Innate Immunity Response to BK Virus Infection in Polyomavirus-Associated Nephropathy in Kidney Transplant Recipients
Abstract
:1. Introduction
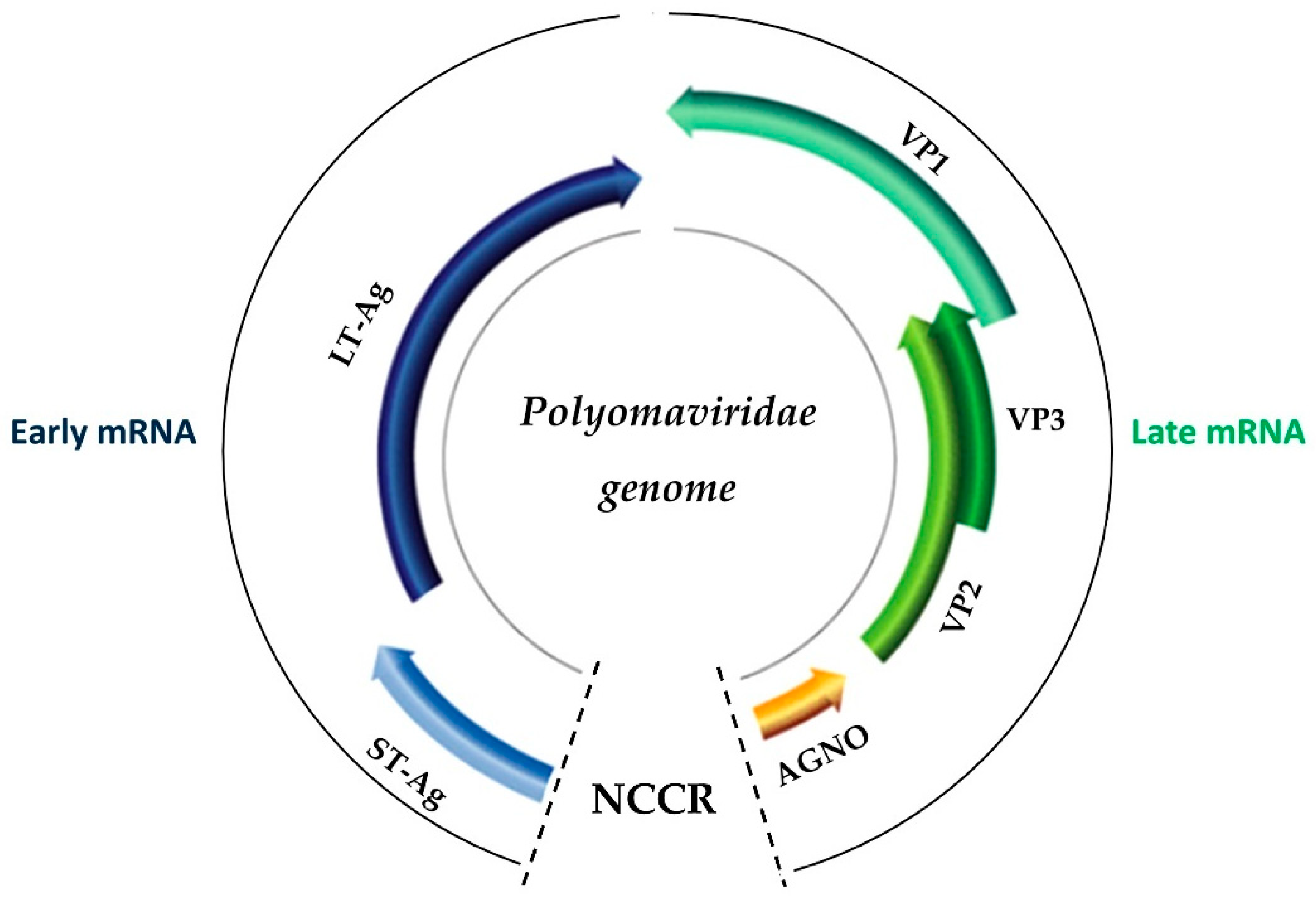
2. The Biology of BK Virus
3. Innate Immunity in the BK Virus
3.1. An Overview of the Innate Immune Response in the BK Virus
3.2. Immunity Cells against the BK Virus
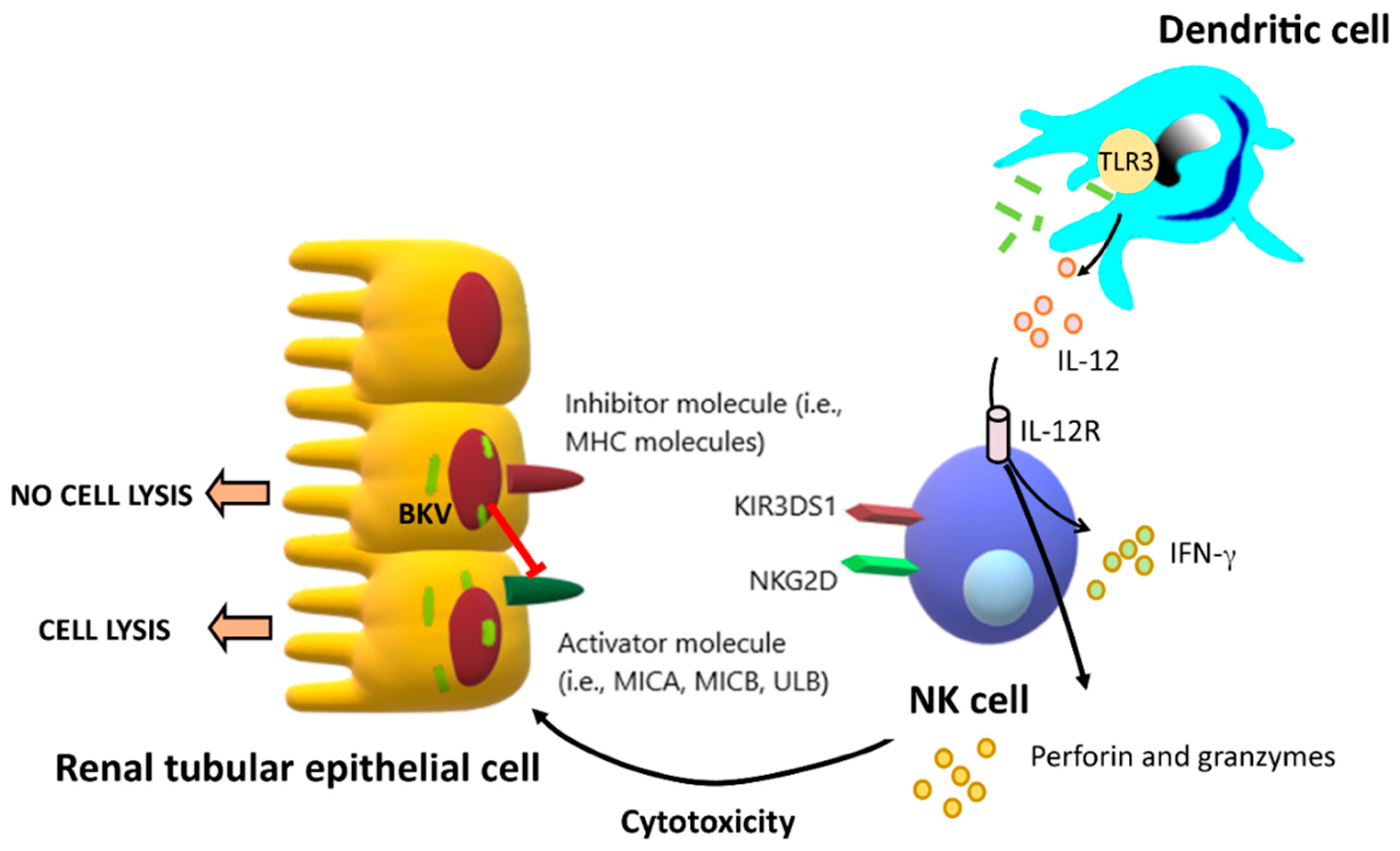
3.2.1. Natural Killer Cells (NK Cells)
3.2.2. Dendritic Cells
3.2.3. Neutrophils and Eosinophils
3.2.4. Gamma-Delta (γδ) T Cells
3.3. Complement System of the Innate Immune Response against the BK Virus
3.4. Toll-like Receptors in the Innate Immunity Response against the BK Virus
3.5. Cytokines in the Innate Immunity Response to the BK Virus
3.6. Notch Signaling and Nuclear Factors
4. BKVAN and Allograft Rejection
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gardner, S.D.; Field, A.M.; Coleman, D.V.; Hulme, B. New human papovavirus (B.K.) isolated from urine after renal transplantation. Lancet 1971, 1, 1253–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, I.; Tasneem, F.; Umer, M.; Pervaiz, A.; Raza, M.; Arshad, M.I.; Shahzad, N. Specific and quantitative detection of Human polyomaviruses BKPyV and JCPyV in the healthy Pakistani population. Virol. J. 2017, 14, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramos, E.; Drachenberg, C.B.; Wali, R.; Hirsch, H.H. The decade of polyomavirus BK-associated nephropathy: State of affairs. Transplantation 2009, 87, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirsch, H.H.; Randhawa, P.; AST Infectious Diseases Community of Practice. BK polyomavirus in solid organ transplantation. Am. J. Transplant. 2013, 13 (Suppl. 4), 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laskin, B.L.; Denburg, M.R.; Furth, S.L.; Moatz, T.; Altrich, M.; Kleiboeker, S.; Lutzko, C.; Zhu, X.; Blackard, J.T.; Jodele, S.; et al. The natural history of BK polyomavirus and the host immune response after stem cell transplantation. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2019, 71, 3044–3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, N.C.; Vilchez, R.A.; Killen, D.E.; Zanwar, P.; Sroller, V.; Eldin, K.W.; López-Terrada, D.; Butel, J.S. Detection of polyomavirus SV40 in tonsils from immunocompetent children. J. Clin. Virol. 2008, 43, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Babel, N.; Fendt, J.; Karaivanov, S.; Bold, G.; Arnold, S.; Sefrin, A.; Lieske, E.; Hoffzimmer, M.; Dziubianau, M.; Bethke, N.; et al. Sustained BK viruria as an early marker for the development of BKV-associated nephropathy: Analysis of 4128 urine and serum samples. Transplantation 2009, 88, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Sato, Y.; Sekizuka, T.; Kuroda, M.; Suzuki, T.; Hasegawa, H.; Katano, H. High expression of JC polyomavirus-encoded microRNAs in progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy tissues and its repressive role in virus replication. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papa, N.; Zanotta, N.; Knowles, A.; Orzan, E.; Comar, M. Detection of Malawi polyomavirus sequences in secondary lymphoid tissues from Italian healthy children: A transient site of infection. Virol. J. 2016, 13, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Comar, M.; Segat, L.; Crovella, S.; Bovenzi, M.; Cortini, E.; Tognon, M. The significance of mannose-binding lectin gene polymorphisms on the risk of BK virus coinfection in women with human papillomavirus–positive cervical lesions. Hum. Immunol. 2011, 72, 663–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longhi, G.; Pietropaolo, V.; Mischitelli, M.; Longhi, C.; Conte, M.P.; Marchetti, M.; Tinari, A.; Valenti, P.; Degener, A.M.; Seganti, L.; et al. Lactoferrin inhibits early steps of human BK polyomavirus infection. Antivir. Res. 2006, 72, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurdiss, D.L.; Frank, M.; Snowden, J.S.; Macdonald, A.; Ranson, N.A. The Structure of an Infectious Human Polyomavirus and Its Interactions with Cellular Receptors. Structure 2018, 26, 839–847.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hurdiss, D.L.; Morgan, E.L.; Thompson, R.F.; Prescott, E.L.; Panou, M.M.; Macdonald, A.; Ranson, N.A. New Structural Insights into the Genome and Minor Capsid Proteins of BK Polyomavirus using Cryo-Electron Microscopy. Structure 2016, 24, 528–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moriyama, T.; Sorokin, A. Intracellular trafficking pathway of BK Virus in human renal proximal tubular epithelial cells. Virology 2008, 371, 336–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cubitt, C.L. Molecular genetics of the BK virus. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2006, 577, 85–95. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, I.; Tasneem, F.; Gilani, U.S.; Arshad, M.I.; Farhan Ul Haque, M.; Abbas, Z.; Umer, M.; Shahzad, N. Human BK and JC polyomaviruses: Molecular insights and prevalence in Asia. Virus Res. 2020, 278, 197860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, G.H.; Hirsch, H.H.; Rinaldo, C.H. Functional analysis of polyomavirus BK non-coding control region quasispecies from kidney-transplanted recipients. J. Med. Virol. 2009, 81, 1959–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, S.; Mieczkowski, P.A.; Weida, C.; Huo, J.; Roehrs, P.; Singh, H.K.; Nickeleit, V. BK polyomavirus nephropathy with systemic viral spread: Whole genome sequencing data from a fatal case of BKPyV infection. Transplant. Infect. Dis. 2020, 22, e13269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, S.; Jeong, B.H.; Ikegaya, H.; Kim, Y.S.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, M.; Chao, Y.; Suzuki, M.; Kitamura, T.; Homma, Y.; et al. Comparison of the distribution patterns of BK polyomavirus lineages among China, Korea and Japan: Implications for human migrations in northeast Asia. Microbiol. Immunol. 2009, 53, 266–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickeleit, V.; Singh, H.K.; Dadhania, D.; Cornea, V.; El-Husseini, A.; Castellanos, A.; Davis, V.G.; Waid, T.; Seshan, S.V. The 2018 Banff Working Group classification of definitive polyomavirus nephropathy: A multicenter validation study in the modern era. Am. J. Transplant. 2020, 21, 669–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zeng, G.; Randhawa, P.S. Detection of BKV encoded mature MicroRNAs in kidney transplant patients: Clinical and biologic insights. J. Clin. Virol. 2019, 119, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trydzenskaya, H.; Juerchott, K.; Lachmann, N.; Kotsch, K.; Kunert, K.; Weist, B.; Schonemann, C.; Schindler, R.; Nickel, P.; Melzig, M.F.; et al. The genetic predisposition of natural killer cell to BK virus-associated nephropathy in renal transplant patients. Kidney Int. 2013, 84, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Womer, K.L.; Huang, Y.; Herren, H.; Dibadj, K.; Peng, R.; Murawski, M.; Shraybman, R.; Patton, P.; Clare-Salzler, M.J.; Kaplan, B. Dendritic cell deficiency associated with development of BK viremia and nephropathy in renal transplant recipients. Transplantation 2010, 89, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yapici, U.; Kers, J.; Slavujevic-Letic, I.; Stokman, G.; Roelofs, J.J.; van Aalderen, M.C.; Groothoff, J.W.; de Boer, O.J.; van der Pant, K.A.; Claessen, N.; et al. Intragraft Blood Dendritic Cell Antigen-1-Positive Myeloid Dendritic Cells Increase during BK Polyomavirus-Associated Nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 27, 2502–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ribeiro, A.; Wörnle, M.; Motamedi, N.; Anders, H.J.; Gröne, E.F.; Nitschko, H.; Kurktschiev, P.; Debiec, H.; Kretzler, M.; Cohen, C.D.; et al. Activation of innate immune defense mechanisms contributes to polyomavirus BK-associated nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2012, 81, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mannon, R.B.; Hoffmann, S.C.; Kampen, R.L.; Cheng, O.C.; Kleiner, D.E.; Ryschkewitsch, C.; Curfman, B.; Major, E.; Hale, D.A.; Kirk, A.D. Molecular evaluation of BK polyomavirus nephropathy. Am. J. Transplant. 2005, 5, 2883–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Federico, S.; Pozzetti, L.; Papa, A.; Carullo, G.; Gemma, S.; Butini, S.; Campiani, G.; Relitti, N. Modulation of the Innate Immune Response by Targeting Toll-like Receptors: A Perspective on their Agonists and Antagonists. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 13466–13513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kariminik, A.; Yaghobi, R.; Dabiri, S. Innate Immunity and BK Virus: Prospective Strategies. Viral. Immunol. 2016, 29, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nainu, F.; Shiratsuchi, A.; Nakanishi, Y. Induction of Apoptosis and Subsequent Phagocytosis of Virus-Infected Cells as an Antiviral Mechanism. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, H.S.; Smyth, M.J. NK cells and apoptosis. Immunol. Cell Biol. 1999, 77, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raulet, D.H. Roles of the NKG2D immunoreceptor and its ligands. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 3, 781–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauman, Y.; Nachmani, D.; Vitenshtein, A.; Tsukerman, P.; Drayman, N.; Stern-Ginossar, N.; Lankry, D.; Gruda, R.; Mandelboim, O. An identical miRNA of the human JC and BK polyoma viruses targets the stress-induced ligand ULBP3 to escape immune elimination. Cell Host Microbe 2011, 9, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koch, C.; Kim, Y.; Zöller, T.; Born, C.; Steinle, A. Chronic NKG2D Engagement In Vivo Differentially Impacts NK Cell Responsiveness by Activating NK Receptors. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McNerney, M.E.; Lee, K.-M.; Zhou, P.; Molinero, L.; Mashayekhi, M.; Guzior, D.; Sattar, H.; Kuppireddi, S.; Wang, C.-R.; Kumar, V.; et al. Role of Natural Killer Cell Subsets in Cardiac Allograft Rejection. Am. J. Transplant. 2006, 6, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Bergen, J.; Thompson, A.; Haasnoot, G.W.; Roodnat, J.I.; de Fijter, J.W.; Claas, F.H.; Koning, F.; Doxiadis, I.I. KIR-ligand mismatches are associated with reduced long-term graft survival in HLA-compatible kidney transplantation. Am. J. Transplant. 2011, 11, 1959–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lubetzky, M.; Bao, Y.; Broin, P.O.; Marfo, K.; Ajaimy, M.; Aljanabi, A.; de Boccardo, G.; Golden, A.; Akalin, E. Genomics of BK viremia in kidney-transplanted recipients. Transplantation 2014, 97, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Luo, L.; Tian, L.; Yin, S.; Ma, X.; Cheng, S.; Tang, W.; Yu, J.; Ma, W.; Zhou, X.; et al. Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Promotes IL-10 Expression in Inflammatory Macrophages Through Src-STAT3 Signaling Pathway. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bouatou, Y.; Stokman, G.; Claessen, N.; Roelofs, J.J.T.H.; Bemelman, F.; Kers, J.; Florquin, S. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor expression by macrophages and lymphocytes within infiltrates in BK polyomavirus associated nephropathy. Transplant. Immunol. 2018, 47, 18–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, J.A.; Gálvez, N.M.S.; Andrade, C.A.; Pacheco, G.A.; Bohmwald, K.; Berrios, R.V.; Bueno, S.M.; Kalergis, A.M. The Role of Dendritic Cells During Infections Caused by Highly Prevalent Viruses. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Womer, K.L.; Peng, R.; Patton, P.R.; Murawski, M.R.; Bucci, M.; Kaleem, A.; Schold, J.; Efron, P.A.; Hemming, A.W.; Srinivas, T.R.; et al. The effects of renal transplantation on peripheral blood dendritic cells. Clin. Transplant. 2005, 19, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Audiger, C.; Rahman, M.J.; Yun, T.J.; Tarbell, K.V.; Lesage, S. The Importance of Dendritic Cells in Maintaining Immune Tolerance. J. Immunol. 2017, 198, 2223–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Winde, C.M.; Munday, C.; Acton, S.E. Molecular mechanisms of dendritic cell migration in immunity and cancer. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2020, 209, 515–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorn, D.C.; Lawatscheck, R.; Zvirbliene, A.; Aleksaite, E.; Pecher, G.; Sasnauskas, K.; Ozel, M.; Raftery, M.; Schönrich, G.; Ulrich, R.G.; et al. Cellular and humoral immunogenicity of hamster polyomavirus-derived virus-like particles harboring a mucin 1 cytotoxic T-cell epitope. Viral. Immunol. 2008, 21, 12–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelm, M.; Kaur, A.; Wernli, M.; Hirsch, H.H. BK Polyomavirus (BKPyV)-specific CD8 T-cell expansion in vitro using 27mer peptide antigens for developing adoptive T-cell transfer and vaccination. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 223, 1410–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naumenko, V.; Turk, M.; Jenne, C.N.; Kim, S.-J. Neutrophils in viral infection. Cell Tissue Res. 2018, 371, 505–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinkmann, V.; Reichard, U.; Goosmann, C.; Fauler, B.; Uhlemann, Y.; Weiss, D.S.; Weinrauch, Y.; Zychlinsky, A. Neutrophil extracellular traps kill bacteria. Science 2004, 303, 1532–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rau, S.; Schönermarck, U.; Jäger, G.; Stangl, M.; Guba, M.; Meiser, B.; Fischereder, M.; Habicht, A. BK virus-associated nephropathy: Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as a new diagnostic tool? Clin. Transplant. 2013, 27, E184–E191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klotman, M.E.; Chang, T.L. Defensins in innate antiviral immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 6, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dugan, A.S.; Maginnis, M.S.; Jordan, J.A.; Gasparovic, M.L.; Manley, K.; Page, R.; Williams, G.; Porter, E.; O’Hara, B.A.; Atwood, W.J. Human alpha-defensins inhibit BK virus infection by aggregating virions and blocking binding to host cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 31125–31132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamanaka, K.; Oka, K.; Nakazawa, S.; Hirai, T.; Kishikawa, H.; Nishimura, K.; Kyo, M.; Ichikawa, Y. Immunohistochemical features of BK virus nephropathy in renal transplant recipients. Clin. Transplant. 2012, 26 (Suppl. 24), 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, A.; Madrigal, A.J.; Grace, S.; Sivakumaran, J.; Kottaridis, P.; Mackinnon, S.; Travers, P.J.; Lowdell, M.W. The role of Vδ2-negative γδ T cells during cytomegalovirus reactivation in recipients of allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Blood 2010, 116, 2164–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Couzi, L.; Pitard, V.; Sicard, X.; Garrigue, I.; Hawchar, O.; Merville, P.; Moreau, J.F.; Déchanet-Merville, J. Antibody-dependent anti-cytomegalovirus activity of human γδ T cells expressing CD16 (FcγRIIIa). Blood 2012, 119, 1418–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comoli, P.; Basso, S.; Azzi, A.; Moretta, A.; De Santis, R.; Del Galdo, F.; De Palma, R.; Valente, U.; Nocera, A.; Perfumo, F.; et al. Dendritic cells pulsed with polyomavirus BK antigen induce ex vivo polyoma BK virus-specific cytotoxic T-cell lines in seropositive healthy individuals and renal transplant recipients. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2003, 14, 3197–3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Honsová, E.; Lodererová, A.; Viklický, O.; Boucek, P. BK-virus nephropathy and simultaneous C4d positive staining in renal allografts. Cesk. Patol. 2005, 41, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liman, P.; Babel, N.; Schachtner, T.; Unterwalder, N.; König, J.; Hofmann, J.; Reinke, P.; Nickel, P. Mannose-binding lectin deficiency is not associated with increased risk for polyomavirus nephropathy. Transpl. Immunol. 2012, 26, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heutinck, K.M.; Kassies, J.; Florquin, S.; ten Berge, I.J.; Hamann, J.; Rowshani, A.T. SerpinB9 expression in human renal tubular epithelial cells is induced by triggering of the viral dsRNA sensors TLR3, MDA5 and RIG-I. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2012, 27, 2746–2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mitoma, H.; Hanabuchi, S.; Kim, T.; Bao, M.; Zhang, Z.; Sugimoto, N.; Liu, Y.J. The DHX33 RNA helicase senses cytosolic RNA and activates the NLRP3 inflammasome. Immunity 2013, 39, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Swanson, K.V.; Deng, M.; Ting, J.P.Y. The NLRP3 inflammasome: Molecular activation and regulation to therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 19, 477–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Zhao, W. NLRP3 Inflammasome—A Key Player in Antiviral Responses. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mogensen, T.H.; Paludan, S.R. Molecular pathways in virus-induced cytokine production. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2001, 65, 131–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferrari, L.; Martelli, P.; Saleri, R.; De Angelis, E.; Ferrarini, G.; Cavalli, V.; Passeri, B.; Bazzoli, G.; Ogno, G.; Magliani, W.; et al. An engineered anti-idiotypic antibody-derived killer peptide (KP) early activates swine inflammatory monocytes, CD3(+)CD16(+) natural killer T cells and CD4(+)CD8α(+) double positive CD8β(+) cytotoxic T lymphocytes associated with TNF-α and IFN-γ secretion. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 72, 101523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heutinck, K.M.; Rowshani, A.T.; Kassies, J.; Claessen, N.; van Donselaar-van der Pant, K.A.; Bemelman, F.J.; Eldering, E.; van Lier, R.A.; Florquin, S.; Ten Berge, I.J.; et al. Viral double-stranded RNA sensors induce antiviral, pro-inflammatory, and pro-apoptotic responses in human renal tubular epithelial cells. Kidney Int. 2012, 82, 664–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lenz, P.; Day, P.M.; Pang, Y.Y.; Frye, S.A.; Jensen, P.N.; Lowy, D.R.; Schiller, J.T. Papillomavirus-like particles induce acute activation of dendritic cells. J. Immunol. 2001, 166, 5346–5355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, R.; Murillo, F.M.; Cui, H.; Blosser, R.; Uematsu, S.; Takeda, K.; Akira, S.; Viscidi, R.P.; Roden, R.B. Papillomavirus-like particles stimulate murine bone marrow-derived dendritic cells to produce alpha interferon and Th1 immune responses via MyD88. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 11152–11160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, S.; Hu, J.; Xu, W.; Liu, D.; Liao, J.; Liao, G.; Guo, Z.; Li, Y.; Yang, S.; et al. Characterization of aberrant pathways activation and immune microenviroment of BK virus associated nephropathy. Aging 2020, 12, 14434–14451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radtke, F.; Fasnacht, N.; Macdonald, H.R. Notch signaling in the immune system. Immunity 2010, 32, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tanigaki, K.; Honjo, T. Regulation of lymphocyte development by Notch signaling. Nat. Immunol. 2007, 8, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostroukhova, M.; Qi, Z.; Oriss, T.B.; Dixon-McCarthy, B.; Ray, P.; Ray, A. Treg-mediated immunosuppression involves activation of the Notch-HES1 axis by membrane-bound TGF-beta. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 996–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eagar, T.N.; Tang, Q.; Wolfe, M.; He, Y.; Pear, W.S.; Bluestone, J.A. Notch 1 signaling regulates peripheral T cell activation. Immunity 2004, 20, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amsen, D.; Antov, A.; Jankovic, D.; Sher, A.; Radtke, F.; Souabni, A.; Busslinger, M.; McCright, B.; Gridley, T.; Flavell, R.A. Direct regulation of Gata3 expression determines the T helper differentiation potential of Notch. Immunity 2007, 27, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sakaguchi, S.; Ono, M.; Setoguchi, R.; Yagi, H.; Hori, S.; Fehervari, Z.; Shimizu, J.; Takahashi, T.; Nomura, T. Foxp3+ CD25+ CD4+ natural regulatory T cells in dominant self-tolerance and autoimmune disease. Immunol. Rev. 2006, 212, 8–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josefowicz, S.Z.; Lu, L.F.; Rudensky, A.Y. Regulatory T cells: Mechanisms of differentiation and function. Ann. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 30, 531–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oeckinghaus, A.; Hayden, M.S.; Ghosh, S. Crosstalk in NF-κB signaling pathways. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 695–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manley, K.; O’Hara, B.A.; Atwood, W.J. Nuclear factor of activated T-cells (NFAT) plays a role in SV40 infection. Virology 2008, 372, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schaller, M.A.; Neupane, R.; Rudd, B.D.; Kunkel, S.L.; Kallal, L.E.; Lincoln, P.; Lowe, J.B.; Man, Y.; Lukacs, N.W. Notch ligand Delta-like 4 regulates disease pathogenesis during respiratory viral infections by modulating Th2 cytokines. J. Exp. Med. 2007, 204, 2925–2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ting, H.A.; de Almeida Nagata, D.; Rasky, A.J.; Malinczak, C.A.; Maillard, I.P.; Schaller, M.A.; Lukacs, N.W. Notch ligand Delta-like 4 induces epigenetic regulation of Treg cell differentiation and function in viral infection. Mucosal Immunol. 2018, 11, 1524–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sontag, E.; Fedorov, S.; Kamibayashi, C.; Robbins, D.; Cobb, M.; Mumby, M. The interaction of SV40 small tumor antigen with protein phosphatase 2A stimulates the map kinase pathway and induces cell proliferation. Cell 1993, 75, 887–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadimitriou, J.C.; Randhawa, P.; Rinaldo, C.H.; Drachenberg, C.B.; Alexiev, B.; Hirsch, H.H. BK Polyomavirus Infection and Renourinary Tumorigenesis. Am. J. Transplant. 2016, 16, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moens, U.; Van Ghelue, M.; Johannessen, M. Oncogenic potentials of the human polyomavirus regulatory proteins. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2007, 64, 1656–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, R.C.; Gonçales, R.A.; Zambuzi, F.A.; Frantz, F.G. Notch signaling pathway in infectious diseases: Role in the regulation of immune response. Inflamm. Res. 2021, 70, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Sharma, M.; Martinez, J.; Srivastava, T.; Diamond, D.J.; Knowles, W.; Lacey, S.F. Functional characterization of BK virus-specific CD4+ T cells with cytotoxic potential in seropositive adults. Viral Immunol. 2007, 20, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, M.H.; Brestrich, G.; Andree, H.; Engelmann, E.; Rosenberger, C.; Tillmann, H.; Zwinger, S.; Babel, N.; Nickel, P.; Volk, H.D.; et al. HLA type-independent method to monitor polyoma BK virus-specific CD4 and CD8 T-cell immunity. Am. J. Transplant. 2006, 6, 625–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comoli, P.; Azzi, A.; Maccario, R.; Basso, S.; Botti, G.; Basile, G.; Fontana, I.; Labirio, M.; Cometa, A.; Poli, F.; et al. Polyomavirus BK-specific immunity after kidney transplantation. Transplantation 2004, 78, 1229–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chakera, A.; Bennett, S.; Lawrence, S.; Morteau, O.; Mason, P.D.; O’Callaghan, C.A.; Cornall, R.J. Antigen-specific T cell responses to BK polyomavirus antigens identify functional anti-viral immunity and may help to guide immunosuppression following renal transplantation. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2011, 165, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schachtner, T.; Müller, K.; Stein, M.; Diezemann, C.; Sefrin, A.; Babel, N.; Reinke, P. BK virus-specific immunity kinetics: A predictor of recovery from polyomavirus BK-associated nephropathy. Am. J. Transplant. 2011, 11, 2443–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, T.; Adam, C.; Hirsch, H.H.; Janssen, M.W.; Wolf, M.; Dirks, J.; Kardas, P.; Ahlenstiel-Grunow, T.; Pape, L.; Rohrer, T.; et al. BK polyomavirus-specific cellular immune responses are age-dependent and strongly correlate with phases of virus replication. Am. J. Transplant. 2014, 14, 1334–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Awadalla, Y.; Randhawa, P.; Ruppert, K.; Zeevi, A.; Duquesnoy, R.J. HLA mismatching increases the risk of BK virus nephropathy in renal transplant recipients. Am. J. Transplant. 2004, 4, 1691–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masutani, K.; Ninomiya, T.; Randhawa, P. HLA-A2, HLA-B44 and HLA-DR15 are associated with lower risk of BK viremia. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2013, 28, 3119–3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menter, T.; Mayr, M.; Schaub, S.; Mihatsch, M.J.; Hirsch, H.H.; Hopfer, H. Pathology of resolving polyomavirus-associated nephropathy. Am. J. Transplant. 2013, 13, 1474–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kojc, N.; Aleš Rigler, A.; Mlinšek, G.; Kovač, D.; Ferluga, D.; Arnol, M. Outcome of polyomavirus nephropathy in renal transplant patients: A single-center experience. Clin. Nephrol. 2017, 88, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burek Kamenaric, M.; Ivkovic, V.; Kovacevic Vojtusek, I.; Zunec, R. The Role of HLA and KIR Immunogenetics in BK Virus Infection after Kidney Transplantation. Viruses 2020, 12, 1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, S.J.; Kuten, S.A.; Knight, R.J.; Graviss, E.A.; Nguyen, D.; Gaber, A.O. Incidence and Factors Associated with De Novo DSA After BK Viremia in Renal Transplant Recipients. Clin. Transplant. 2016, 32, 103–109. [Google Scholar]
- Cheungpasitporn, W.; Kremers, W.K.; Lorenz, E.; Amer, H.; Cosio, F.G.; Stegall, M.D.; Gandhi, M.J.; Schinstock, C.A. De novo donor-specific antibody following BK nephropathy: The incidence and association with antibody-mediated rejection. Clin. Transplant. 2018, 32, e13194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chancharoenthana, W.; Leelahavanichkul, A. Innate Immunity Response to BK Virus Infection in Polyomavirus-Associated Nephropathy in Kidney Transplant Recipients. Transplantology 2022, 3, 20-32. https://doi.org/10.3390/transplantology3010003
Chancharoenthana W, Leelahavanichkul A. Innate Immunity Response to BK Virus Infection in Polyomavirus-Associated Nephropathy in Kidney Transplant Recipients. Transplantology. 2022; 3(1):20-32. https://doi.org/10.3390/transplantology3010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleChancharoenthana, Wiwat, and Asada Leelahavanichkul. 2022. "Innate Immunity Response to BK Virus Infection in Polyomavirus-Associated Nephropathy in Kidney Transplant Recipients" Transplantology 3, no. 1: 20-32. https://doi.org/10.3390/transplantology3010003
APA StyleChancharoenthana, W., & Leelahavanichkul, A. (2022). Innate Immunity Response to BK Virus Infection in Polyomavirus-Associated Nephropathy in Kidney Transplant Recipients. Transplantology, 3(1), 20-32. https://doi.org/10.3390/transplantology3010003






