Effects of Ghrelin on Plasminogen Activator Activity in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cell Cultures
2.3. Total RNA Extraction and Quantification
2.4. Gel Electrophoresis and Casein Underlay
2.5. Dissociation of High-Molecular-Weight PA Forms
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
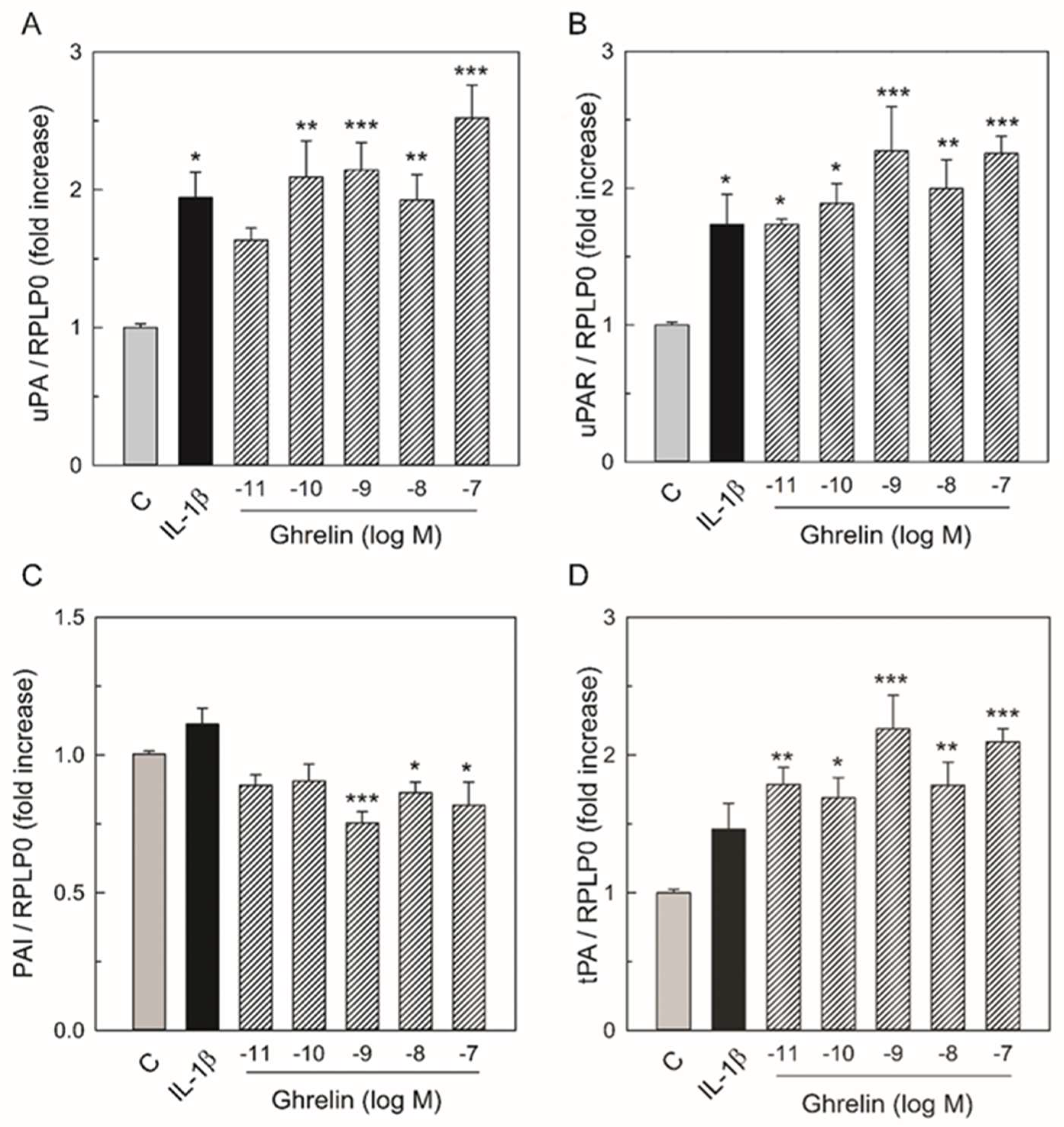
3.1. Effects of Ghrelin on uPA, uPAR, tPA, PAI-1 mRNA Expression
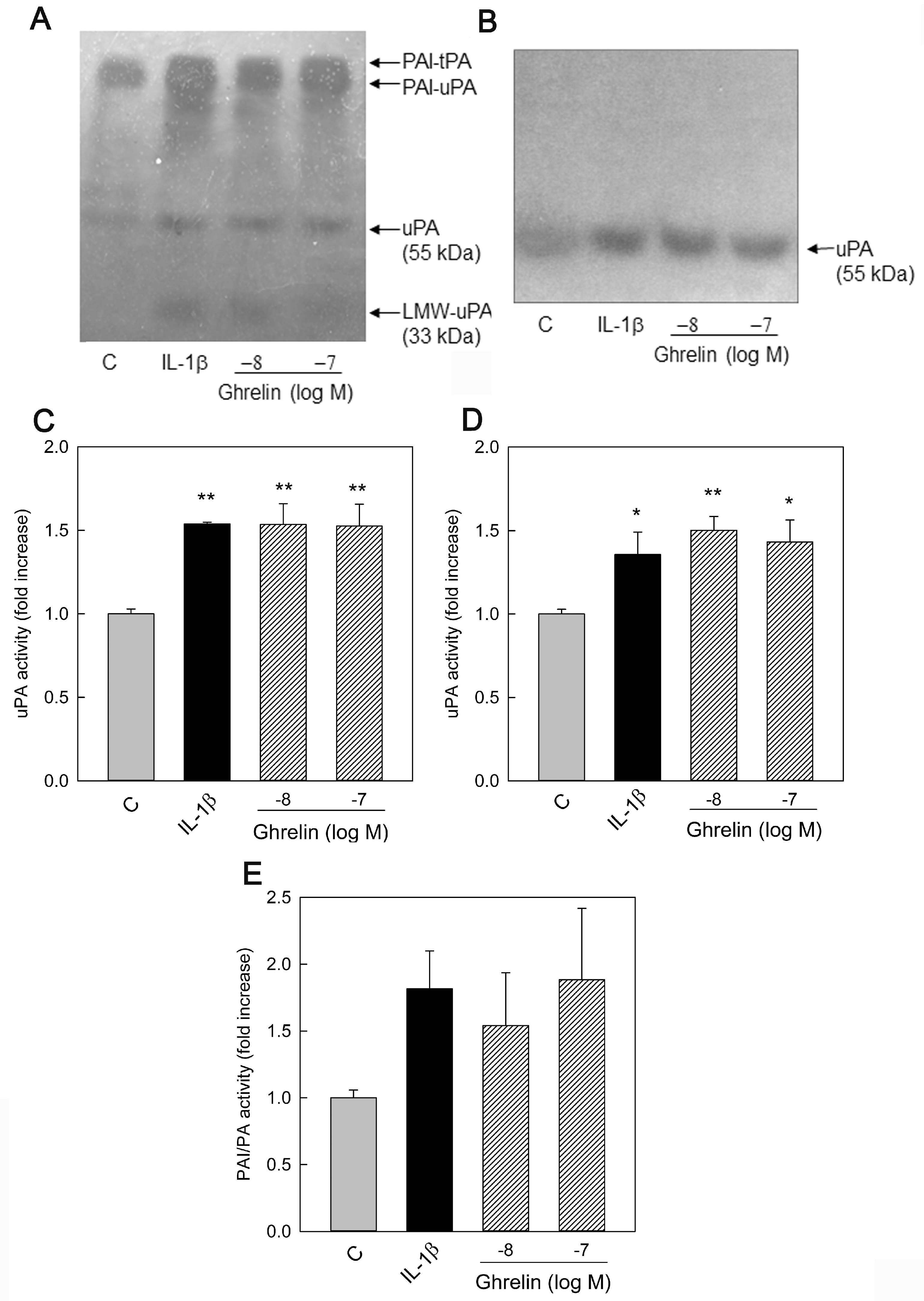
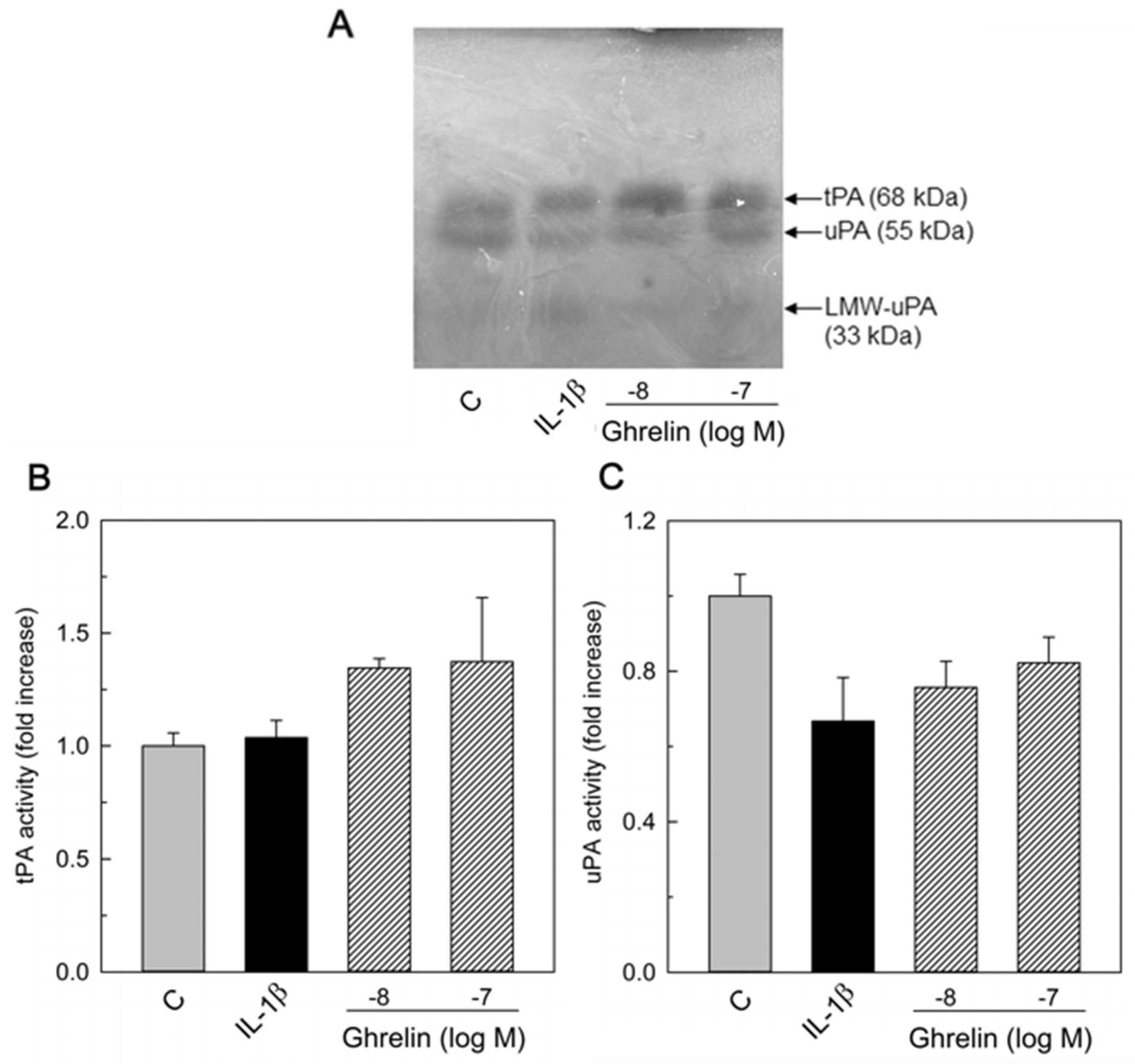
3.2. Effects of Ghrelin on uPA, tPA, and PAI-1 Production
3.3. PAI and PA Dissociation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mao, Y.; Tokudome, T.; Kishimoto, I. Ghrelin and Blood Pressure Regulation. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2016, 18, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gualillo, O.; Caminos, J.; Blanco, M.; Garcia-Caballero, T.; Kojima, M.; Kangawa, K.; Dieguez, C.; Casanueva, F. Ghrelin, a novel placental-derived hormone. Endocrinology 2001, 142, 788–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yang, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fei, H. Ghrelin promotes angiogenesis by activating the Jagged1/Notch2/VEGF pathway in preeclampsia. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 2021, 47, 486–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rak-Mardyla, A.; Gregoraszczuk, E. Effect of ghrelin on proliferation, apoptosis and secretion of progesterone and hCG in the placental JEG-3 cell line. Reprod. Biol. 2010, 10, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Dominguez, M.I.; Lazo-de-la-Vega-Monroy, M.L.; Zaina, S.; Sabanero, M.; Daza-Benitez, L.; Malacara, J.M.; Barbosa-Sabanero, G. Association of cord blood des-acyl ghrelin with birth weight, and placental GHS-R1 receptor expression in SGA, AGA, and LGA newborns. Endocrine 2016, 53, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donahue, S.M.A.; Kleinman, K.P.; Gillman, M.W.; Oken, E. Trends in birth weight and gestational length among singleton term births in the United States: 1990–2005. Obstet. Gynecol. 2010, 115, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sappino, A.P.; Huarte, J.; Belin, D.; Vassalli, J.D. Plasminogen activators in tissue remodeling and invasion: mRNA localization in mouse ovaries and implanting embryos. J. Cell Biol. 1989, 109, 2471–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattori, N.; Saito, T.; Yagyu, T.; Jiang, B.H.; Kitagawa, K.; Inagaki, C. GH, GH receptor, GH secretagogue receptor, and ghrelin expression in human T cells, B cells, and neutrophils. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 4284–4291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, V.D.; Schaffer, E.M.; Pyle, R.S.; Collins, G.D.; Sakthivel, S.K.; Palaniappan, R.; Lillard, J.W., Jr.; Taub, D.D. Ghrelin inhibits leptin- and activation-induced proinflammatory cytokine expression by human monocytes and T cells. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 114, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; Ida, T.; Shiimura, Y.; Matsui, K.; Oishi, K.; Kojima, M. Insights into the Regulation of Offspring Growth by Maternally Derived Ghrelin. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 852636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Trujillo, L.; Garcia-Montero, C.; Fraile-Martinez, O.; Guijarro, L.G.; Bravo, C.; De Leon-Luis, J.A.; Saez, J.V.; Bujan, J.; Alvarez-Mon, M.; Garcia-Honduvilla, N.; et al. Considering the Effects and Maternofoetal Implications of Vascular Disorders and the Umbilical Cord. Medicina 2022, 58, 1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gathiram, P.; Moodley, J. Pre-eclampsia: Its pathogenesis and pathophysiolgy. Cardiovasc. J. Afr. 2016, 27, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boeldt, D.S.; Bird, I.M. Vascular adaptation in pregnancy and endothelial dysfunction in preeclampsia. J. Endocrinol. 2017, 232, R27–R44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Mao, S.J.; McLean, L.R.; Powers, R.W.; Larsen, W.J. Proteins of the inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor family stabilize the cumulus extracellular matrix through their direct binding with hyaluronic acid. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 28282–28287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesauro, M.; Schinzari, F.; Iantorno, M.; Rizza, S.; Melina, D.; Lauro, D.; Cardillo, C. Ghrelin improves endothelial function in patients with metabolic syndrome. Circulation 2005, 112, 2986–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedayati, N.; Annambhotla, S.; Jiang, J.; Wang, X.; Chai, H.; Lin, P.H.; Yao, Q.; Chen, C. Growth hormone-releasing peptide ghrelin inhibits homocysteine-induced endothelial dysfunction in porcine coronary arteries and human endothelial cells. J. Vasc. Surg. 2009, 49, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iantorno, M.; Chen, H.; Kim, J.A.; Tesauro, M.; Lauro, D.; Cardillo, C.; Quon, M.J. Ghrelin has novel vascular actions that mimic PI 3-kinase-dependent actions of insulin to stimulate production of NO from endothelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 292, E756–E764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okumura, H.; Nagaya, N.; Enomoto, M.; Nakagawa, E.; Oya, H.; Kangawa, K. Vasodilatory effect of ghrelin, an endogenous peptide from the stomach. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2002, 39, 779–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landin, K.; Tengborn, L.; Smith, U. Elevated fibrinogen and plasminogen activator inhibitor (PAI-1) in hypertension are related to metabolic risk factors for cardiovascular disease. J. Intern. Med. 1990, 227, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fay, W.P.; Garg, N.; Sunkar, M. Vascular functions of the plasminogen activation system. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2007, 27, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dano, K.; Andreasen, A.; Grondahl-Hansen, J.; Kristensen, P.; Nielsen, L.S.; Skriver, L. Plasminogen activators, tissue degradation and cancer. Adv. Cancer Res. 1985, 44, 139–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharadwaj, A.G.; Holloway, R.W.; Miller, V.A.; Waisman, D.M. Plasmin and Plasminogen System in the Tumor Microenvironment: Implications for Cancer Diagnosis, Prognosis, and Therapy. Cancers 2021, 13, 1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepper, M.S. Role of the matrix metalloproteinase and plasminogen activator-plasmin systems in angiogenesis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2001, 21, 1104–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreasen, A.; Georg, B.; Lund, L.R.; Riccio, A.; Stacey, S.N. Plasminogen activator inhibitors: Hormonally regulated serpins. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 1990, 68, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajou, K.; Masson, V.; Gerard, R.D.; Schmitt, P.M.; Albert, V.; Praus, M.; Lund, L.R.; Frandsen, T.L.; Brunner, N.; Dano, K.; et al. The plasminogen activator inhibitor PAI-1 controls in vivo tumor vascularization by interaction with proteases, not vitronectin. Implications for antiangiogenic strategies. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 152, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seferovic, M.D.; Gupta, M.B. Increased Umbilical Cord PAI-1 Levels in Placental Insufficiency Are Associated with Fetal Hypoxia and Angiogenesis. Dis. Markers 2016, 2016, 7124186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, S.C.; Anandakumar, C.; Montan, S.; Ratnam, S.S. Plasminogen activators, plasminogen activator inhibitors and markers of intravascular coagulation in pre-eclampsia. Gynecol. Obstet. Investig. 1993, 35, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindoff, C.; Astedt, B. Plasminogen activator of urokinase type and its inhibitor of placental type in hypertensive pregnancies and in intrauterine growth retardation: Possible markers of placental function. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1994, 171, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, K.H.; Koh, S.C.; Malcus, P.; SvenMontan, S.; Biswas, A.; Arulkumaran, S.; Ratnam, S.S. Preeclampsia: Haemostatic status and the short-term effects of methyldopa and isradipine therapy. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 1998, 24, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estelles, A.; Gilabert, J.; Aznar, J.; Loskutoff, D.J.; Schleef, R.R. Changes in the plasma levels of type 1 and type 2 plasminogen activator inhibitors in normal pregnancy and in patients with severe preeclampsia. Blood 1989, 74, 1332–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roes, E.M.; Sweep, C.G.; Thomas, C.M.; Zusterzeel, P.L.; Geurts-Moespot, A.; Peters, W.H.; Steegers, E.A. Levels of plasminogen activators and their inhibitors in maternal and umbilical cord plasma in severe preeclampsia. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2002, 187, 1019–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conconi, M.T.; Nico, B.; Guidolin, D.; Baiguera, S.; Spinazzi, R.; Rebuffat, P.; Malendowicz, L.K.; Vacca, A.; Carraro, G.; Parnigotto, P.P.; et al. Ghrelin inhibits FGF-2-mediated angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo. Peptides 2004, 25, 2179–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miceli, F.; Tropea, A.; Minici, F.; Orlando, M.; Lamanna, G.; Gangale, M.F.; Panetta, B.; Tiberi, F.; Vaccari, S.; Canipari, R.; et al. Effects of insulin-like growth factor I and II on prostaglandin synthesis and plasminogen activator activity in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 90, 372–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakhashab, S.; Lary, S.; Ahmed, F.; Schulten, H.J.; Bashir, A.; Ahmed, F.W.; Al-Malki, A.L.; Jamal, H.S.; Gari, M.A.; Weaver, J.U. Reference genes for expression studies in hypoxia and hyperglycemia models in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. G3 2014, 4, 2159–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belin, D.; Godeau, F.; Vassalli, J.D. Tumor promoter PMA stimulates the synthesis and secretion of mouse pro-urokinase in MSV-transformed 3T3 cells: This is mediated by an increase in urokinase mRNA content. EMBO J. 1984, 3, 1901–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Booyse, F.M.; Scheinbuks, J.; Lin, P.H.; Traylor, M.; Bruce, R. Isolation and interrelationships of the multiple molecular tissue-type and urokinase-type plasminogen activator forms produced by cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1988, 263, 15129–15138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasai, S.; Arimura, H.; Nishida, M.; Suyama, T. Primary structure of single-chain pro-urokinase. J. Biol. Chem. 1985, 260, 12382–12389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makino, Y.; Hosoda, H.; Shibata, K.; Makino, I.; Kojima, M.; Kangawa, K.; Kawarabayashi, T. Alteration of plasma ghrelin levels associated with the blood pressure in pregnancy. Hypertension 2002, 39, 781–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erol, O.; Ellidag, H.Y.; Ayik, H.; Bulbul, G.A.; Derbent, A.U.; Kulaksizoglu, S.; Yilmaz, N. Increased serum ghrelin in preeclampsia: Is ghrelin a friend or a foe? Ginekol. Pol. 2016, 87, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, Y.; Nagaya, N.; Teranishi, Y.; Imazu, M.; Yamamoto, H.; Shokawa, T.; Kangawa, K.; Kohno, N.; Yoshizumi, M. Ghrelin improves endothelial dysfunction through growth hormone-independent mechanisms in rats. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 310, 830–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiley, K.E.; Davenport, A.P. Comparison of vasodilators in human internal mammary artery: Ghrelin is a potent physiological antagonist of endothelin-1. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 136, 1146–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismail, A.A.; Shaker, B.T.; Bajou, K. The Plasminogen-Activator Plasmin System in Physiological and Pathophysiological Angiogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 23, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dusse, L.M.; Rios, D.R.; Pinheiro, M.B.; Cooper, A.J.; Lwaleed, B.A. Pre-eclampsia: Relationship between coagulation, fibrinolysis and inflammation. Clin. Chim. Acta 2011, 412, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loskutoff, D.J.; Ny, T.; Sawdey, M.; Lawrence, D. Fibrinolytic system of cultured endothelial cells: Regulation by plasminogen activator inhibitor. J. Cell. Biochem. 1986, 32, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sprengers, E.D.; Kluft, C. Plasminogen activator inhibitors. Blood 1987, 69, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasi, F.; Sidenius, N. The urokinase receptor: Focused cell surface proteolysis, cell adhesion and signaling. FEBS Lett. 2010, 584, 1923–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandberg, T.; Casslen, B.; Gustavsson, B.; Benraad, T.J. Human endothelial cell migration is stimulated by urokinase plasminogen activator:plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 complex released from endometrial stromal cells stimulated with transforming growth factor beta1; possible mechanism for paracrine stimulation of endometrial angiogenesis. Biol. Reprod. 1998, 59, 759–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildenbrand, R.; Gandhari, M.; Stroebel, P.; Marx, A.; Allgayer, H.; Arens, N. The urokinase-system--role of cell proliferation and apoptosis. Histol. Histopathol. 2008, 23, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymond, D.; Peterson, E. A critical review of early-onset and late-onset preeclampsia. Obstet. Gynecol. Surv. 2011, 66, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, J.L.; Adam, C.L.; Brown, Y.A.; Wallace, J.M.; Aitken, R.P.; Lea, R.G.; Miller, D.W. An immunohistochemical study of the localization and developmental expression of ghrelin and its functional receptor in the ovine placenta. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2007, 5, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, S.; Pan, Z.; Ou, T.; Ma, J.; Liu, H.; Li, R.; Yang, P.; Han, W.; Guan, S.; et al. AMPK/NF-kappaB signaling pathway regulated by ghrelin participates in the regulation of HUVEC and THP1 Inflammation. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 437, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, F. Ghrelin improves endothelial function and reduces blood pressure in Ang II-induced hypertensive mice: Role of AMPK. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 2023, 45, 2208774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komiya, M.; Fujii, G.; Takahashi, M.; Shimura, M.; Noma, N.; Shimizu, S.; Onuma, W.; Mutoh, M. Bi-directional regulation between adiponectin and plasminogen activator-inhibitor-1 in 3T3-L1 cells. In Vivo 2014, 28, 13–19. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, L.; Lin, C.; Liao, C.; Xin, L.; Zhong, S.; Cheng, Q.; Zhang, L. Adiponectin Inhibits TNF-alpha-Activated PAI-1 Expression Via the cAMP-PKA-AMPK-NF-kappaB Axis in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 42, 2342–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Gene | Primers | Product Length (bp) |
|---|---|---|
| RPLP0 | Fw:5′-TAAACCCTGCGTGGCAATCC-3′ Rv:5′-CTTGGAGCCCACATTGTCTG-3′ | 150 |
| uPA | Fw:5′-GGGAGATGAAGTTGAGGTGG-3′ Rv:5′-GTTATACATCGAGGGCAGGC-3′ | 166 |
| uPAR | Fw:5′-CTATCGGACTGGCTTGAAGATC-3′ Rv:5′-GCTTCGGGAATAGGTGACAG-3′ | 103 |
| PAI-1 | Fw:5′-AGAACCTGGGAATGACCGAC-3′ Rv:5′-ATGCGGGCTGAGACTATGAC-3′ | 169 |
| tPA | Fw:5′-CGCAGGCTGACGTGGGAGTA-3′ Rv:5′-GTGGGCGGCAGAGAGAATCC-3′ | 222 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fiacco, E.; Notaristefano, G.; Tropea, A.; Apa, R.; Canipari, R. Effects of Ghrelin on Plasminogen Activator Activity in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells. Endocrines 2024, 5, 24-35. https://doi.org/10.3390/endocrines5010002
Fiacco E, Notaristefano G, Tropea A, Apa R, Canipari R. Effects of Ghrelin on Plasminogen Activator Activity in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells. Endocrines. 2024; 5(1):24-35. https://doi.org/10.3390/endocrines5010002
Chicago/Turabian StyleFiacco, Elisabetta, Giovanna Notaristefano, Anna Tropea, Rosanna Apa, and Rita Canipari. 2024. "Effects of Ghrelin on Plasminogen Activator Activity in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells" Endocrines 5, no. 1: 24-35. https://doi.org/10.3390/endocrines5010002
APA StyleFiacco, E., Notaristefano, G., Tropea, A., Apa, R., & Canipari, R. (2024). Effects of Ghrelin on Plasminogen Activator Activity in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells. Endocrines, 5(1), 24-35. https://doi.org/10.3390/endocrines5010002






