Abstract
Impaired glucagon secretion is a major component of glucose intolerance in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2D). Glucagon secretion exhibits heterogenous patterns in individuals and across glucose tolerance diagnoses. Characterization of the range of glucagon secretion patterns can help clinicians personalize diabetes care based on glucagon characteristics in addition to glucose and insulin profiles. A total of 102 subjects with normal glucose tolerance, impaired glucose tolerance, and T2D had their glucagon profiles recorded in response to an oral glucose tolerance test. Shapelet analysis was used to identify the most descriptive patterns of early glucagon secretion, and spectral biclustering was employed to identify biclusters of associated subjects and shapelets. The dynamics of glucose, insulin, and glucagon secretion in each cluster were evaluated to identify overall patterns, and the characteristics of the subjects in each cluster were compared. Three clusters were chosen to represent the glucagon patterns. Membership in these three clusters was interpreted based on the presence or lack of extrema in the first 30 min after oral carbohydrate intake. Cluster 1 (n = 23) had a minimum at 30 min and only negative trends. Cluster 2 had a minimum at 10 min and a maximum at 20 min (n = 25). Cluster 3 (n = 40) had a maximum at 10 min and a minimum at 20 min. Subjects in cluster 1 had the lowest average fasting plasma glucose (90.17 mg/dL) and average age (41.39 years) and the highest HOMA-beta score (87.5%), while subjects in cluster 2 had the highest average fasting plasma glucose (102.56 mg/dL) and average age (53.16 years) and the lowest HOMA-beta score (55.77%). Characterization of glucagon dynamics, in addition to glucose and insulin, can aid in personalized treatment approaches and provide greater insight about the underlying dysfunction in glucose regulation.
1. Introduction
Type 2 diabetes (T2D) is characterized by an inability to regulate blood glucose levels, and individuals with T2D can frequently experience hyperglycemia (high blood glucose) in both fasting and postprandial states [1,2]. T2D is associated with a variety of complications and comorbidities, such as heart disease, kidney disease, impaired wound healing, and neuropathy [1,3,4]. Treatment of T2D and associated comorbidities typically includes lifestyle modifications through diet and exercise, and combination pharmacotherapy [4,5,6,7,8]. However, the combination of glucose intolerance, comorbidities, and lifestyle and socioeconomic factors can vary greatly between individuals, leading to difficulty in identifying an optimal treatment approach.
Blood glucose levels are regulated by both glucagon and insulin [1,9]. Insulin is secreted from pancreatic beta cells to reduce blood glucose levels by increasing the uptake of glucose by various cell types and suppressing hepatic glucose production [1]. Glucagon is secreted by pancreatic alpha cells in response to low blood glucose levels and stimulates the liver to convert stored glycogen to glucose, leading to an increase in blood glucose levels [9]. Together, these hormones work to regulate blood glucose while avoiding hypoglycemia (low blood glucose) and hyperglycemia. In T2D, this regulation is unable to adequately control blood glucose levels [1,9].
The link between impaired glucagon secretion and T2D is well recognized [1,2,10,11,12]. Altered blood glucagon concentration is not only an important pathophysiological mechanism in the development of T2D, but is also a therapeutic target [2,9]. Impaired endogenous glucose production plays a critical role in the pathology of T2D [1]. This is partially attributed to both elevated secretion and reduced suppression of glucagon, while glucagon clearance remains relatively unchanged in T2D [1,2,10,11,12,13,14]. Hyperglucagonemia is associated with both fasting and postprandial hyperglycemia [1,2,9]. Understanding the behavior of glucagon in T2D can aid in the treatment of hyperglycemia, and glucagon secretion and activity have been identified as potential pharmacodynamic targets for glucose-lowering pharmacological treatments [1,2,6,9].
Despite the critical role glucagon plays in T2D and blood glucose regulation, glucagon dynamics are not yet fully understood. Studies have observed that glucagon dynamics vary significantly with many factors, such as diabetes diagnosis and route of carbohydrate intake [12,14,15,16]. This presents a challenge for quantifying the individual response of glucagon to oral carbohydrate intake. Comprehensively identifying underlying patterns of glucagon secretion can allow clinicians to understand an individual’s glucose regulation characteristics and personalize treatment decisions more clearly.
Identifying groups with shared glucose intolerance characteristics has been investigated using cluster analysis [17,18]. While glucagon dynamics have received greater attention in recent years, to our knowledge, unsupervised learning techniques have not been extensively used to quantify glucagon characteristics in a time series context. The approach used in this work builds upon previous work by extracting characteristic glucagon secretion features directly from the data in an interpretable and explainable way [15,16,19].
The overall goal of this project was to combine multivariate statistical tools with time series analysis to elucidate the characteristics of impaired glucagon secretion based on patterns of secretion in the first 30 min of an oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT). The objectives of this work were to (1) identify initial patterns of glucagon secretion dynamics stratified by diagnosis classification, (2) develop alternative clusters of subjects by identifying glucagon secretion patterns independent of diagnosis, and (3) quantify the glucagon dynamics and subject characteristics in each cluster.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Data
Data from a previously conducted study were used for this work, and no additional clinical experiments were conducted [12]. In the original study, an OGTT was administered to 102 subjects (54 with normal glucose tolerance [NGT], 20 with impaired glucose tolerance [IGT], and 28 with T2D). These classifications were also used for this work without modification. The subjects were 20 to 65 years old, non-obese, and were excluded based on type 1 diabetes, various comorbidities, antidiabetic medications, an HbA1c > 7.9%, or fasting plasma glucose > 110 mg/dL for subjects with normal glucose tolerance. The subjects were diagnosed as having normal glucose tolerance (NGT), impaired glucose tolerance (IGT), or T2D. Glucagon was measured at 0, 10, 20, 30, 60, and 120 min following oral carbohydrate intake. Glucose and insulin measurements were taken at 0, 10, 20, 30, 60, 90, and 120 min. The demographic information of the subjects, including age, weight, height, body mass index, etc., was recorded and is presented in Section 3.3.2. The estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) was calculated from age, sex, and serum creatinine concentration using the CKD-EPI 2021 equation [20]. The fasting plasma glucose, insulin, and glucagon values were considered the concentrations measured at 0 min.
2.2. Shapelet Extraction and Feature Generation
A single subject was identified as an outlier and initially removed due to exceedingly high plasma glucagon values. For the remaining 101 subjects, the initial starting glucagon value prior to carbohydrate intake (glucagon concentration at 0 min) was subtracted from each glucagon measurement for each subject to convert the glucagon concentration measurements to the change in glucagon relative to the fasting glucagon concentration. A change in glucagon was used instead of the original glucagon values for the rest of the study. The first 30 min of the glucagon change measurements were isolated and upsampled from 10 to 1 min by interpolation with a piecewise cubic Hermite interpolating polynomial (PCHIP) [21]. PCHIP was chosen because it preserves the shape of the data and the original points without the possibility of overshoot.
The changes in glucose, insulin, and glucagon were considered instead of the absolute values. Time series clustering is sensitive to magnitude differences between subjects and is therefore prone to sorting subjects based on their fasting values. Subtracting the fasting value converts each subject’s measurements to a change in plasma hormone level and removes the bias from their starting value. Fasting glucose, insulin, and glucagon levels were considered separately with post hoc analysis after the clustering.
Following the preprocessing, shapelets were extracted from the interpolated data by computing the multivariate matrix profile with 10- and 15-min windows [22,23,24,25,26]. Shapelets are short subsequences and are commonly used to classify and identify time series data. Shapelets capture specific patterns or characteristics present in data and can be used to compare different time series by how well they match the shapelet [22]. The minimum number of shapelets was identified using the minimum description limit, and the rest were discarded [23,24]. The process of extracting shapelets using the minimum description limit finds the fewest shapelets needed to adequately describe the data while minimizing redundancy [23].
Extracting shapelets from the glucagon data allowed for characteristic secretion patterns to be identified, and these patterns were converted to a feature matrix for clustering analysis [22,23,24,27]. Each shapelet was scanned over each subject’s measurements incrementally. At each increment, the Euclidean distance between the shapelet and the current data subsequence was calculated, and the minimum distance for that subject and shapelet was saved. The distance represented the similarity of the shapelet and the subsequence, with a larger distance indicating less similarity and a low distance indicating the shapelet and the subsequence match closely. This was repeated for each combination of subject measurements and shapelet. The resulting table of distances comprised the feature matrix used for clustering [27,28,29].
Several subjects exhibited unusual and unique dynamics that did not correspond to the extracted shapelets and were considered outliers. The presence of outliers often results in shapelets being extracted from each outlier to capture their dynamics, but these shapelets will poorly describe all or most of the other subjects, making it difficult to cluster other subjects based on that specific shapelet.
Detecting and removing the outliers allowed for the most discriminative shapelets to be extracted and to form clusters as uniformly as possible. First, principal component analysis was used to reduce the dimensionality of the feature matrix and analyze the data in a lower-dimensional space defined by the first two principal components [30,31]. Next, a local outlier factor model was used to identify the outliers and remove them [31,32]. The local outlier factor examines the local grouping of points and identifies outliers based on their distance from the points nearest to them. Once the outliers were removed, a new set of shapelets were extracted, and a new feature matrix was generated [27].
2.3. Clustering
Once the feature matrix was generated, the subjects and shapelets were clustered into groups using spectral biclustering [33,34]. Generally, clustering attempts to define groups in a way that maximizes the intercluster variability and minimizes the intracluster variability [35]. Biclustering identifies a characteristic “checkerboard” pattern in the data defined by groups of samples and features. Spectral biclustering works by applying eigenvector decomposition to represent the data in a grid where certain samples and variables are associated with each other [35]. Our goal was to generate clusters where groups of shapelets were associated with groups of subjects while being dissimilar to the shapelets in other clusters. Spectral biclustering allowed this underlying structure to be revealed.
Spectral biclustering has several hyperparameters that were estimated for 3, 4, and 5 clusters and 10- and 15-min window sizes by choosing the values that yielded the maximum silhouette score in a grid search. The silhouette score compares a sample’s similarity to its cluster versus the other clusters and returns values between −1 (similar to other clusters but dissimilar to its own) and 1 (similar to its cluster but dissimilar to the others) [36,37]. This resulted in 6 total cases: a 10-min window with 3 to 5 clusters and a 15-min window with 3 to 5 clusters. For each case, the average Euclidean distance was calculated for each bicluster and for all biclusters. The optimal number of clusters was selected for the 10- and 15-min cases based on the lowest average bicluster distance.
2.4. Post Hoc Analysis
The percent change in glucose, insulin, and glucagon was calculated at each sample based on (1) to interpret the direction and magnitude of each hormone’s trend. is the percent change of each variable (X = glucose, insulin, or glucagon) at the jth sampling instance. and represent the jth and initial hormone values, respectively. A positive value indicates an increasing trend, while a negative value indicates a decreasing trend.
A Kruskal–Wallis test for continuous variables or a test for categorical variables followed by Dunn’s test for multiple comparisons with a significance value of 5% (p < 0.05) were used [26,38]. The Bonferroni adjustment was used to adjust the significance value for multiple comparisons [26,38]. Any p-values that rounded to 0.05 were considered insignificant as a precaution.
3. Results
3.1. Feature Preparation and Outlier Removal
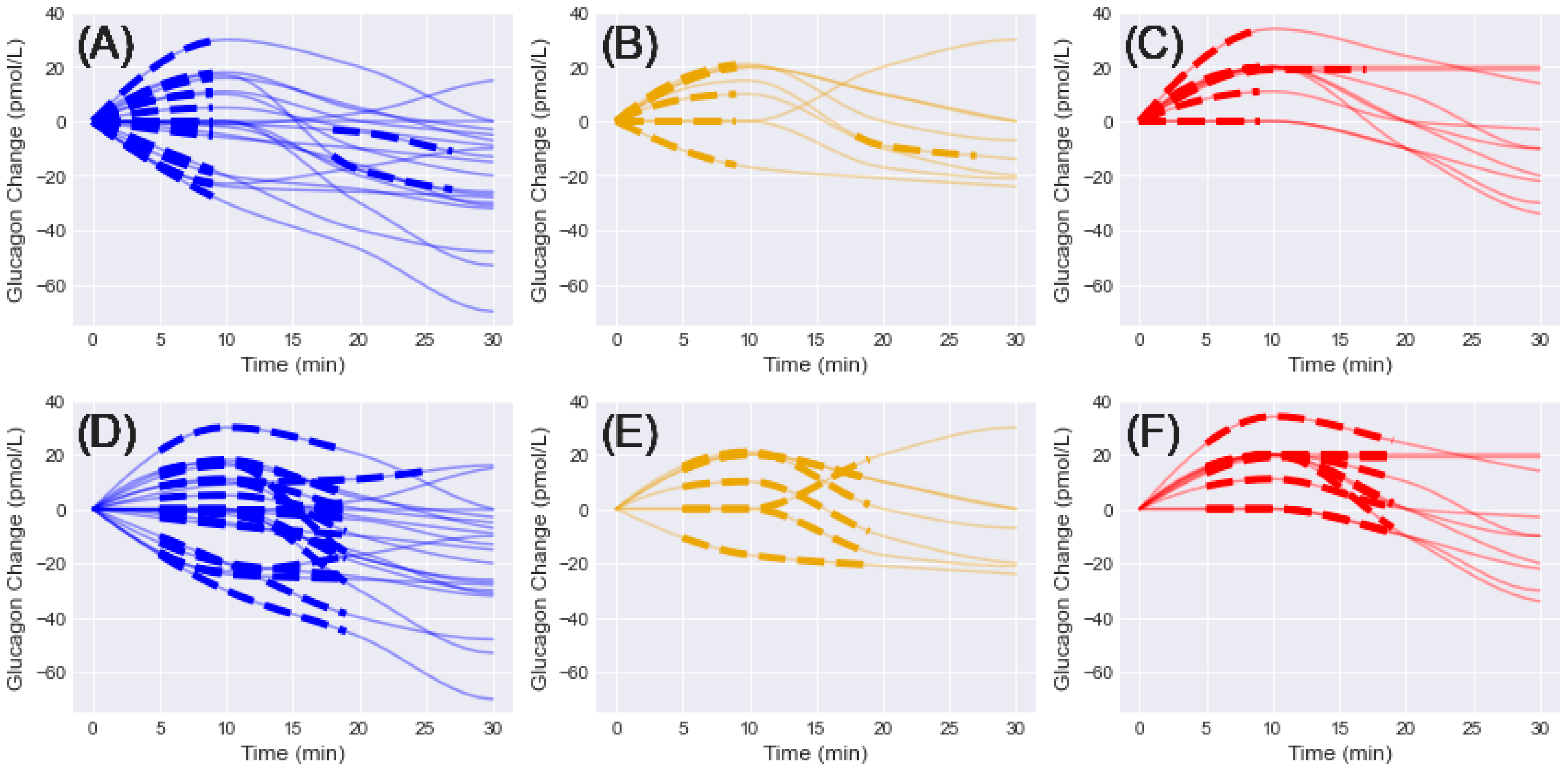
A total of 38 and 37 initial shapelets were extracted from the interpolated glucagon measurements for 10- and 15-min window sizes, respectively (Figure 1). For the 10-min case, 20 shapelets were extracted for NGT, 8 for IGT, and 10 for T2D. For the 15-min case, 20 shapelets were extracted for NGT, 7 for IGT, and 10 for T2D. For the 10-min window, all shapelets except for 3 were selected between 5–20 min, with the others selected for 14–24 min (2 NGT, 1 IGT). For the 15-min window, all shapelets except for two were selected between 5–20 min, with the other selected for 11–26 min (1 NGT, 1 T2D).
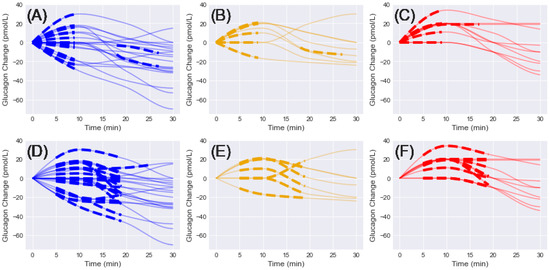
Figure 1.
Initial shapelets extracted from interpolated glucagon changes in the first 30 min and grouped by diagnosis (NGT = blue, IGT = gold, T2D = red). Solid lines = glucagon change, dashed lines = associated shapelet. (A–C) 10-min window shapelets grouped by diagnosis. (D–F) 15-min window shapelets grouped by diagnosis.
Four general trends emerged from the shapelet analysis: (1) initial increase, (2) initial decrease, (3) delayed increase, and (4) delayed decrease. Each of these patterns was present in the NGT and IGT groups for 10- and 15-min windows. For the T2D groups, only the initial increase and delayed increase patterns were observed in the shapelets. A unique pattern was observed in the T2D groups, where the initially positive trend seemed to level off and remain constant for the remainder of the time. No single pattern was observed in any of the groups.
An initial feature matrix was calculated for each case based on the extracted shapelets. and 12 subjects were identified as outliers for the 10-min window case and 13 for the 15-min window case. After reducing the dimensionality with principal component analysis and applying the local outlier factor method subjects were eliminated due to high variation and low density in the first principal component. Variation in the second principal component was mostly unaffected, indicating that the outliers mostly comprised variation in the first principal component direction. The remaining subjects were used for the rest of this work.
3.2. Clustering and Model Selection
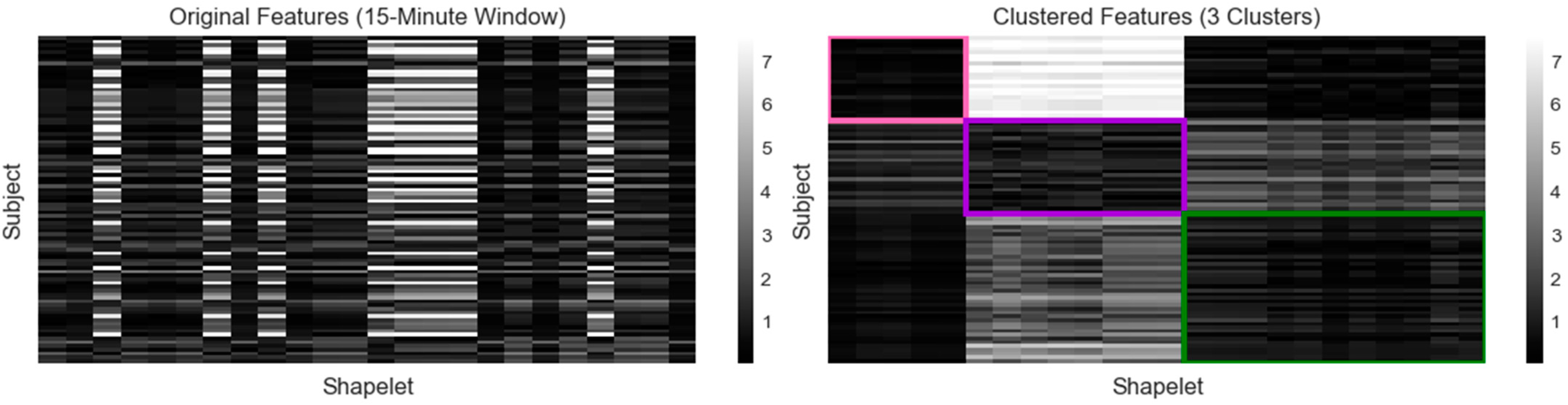
The final six clustering results were compared by calculating the average distance in each cluster (Table 1). The lowest average distance was in the three clusters and 15-min window case (0.795). The highest average distance was in the five clusters and 15-min window case (2.432). Each of the 10-min window cases had an average mean higher than 1. The 15-min cases had both the lowest (0.795, 3 clusters) and the highest (2.432, 5 clusters) overall average (Figure 2).

Table 1.
Total and individual cluster distances by case as mean (SD). The 15-min window, three-cluster case had the lowest overall distance, while the 15-min five-cluster case had the highest overall distance.
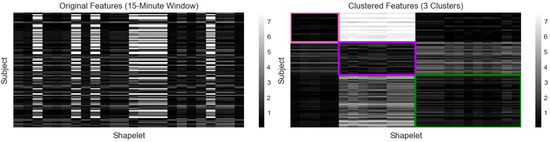
Figure 2.
Calculated features for 15-min window clustering (1 = pink, 2 = purple, 3 = green). The original feature matrix (left) was constructed by calculating the minimum distance between each subject’s glucagon measurements and each shapelet. Darker shades indicate a lower distance and a closer match, while lighter shades indicate a higher distance and a poorer match. The subjects and shapelets were grouped into rectangular biclusters outlined by the assigned color (right).
The optimal clustering was produced using the 15-min window three-cluster case (Figure 2, Table 1). Three biclusters, designated by colors (1 = pink, 2 = purple, 3 = green), were generated by identifying both the subjects and shapelets that grouped together. A total of 24 final shapelets were extracted and distributed relative to cluster size. Five shapelets were associated with cluster 1 (n = 23), eight with cluster 2 (n = 25), and eleven with cluster 3 (n = 40). Cluster 1 was associated with the shapelets in clusters 1 and 3 but was distinctly different from the cluster 2 shapelets. Cluster 2 was associated with shapelets from cluster 2, somewhat associated with shapelets from cluster 1, and less associated with cluster 3 shapelets. Cluster 3 was associated with cluster 1 and 3 shapelets, but less with cluster 2 shapelets. Therefore, for each cluster, the subjects were strongly associated with at least one cluster of shapelets and less associated with shapelets from another cluster.
3.3. Analysis of Clusters
3.3.1. Shapelets and Time Series Analysis
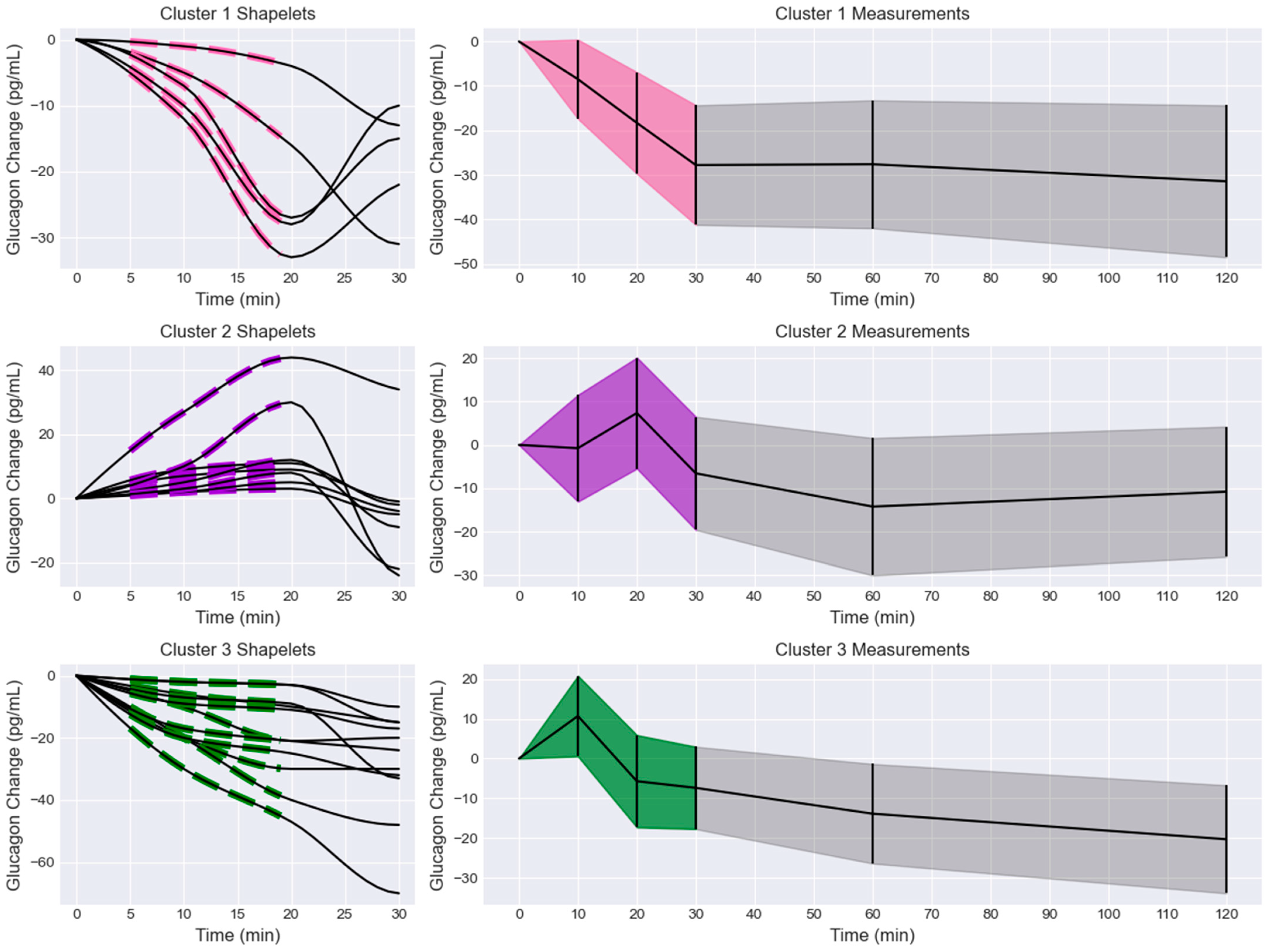
The shapelets and associated glucagon measurements were extracted from the biclusters and compared to the overall glucagon measurements for that bicluster (Figure 3). Cluster 1 shapelets exhibited initial and delayed decreases with three distinct slopes. One slope was a delayed decrease, another was an initial decrease with a moderate slope, and the last pattern was an initial decrease that rapidly trended towards a minimum at 20 min. This was reflected in the overall glucagon measurement trend, where the glucagon decreased in the first 30 min and then remained at a reduced level for the next 90 min. However, the minimum at 20 min observed in some of the shapelets was not observed in the trend of the overall measurements. This cluster also had the largest magnitude of glucagon decrease, with the mean trend dropping by 31.43 pg/mL after 120 min.
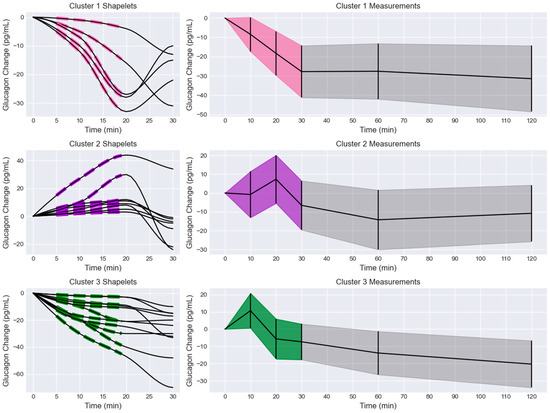
Figure 3.
Extracted shapelets and glucagon measurements grouped by cluster (1 = pink, 2 = purple, 3 = green). Left column: extracted shapelets (dashed lines) and associated measurements (solid lines). Right column: glucagon measurements with the shapelet extraction region shaded by cluster label color and the remaining measurements in black. The data are presented as mean +/− standard deviation (shaded).
Cluster 2 shapelets exhibited initial and delayed increases with three distinct slopes. One shapelet had a rapid initial increase, one had a slow initial increase followed by a rapid increase, and the rest had a modest, delayed increase. The associated measurements increased to a maximum at 20 min before decreasing. The overall glucagon measurements for that cluster generally increased to a maximum at 20 min before decreasing. An inflection was observed in the overall trend at 60 min, where the curves seemed to increase. At 120 min, the trend had decreased by 9.11 pg/mL. It was observed that several subjects exhibited an initial decrease in glucagon measurements, leading to a minimum at 10 min before trending towards a maximum at 20 min. This behavior was not represented by the shapelets but was observed in the overall trend and measurements.
Cluster 3 shapelets all showed an initial or delayed decrease from the fasting level. None of the shapelets showed an initial increase, and no major oscillations or inflections were observed. The associated measurements showed various trends after 20 min, but no major increases were observed. The overall glucagon measurements showed a maximum peak at 10 min, followed by an elbow point at 20 min, and a sustained decrease for the remainder of the test. The 10 min peak was not represented in the shapelets or the associated measurements. The overall measurement trend was reduced by 20.29 pg/mL at 120 min and continued to decrease.
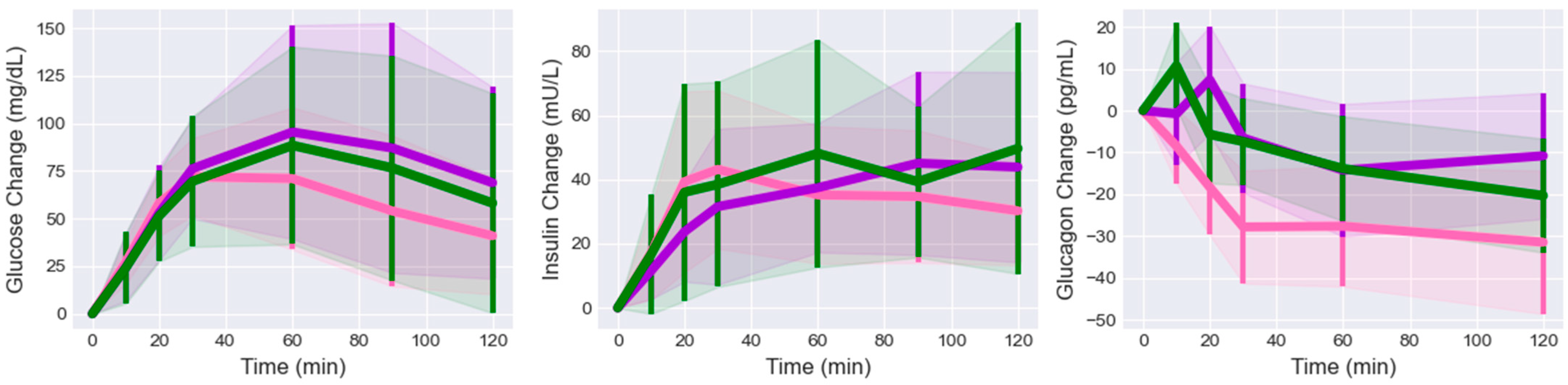
The glucose and insulin values were isolated for the subjects in each cluster (Figure 4). The initial values were subtracted from each measurement for each subject to make them consistent with the glucagon change values. The changes in glucose trends remained relatively consistent with each other for the first 30 min. After 60 min, the cluster 1 glucose trend dropped below the others and remained lower for the rest of the time. The changes in insulin trends were less consistent than the glucose trends. The cluster 1 insulin trend rose above the other after 20 min, followed by the cluster 3 and 2 trends. After 60 min, cluster 3 had the highest value. The cluster 1 glucose, insulin, and glucagon trends all showed an elbow or knee point at the 30 min sample, at which point glucose and insulin began to trend down, while glucagon behavior was cluster-dependent.
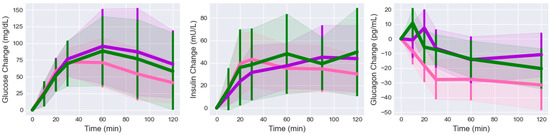
Figure 4.
Glucose, insulin, and glucagon changes grouped by cluster (mean +/− standard deviation, 1 = pink, 2 = purple, 3 = green). Glucose and insulin trends stayed at or above the fasting level for all clusters. Cluster 2 and 3 glucagon trends initially peaked before dropping below the fasting level. Cluster 1 glucagon trended immediately downward.
The percent change in glucagon was calculated for each sample after the initial sample and subject and compared across the clusters (Table 2). The initial sample was excluded because each subject was normalized to start at 0 pg/mL. No significant difference was found between any sample or cluster for glucose or insulin. For glucagon, significant differences were found for each time sample. The only sample where all cluster percent changes were significantly different was 20 min. Clusters 1 and 3 were significantly different at all time samples except for 120 min. Clusters 1 and 2 were not significantly different at 10 and 60 min. Clusters 2 and 3 were not significantly different at 30, 60, or 120 min, but were at 10 and 20 min.

Table 2.
Post hoc analysis of glucagon percent change by sample and cluster. Results are presented as mean (SD), and insignificant p-values are indicated as NS.
3.3.2. Subject Characteristics
The characteristics of the subjects in each cluster were compared (Table 3). Cluster 1 was the smallest, with 23 subjects; cluster 2 had 25 subjects; and cluster 3 had 40 subjects. Various demographic information (age, sex, body mass index [BMI], eGFR, diagnosis), HbA1c, insulin sensitivity (HOMA-IR, HOMA-beta), and fasting values (fasting plasma glucose [FPG], fasting plasma insulin [FPI], fasting plasma glucagon [FPGn]) were compared. The mean and standard deviation of each variable were computed from the inlier subjects.

Table 3.
Post hoc analysis of clustered subject characteristics. Results are presented as mean (SD), and insignificant p-values are indicated as NS.
No significant difference was found between any variables for clusters 1 and 3 or 2 and 3. Age, HOMA-beta, and FPG were significantly different between clusters 1 and 2. Cluster 1 had the lowest average age (41.39 years), and cluster 2 had the highest (53.16 years). Cluster 1 had the highest average HOMA-beta value (87.5%), while cluster 2 had the lowest (55.77%). Cluster 1 had the lowest FPG value (90.17 mg/dL), while cluster 2 had the highest FPG (102.56 mg/dL). While not statistically significant, cluster 1 had the highest ratio of NGT to IGT or T2D subjects (17:3:3), and cluster 2 had an almost even breakdown between diagnoses (8:9:8).
4. Discussion
We identified a variety of glucagon dynamics within the study dataset. While impaired glucagon dynamics have been observed in many populations and settings, we observed a wide range of dynamics across diagnosis classifications. Broadly, we saw (1) an initially positive trend, (2) an initially negative trend, (3) a delayed positive trend, and (4) a delayed negative trend. However, within each of these groups, there was significant variation in terms of oscillation and inflections, the presence or lack of extrema, and the magnitude of glucagon change. Most of these dynamics occurred in the first 30 min, while the 30–120 min trends were more consistent. We hypothesized that the glucagon dynamics within the first 30 min could be quantified and used to describe longer glucagon dynamics.
Previous studies have similarly investigated glucagon dynamics in response to oral carbohydrates. A multivariate statistical approach was used to cluster young women into four distinct subgroups [15]. However, the approach and glucagon dynamics in the study population differed from ours. Fasting values and overall elevation or suppression of hormone levels were major variables in the previous analysis, whereas we normalized our data to remove their effects. While the observed glucagon dynamics differed from those in this data set, the presence of great interpersonal variation in glucagon dynamics was similar and provided a foundation for our approach. Morettini et al. expanded on the results of that study by applying a dynamic model approach. A set of structured differential equations was used to model and simulate the glucagon response of each cluster in response to oral carbohydrate intake [19]. Another line of work applied a form of quantitative trend analysis to identify glucagon dynamic patterns based on the number of inflections in the data [16]. The analysis counted the number of inflections in the data and compared the change in area under the curve for glucagon across several conditions. While the goal was not to automatically cluster the subjects with unsupervised learning, the results do confirm that glucagon dynamics are highly variable, with major differences in the number of fluctuations between subjects even under similar conditions.
We chose to approach this as a time series analysis problem. Our goal was to identify characteristic subsequences in the glucagon measurements that would accurately capture the glucagon dynamics in each cluster while clearly distinguishing clusters from each other. We chose to use biclusters, as opposed to more traditional clustering techniques, to identify not only the subjects in each cluster, but also their associated shapelets. Additionally, clustering suffers from a lack of interpretability, and the reasoning for specific clusters may not be immediately clear. These biclusters visualize which features are correlated with which clusters and the magnitude of the association. To further emphasize the dynamics patterns and improve interpretability, we chose to first identify the patterns in the data and then apply clustering to automatically sort them. This was performed by calculating our feature matrix based on how well each subject matched with each shapelet.
Our results suggest that the clustering was largely based on extrema in the first 30 min. Cluster 1 exhibited a minimum at 30 min and a constant trend, which was not observed in other clusters. Clusters 2 and 3 had a mix of dynamics, with different patterns of fluctuations and varying trends within each cluster. However, cluster 2 exhibited a minimum at 10 min and a maximum at 20 min, while cluster 3 measurements showed a maximum at 10 min and a minimum at 20 min. Post hoc analysis of the percent change of glucagon at each sample across clusters revealed that the 20 min sample was the only one where all clustered glucagon trends were significantly different from each other, further indicating that was the significant feature identified through clustering. Additionally, clusters 1 and 3 and 2 and 3 were significantly different in the 10-min sample. This indicates the minimum and maximum locations are significant characteristics of each cluster and would also account for the presence of two different sets of initial dynamics in both clusters 2 and 3.
Defining glucagon clusters based on extrema is reasonable from a pharmacokinetic perspective. Plasma concentration curves for exogenous compounds, such as drugs, or endogenous compounds, like secreted hormones, are often evaluated based on their shape. Several studies have identified the shape of glucose responses, defined by peak glucose concentration, as an indication of glucose tolerance [39,40]. However, defining the shape is not necessarily straightforward, and various metrics are used, such as area under the curve, maximum concentration, and time to maximum concentration [41]. Defining the clusters based on extrema may therefore be an intuitive and interpretable way to group the subjects. This was not the explicit intent when the feature matrix was designed, but it is noteworthy that the model seems to have identified these characteristics and extracted the shapelets that would emphasize them.
The mix of dynamics in clusters 2 and 3, and the differences between the shapelets and overall trends, may be partly explained by the shapelet extraction and feature calculation processes. The shapelet analysis extracted time subsequences, and these were compared to each subject’s measurements. However, the shapelets were not required to match with subsequences at the time when the shapelet was extracted. Because of this, shapelets extracted in the earlier phase could closely match subsequences from the later phase or vice versa. This may explain the different dynamics in clusters 2 and 3; the shapelets extracted from the 0–30 min region for the first set of dynamics also describe the second set of dynamics. Even though they occur at different times, the subsequences still match to some degree based on a different portion of the data in that cluster.
One of the goals of this work was to evaluate whether the extracted glucagon shapelets could be used to separate longer glucagon dynamics. While the shapelets were extracted only from the first 30 min of measurements, the overall trends were noticeably different between clusters, and significant differences were measured for the 60- and 120-min measurements. This suggests that the initial dynamics are critical in determining the overall glucagon dynamics. Interestingly, fasting plasma glucagon levels were not significantly different across the clusters, indicating that elevated fasting levels were not representative of the different dynamics. However, it should be noted that the relatively small IGT and T2D proportions may not be large enough to accurately represent possible relationships.
Post hoc analysis of the glucose and insulin trends associated with each cluster revealed no significant differences. Despite stark differences in glucagon dynamics across the clusters, the glucose and insulin trends are relatively unchanged. In particular, the lack of glucose or insulin differences in the 10- and 20-min samples, where glucagon characteristics were most notable, suggests that the glucagon characteristics in each cluster were also not directly and immediately related to glucose-insulin dynamics in that cluster. However, this is not sufficient evidence for the interaction between glucagon, insulin, and glucose.
The subject characteristics seem to mirror the diagnosis distribution between clusters when comparing the ratio of subjects with NGT to those with some degree of glucose intolerance (IGT + T2D). Cluster 1 (n = 23) was largely characterized by NGT subjects (17:6) (NGT:IGT + T2D), cluster 2 (n = 25) was mostly IGT and T2D subjects (8:17) (NGT:IGT + T2D), and cluster 3 (n = 40) was a nearly even mix of NGT, and IGT and T2D (21:19) (NGT:IGT + T2D). This may explain why cluster 1 subjects had a lower FPG and a higher HOMA-beta, cluster 2 subjects had a higher FPG and a lower HOMA-beta, and cluster 3 subjects had no significant differences. Interestingly, the FPG and HOMA-beta differences do not correspond to differences in glucose and insulin trends across clusters. This may indicate that, while measurable, differences in subject characteristics between clusters are not enough to substantially differentiate glucose and insulin dynamics.
We initially observed four general patterns of glucagon dynamics ((1) initially positive, (2) initially negative, (3) delayed positive, and (4) delayed negative), and some of the patterns were present in 2 or 3 of the diagnosis classifications. Our clustering yielded three clusters, with each cluster exhibiting more than one of the initial patterns. The mixture of NGT, IGT, and T2D across clusters seems consistent with those initial findings. Even though the clustering was undertaken solely based on glucagon dynamics, the resulting clusters have a non-negligible but statistically insignificant proportion of NGT and IGT/T2D subjects in each. While this may complicate the interpretation of why glucagon dynamics exist, that was not the goal of the study.
This work was focused on identifying and quantifying subgroups of glucagon patterns, and future work may focus on identifying causal factors leading to various patterns of glucagon secretion. Our approach is easily interpretable by using the glucagon measurements alone. Clear differences in glucagon trends are observed across clusters, along with characteristic extrema. The use of shapelets extracted directly from the time series measurements allows the clustering to act on features emphasizing the patterns we have targeted for clustering. Converting the absolute glucagon measurements to changes in glucagon emphasized the dynamics of the fasting levels. Removing the outliers allowed for the identification of more uniform clusters. The use of a conservative interpolator that preserved the glucagon shape helped ensure the extracted shapelets were accurate and smooth representations of the actual glucagon measurements.
The population used in this study comprised individuals with NGT, IGT, and T2D. This allowed us to identify patterns in all three populations and extract a wide range of shapelets independent of diagnosis. This allowed us to observe that certain glucagon shapes were conserved across diagnosis classifications, while others seemed to only be present in specific classifications. Additionally, this will allow for the possibility of extending these clusters to subjects from other populations if their glucagon dynamics have been observed in this data set.
Our choice of three clusters with a 15-min window was based on the model selection criteria and visual analysis of the clusters weighed against the complexity imposed by additional clusters. The heterogeneity of clusters 2 and 3 suggests other sets of dynamics that could be used, perhaps by increasing the number of clusters to 5 and allowing clusters 2 and 3 to be separated into two additional clusters. However, we found that increasing the number of clusters did not stratify the dynamics in this way. Experimenting with other clustering approaches, such as hierarchical clustering, did not provide a clear improvement over the current approach and was limited to monoclusters. In future work, another approach could be chosen to separate the characteristics in question.
Our focus on glucagon allows us to identify secretion patterns, but further analysis taking the interactions between glucose, insulin, and other incretin hormones into account is necessary before making any claims about the causal factors differentiating the subject dynamics. Our goal was to identify patterns of glucagon secretion in our study population, not to assign causal factors to these secretions, which is why we chose to include only glucagon in the clustering.
The findings of this work may shed light on how glucagon characteristics can impact blood glucose regulation in subjects that are either glucose-tolerant or intolerant. Categorizing glucose and insulin responses during OGTTs has been effectively used to study glucose regulation for various types of diabetes, and our approach has the potential to augment diagnosis and classification by including glucagon characteristics. Additionally, understanding the dynamics of glucagon secretion may lead to advances in various glucagon-based diabetes treatments, such as dual-hormone artificial pancreas technology or glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists.
Several limiting factors may have influenced the results. The study population was relatively homogenous, and their glucose levels were well controlled. While the population comprised individuals with varying degrees of glucose intolerance, it did not include subjects with very elevated HbA1c, so we could not assess the dynamics of more serious glucose intolerance. Additionally, more than half of the subjects had NGT. While glucagon dynamics are not solely explained by diagnosis classification, the relatively small IGT and T2D sample sizes, combined with the homogeneity, mean that it cannot be assumed that all or most possible glucagon dynamics are captured in this study. It is possible that some influential glucagon dynamics occur after 120 min, while glucose, insulin, and glucagon levels return to the fasting state. However, it is reasonable to assume that the large number of individual shapes identified is a significant portion of the possible major glucagon dynamics observed in OGTTs. Also, the overrepresentation of NGT may have caused important glucagon dynamics or relations between physiological variables to be undetectable from this data set.
Some limitations were imposed by the quantitative approach used in this work. The outlier removal step may have eliminated subjects with unusual but important secretion patterns. The use of another data set for comparison could illustrate this, but it was not available for this work. The shapelet extraction was applied to a relatively short section of the data. While that was chosen due to the dynamics of interest occurring in the first 30 min, it is possible that relaxing this constraint could provide insight into different phases of the glucagon secretion profiles.
We found that a few of the variables were significantly different during the post hoc analysis. This may be partly attributed to the approach of considering p-values that round to 0.05 (0.045–0.049) as insignificant. This was done as a precaution to account for numerical inaccuracy and to emphasize variables with clear differences between clusters. Relaxing this constraint could allow for deeper analysis into the differences between the subjects in each cluster, but it was deemed unnecessary because the focus of this work was on the glucagon dynamics and not underlying causal factors.
5. Conclusions
Glucagon dynamics shortly after carbohydrate intake vary greatly between individuals and across glucose intolerance diagnoses. Identification of subject-specific dynamics based on limited data would be useful in experimental settings where accurate plasma hormone measurement requires frequent blood tests. We have successfully identified subsets of glucagon dynamics based on the presence of extrema using only the first 30 min of measurements. Future work will investigate the effect of glucose and insulin dynamics on different glucagon secretion patterns and the extension of these clusters to mixed nutrient intake.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.S., M.R., M.R.A. and A.C.; methodology, A.S., M.R., M.R.A. and A.C.; software, A.S.; writing—original draft preparation, A.S.; writing—review and editing, A.S., M.R., M.R.A., M.A. and A.C.; supervision, M.R. and A.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Financial support from the Hyosung S. R. Cho Endowed Chair at the Illinois Institute of Technology provided to A. Shahidehpour and A. Cinar is gratefully acknowledged.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Restrictions apply to the availability of these data. Data was obtained from a third party. Inquiries on data availability should be directed to the original authors.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Daisuke Yabe for providing the data used in this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- DeFronzo, R.A.; Ferrannini, E.; Groop, L.; Henry, R.R.; Herman, W.H.; Holst, J.J.; Hu, F.B.; Kahn, C.R.; Raz, I.; Shulman, G.I.; et al. Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2015, 1, 15019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’alessio, D. The role of dysregulated glucagon secretion in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2011, 13 (Suppl. S1), 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ElSayed, N.A.; Aleppo, G.; Aroda, V.R.; Bannuru, R.R.; Brown, F.M.; Bruemmer, D.; Collins, B.S.; Gibbons, C.H.; Giurini, J.M.; Hilliard, M.E.; et al. 12. Retinopathy, Neuropathy, and Foot Care: Standards of Care in Diabetes—2023. Diabetes Care 2023, 46, S203–S215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ElSayed, N.A.; Aleppo, G.; Aroda, V.R.; Bannuru, R.R.; Brown, F.M.; Bruemmer, D.; Collins, B.S.; Gaglia, J.L.; Hilliard, M.E.; Isaacs, D.; et al. 3. Prevention or Delay of Type 2 Diabetes and Associated Comorbidities: Standards of Care in Diabetes—2023. Diabetes Care 2023, 46, S41–S48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marín-Peñalver, J.J.; Martín-Timón, I.; Sevillano-Collantes, C.; Del Cañizo-Gómez, F.J. Update on the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. World J. Diabetes 2016, 7, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ElSayed, N.A.; Aleppo, G.; Aroda, V.R.; Bannuru, R.R.; Brown, F.M.; Bruemmer, D.; Collins, B.S.; Hilliard, M.E.; Isaacs, D.; Johnson, E.L.; et al. 9. Pharmacologic Approaches to Glycemic Treatment: Standards of Care in Diabetes—2023. Diabetes Care 2023, 46, S140–S157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElSayed, N.A.; Aleppo, G.; Aroda, V.R.; Bannuru, R.R.; Brown, F.M.; Bruemmer, D.; Collins, B.S.; Hilliard, M.E.; Isaacs, D.; Johnson, E.L.; et al. 5. Facilitating Positive Health Behaviors and Well-being to Improve Health Outcomes: Standards of Care in Diabetes—2023. Diabetes Care 2023, 46, S68–S96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElSayed, N.A.; Aleppo, G.; Aroda, V.R.; Bannuru, R.R.; Brown, F.M.; Bruemmer, D.; Collins, B.S.; Hilliard, M.E.; Isaacs, D.; Johnson, E.L.; et al. 8. Obesity and Weight Management for the Prevention and Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes: Standards of Care in Diabetes—2023. Diabetes Care 2023, 46, S128–S139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hædersdal, S.; Lund, A.; Knop, F.K.; Vilsbøll, T. The Role of Glucagon in the Pathophysiology and Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2018, 93, 217–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wewer Albrechtsen, N.J.; Kuhre, R.E.; Pedersen, J.; Knop, F.K.; Holst, J.J. The biology of glucagon and the consequences of hyperglucagonemia. Biomarks Med. 2016, 10, 1141–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, P.; Vella, A.; Basu, A.; Basu, R.; Schwenk, W.F.; Rizza, R.A. Lack of Suppression of Glucagon Contributes to Postprandial Hyperglycemia in Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2000, 85, 4053–4059. Available online: https://academic.oup.com/jcem/article/85/11/4053/2852644 (accessed on 1 January 2023). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yabe, D.; Kuroe, A.; Watanabe, K.; Iwasaki, M.; Hamasaki, A.; Hamamoto, Y.; Harada, N.; Yamane, S.; Lee, S.; Murotani, K.; et al. Early phase glucagon and insulin secretory abnormalities, but not incretin secretion, are similarly responsible for hyperglycemia after ingestion of nutrients. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2015, 29, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grøndahl, M.F.; Lund, A.B.; Bagger, J.I.; Petersen, T.S.; Albrechtsen, N.J.W.; Holst, J.J.; Vilsbøll, T.; Christensen, M.B.; Knop, F.K. Glucagon Clearance Is Preserved in Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes 2022, 71, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knop, F.K.; Aaboe, K.; Vilsbøll, T.; Vølund, A.; Holst, J.J.; Krarup, T.; Madsbad, S. Impaired incretin effect and fasting hyperglucagonaemia characterizing type 2 diabetic subjects are early signs of dysmetabolism in obesity. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2012, 14, 500–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gar, C.; Rottenkolber, M.; Sacco, V.; Moschko, S.; Banning, F.; Hesse, N.; Popp, D.; Hübener, C.; Seissler, J.; Lechner, A. Patterns of plasma glucagon dynamics do not match metabolic phenotypes in young women. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 103, 972–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Göbl, C.; Morettini, M.; Salvatori, B.; Alsalim, W.; Kahleova, H.; Ahrén, B.; Tura, A. Temporal Patterns of Glucagon and Its Relationships with Glucose and Insulin following Ingestion of Different Classes of Macronutrients. Nutrients 2022, 14, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahlqvist, E.; Storm, P.; Käräjämäki, A.; Martinell, M.; Dorkhan, M.; Carlsson, A.; Vikman, P.; Prasad, R.B.; Aly, D.M.; Almgren, P.; et al. Novel subgroups of adult-onset diabetes and their association with outcomes: A data-driven cluster analysis of six variables. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018, 6, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarría-Santamera, A.; Orazumbekova, B.; Maulenkul, T.; Gaipov, A.; Atageldiyeva, K. The identification of diabetes mellitus subtypes applying cluster analysis techniques: A systematic review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 9523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morettini, M.; Burattini, L.; Göbl, C.; Pacini, G.; Ahrén, B.; Tura, A. Mathematical Model of Glucagon Kinetics for the Assessment of Insulin-Mediated Glucagon Inhibition During an Oral Glucose Tolerance Test. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 611147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, C.; Baweja, M.; Crews, D.C.; Eneanya, N.D.; Gadegbeku, C.A.; Inker, L.A.; Mendu, M.L.; Miller, W.G.; Moxey-Mims, M.M.; Roberts, G.V.; et al. A Unifying Approach for GFR Estimation: Recommendations of the NKF-ASN Task Force on Reassessing the Inclusion of Race in Diagnosing Kidney Disease. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2022, 79, 268–288.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabbath, C.A.; Corriveau, D. A comparison of piecewise cubic Hermite interpolating polynomials, cubic splines and piecewise linear functions for the approximation of projectile aerodynamics. Def. Technol. 2019, 15, 741–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, C.-C.M.; Zhu, Y.; Ulanova, L.; Begum, N.; Ding, Y.; Dau, H.A.; Silva, D.F.; Mueen, A.; Keogh, E. Matrix profile I: All pairs similarity joins for time series: A unifying view that includes motifs, discords and shapelets. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Data Mining, ICDM, Barcelona, Spain, 12–15 December 2016; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1317–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, C.C.M.; Kavantzas, N.; Keogh, E. Matrix profile VI: Meaningful multidimensional motif discovery. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Data Mining, ICDM, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–21 November 2017; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, S. STUMPY: A Powerful and Scalable Python Library for Time Series Data Mining. J. Open Source Softw. 2019, 4, 1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, C.R.; Millman, K.J.; van der Walt, S.J.; Gommers, R.; Virtanen, P.; Cournapeau, D.; Wieser, E.; Taylor, J.; Berg, S.; Smith, N.J.; et al. Array programming with NumPy. Nature 2020, 585, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virtanen, P.; Gommers, R.; Oliphant, T.E.; Haberland, M.; Reddy, T.; Cournapeau, D.; Burovski, E.; Peterson, P.; Weckesser, W.; Bright, J.; et al. SciPy 1.0: Fundamental algorithms for scientific computing in Python. Nat. Methods 2020, 17, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Gharghabi, S.; Silva, D.F.; Dau, H.A.; Yeh, C.-C.M.; Senobari, N.S.; Almaslukh, A.; Kamgar, K.; Zimmerman, Z.; Funning, G.; et al. The Swiss army knife of time series data mining: Ten useful things you can do with the matrix profile and ten lines of code. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2020, 34, 949–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waskom, M. seaborn: Statistical data visualization. J. Open Source Softw. 2021, 6, 3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mckinney, W. Data Structures for Statistical Computing in Python. In Proceedings of the 9th Python in Science Conference, Austin, TX, USA, 28 June–3 July 2010; Van der Walt, S., Millman, J., Eds.; pp. 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi, H.; Williams, L.J. Principal component analysis. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Stat. 2010, 2, 433–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V.; et al. Scikit-learn: Machine Learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Z.; Zou, C.; Dong, J. Outlier detection using isolation forest and local outlier. In Proceedings of the 2019 Research in Adaptive and Convergent Systems, RACS 2019, Chongqing, China, 24–27 September 2019; Association for Computing Machinery, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluger, Y.; Basri, R.; Chang, J.T.; Gerstein, M. Spectral biclustering of microarray data: Coclustering genes and conditions. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 703–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madeira, S.C.; Oliveira, A.L. Biclustering algorithms for biological data analysis: A survey. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2004, 1, 24–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Wunsch, D. Survey of clustering algorithms. IEEE Trans. Neural. Netw. 2005, 16, 645–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahapure, K.R.; Nicholas, C. Cluster quality analysis using silhouette score. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 7th International Conference on Data Science and Advanced Analytics, DSAA 2020, Sydney, Australia, 6–9 October 2020; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 747–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousseeuw, P.J. Silhouettes: A Graphical Aid to the Interpretation and Validation of Cluster Analysis. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 1987, 20, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terpilowski, M. Scikit-posthocs: Pairwise multiple comparison tests in Python. J. Open Source Softw. 2019, 4, 1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Ghani, M.A.; Lyssenko, V.; Tuomi, T.; DeFronzo, R.A.; Groop, L. The shape of plasma glucose concentration curve during OGTT predicts future risk of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2010, 26, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tschritter, O.; Fritsche, A.; Machicao, F.; Häring, H.H.; Stumvoll, M. Assessing the Shape of the Glucose Curve During an Oral Glucose Tolerance Test. Diabetes Care 2003, 26, 1026–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenbaum, S.E. Basic Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics: An Integrated Textbook and Computer Simulations, 1st ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).