Evaluating the Efficacy and Safety of Long-Acting GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in T1DM Patients
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hinnen, D. Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists for Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Spectr. 2017, 30, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nauck, M.A.; Kleine, N.; Orskov, C.; Holst, J.J.; Willms, B.; Creutzfeldt, W. Normalization of Fasting Hyperglycaemia by Exogenous Glucagon-like Peptide 1 (7-36 Amide) in Type 2 (Non-Insulin-Dependent) Diabetic Patients. Diabetologia 1993, 36, 741–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aroda, V.R.; Ahmann, A.; Cariou, B.; Chow, F.; Davies, M.J.; Jódar, E.; Mehta, R.; Woo, V.; Lingvay, I. Comparative Efficacy, Safety, and Cardiovascular Outcomes with Once-Weekly Subcutaneous Semaglutide in the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes: Insights from the SUSTAIN 1–7 Trials. Diabetes Metab. 2019, 45, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirabelli, M.; Chiefari, E.; Tocci, V.; Caroleo, P.; Giuliano, S.; Greco, E.; Luque, R.M.; Puccio, L.; Foti, D.P.; Aversa, A.; et al. Clinical Effectiveness and Safety of Once-Weekly GLP-1 Receptor Agonist Dulaglutide as Add-On to Metformin or Metformin Plus Insulin Secretagogues in Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.R.; Everett, B.M.; Birtcher, K.K.; Brown, J.M.; Januzzi, J.L.; Kalyani, R.R.; Kosiborod, M.; Magwire, M.; Morris, P.B.; Neumiller, J.J.; et al. 2020 Expert Consensus Decision Pathway on Novel Therapies for Cardiovascular Risk Reduction in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: A Report of the American College of Cardiology Solution Set Oversight Committee. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 1117–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fellinger, P.; Fuchs, D.; Wolf, P.; Heinze, G.; Luger, A.; Krebs, M.; Winhofer, Y. Overweight and Obesity in Type 1 Diabetes Equal Those of the General Population. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 2019, 131, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lind, M.; Svensson, A.-M.; Kosiborod, M.; Gudbjörnsdottir, S.; Pivodic, A.; Wedel, H.; Dahlqvist, S.; Clements, M.; Rosengren, A. Glycemic Control and Excess Mortality in Type 1 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 1972–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teoh, I.H.; Elisaus, P.; Schofield, J.D. Cardiovascular Risk Management in Type 1 Diabetes. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2021, 21, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bode, B.W.; Garg, S.K. The Emerging Role Of Adjunctive Noninsulin Antihyperglycemic Therapy in The Management of Type 1 Diabetes. Endocr. Practi. 2016, 22, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayati, A.; Haidar, A.; Tsoukas, M.A. Glucagon-like peptide -1 Receptor Agonists as Adjunctive Treatment for Type 1 Diabetes: Renewed Opportunities through Tailored Approaches? Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2022, 24, 769–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanim, H.; Batra, M.; Green, K.; Abuaysheh, S.; Hejna, J.; Makdissi, A.; Borowski, R.; Kuhadiya, N.D.; Chaudhuri, A.; Dandona, P. Liraglutide Treatment in Overweight and Obese Patients with Type 1 Diabetes: A 26-Week Randomized Controlled Trial; Mechanisms of Weight Loss. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2020, 22, 1742–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubé, M.-C.; D’Amours, M.; Weisnagel, S.J. Effect of Liraglutide on Food Consumption, Appetite Sensations and Eating Behaviours in Overweight People with Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2020, 22, 1417–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guyton, J.; Jeon, M.; Brooks, A. Glucagon-like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. Am. J. Health-Syst. Pharm. 2019, 76, 1739–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garber, A.J. Long-Acting Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists. Diabetes Care 2011, 34 (Suppl. 2), S279–S284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahrén, B.; Hirsch, I.B.; Pieber, T.R.; Mathieu, C.; Gómez-Peralta, F.; Hansen, T.K.; Philotheou, A.; Birch, S.; Christiansen, E.; Jensen, T.J.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Liraglutide Added to Capped Insulin Treatment in Subjects With Type 1 Diabetes: The ADJUNCT TWO Randomized Trial. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 1693–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traina, A.N.; Lull, M.E.; Hui, A.C.; Zahorian, T.M.; Lyons-Patterson, J. Once-Weekly Exenatide as Adjunct Treatment of Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus in Patients Receiving Continuous Subcutaneous Insulin Infusion Therapy. Can. J. Diabetes 2014, 38, 269–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herold, K.C.; Reynolds, J.; Dziura, J.; Baidal, D.; Gaglia, J.; Gitelman, S.E.; Gottlieb, P.A.; Marks, J.; Philipson, L.H.; Pop-Busui, R.; et al. Exenatide Extended Release in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes with and without Residual Insulin Production. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2020, 22, 2045–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantley, N.W.; Lonnen, K.; Kyrou, I.; Tahrani, A.A.; Kahal, H. The Association between Overweight/Obesity and Double Diabetes in Adults with Type 1 Diabetes; a Cross-Sectional Study. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2021, 21, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Dijon. Effect of Weekly GLP1 Agonist Treatment in “Double Diabetes”: A Randomized Open-label Study (TOLEDDO). ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT05305794. Updated 19 July 2022. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05305794 (accessed on 11 November 2022).
- Harris, P.A.; Taylor, R.; Thielke, R.; Payne, J.; Gonzalez, N.; Conde, J.G. Research Electronic Data Capture (REDCap)--a Metadata-Driven Methodology and Workflow Process for Providing Translational Research Informatics Support. J. Biomed. Inform. 2009, 42, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, P.A.; Taylor, R.; Minor, B.L.; Elliott, V.; Fernandez, M.; O’Neal, L.; McLeod, L.; Delacqua, G.; Delacqua, F.; Kirby, J.; et al. The REDCap Consortium: Building an International Community of Software Platform Partners. J. Biomed. Inform. 2019, 95, 103208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejgaard, T.F.; von Scholten, B.J.; Christiansen, E.; Kreiner, F.F.; Bardtrum, L.; von Herrath, M.; Mathieu, C.; Madsbad, S.; ADJUNCT ONE and ADJUNCT TWO Investigators. Efficacy and Safety of Liraglutide in Type 1 Diabetes by Baseline Characteristics in the ADJUNCT ONE and ADJUNCT TWO Randomized Controlled Trials. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2021, 23, 2752–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimitrios, P.; Michael, D.; Vasilios, K.; Konstantinos, S.; Konstantinos, I.; Ioanna, Z.; Konstantinos, P.; Spyridon, B.; Asterios, K. Liraglutide as Adjunct to Insulin Treatment in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2020, 16, 313–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Demographics (n = 54) | Mean ± SD |
|---|---|
| Age—years | 41.54 ± 13.89 |
| Time since Type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) Diagnosis—years (n = 18) | 16.37 ± 12.92 |
| Time on long-acting glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist (GLP-1)—months | 23.85 ± 15.46 |
| Sex—n (%) 1 | |
| Female | 35 (64.8%) |
| Male | 19 (35.2%) |
| Race—n (%) 1 | |
| White | 31 (58.5%) |
| Asian | 4 (7.5%) |
| Black | 1 (1.9%) |
| Other | 14 (26.4%) |
| Unknown | 3 (5.7%) |
| Ethnicity—n (%) 1 | |
| Hispanic/Latino | 10 (18.9%) |
| Non-Hispanic | 39 (73.6%) |
| Unknown | 4 (7.5%) |
| Insulin Treatment Type—n (%) 2 | |
| Multiple Daily Injections (MDIs) | 16 (29.6%) |
| Insulin Pump | 36 (66.7%) |
| Closed loop | 28 (51.6%) |
| Continuous Glucose Monitor (CGM) | 42 (77.8%) |
| Glucometer | 6 (11.1%) |
| GLP-1 Type—n (%) | |
| Trulicity | 19 (35.2%) |
| Bydreon | 2 (3.7%) |
| Ozempic | 34 (63.0%) |
| Tanzeum | 2 (3.7%) |
| Time on GLP-1—months | 23.85 ± 15.46 |
| C-peptide level (n = 36) (mean ± SD) | 0.32 nm/L ± 0.51 |
| Positive C-peptide | |
| Yes | 13 (36.1%) |
| No | 23 (63.9%) |
| (n = 54) | n (%) |
|---|---|
| Discontinued GLP-1 | |
| Yes | 15 (27.8%) |
| No | 39 (72.2%) |
| Reason for Discontinuing | |
| GI Symptoms | 35 (64.8%) |
| Minimal or negative impact on glycemic control | 19 (35.2%) |
| Minimal or negative impact on weight control | 0 (0.0%) |
| Lack of insurance coverage | 1 (6.7%) |
| Unknown | 5 (33.3%) |
| Parameter (n of Patients with Available Data) | Baseline (Mean ± SD) | Post GLP-1 (Mean ± SD) | Mean Difference | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HbA1c (%-points) (n = 43) | 7.76 ± 1.40 | 7.05 ± 1.00 | −0.71 | 0.0018 |
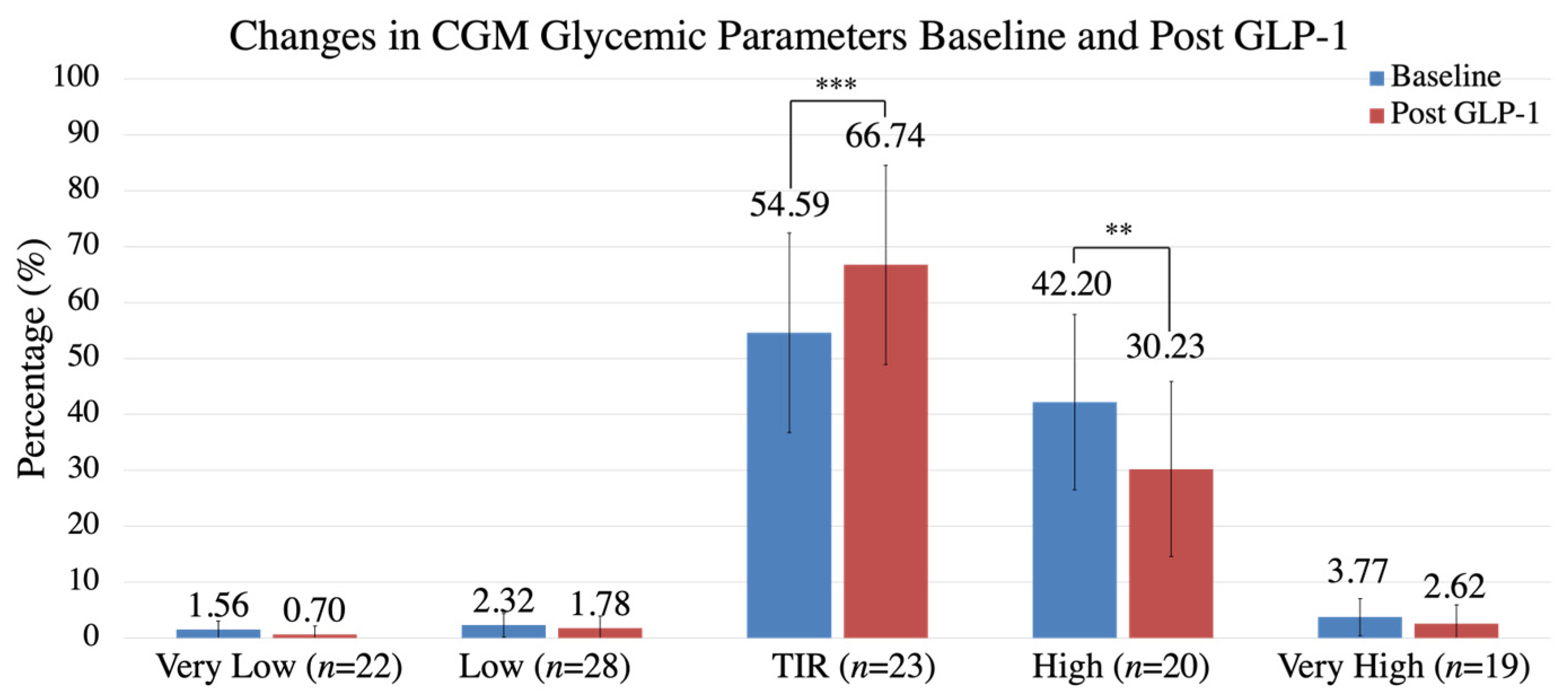
| Time in Range (TIR) (%) (n = 23) | 54.59 ± 23.12 | 66.74 ± 17.82 | +12.15 | 0.000850 |
| Time in Hypoglycemia (%) (n = 28) | 2.32 ± 2.63 | 1.78 ± 2.15 | −0.54 | 0.0900 |
| Time in Hyperglycemia (%) (n = 20) | 42.20 ± 21.47 | 30.23 ± 15.66 | −11.97 | 0.00628 |
| 14-day Avg Blood Glucose (BG) (mg/dL) (n = 27) | 182 ± 32.0 | 163 ± 24.9 | −19 | 0.0145 |
| CGM SD (n = 17) | 56.09 ± 18.26 | 47.64 ± 12.62 | −8.45 | 0.006665 |
| Total Daily Insulin Dose (TDD) (units) (n = 22) | 58.18 ± 32.32 | 55.17 ± 29.92 | −3.01 | 0.2963 |
| Insulin Requirement (units/kg) (n = 18) | 0.553 ± 0.22 | 0.547 ± 0.19 | 0.006 | 0.827 |
| Creatinine (n = 37) | 0.97 ± 0.68 | 1.09 ± 1.47 | +0.12 | 0.54 |
| Total Cholesterol (n = 27) | 157.85 ± 32.97 | 155.07 ± 31.70 | −2.78 | 0.63 |
| LDL-Cholesterol (n = 24) | 81.71 ± 26.70 | 85.83 ± 29.50 | +4.12 | 0.38 |
| Weight (kgs) (n = 36) | 86.66 ± 19.24 | 83.50 ± 20.83 | −3.16 | 0.007 |
| Systolic Blood Pressure (mmHg) (n = 19) | 126.05 ± 17.24 | 126.79 ± 15.48 | +0.74 | 0.761 |
| Diastolic Blood Pressure (mmHg) (n = 19) | 72.74 ± 12.17 | 70.74 ± 12.48 | −2.00 | 0.408 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mohandas, D.; Calma, J.; Gao, C.; Basina, M. Evaluating the Efficacy and Safety of Long-Acting GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in T1DM Patients. Endocrines 2023, 4, 93-101. https://doi.org/10.3390/endocrines4010008
Mohandas D, Calma J, Gao C, Basina M. Evaluating the Efficacy and Safety of Long-Acting GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in T1DM Patients. Endocrines. 2023; 4(1):93-101. https://doi.org/10.3390/endocrines4010008
Chicago/Turabian StyleMohandas, Deene, Jamie Calma, Catherine Gao, and Marina Basina. 2023. "Evaluating the Efficacy and Safety of Long-Acting GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in T1DM Patients" Endocrines 4, no. 1: 93-101. https://doi.org/10.3390/endocrines4010008
APA StyleMohandas, D., Calma, J., Gao, C., & Basina, M. (2023). Evaluating the Efficacy and Safety of Long-Acting GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in T1DM Patients. Endocrines, 4(1), 93-101. https://doi.org/10.3390/endocrines4010008







