Frequency Selective Surfaces: Design, Analysis, and Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction

2. Applications of FSSs
2.1. Intelligent Reflecting Surfaces (IRSs)
2.2. IRSs for Cellular Networks
2.2.1. Enhancing Secrecy Rates
2.2.2. Interference Mitigation
2.2.3. Beamforming Integration
2.2.4. Phase Shifts and Real-Time Adaptation
2.3. FSS in Wireless Communications
2.3.1. Beamwidth Control
2.3.2. Sidelobe Level Reduction
2.3.3. Enhancing Front-to-Back Gain
2.3.4. Bandwidth Expansion
- is the upper cutoff frequency.
- is the lower cutoff frequency.
- is the center frequency.
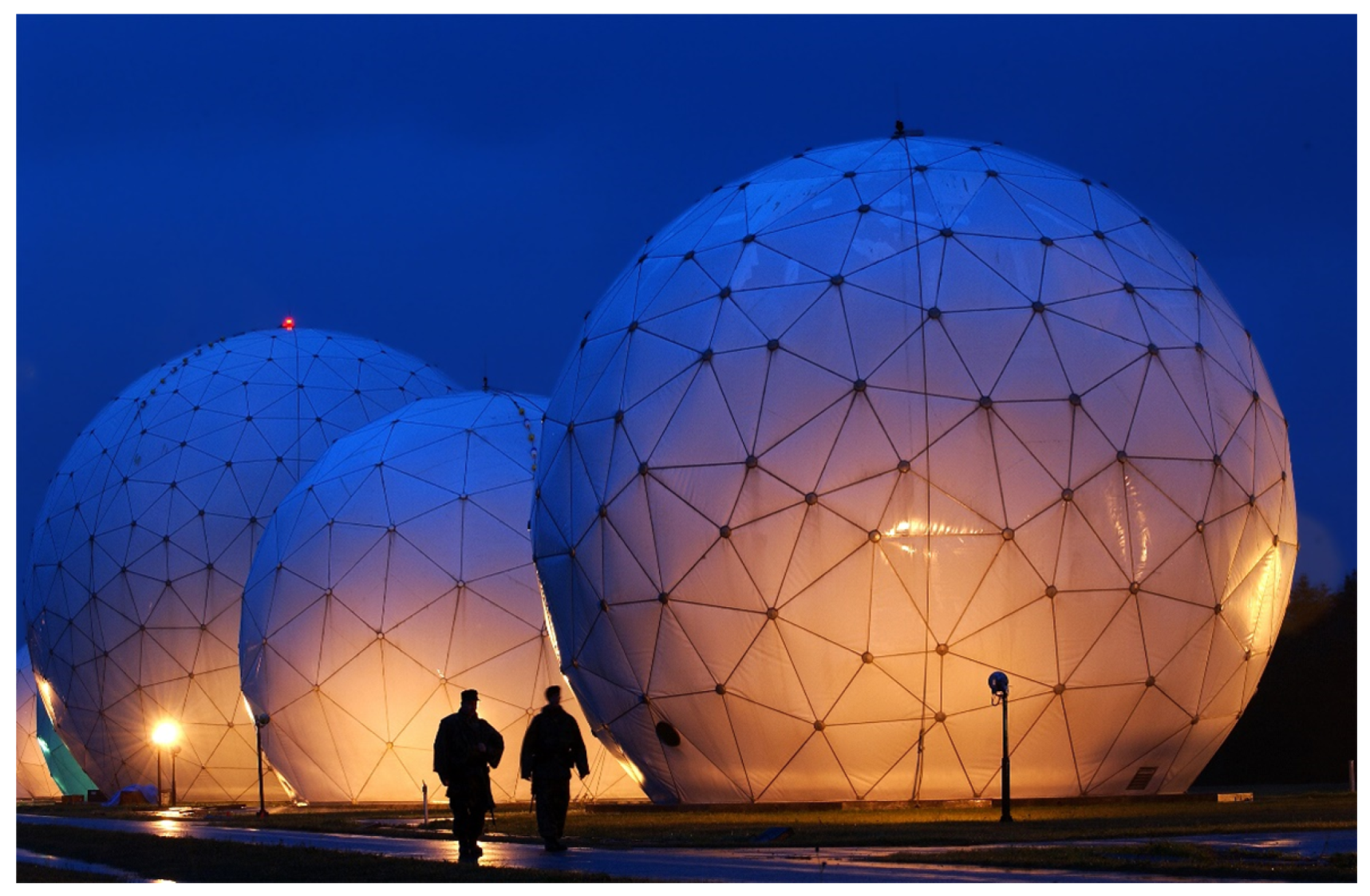
2.4. Microwave and Millimeter-Wave Applications
- -
- is the amplitude of the reflected wave.
- -
- is the amplitude of the incident wave.
- -
- is the amplitude of the transmitted wave.
- -
- is the amplitude of the incident wave.
3. Elements of Frequency Selective Surfaces
- N-poles or center-connected, such as dipole, three-legged element or tri-poles, Jerusalem cross, cross dipoles, and the square spiral, as shown in Figure 7a.
- Loop types, such as the three- and four-legged loaded elements, the circular loops or rings, square, and hexagonal loops, as shown in Figure 7b.
- Solid interiors or plate types mainly in patch or aperture forms, i.e., square meshes and circular patches, as shown in Figure 7c.
- Combinations or sophisticated patterns, i.e., combination of solid interior shapes or center-connected loops to overcome the deficiencies with simple shaped elements as shown in Figure 7d.
3.1. Class 1: N-Pole or Center-Connected Elements
3.2. Class 2: Loop Type
3.3. Class 3: Solid Interiors or Plate Type Elements
3.4. Class 4: Combination Elements
3.5. Evaluation of the Four Classes of FSSs
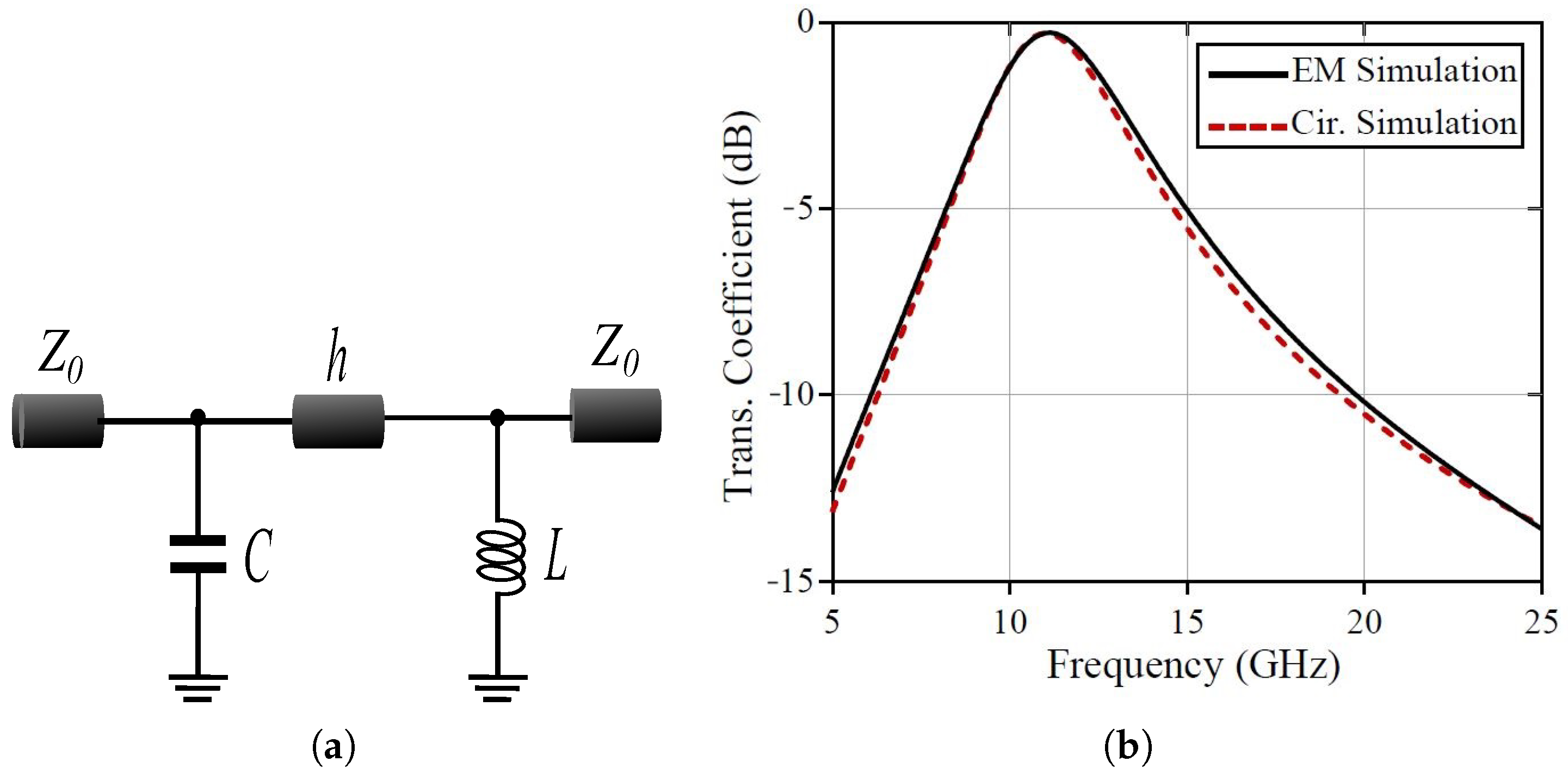
4. Methods for Analysis of FSS
5. FSS Measurements
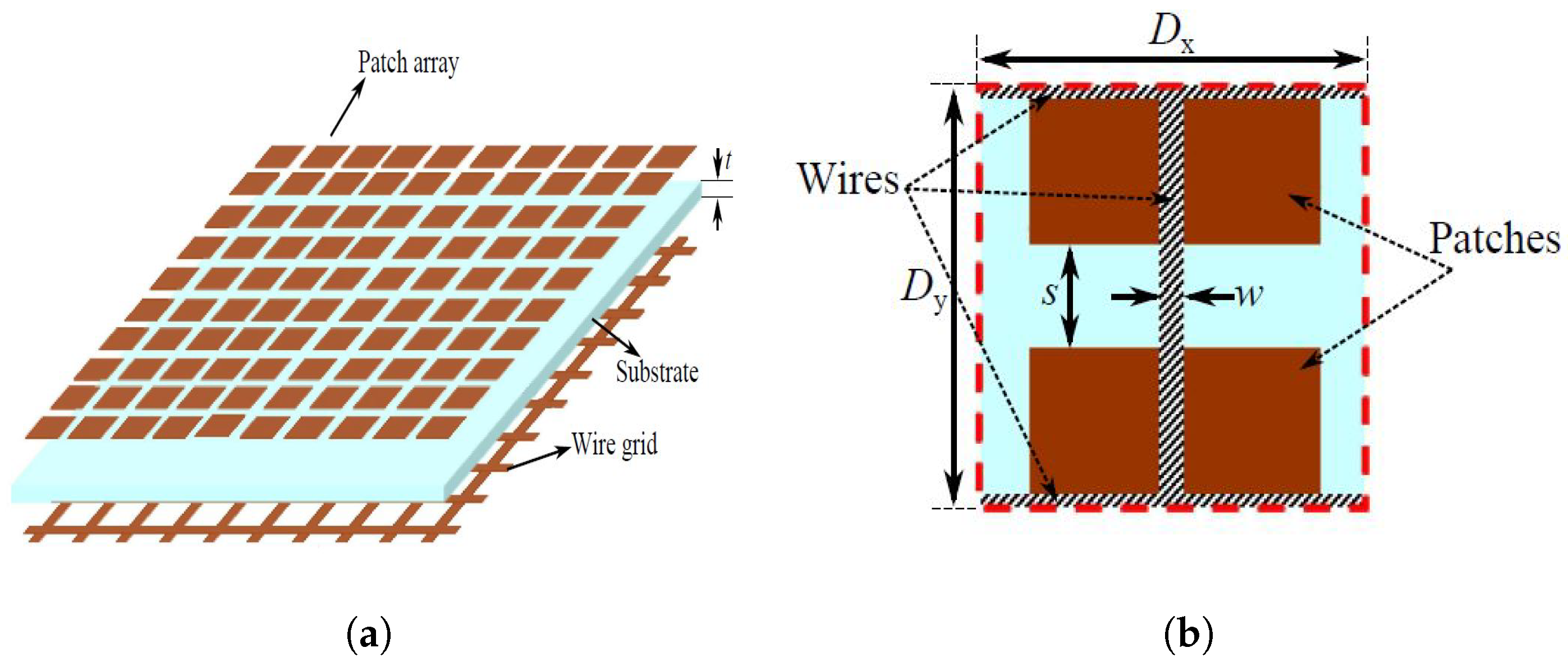
5.1. Multi-Layer Frequency Selective Surfaces
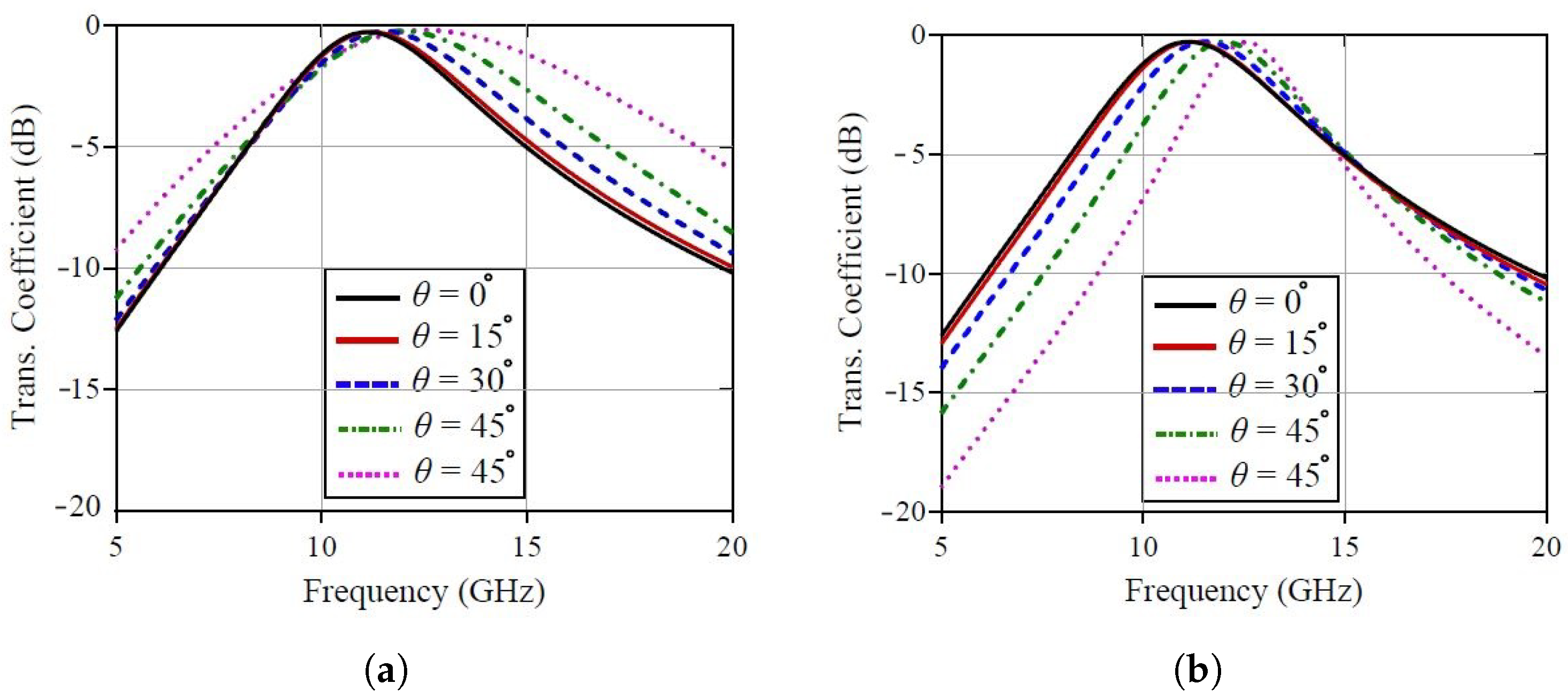
5.2. Angular Stability
6. Pros and Cons of Traditional FSSs
7. 2.5-Dimensional FSSs
8. 3D Frequency Selective Structures
9. Miniaturized Element FSSs
10. Switchable and Tunable FSSs
11. Discussion
12. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, L.; Chen, Q.; Yuan, Q.; Sawaya, K.; Maruyama, T.; Furuno, T.; Uebayashi, S. Frequency selective reflectarray using crossed-dipole elements with square loops for wireless communication applications. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2011, 59, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, A.; Lee, C.K. Analysis of gridded square frequency selective surfaces. In Proceedings of the IEEE Asia-Pacific Microwave Conference, Sydney, Australia, 3–6 December 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Junior, A.G.D.A.; Fontgalland, G.; Titaouine, M.; Baudrand, H.; Neto, A.G. Analysis of quasi-square open ring frequency selective surface using the Wave Concept Iterative Procedure. In Proceedings of the International Microwave and Optoelectronics Conference (IMOC), Belem, Brazil, 3–6 November 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Jha, K.R.; Singh, G.; Jyoti, R. A simple synthesis technique of single-square loop frequency selective surface. Prog. Electromagn. Res. 2012, 45, 165–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Yang, G.H.; Li, W.L.; Wu, Q. A novel double-layer semi-circle fractal multi-band frequency selective surface. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Antennas Propagation and EM Theory (ISAPE), Guangzhou, China, 29 November–2 December 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Sakran, F.; Neve-Oz, Y.; Ron, A.; Golosovsky, M.; Davidov, D.; Frenkel, A. Absorbing frequency-selective-surface for the mm-wave range. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2008, 56, 2649–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Yin, Y.; Ren, X. Interdigitated hexagon loop unit cells for wideband miniaturized frequency selective surfaces. In Proceedings of the IEEE, 9th International Symposium on Antennas Propagation and EM Theory (ISAPE), Guangzhou, China, 29 November–2 December 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Z.; Shen, R.; Yan, X. A novel wideband frequency selective surface composite structure. In Proceedings of the China-Japan Joint Microwave Conference Proceedings (CJMW), Hangzhou, China, 20–22 April 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Brito, D.B.; Araújo, L.M.; D’Assunção, A.G.; Maniçoba, R.H. A Minkowski fractal Frequency Selective Surface with high angular stability. In Proceedings of the International Microwave and Optoelectronics Conference (IMOC), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 4–7 August 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Anuradha; Patnaik, A.; Sinha, S.N.; Mosig, J.R. Design of customized fractal FSS. In Proceedings of the Antennas and Propagation Society International Symposium (APSURSI), Chicago, IL, USA, 8–14 July 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Mathivanan, A.; Saravanan, P. Miniaturized multiband frequency selective surface with wide frequency ratio. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2022, 64, 1991–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, M. A new miniaturized active frequency selective surface with convoluted element for uhf applications. J. Microw. Optoelectron. Electromagn. Appl. 2024, 23, e2024278519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Chen, M.; Peng, L. A dual-function switchable and frequency tunable active frequency selective surface. Int. J. Microw. Comput. Aided Eng. 2021, 31, e22897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Song, K.; Xiao, J. Two-Dimensional Optical Metasurfaces: From Plasmons to Dielectrics. Adv. Condens. Matter Phys. 2019, 2019, 2329168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Saleem, R.; Abbasi, Q.; Kasi, B.; Shafique, M. Miniaturized and flexible fss-based em shields for conformal applications. IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 2020, 62, 1703–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Feng, S.; Chen, J.; Chang, Y.; Liao, S.; Che, W. Design of paper-based bandpass frequency selective surface using slotlines. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2022, 64, 1339–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njogu, P.; Sanz-Izquierdo, B.; Parker, E. A liquid sensor based on frequency selective surfaces. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2023, 71, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, S.; Taylor, P.; Parker, E.; Batchelor, J. Popup tunable frequency selective surfaces for strain sensing. IEEE Sens. Lett. 2020, 4, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Xiao, Z.; Fan, L.; Zhou, M.; Leung, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, F.; Poo, Y. High-temperature-resistant frequency selective metasurface with low-frequency diffusion and high-frequency transmission. J. Phys. Appl. Phys. 2022, 55, 215102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Can, S.; Kapusuz, K.; Yılmaz, A. Optically transparent dual-band frequency selective surfaces for smart surfaces. In Proceedings of the 2022 Sixteenth International Congress on Artificial Materials for Novel Wave Phenomena (Metamaterials), Siena, Italy, 12–17 September 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J. Absorption-transmission-diffusion-type radar cross section reduction metasurfaces based on frequency selective absorber and polarization conversion chessboard structure. J. Phys. Appl. Phys. 2024, 57, 225101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Xu, B.; Tao, Z. Design of a 3-d tunable band-stop frequency selective surface with wide tuning range. Prog. Electromagn. Res. Lett. 2020, 92, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Fan, Q.; Wang, J.; Xu, C.; Wang, B.; Yang, B.; Tian, C.; Meng, Z. Multi-spectral metasurface with high optical transparency, low infrared surface emissivity, and wideband microwave absorption. Front. Phys. 2020, 8, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Zhang, K.; Zhao, B.; Su, Y.; Gong, S. Design of miniaturised frequency selective rasorber using parallel lc resonators. IET Microw. Antennas Propag. 2019, 13, 554–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Xia, Y.; Zhu, J.; Wang, C.; Shi, Y.; Tang, W. Dual-band three-dimensional fss with high selectivity and small band ratio. Electron. Lett. 2019, 55, 798–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Guo, Q.; Li, Z. Tunable frequency selective surface based on a sliding 3d-printed inserted dielectric. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 19743–19748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, W.; Glazunov, A. Miniaturization of a fully metallic bandpass frequency selective surface for millimeter-wave band applications. IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 2023, 65, 1072–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, F.; Monorchio, A. A Frequency Selective Radome With Wideband Absorbing Properties. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2012, 60, 2740–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schennum, G.H. Frequency selective surfaces for multiple frequency antennas. Microw. J. 1973, 16, 55–57. [Google Scholar]
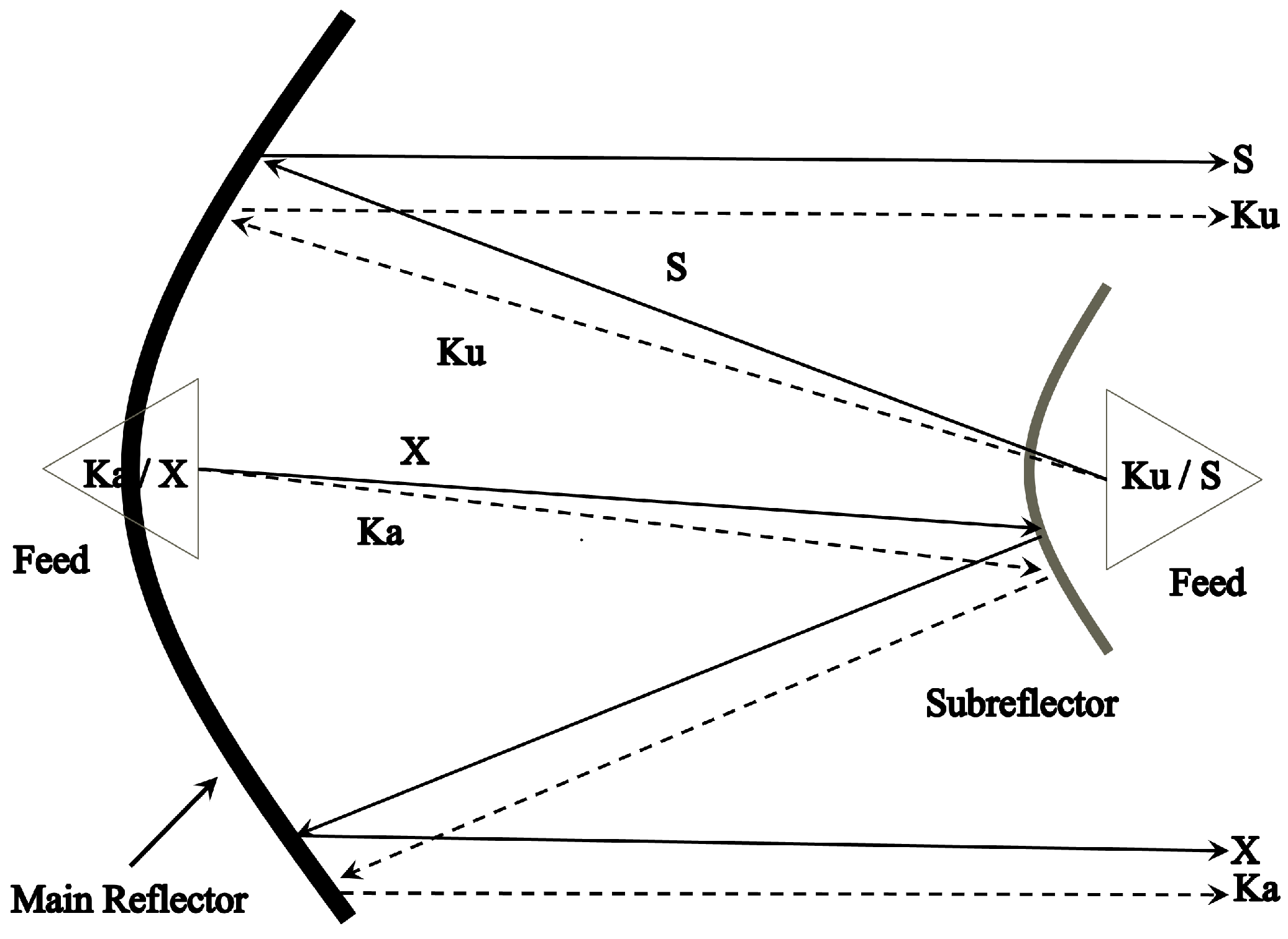
- Agrawal, V.D.; Imbriale, W.A. Design of a dichroic Cassegrah subrefrector. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1979, 27, 466–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.K. Four-band frequency selective surface with double-square-loop patch. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1994, 42, 1659–1663. [Google Scholar]
- Comtesse, L.E.; Langley, R.J.; Parker, E.A.; Vardaxoglou, J.C. Frequency selective surfaces in dual and triple band offset reflector antennas. Eur. Microw. Conf. 1987, 17, 208–213. [Google Scholar]
- Bayatpur, F.; Sarabandi, K. Tuning performance of metamaterial-based frequency selective surfaces. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2009, 57, 590–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Ma, H.; Du, H.; Zhang, J.; Qu, S.; Xu, Z. Reconfigurable all-dielectric metamaterial frequency selective surface based on high-permittivity ceramics. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossard, J.A.; Liang, X.; Li, L.; Yun, S.; Werner, D.H.; Weiner, B.; Mayer, T.S.; Cristman, P.F.; Diaz, A.; Khoo, I.C. Tunable frequency selective surfaces and negative-zero-positive index metamaterials based on liquid crystals. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2008, 56, 1308–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, J.; Ford, K.L.; Rigelsford, J.M. Secure electromagnetic buildings using slow phase-switching frequency-selective surfaces. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2016, 64, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Cao, Q.; Wang, Y. A Novel 2-B Multifunctional Active Frequency Selective Surface for LTE-2.1 GHz. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2017, 65, 3084–3092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.W.; Fong, T.J. Electromagnetic wave scattering from an active corrugated structure. J. Appl. Phys. 1972, 43, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozar, D. Flat lens antenna concept using aperture coupled microstrip patches. Electron. Lett. 1996, 32, 2109–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.F.; Cui, T.J. Three-dimensional broadband and broad-angle transformation-optics lens. Nat. Commun. 2010, 1, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pendry, J.B. Negative refraction makes a perfect lens. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 85, 3966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauman, M.; Saleem, R.; Rashid, A.K.; Shafique, M.F. A miniaturized flexible frequency selective surface for X-band applications. IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 2016, 58, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Zhu, B.O.; Feng, Y. A frequency and bandwidth tunable metamaterial absorber in x-band. J. Appl. Phys. 2015, 117, 173103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghebrebrhan, M.; Aranda, F.; Walsh, G.; Ziegler, D.; Giardini, S.; Carlson, J.; Kimball, B.; Steeves, D.; Xia, Z.; Yu, S.; et al. Textile Frequency Selective Surface. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 2017, 27, 989–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tennant, A.; Hurley, W.; Dias, T. Experimental knitted, textile frequency selective surfaces. Electron. Lett. 2012, 48, 1386–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seager, R.D.; Chauraya, A.; Bowman, J.; Broughton, M.; Philpott, R.; Nimkulrat, N. Fabric based frequency selective surfaces using weaving and screen printing. Electron. Lett. 2013, 49, 1507–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Yin, Y.; Fan, J.; Yang, X.; Li, B.; Liu, W. Analysis of miniature frequency selective surfaces based on fractal antenna–filter–antenna arrays. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2012, 11, 240–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puente, C.; Romeu, J.; Bartoleme, R.; Pous, R. Perturbation of the Sierpinski antenna to allocate operating bands. Electron. Lett. 1996, 32, 2186–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monti, A.; Bilotti, F.; Toscano, A.; Vegni, L. Possible implementation of epsilon-near-zero metamaterials working at optical frequencies. Opt. Commun. 2012, 285, 3412–3418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Falco, A.; Zhao, Y.; Alú, A. Optical metasurfaces with robust angular response on flexible substrates. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 99, 163110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeidi, C.; van der Weide, D. Nanoparticle array based optical frequency selective surfaces: Theory and design. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 16170–16180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Li, T.W.; Li, E.P.; Zhang, Y.J. A 2.5-D Angularly Stable Frequency Selective Surface Using Via-Based Structure for 5G EMI Shielding. IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 2018, 60, 768–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindaswamy, S.; East, J.; Terry, F.; Topsakal, E.; Volakis, J.L.; Haddad, G.I. Frequency-selective surface based bandpass filters in the near-infrared region. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2004, 41, 266–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, H.A.; Rebbert, M.; Sternberg, O. Designer infrared filters using stacked metal lattices. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2003, 82, 3605–3607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossard, J.A.; Werner, D.H.; Mayer, T.S.; Smith, J.A.; Tang, Y.U.; Drupp, R.P.; Li, L. The design and fabrication of planar multiband metallodielectric frequency selective surfaces for infrared applications. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2006, 54, 1265–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Döken, B.; Kartal, M. Easily Optimizable Dual-Band Frequency Selective Surface Design. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2017, 16, 2979–2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lucena Nóbrega, C.; Ribeiro da Silva, M.; da Fonseca Silva, P.H.; D’Assunção, A.G. Analysis and design of frequency selective surfaces using teragon patch elements for WLAN applications. J. Electromagn. Waves Appl. 2014, 28, 1282–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yang, C.; Cao, Q.; Wang, Y. A novel active frequency selective surface with switching performance for 2.45 GHz WLAN band. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2016, 58, 1586–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, D.H.; Mayer, T.S.; Baleine, C.R. Multi-Spectral Filters, Mirrors and Anti-Reflective Coatings with Subwavelength Periodic Features for Optical Devices. U.S. Patent 12/900,967, 14 April 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Shen, Z. Bandpass frequency selective structure with wideband spurious rejection. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2014, 13, 145–148. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, P.; Bai, F.; Xue, Q.; Liu, X.; Hui, S.R. Use of frequency-selective surface for suppressing radio-frequency interference from wireless charging pads. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 3969–3977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Zhang, T.; Li, W.; Wu, Q. A novel stable miniaturized frequency selective surface. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2010, 9, 1018–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewani, A.A.; O’Keefe, S.G.; Thiel, D.V.; Galehdar, A. Window RF Shielding Film Using Printed FSS. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2018, 66, 790–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, N.; Liu, H.; Li, L. A Transplantable Frequency Selective Metasurface for High-Order Harmonic Suppression. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo, J.; Lázaro, A.; Villarino, R.; Girbau, D. Modulated frequency selective surfaces for wearable RFID and sensor applications. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2016, 64, 4447–4456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo, J.; Lazaro, A.; Girbau, D.; Villarino, R.; Gil, E. Analysis of on-body transponders based on frequency selective surfaces. Prog. Electromagn. Res. 2016, 157, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo, J.; Lazaro, A.; Villarino, R.; Girbau, D. Diversity Study of a Frequency Selective Surface Transponder for Wearable Applications. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2017, 65, 2701–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Liu, P.; Yang, M.; Wang, Q.; Song, J.; Dong, L. From flexible and stretchable meta-atom to metamaterial: A wearable microwave meta-skin with tunable frequency selective and cloaking effects. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, I.S.; Ranga, Y.; Matekovits, L.; Esselle, K.P.; Hay, S.G. A single-layer frequency-selective surface for ultrawideband electromagnetic shielding. IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 2014, 56, 1404–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiani, G.I.; Ford, K.L.; Esselle, K.P.; Weily, A.R.; Panagamuwa, C.; Batchelor, J.C. Single-layer bandpass active frequency selective surface. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2008, 50, 2149–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Srivastava, K.V. Broadband polarization-insensitive tunable frequency selective surface for wideband shielding. IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 2018, 60, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Kong, P.; Cheng, W.; Bao, W.; Yu, X.; Miao, L.; Jiang, J. Broadband tunability of polarization-insensitive absorber based on frequency selective surface. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Lim, S. Wide incidence angle-insensitive metamaterial absorber for both TE and TM polarization using eight-circular-sector. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, G.; Xia, T.; Fang, Y.; Yang, J.; Yin, Z. A Polarization-Dependent Frequency-Selective Metamaterial Absorber with Multiple Absorption Peaks. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Z.; Gong, R.; Nie, Y.; Wang, T.; Wang, X. Absorption enhancement of fractal frequency selective surface absorbers by using microwave absorbing material based substrates. Photonics Nanostruct. Fundam. Appl. 2011, 9, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Hansen, V.; Gemuend, H.P.; Kreysa, E. Multi-layered Submillimeter FSS of Shifted Crossed Slot Elements for Applications in Radio Astronomy. In Proceedings of the German Microwave Conference, Ulm, Germany, 5–7 April 2005; pp. 5–7. [Google Scholar]
- Song, K.; Mazumder, P. Design of highly selective metamaterials for sensing platforms. IEEE Sens. J. 2013, 13, 3377–3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Kim, S.J.; Park, H.; Lee, B. Metamaterials and Metasurfaces for Sensor Applications. Sensors 2017, 17, 1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agahi, S.; Mittra, R. Design of a cascaded frequency selective surface as a dichroic subreflector. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation Society, Merging Technologies for the 90’s, Dallas, TX, USA, 7–11 May 1990; pp. 88–91. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, F.; Genovesi, S.; Monorchio, A.; Manara, G. A robust differential-amplitude codification for chipless RFID. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 2015, 25, 832–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazaro, A.; Ramos, A.; Girbau, D.; Villarino, R. A novel UWB RFID tag using active frequency selective surface. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2013, 61, 1155–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puente Baliarda, C.; Romeu Robert, J.; Pous Andrés, R.; Garcia, X.; Benitez, F. Fractal multiband antenna based on the Sierpinski gasket. Electron. Lett. 1996, 32, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.B.; Yue, G.T.; Shi, Y.; Liao, J.X.; Wang, P. Miniaturized Bandpass Filter with Mixed Electric and Magnetic Coupling Using Hexagonal Stepped Impedance Resonators. Electromagnetics 2013, 33, 550–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhang, X.; Hu, Z.; Aqeeli, M.; Alburaikan, A. Design of broadband and tunable terahertz absorbers based on graphene metasurface: Equivalent circuit model approach. IET Microw. Antennas Propag. 2014, 9, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wu, Q.; Denidni, T.A. Electronically radiation pattern steerable antennas using active frequency selective surfaces. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2013, 61, 6000–6007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, H.; Ando, A.; Seki, T.; Kawashima, M.; Sugiyama, T. Directional multi-band antenna employing frequency selective surfaces. Electron. Lett. 2013, 49, 243–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, M.R.; de Melo, M.T.; Llamas-Garro, I.; Neto, A.G. Reconfigurable Cross Dipole-Hash Frequency Selective Surface. IET Microw. Antennas Propag. 2017, 12, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.; Zhang, L.; Yang, G.; Gu, X. A electronically steerable radiator and reflector array antenna based on Three-Dimensional Frequency Selective Structure. In Proceedings of the 2012 5th Global Symposium on Millimeter-Waves, Harbin, China, 27–30 May 2012; pp. 119–122. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, C. Design and synthesis of multilayer frequency selective surface based on antenna-filter-antenna using Minkowski fractal structures. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2015, 63, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Sheng, X.; Zhang, C.; Guo, D. Design of Frequency Selective Surface Structure with High Angular Stability for Radome Application. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2018, 17, 138–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, P.C.; Seo, I.S.; Kim, G.H. Nanocomposite stealth radomes with frequency selective surfaces. Compos. Struct. 2008, 86, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, P.; Yu, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, K.; He, Y.; Miao, L.; Jiang, J. A novel tunable frequency selective surface absorber with dual-DOF for broadband applications. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 30217–30224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Yeo, J.; Choi, J. Compact Spatial Triple-Band-Stop Filter for Cellular/PCS/IMT-2000 Systems. ETRI J. 2008, 30, 735–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, D.; Yeo, T.D.; Oh, K.S.; Yu, J.W.; Lee, W.S. Dual resonance frequency selective loop of near-field wireless charging and communications systems for portable device. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 2015, 25, 624–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Zhang, S.; Zheng, B.; You, C.; Zhang, R. Intelligent Reflecting Surface-Aided Wireless Communications: A Tutorial. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2021, 69, 3313–3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basar, E.; Di Renzo, M.; De Rosny, J.; Debbah, M.; Alouini, M.S.; Zhang, R. Wireless Communications through Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 116753–116773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Chen, J.; Wu, Q. Joint Active and Passive Beamforming for Intelligent Reflecting Surface-Assisted SWIPT Under QoS Constraints. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2020, 24, 893–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, W.; Xu, X. Intelligent Reflecting Surfaces for 6G Wireless Networks: Opportunities and Challenges. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2021, 28, 38–45. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, C.; Jin, S. Large Intelligent Surface-Assisted Wireless Communication Exploiting Statistical CSI. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2021, 70, 1372–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, M.; Jamali, V.; Schober, R.; Matolak, D.W. Physics-Based Modeling of Large Intelligent Reflecting Surfaces for Vehicular Communications. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2021, 20, 3606–3621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renzo, M.D.; Debbah, M.; Phan-Huy, D.T.; Zhang, R. Smart Radio Environments Empowered by Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces: How It Works, State of Research, and The Road Ahead. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2020, 38, 2450–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Yan, J.; Poor, H.V. Phase-Shift Modeling and Beamforming with Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces: An Overview. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2020, 37, 141–150. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, W.; Chen, M.Z.; Zeng, S.; Zhang, R. Wireless Communications with Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface: Path Loss Modeling and Experimental Measurement. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2020, 20, 421–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, T.J. Hexagonal and Fractal FSS Designs for Bandwidth and Beamwidth Optimization. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 10397–10406. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Chen, J.; Wu, Q. A Novel Frequency Selective Surface for Wideband Sidelobe Suppression in High-Gain Antennas. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2022, 70, 12–23. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, S.; Srivastava, K.V.; Behera, A. Design and Optimization of FSS for Sidelobe Suppression in Antenna Arrays. IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 2021, 63, 730–740. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Shen, Z. Advanced Fractal-Based FSS for High-Gain Antennas with Enhanced Bandwidth. IEEE Antennas Propag. Mag. 2020, 62, 95–103. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y. Multilayer FSS for Wideband Applications in Wireless Communications. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2022, 21, 3720–3730. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.; Yuen, C.; Zhang, R. Frequency Selective Surfaces for 5G Applications: Enhancing Gain and Reducing Interference. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2020, 58, 144–150. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, X. Frequency-Selective Surfaces for Microwave and Terahertz Spectra. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Adelaide, Adelaide, Australia, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Munk, B.A. Frequency Selective Surfaces: Theory and Design; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Ebrahimi, A. Metamaterial-Inspired Structures for Microwave and Terahertz Applications. Ph.D. Thesis, School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, The University of Adelaide, Adelaide, Australia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, T. Frequency Selective Surface and Grid Array; Wiley-Interscience: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1995; Volume 40. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Su, T.; Wan, T. Efficient numerical analysis of finite FSS with multilayered media by MLACA. IET Microw. Antennas Propag. 2019, 13, 1804–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balta, S.; Kartal, M. A novel double-layer low-profile multiband frequency selective surface for 4G mobile communication system. Appl. Comput. Electromagn. Soc. 2022, 37, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molero, C.; Alex-Amor, A.; Mesa, F.; Palomares-Caballero, Á.; Padilla, P. Cross-polarization control in FSSs by means of an equivalent circuit approach. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 99513–99525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, S. A perspective on the relative merits/demerits of time-propagators based on Floquet theorem. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2023, 25, 29747–29773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabata, A.; Matekovits, L.; Buta, A.; Dassano, G.; Silaghi, A. Frequency selective surface for ultra-wide band filtering and shielding. Sensors 2022, 22, 1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mistry, K.; Lazaridis, P.; Zaharis, Z.; Akinsolu, M.; Liu, B.; Loh, T. Accurate antenna gain estimation using the two-antenna method. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference Publications, Birmingham, UK, 11–12 November 2019. 4p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, T.; Huang, C.; Cai, Y.; Lin, X. Dual-band frequency selective surface with different polarization selectivity for wireless communication application. Sensors 2023, 23, 4264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Kong, X.; Wang, Q.; Xing, L.; Feng, X.; Xu, Y.; Jiang, S. Water-based reconfigurable frequency selective rasorber with thermally tunable absorption band. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2020, 68, 6162–6171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urul, B.; Tütüncü, B.; Helhel, S. A fast and novel method for determining working volume in the reverberation chamber: Position of TX antenna affect. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2019, 62, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wang, L.; Shen, X.; Liu, X.; Qi, T.; Zhou, Y. Single-substrate double-side high selectivity frequency selective surface. Prog. Electromagn. Res. Lett. 2020, 92, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chomtong, P.; Krachodnok, P.; Bandudej, K.; Akkaraekthalin, P. A multiband FSS director using aperture interdigital structure for wireless communication systems. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 11206–11219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boursianis, A.; Papadopoulou, M.; Nikolaidis, S.; Sarigiannidis, P.; Psannis, K.; Georgiadis, A.; Tentzeris, M.; Goudos, S. Novel design framework for dual-band frequency selective surfaces using multi-variant differential evolution. Mathematics 2021, 9, 2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahvand, M.; Martinez-de-Rioja, E.; Forooraghi, K.; Atlasbaf, Z.; Encinar, J.; Ghosh, S.; Ebrahimi, A. Active frequency selective surface with switchable response for satellite communications in X and Ka bands. Int. J. Microw. Comput. Aided Eng. 2022, 32, e23255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, G.; Das, S. A bi-directional dual-bandwidth microwave absorber for applications in X and Ku bands. Int. J. Microw. Wirel. Technol. 2019, 11, 983–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Lin, X.; Yang, X. An FSS-based shared-aperture antenna for 5G/Wi-Fi communication and indoor 5G blind compensation. Int. J. Microw. Wirel. Technol. 2022, 15, 1373–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindan, T.; Palaniswamy, S.; Kanagasabai, M.; Kumar, S.; Alsath, G. Low specific absorption rate quad-port multiple-input-multiple-output limber antenna integrated with flexible frequency selective surface for WBAN applications. Flex. Print. Electron. 2023, 8, 015018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zheng, L.; Yan, M.; Wang, J.; Qu, S.; Luo, R. Design and analysis of miniaturized low profile and second-order multi-band polarization selective surface for multipath communication application. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 13455–13467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baena, J.D.; Jelinek, L.; Marques, R.; Mock, J.J.; Gollub, J.; Smith, D.R. Isotropic frequency selective surfaces made of cubic resonators. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 91, 191105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayatpur, F.; Sarabandi, K. Miniaturized FSS and patch antenna array coupling for angle-independent, high-order spatial filtering. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 2010, 20, 79–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranga, Y.; Matekovits, L.; Esselle, K.P.; Weily, A.R. Oblique incidence performance of UWB frequency selective surfaces for reflector applications. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation (APSURSI), Spokane, WA, USA, 3–8 July 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, T.; Zhou, H.; Yang, Y.; Liu, B. A FSS with stable performance under large incident angles. Prog. Electromagn. Res. Lett. 2013, 41, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Qu, S.; Xu, Z.; Wang, J.; Ma, H.; Peng, W.; Lin, B.; Bai, P. A triband second-order frequency selective surface. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2011, 10, 507–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.Q.; Hong, W.; Lai, Q.H.; Wu, K.; Sun, L.L. Design and Experimental Verification of Compact Frequency-Selective Surface With Quasi-Elliptic Bandpass Response. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2007, 55, 2481–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Roberts, A. Angle-robust resonances in cross-shaped aperture arrays. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 97, 061109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, M.; Pirhadi, A.; Hakkak, M. A novel AMC with little sensitivity to the angle of incidence using 2-layer jerusalem cross FSS. Prog. Electromagn. Res. 2006, 64, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Qu, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, A.; Xia, S.; Wang, W. A novel miniaturized frequency selective surface with stable resonance. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2014, 13, 639–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azemi, S.N. 3-D Frequency Selective Structures. Ph.D. Thesis, RMIT University, Melbourne, Australia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Shen, Z. Three-dimensional bandpass frequency-selective structures with multiple transmission zeros. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2013, 61, 3578–3589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, A.K.; Shen, Z. Three-dimensional monolithic frequency selective structure with dielectric loading. In Proceedings of the Asia-Pacific in Microwave Conference Proceedings (APMC), Yokohama, Japan, 7–10 December 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Afzal, W. Highly Selective Miniaturised-Element Frequency Selective Surfaces with Tuning Capabilities. Ph.D. Thesis, RMIT University, Melbourne, Australia, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Rashid, A.K.; Li, B.; Shen, Z. An overview of three-dimensional frequency-selective structures. IEEE Antennas Propag. Mag. 2014, 56, 43–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azemi, S.N.; Ghorbani, K.; Rowe, W. 3D frequency selective surfaces. Prog. Electromagn. Res. 2012, 29, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bihan, P.L.; García-Vigueras, M.; Fourn, E.; Gillard, R.; Naneix, I.L.R.; Varault, S.; Renard, C. Three-Dimensional Frequency Selective Surface for Single-Polarized Filtering Applications with Angular Stability. In Proceedings of the 2020 14th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EuCAP), Copenhagen, Denmark, 15–20 March 2020; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, B.; Bai, M. Subwavelength three-dimensional frequency selective surface based on surface wave tunneling. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 14697–14702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Shen, Z. Miniaturized bandstop frequency-selective structure using stepped-impedance resonators. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2012, 11, 1112–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.J.; Yang, C.; Lu, Z.H.; Liu, P.G. A Novel Frequency Selective Structure with Quasi-Elliptic Bandpass Response. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2012, 11, 1497–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelletti, C.; Mittra, R.; Bianconi, G. Three-dimensional FSS elements with wide frequency and angular response. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Symposium on Electromagnetic Theory, Hiroshima, Japan, 20–24 May 2013; pp. 698–700. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Zhuang, W.; Tang, W. Novel three-dimensional frequency selective surface with incident angle and polarization independence. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation (ISAP), Hobart, Australia, 9–12 November 2015; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Shen, Z. Three-dimensional dual-polarized frequency selective structure with wide out-of-band rejection. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2014, 62, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momeni Hasan Abadi, S.; Behdad, N. Inductively-Coupled Miniaturized-Element Frequency Selective Surfaces With Narrowband, High-Order Bandpass Responses. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2015, 63, 4766–4774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, W.; Ebrahimi, A.; Robel, M.R.; Rowe, W.S.T. Low-Profile Higher-Order Narrowband Bandpass Miniaturized-Element Frequency-Selective Surface. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2023, 71, 3736–3740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarabandi, K.; Behdad, N. A Frequency Selective Surface with Miniaturized Elements. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2007, 55, 1239–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Joumayly, M.; Behdad, N. A New Technique for Design of Low-Profile, Second-Order, Bandpass Frequency Selective Surfaces. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2009, 57, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Qu, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, A.; Zheng, L.; Pang, Y.; Zhou, H. A Miniaturized Dual-Band FSS With Second-Order Response and Large Band Separation. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2015, 14, 1602–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Momeni Hasan Abadi, S.M.A.; Behdad, N. A Dual-Band, Inductively Coupled Miniaturized-Element Frequency Selective Surface With Higher Order Bandpass Response. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2016, 64, 3729–3734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Abadi, S.M.A.M.H.; Behdad, N. A Hybrid Miniaturized-Element Frequency Selective Surface With a Third-Order Bandpass Response. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2017, 16, 708–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- d’Elia, U.; Pelosi, G.; Pichot, C.; Selleri, S.; Zoppi, M. A physical optics approach to the analysis of large frequency selective radomes. Prog. Electromagn. Res. 2013, 138, 537–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niroo-Jazi, M.; Denidni, T. Reconfigurable dual-band frequency selective surfaces using a new hybrid element. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation (APSURSI), Spokane, WA, USA, 3–8 July 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Munir, A.; Fusco, V.; Malyuskin, O. Tunable frequency selective surfaces characterisation. In Proceedings of the 38th European Microwave Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 27–31 October 2008; pp. 813–816. [Google Scholar]
- Amjadi, S.M.; Soleimani, M. Design of band-pass waveguide filter using frequency selective surfaces loaded with surface mount capacitors based on split-field update FDTD method. Prog. Electromagn. Res. 2008, 1, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mias, C. Varactor-tunable frequency selective surface with resistive-lumpedelement biasing grids. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 2005, 15, 570–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ucar, M.H.; Sondas, A.; Erdemli, Y.E. Switchable split-ring frequency selective surfaces. Prog. Electromagn. Res. 2008, 6, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossard, J.A.; Werner, D.H.; Mayer, T.S.; Drupp, R.P. A novel design methodology for reconfigurable frequency selective surfaces using genetic algorithms. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2005, 53, 1390–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zendejas, J.M.; Gianvittorio, J.P.; Rahmat-Samii, Y.; Judy, J.W. Magnetic MEMS reconfigurable frequency-selective surfaces. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2006, 15, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, W.; Ebrahimi, A.; Robel, M.R.; Rowe, W.S. Mechanistically Independent Tunable Dual Band FSS. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation and INC/USNC-URSI Radio Science Meeting (AP-S/INC-USNC-URSI), Firenze, Italy, 14–19 July 2024; pp. 1829–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Withayachumnankul, W.; Fumeaux, C.; Abbott, D. Planar Array of Electric- LC Resonators With Broadband Tunability. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2011, 10, 577–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz-Izquierdo, B.; Parker, E.A.; Robertson, J.B.; Batchelor, J.C. Tuning patch-form FSS. Electron. Lett. 2010, 46, 329–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.G.; Shen, Z.; Feng, Q.Y.; Li, B. Tunable 3D bandpass frequency-selective structure with wide tuning range. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2015, 63, 3297–3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.Q.; Qu, S.B.; Tong, C.M.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, H.Y.; Li, W. Varactor-tunable frequency selective surface with an embedded bias network. Chin. Phys. 2013, 22, 094103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



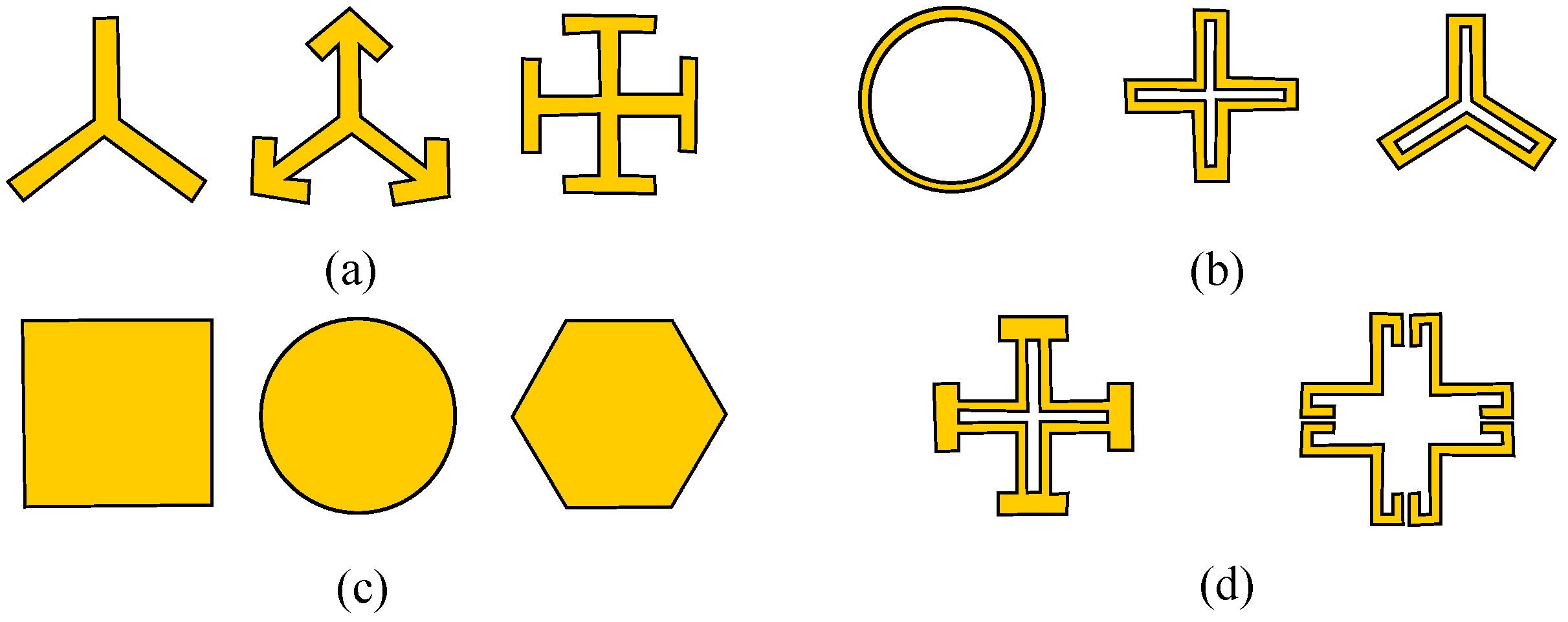


| FSS Refs. | Application | FSS Refs. | Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| [33,34,35] | MMs FSS | [36,37,38] | FSS for mobile communication |
| [39,40,41] | MM/MSs Lens | [33,42,43] | X band |
| [44,45,46] | Textile FSS | [47,48] | C band |
| [49,50,51] | Optical FSS/MSs | [52] | 5G EMI reduction |
| [53] | Near Infrared | [34] | RCS reduction |
| [54,55] | Infrared | [56,57,58] | Secure wireless network |
| [59] | Filtering/Anti-reflecting coating | [60,61,62,63,64] | RF interference and harmonic suppression |
| [65,66,67,68] | Wearable FSS | [52,69,70,71] | EMI shielding |
| [72,73,74,75] | FSS absorber | [76] | Radio Astronomy |
| [77,78] | Sensors | [79] | Dichroic sub-reflector |
| [80,81,82] | RFID | [83,84] | Terahertz band |
| [82,85,86,87,88] | FSS antenna | [72,89,90,91,92] | Stealth radomes |
| [93] | Reconfigurable mechanisms | [94] | Wireless Charging |
| Shape of Elements | Cross Polarization | Angular Stability | Band Separation | Larger Bandwidth |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jerusalem Cross | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Dipole | 1 | 4 | 1 | 4 |
| Tripole | 3 | 3 | 2 | 3 |
| Ring | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Square Loop | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Cross Dipole | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Pros | Cons | |
|---|---|---|
| Single-Layer FSS | Simple planar | Dependent on polarization and angle of incident. Bandwidth is narrow. |
| Multi-layer FSS | Bandwidth is wider. Multiband | Coupling effect. Costly and difficult to construct. |
| Multiband responses | More Selective FSS | Fabrication process needs strict requirements. Concentric elements have unexpected coupling. |
| Tunable FSS | Frequency properties varies | Numerous active elements required. High cost and complex. More potential for failure. |
| Article | Element Used | Size (mm) | Frequency (GHz) |
|---|---|---|---|
| [141] | Split microstrip lines with a thin rectangular metallic bar | 10.5 × 3 | 5–10 |
| [144] | U-shaped strip lines printed on a thin substrate | 10 × 10 | 8.4–16.2 |
| [145] | Circular ring unit cell | 34 × 34 | 2.5–4.5 |
| [146] | Rectangular waveguide loaded by a wire resonator | 5.4 × 3 | 11–24 |
| [147] | Staggered geometry of metallic rectangular frames | 4.50 × 1.30 | 11.8–13.2 |
| [148] | Lumped capacitor added with impedance resonator | 7.5 × 3.4 | 4.3–4.8 |
| [149] | 3D symmetric unit cell | 10 × 10 | 12.4–16.3 |
| [150] | Square waveguide | 9 × 7 | 12–24.7 |
| [151] | Slots integrated in square waveguide | 13 × 11 | 3.7–4 |
| [152] | Strip lines with metallic plates | 8 × 8 | 7–8.3 |
| Article | Frequency (GHz) | Thickness | Order | Bandwidth |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [153] | 21 | second | 5% | |
| [156] | 10 | second | 20% | |
| [157] | 10 | second | 21% | |
| [158] | 16.5 | second | 10% | |
| [159] | 8.5 | third | 15% |
| FSS Ref. | Type of AFSS | Switching/Tuning | FBW | Tuning | Polarization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [70] | Switchable(Passband) | PIN diodes | 17 | No | |
| [169] | Tunable(Stopband) | Varactor diode | 12.5 | 32 | No |
| [43] | Tunable Absorber(Passband) | Varactor diode | 4 | 5 | No |
| [170] | Tunable(Stopband) | Varactor diode | 81.4 | 69.5 | No |
| [71] | Tunable | Varactor diode | 152.4 | 129 | Yes |
| [34] | Tunable(Stopband) | High-permittivity ceramics | 25.8 | 22.9 | No |
| [72] | Tunable Absorber | PIN diode | 91 | 31.6 | Yes |
| [33] | Tunable(Passband) | Chip capacitor | 5.9 | 30 | No |
| [83] | 3D Tunable AFSS(Stopband) | Graphene micro-ribbons | 5.5 | 10 | No |
| [92] | Tunable Absorber | PIN, Varactor diode | 113 | 47.3 | No |
| [171] | Tunable 3D AFSS(Passband) | Varactor diode | 14 | 65 | No |
| [172] | Tunable(Passband) | Varactor diode | 11.5 | 24.6 | No |
| Key Findings | Description | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Improved Design of FSS Structures | Research contributes to the development of novel FSS designs (e.g., 2.5D, miniaturized configurations) to enhance performance. | Wearable devices, IoT, healthcare devices |
| Electromagnetic Filtering and Interference Control | Research demonstrates how FSS can filter specific frequency bands and reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI). | Smart textiles, communication systems, radar systems |
| Tunable and Reconfigurable FSS | The study explored tunable FSSs using MEMS switches or varactor diodes for dynamic frequency response adaptation. | Dynamic wireless communication systems, adaptive sensors |
| Enhanced Bandwidth and Gain | The research shows how multi-layered and fractal-based FSS designs improve bandwidth and front-to-back gain. | 5G networks, satellite communication, high-frequency antennas |
| Low Reflection and Return Loss | The study investigated FSS designs for low return loss and reflection in microwave and millimeter-wave applications. | Wireless communication systems, radar, medical implants |
| Compact and Lightweight Designs | Miniaturized designs allow FSSs to be integrated into smaller devices without compromising performance. | IoT, wearable devices, mobile communication devices |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Afzal, W.; Baig, M.Z.; Ebrahimi, A.; Robel, M.R.; Rana, M.T.A.; Rowe, W. Frequency Selective Surfaces: Design, Analysis, and Applications. Telecom 2024, 5, 1102-1128. https://doi.org/10.3390/telecom5040056
Afzal W, Baig MZ, Ebrahimi A, Robel MR, Rana MTA, Rowe W. Frequency Selective Surfaces: Design, Analysis, and Applications. Telecom. 2024; 5(4):1102-1128. https://doi.org/10.3390/telecom5040056
Chicago/Turabian StyleAfzal, Waseem, Muhammad Zeeshan Baig, Amir Ebrahimi, Md. Rokunuzzaman Robel, Muhammad Tausif Afzal Rana, and Wayne Rowe. 2024. "Frequency Selective Surfaces: Design, Analysis, and Applications" Telecom 5, no. 4: 1102-1128. https://doi.org/10.3390/telecom5040056
APA StyleAfzal, W., Baig, M. Z., Ebrahimi, A., Robel, M. R., Rana, M. T. A., & Rowe, W. (2024). Frequency Selective Surfaces: Design, Analysis, and Applications. Telecom, 5(4), 1102-1128. https://doi.org/10.3390/telecom5040056







