Extracellular Vesicles in Autologous Cell Salvaged Blood in Orthopedic Surgery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Data
3.2. Flow Cytometry Data
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EV | Extracellular Vesicle |
| PBM | Patient Blood Management |
| RBC | Red Blood Cell Concentrate |
References
- Kozek-Langenecker, S.A.; Afshari, A.; Albaladejo, P.; Santullano, C.A.; De Robertis, E.; Filipescu, D.C.; Fries, D.; Goerlinger, K.; Haas, T.; Imberger, G.; et al. Management of severe perioperative bleeding: Guidelines from the European Society of Anesthesiology. Eur. J. Anesthesiol. 2017, 34, 332–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carless, P.A.; Henry, D.A.; Moxey, A.J.; O’Connell, D.; Brown, T.; Fergusson, D.A. Cell salvage for minimising perioperative allogeneic blood transfusion. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2010, 4, CD001888. [Google Scholar]
- van Bodegom-Vos, L.; Voorn, V.M.; So-Osman, C.; Vlieland, T.P.; Dahan, A.; Koopman-van Gemert, A.W.; Vehmeijer, S.B.; Nelissen, R.G.; Marang-van de Mheen, P.J. Cell salvage in hip and knee arthroplasty: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2015, 97, 1012–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Feng, X.; Ma, J.; Kang, P.; Shen, B.; Yang, J.; Zhou, Z.; Pei, F. Is postoperative cell salvage necessary in total hip or knee replacement? A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Int. J. Surg. 2015, 21, 135–144. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, B.; Wang, L.; Djaiani, G.; Mazer, C.D. Continuous and discontinuous cell-washing autotransfusion systems. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2004, 18, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donadee, C.; Raat, N.J.; Kanias, T.; Tejero, J.; Lee, J.; Kelley, E.; Zhao, X.; Liu, C.; Reynolds, H.; Azarov, I.; et al. Nitric oxide scavenging by red blood cell microparticles and cell-free hemoglobin as a mechanism for the red cell storage lesion. Circulation 2011, 26, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thery, C.; Ostrowski, M.; Segura, E. Membrane vesicles as conveyors of immune responses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 581–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, D.; Büssow, J.; Meybohm, P.; Weber, C.F.; Zacharowski, K.; Urbschat, A.; Müller, M.M.; Jennewein, C. Microparticles from stored blood cells enhance procoagulant and proinflammatory activity. Transfusion 2017, 57, 2701–2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overdevest, E.; Lanen, P.; Feron, J.; van Hees, J.; Tan, M. Clinical evaluation of the Sorin Xtra autotransfusion system. Perfusion 2012, 27, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wisgrill, L.; Lamm, C.; Hartmann, J.; Preißing, F.; Dragosits, K.; Bee, A.; Hell, L.; Thaler, J.; Ay, C.; Pabinger, I.; et al. Peripheral blood microvesicles secretion is influenced by storage time, temperature, and anticoagulants. Cytometry A 2016, 89, 663–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bratton, D.L.; Fadok, V.A.; Richter, D.A.; Kailey, J.M.; Frasch, S.C.; Nakamura, T.; Henson, P.M. Polyamine regulation of plasma membrane phospholipid flip-flop during apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 74, 28113–28120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arraud, N.; Gounou, C.; Turpin, D.; Brisson, A.R. Fluorescence triggering: A general strategy for enumerating and phenotyping extracellular vesicles by flow cytometry. Cytometry A 2016, 89, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keuren, J.F.; Magdeleyns, E.J.; Govers-Riemslag, J.W.; Lindhout, T.; Curvers, J. Effects of storage-induced platelet microparticles on the initiation and propagation phase of blood coagulation. Br. J. Haematol. 2006, 134, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kireev, D.A.; Popenko, N.Y.; Pichugin, A.V.; Panteleev, M.A.; Krymskaya, O.V.; Ataullakhanov, F.I.; Sinauridze, E.I. Platelet microparticle membranes have 50- to 100-fold higher specific procoagulant activity than activated platelets. Thromb. Haemost. 2007, 97, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonova, O.A.; Shustova, O.N.; Golubeva, N.V.; Yakushkin, V.V.; Alchinova, I.B.; Karganov, M.Y.; Mazurov, A.V. Coagulation properties of erythrocyte derived membrane microparticles. Biomed. Khim. 2019, 65, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horstmann, L.L.; McCauley, R.F.; Jy, W.; Ahn, Y.S. Tissue factor-negative cell-derived microparticles play a distinctive role in hemostasis: A viewpoint review. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2019, 45, 509–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Projahn, D.; Koenen, R.R. Platelets: Key players in vascular inflammation. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2012, 92, 1167–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biro, E.; van den Goor, J.M.; de Mol, B.A.; Schaap, M.C.; Ko, L.Y.; Sturk, A.; Hack, C.E.; Nieuwland, R. Complement activation on the surface of cell-derived microparticles during cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass—Is retransfusion of pericardial blood harmful? Perfusion 2011, 26, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozek-Langenecker, S.; Fenger-Eriksen, C.; Thienpont, E.; Barauskas, G. European guidelines on perioperative venous thrombiembolism prophylaxis. Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. 2017, 34, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Oswald, E.; Streif, W.; Hermann, M.; Hengster, P.; Mittermayr, M.; Innerhofer, P. Intraoperative salvaged red blood cells contain nearuly no functionally active platelets, but exhibit formation of microparticles: Results of a pilot study in orthopedic patients. Transfusion 2010, 50, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, P.; Che, J.; Li, X.; Tian, M.; Smith, F.G. Quick biochemical markers for assessment of quality control of intraoperative cell salvage: A prospective observational study. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2014, 9, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Ji, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Liu, J.; Long, C.; Zheng, Z. Comparison of the effects of three cell saver devices on erythrocyte function during cardiopulmonary bypass procedure—A pilot study. Artif. Organs 2012, 36, 931–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrick, C.J.; Scholz, M.; Melo, A.; Singh, O.; Noel, D. Quality of red blood cells using qutotransfusion devices: A comparative analysis. J. Extracorpor. Technol. 2003, 35, 28–34. [Google Scholar]
- Almizraq, R.J.; Seghatchian, J.; Acker, J.P. Extracellular Vesicles in Transfusion-Related Immunomodulation and the Role of Blood Component Manufacturing. Transfus. Apher. Sci. 2016, 55, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wannez, A.; Devalet, B.; Chatelain, B.; Chatelain, C.; Dogné, J.-M.; Mullier, F. Extracellular vesicles in red blood cell concentrates: An overview. Transfus. Med. Rev. 2019, 33, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hariri, G.; Bourcier, S.; Marjanovic, Z.; Joffre, J.; Lemarié, J.; Lavillegrand, J.-R.; Charue, D.; Duflot, T.; Bigé, N.; Baudel, J.-L.; et al. Exploring the microvascular impact of red blood cell transfusion in intensive care unit patients. Crit. Care 2019, 23, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tissot, J.; Rubin, O.; Canellini, G. Analysis and clinical relevance of microparticles from red blood cells. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2010, 17, 571–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramani, K.; Raju, S.P.; Chu, X.; Warren, M.; Pandya, C.D.; Hoda, N.; Fulzele, S.; Raju, R.P. Effect of plasma-derived extracellular vesicles on erythrocyte deformability in polymicrobial sepsis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2018, 65, 244–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almizraq, R.J.; Norris, P.J.; Inglis, H.; Menocha, S.; Wirtz, M.R.; Juffermans, N.P.; Pandey, S.; Spinella, P.C.; Acker, J.P.; Muszynski, J.A. Blood manufacturing methods affect red blood cell product characteristics and immunomodulatory activity. Blood Adv. 2018, 25, 2296–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Noulsri, E. Quantification of cell-derived microparticles in blood products and its potential application in transfusion laboratories. Lab. Med. 2020, 51, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, S.C.; Iv, F.T.M.; McDonough, R.; Timm, D.D.; Hovmand-Warner, E.; Frazier, E.; Thomas, K.A.; Spinella, P.C.; Doctor, A. Effect of plasma processing and storage on microparticle abundance, nitric oxide scavenging and vasoactivity. Transfusion 2019, 59, 1568–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seyfried, T.; Breu, A.; Gruber, M.; Reipert, J.; Hansen, E. Processing of small volumes in blood salvage devices. Transfusion 2014, 54, 2775–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
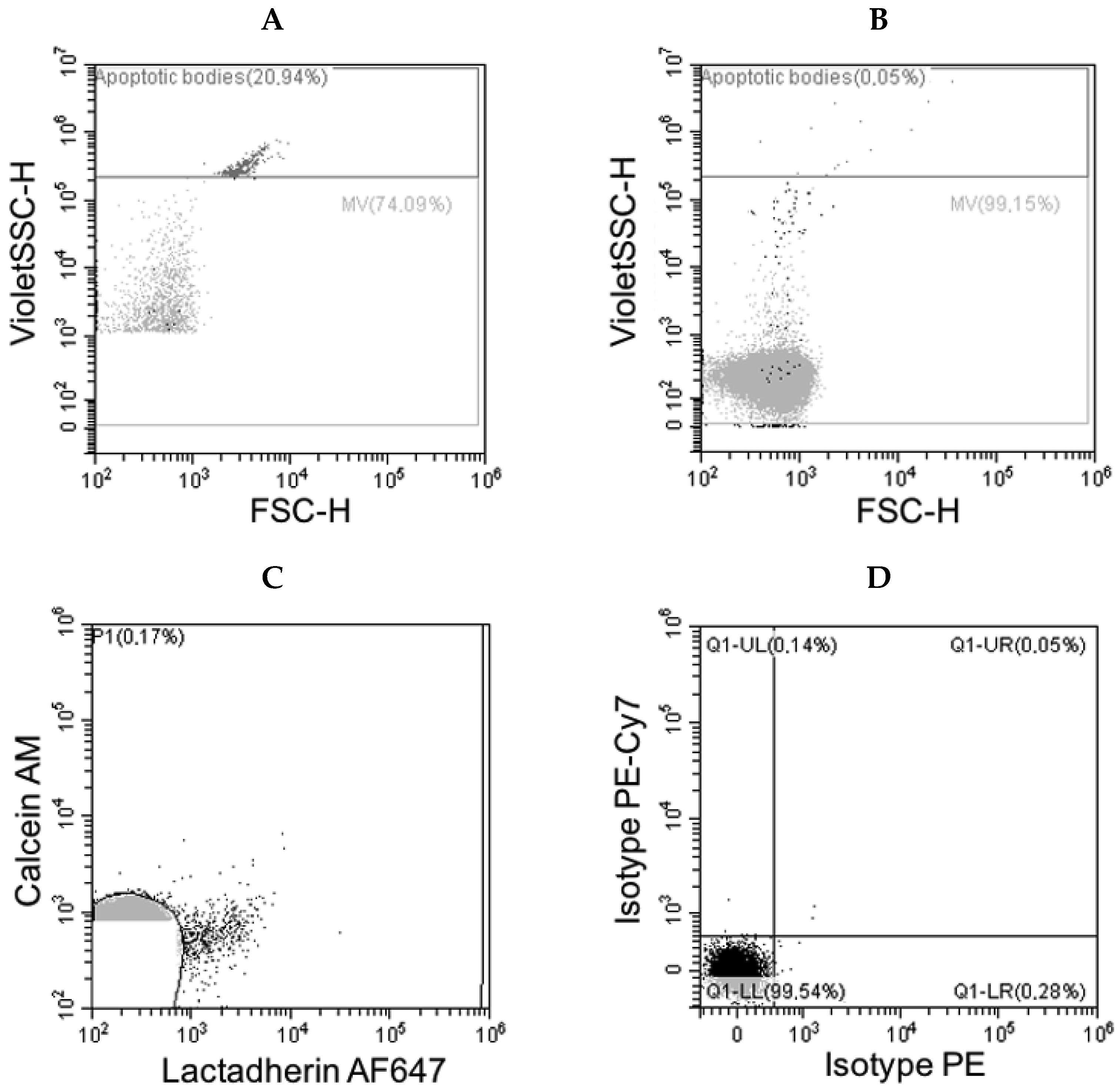
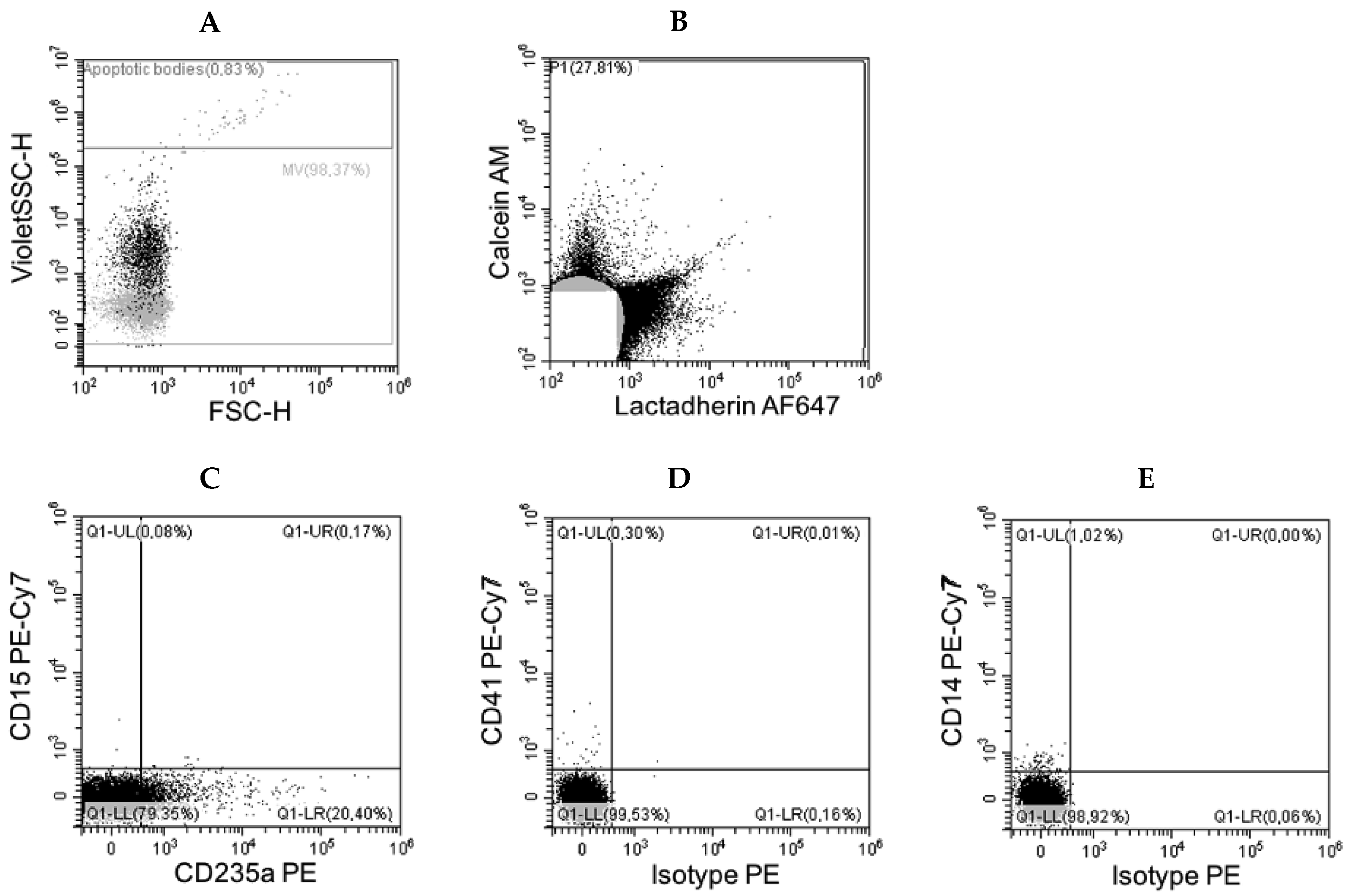
| Antigen | Origin | Events/µL Mean (Range) |
|---|---|---|
| CD235a | erythrocytes | 17,042 (12–81,164) |
| CD14 | monocytes | <2 |
| CD15 | myelocytes | <2 |
| CD41 | platelets | <1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kutschera, M.; Pischlaeger, A.; Sztulman, L.; Kietaibl, S.; Spittler, A. Extracellular Vesicles in Autologous Cell Salvaged Blood in Orthopedic Surgery. Surgeries 2021, 2, 84-91. https://doi.org/10.3390/surgeries2010007
Kutschera M, Pischlaeger A, Sztulman L, Kietaibl S, Spittler A. Extracellular Vesicles in Autologous Cell Salvaged Blood in Orthopedic Surgery. Surgeries. 2021; 2(1):84-91. https://doi.org/10.3390/surgeries2010007
Chicago/Turabian StyleKutschera, Maximilian, Agnes Pischlaeger, Larissa Sztulman, Sibylle Kietaibl, and Andreas Spittler. 2021. "Extracellular Vesicles in Autologous Cell Salvaged Blood in Orthopedic Surgery" Surgeries 2, no. 1: 84-91. https://doi.org/10.3390/surgeries2010007
APA StyleKutschera, M., Pischlaeger, A., Sztulman, L., Kietaibl, S., & Spittler, A. (2021). Extracellular Vesicles in Autologous Cell Salvaged Blood in Orthopedic Surgery. Surgeries, 2(1), 84-91. https://doi.org/10.3390/surgeries2010007








