5G New Radio Open Radio Access Network Implementation in Brazil: Review and Cost Assessment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Background
2.1. 5G NR (New Radio) Technology
2.2. Open RAN Architecture
2.2.1. CAPEX and OPEX Efficiency
2.2.2. Latency and Reliability
2.2.3. Flexibility and Scalability
2.2.4. Energy Efficiency
2.2.5. Resource Utilization
2.2.6. Network Scalability
2.2.7. Deployment Flexibility
2.2.8. Vendor Lock-in Risk
3. Current Telecommunications Landscape in Brazil
3.1. Existing Infrastructure
3.2. Market Players and Competition
3.3. Regulatory Environment
4. Challenges and Opportunities in Implementing 5G NR Open RAN in Brazil
4.1. Challenges
4.1.1. Technical Challenges
- System Integration Complexity: o-RAN introduces a disaggregated architecture, which requires the integration of components from multiple vendors. The integration can lead to interoperability issues and increased complexity in system integration [35]. The regulatory agencies might be present in the discussions with the development group to achieve an agreement and make the integration between different vendors easily supported and in-coded prepared.
- Performance Optimization: Ensuring that the disaggregated components work together efficiently to deliver performance comparable to or better than traditional RAN solutions is a significant challenge [36].
- Security Concerns: The open nature of o-RAN can potentially introduce new security vulnerabilities that need to be addressed [15].
- Operational Complexity: Managing a multi-vendor o-RAN environment can be more complex than traditional single-vendor solutions, potentially increasing operational costs [37].
- AI/ML Integration: Implementing and optimizing AI/ML algorithms for network management and optimization in o-RAN can be challenging [38].
- Fronthaul Network Requirements: o-RAN’s split architecture places higher demands on the fronthaul network in terms of bandwidth and latency [39].
- Energy Efficiency: Ensuring that the disaggregated o-RAN architecture is as energy efficient as traditional RAN solutions is crucial for operational costs and environmental considerations [40].
- Spectrum Efficiency: Optimizing spectrum usage in a multivendor o-RAN environment to ensure efficient utilization of this valuable resource [41].
4.1.2. Economic Challenges
- Performance trade-off—Quality and equipment cost in return for the end user’s better rates and service excellence.
- Integration costs—Interoperability configurations and adaptation cost to workability.
- Lack of knowledge/experience—Network deployment and configuration require high expertise in managing and preparing the network. In some cases, the cost of failure can make the project impracticable and waste resources, time, and equipment.
4.1.3. Regulatory Challenges
4.2. Opportunities
5. Implementation Strategies
5.1. Government Initiatives and Policies
- Longer license terms;
- Secondary spectrum market;
- Unlimited renewal terms.
5.2. Industry Collaboration and Partnerships
5.3. Spectrum Allocation and Management
5.4. Infrastructure Development Plan
- Bring high-capacity data transport networks to all Brazilian municipalities;
- Expand the mobile and fixed broadband access networks in urban and rural areas;
- Disseminate digital inclusion initiatives.
5.5. Pilot Projects in Brazil
5.6. Lessons from International Implementations
- Less time on the mixed vendors network, enabling services, especially in business services.
- Facile escalation of new demands and usage cases.
- Higher capacity in edge cloud integration.
- Lesser cost in network management.
- Network automation.
6. Open RAN Costs in Brazil
6.1. Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
- CAPEX
- RU costs, DU costs, CU costs;
- 5G network core cost;
- Equipment cooling costs;
- Antenna tower construction costs.
- OPEX
- Electrical costs;
- Operation and maintenance costs;
- Equipment and site rental costs;
- License and SW costs and updates;
- Cost of renting an area for the sites.
6.1.1. CAPEX Calculation
6.1.2. OPEX Calculation
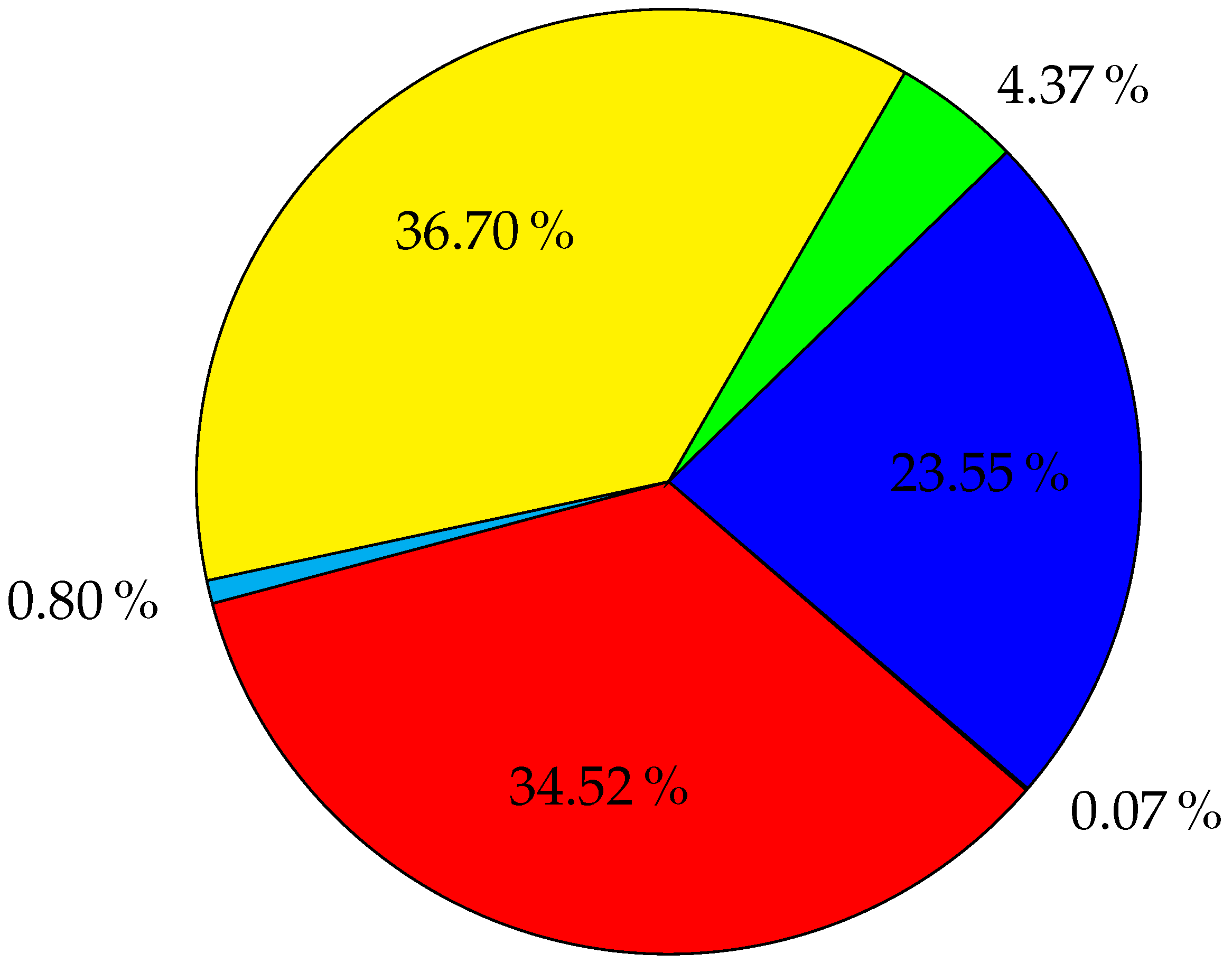
6.2. Open RAN Cost
7. Future Outlook
7.1. Projected Timeline for Nationwide Implementation
7.2. Potential Impact on Various Sectors
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peng, M.; Yan, S.; Zhang, K.; Wang, C. Fog-computing-based radio access networks: Issues and challenges. IEEE Netw. 2016, 30, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brik, B.; Boutiba, K.; Ksentini, A. Deep Learning for B5G Open Radio Access Network: Evolution, Survey, Case Studies, and Challenges. IEEE Open J. Commun. Soc. 2022, 3, 228–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, N.N.; Pham, Q.V.; Tu, N.H.; Thanh, T.T.; Bao, V.N.Q.; Lakew, D.S.; Cho, S. Survey on Aerial Radio Access Networks: Toward a Comprehensive 6G Access Infrastructure. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2021, 23, 1193–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polese, M.; Bonati, L.; D’Oro, S.; Basagni, S.; Melodia, T. Understanding O-RAN: Architecture, Interfaces, Algorithms, Security, and Research Challenges. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2023, 25, 1376–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UnB. Estudo Sobre Estado da Arte do Open RAN Aplicado ao Ecossistema de Telecomunicações Brasileiro; Technical Report; UnB: Fredericton, NB, Canada, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Gabriel, C. Open RAN: Ready for Prime Time? Technical Report; Analysys Mason: Bonn, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Gadge, P.C.; Panda, S.S.; Kumar, P. A Survey on the Progressing 5G (NR) Modern Technologies and their Challenges. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Computing, Communication, and Intelligent Systems (ICCCIS), Greater Noida, India, 19–20 February 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 834–839. [Google Scholar]
- Adebusola, J.A.; Ariyo, A.A.; Elisha, O.A.; Olubunmi, A.M.; Julius, O.O. An overview of 5G technology. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference in Mathematics, Computer Engineering and Computer Science (ICMCECS), Ayobo, Nigeria, 18–21 March 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Mwanje, S.; Decarreau, G.; Mannweiler, C.; Naseer-ul Islam, M.; Schmelz, L.C. Network management automation in 5G: Challenges and opportunities. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 27th Annual International Symposium on Personal, Indoor, and Mobile Radio Communications (PIMRC), Valencia, Spain, 4–8 September 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, M.M.d.; Guerreiro, J. On the 5G and Beyond. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavan, V.; Li, J. Evolution of physical-layer communications research in the post-5G era. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 10392–10401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkvall, S.; Dahlman, E.; Furuskar, A.; Frenne, M. NR: The new 5G radio access technology. IEEE Commun. Stand. Mag. 2017, 1, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, E.G.; Edfors, O.; Tufvesson, F.; Marzetta, T.L. Massive MIMO for next generation wireless systems. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2014, 52, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzaïd, C.; Taleb, T. AI for beyond 5G networks: A cyber-security defense or offense enabler? IEEE Netw. 2020, 34, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.; Kumar, T.; Liyanage, M.; Okwuibe, J.; Ylianttila, M.; Gurtov, A. 5G security: Analysis of threats and solutions. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Standards for Communications and Networking (CSCN), Helsinki, Finland, 18–20 September 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 193–199. [Google Scholar]
- Agiwal, Mamta and Roy, Abhishek and Saxena, Navrati Next generation 5G wireless networks: A comprehensive survey IEEE communications surveys & tutorials. IEEE 2016, 18, 1617–1655. [CrossRef]
- Mei, W.; Zheng, B.; You, C.; Zhang, R. Intelligent reflecting surface-aided wireless networks: From single-reflection to multireflection design and optimization. Proc. IEEE 2022, 110, 1380–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azariah, W.; Bimo, F.A.; Lin, C.W.; Cheng, R.G.; Nikaein, N.; Jana, R. A Survey on Open Radio Access Networks: Challenges, Research Directions, and Open Source Approaches. Sensors 2024, 24, 1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parallel Wireless. Everything You Need to Know About Open Ran. Available online: https://www.parallelwireless.com/wp-content/uploads/Parallel-Wireless-e-Book-Everything-You-Need-to-Know-about-Open-RAN.pdf (accessed on 6 March 2025).
- Zeydan, E.; Blanco, L.; Barrachina-Muñoz, S.; Rezazadeh, F.; Vettori, L.; Mangues, J. A Marketplace Solution for Distributed Network Management and Orchestration of Slices. In Proceedings of the 2023 19th International Conference on Network and Service Management (CNSM), Niagara Falls, ON, Canada, 30 October–2 November 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacava, A.; Bonati, L.; Mohamadi, N.; Gangula, R.; Kaltenberger, F.; Johari, P.; D’Oro, S.; Cuomo, F.; Polese, M.; Melodia, T. dApps: Enabling Real-Time AI-Based Open RAN Control. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2501.16502. [Google Scholar]
- Gismalla, M.S.M.; Azmi, A.I.; Salim, M.R.; Abdullah, M.F.L.; Iqbal, F.; Mabrouk, W.A.; Othman, M.B.; Ashyap, A.Y.I.; Supa’at, A.S.M. Survey on Device to Device (D2D) Communication for 5GB/6G Networks: Concept, Applications, Challenges, and Future Directions. Inst. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2022, 10, 30792–30821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, L.B.; Lau, V.K.N.; Jorswieck, E.A.; Đào, N.D.; Haghighat, A.; Kim, D.I.; Le-Ngoc, T. Enabling 5G mobile wireless technologies. EURASIP J. Wirel. Commun. Netw. 2015, 2015, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, C. System architecture and key technologies for 5G heterogeneous cloud radio access networks. Inst. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2015, 29, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.; Vu, T.X.; Nguyen, N.T.; Nguyen, D.C.; Juntti, M.; Luong, N.C.; Hoang, D.T.; Nguyen, D.N.; Chatzinotas, S. Network-Aided Intelligent Traffic Steering in 6G O-RAN: A Multi-Layer Optimization Framework. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2302.02711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannone, F.; Gupta, H.; Manicone, D.; Kondepu, K.; Franklin, A.A.; Castoldi, P.; Valcarenghi, L. Impact of RAN Virtualization on Fronthaul Latency Budget: An Experimental Evaluation. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1708.00366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ABRINTEL. Brasil: É Possível Ter Banda-Larga Para Todos? Technical Report; ABRINTEL: São Paulo, Brazil, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- ANATEL. Agencia Nacial de Telecomunicações, Plano Estrutural de Redes de Telecomunicações—PERT. Available online: https://www.gov.br/anatel/pt-br/dados/infraestrutura/pert (accessed on 6 March 2025).
- bnamericas.com. Industry Players Create Open RAN lobby Group in Brazil. Available online: https://www.bnamericas.com/en/news/industry-players-create-open-ran-lobby-group-in-brazil (accessed on 6 March 2025).
- Hobday, M. Telecommunications in Developing Countries: The Challenge from Brazil; Technical Report; Routledge: Abingdon-on-Thames, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Communications, Media and Internet Concentration in Brazil, 2019–2021; Technical Report; Global Media & Internet Concentration Project: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2021.
- Falch, M.; Iaskio, E. National Broadband Strategies—The case of Brazil. In Proceedings of the 2nd Regional African Conference of the International Telecommunications Society, Lusaka, Zambia, 15–16 March 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Office of the President of the Federative Republic of Brazil. Establishes the National Broadband Program-PNBL and Other Resolutions. Available online: https://www.global-regulation.com/translation/brazil/2899981/decree-no.-7175%252c-may-12-2010.html (accessed on 9 May 2024).
- da Cunha, M.B. The Brazilian and the US National Broadband Plan: A Comparative Review on Policies and Actions; Institute of Brazilian Issues, XXXI Minerva Program-Spring; The George Washington University: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Gavrilovska, L.; Rakovic, V.; Atanasovski, V. Visions Towards 5G: Technical Requirements and Potential Enablers. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2016, 87, 731–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonati, L.; Polese, M.; D’Oro, S.; Basagni, S.; Melodia, T. Open, Programmable, and Virtualized 5G Networks: State-of-the-Art and the Road Ahead. Comput. Netw. 2020, 182, 107516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghrah, A.; Pourmohammad Abdollahi, M.; Azarhava, H.; Musevi Niya, J. A survey on the handover management in 5G-NR cellular networks: Aspects, approaches and challenges. EURASIP J. Wirel. Commun. Netw. 2023, 2023, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Jiang, C.; Zhang, H.; Ren, Y.; Chen, K.C.; Hanzo, L. Thirty Years of Machine Learning: The Road to Pareto-Optimal Wireless Networks. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2020, 22, 1472–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, L.M.P.; Checko, A.; Christiansen, H.L. A Survey of the Functional Splits Proposed for 5G Mobile Crosshaul Networks. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2019, 21, 146–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zukerman, M.; Yung, E.K.N. Energy-Efficient Base-Stations Sleep-Mode Techniques in Green Cellular Networks: A Survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2015, 17, 803–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akyildiz, I.F.; Kak, A.; Nie, S. 6G and Beyond: The Future of Wireless Communications Systems. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 133995–134030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GSMA. 5G an América Latina Desencadeando o Potencial; Technical Report; GSMA: London, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Teletime. Vivo, Claro e TIM Somam Receita de R$ 121 Bilhões em 2023, Alta de 8.5%. Available online: https://teletime.com.br/23/02/2024/vivo-claro-e-tim-somam-receita-de-r-121-bilhoes-em-2023-alta-de-85/ (accessed on 6 March 2025).
- Telecoms.com. Can Open RAN Be the Silver Bullet for Rural Connectivity? Available online: https://valor.globo.com/empresas/noticia/2024/07/09/avanco-do-5g-esbarra-na-falta-de-antenas.ghtml (accessed on 6 March 2025).
- GSMA. Brazil’s Multi-Band Auction: One of the Largest in the History of Mobile Communications; Technical Report. Available online: https://www.gsma.com/connectivity-for-good/spectrum/brazil-multi-band-auction-one-of-the-largest-in-mobile-history/ (accessed on 25 April 2024).
- GSMA. Spectrum Management in Latin America, Impacts on Economic and Social Development; Technical Report; GSMA: London, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalo, M.; Harfuch, M.P.; Haro Sly, M.J.; Lavarello, P. 5G Kick-off in India and Brazil: InterState Competition, National Systems of Innovation, and Catch-up Implications for the Global South. Seoul J. Econ. 2023, 36, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Center for Strategic Studies and Management (CGEE). Brazilian Digital Transformation Strategy (E-Digital). 2022–2026 Cycle; Technical Report; Ministry of Science, Technology and Innovations (MCTI): Brasília, Brazil, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Julião, H. TIM Organiza Campus no Inatel Para Testes de Fornecedores OpenRAN. Available online: https://teletime.com.br/30/06/2020/tim-organiza-campus-no-inatel-para-testes-de-fornecedores-openran (accessed on 6 March 2025).
- Julião, H. Vivo já Realiza Pilotos da Tecnologia OpenRAN em Petrolina e Juazeiro. Available online: https://teletime.com.br/30/06/2020/vivo-ja-realiza-pilotos-da-tecnologia-openran-em-petrolina-e-juazeiro (accessed on 6 March 2025).
- Channel, I. Algar Telecom Participa de Testes com Open RAN. Available online: https://inforchannel.com.br/2020/12/15/algar-telecom-participa-de-testes-com-open-ran (accessed on 6 March 2025).
- Frank, H.; Tessinari, R.S.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, Z.; Meixner, C.C.; Yan, S.; Simeonidou, D. Resource Analysis and Cost Modeling for End-to-End 5G Mobile Networks. In Proceedings of the Optical Network Design and Modeling, Barcelona, Spain, 18–21 May 2020; Tzanakaki, A., Varvarigos, M., Muñoz, R., Nejabati, R., Yoshikane, N., Anastasopoulos, M., Marquez-Barja, J., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 492–503. [Google Scholar]
- da Silva Souza, D. Uma Análise Técnico-Econômica para Implantação de Arquiteturas Centralizadas de Redes de Telefonia Móveis. Available online: https://repositorio.ufpa.br/jspui/bitstream/2011/10036/1/Dissertacao_AnaliseTecnicoEconomica.pdf (accessed on 19 March 2024).
- SMC+. A Gestão da Infraestrutura de Telecomunicações Como um Pilar Fundamental Para o Futuro da América Latina; Technical Report; ABRINTEL: São Paulo, Brazil, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Mendes, L.L.; Moreno, C.S.; Marquezini, M.V.; Cavalcante, A.M.; Neuhaus, P.; Seki, J.; Aniceto, N.F.T.; Karvonen, H.; Vidal, I.; Valera, F.; et al. Enhanced remote areas communications: The missing scenario for 5G and beyond 5G networks. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 219859–219880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolfe, É.L.; Jorge, L.A.d.C.; Sanches, I.D.; Luchiari Júnior, A.; da Costa, C.C.; Victoria, D.d.C.; Inamasu, R.Y.; Grego, C.R.; Ferreira, V.R.; Ramirez, A.R. Precision and digital agriculture: Adoption of technologies and perception of Brazilian farmers. Agriculture 2020, 10, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidi-Sepehr, F.; Sajadieh, M.; Panteleev, S.; Islam, T.; Karls, I.; Chatterjee, D.; Ansari, J. 5G URLLC: Evolution of high-performance wireless networking for industrial automation. IEEE Commun. Stand. Mag. 2021, 5, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farias, G.F. 5G–Redes de comunicações móveis de quinta geração: Evolução, tecnologia, aplicações e mercado. Engenharia Elétrica-Pedra Branca 2019. Available online: https://repositorio.animaeducacao.com.br/handle/ANIMA/4176 (accessed on 6 March 2025).
- Guidotti, A.; Vanelli-Coralli, A.; Conti, M.; Andrenacci, S.; Chatzinotas, S.; Maturo, N.; Evans, B.; Awoseyila, A.; Ugolini, A.; Foggi, T.; et al. Architectures and Key Technical Challenges for 5G Systems Incorporating Satellites. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1806.02088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogale, T.E.; Le, L.B. Massive MIMO and Millimeter Wave for 5G Wireless HetNet: Potentials and Challenges. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1510.06359. [Google Scholar]
- Alper, M.E.; Miktus, M. Bridging the Mobile Digital Divide in Sub-Saharan Africa: Costing Under Demographic Change and Urbanization; International Monetary Fund: Washington, DC, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Shehab, M.J.; Kassem, I.; Kutty, A.A.; Kucukvar, M.; Onat, N.; Khattab, T. 5G Networks Towards Smart and Sustainable Cities: A Review of Recent Developments, Applications and Future Perspectives. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 2987–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsatti, D.; Grasselli, C.; Contoli, C.; Micciullo, L.; Spinacci, L.; Settembre, M.; Cerroni, W.; Callegati, F. Mission Critical Communications Support with 5G and Network Slicing. IEEE Trans. Netw. Serv. Manag. 2023, 20, 595–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spantideas, S.T.; Giannopoulos, A.E.; Trakadas, P. Smart Mission Critical Service Management: Architecture, Deployment Options, and Experimental Results. IEEE Trans. Netw. Serv. Manag. 2024, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.; Ge, X.; Wang, L.; Kwak, K.S.; Han, Y.; Liu, X. 5G Converged Cell-Less Communications in Smart Cities. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2017, 55, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| KPI Category | c-RAN | o-RAN | d-RAN | v-RAN |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAPEX | Moderate | High | Low | Moderate |
| OPEX | Low | Moderate | High | Low |
| Latency | Low | Moderate | High | Low |
| Reliability | Moderate | High | High | Moderate |
| Flexibility | High | High | Low | High |
| Deployment flexibility | High | High | Low | High |
| Network scalability | High | High | Low | High |
| Energy Efficiency | High | Medium | Low | High |
| Resource Utilization | High | Medium | Low | High |
| 698–960 MHz | 700 MHz used for 4G |
| 850 MHz for GSM; | |
| 900 MHz used for GSM and 3G; | |
| 1710–2025 MHz 2110–2200 MHz | Used for GSM, 3G and more recently 4G; |
| 2300–2390 MHz | Tenders for 5G in 2021 |
| 2500–2690 MHz | 2500 MHz used for 4G (LTE). |
| 3300–3700 MHz | Auctioned for 5G in 2021. |
| 24.3 GHz to 27.50 GHz | Tenders for 5G in 2021 |
| 2.390 MHz to 2.400 MHz | 34 authorizations, held by 6 companies |
| 3.700 MHz to 3.800 MHz | 30 authorizations, held by 6 companies |
| 27.5 GHz to 27.9 GHz | 2 authorizations, held by 1 company |
| Equipment | CAPEX | OPEX | Variation | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rural Mast | R$ 539.052,04 | 6.12% | 2.78% | 10 |
| Rural Roof Mast | R$ 174.480,04 | 18.92% | 2.78% | 10 |
| Urban Mast | R$ 441.944,47 | 8.66% | 2.78% | 10 |
| Urban Roof Mast | R$ 174.480,04 | 28.54% | 2.78% | 10 |
| SmallCell Mast | R$ 23.218,89 | 4.56% | 2.78% | 10 |
| Macrocell 5G | R$ 131.223,87 | 7.84% | −1.63% | 5 |
| SmallCell 5G | R$ 89.875,55 | 4.56% | −1.63% | 5 |
| Rack | R$ 185.892,25 | 29.69% | −1.63% | 5 |
| Backhaul DWDM 10 Gbps | R$ 112.992,13 | 17.60% | −0.08% | 5 |
| Optic Fiber (km) | R$ 57.193,89 | 4.80% | −0.08% | 20 |
| 2025 | 2030 | |
|---|---|---|
| 5G Mobiles | 36.2 million | 179 million |
| 5G Adoption | 16% | 77% |
| 5G Economic | US$ 5 billion | US$ 26 billion |
| Contribution | 0.3% GDP | 1.2% GDP |
| 5G Coverage | 47% | 84% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Notari, E.F.; Travassos, X.L. 5G New Radio Open Radio Access Network Implementation in Brazil: Review and Cost Assessment. Telecom 2025, 6, 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/telecom6020024
Notari EF, Travassos XL. 5G New Radio Open Radio Access Network Implementation in Brazil: Review and Cost Assessment. Telecom. 2025; 6(2):24. https://doi.org/10.3390/telecom6020024
Chicago/Turabian StyleNotari, Eduardo Fabricio, and Xisto Lucas Travassos. 2025. "5G New Radio Open Radio Access Network Implementation in Brazil: Review and Cost Assessment" Telecom 6, no. 2: 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/telecom6020024
APA StyleNotari, E. F., & Travassos, X. L. (2025). 5G New Radio Open Radio Access Network Implementation in Brazil: Review and Cost Assessment. Telecom, 6(2), 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/telecom6020024





