie, H.; Kalder, J.; Jacobs, M.J.; Kotelis, D. Xenogeneic materials for the surgical treatment of aortic infections. J. Thorac. Dis. 2021, 13, 3021–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakfé, N.; Dieval, F.; Thaveau, F.; Rinckenbach, S.; Hassani, O.; Camelot, G.; Durand, B.; Kretz, J.G.; Groupe européen de recherche sur les prothèses appliquées à la chirurgie vasculaire. Substituts vasculaires. Vascular graft prosthesis. Ann. Chir. 2004, 129, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lejay, A.; Vento, V.; Kuntz, S.; Steinmetz, L.; Georg, Y.; Thaveau, F.; Heim, F.; Chakfé, N. Current status on vascular substitutes. J. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2020, 61, 538–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Droc, I.; Calinescu, F.B.; Droc, G.; Blaj, C.; Dammrau, R. Aortic stenting. Minim. Invasive Ther. Allied Technol. MITAT Off. J. Soc. Minim. Invasive Ther. 2015, 24, 296–304. [Google Scholar]
- Vento, V.; Lejay, A.; Kuntz, S.; Ancetti, S.; Heim, F.; Chakfé, N.; Gargiulo, M. Current status on aortic endografts. J. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2020, 61, 544–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnon-Sheleg, E.; Keidar, Z. Vascular Graft Infection Imaging. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2023, 53, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakfé, N.; Diener, H.; Lejay, A.; Assadian, O.; Berard, X.; Caillon, J.; Fourneau, I.; Glaudemans, A.W.J.M.; Koncar, I.; Lindholt, J.; et al. Editor’s Choice—European Society for Vascular Surgery (ESVS) 2020 Clinical Practice Guidelines on the Management of Vascular Graft and Endograft Infections. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2020, 59, 339–384, Erratum in: Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2020, 60, 958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Puges, M.; Bérard, X.; Caradu, C.; Accoceberry, I.; Gabriel, F.; Cazanave, C. Fungal Vascular Graft and Endograft Infections are Frequently Associated with Aorto-Enteric Fistulas. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Vasc. Surg. 2021, 62, 819–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Čertík, B.; Třeška, V.; Moláček, J.; Šulc, R.; Houdek, K.; Opatrný, V. Infections associated with vascular reconstruction procedures at the Department of Surgery in Pilsen in retrospect. Ohlédnutí za infekcemi cévních rekonstrukcí na chirurgické klinice v Plzni. Rozhl. Chir. Mesic. Ceskoslovenske Chir. Spol. 2022, 101, 318–325. [Google Scholar]
- Yolgosteren, A.; Kumtepe, G.; Payaslioglu, M.; Ozakin, C. In-vivo evaluation of the effect of cyanoacrylate on prosthetic vascular graft infection—Does cyanoacrylate increase the severity of infection? VASA. Z. Gefasskrankh. 2020, 49, 281–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mufty, H.; Van Den Eynde, J.; Meuris, B.; Metsemakers, W.J.; Van Wijngaerden, E.; Vandendriessche, T.; Steenackers, H.P.; Fourneau, I. Pre-clinical in vivo Models of Vascular Graft Coating in the Prevention of Vascular Graft Infection: A Systematic Review. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Vasc. Surg. 2021, 62, 99–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, W.R.; Bower, T.C.; Creager, M.A.; Amin-Hanjani, S.; O’Gara, P.T.; Lockhart, P.B.; Darouiche, R.O.; Ramlawi, B.; Derdeyn, C.P.; Bolger, A.F.; et al. Vascular Graft Infections, Mycotic Aneurysms, and Endovascular Infections: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2016, 134, e412–e460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smeds, M.R.; Duncan, A.A.; Harlander-Locke, M.P.; Lawrence, P.F.; Lyden, S.; Fatima, J.; Eskandari, M.K.; Vascular Low-Frequency Disease Consortium. Treatment and outcomes of aortic endograft infection. J. Vasc. Surg. 2016, 63, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argyriou, C.; Georgiadis, G.S.; Lazarides, M.K.; Georgakarakos, E.; Antoniou, G.A. Endograft Infection After Endovascular Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Repair: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J. Endovasc. Ther. Off. J. Int. Soc. Endovasc. Spec. 2017, 24, 688–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczot, M.; Meybeck, A.; Legout, L.; Pasquet, A.; Van Grunderbeeck, N.; Langlois, J.; Sarraz-Bournet, B.; Devos, P.; Leroy, O. Vascular graft infections in the intensive care unit: Clinical spectrum and prognostic factors. J. Infect. 2011, 62, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingsmore, D.; Stevenson, K.; Jackson, A.; Richarz, S.; Isaak, A.; White, B.; Thomson, P. Application and implications of a standardised reporting system for arteriovenous access graft infection. J. Vasc. Access 2022, 23, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husmann, L.; Eberhard, N.; Huellner, M.W.; Ledergerber, B.; Mueller, A.; Gruenig, H.; Messerli, M.; Mestres, C.A.; Rancic, Z.; Zimmermann, A.; et al. Impact of unknown incidental findings in PET/CT examinations of patients with proven or suspected vascular graft or endograft infections. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 13747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wouthuyzen-Bakker, M.; van Oosten, M.; Bierman, W.; Winter, R.; Glaudemans, A.; Slart, R.; Toren-Wielema, M.; Tielliu, I.; Zeebregts, C.J.; Prakken, N.H.J.; et al. Diagnosis and treatment of vascular graft and endograft infections: A structured clinical approach. Int. J. Infect. Dis. IJID Off. Publ. Int. Soc. Infect. Dis. 2022, 126, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, M.H.; Upchurch, G.R., Jr.; Malani, P.N. Vascular graft infections. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2012, 26, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hemelrijck, M.; Sromicki, J.; Husmann, L.; Rancic, Z.; Hasse, B.; Carrel, T.P. Vascular graft infections. Vessel Plus 2022, 6, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasse, B.; Husmann, L.; Zinkernagel, A.; Weber, R.; Lachat, M.; Mayer, D. Vascular graft infections. Swiss Med. Wkly. 2013, 143, w13754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andercou, O.; Marian, D.; Olteanu, G.; Stancu, B.; Cucuruz, B.; Noppeney, T. Complex treatment of vascular prostheses infections. Medicine 2018, 97, e11350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratliff, C.R.; Strider, D.; Flohr, T.; Moses, D.; Rovnyak, V.; Armatas, J.; Johnson, J.; Okerlund, A.; Baldwin, M.; Lawson, M.; et al. Vascular Graft Infection: Incidence and Potential Risk Factors. J. Wound Ostomy Cont. Nurs. Off. Publ. Wound Ostomy Cont. Nurses Soc. 2017, 44, 524–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anagnostopoulos, A.; Ledergerber, B.; Kuster, S.P.; Scherrer, A.U.; Näf, B.; Greiner, M.A.; Rancic, Z.; Kobe, A.; Bettex, D.; Hasse, B.; et al. Inadequate Perioperative Prophylaxis and Postsurgical Complications After Graft Implantation Are Important Risk Factors for Subsequent Vascular Graft Infections: Prospective Results From the Vascular Graft Infection Cohort Study. Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2019, 69, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukuzawa, K.; Ohki, T.; Maeda, K.; Kanaoka, Y. Risk factors and treatment outcomes for stent graft infection after endovascular aortic aneurysm repair. J. Vasc. Surg. 2019, 70, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duarte, A.; Gouveia, E.; Melo, R.; Mendes Pedro, D.; Martins, B.; Sobrinho, G.; Fernandes, E.; Fernandes, R.; Santos, C.M.; Mendes Pedro, L. Predictive Factors for Aortic Graft Infection: A Case-Control Study. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2022, 87, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manian, F.A. Vascular and cardiac infections in end-stage renal disease. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2003, 325, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Opelami, O.; Sakhuja, A.; Liu, X.; Tang, W.H.; Schold, J.D.; Navaneethan, S.D. Outcomes of infected cardiovascular implantable devices in dialysis patients. Am. J. Nephrol. 2014, 40, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Antonios, V.S.; Noel, A.A.; Steckelberg, J.M.; Wilson, W.R.; Mandrekar, J.N.; Harmsen, W.S.; Baddour, L.M. Prosthetic vascular graft infection: A risk factor analysis using a case-control study. J. Infect. 2006, 53, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legout, L.; Sarraz-Bournet, B.; D’Elia, P.V.; Devos, P.; Pasquet, A.; Caillaux, M.; Wallet, F.; Yazdanpanah, Y.; Senneville, E.; Haulon, S.; et al. Characteristics and prognosis in patients with prosthetic vascular graft infection: A prospective observational cohort study. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Off. Publ. Eur. Soc. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sano, N.; Matsunaga, S.; Akiyama, T.; Nakashima, Y.; Kusaba, K.; Nagasawa, Z.; Koizumi, S.; Goto, M.; Miyamoto, H. Moraxella catarrhalis bacteraemia associated with prosthetic vascular graft infection. J. Med. Microbiol. 2010, 59, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radak, D.; Tanaskovic, S.; Neskovic, M. The Obesity-associated Risk in Open and Endovascular Repair of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2019, 25, 2033–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouveia, E.; Melo, R.; Martins, B.; Pedro, D.M.; Santos, C.M.; Duarte, A.; Fernandes, E.; Fernandes, R.; Garrido, P.; Mendes Pedro, L. Microbial evolution of vascular graft infections in a tertiary hospital based on positive graft cultures. J. Vasc. Surg. 2021, 74, 276–284.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atahan, E.; Katrancioglu, N.; Oztop, Y.; Tuncer, E.; Ozer, H.; Manduz, S.; Engin, E.; Yalta, T.D.; Berkan, O.; Dogan, K. Vascular graft infection by Staphylococcus aureus: Efficacy of linezolid, teicoplanin and vancomycin systemic prophylaxis protocols in a rat model. Cardiovasc. J. Afr. 2009, 20, 122–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, P.A.; Back, M.R.; Armstrong, P.A.; Brumberg, R.S.; Flaherty, S.K.; Johnson, B.L.; Shames, M.L.; Bandyk, D.F. Evolving microbiology and treatment of extracavitary prosthetic graft infections. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2008, 42, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawson, T.M.; Lee, M.J.; Khanna, P.; Gopal Rao, G.; Renton, S.; Buckley, J. Microbiological characterisation of prosthetic vascular graft infection. J. Infect. 2015, 71, 400–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puges, M.; Pereyre, S.; Bérard, X.; Accoceberry, I.; Le Roy, C.; Stecken, L.; Pinaquy, J.B.; Desclaux, A.; Dupon, M.; Bébéar, C.; et al. Comparison of Genus Specific PCR and Culture with or without Sonication for Microbiological Diagnosis of Vascular Graft Infection. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Vasc. Surg. 2018, 56, 562–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zetrenne, E.; McIntosh, B.C.; McRae, M.H.; Gusberg, R.; Evans, G.R.; Narayan, D. Prosthetic vascular graft infection: A multi-center review of surgical management. Yale J. Biol. Med. 2007, 80, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Plotkin, A.; Magee, G.A.; Elsayed, R.S.; Byerly, S.; Ham, S.W.; Han, S.M.; Manzur, M.F.; Rowe, V.L.; Weaver, F.A. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus portends a poor prognosis after endovascular repair of mycotic aortic aneurysms and aortic graft infections. J. Vasc. Surg. 2020, 72, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stonebridge, P.A.; Mutirangura, P.; Clason, A.E.; Ruckley, C.V.; Jenkins, A.M. Bacteriology of aortic aneurysm sac contents. J. R. Coll. Surg. Edinb. 1990, 35, 42–43. [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak, S.; Bizzini, A. Streptococcus anginosus and Coxiella burnetii vascular graft co-infection. IDCases 2020, 19, e00697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, R.; Grande, R.; Butrico, L.; Rossi, A.; Settimio, U.F.; Caroleo, B.; Amato, B.; Gallelli, L.; de Franciscis, S. Chronic wound infections: The role of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2015, 13, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharamti, A.; Kanafani, Z.A. Vascular Graft Infections: An update. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 32, 789–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ielapi, N.; Nicoletti, E.; Lorè, C.; Guasticchi, G.; Avenoso, T.; Barbetta, A.; de Franciscis, S.; Andreucci, M.; Sapienza, P.; Serra, R. The Role of Biofilm in Central Venous Catheter Related Bloodstream Infections: Evidence-based Nursing and Review of the Literature. Rev. Recent Clin. Trials 2020, 15, 22–27. [Google Scholar]
- Puges, M.; M’Zali, F.; Pereyre, S.; Bébéar, C.; Cazanave, C.; Bérard, X. A Narrative Review of Experimental Models to Study Vascular Grafts Infections. EJVES Vasc. Forum 2022, 55, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroy, O.; Meybeck, A.; Sarraz-Bournet, B.; d’Elia, P.; Legout, L. Vascular graft infections. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 25, 154–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frei, E.; Hodgkiss-Harlow, K.; Rossi, P.J.; Edmiston, C.E., Jr.; Bandyk, D.F. Microbial pathogenesis of bacterial biofilms: A causative factor of vascular surgical site infection. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2011, 45, 688–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staneviciute, E.; Na’amnih, W.; Kavaliauskas, P.; Prakapaite, R.; Ridziauskas, M.; Kevlicius, L.; Kirkliauskiene, A.; Zabulis, V.; Urboniene, J.; Triponis, V. New in vitro model evaluating antiseptics’ efficacy in biofilm-associated Staphylococcus aureus prosthetic vascular graft infection. J. Med. Microbiol. 2019, 68, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirioni, O.; Mocchegiani, F.; Ghiselli, R.; Silvestri, C.; Gabrielli, E.; Marchionni, E.; Orlando, F.; Nicolini, D.; Risaliti, A.; Giacometti, A. Daptomycin and rifampin alone and in combination prevent vascular graft biofilm formation and emergence of antibiotic resistance in a subcutaneous rat pouch model of staphylococcal infection. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Vasc. Surg. 2010, 40, 817–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Vyver, H.; Bovenkamp, P.R.; Hoerr, V.; Schwegmann, K.; Tuchscherr, L.; Niemann, S.; Kursawe, L.; Grosse, C.; Moter, A.; Hansen, U.; et al. A Novel Mouse Model of Staphylococcus aureus Vascular Graft Infection: Noninvasive Imaging of Biofilm Development in Vivo. Am. J. Pathol. 2017, 187, 268–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cirioni, O.; Giacometti, A.; Ghiselli, R.; Kamysz, W.; Silvestri, C.; Orlando, F.; Mocchegiani, F.; Vittoria, A.D.; Kamysz, E.; Saba, V.; et al. The lipopeptides Pal-Lys-Lys-NH(2) and Pal-Lys-Lys soaking alone and in combination with intraperitoneal vancomycin prevent vascular graft biofilm in a subcutaneous rat pouch model of staphylococcal infection. Peptides 2007, 28, 1299–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herten, M.; Bisdas, T.; Knaack, D.; Becker, K.; Osada, N.; Torsello, G.B.; Idelevich, E.A. Rapid in Vitro Quantification of S. aureus Biofilms on Vascular Graft Surfaces. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, U.; Schäfer, T.; Ohlsen, K.; Tiurbe, G.C.; Bühler, C.; Germer, C.T.; Kellersmann, R. In vivo detection of Staphylococcus aureus in biofilm on vascular prostheses using non-invasive biophotonic imaging. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Vasc. Surg. 2011, 41, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona-Torre, F.; Rua, M.; Del Pozo, J.L. Non-valvular intravascular device and endovascular graft-related infection. Rev. Esp. Quimioter. Publ. Of. La Soc. Esp. Quimioter. 2017, 30, 42–47. [Google Scholar]
- Bergamini, T.M.; Bandyk, D.F.; Govostis, D.; Vetsch, R.; Towne, J.B. Identification of Staphylococcus epidermidis vascular graft infections: A comparison of culture techniques. J. Vasc. Surg. 1989, 9, 665–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, O.T.; Baguneid, M.; Barwick, T.D.; Bell, R.E.; Foster, N.; Homer-Vanniasinkam, S.; Hopkins, S.; Hussain, A.; Katsanos, K.; Modarai, B.; et al. Diagnosis of Aortic Graft Infection: A Case Definition by the Management of Aortic Graft Infection Collaboration (MAGIC). Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Vasc. Surg. 2016, 52, 758–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, W.; Puges, M.; Stenson, K.; Cazanave, C.; Ducasse, E.; Caradu, C.; Berard, X. Referral Centre Experience with Infected Abdominal Aortic Endograft Explantation. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2023, 65, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anagnostopoulos, A.; Mayer, F.; Ledergerber, B.; Bergadà-Pijuan, J.; Husmann, L.; Mestres, C.A.; Rancic, Z.; Hasse, B.; VASGRA Cohort Study. Editor’s Choice—Validation of the Management of Aortic Graft Infection Collaboration (MAGIC) Criteria for the Diagnosis of Vascular Graft/Endograft Infection: Results from the Prospective Vascular Graft Cohort Study. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Vasc. Surg. 2021, 62, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umpleby, H.C.; Turnbull, A.R. Arterioenteric fistulas. Br. J. Hosp. Med. 1988, 39, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jeon, Y.J.; Kim, H.K.; Kim, W.S.; Cho, J.H.; Sung, K. Repair of aortoesophageal fistula with homograft aortic replacement and primary esophageal closure. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2022, 163, 2002–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Igari, K.; Toyofuku, T.; Kudo, T.; Inoue, Y. Late Stent Graft Infection after the Emergency Endovascular Repair of a Secondary Iliac Artery-Enteric Fistula Treated with Graft Removal and In Situ Aortic Reconstruction Using Femoral Veins. Ann. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. Off. J. Assoc. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. Asia 2017, 23, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raman, S.P.; Kamaya, A.; Federle, M.; Fishman, E.K. Aortoenteric fistulas: Spectrum of CT findings. Abdom. Imaging 2013, 38, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnet, E.P.; Arista, S.; Archambaud, M.; Boot, B.; Clave, D.; Massip, P.; Marchou, B. Streptococcus milleri group infection associated with digestive fistula in patients with vascular graft: Report of seven cases and review. Infection 2007, 35, 182–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenu, C.; Marcheix, B.; Barcelo, C.; Rousseau, H. Aorto-enteric fistula after endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair: Case report and review. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Vasc. Surg. 2009, 37, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busuttil, S.J.; Goldstone, J. Diagnosis and management of aortoenteric fistulas. Semin. Vasc. Surg. 2001, 14, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Končar, I.B.; Dragaš, M.; Sabljak, P.; Peško, P.; Marković, M.; Davidović, L. Aortoesophageal and aortobronchial fistula caused by Candida albicans after thoracic endovascular aortic repair. Vojnosanit. Pregl. 2016, 73, 684–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadela, T.; Paravathaneni, M.; Manney, D.; Bandla, H. A Rare Cause of Gastrointestinal Bleeding: Aorto-Enteric Fistula. Cureus 2022, 14, e27023. [Google Scholar]
- Vandermeulen, M.; Verscheure, D.; Genser, L. Aorto-duodenal fistula secondary to aortic graft replacement. Acta Chir. Belg. 2022, 122, 74–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Li, Y.; Zhu, J.; Xia, J.; He, L.; Yun, M.; Jiao, J.; Zhu, G.; Hacker, M.; Wei, Y.; et al. Detection of aortic prosthetic graft infection with 18F-FDG PET/CT imaging, concordance with consensus MAGIC graft infection criteria. J. Nucl. Cardiol. Off. Publ. Am. Soc. Nucl. Cardiol. 2021, 28, 1005–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinders Folmer, E.I.; Von Meijenfeldt, G.C.I.; Van der Laan, M.J.; Glaudemans, A.W.J.M.; Slart, R.H.J.A.; Saleem, B.R.; Zeebregts, C.J. Diagnostic Imaging in Vascular Graft Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Vasc. Surg. 2018, 56, 719–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puges, M.; Bérard, X.; Ruiz, J.B.; Debordeaux, F.; Desclaux, A.; Stecken, L.; Pereyre, S.; Hocquelet, A.; Bordenave, L.; Pinaquy, J.B.; et al. Retrospective Study Comparing WBC scan and 18F-FDG PET/CT in Patients with Suspected Prosthetic Vascular Graft Infection. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Vasc. Surg. 2019, 57, 876–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, A.; Pencharz, D.; Davis, M.; Wagner, T. Determining the Diagnostic Value of 18F-Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission/Computed Tomography in Detecting Prosthetic Aortic Graft Infection. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2018, 53, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Lee, S.W.; Jeong, S.Y.; Pak, K.; Kim, K. A systematic review and meta-analysis of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography or positron emission tomography/computed tomography for detection of infected prosthetic vascular grafts. J. Vasc. Surg. 2019, 70, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruggink, J.L.; Glaudemans, A.W.; Saleem, B.R.; Meerwaldt, R.; Alkefaji, H.; Prins, T.R.; Slart, R.H.; Zeebregts, C.J. Accuracy of FDG-PET-CT in the diagnostic work-up of vascular prosthetic graft infection. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Vasc. Surg. 2010, 40, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojoa, D.; Kontopodis, N.; Antoniou, S.A.; Ioannou, C.V.; Antoniou, G.A. 18F-FDG PET in the Diagnosis of Vascular Prosthetic Graft Infection: A Diagnostic Test Accuracy Meta-Analysis. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Vasc. Surg. 2019, 57, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinders Folmer, E.I.; von Meijenfeldt, G.C.I.; Te Riet Ook Genaamd Scholten, R.S.; van der Laan, M.J.; Glaudemans, A.W.J.M.; Slart, R.H.J.A.; Zeebregts, C.J.; Saleem, B.R. A systematic review and meta-analysis of 18F-fluoro-d-deoxyglucose positron emission tomography interpretation methods in vascular graft and endograft infection. J. Vasc. Surg. 2020, 72, 2174–2185.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.; Koshevarova, V.; Shure, A.; Joseph, S.; Villanueva-Meyer, J.; Bhargava, P. FDG PET/CT in abdominal aortic graft infection: A case report and literature review. Radiol. Case Rep. 2022, 18, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Rubia-Marcos, M.; García-Alonso, P.; Mena-Melgar, C.; Tagliatori-Nogueira, B.; Herrero-Muñoz, A.; Sandoval-Moreno, C.; Paniagua-Correa, C.; Castillejos-Rodríguez, L.; Ortega-Valle, A.; Balsa-Bretón, M.A. 99mTC-white blood cell scintigraphy with SPECT/CT in the diagnosis of vascular graft infection. Gammagrafía con leucocitos marcados y SPECT/TC en el diagnóstico de infección de prótesis vasculares. Rev. Esp. Med. Nucl. E Imagen Mol. 2020, 39, 347–352. [Google Scholar]
- Erba, P.A.; Sollini, M.; Conti, U.; Bandera, F.; Tascini, C.; De Tommasi, S.M.; Zucchelli, G.; Doria, R.; Menichetti, F.; Bongiorni, M.G.; et al. Radiolabeled WBC scintigraphy in the diagnostic workup of patients with suspected device-related infections. JACC. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2013, 6, 1075–1086. [Google Scholar]
- Erba, P.A.; Leo, G.; Sollini, M.; Tascini, C.; Boni, R.; Berchiolli, R.N.; Menichetti, F.; Ferrari, M.; Lazzeri, E.; Mariani, G. Radiolabelled leucocyte scintigraphy versus conventional radiological imaging for the management of late, low-grade vascular prosthesis infections. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2014, 41, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauri, C.; Signore, A.; Glaudemans, A.W.J.M.; Treglia, G.; Gheysens, O.; Slart, R.H.J.A.; Iezzi, R.; Prakken, N.H.J.; Debus, E.S.; Honig, S.; et al. Evidence-based guideline of the European Association of Nuclear Medicine (EANM) on imaging infection in vascular grafts. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2022, 49, 3430–3451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaja, M.S.; Sildiroglu, O.; Hagspiel, K.; Rehm, P.K.; Cherry, K.J.; Turba, U.C. Prosthetic vascular graft infection imaging. Clin. Imaging 2013, 37, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrapko, B.E.; Chrapko, M.; Nocuń, A.; Zubilewicz, T.; Stefaniak, B.; Mitura, J.; Wolski, A.; Terelecki, P. Patterns of vascular graft infection in 18F-FDG PET/CT. Nucl. Med. Rev. Cent. East. Eur. 2020, 23, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuda, K.; Washiyama, N.; Takahashi, D.; Natsume, K.; Ohashi, Y.; Hirano, M.; Takeuchi, Y.; Shiiya, N. 18-Fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography in the diagnosis of prosthetic aortic graft infection: The difference between open and endovascular repair. Eur. J. Cardio-Thorac. Surg. Off. J. Eur. Assoc. Cardio-Thorac. Surg. 2022, 63, ezac542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowles, H.; Ambrosioni, J.; Mestres, G.; Hernández-Meneses, M.; Sánchez, N.; Llopis, J.; Yugueros, X.; Almela, M.; Moreno, A.; Riambau, V.; et al. Diagnostic yield of 18F-FDG PET/CT in suspected diagnosis of vascular graft infection: A prospective cohort study. J. Nucl. Cardiol. Off. Publ. Am. Soc. Nucl. Cardiol. 2020, 27, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaca, S.; Rager, O.; Ratib, O.; Kalangos, A. Long-term results confirmed that 18F-FDG-PET/CT was an excellent diagnostic modality for early detection of vascular grafts infection. Q. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2018, 62, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husmann, L.; Huellner, M.W.; Ledergerber, B.; Anagnostopoulos, A.; Stolzmann, P.; Sah, B.R.; Burger, I.A.; Rancic, Z.; Hasse, B.; the Vasgra Cohort. Comparing diagnostic accuracy of 18F-FDG-PET/CT, contrast enhanced CT and combined imaging in patients with suspected vascular graft infections. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2019, 46, 1359–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Einspieler, I.; Mergen, V.; Wendorff, H.; Haller, B.; Eiber, M.; Schwaiger, M.; Nekolla, S.G.; Mustafa, M. Diagnostic performance of quantitative and qualitative parameters for the diagnosis of aortic graft infection using [18F]-FDG PET/CT. J. Nucl. Cardiol. Off. Publ. Am. Soc. Nucl. Cardiol. 2021, 28, 2220–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lejay, A.; Koncar, I.; Diener, H.; Vega de Ceniga, M.; Chakfé, N. Post-operative Infection of Prosthetic Materials or Stents Involving the Supra-aortic Trunks: A Comprehensive Review. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Vasc. Surg. 2018, 56, 885–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langenberg, J.C.M.; Kluytmans, J.A.J.W.; Mulder, P.G.H.; Romme, J.; Ho, G.H.; Van Der Laan, L. Peri-Operative Nasal Eradication Therapy Prevents Staphylococcus aureus Surgical Site Infections in Aortoiliac Surgery. Surg. Infect. 2018, 19, 510–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norman, G.; Goh, E.L.; Dumville, J.C.; Shi, C.; Liu, Z.; Chiverton, L.; Stankiewicz, M.; Reid, A. Negative pressure wound therapy for surgical wounds healing by primary closure. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 6, CD009261. [Google Scholar]
- Svensson-Björk, R.; Hasselmann, J.; Asciutto, G.; Zarrouk, M.; Björk, J.; Bilos, L.; Pirouzram, A.; Acosta, S. Negative Pressure Wound Therapy for the Prevention of Surgical Site Infections Using Fascia Closure After EVAR-A Randomized Trial. World J. Surg. 2022, 46, 3111–3120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.T.; Hsu, Y.C.; Wu, C.I. Efficacy and safety of negative pressure wound therapy for Szilagyi grade III peripheral vascular graft infection. Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2014, 19, 1048–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, S.; Monsen, C.; Acosta, S. Outcome and Complications Using Negative Pressure Wound Therapy in the Groin for Perivascular Surgical Site Infections after Vascular Surgery. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2018, 48, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Malley, P.; McDonnell, C. Negative pressure wound therapy-two novel approaches to healing dehisced vascular bypass wounds. J. Wound Care 2021, 30, 449–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta, S.; Björck, M.; Wanhainen, A. Negative-pressure wound therapy for prevention and treatment of surgical-site infections after vascular surgery. Br. J. Surg. 2017, 104, e75–e84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, J.; Staley, C.; McCullough, M.; Goss, S.; Arosemena, M.; Abai, B.; Salvatore, D.; Reiter, D.; DiMuzio, P. A randomized clinical trial evaluating negative pressure therapy to decrease vascular groin incision complications. J. Vasc. Surg. 2018, 68, 1744–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Murphy, P.B.; Ingves, M.V.; Duncan, A.; DeRose, G.; Dubois, L.; Forbes, T.L.; Power, A. Randomized clinical trial of negative pressure wound therapy for high-risk groin wounds in lower extremity revascularization. J. Vasc. Surg. 2017, 66, 1814–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeno, Y.; Sakakibara, S.; Yokawa, K.; Kitani, K.; Nakai, H.; Yamanaka, K.; Inoue, T.; Tanaka, H.; Terashi, H.; Okita, Y. Post-sternotomy deep wound infection following aortic surgery: Wound care strategies to prevent prosthetic graft replacement†. Eur. J. Cardio-Thorac. Surg. Off. J. Eur. Assoc. Cardio-Thorac. Surg. 2019, 55, 975–983. [Google Scholar]
- Lafaurie, G.I.; Noriega, L.A.; Torres, C.C.; Castillo, Y.; Moscoso, S.B.; Mosquera, S.; Díaz-Báez, D.; Chambrone, L. Impact of antibiotic prophylaxis on the incidence, nature, magnitude, and duration of bacteremia associated with dental procedures: A systematic review. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 2019, 150, 948–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavali, H.; Mani, K.; Furebring, M.; Olsson, K.W.; Lindström, D.; Sörelius, K.; Sigvant, B.; Gidlund, K.D.; Torstensson, G.; Andersson, M.; et al. Editor’s Choice—Outcome of Radical Surgical Treatment of Abdominal Aortic Graft and Endograft Infections Comparing Extra-anatomic Bypass with In Situ Reconstruction: A Nationwide Multicentre Study. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Vasc. Surg. 2021, 62, 918–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, B.R.; Meerwaldt, R.; Tielliu, I.F.; Verhoeven, E.L.; van den Dungen, J.J.; Zeebregts, C.J. Conservative treatment of vascular prosthetic graft infection is associated with high mortality. Am. J. Surg. 2010, 200, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caradu, C.; Puges, M.; Cazanave, C.; Martin, G.; Ducasse, E.; Bérard, X.; Bicknell, C.; Imperial Vascular Unit and the University Hospital of Bordeaux Vascular Unit. Outcomes of patients with aortic vascular graft and endograft infections initially contra-indicated for complete graft explantation. J. Vasc. Surg. 2022, 76, 1364–1373.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masabni, K.; Weaver, M.R.; Kandagatla, P.; Shepard, A.D.; Huang, J.; Al Adas, Z.; Liang, L.; Balraj, P.; Nypaver, T.J.; Kabbani, L.S. Cryopreserved Allograft in the Management of Native and Prosthetic Aortic Infections. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2019, 56, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mestres, C.A.; Quintana, E.; Kopjar, T.; Ambrosioni, J.; Almela, M.; Fuster, D.; Ninot, S.; Miró, J.M.; Hospital Clinic Infective Endocarditis Investigators. Twenty-year experience with cryopreserved arterial allografts for vascular infections. Eur. J. Cardio-Thorac. Surg. Off. J. Eur. Assoc. Cardio-Thorac. Surg. 2019, 55, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couture, T.; Gaudric, J.; Davaine, J.M.; Jayet, J.; Chiche, L.; Jarraya, M.; Koskas, F. Results of cryopreserved arterial allograft replacement for thoracic and thoracoabdominal aortic infections. J. Vasc. Surg. 2021, 73, 626–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Chan, M.C.; James, C.; Lantis, J.C., 2nd. Cryopreserved Allograft Use in Vascular Surgery. Surg. Technol. Int. 2020, 37, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Touma, J.; Cochennec, F.; Parisot, J.; Fialaire Legendre, A.; Becquemin, J.P.; Desgranges, P. In situ reconstruction in native and prosthetic aortic infections using cryopreserved arterial allografts. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Vasc. Surg. 2014, 48, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, S.; Bachofen, B.; Widmer, M.K.; Makaloski, V.; Schmidli, J.; Wyss, T.R. Long-term results of cryopreserved allografts in aortoiliac graft infections. J. Vasc. Surg. 2021, 74, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Špaček, M.; Měřička, P.; Janoušek, L.; Štádler, P.; Adamec, M.; Vlachovský, R.; Guňka, I.; Navrátil, P.; Thieme, F.; Špunda, R.; et al. Current vascular allograft procurement, cryopreservation and transplantation techniques in the Czech Republic. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. Off. Organ Wroc. Med. Univ. 2019, 28, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lejay, A.; Delay, C.; Girsowicz, E.; Chenesseau, B.; Bonnin, E.; Ghariani, M.Z.; Thaveau, F.; Georg, Y.; Geny, B.; Chakfe, N. Cryopreserved Cadaveric Arterial Allograft for Arterial Reconstruction in Patients with Prosthetic Infection. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Vasc. Surg. 2017, 54, 636–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janko, M.R.; Bose, S.; Lawrence, P.F. Current status of treatment for aortic graft infection: When should cryopreserved allografts be used? Semin. Vasc. Surg. 2019, 32, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonopoulos, C.N.; Papakonstantinou, N.A.; Hardy, D.; Lyden, S.P. Editor’s Choice—Cryopreserved Allografts for Arterial Reconstruction after Aorto-Iliac Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Vasc. Surg. 2019, 58, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goëau-Brissonnière, O.; Javerliat, I.; Koskas, F.; Coggia, M.; Pechère, J.C. Rifampin-bonded vascular grafts and postoperative infections. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2011, 25, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okita, Y.; Yamanaka, K.; Okada, K. Opinion: Aortic Graft Infection-Any Guidelines or Just Surgeon’s Experience Lines! Semin. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2019, 31, 674–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mufty, H.; Van den Eynde, J.; Steenackers, H.P.; Metsemakers, W.J.; Meuris, B.; Fourneau, I. A systematic review of preclinical data regarding commercial silver-coated vascular grafts. J. Vasc. Surg. 2021, 74, 1386–1393.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricco, J.B.; Assadian, O. Antimicrobial silver grafts for prevention and treatment of vascular graft infection. Semin. Vasc. Surg. 2011, 24, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matic, P.; Tanaskovic, S.; Babic, S.; Gajin, P.; Jocic, D.; Nenezic, D.; Ilijevski, N.; Vucurevic, G.; Radak, D.J. In situ revascularisation for femoropopliteal graft infection: Ten years of experience with silver grafts. Vascular 2014, 22, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berard, X.; Puges, M.; Pinaquy, J.B.; Cazanave, C.; Stecken, L.; Bordenave, L.; Pereyre, S.; M’Zali, F. In vitro Evidence of Improved Antimicrobial Efficacy of Silver and Triclosan Containing Vascular Grafts Compared with Rifampicin Soaked Grafts. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Vasc. Surg. 2019, 57, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batt, M.; Jean-Baptiste, E.; O’Connor, S.; Bouillanne, P.J.; Haudebourg, P.; Hassen-Khodja, R.; Declemy, S.; Farhad, R. In-situ revascularisation for patients with aortic graft infection: A single centre experience with silver coated polyester grafts. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Vasc. Surg. 2008, 36, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molacek, J.; Treska, V.; Houdek, K.; Opatrný, V.; Certik, B.; Baxa, J. Use of a Silver-Impregnated Vascular Graft: Single-Center Experience. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savlania, A.; Tripathi, R.K. Aortic reconstruction in infected aortic pathology by femoral vein “neo-aorta”. Semin. Vasc. Surg. 2019, 32, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordanstig, J.; Törngren, K.; Smidfelt, K.; Roos, H.; Langenskiöld, M. Deep Femoral Vein Reconstruction of the Abdominal Aorta and Adaptation of the Neo-Aortoiliac System Bypass Technique in an Endovascular Era. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2019, 53, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laohapensang, K.; Arworn, S.; Orrapin, S.; Reanpang, T.; Orrapin, S. Management of the infected aortic endograft. Semin. Vasc. Surg. 2017, 30, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.T.; Clagett, G.P. Femoral vein harvest for vascular reconstructions: Pitfalls and tips for success. Semin. Vasc. Surg. 2008, 21, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorber, R.; Osgood, M.J.; Abularrage, C.J.; Black, J.H., 3rd; Lum, Y.W. Treatment of Aortic Graft Infection in the Endovascular Era. Curr. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2017, 19, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeger, J.M. Management of patients with prosthetic vascular graft infection. Am. Surg. 2000, 66, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uslu, H.Y.; Kurt, H. A case report of a unique aorto-bifemoral graft infection and its treatment. J. Surg. Case Rep. 2020, 11, rjaa382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, T.; Watanabe, Y. Multidisciplinary Treatment Approach for Prosthetic Vascular Graft Infection in the Thoracic Aortic Area. Ann. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2015, 21, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, P.; Moll, F.L. Aortic graft infections: Is there still a role for axillobifemoral reconstruction? Semin. Vasc. Surg. 2011, 24, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harky, A.; Othman, A.; Nistal De Paz, C.; Shaw, M.; Nawaytou, O.; Harrington, D.; Kuduvalli, M.; Field, M. Systematic approach to diagnosis and management of infected prosthetic grafts in the proximal aorta. J. Card. Surg. 2021, 36, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revest, M.; Camou, F.; Senneville, E.; Caillon, J.; Laurent, F.; Calvet, B.; Feugier, P.; Batt, M.; Chidiac, C.; Groupe de Réflexion sur les Infections de Prothèses vasculaires (GRIP). Medical treatment of prosthetic vascular graft infections: Review of the literature and proposals of a Working Group. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2015, 46, 254–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graulus, E.; Schepens, M. Perspective: Options in managing aortic graft infections. Indian J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2019, 35, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, E.; Serpelloni, S.; Alvear, P.; Rahimi, M.; Taraballi, F. Vascular Graft Infections: An Overview of Novel Treatments Using Nanoparticles and Nanofibers. Fibers 2022, 10, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallis, P.; Kostakis, A.; Stavropoulos-Giokas, C.; Michalopoulos, E. Future Perspectives in Small-Diameter Vascular Graft Engineering. Bioengineering 2020, 7, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.G.; Ugwu, F.; Li, W.C.; Caplice, N.M.; Petcu, E.; Yip, S.P.; Huang, C.L. Vascular Tissue Engineering: Advanced Techniques and Gene Editing in Stem Cells for Graft Generation. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2021, 27, 14–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weekes, A.; Bartnikowski, N.; Pinto, N.; Jenkins, J.; Meinert, C.; Klein, T.J. Biofabrication of small diameter tissue-engineered vascular grafts. Acta Biomater. 2022, 138, 92–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, P.; Ayan, B.; Ozbolat, I.T. Bioprinting for vascular and vascularized tissue biofabrication. Acta Biomater. 2017, 51, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhong, L.; Pan, F.; Wang, J. Advances in tissue engineering of vasculature through three-dimensional bioprinting. Dev. Dyn. Off. Publ. Am. Assoc. Anat. 2021, 250, 1717–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugan, D.; Rangasamy, L. The use of antimicrobial biomaterials as a savior from post-operative vascular graft-related infections: A review. Results Eng. 2022, 16, 100662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patelis, N.; Schizas, D.; Liakakos, T.; Klonaris, C. Aortic Graft Infection: Graphene Shows the Way to an Infection-Resistant Vascular Graft. Front. Surg. 2017, 4, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syama, S.; Mohanan, P.V. Safety and biocompatibility of graphene: A new generation nanomaterial for biomedical application. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 86, 546–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wawrzyńska, M.; Bil-Lula, I.; Krzywonos-Zawadzka, A.; Arkowski, J.; Łukaszewicz, M.; Hreniak, D.; Stręk, W.; Sawicki, G.; Woźniak, M.; Drab, M.; et al. Biocompatible Carbon-Based Coating as Potential Endovascular Material for Stent Surface. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 2758347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouda, H.; Larrea Murillo, L.; Wang, T. Current Progress in Vascular Engineering and Its Clinical Applications. Cells 2022, 11, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Shi, X.; Lin, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Kural, M.H.; Wang, J.; Ellis, M.W.; Anderson, C.W.; Zhang, S.M.; Riaz, M.; et al. Efficient Differentiation of Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells into Endothelial Cells under Xenogeneic-free Conditions for Vascular Tissue Engineering. Acta Biomater. 2021, 119, 184–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Qin, L.; Zhao, L.; Gui, L.; Ellis, M.W.; Huang, Y.; Kural, M.H.; Clark, J.A.; Ono, S.; Wang, J.; et al. Tissue-Engineered Vascular Grafts with Advanced Mechanical Strength from Human iPSCs. Cell Stem Cell 2020, 26, 251–261.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abutaleb, N.O.; Truskey, G.A. Human iPSCs Stretch to Improve Tissue-Engineered Vascular Grafts. Cell Stem Cell 2020, 26, 136–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cong, X.; Zhang, S.M.; Batty, L.; Luo, J. Application of Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells in Generating Tissue-Engineered Blood Vessels as Vascular Grafts. Stem Cells Dev. 2019, 28, 1581–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.; Cyganek, L.; Nitschke, K.; Uhlig, S.; Nuhn, P.; Bieback, K.; Duerschmied, D.; El-Battrawy, I.; Zhou, X.; Akin, I. Functional Characterization of Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Endothelial Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Clinical/Surgical | Radiology | Laboratory |
|---|---|---|
Major:
| Major:
| Major:
|
Minor:
| Minor:
| Minor:
|
| District | Clinical Presentation |
|---|---|
| Thoracic Aorta |
|
| Abdominal Aorta |
|
| Peripheral Arteries |
|
| Supra-aortic trunks |
|
| Prosthetic arteriovenous hemodialysis grafts |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Costa, D.; Andreucci, M.; Ielapi, N.; Serraino, G.F.; Mastroroberto, P.; Bracale, U.M.; Serra, R. Infection of Vascular Prostheses: A Comprehensive Review. Prosthesis 2023, 5, 148-166. https://doi.org/10.3390/prosthesis5010012
Costa D, Andreucci M, Ielapi N, Serraino GF, Mastroroberto P, Bracale UM, Serra R. Infection of Vascular Prostheses: A Comprehensive Review. Prosthesis. 2023; 5(1):148-166. https://doi.org/10.3390/prosthesis5010012
Chicago/Turabian StyleCosta, Davide, Michele Andreucci, Nicola Ielapi, Giuseppe Filiberto Serraino, Pasquale Mastroroberto, Umberto Marcello Bracale, and Raffaele Serra. 2023. "Infection of Vascular Prostheses: A Comprehensive Review" Prosthesis 5, no. 1: 148-166. https://doi.org/10.3390/prosthesis5010012
APA StyleCosta, D., Andreucci, M., Ielapi, N., Serraino, G. F., Mastroroberto, P., Bracale, U. M., & Serra, R. (2023). Infection of Vascular Prostheses: A Comprehensive Review. Prosthesis, 5(1), 148-166. https://doi.org/10.3390/prosthesis5010012








