Systematic Review Comparing the Effectiveness of Robotic verse Laparoscopic Liver Surgery in Colorectal Liver Metastasis (CRLM)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- Robotic Surgery AND ((Colorectal Liver Metastasis OR (CRLM))—25
- Laparoscopic surgery AND ((Colorectal Liver Metastasis OR (CRLM))—269
- Liver resection AND ((Colorectal Liver Metastasis OR (CRLM)) AND Robotic Surgery—21
- Liver resection AND ((Colorectal Liver Metastasis OR (CRLM)) AND Laparoscopic surgery—249
- ((COLORECTAL LIVER METASTASIS) OR (CRLM)) AND ((“robotic liver surgery” OR (“liver surgery”) OR (ROBOT ASSISTED SURGERY) OR (LAPAROSCOPIC SURGERY)) AND ((COST EFFECTIVENESS ANALYSIS) OR (cost effective))—26
- That all studies were appropriate prospective and retrospective studies specifically addressing outcomes of patients with CRLM who underwent either laparoscopic or robotics resection.
- Studies that reported on perioperative characteristics, at least one postoperative outcome and oncological outcomes for CRLM, morbidity or mortality and cost-effectiveness on robotic or laparoscopic surgery were included.
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Salvatore, L.; Aprile, G.; Arnoldi, E.; Aschele, C.; Carnaghi, C.; Cosimelli, M.; Maiello, E.; Normanno, N.; Sciallero, S.; Valvo, F.; et al. Management of metastatic colorectal cancer patients: Guidelines of the Italian Medical Oncology Association (AIOM). ESMO Open 2017, 2, e000147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cancer Research UK. Available online: https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/health-professional/cancer%20statistics/statistics-by-cancer-type/bowel-cancer#heading-Zero (accessed on 9 February 2020).
- Weiss, L.; Grundmann, E.; Torhorst, J.; Hartveit, F.; Moberg, I.; Eder, M.; Fenoglio-Preiser, C.M.; Napier, J.; Horne, C.H.W.; Lopez, M.J.; et al. Haematogenous metastatic patterns in colonic carcinoma: An analysis of 1541 necropsies. J. Pathol. 1986, 150, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jongen, J.M. Disease Progression and Therapy-Induced Changes in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Ph.D. Thesis, Utrecht University, Utrecht, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wayand, W.; Woisetschläger, R. Laparoscopic resection of liver metastasis. Chir. Z. Geb. Oper. Medizen 1993, 64, 195–197. [Google Scholar]
- Fretland, Å.A.; Dagenborg, V.J.; Bjørnelv, G.M.W.; Kazaryan, A.M.; Kristiansen, R.; Fagerland, M.W.; Hausken, J.; Tønnessen, T.I.; Abildgaard, A.; Barkhatov, L.; et al. Laparoscopic Versus Open Resection for Colorectal Liver Metastases: The OSLO-COMET Randomized Controlled Trial. Ann. Surg. 2018, 267, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Royal College of Pathology. Standards and Datasets for Reporting Cancers. Available online: http://www.rcpath.org/index (accessed on 4 April 2020).
- Guerra, F.; Guadagni, S.; Pesi, B.; Furbetta, N.; Di Franco, G.; Palmeri, M.; Annecchiarico, M.; Eugeni, E.; Coratti, A.; Patriti, A.; et al. Outcomes of robotic liver resections for colorectal liver metastases. A multi-institutional analysis of minimally invasive ultrasound-guided robotic surgery. Surg. Oncol. 2019, 28, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guadagni, S.; Furbetta, N.; Di Franco, G.; Palmeri, M.; Gianardi, D.; Bianchini, M.; Guadagnucci, M.; Pollina, L.; Masi, G.; Cremolini, C.; et al. Robotic-assisted surgery for colorectal liver metastasis: A single-centre experience. J. Minim. Access Surg. 2019, 16, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, M.; Li, S.; Yan, G.; Li, C.; Kang, Z. Short- and long-term outcomes of laparoscopic hepatectomy for colorectal liver metastases in elderly patients. Cancer Manag. Res. 2018, 10, 2581–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schiffman, S.C.; Kim, K.H.; Tsung, A.; Marsh, J.W.; Geller, D.A. Laparoscopic versus Open Liver Resection for Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: A Metaanalysis of 610 Patients. Surgery 2015, 157, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, J.R.; Lee, S.D.; Park, H.M.; Lee, E.C.; Park, B.; Han, S.S.; Kim, S.H.; Park, S.J. Outcomes of liver resection in patients with colorectal liver metastases by laparoscopic or open surgery. Ann. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Surg. 2018, 22, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferretti, S.; Tranchart, H.; Buell, J.F.; Eretta, C.; Patriti, A.; Spampinato, M.G.; Huh, J.W.; Vigano, L.; Han, H.S.; Ettorre, G.M.; et al. Laparoscopic Simultaneous Resection of Colorectal Primary Tumor and Liver Metastases: Results of a Multicenter International Study. World J. Surg. 2015, 39, 2052–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilal, M.A.; Di Fabio, F.; Salameh, M.A.; Pearce, N.W. Oncological efficiency analysis of laparoscopic liver resection for primary and metastatic cancer: A singlecenter UK experience. Arch. Surg. 2012, 147, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Casciola, L.; Patriti, A.; Ceccarelli, G.; Bartoli, A.; Ceribelli, C.; Spaziani, A. Robot-assisted parenchymal-sparing liver surgery including lesions located in the posterosuperior segments. Surg. Endosc. 2011, 25, 3815–3824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingham, T.P.; Scherer, M.A.; Neese, B.W.; Clements, L.W.; Stefansic, J.D.; Jarnagin, W.R. Image-guided liver surgery: Intraoperative projection of computed tomography images utilizing tracked ultrasound. HPB 2012, 14, 594–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pesi, B.; Moraldi, L.; Guerra, F.; Tofani, F.; Nerini, A.; Annecchiarico, M.; Coratti, A. Surgical and oncological outcomes after ultrasound-guided robotic liver resections for malignant tumor. Analysis of a prospective database. Int. J. Med Robot. Comput. Assist. Surg. 2019, 15, e2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fruscione, M.; Pickens, R.; Baker, E.H.; Cochran, A.; Khan, A.; Ocuin, L.; Iannitti, D.A.; Vrochides, D.; Martinie, J.B. Robotic-assisted versus laparoscopic major liver resection: Analysis of outcomes from a single center. HPB 2019, 21, 906–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwyer, R.H.; Scheidt, M.J.; Marshall, J.S.; Tsoraides, S.S. Safety and efficacy of synchronous robotic surgery for colorectal cancer with liver metastases. J. Robot Surg. 2018, 12, 603–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsung, A.; Geller, D.A.; Sukato, D.C.; Sabbaghian, S.; Tohme, S.; Steel, J.; Marsh, W.; Reddy, S.K.; Bartlett, D.L. Robotic Versus Laparoscopic Hepatectomy: A matched comparison. Ann. Surg. 2014, 259, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montalti, R.; Scuderi, V.; Patriti, A.; Vivarelli, M.; Troisi, R.I. Robotic versus laparoscopic resections of posterosuperior segments of the liver: A propensity score-matched comparison. Surg. Endosc. 2016, 30, 1004–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziogas, I.A.; Giannis, D.; Esagian, S.M.; Economopoulos, K.P.; Tohme, S.; Geller, D.A. Laparoscopic versus robotic major hepatectomy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Surg. Endosc. 2021, 35, 524–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimli, M.; Perrakis, A.; Schellerer, V.; Gumbs, A.; Lorenz, E.; Franz, M.; Arend, J.; Negrini, V.R.; Croner, R.S. Robotic and laparoscopic liver surgery for colorectal liver metastases: An experience from a German Academic Center. World J. Surg. Onc. 2020, 18, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daskalaki, D.; Gonzalez-Heredia, R.; Brown, M.; Bianco, F.M.; Tzvetanov, I.; Davis, M.; Kim, J.; Benedetti, E.; Giulianotti, P.C. Financial Impact of the Robotic Approach in Liver Surgery: A Comparative Study of Clinical Outcomes and Costs Between the Robotic and Open Technique in a Single Institution. J. Laparoendosc. Adv. Surg. Tech. 2017, 27, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanounou, T.; Steel, J.L.; Nguyen, K.T.; Tsung, A.; Marsh, J.W.; Geller, D.A.; Gamblin, T.C. Comparing the clinical and economic impact of laparoscopic versus open liver resection. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2010, 17, 998–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Berber, E.; Akyildiz, H.Y.; Aucejo, F.; Gunasekaran, G.; Chalikonda, S.; Fung, J. Robotic versus laparoscopic resection of liver tumours. HPB 2010, 12, 583–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| Article | Yue et al., 2018 | J. Shim et al., 2018 | A. Fretland et al., 2018 | T. Nomi et al., 2016 | S. Ferretii et al., 2015 | R. Montalti et al., 2014 | S. Schiffman et al., 2014 | B. Topal et. al. 2012 | H. Topal et al., 2012 | A. Hilal 2012 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type of study | Retrospective | Retrospective | Randomised control trial | Retrospective | Retrospective | Retrospective | Retrospective, case series | Retrospective | Prospective study | retrospective, single centre |
| No. of Cases | 241 | 22 | 129 | 120 | 142 | 114 | 242 | 81 | 20 | 83 |
| Age (years) | 67 (60–69) & 74 (70–78) NB: Two Age Groups | 65.6 | 67 | 61 | 66 | 66.4 | 60.8 | 64.3 | 57.6 | 66 (32–85) |
| Preoperative systemic chemotherapy | 187 | 21 | 77 | 71 | 25 | 78 | 128 | 55 | 15 | Not mentioned |
| Type of liver resection | 18 Major (Left lateral sectionectomy), 223 Minor (wedge/sectionectomy) | 2 Major, 20 Minor | Not mentioned | 83 Major cases | 39 Major cases, 103 Minor cases | 8 major cases, Postero-superior resections 52 (45.6%) | 104 major cases, 133 minor cases | 18 Major, 34 Minor | 20 Major | Major 27, Minor 56 |
| Tumour Size | 30 mm (10–50) & 20 mm (10–40) | 16 mm (6–101) | Not mentioned | 33 mm (5–170) | 28 mm (2–100) | 40.8 mm ± 2.9 | 31 mm | >50 mm—7 cases | 40 mm (4–70) | 25 mm (5–105) |
| No. of CRLM | 2 (1–4) | 1 (1–2) | 1.5 | 2 (1–8) | 1 (1–9) | 1.7 | 1.37 | 2 | 2 (1–6) | 1 lesion (54 cases), 2 lesions (21 cases), >3 lesions (8 cases) |
| CRLM | Not mentioned | 14 synchronous, 8 Metachronous | 77 Synchronous | 67 synchronous | 142 synchronous | 54 synchronous | Not mentioned | Metachronous 45, synchronous 36 | 3 synchronous resection | not mentioned |
| Duration of surgery (min) | 190 (150–290) & 180 (160–260) | 135 (40–360) | 123 (108–138) | 245 (60–540) | 120 (15–600) | 276 ± 10.1 | 248.7 | 120 (80–200) | 257.5 (75–360) | 220 min (40–540) |
| conversion rate (lap to open) | 8 cases | Not mentioned | 9 cases | 8 cases (6.7%) | 7 cases | 17 cases | Not mentioned | 6 cases | Not mentioned | 5 cases |
| estimated blood loss median (range) | 240 (160–410) & 260 (180–430) | 100 (30–950) | 300 (224–375) | 200 (0–3000) | 200 (0–1800) | 250 (0–2800) | 262.5 mL | 50 (10–300) | 550 (100–4000) | 300 (20–3000) |
| Pringle maneuver use | Not mentioned | 22 cases | Not mentioned | Yes performed, pringle time median range: 25 (8–75) | 17 cases | 12 (10.5%) | Not mentioned | Not mentioned | 4 cases | Yes performed for all cases |
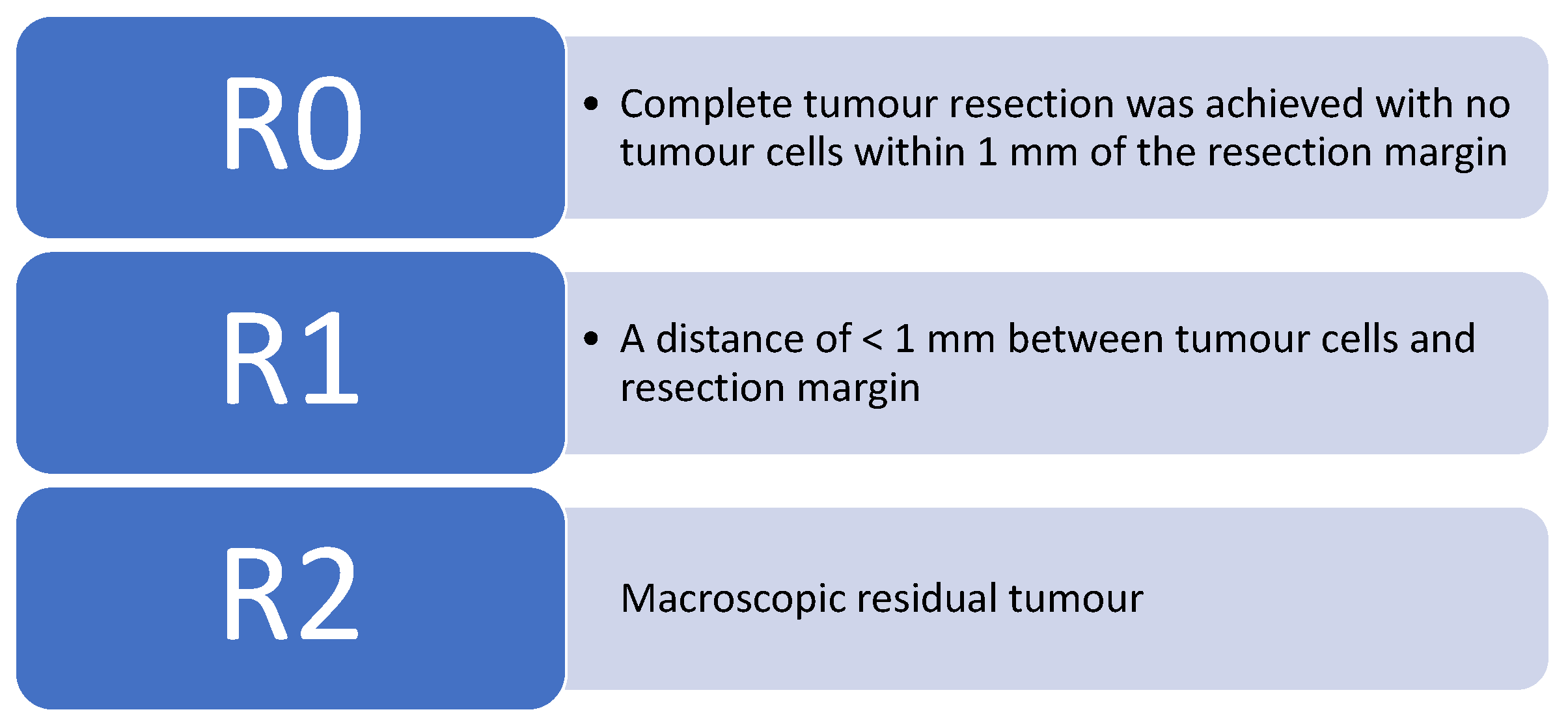
| Resection margin size, R1, etc. | (R0 = 241/R1 = 0/R2 = 0) | Not mentioned | <1 mm (29 cases), >1 mm (92 cases), involved (8 cases), missed (4 cases) | R0 resection = 113 cases (94.2%) | postive surgical margins = 10 cases | R1 < 1 mm = 14 cases, R0 = 100 cases | R1 Margin positivity 5.5 % = 12 Cases | Not mentioned | R1—1 Case, R0 = 19 Cases with median tumour free margin of 7.5 mm (0–20) | R0—80 Cases (97%) R1—3 cases |
| RO resection % per cases (LLR) | 240/240 | N/A | 121/129 | 113/120 | 132/142 | 100/114 | 230/242 | N/A | 19/20 | 80/83 |
| Length of hospital stay | 9 (7–23) & 10 (7–32) | 8.5 (5–22) | 2.3 days (1.8–3) | 7 (4–42) | 8 (3–84) | 6.0 days ± 0.28 | 6.5 days | 5 days (3–7) | 8 (5–51) | 5 (2–12) |
| readmission rate within 30 days | Not Mentioned | 0 | 13 cases | Not Mentioned | Not Mentioned | Not Mentioned | Not Mentioned | 0 | 0 cases | 0 |
| Re admission Operation rate within 30 days | Not Mentioned | 0 | 5 cases | Not Mentioned | 11 | 6 cases | Not Mentioned | 0 | 0 cases | Not specifically mentioned for CRLMs, however 5 cases returned to theatre |
| Complication % | 30 | 9 | 18 | 41 | 31 | 20 | 20 | 14 | 35 | 11 |
| No. of Complications | 73 cases, Not specified | 2 cases | 24 cases | 50 cases (39 liver specific), overall 21 of 50 cases were major complications | 44 cases, | 23 cases | 48 cases (12.8% Liver specific) | 11 cases | 7 cases | 9 major complications (11%) |
| Type of complication | major | |||||||||
| Clavien-Dindo system Grade (G1–5) | Not mentioned | Grade 1 (2 cases) | Not mentioned | G5 = 1 | G1 = 2, G2 = 14, G3 = 20, G4 = 5, G5 = 3 | Not mentioned | G5 = 1 | Not mentioned | Not mentioned | not mentioned |
| SSI | n/a | 0 | 7 | n/a | 0 | n/a | 0 | |||
| Bleeding | n/a | 0 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 10 | n/a | 2 | 1 | 5 |
| Liver abscess | n/a | 0 | 2 | n/a | 0 | n/a | n/a | 1 | 0 | 2 |
| Biliary Leakage | n/a | 0 | 1 | 20 | 6 | n/a | n/a | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| Liver insufficiency | n/a | 0 | 1 | 12 | 1 | n/a | n/a | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| DVC Sepsis | n/a | 0 | 0 | n/a | 0 | n/a | n/a | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| colorectal leaakge | n/a | 1 | 0 | n/a | 8 | n/a | n/a | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Pulmonary/Cardiac | n/a | 0 | 6 | 4 | 8 | n/a | n/a | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MOF (Perionitis) | n/a | 0 | 3 | 8 | 1 | n/a | n/a | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Death | n/a | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 | n/a | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 90-days mortality rate and Estimated DFS/OS | 2 cases = 1 case in the elderly group due to liver failure and 1 case in Middle age group due to metastasis to CNS. FU at 34 months in elderly group = 32 deaths (29 reoccurence of disease), Middle age group = 53 deaths (48 reoccurence) | 0 | Not mentioned | one case, study showed that OS and RFS were acceptable in patients with CRLMs (5 cm). Furthermore, multivariate analysis did not identify the tumor size as a prognostic factor | 3 deaths within 30 day mortalitiy Median FU of 29 (1–108 months), 40 patients developed tumour reoccurence | 66 (57.9 %) of the cases reoccurence of disease in 30 month follow up R1 margins were significantly related to lower RFS survival (p = 0.038) but did not affect OS. | 1 death—massive bleed from portal vein | Not mentioned | The estimated DFS and OS rates in the LMLR group at 1, 2, and 5 years were 60, 49, and 43 and 90, 80, and 48% respectively | 22 months FU 2 Year DFS/OS 64%/80% |
| Cost (might not be directly stated) | Not Mentioned | In conclusion, no significant differences in postoperative outcomes were observed between LSLR and OSLR except length of hospital stay, the number of liver metastasis, and the resection margin. | cost difference from open surgery is $94,000 | study suggests that LLR for large CRLMs can be performed safely with acceptable long-term outcomes in selected patients. Therefore, tumor size of CRLM should not interfere when selecting the surgical approach | Not Mentioned | Not Mentioned | Not Mentioned | Not mentioned | Not Mentioned | Overall, our data including a large proportion of major hepatectomies confirm the well-established advantages of laparoscopic liver surgery in terms of reduced high-dependency unit and postoperative length of stay. |
| Article | R. Beard et al., 2020 | S. Guadagni et al., 2019 | F. Guerra et al., 2018 | R. Dwyer et al., 2018 | A. Tsung et al., 2014 | Eric C.H. Lai et al., 2011 | P.C. Giulianotti et al., 2011 | L. Casciola et al., 2011 | E. Berber et al., 2010 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type of Study | retrospective multicentre | Retrospective | retrospective multicentre | retrospective single centre | Retrospective Single centre | Retrospective | retrospective, 2 different centers by a single surgeon. | Prospective series single study | retrospective single centre, 9 robotic cases (4 for CRLM) |
| No. of Patients | 115 | 20 robotic assisted | 59 (USS guided Robotic) | 6 | 21 | 6 Robtic assisted | 16 | 14 Robotic assited LHR | 4 |
| Age (years) | 61 | 66 | 64 | 59.3 | 58.4 | 68.2 | 57 | 66.4 | 68.6 |
| Preoperative systemic chemotherapy cases | 63 (54.8%) | 12 | 14 (17%) | 6 | Not mentioned | Not mentioned | not mentioned | not mentioned | not mentioned |
| Type of liver resection | 18 Minor, 97 Major | 20 Major, (3 simultaneous) | 39 major, 43 minor | 1 Major, 3 Minor, 1 ablation (large segement 7 near vascular structures), 1 no identifiable lesion | 16 minor, 4 major | 6 Major (3 wedge resections, 3 left lateral sectionectomy) | 4 minor (<3 segments) and 12 major resections | 14 minor resections, 11 simultaneous procedues | 4 minor (peripheral segments) |
| Tumour Size | 25 mm (3 mm–122 mm) | 30 mm ± (18) | 27 mm (4–130) | Not mentioned | Minor—31 mm (20–55), Major—37 mm (24.5–50 mm) | 33 mm ± (16) | 47 mm (range, 12–110) | not mentioned | 32 ± 13 mm |
| No. of Metastasis median (range) | 1 metastasis = 78 (67.8%), 2 metastasis = 24 (20.9%), >3 metastasis = 13 (11.3%) | 2 (2–4) | 27 patients had multiple leisons | 2 | 1 (1–2) | Not mentioned | not mentioned | not mentioned | not mentioned |
| CRLM | 49 synchronous cases | 6 synchronous cases | 16 synchronous | 6 (Liver first approach) | not mentioned | 9 metachronous, 5 synchronous | not mentioned | 3 metachronous, 11 synchronous | not mentioned |
| Duration of surgery (min) | 272 ± 115 | 198.5 ± (98) | 210 min (50–600) | 401 (349–506) | 253 min (180–355) | 190.2 ± 91.6 | 270 min (range, 90–660) | 280 ± 115 min, | 258.5 ± 27.9 min |
| Conversion rate (robotic to open) | 6 (5.2%) | 0 | 7 cases (12%) | 0 | 4 cases | 0 | 4 cases | 1 case | 1 case |
| estimated blood loss median (range) | Not mentioned | 250 (200–300) | 200ml (0–1500) | 316 (150–1000) | 200 (50–337.5) | 75 (20–200) | 262 mL (range, 20–2000) | 245 ± 254 (0–1000) | 136 ± 61 mL |
| Pringle maneuver use | Used at the discretion of the surgeon | Not mentioned | 18 cases (30%) during parenchymal transection | Not mentioned | not mentioned | 3 cases, Mean time 46.7 min | 0 | 12 cases, mean clamp time 68.9 ± 31.7 | not mentioned |
| Resection margin size, R1, etc. | R0 = 84 (73.7%), R1 = 19 (16.7%) | R0—20 cases (100%) | R0 resection—54 cases (92%), R1—5 cases | R0 resection—100% | R0 negative margin—95 % of cases | RO—5 cases, R1—1 case | mean surgical resection margin 25 mm (range, 5–70). | not mentioned | resection margin 11 mm, Resectionmargins were negative for a tumour at the time of resection. |
| No. of R0 resection per cases | 84/115 | 20/20 | 27/29 | 6/6 | 20/21 | 5/6 | n/a | n/a | 4/4 |
| Length of hospital stay | 5 (3–6) | 4.7 ± 1.8 day | 6.7 ± 6.2 days | 4.5 (3–10) | 4.0 (3.0–5.5) | 6.8 mean day ± 2.8 | 7 days median (2–26) | 6.8 ± 2.8 days, NB for synchronous CRLM it was 9 ± 2.6 days | not mentioned |
| readmission rate within 30 days | 8 (7.0%) | 0 | Not mentioned | 0 | 0 | 0 | not mentioned | 0 | 0 |
| Re admission Operation rate within 30 days | 1 (0.9%) | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | not mentioned | 1 | not mentioned |
| Complication % | 10.4 | 25 | 27 | 67 | 52 | 16 | not mentioned | 28 | 11 |
| No. of Complications | 12 | 5 cases | 16 cases (27%) | 4 Cases | 11 cases | 1 case | not mentioned | 4 cases | 11% of the robotic (mixed result) |
| Type of complication (Claven-Dindo) Grade (G1–5) | G3 = 12 cases | G1—1 case, G2—4 cases | G1–2 (13 cases, 22%), G3–4 (3 cases 5%) | Not mentioned | G3–4—one case | G2 (1 case) | unable to distinguish complications from other cases (heterogenous data) | 4 cases, unable to distinguish complications from other cases (heterogenous data) | unable to distinguish complications from other cases (heterogenous data) |
| SSI | n/a | n/a | n/a | 1 | n/a | 0 | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| Bleeding | 3 | n/a | 3 | 0 | n/a | 0 | n/a | 2 | 1 |
| Liver/Intraabdominal abscess/collection | 7 | n/a | n/a | 2 pelvic | n/a | 0 | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| Biliary Leakage | n/a | n/a | 1 | 0 | n/a | 1 | n/a | 1 | n/a |
| Liver insufficiency | n/a | n/a | n/a | 0 | n/a | 0 | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| DVC Sepsis | n/a | n/a | n/a | 0 | n/a | 0 | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| colorectal leaakge | n/a | n/a | n/a | 1 | n/a | 0 | n/a | 1 | n/a |
| Pulmonary/Cardiac | n/a | n/a | 2 | 0 | n/a | 0 | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| MOF (Perionitis) | n/a | n/a | n/a | 0 | n/a | 0 | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| Death | 1 | n/a | 0 | 0 | n/a | 0 | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| Other | 5 | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | |
| 90-days mortality rate and Estimated DFS/OS | 60 patients (52.2%) had recurrence of their metastatic colorectal cancer following liver resection | FU 22.5 Months, 0 cases of local recurrence 1 Year DFS—89.5%, 3 Year DFS—35.8% | FU 19.5 months—9 disease deaths, 16 cases recurrent disease 1 Year DFS/OS 83.5%/90.4%, 3 Year DFS/OS 41.9%/66.1% | 0 Not mentioned | 0 NB: Unable to extract true data of CRLM from robotic arm (heterogenous data) | 0 1 Year DFS/OS 85%/96%, 3 Year DFS/OS 47%/67% | 0 NB: Unable to extract true data of CRLM from robotic arm (heterogenous data) | FU 25.1 ± 11.7 months, two deaths—reoccurence of disease NB: Unable to extract true data of CRLM from robotic arm (heterogenous data) | 0 Not mentioned |
| Cost (might not be directly stated) | accurate data on cost that would allow for a comparison between the RLR and LLR groups are not available. | In our experience, RAS for CRLM surgical treatment was feasible and played a positive role even in patients with multiple metastases and previous or synchronous surgery. RAS seemed to be oncologically effective in this setting, as no patients experienced local relapse in the treated area. | Robotic surgery as a valid option to resect CRLMs competently in terms of both surgical and oncological outcomes. | All were performed without the need for conversion, thus supporting efficacy. The role of robotic surgery in the management | Although a greater proportion of robotic cases were completed in a totally minimally invasive manner, there were no significant benefits over laparoscopic techniques in operative outcomes. | The main drawback of advanced robotic surgery is the associated cost. At the current stage of development, the benefits of robot-assisted surgery in liver surgery have not yet been defined. | This preliminary experience shows that robotic surgery can be used safely for liver resections with a limited conversion rate, blood loss, and postoperative morbidity. | Finally, results of this series show that robot-assisted LHR is safe and feasible and provide considerable evidence that robotics could overcome limitations of traditional LHR associated with tumor location, supporting robot use only for complex resections. | The additional cost incurred by the robot is a concern when justifying its use. Although a case-by-case cost analysis was not done, the robotic instrumentation in general adds $500 per case to the laparoscopic equipment cost. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Merali, N.; Ashraf, H.; Chouari, T.; Araimi, B.A.; Lahiri, R.; Rockall, T.A.; Frampton, A.E. Systematic Review Comparing the Effectiveness of Robotic verse Laparoscopic Liver Surgery in Colorectal Liver Metastasis (CRLM). Surgeries 2021, 2, 357-370. https://doi.org/10.3390/surgeries2040035
Merali N, Ashraf H, Chouari T, Araimi BA, Lahiri R, Rockall TA, Frampton AE. Systematic Review Comparing the Effectiveness of Robotic verse Laparoscopic Liver Surgery in Colorectal Liver Metastasis (CRLM). Surgeries. 2021; 2(4):357-370. https://doi.org/10.3390/surgeries2040035
Chicago/Turabian StyleMerali, Nabeel, Hajra Ashraf, Tarak Chouari, Badriya Al Araimi, Rajiv Lahiri, Timothy A. Rockall, and Adam E. Frampton. 2021. "Systematic Review Comparing the Effectiveness of Robotic verse Laparoscopic Liver Surgery in Colorectal Liver Metastasis (CRLM)" Surgeries 2, no. 4: 357-370. https://doi.org/10.3390/surgeries2040035
APA StyleMerali, N., Ashraf, H., Chouari, T., Araimi, B. A., Lahiri, R., Rockall, T. A., & Frampton, A. E. (2021). Systematic Review Comparing the Effectiveness of Robotic verse Laparoscopic Liver Surgery in Colorectal Liver Metastasis (CRLM). Surgeries, 2(4), 357-370. https://doi.org/10.3390/surgeries2040035






