Towards Sustainable Crossbar Artificial Synapses with Zinc-Tin Oxide
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
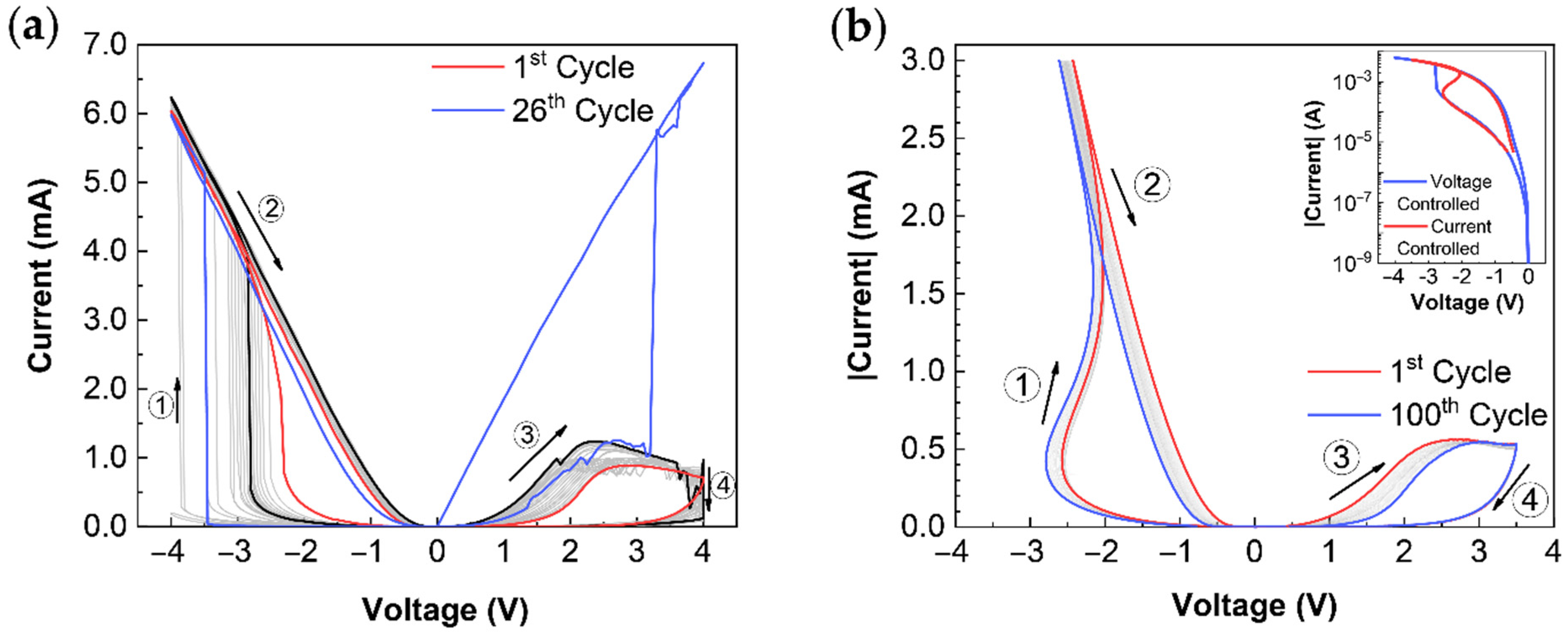
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahad, M.A.; Tripathi, G.; Zafar, S.; Doja, F. IoT Data Management—Security Aspects of Information Linkage in IoT Systems. In Principles of Internet of Things (IoT) Ecosystem: Insight Paradigm; Peng, S.-L., Pal, S., Huang, L., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 439–464. ISBN 978-3-030-33596-0. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Yang, C.; Wen, J.; Gai, S. Emerging nonvolatile memories to go beyond scaling limits of conventional CMOS nanodevices. J. Nanomater. 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, I.T.; Lin, Y.C.; Wang, Y.F.; Hsu, C.W.; Hou, T.H. 3D synaptic architecture with ultralow sub-10 fJ energy per spike for neuromorphic computation. Tech. Dig. Int. Electron Devices Meet. IEDM 2015, 28.5.1–28.5.4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burr, G.W.; Shelby, R.M.; Sebastian, A.; Kim, S.; Kim, S.; Sidler, S.; Virwani, K.; Ishii, M.; Narayanan, P.; Fumarola, A.; et al. Neuromorphic computing using non-volatile memory. Adv. Phys. X 2017, 2, 89–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, K.; Fumarola, A.; Sidler, S.; Jang, J.; Narayanan, P.; Shelby, R.M.; Burr, G.W.; Hwang, H. Bidirectional non-filamentary RRAM as an analog neuromorphic synapse, Part I: Al/Mo/Pr0.7Ca0.3MnO3 material improvements and device measurements. IEEE J. Electron Devices Soc. 2018, 6, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, S.; Lee, S.Y.; Park, J.; Seo, H. Forming-less and Non-Volatile Resistive Switching in by Oxygen Vacancy Control at Interfaces. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Joshi, S.; Savel’ev, S.E.; Jiang, H.; Midya, R.; Lin, P.; Hu, M.; Ge, N.; Strachan, J.P.; Li, Z.; et al. Memristors with diffusive dynamics as synaptic emulators for neuromorphic computing. Nat. Mater. 2017, 16, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carlos, E.; Deuermeier, J.; Branquinho, R.; Gaspar, C.; Martins, R.; Kiazadeh, A.; Fortunato, E. Design and synthesis of low temperature printed metal oxide memristors. J. Mater. Chem. C 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, M.; Sumida, R.; Kurasaki, A.; Imai, T.; Takishita, Y.; Nakashima, Y. Amorphous metal oxide semiconductor thin film, analog memristor, and autonomous local learning for neuromorphic systems. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlos, E.; Branquinho, R.; Martins, R.; Kiazadeh, A.; Fortunato, E. Recent Progress in Solution-Based Metal Oxide Resistive Switching Devices. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2004328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Z.; Freitas, P.; Zhang, W.; Hatem, F.; Zhang, J.F.; Marsland, J.; Govoreanu, B.; Goux, L.; Kar, G.S. Impact of RTN on Pattern Recognition Accuracy of RRAM-Based Synaptic Neural Network. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2018, 39, 1652–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pereira, M.; Deuermeier, J.; Nogueira, R.; Carvalho, P.A.; Martins, R.; Fortunato, E.; Kiazadeh, A. Noble-Metal-Free Memristive Devices Based on IGZO for Neuromorphic Applications. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2020, 2000242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiazadeh, A.; Gomes, H.L.; Barquinha, P.; Martins, J.; Rovisco, A.; Pinto, J.V.; Martins, R.; Fortunato, E. Improving positive and negative bias illumination stress stability in parylene passivated IGZO transistors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, J.; Kiazadeh, A.; Santos, L.; Deuermeier, J.; Martins, R.; Gomes, H.L.; Fortunato, E. Memristors Using Solution-Based IGZO Nanoparticles. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 8366–8372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, C.; Santa, A.; Santos, Â.; Bahubalindruni, P.; Deuermeier, J.; Martins, R.; Fortunato, E.; Barquinha, P. A Sustainable Approach to Flexible Electronics with Zinc-Tin Oxide Thin-Film Transistors. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2018, 4, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branquinho, R.; Salgueiro, D.; Santa, A.; Kiazadeh, A.; Barquinha, P.; Pereira, L.; Martins, R.; Fortunato, E. Towards environmental friendly solution-based ZTO/AlOx TFTs. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2015, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.H.; Kim, B.; Hussain, F.; Ismail, M.; Mahata, C.; Oh, T.; Imran, M.; Min, K.K.; Kim, T.H.; Yang, B.D.; et al. Zinc Tin Oxide Synaptic Device for Neuromorphic Engineering. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 130678–130686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casa Branca, N.; Deuermeier, J.; Martins, J.; Carlos, E.; Pereira, M.; Martins, R.; Fortunato, E.; Kiazadeh, A. 2D Resistive Switching Based on Amorphous Zinc–Tin Oxide Schottky Diodes. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2020, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.; Abbas, H.; Choi, C.; Kim, S. Controllable analog resistive switching and synaptic characteristics in ZrO2/ZTO bilayer memristive device for neuromorphic systems. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 529, 147107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, M.K.; Ismail, M.; Mahata, C.; Kim, S. Effect of interlayer on resistive switching properties of SnO2-based memristor for synaptic application. Results Phys. 2020, 18, 103325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.-H.; Kim, B.; Hussain, F.; Mahata, C.; Ismail, M.; Kim, Y.; Kim, S. Bio-inspired synaptic functions from a transparent zinc-tin-oxide-based memristor for neuromorphic engineering. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 544, 148796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.; Mahata, C.; Abbas, H.; Choi, C.; Kim, S. Bipolar, complementary resistive switching and synaptic properties of sputtering deposited ZnSnO-based devices for electronic synapses. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 862, 158416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murali, S.; Rajachidambaram, J.S.; Han, S.-Y.; Chang, C.-H.; Herman, G.S.; Conley, J.F. Resistive switching in zinc–tin-oxide. Solid. State. Electron. 2013, 79, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ham, S.; Choi, S.; Cho, H.; Na, S.-I.; Wang, G. Photonic Organolead Halide Perovskite Artificial Synapse Capable of Accelerated Learning at Low Power Inspired by Dopamine-Facilitated Synaptic Activity. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1806646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapkin, D.A.; Korovin, A.N.; Malakhov, S.N.; Emelyanov, A.V.; Demin, V.A.; Erokhin, V.V. Optical Monitoring of the Resistive States of a Polyaniline-Based Memristive Device. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2020, 6, 2000511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Williams, R.S.; Wang, Z. Third-order nanocircuit elements for neuromorphic engineering. Nature 2020, 585, 518–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, C.H.; Fan, Y.S.; Liu, P.T. Multilevel resistive switching memory with amorphous InGaZnO-based thin film. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 102, 2011–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.Q.; Xu, H.Y.; Li, X.H.; Yu, H.; Liu, Y.C.; Zhu, X.J. Synaptic Learning and Memory Functions Achieved Using Oxygen Ion Migration/Diffusion in an Amorphous InGaZnO Memristor. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 2759–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waser, R.; Bruchhaus, R.; Menzel, S. Redox-based Resistive Switching Memories. In Nanoelectronics and Information Technology, 3rd ed.; Waser, R., Ed.; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH: Berlin, Germany, 2012; pp. 683–710. ISBN 978-3-527-40927-3. [Google Scholar]
- Sung, C.; Hwang, H.; Yoo, I.K. Perspective: A review on memristive hardware for neuromorphic computation. J. Appl. Phys. 2018, 124, 151903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Long, S.; Liu, Y.; Hu, C.; Teng, J.; Liu, Q.; Lv, H.; Suñé, J.; Liu, M. Conductance Quantization in Resistive Random Access Memory. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2015, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.; Song, W.; Yao, P.; Li, Y.; Van Nostrand, J.; Qiu, Q.; Ielmini, D.; Yang, J.J. Integration and Co-design of Memristive Devices and Algorithms for Artificial Intelligence. iScience 2020, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, J.H. Schottky barrier and pn-junctionI/V plots—Small signal evaluation. Appl. Phys. A 1988, 47, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, J.H.; Güttler, H.H. Barrier inhomogeneities at Schottky contacts. J. Appl. Phys. 1991, 69, 1522–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lajn, A.; von Wenckstern, H.; Grundmann, M.; Wagner, G.; Barquinha, P.; Fortunato, E.; Martins, R. Comparative study of transparent rectifying contacts on semiconducting oxide single crystals and amorphous thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 113, 44511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlupp, P.; von Wenckstern, H.; Grundmann, M. Schottky barrier diodes based on room temperature fabricated amorphous zinc tin oxide thin films. Phys. Status Solidi Appl. Mater. Sci. 2017, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, F.-C. A Review on Conduction Mechanisms in Dielectric Films. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2014, 2014, 578168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wiefels, S.; von Witzleben, M.; Huttemann, M.; Bottger, U.; Waser, R.; Menzel, S. Impact of the Ohmic Electrode on the Endurance of Oxide-Based Resistive Switching Memory. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2021, 68, 1024–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkle, R.; Maier, J. How Is Oxygen Incorporated into Oxides? A Comprehensive Kinetic Study of a Simple Solid-State Reaction with SrTiO3 as a Model Material. Angew. Chemie Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 3874–3894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Year /Ref. | Switching Material | Structure | BE/TE Interface | Electrical Behavior | Switching Mechanism | Switching Behavior | RON/OFF | Retention (s) | Endurance (Cycles) | Synaptic Functions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 [current work] | ZTO | Crosspoint | Pt/Au | Bipolar | Area-dependent | Gradual and Abrupt SET/Gradual RESET | >102 | - | 100 | Yes |
| 2021 [21] | ZTO | Common BE | ITO/ITO | Unipolar/ Bipolar | Filamentary | Gradual and Abrupt SET and RESET | ≈103 | 103 | 150 | Yes |
| 2021 [22] | ZTO | Common BE | TiN/Ta | Bipolar | Filamentary | Gradual SET and RESET | >10 | >104 | 2000 | Yes |
| 2020 [18] | ZTO | Common BE | Pt/Au | Bipolar | Filamentary | Abrupt SET and RESET | ≈103 | 105 | 100 | - |
| 2020 [18] | ZTO | Common BE | Pt/Au | Bipolar | Area-dependent | Abrupt SET/ Gradual RESET | >10 | - | 100 | - |
| 2020 [18] | ZTO | Common BE | Pt/Au | Unipolar | Filamentary | Abrupt SET and RESET | >103 | 105 | 50 | - |
| 2020 [19] | ZrO2/ZTO | Common BE | TiN/Ta | Bipolar | Filamentary | Abrupt SET/Gradual RESET | ≈102 | - | 100 | Yes |
| 2020 [20] | SnO2/ZTO | Common BE | TiN/W | Bipolar | Filamentary | Gradual SET and RESET | >10 | - | 300 | Yes |
| 2020 [12] | IGZO | Crosspoint | Mo/Mo | Bipolar | Area-dependent | Gradual SET and RESET | ≈102 | - | - | Yes |
| 2017 [14] | IGZO | Common BE | Ti/Ag | Bipolar | Filamentary | Abrupt and Gradual SET and RESET | >10 | 104 | 100 | - |
| 2013 [23] | ZTO | Crosspoint | Pt/Al | Bipolar | Filamentary | Abrupt SET and RESET | >103 | > 103 | 50 | - |
| 2013 [27] | IGZO | Common BE | Pt/TiN | Bipolar | Filamentary | Abrupt SET and RESET | >102 | 103 | 150 | - |
| 2012 [28] | IGZO | Common BE | Pt/Pt | Bipolar | Area-dependent | Gradual SET/ Gradual RESET | ≈10 | - | - | Yes |
| 1.186 | 0.169 | 0.314 | 13.7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Silva, C.; Martins, J.; Deuermeier, J.; Pereira, M.E.; Rovisco, A.; Barquinha, P.; Goes, J.; Martins, R.; Fortunato, E.; Kiazadeh, A. Towards Sustainable Crossbar Artificial Synapses with Zinc-Tin Oxide. Electron. Mater. 2021, 2, 105-115. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronicmat2020009
Silva C, Martins J, Deuermeier J, Pereira ME, Rovisco A, Barquinha P, Goes J, Martins R, Fortunato E, Kiazadeh A. Towards Sustainable Crossbar Artificial Synapses with Zinc-Tin Oxide. Electronic Materials. 2021; 2(2):105-115. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronicmat2020009
Chicago/Turabian StyleSilva, Carlos, Jorge Martins, Jonas Deuermeier, Maria Elias Pereira, Ana Rovisco, Pedro Barquinha, João Goes, Rodrigo Martins, Elvira Fortunato, and Asal Kiazadeh. 2021. "Towards Sustainable Crossbar Artificial Synapses with Zinc-Tin Oxide" Electronic Materials 2, no. 2: 105-115. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronicmat2020009
APA StyleSilva, C., Martins, J., Deuermeier, J., Pereira, M. E., Rovisco, A., Barquinha, P., Goes, J., Martins, R., Fortunato, E., & Kiazadeh, A. (2021). Towards Sustainable Crossbar Artificial Synapses with Zinc-Tin Oxide. Electronic Materials, 2(2), 105-115. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronicmat2020009













