Investigation of Elastic Properties of WO3 Thin Films Supported on Quartz in Surface Acoustic Wave Sensing Devices
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental and Theoretical Approach
2.1. SAW Sensing Device
2.2. Experimental Setup
2.3. Simulation
- For the electrical domain, a potential difference is assigned to the electrodes;
- The mechanical stress T is zero at the free surfaces of WO3 and the electrodes;
- The boundary conditions at the piezoelectric substrate-electrode and piezoelectric substrate–WO3 interfaces require continuous mechanical displacements and stresses.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Structural and Morphological Characterization of WO3 Thin Films
3.2. Piezoelectric Characteristic
3.2.1. Sensitivity to the Gravimetric Effect
3.2.2. Sensitivity to the Variations of the WO3 Films Dielectric Properties
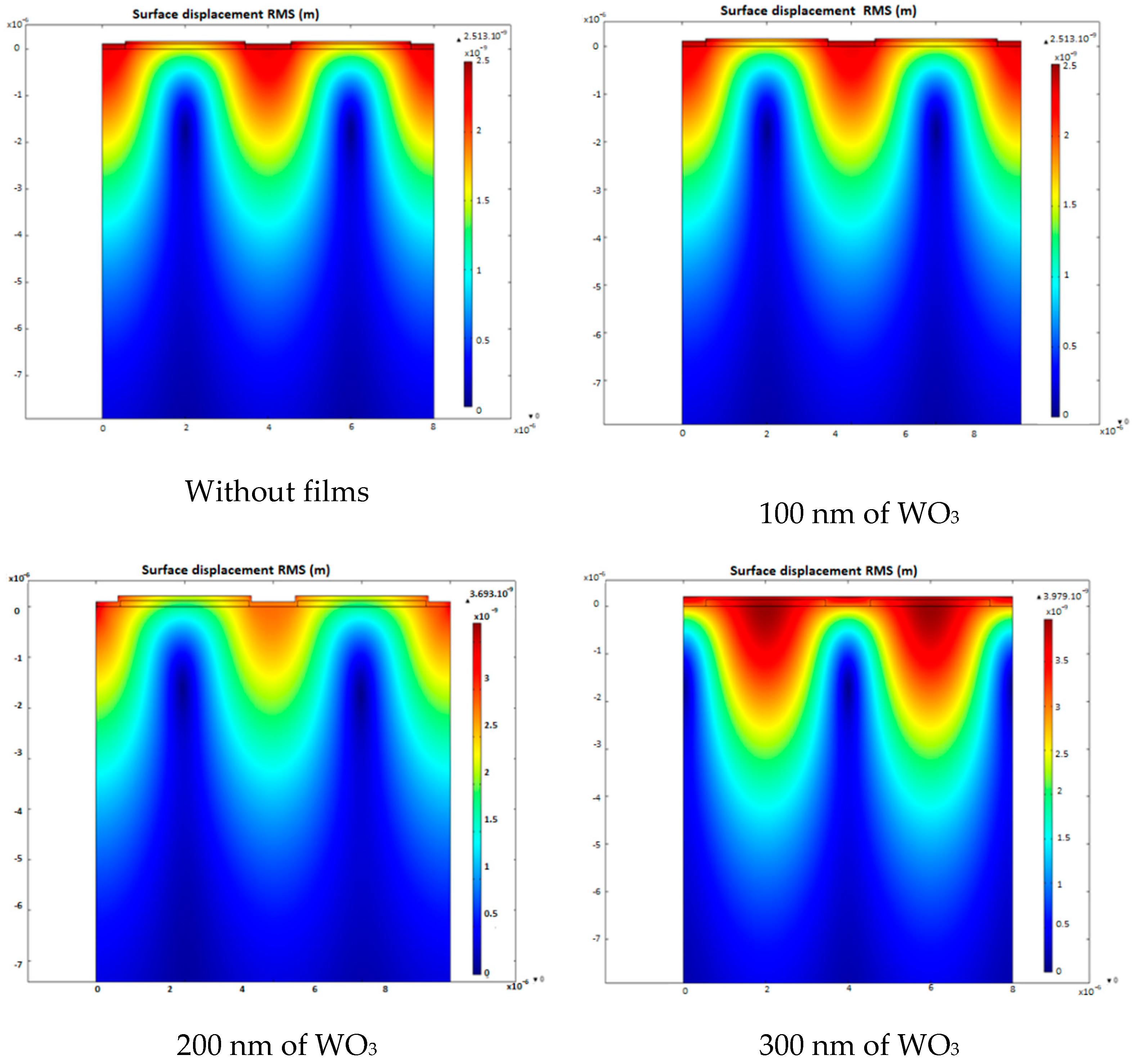
3.2.3. Elastic Properties of WO3 Thin Films
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pan, Y.; Molin, Q.; Guo, T.; Zhang, L.; Cao, B.; Yang, J.; Wang, W.; Xue, X. Wireless passive surface acoustic wave (SAW) technology in gas sensing. Sens. Rev. 2021, 41, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palla-Papavlu, A.; Voicu, S.; Dinescu, M. Sensitive Materials and Coating Technologies for Surface Acoustic Wave Sensors. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, M.; Arab, M.; Martino, C.; Delmas, L.; Guinneton, F.; Gavarri, J.-R. Carbon nanotubes/ceria composite layers deposited on surface acoustic wave devices for gas detection at room temperature. Thin Solid Films 2012, 520, 4786–4791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devkota, J.; Ohodnicki, P.R.; Greve, D.W. SAW Sensors for Chemical Vapors and Gases. Sensors 2017, 17, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Briscoe, J.; Dunn, S. Piezoelectric nanogenerators—A review of nanostructured piezoelectric energy harvesters. Nano Energy 2015, 14, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauder, A. SAW gas sensors: Comparison between delay line and two port resonator. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1995, 26, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anisimkin, V.; Kotelyanskii, I.; Fedosov, V.; Caliendo, C.; Verardi, P.; Verona, E. Analysis of the different contributions to the response of SAW gas sensors. In Proceedings of the 1995 IEEE Ultrasonics Symposium: An International Symposium, Seattle, WA, USA, 7–10 November 1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricco, A.J.; Martin, S.J. Thin metal film characterization and chemical sensors: Monitoring electronic conductivity, mass loading and mechanical properties with surface acoustic wave devices. Thin Solid Films 1991, 206, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakubik, W.P. Surface acoustic wave-based gas sensors. Thin Solid Films 2011, 520, 986–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ippolito, S.J.; Kandasamy, S.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Wlodarski, W. Layered SAW hydrogen sensor with modified tungsten trioxide selective layer. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2005, 108, 553–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadek, A.Z.; Wlodarski, W.; Shin, K.; Kaner, R.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. A polyaniline/WO3 nanofiber composite-based ZnO/64° YX LiNbO3 SAW hydrogen gas sensor. Synth. Met. 2008, 158, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guérin, J.; Bendahan, M.; Aguir, K. A dynamic response model for the WO3-based ozone sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2008, 128, 462–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faleh, R.; Gomri, S.; Aguir, K.; Kachouri, A. A new combined transient extraction method coupled with WO3 gas sensors for polluting gases classification. Sens. Rev. 2021, 41, 437–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovcharenko, N.V.; Smirnova, T.V. High refractive index and magneto–optical glasses in the systems TeO2–WO3–Bi2O3 and TeO2–WO3–PbO. J. Non-Crystalline Solids 2001, 291, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, I.S.; Issa, S.A.M.; Zakaly, H.M.H.; Saudi, H.A.; Ali, A.S.; Saddeek, Y.B.; Alharbi, T.; Tekin, H.O. Material characterization of WO3/Bi2O3 substituted calcium-borosilicate glasses: Structural, physical, mechanical properties and gamma-ray resistance competencies. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 888, 161419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirany, N.; Arab, M.; Madigou, V.; Leroux, C.; Gavarri, J.R. A facile one step route to synthesize WO3 nanoplatelets for CO oxidation and photodegradation of RhB: Microstructural, optical and electrical studies. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 69615–69626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatten, R.; Chadwick, A.V.; Rougier, A.A.; Lindan, P.J.D. The Oxygen Vacancy in Crystal Phases of WO3. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 3146–3156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dendzik, Z.; Dhrobak, D.; Nowak, R. Elastic constants and analytic bond order potential for atomistic simulations of simple cubic tungsten trioxide. Task Q. 2009, 13, 93–98. [Google Scholar]
- Ventura, P.; Steichen, W. Pascal FEM/BEM Analysis of a Generalized Periodic Array. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control. 2007, 54, 2052–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perois, X.; Pastureaud, T.; Girard, P.-A.; Lardat, R. Analysis of saw devices using FEM/BEM method and parallel computing. In Proceedings of the IEEE Ultrasonics Symposium, Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 18–21 September 2005; IEEE: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; Volume 3, pp. 1564–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, P.; Gratier, J. FEM/BEM analysis of infinite periodic grating covered with an SiO2 overlay. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Ultrasonics Symposium, Beijing, China, 2–5 November 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Lu, Z.; Ke, Y.; Tian, Y.; Luo, W. A Fast Optimization Algorithm of FEM/BEM Simulation for Periodic Surface Acoustic Wave Structures. Information 2019, 10, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arab, M.; Dirany, N.; David, M. BAW Resonator as Elastic Characterization Tools of WO3 Thin Films. Mater. Today Proc. 2016, 3, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahmy, A.H.; Adler, E.L. Propagation of acoustic surface waves in multilayers: A matrix description. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1973, 22, 495–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, I. Review of State of Art of Smart Structures and Integrated Systems. AIAA J. 2002, 40, 2145–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covaci, C.; Gontean, A. Piezoelectric Energy Harvesting Solutions: A Review. Sensors 2020, 20, 3512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ventura, P.; Dufilie, P.; Hecht, F. Full analysis of the mixed matrix parameters for a SAW transducer having aperiodic multi electrode cells. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium, Chicago, IL, USA, 3–6 September 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichinger, H.; Baghai-Wadji, A. Dynamic 2D analysis of SAW-devices including massloading. In Proceedings of the IEEE 1992 Ultrasonics Symposium, Tucson, AZ, USA, 20–23 October 1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salje, E. Lattice dynamics of WO3. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A 1975, 31, 360–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royer, D.; Dieulesaint, E. Ondes Elastiques dans les Solides; Masson: Paris, France, 1996. [Google Scholar]
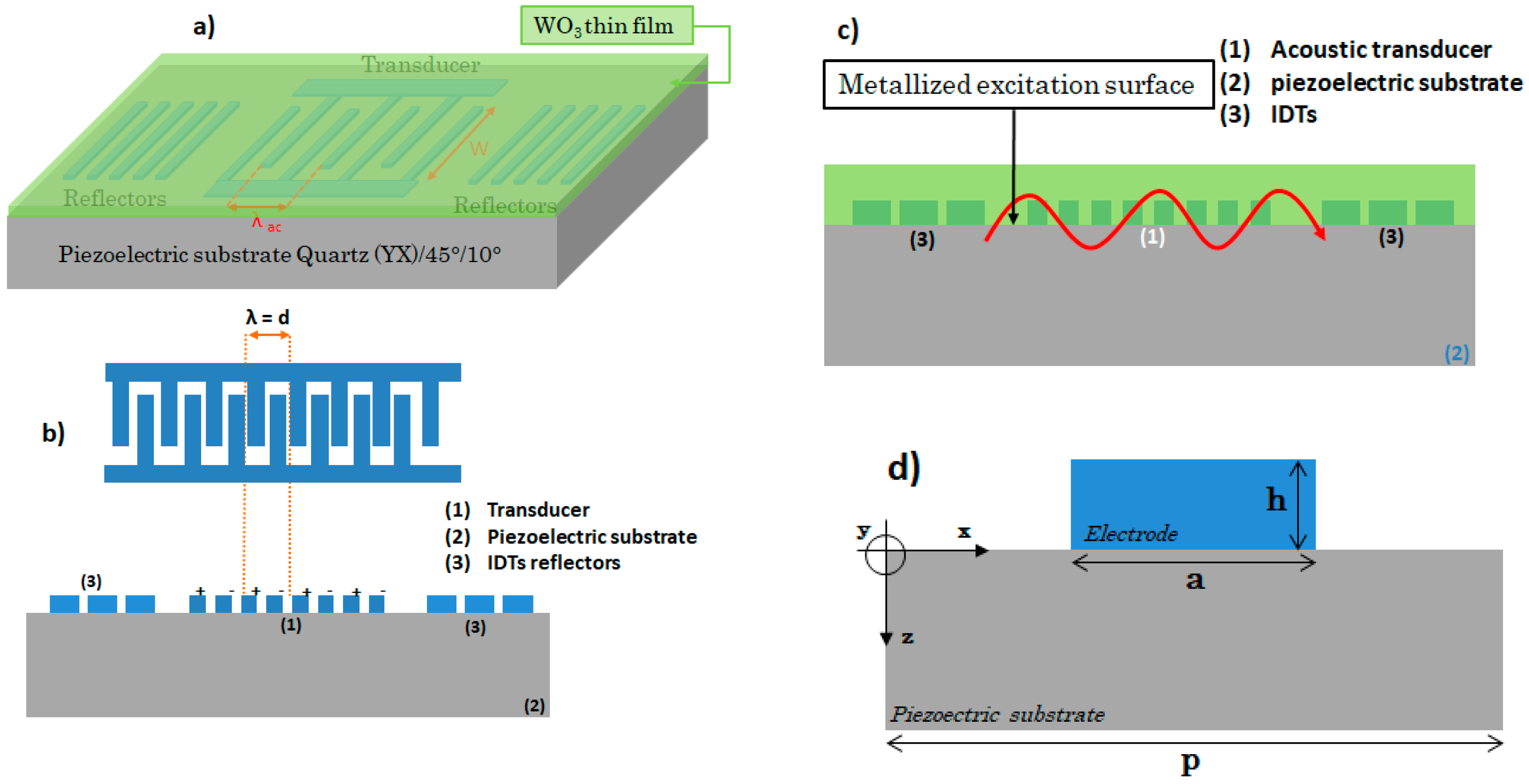
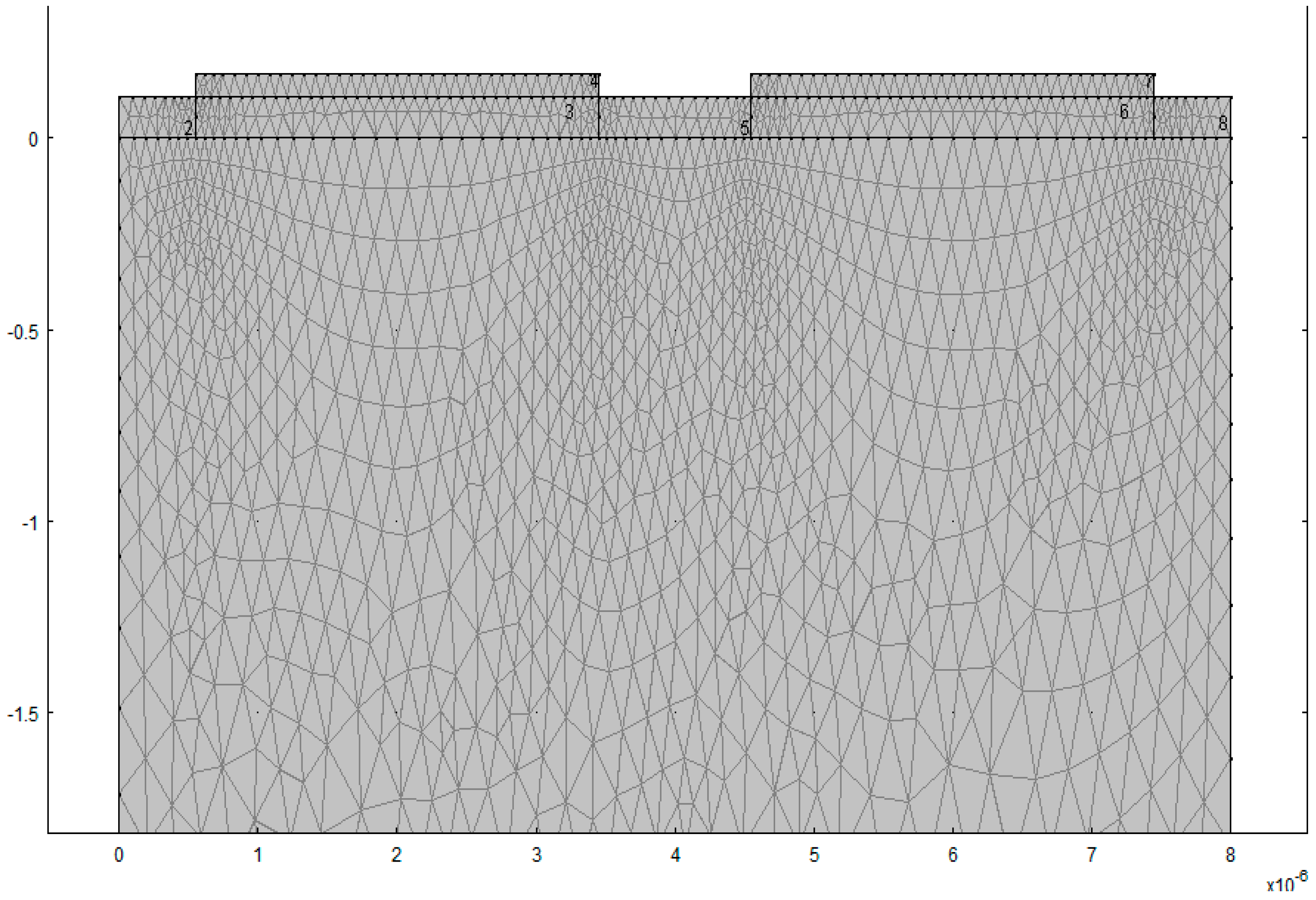


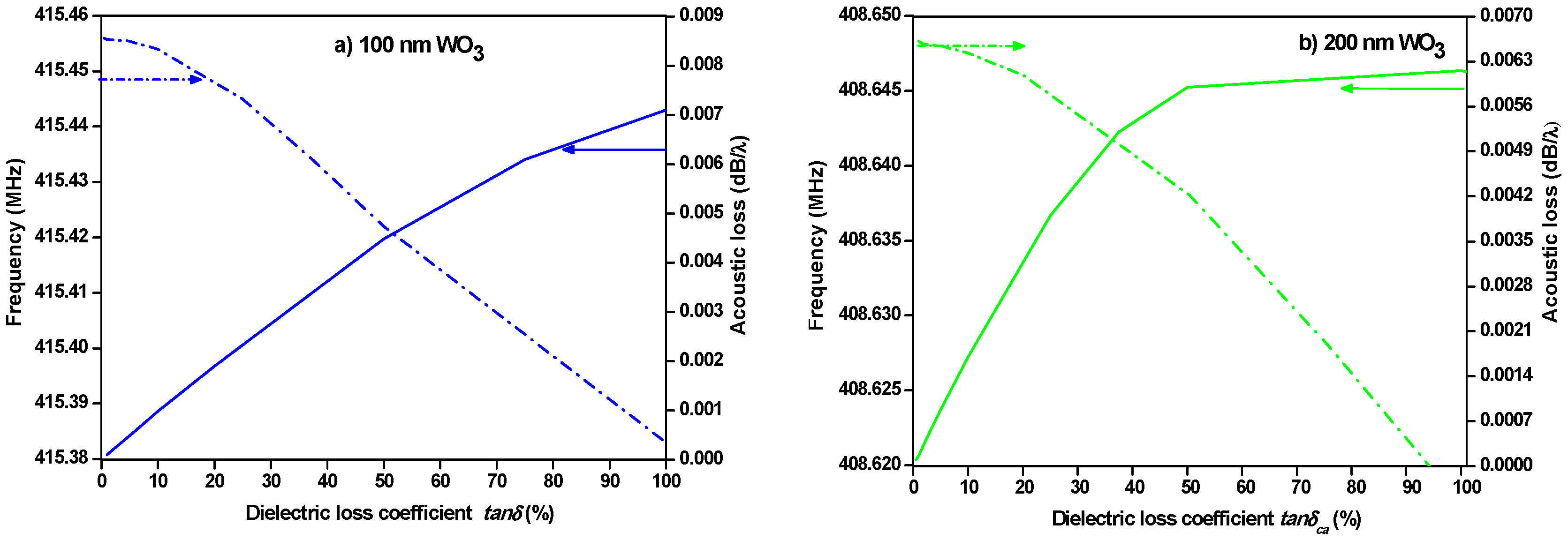
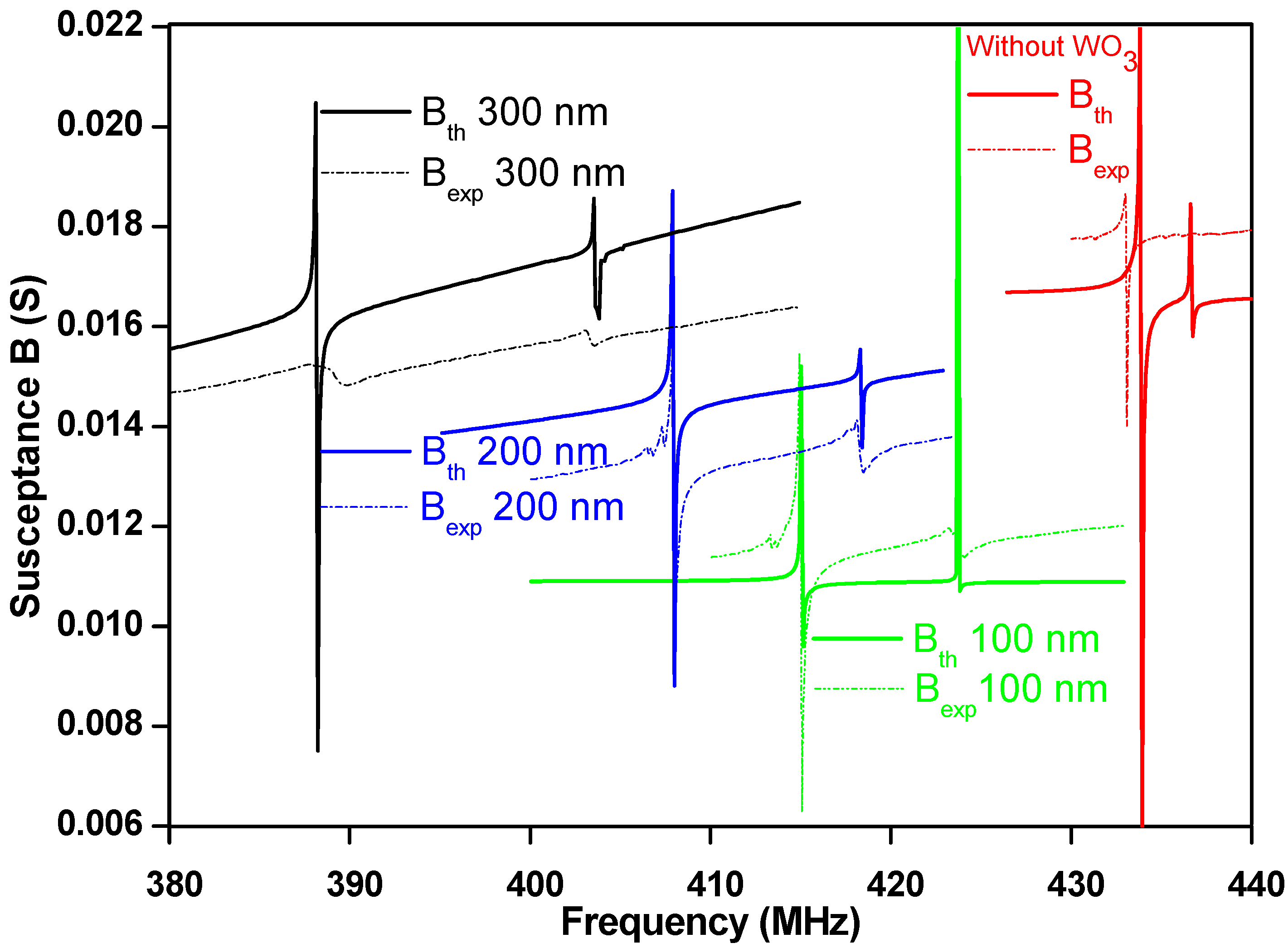
| Resonator Type | Quartz (YX/45°/10°) |
|---|---|
| Type of Electrodes | Aluminium |
| Electrode width a (µm) | 2.9 |
| IDT period p (µm) | 3.63 |
| Wavelegnth λ (µm) | 8 |
| Electrode thickness h (nm) | 120 |
| Metallization ratio a/p | 0.8 |
| Metallization thickness h/λ (%) | 1.5 |
| Acoustic velocity v (m/s) | 3462 |
| Resonator | Quartz (YX)/45°/10° | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Thickness of WO3 | 100 nm | 200 nm | 300 nm |
| Density ρ (kg/m3) | 6500 | 4700 | 3900 |
| C11 (GPa) | 14 | 15 | 12.5 |
| C12 (GPa) | 8 | 8 | 7 |
| C66 (GPa) | 2.5 | 2.5 | 2.5 |
| Poisson Coefficient ν | 0.57 | 0.53 | 0.56 |
| Young’s modulus E (GPa) | 8.2 | 8.3 | 8.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arab, M.; Madigou, V.; Chevallier, V.; Turquat, C.; Leroux, C. Investigation of Elastic Properties of WO3 Thin Films Supported on Quartz in Surface Acoustic Wave Sensing Devices. Electron. Mater. 2022, 3, 124-135. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronicmat3010012
Arab M, Madigou V, Chevallier V, Turquat C, Leroux C. Investigation of Elastic Properties of WO3 Thin Films Supported on Quartz in Surface Acoustic Wave Sensing Devices. Electronic Materials. 2022; 3(1):124-135. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronicmat3010012
Chicago/Turabian StyleArab, Madjid, Véronique Madigou, Virginie Chevallier, Christian Turquat, and Christine Leroux. 2022. "Investigation of Elastic Properties of WO3 Thin Films Supported on Quartz in Surface Acoustic Wave Sensing Devices" Electronic Materials 3, no. 1: 124-135. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronicmat3010012
APA StyleArab, M., Madigou, V., Chevallier, V., Turquat, C., & Leroux, C. (2022). Investigation of Elastic Properties of WO3 Thin Films Supported on Quartz in Surface Acoustic Wave Sensing Devices. Electronic Materials, 3(1), 124-135. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronicmat3010012








