Resident Harbor Porpoises (Phocoena phocoena vomerina) in the Salish Sea: Photo-Identification Shows Long-Term Site Fidelity, Natal Philopatry, and Provides Insights into Longevity and Behavior
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
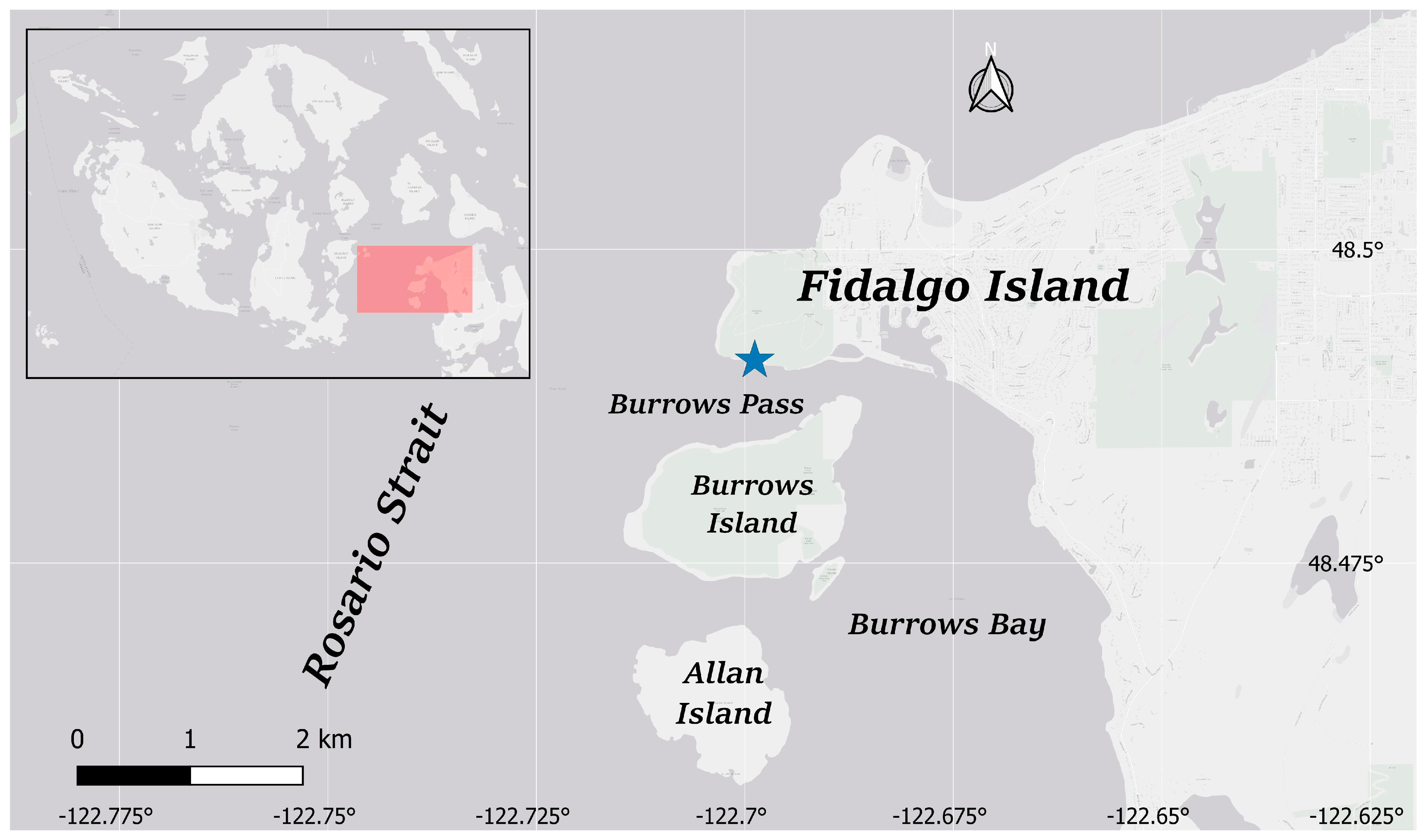
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effort
3.2. Group Size
3.3. Site Fidelity and Re-Sighting History
3.4. Seasonality
3.5. Mothers and Calves
3.6. Behavior
4. Discussion
4.1. Group Size
4.2. Site Fidelity and Re-Sighting History
4.3. Seasonality
4.4. Mothers and Calves
4.5. Behavior
4.6. Longevity
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Switzer, P.V. Site fidelity in predictable and unpredictable habitats. Evol. Ecol. 1993, 7, 533–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, R.; Getz, W.M.; Revilla, E.; Holyoak, M.; Kadmon, R.; Saltz, D.; Smouse, P.E.A. Movement ecology paradigm for unifying organismal movement research. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 19052–19059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaskin, D.E. The harbor porpoise Phocoena phocoena: Regional populations, status, and information on direct and indirect catches. Rep. Int. Whal. Comm. 1984, 34, 569–586. [Google Scholar]
- Fontaine, M.C.; Thatcher, O.; Ray, N.; Piry, S.; Brownlow, A.; Davison, N.J.; Jepson, P.; Deaville, R.; Goodman, S.J. Mixing of porpoise ecotypes in southwestern UK waters revealed by genetic profiling. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2017, 4, 160992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passadore, C.; Möller, L.; Diaz-Aguirre, F.; Parra, G.J. High site fidelity and restricted ranging patterns in southern Australian bottlenose dolphins. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 8, 242–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chivers, S.J.; Hanson, B.; Laake, J.; Gearin, P.; Muto, M.M.; Calambokidis, J.; Duffield, D.; McGuire, T.; Hodder, J.; Greig, D.; et al. Additional Genetic Evidence for Population Structure of Phocoena phocoena off the Coasts of California, Oregon, and Washington; Southwest Fisheries Science Center: La Jolla, CA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Hobbs, R.C.; Waite, J.M. Abundance of harbor porpoise (Phocoena phocoena) in three Alaskan regions, corrected for observer errors due to perception bias and species misidentification, and corrected for animals submerged from view. Fish. Bull. 2010, 108, 251–267. [Google Scholar]
- Huggins, J.L.; Raverty, S.A.; Norman, S.A.; Calambokidis, J.; Gaydos, J.K.; Duffield, D.A.; Lambourn, D.M.; Rice, J.M.; Hanson, B.; Wilkinson, K.; et al. Increased harbor porpoise mortality in the Pacific Northwest, USA: Understanding when higher levels may be normal. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2015, 115, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jefferson, T.A.; Smultea, M.A.; Courbis, S.S.; Campbell, G.S. Harbor porpoise (Phocoena phocoena) recovery in the inland waters of Washington: Estimates of density and abundance from aerial surveys, 2013–2015. Can. J. Zool. 2016, 94, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, S.A.; Hanson, M.B.; Huggins, J.; Lambourn, D.; Calambokidis, J.; Cottrell, P.; Greene, A.; Raverty, S.; Berta, S.; Dubpernell, S.; et al. Conception, fetal growth, and calving seasonality of harbor porpoise (Phocoena phocoena) in the Salish Sea waters of Washington, USA, and southern British Columbia, Canada. Can. J. Zool. 2018, 96, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forney, K.A.; Carretta, J.V.; Benson, S.R. Preliminary Estimates of Harbor Porpoise Abundance in Pacific Coast Waters of California, Oregon, and Washington, 2007–2012; NOAA Technical Memorandum NMFS; Southwest Fisheries Science Center: La Jolla, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Forney, K.A.; Moore, J.E.; Barlow, J.; Carretta, J.V.; Benson, S.R. A multidecadal Bayesian trend analysis of harbor porpoise (Phocoena phocoena) populations off California relative to past fishery bycatch. Mar. Mamm. Sci. 2021, 37, 546–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forney, K.A.; Benson, S.R.; Becker, E.A. A Habitat-Based Spatial Density Model for Harbor Porpoise (Phocoena phocoena) off Oregon and Washington Based on 2021–2022 Aerial Surveys; NOAA Technical Memorandum NMFS, Southwest Fisheries Science Center: La Jolla, CA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, K.M.; Everett, M.; Dahlheim, M.; Park, L. Water, water everywhere: Environmental DNA can unlock population structure in elusive marine species. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2018, 5, 180537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsons, K.M.; May, S.A.; Gold, Z.; Dahlheim, M.; Gabriele, C.; Straley, J.M.; Moran, J.R.; Goetz, K.; Zerbini, A.N.; Park, L.; et al. Using eDNA to supplement population genetic analyses for cryptic marine species: Identifying population boundaries for Alaska harbour porpoises. Mol. Ecol. 2024, e17563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keener, W.; Webber, M.A.; Szczepaniak, I.D.; Markowitz, T.M.; Orbach, D.N. The sex life of harbor porpoises (Phocoena phocoena): Lateralized and aerial behavior. Aquat. Mamm. 2018, 44, 620–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orbach, D.N.; Brennan, P.L.R.; Hedrick, B.P.; Keener, W.; Webber, M.A.; Mesnick, S.L. Asymmetric and spiraled genitalia coevolve with unique lateralized mating behavior. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webber, M.A.; Keener, W.; Wahlberg, M.; Elliser, C.R.; MacIver, K.; Torres Ortiz, S.; Jakobsen, F.; Hamel, H.; Rieger, A.; Siebert, U.; et al. Sexual Behavior and Anatomy in Porpoises. In Sex in Cetaceans: Morphology, Behavior, and the Evolution of Sexual Strategies; Würsig, B., Orbach, D., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 415–441. ISBN 978-3-031-35650-6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nachtshelm, D.A.; Viquerat, S.; Ramirez-Martinez, N.C.; Unger, B.; Siebert, U.; Gilles, A. Small Cetacean in a Human High-Use Area: Trends in Harbor Porpoise Abundance in the North Sea Over Two Decades. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 7, 606609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IJsseldijk, L.L.; van den Broek, J.; Kik, M.J.L.; Leopold, M.F.; Rebolledo, E.B.; Gröne, A.; Heesterbeek, H. Using marine mammal necropsy data in animal health surveillance: The case of the harbor porpoise in the Southern North Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 10, 1306294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benke, H.; Bräger, S.; Dähne, M.; Gallus, A.; Hansen, S.; Honnef, C.G.; Jabbusch, M.; Koblitz, J.C.; Krügel, K.; Liebschner, A.; et al. Baltic Sea harbour porpoise populations: Status and conservation needs derived from recent survey results. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2014, 495, 275–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabe-Nielsen, J.; Sibly, R.M.; Tougaard, J.; Teilmann, J.; Sveegaard, S. Effects of noise and by-catch on a Danish harbour porpoise population. Ecol. Mod. 2014, 272, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, K.; Siebert, U.; Fontaine, M.; Jauniaux, T.; Holsbeek, L.; Bouquegneau, J.-M. Ecological and pathological factors related to trace metal concentrations in harbour porpoises Phocoena phocoena from the North Sea and adjacent areas. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2004, 281, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verfuß, U.K.; Honnef, C.G.; Meding, A.; Dähne, M.; Mundry, R.; Benke, H. Geographical and seasonal variation of harbour porpoise (Phocoena phocoena) presence in the German Baltic Sea revealed by passive acoustic monitoring. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2007, 87, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sveegaard, S.; Andreasen, H.; Mouritsen, K.N.; Jeppesen, J.P.; Teilmann, J.; Kinze, C.C. Correlation between the seasonal distribution of harbour porpoises and their prey in the Sound, Baltic Sea. Mar. Biol. 2012, 159, 1029–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamins, S.; Dale, A.; Hastie, G.; Waggitt, J.J.; Lea, M.-A.; Scott, B.; Wilson, B. Confusion reigns? A review of marine megafauna interactions with tidal-stream environments. In Oceanography and Marine Biology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015; Volume 53, pp. 1–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamins, S.; van Geel, N.; Hastie, G.; Elliott, J.; Wilson, B. Harbour porpoise distribution can vary at small spatiotemporal scales in energetic habitats. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2016, 141, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Beest, F.M.; Teilmann, J.; Dietz, R.; Galatius, A.; Mikkelsen, L.; Stalder, D.; Sveegaard, S.; Nabe-Nielsen, J. Environmental drivers of harbour porpoise fine-scale movements. Mar. Biol. 2018, 165, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stalder, D.; van Beest, F.M.; Sveegaard, S.; Dietz, R.; Teilmann, J.; Nabe-Nielsen, J. Influence of environmental variability on harbour porpoise movement. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2020, 648, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dracott, K.; Robinson, C.V.; Brown-Dussault, A.; Birdsall, C.; Barrett-Lennard, L. Porpoises after dark: Seasonal and diel patterns in Pacific harbour porpoise (Phocoena phocoena vomerina) aggregations at one of North America’s fastest growing ports. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 1010095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stedt, J.; Wahlberg, M.; Calström, J.; Nilsson, P.A.; Amundin, M.; Oskolkov, N.; Carlsson, P. Micro-scale spatial preference and temporal cyclicity linked to foraging in harbour porpoises. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2023, 708, 143–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliser, C.R.; MacIver, K.H.; Green, M. Group characteristics, site fidelity, and photo-identification of harbor porpoises, Phocoena phocoena, in Burrows Pass, Fidalgo Island, Washington. Mar. Mamm. Sci. 2018, 34, 365–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliser, C.R.; Hall, A. Return of the Salish Sea Harbor Porpoise, Phocoena phocoena: Knowledge Gaps, Current Research, and What We Need to Do to Protect Their Future. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 618177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, P.A.; Forester, B.R.; Forney, K.A.; Crossman, C.A.; Hancock-Hanser, B.L.; Robertson, K.M.; Barrett-Lennard, L.G.; Baird, R.W.; Calambokidis, J.; Gearin, P.; et al. Population structure in a continuously distributed coastal marine species, the harbor porpoise, based on microhaplotypes derived from poor-quality samples. Mol. Ecol. 2021, 30, 1457–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, R.; Hall, A.; Winship, A. Potential limits to anthropogenic mortality of small cetaceans in coastal waters of British Columbia. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2008, 65, 1867–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlén, I.; Nunny, L.; Simmonds, M.P. Out of sight, out of mind: How conservation is failing European porpoises. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 61748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, P.G.H. European Whales, Dolphins and Porpoises: Maine Mammal Conservation in Practice; Academic Press: London, UK, 2020; pp. 1–306. ISBN 9780128190531. [Google Scholar]
- Government of Canada Species at Risk Act: Harbour Porpoise. Available online: https://www.canada.ca/en/environment-climate-change/services/species-risk-public-registry/consultation-documents/harbour-porpoise-2023.html (accessed on 17 January 2025).
- Washington Department of Fish and Wildlife, Species & Habitats: Harbor Porpoise. Available online: https://wdfw.wa.gov/species-habitats/species/phocoena-phocoena (accessed on 17 January 2025).
- Scheffer, V.B.; Slipp, J.W. The whales and dolphins of Washington State with the key to the cetaceans of the west coast of North America. Am. Midl. Nat. 1948, 39, 257–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calambokidis, J.; Steiger, G.H.; Cubbage, J.C. Marine Mammals in the Southwestern Strait of Juan de Fuca: Natural History and Potential Impacts of Harbor Development in Neah Bay; Cascadia Research Collective: Olympia, WA, USA, 1987; pp. 1–109. [Google Scholar]
- Barlow, J. Harbor porpoise, Phocoena phocoena, abundance estimation for California, Oregon, and Washington: I. Ship surveys. Fish. Bull. 1988, 86, 417–432. [Google Scholar]
- Raum-Suryan, K.L.; Harvey, J.T. Distribution and abundance of and habitat use by harbor porpoise, Phocoena phocoena, off the northern San Juan Islands, Washington. Fish. Bull. 1998, 96, 808–822. [Google Scholar]
- Gaydos, J.K.; Pearson, S.F. Birds and mammals that depend on the Salish Sea: A compilation. Northwestern Nat. 2011, 92, 79–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osmek, S.; Calambokidis, J.; Laake, J.; Gearin, P.; Delong, R.; Scordino, J.; Jeffries, S.; Brown, R. Assessment of the Status of Harbor Porpoise (Phocoena phocoena) in Oregon and Washington Waters; Department of Commerce, NOAA, National Marine Fisheries Service, Alaska Fisheries Center: Seattle, WA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Evenson, J.R.; Anderson, D.; Murphie, B.L.; Cyra, T.A.; Calambokidis, J. Disappearance and Return of Harbor Porpoise to Puget Sound: 20 Year Pattern Revealed from Winter Aerial Surveys; Technical Report; Washington Department of Fish and Wildlife, Wildlife Program and Cascadia Research Collective: Olympia, WA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Carretta, J.V.; Oleson, E.; Baker, J.; Weller, D.W.; Lang, A.R.; Forney, K.A.; Muto, M.M.; Hanson, B.; Orr, A.J.; Huber, H.; et al. U.S. Pacific Draft Marine Mammal Stock Assessments: 2015; Department of Commerce, NOAA Southwest Fisheries Science Center: San Diego, CA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Vallejo, G.C.; Grellier, K.; Nelson, E.J.; McGregor, R.M.; Canning, S.J.; Caryl, F.M.; McLean, N. Responses of two marine top predators to an offshore wind farm. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 7, 8698–8708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenton, H.; Daoust, P.-Y.; Forzán, M.J.; Vanderstichel, R.V.; Ford, J.B.K.; Spaven, L.; Lair, S.; Raverty, S. Causes of mortality of harbor porpoises Phocoena phocoena along the Atlantic and Pacific coasts of Canada. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2017, 122, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calambokidis, J.; Barlow, J. Chlorinated hydrocarbon concentrations and their use for describing population discreteness in harbor porpoises from Washington, Oregon, and California. In Marine Mammal Strandings in the United States, Proceedings of the Second Marine Mammal Stranding Workshop, Miami, FL, USA, 3–5 December 1987; Reynolds, J.E., III, Odell, D.K., Eds.; NOAA Technical Report NMFS: Miami, FL, USA, 1991; pp. 101–110. [Google Scholar]
- Norman, S.A.; Winfield, Z.C.; Rickman, B.H.; Usenko, S.; Klope, M.; Berta, S.; Dubpernell, S.; Garrett, H.; Adams, M.J.; Lambourn, D.; et al. Persistent Organic Pollutant and Hormone Levels in Harbor Porpoise with B Cell Lymphoma. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2017, 72, 596–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, R.S.; Curnick, D.J.; Brownlow, A.; Barber, J.L.; Barnett, J.; Davison, N.J.; Deaville, R.; Doeschate, M.T.; Perkins, M.; Jepson, P.D.; et al. Polychlorinated biphenyls are associated with reduced testes weights in harbour porpoises (Phocoena phocoena). Environ. Int. 2021, 150, 106303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, J.K.B.; Ellis, G.M.; Barrett-Lennard, L.G.; Morton, A.B.; Palm, R.S.; Balcomb, K.C., III. Dietary specialization in two sympatric populations of killer whales (Orcinus orca) in coastal British Columbia and adjacent waters. Can. J. Zool. 1998, 76, 1456–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalheim, M.E.; White, P.A. Ecological aspects of transient killer whales (Orcinus orca) as predators in southeastern Alaska. Wildl. Biol. 2010, 16, 308–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, R.S. The role of long-term study in understanding the social structure of a bottlenose dolphin community. In Dolphin Societies; Pryor, K., Norris, K.S., Eds.; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1991; pp. 199–255. [Google Scholar]
- Connor, R.C.; Smolker, R.A.; Richards, A.F. Two levels of alliance formation among male bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops sp.). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 987–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, J.; Connor, R.C.; Barre, L.M.; Heithaus, M.R. Female reproductive success in bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops sp.): Life history, habitat, provisioning, and group-size effects. Behav. Ecol. 2000, 11, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, C.A.; Brunnick, B.J.; Herzing, D.L.; Baldwin, J.D. The social structure of bottlenose dolphins, Tursiops truncatus, in the Bahamas. Mar. Mamm. Sci. 2004, 20, 688–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kent, E.E.; Mazzoil, M.; McCulloch, S.D.; Defran, R.H. Group characteristics and social affiliation patterns of bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) in the Indian River Lagoon, Florida. Fla. Sci. 2008, 71, 149–168. [Google Scholar]
- Elliser, C.R.; Herzing, D.L. Community structure and cluster definition of Atlantic spotted dolphins, Stenella frontalis, in the Bahamas. Mar. Mamm. Sci. 2012, 28, e486–e502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliser, C.R.; Volker, C.L.; Herzing, D.L. Integration of a social cluster of Atlantic spotted dolphins (Stenella frontalis) after a large immigration event in 2013. Mar. Mamm. Sci. 2022, 39, 114–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliser, C.R.; Herzing, D.L. Long-term social structure of a resident community of Atlantic spotted dolphins, Stenella frontalis, in the Bahamas 1991–2002. Mar. Mamm. Sci. 2014, 30, 308–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaskin, D.E.; Watson, A.P. The harbor porpoise, Phocoena phocoena, in Fish Harbour, New Brunswick, Canada: Occupancy, distribution, and movements. Fish. Bull. 1985, 83, 427–442. [Google Scholar]
- Koopman, H.N.; Gaskin, D.E. Individual and geographical variation in pigmentation patterns of the harbour porpoise, Phocoena phocoena (L.). Can. J. Zool. 1994, 72, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flaherty, C.; Stark, S. Harbor Porpoise (Phocoena phocoena) Assessment, in Washington Sound; Final Report for Subcontract #80-ABA-3584 to the National Marine Mammal Laboratory; NMFS: Seattle, WA, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Hammond, P.S.; Berggren, P.; Benke, H.; Borchers, D.L.; Collet, A.; Heide-Jørgensen, M.P.; Heimlich, S.; Hiby, A.R.; Leopold, M.F.; Øien, N. Abundance of harbour porpoise and other cetaceans in the North Sea and adjacent waters. J. Appl. Ecol. 2002, 39, 361–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliser, C.R.; van der Linde, K.; MacIver, K. Adapting photo-identification methods to study poorly marked cetaceans: A case study for common dolphins and harbor porpoises. Mamm. Biol. 2022, 102, 811–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercer, M.C. Observations on distribution and intraspecific variation in pigmentation patterns of odontocete Cetacea in the western North Atlantic. J. Fish. Res. Board Can. 1973, 30, 1111–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Read, A.J.; Keener, W.; Webber, M.A.; Siebert, U. Harbor porpoise Phocoena phocoena. In Ridgeway and Harrison’s Handbook of Marine Mammals, Vol. 1, Coastal Dolphins & Porpoises, 2nd ed.; Jefferson, T.A., Ed.; Elsevier: San Diego, CA, USA, 2024; pp. 421–486. ISBN 9780443137464. [Google Scholar]
- Dunn, H. People’s porpoise project 2018–19: Photo-ID methods. Sea Trust CIC 2019, 1–14. Available online: https://www.seatrust.org.uk/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/Peoples-Porpoise-Project-Photo-ID-Methods.pdf (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- Olie, R.; Zanderink, F. Bruinvissen herkennen: Wendy of Elliptica? Zoogdier 2023, 34, 12–14. Available online: https://rugvin.nl/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/Zoogdier-december-23-Foto-ID-Bruinvissen.pdf (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- Hamel, H.; Ortiz, S.T.; Wahlberg, M. Long-term observations reveal short-term mother-calf affiliation in wild harbour porpoises. Anim. Behav. 2024, 219, 122992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shane, S.H. Behavior and ecology of the bottlenose dolphin at Sanibel Island, Florida. In The Bottlenose Dolphin; Leatherwood, S., Reeves, R.R., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1990; pp. 245–265. ISBN 0-12-440280-1. [Google Scholar]
- Noren, S.R.; Noren, D.P.; Gaydos, J.K. Living in the fast lane: Rapid development of the locomotor muscle in immature harbor porpoises (Phocoena phocoena). J. Comp. Physiol. B. 2014, 184, 1065–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, J.D.; Speakman, T.; Zolman, E.; Schwacke, L.H. Automating image matching, cataloging, and analysis for photo-identification research. Aquat. Mamm. 2006, 32, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seabold, S.; Perktold, J. Statsmodels: Econometric and statistical modeling with python. In Proceedings of the SciPly, Austin, TX, USA, 28 June–3 July 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Terpilowski, M.A. scikit-posthocs: Pairwise multiple comparison tests in Python. J. Open Source Softw. 2019, 4, 1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaps, M.; Lamberson, W.R. Biostatistics for Animal Science, 3rd ed.; CABI Publishing: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; ISBN 978-1-78639-035-6. [Google Scholar]
- Chabanne, D.B.H.; Finn, H.; Bejder, L. Identifying the relevant local population for environmental impact assessments of mobile marine fauna. Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockyer, C.; Kinze, C. Status, ecology and life history of harbour porpoise (Phocoena phocoena), in Danish waters. NAMMCO Sci. Publ. 2003, 5, 143–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, S.J.; Keener, W.; Szczepaniak, I.D.; Webber, M.A. Return of harbor porpoises (Phocoena phocoena) to San Francisco Bay. Aquat. Mamm. 2017, 43, 691–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.; Shuster, L.; Elliser, C.R.; MacIver, K.; Gless, E.J.; Krieger, J.; Hall, A. Harbor Porpoise Aggregations in the Salish Sea. Oceans 2023, 4, 269–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camphuysen, K.C.J.; Krop, A. Maternal care, calf training and site fidelity in a wild harbour porpoise in the North Sea. Lutra 2011, 54, 123–126. [Google Scholar]
- Zerbini, A.N.; Goetz, K.T.; Forney, K.A.; Boyd, C. Estimating abundance of an elusive cetacean in a complex environment: Harbor porpoises (Phocoena phocoena) in inland waters of Southeast Alaska. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 966489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerbini, A.N.; Parsons, K.M.; Goetz, K.T.; Angliss, R.P.; Young, N.C. Identification of Demographically Independent Populations Within the Currently Designated Southeast Alaska Harbor Porpoise Stock; NOAA Technical Memorandum NMFS, Alaska Fisheries Science Center: Juneau, AK, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, D.W.; Westgate, A.J.; Read, A.J. Effects of fine-scale oceanographic features on the distribution and movements of harbour porpoises Phocoena phocoena in the Bay of Fundy. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2005, 295, 279–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, N.H.; Teilmann, J.; Sveegaard, S.; Hansen, R.G.; Sinding, M.-H.S.; Dietz, R.; Heide-Jørgensen, M.P. Oceanic movements, site fidelity and deep diving in harbour porpoises from Greenland show limited similarities to animals from the North Sea. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2018, 597, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilles, A.; Adler, S.; Kaschner, K.; Scheidat, M.; Siebert, U. Modelling harbour porpoise seasonal density as a function of the German Bight environment: Implications for management. Endang. Species Res. 2011, 14, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheidat, M.; Verdaat, H.; Aarts, G. Using aerial surveys to estimate density and distribution of harbour porpoises in Dutch waters. J. Sea Res. 2012, 69, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peschko, V.; Ronnenberg, K.; Siebert, U.; Gilles, A. Trends of harbour porpoise (Phocoena phocoena) density in the southern North Sea. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 60, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliser, C.R.; Hessing, S.; MacIver, K.H.; Webber, M.A.; Keener, W. Harbor porpoises (Phocoena phocoena vomerina) catching and handling large fish on the U.S. West Coast. Aquat. Mamm. 2020, 46, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skov, H.; Thomsen, F. Resolving fine-scale spatio-temporal dynamics in the harbour porpoise Phocoena phocoena. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2008, 373, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stedt, J.; Hamel, H.; Ortiz, S.T.; Kristensen, J.H.; Wahlberg, M. Harbour porpoises are flexible predators displaying context-dependent foraging behaviours. Ecol. Evol. 2024, 14, e70671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehls, G.; Zydelis, R.; Matuschek, R.; Brandt, M.; Diederichs, A.; Hoeschle, C.; Thomsen, F. Impact of high marine traffic on harbor porpoise: Effect on abundance and distribution. In The Effects of Noise on Aquatic Life; Popper, A.N., Sisneros, J., Hawkins, A.D., Thomsen, F., Eds.; Springer Nature: Cham. Switzerland, 2024; pp. 1–28. ISBN 9783031104176. [Google Scholar]
- Wisniewska, D.M.; Johnson, M.; Teilmann, J.; Siebert, U.; Galatius, A.; Dietz, R.; Madsen, P.T. High rates of vessel noise disrupt foraging in wild harbour porpoises (Phocoena phocoena). Proc. R. Soc. B 2018, 285, 20172314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjørge, A.; Tolley, K.A. Harbor porpoise. In Encyclopedia of Marine Mammals, 3rd ed.; Würsig, B., Thewissen, J.G.M., Kovacs, K.M., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2018; pp. 448–451. ISBN 9780128043271. [Google Scholar]
- Møhl-Hansen, U. Investigations on reproduction and growth of the porpoise (Phocaena phocaena (L.)) from the Baltic. Vidensk. Meddr. Dan. Naturh. Foren 1954, 116, 369–396. [Google Scholar]
- Sørensen, T.B.; Kinze, C.C. Reproduction and reproductive seasonality in Danish harbour porpoises, Phocoena phocoena. Ophelia 1994, 39, 159–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, J.; Smuts, B.B. Natal attraction: Allomaternal care and mother-infant separations in wild bottlenose dolphins. Anim. Behav. 1998, 55, 1097–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, H.M.; Greer, T.; Solangi, M.; Kuczaj, S.A., II. All mothers are not the same: Maternal styles in bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus). Int. J. Comp. Psychol. 2007, 20, 35–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudenski, K.M.; Ribic, C.A.; Hill, H.M.M.; Bolton, T.T. Evidence for maternal style among adult female dolphins when sharing pectoral fin contacts with their calves. Anim. Behav. Cogn. 2021, 8, 52–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zein, B.; Woelfing, B.; Dähne, M.; Schaffeld, T.; Ludwig, S.; Rye, J.H.; Baltzer, J.; Ruser, A.; Siebert, U. Time and tide: Seasonal, diel and tidal rhythms in Wadden Sea harbour porpoises (Phocoena phocoena). PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0213348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holdman, A.K.; Haxel, J.H.; Klinck, H.; Torres, L.G. Acoustic monitoring reveals the times and tides of harbor porpoise (Phocoena phocoena) distribution off central Oregon, U.S.A. Mar. Mamm. Sci. 2019, 35, 164–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, L. Diurnal and tidal variations in habitat use of the harbour porpoise (Phocoena phocoena) in southwest Britain. Aquat. Mamm. 2008, 34, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirotta, E.; Thompson, P.M.; Miller, P.I.; Brookes, K.L.; Cheney, B.; Barton, T.R.; Graham, I.M.; Lusseau, D. Scale-dependent foraging ecology of a marine top predator modelled using passive acoustic data. Func. Ecol. 2014, 28, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Read, A.J.; Hohn, A.A. Life in the fast lane: The life history of harbor porpoises from the Gulf of Maine. Mar. Mamm. Sci. 1995, 11, 423–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Read, A.J. Age at Sexual Maturity and Pregnancy Rates of Harbour Porpoises Phocoena phocoena from the Bay of Fundy. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1990, 47, 561–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calambokidis, J.; Steiger, G.H.; Curtice, C.; Harrison, J.; Van Parijs, S.M.; Halpin, P.N. Biologically important areas for selected cetaceans within U.S. waters—West coast region. In Biologically Important Areas for Cetaceans Within U.S. Water; Van Parijs, S.M., Curtice, C., Ferguson, M.C., Eds. Aquat. Mamm. (Spec. Issue) 2015, 41, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Season | Number of Observations | Number of Sightings | Percentage (%) of Observations with Sightings | Percentage (%) of Time Observing Porpoises | SPUE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Winter | 192 | 334 | 86.5% | 42.1% | 1.74 |
| Spring | 322 | 610 | 89.8% | 53.9% | 1.89 |
| Summer | 338 | 488 | 75.7% | 31.3% | 1.44 |
| Fall | 282 | 487 | 90.4% | 53.2% | 1.73 |
| Total | 1134 | 1919 | 85.19% | 45.0% | 1.69 |
| Number of Total Sightings | Mean Re-Sighting Rate | |
|---|---|---|
| All non-calf individuals (n = 164) | 1–125 | 5.4 |
| Re-sighted at least twice (n = 113) | 2–125 | 9.1 |
| Re-sighted in at least 2 different years (n = 65) | 2–125 | 12.8 |
| Mom | Re-Sights | # Calves | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ARC | 2 | 1 | UN | ||||||||||
| AUR | 4 | 2 | UN | AUS | |||||||||
| DOL | 1 | 1 | X | ||||||||||
| DRA | 2 | 2 | UN | DAM | |||||||||
| FAL | 19 | 1 | UN | ||||||||||
| FLI | 7 | 2 | UN | UN | |||||||||
| MIL | 39 | 2 | MIN | MEL | |||||||||
| PEA | 2 | 2 | UN | PAP | |||||||||
| PIA * | 45 | 4 | UN | PIC * | UN | PIZ | ** | PER | PIO | ||||
| POI | 124 | 4 | PHA | PHS | UN | UN | |||||||
| PIC * | 10 | 1 | born | NA | PIP * | ||||||||
| POL | 2 | 1 | UN | ||||||||||
| RAI | 71 | 6 | UN | RAN | UN | ** | RAB | UN | UN | ||||
| SLE | 11 | 1 | UN | ||||||||||
| SIC | 4 | 1 | UN | ||||||||||
| SLI | 41 | 2 | UN | UN | |||||||||
| SMO | 14 | 1 | UN | ||||||||||
| SLO | 2 | 1 | UN |
| Travel | Foraging | Social | Unknown | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Winter | 35.9% (n = 120) | 32.9% (n = 93) | 5.10% (n = 17) | 34.1% (n = 114) |
| Spring | 23.6% (n = 144) | 36.9% (n = 225) | 6.10% (n = 37) | 42.8% (n = 261) |
| Summer | 26.2% (n = 128) | 23.4% (n = 114) | 7.20% (n = 35) | 48.2% (n = 235) |
| Fall | 24.4% (n = 119) | 38.4% (n = 187) | 9.90% (n = 48) | 40.7% (n = 198) |
| Slack low | 31.28% (n = 56) | 35.19% (n = 63) | 6.15% (n = 11) | 34.08% (n = 61) |
| Flood | 18.31% (n = 156) | 40.02% (n = 341) | 11.62% (n = 99) | 41.31% (n = 352) |
| Slack High | 19.67% (n = 24) | 46.72% (n = 57) | 9.02% (n = 11) | 40.98% (n = 50) |
| Ebb | 36.57% (n = 325) | 20.88% (n = 157) | 2.13% (n = 16) | 44.15% (n = 332) |
| Year | Number of Mating Attempts | Number of Months | Seasons |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2015 | 1 | 1 | Sp |
| 2017 | 4 | 3 | Sp, F, W |
| 2018 | 4 | 4 | Sp, F, W |
| 2019 | 9 | 5 | Sp, Su, F, W |
| 2020 | 17 | 8 | Sp, Su, F, W |
| 2021 | 17 | 9 | Sp, Su, F, W |
| 2022 | 3 | 3 | Su, F |
| 2023 | 11 | 7 | Sp, Su, F, W |
| 2024 | 18 | 8 | Sp, Su, F, W |
| Total | 84 | Seen in every month | In all seasons |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Elliser, C.R.; White, K.H.; Hansen, M.C. Resident Harbor Porpoises (Phocoena phocoena vomerina) in the Salish Sea: Photo-Identification Shows Long-Term Site Fidelity, Natal Philopatry, and Provides Insights into Longevity and Behavior. Oceans 2025, 6, 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/oceans6010009
Elliser CR, White KH, Hansen MC. Resident Harbor Porpoises (Phocoena phocoena vomerina) in the Salish Sea: Photo-Identification Shows Long-Term Site Fidelity, Natal Philopatry, and Provides Insights into Longevity and Behavior. Oceans. 2025; 6(1):9. https://doi.org/10.3390/oceans6010009
Chicago/Turabian StyleElliser, Cindy R., Katrina H. White, and Maia C. Hansen. 2025. "Resident Harbor Porpoises (Phocoena phocoena vomerina) in the Salish Sea: Photo-Identification Shows Long-Term Site Fidelity, Natal Philopatry, and Provides Insights into Longevity and Behavior" Oceans 6, no. 1: 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/oceans6010009
APA StyleElliser, C. R., White, K. H., & Hansen, M. C. (2025). Resident Harbor Porpoises (Phocoena phocoena vomerina) in the Salish Sea: Photo-Identification Shows Long-Term Site Fidelity, Natal Philopatry, and Provides Insights into Longevity and Behavior. Oceans, 6(1), 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/oceans6010009






