Clinical Observations Associated with Phenobarbital Serum Monitoring to Manage Epilepsy in a California Sea Lion with Domoic Acid Toxicosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Case
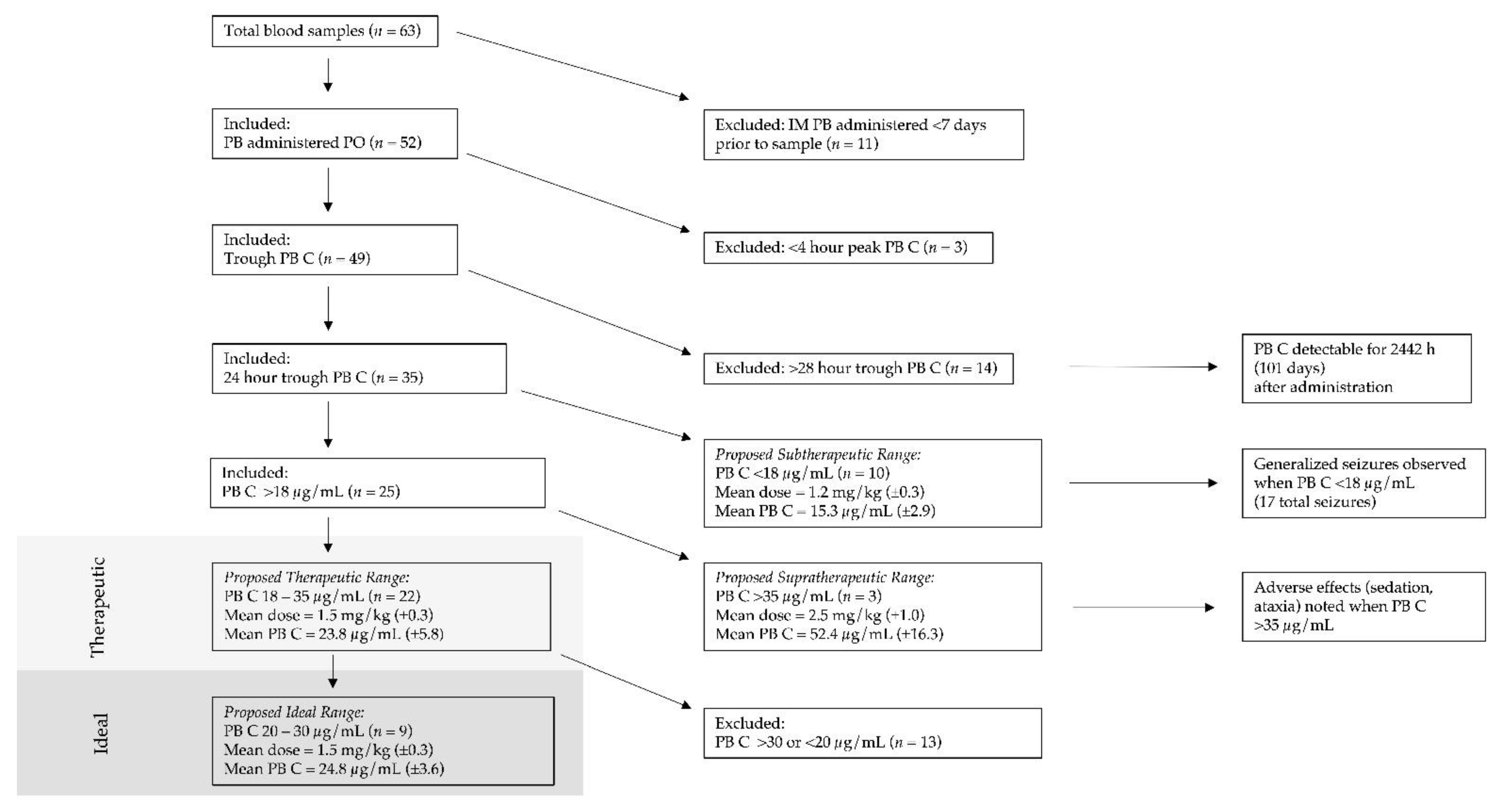
2.2. Medical Record Review
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Simeone, C.A.; Gulland, F.M.D.; Norris, T.; Rowles, T.K. A Systematic Review of Changes in Marine Mammal Health in North America, 1972–2012: The Need for a Novel Integrated Approach. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Glibert, P.M.; Anderson, D.M.; Gentien, P.; Granéli, E.; Sellner, K.G. The Global, Complex Phenomena of Harmful Algal Blooms. Oceanography 2005, 18, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greig, D.J.; Gulland, F.M.D.; Kreuder, C. A Decade of Live California Sea Lion (Zalophus Californianus) Strandings Along the Central California Coast: Causes and Trends, 1991–2000. Aquat. Mamm. 2005, 31, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scholin, C.A.; Gulland, F.; Doucette, G.J.; Benson, S.; Busman, M.; Chavez, F.P.; Cordaro, J.; DeLong, R.; de Vogelaere, A.; Harvey, J.; et al. Mortality of Sea Lions along the Central California Coast Linked to a Toxic Diatom Bloom. Nature 2000, 403, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simeone, C.; Fauquier, D.; Skidmore, J.; Cook, P.; Colegrove, K.; Gulland, F.; Dennison, S.; Rowles, T.K. Clinical Signs and Mortality of Non-Released Stranded California Sea Lions Housed in Display Facilities: The Suspected Role of Prior Exposure to Algal Toxins. Vet. Rec. 2019, 185, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gulland, F.M.D.; Haulena, M.; Fauquier, D.; Langlois, G.; Lander, M.E.; Zabka, T.; Duerr, R. Domoic Acid Toxicity in Californian Sea Lions (Zalophus californianus): Clinical Signs, Treatment and Survival. Vet. Rec. 2002, 150, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, T.; Mazet, J.A.K.; Zabka, T.S.; Langlois, G.; Colegrove, K.M.; Silver, M.; Bargu, S.; van Dolah, F.; Leighfield, T.; Conrad, P.A.; et al. Novel Symptomatology and Changing Epidemiology of Domoic Acid Toxicosis in California Sea Lions (Zalophus californianus): An Increasing Risk to Marine Mammal Health. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2008, 275, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Whaley, J.E.; Borowski, R. Marine Mammal Response, Rehabilitation, and Release: Standards for Release; NOAA National Marine Fisheries Service Marine Mammal Health and Stranding Response Program: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2009; pp. 1–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podell, M. BSAVA Manual of Canine and Feline Neurology; BSAVA: Gloucester, MA, USA, 2013; pp. 117–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plumb, D.C. Phenobarbital. In Plumb’s Veterinary Drug Handbook, 9th ed.; Pharma Vet: Stockholm, Sweden, 2018; pp. 931–935. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, W.B. Idiopathic Epilepsy in Dogs and Cats. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2010, 40, 161–179. [Google Scholar]
- Iwata, E. Epilepsy Suspected Seizure and Control in a California Sea Lion (Zalophus Californianus). Jpn. J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 1998, 3, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gage, L.J. Geriatric Medicine in Aged Captive Pinnipeds. In Proceedings of the International Association for Aquatic Animal Medicine, Session V, Boston, MA, USA; 1999; Volume 30, pp. 130–131. [Google Scholar]
- Field, C.L.; Tuttle, A.D.; Sidor, I.F.; Nyaoke, A.; Deering, K.M.; Gilbert-Marcheterre, K.; Risatti, G.; Spoon, T.; Meegan, J.; Romano, T.A.; et al. Systemic Mycosis in a California Sea Lion (Zalophus californianus) with Detection of Cystofilobasidiales DNA. J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2012, 43, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haulena, M.; Thompson, B.; Neimanis, A.; Gulland, M.; Wiebe, V. Pharmacokinetics of Phenobarbital in California Sea Lions (Zalophus californianus). In Proceedings of the American Association of Zoo Veterinarians, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 4–10 October 2003; pp. 196–197. [Google Scholar]
- Dold, C.; Van Bonn, W.; Smith, C.; Wong, S.; Jensen, E.; Ridgway, S.; Barakos, J.A. Diagnostic and Clinical Approach to Seizures Caused by Intracranial Structural Pathology in a Young California Sea Lion (Zalophus californianus). In Proceedings of the International Association for Aquatic Animal Medicine, Seward, AK, USA, 14–19 May 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, P.F.; Hoard, V.A.; Dolui, S.; de Frederick, B.; Redfern, R.; Dennison, S.E.; Halaska, B.; Bloom, J.; Kruse-Elliott, K.T.; Whitmer, E.R.; et al. An MRI Protocol for Anatomical and Functional Evaluation of the California Sea Lion Brain. J. Neurosci. Methods 2021, 353, 109097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simeone, C.A.; Andrews, J.P.; Johnson, S.P.; Casalia, M.; Kochanski, R.; Chang, E.F.; Cameron, D. Xenotransplantation of Porcine Progenitor Cells in an Epileptic California Sea Lion (Zalophus californianus). J. Neurosurg. Case Lessons. 2021, 3, CASE21417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berendt, M.; Farquhar, R.G.; Mandigers, P.J.J.; Pakozdy, A.; Bhatti, S.F.M.; De Risio, L.; Fischer, A. International Veterinary Epilepsy Task Force Consensus Report on Epilepsy Definition, Classification and Terminology in Companion Animals. BMC Vet. Res. 2015, 11, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fauquier, D.A.; Mazet, J.A.K.; Gulland, F.M.D.; Spraker, T.R.; Christopher, M.M. Distribution of Tissue Enzymes in Three Species of Pinnipeds. J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2008, 39, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulland, F.; Dierauf, L.A.; Whitman, K.L. (Eds.) Appendix 1. Normal Hematology and Serum Chemistry Ranges. In CRC Handbook of Marine Mammal Medicine, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; pp. 1003–1022. [Google Scholar]
- Gaskill, C.L.; Miller, L.M.; Mattoon, J.S.; Hoffmann, W.E.; Burton, S.A.; Gelens, H.C.J.; Ihle, S.L.; Miller, J.B.; Shaw, D.H.; Cribb, A.E. Liver Histopathology and Liver and Serum Alanine Aminotransferase and Alkaline Phosphatase Activities in Epileptic Dogs Receiving Phenobarbital. Vet. Pathol. 2005, 42, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnerty, K.E.; Barnes Heller, H.L.; Mercier, M.N.; Giovanella, C.J.; Lau, V.W.; Rylander, H. Evaluation of Therapeutic Phenobarbital Concentrations and Application of a Classification System for Seizures in Cats: 30 Cases (2004–2013). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2014, 244, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalmora, S.L.; da Silva Sangoi, M.; Nogueira, D.R.; D’Avila, F.B.; Moreno, R.A.; Sverdloff, C.E.; de Oliveira, R.A.; Borges, N.C. Determination of Phenobarbital in Human Plasma by a Specific Liquid Chromatography Method: Application to a Bioequivalence Study. Quim. Nova 2010, 33, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wroblewski, B.A.; Garvin, W.H. Once-Daily Administration of Phenobarbital in Adults: Clinical Efficacy and Benefit. Arch. Neurol. 1985, 42, 699–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayrell-Hart, B.; Steinberg, S.A.; van Winkle, T.J.; Farnbach, G.C. Hepatotoxicity of Phenobarbital in Dogs: 18 Cases (1985–1989). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1991, 199, 1060–1066. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, P.B.; Taboada, J.; Hosgood, G.; Partington, B.P.; VanSteenhouse, J.L.; Taylor, H.W.; Wolfsheimer, K.J. Effects of Long-Term Phenobarbital Treatment on the Liver in Dogs. J. Vet. Intern. Med. Am. Coll. Vet. Intern. Med. 2000, 14, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, A.W.; Michalopoulos, G.K. Phenobarbital Regulates Nuclear Expression of HNF-4α in Mouse and Rat Hepatocytes Independent of CAR and PXR. Hepatology 2006, 44, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trepanier, L.A.; van Schoick, A.; Schwark, W.S.; Carrillo, J. Therapeutic Serum Drug Concentrations in Epileptic Dogs Treated with Potassium Bromide Alone or in Combination with Other Anticonvulsants: 122 Cases (1992–1996). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1998, 213, 1449–1453. [Google Scholar]
- Jambroszyk, M.; Tipold, A.; Potschka, H. Add-on Treatment with Verapamil in Pharmacoresistant Canine Epilepsy. Epilepsia 2011, 52, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, K.S.; Dewey, C.W. The Seizuring Cat: Diagnostic Work-up and Therapy. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2009, 11, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, D.; Baumgartner, C.; Löscher, W. Seizure Recurrence after Planned Discontinuation of Antiepileptic Drugs in Seizure-Free Patients after Epilepsy Surgery: A Review of Current Clinical Experience. Epilepsia 2004, 45, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yardi, R.; Irwin, A.; Kayyali, H.; Gupta, A.; Nair, D.; Gonzalez-Martinez, J.; Bingaman, W.; Najm, I.M.; Jehi, L.E. Reducing versus Stopping Antiepileptic Medications after Temporal Lobe Surgery. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2014, 1, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cagnotti, G.; Ferrini, S.; Ala, U.; Bellino, C.; Corona, C.; Dappiano, E.; Di Muro, G. Analysis of Early Assessable Risk Factors for Poor Outcome in Dogs With Cluster Seizures and Status Epilepticus. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 575551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podell, M.; Volk, H.A.; Berendt, M.; Löscher, W.; Muñana, K.; Patterson, E.E.; Platt, S.R. 2015 ACVIM Small Animal Consensus Statement on Seizure Management in Dogs. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2016, 30, 477–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, S.O.; Sams, R.A.; and Podell, M. Chronic Phenobarbital Therapy Reduces Plasma Benzodiazepine Concentrations after Intravenous and Rectal Administration of Diazepam in the Dog. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 1998, 21, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champagne, C.D.; Crocker, D.E.; Fowler, M.A.; Houser, D.S. Fasting Physiology of the Pinnipeds: The Challenges of Fasting While Maintaining High Energy Expenditure and Nutrient Delivery for Lactation. In Comparative Physiology of Fasting, Starvation, and Food Limitation; McCue, M.D., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 309–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lammers, L.A.; Achterbergh, R.; Mathôt, R.A.A.; Romijn, J.A. The Effects of Fasting on Drug Metabolism. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2020, 16, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maguire, P.J.; Fettman, M.J.; Smith, M.O.; Greco, D.S.; Turner, A.S.; Walton, J.A.; Ogilvie, G.K. Effects of Diet on Pharmacokinetics of Phenobarbital in Healthy Dogs. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2000, 217, 847–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Reference | Dose (PO) | Reported PB Serum Concentration a | Number of Animals |
|---|---|---|---|
| Current studyrecommendations | 1.5 mg/kg SID | 20–30μg/mL | 1 |
| Iwata 1998 [12] | 2.0 mg/kg BID | 14.1–20.6 μg/dL | 1 |
| Gage 1999 [13] | 1.0–1.5 mg/kg SID-BID | NR | 1 |
| Gulland et al. 2002 [6] | 2.0 mg/kg | NR | NR |
| 4.0 mg/kg BID for 2d, then 2.0 mg/kg BID for 5d | NR | NR | |
| Field et al. 2012 [14] | 1.0 mg/kg | NR | 1 |
| Haulena et al. 2003 [15] | 2.0 mg/kg BID | 10–30 μg/L | 3 |
| 4.0 mg/kg BID | >30 μg/L | 3 | |
| 6.0 mg/kg BID | >30 μg/L | 3 | |
| Dold et al. 2005 [16] | 4.0 mg/kg SID | NR | 1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Simeone, C.A.; Scott, G.; Navarro, R.A.; Procter, D. Clinical Observations Associated with Phenobarbital Serum Monitoring to Manage Epilepsy in a California Sea Lion with Domoic Acid Toxicosis. Oceans 2022, 3, 331-339. https://doi.org/10.3390/oceans3030023
Simeone CA, Scott G, Navarro RA, Procter D. Clinical Observations Associated with Phenobarbital Serum Monitoring to Manage Epilepsy in a California Sea Lion with Domoic Acid Toxicosis. Oceans. 2022; 3(3):331-339. https://doi.org/10.3390/oceans3030023
Chicago/Turabian StyleSimeone, Claire A., Gregory Scott, Ryan A. Navarro, and Diana Procter. 2022. "Clinical Observations Associated with Phenobarbital Serum Monitoring to Manage Epilepsy in a California Sea Lion with Domoic Acid Toxicosis" Oceans 3, no. 3: 331-339. https://doi.org/10.3390/oceans3030023
APA StyleSimeone, C. A., Scott, G., Navarro, R. A., & Procter, D. (2022). Clinical Observations Associated with Phenobarbital Serum Monitoring to Manage Epilepsy in a California Sea Lion with Domoic Acid Toxicosis. Oceans, 3(3), 331-339. https://doi.org/10.3390/oceans3030023







