Beta-Diversity Enhancement by Archaeological Structures: Bacterial Communities of an Historical Tannery Area of the City of Jena (Germany) Reflect the Ancient Human Impact
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedures
2.1. Soil Samples
2.2. Isolation of DNA and PCR Processes
2.3. Conversion and Analysis of Sequence Data
3. Results and Discussions
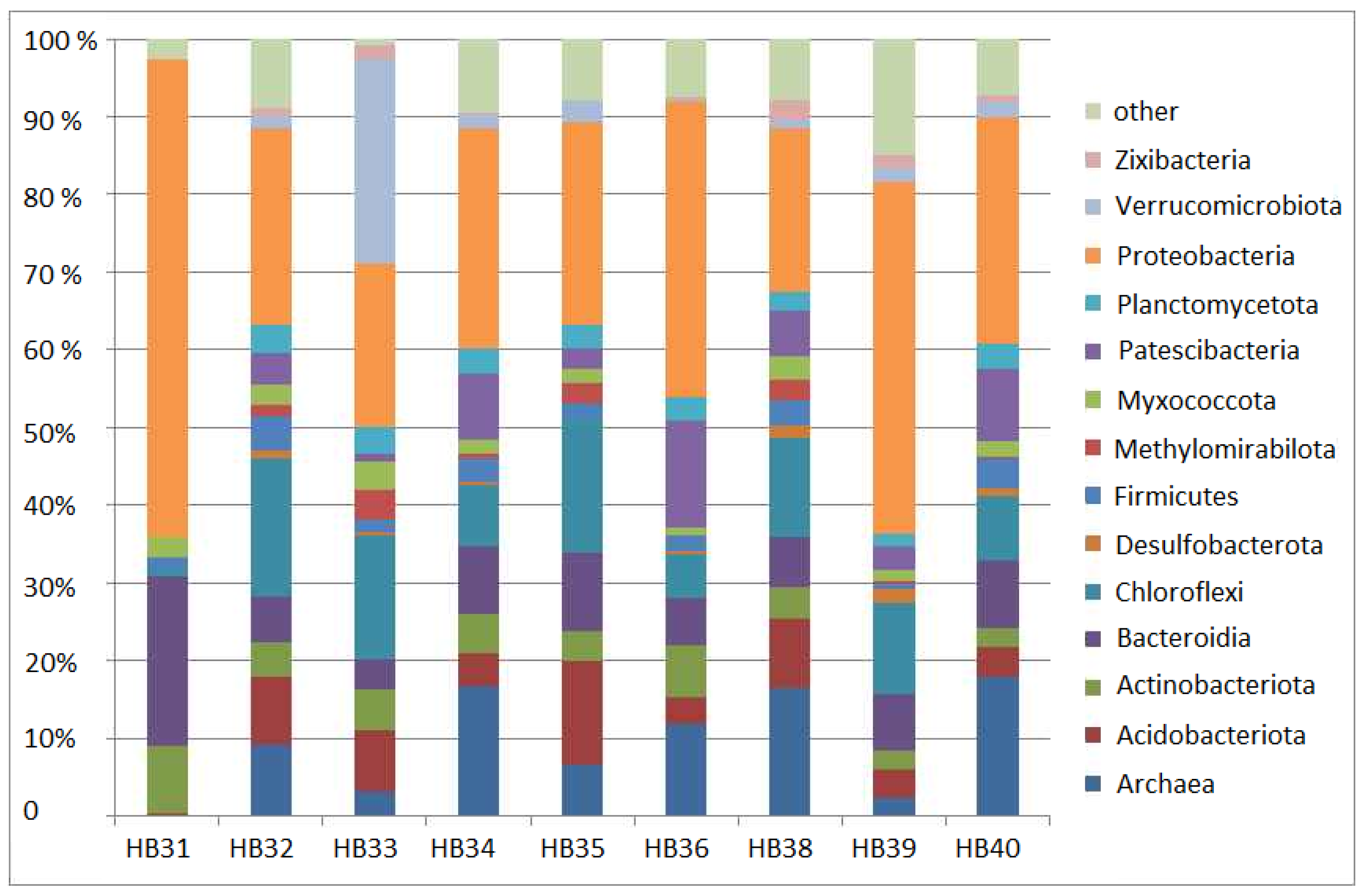
3.1. General Comparison of Soil Bacterial Communities at the Phylum Level
3.2. Comparison of Soil Sample Communities on the OTU Level
3.3. Comparison by Dominating OTUs
3.4. Specificity of Sampling Sites
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hedrich, S.; Schippers, A. Metallgewinnung mittels Geobiotechnologie. Chem. Ing. Tech. 2017, 89, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thavamani, P.; Samkumar, R.A.; Sathees, V.; Subashchandrabose, S.R.; Ramadass, K.; Naidu, R.; Venkateswarlu, K.; Megharaj, M. Microbes from mined sites: Harnessing their potential for reclamation of derelicted mine sites. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 230, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barns, S.M.; Cain, E.C.; Sommerville, L.; Kuske, C.R. Acidobacteria phylum sequences in uranium-contaminated subsurface sediments greatly expand the known diversity within the phylum. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 3113–3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margesin, R.; Siles, J.A.; Cajthaml, T.; Ohlinger, B.; Kistler, E. Microbiology meets archaeology: Soil microbial communities reveal different human activities at archaic Monte Iato (Sixth century BC). Microbial Ecol. 2017, 73, 925–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köhler, J.M.; Kalensee, F.; Günther, P.M.; Schüler, T.; Cao, J. The local ecological memory of soil: Majority and minority components of bacterial communities in prehistoric urns from Schöps (Germany). Int. J. Environ. Res. 2018, 12, 575–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhler, J.M.; Beetz, N.; Günther, P.M.; Möller, F.; Schüler, T.; Cao, J. Microbial community types and signature-like soil bacterial patterns from fortified prehistoric hills of Thuringia (Germany). Community Ecol. 2020, 21, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernysheva, E.; Korobov, D.; Borisov, A. Thermophilic microorganisms in arable land around medieval archaeological sites in Northern Caucasus, Russia: Novel evidence of past manuring practices. Geoarchaeology Int. J. 2017, 32, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, S.E.; Lennon, J.T. Dormancy contributes to the maintenance of microbial diversity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 5881–5886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhler, J.M.; Kalensee, F.; Cao, J.; Günther, P.M. Hadesarchaea and other extremophile bacteria from ancient mining areas of the East Harz region (Germany) suggest an ecological long-term memory of soil. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glockner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klindworth, A.; Pruesse, E.; Schwee, T.; Peplies, J.; Quast, C.; Horn, M.; Glockner, F.O. Evaluation of general 16S ribosomal RNA gene PCR primers for classical and next-generation sequenc-ing-based diversity studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, P.; Parfrey, L.-W.; Yarza, P.; Gerken, J.; Pruesse, E.; Quast, C.; Schweer, T.; Peplies, J.; Ludwig, W.; Glockner, F.O. The SILVA and “All-species Living Tree Project (LTP)” taxonomic frameworks. Nucleic Acid Res. 2014, 42, D643–D648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.W.; Han, J.G.; Wu, H.B.; Zhong, Q.C.; Liu, W.; He, S.W.; Zhang, L. Diversity patterns and drivers of soil microbial communities in urban and suburban park soils of Shanghai, China. PeerJ 2021, 9, 11231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrhardt, L.; Köhler, J.M. Three soil bacterial communities from an archaeological excavation site of an ancient coal mine near Bennstedt (Germany) characterized by 16S r-RNA sequencing. Environments 2022, 9, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janvier, M.; Frehel, C.; Grimont, F.; Gasser, F. Methylophaga marina gen. nov., sp. nov. and Methylophaga thalassica sp. nov., Marine Methylotrophs. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1985, 35, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, S.H.; Lee, D.S.; Park, M.; Wang, Q.; Jang, H.H.; Park, W.; Jeon, C.O. Caenimonas koreensis gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from activated sludge. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2008, 58, 1064–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, M.W.; Kasalický, V.; Jezbera, J.; Brandt, U.; Jezberová, J.; Šimek, K. Limnohabitans curvus gen. nov., sp. nov., a planktonic bacterium isolated from a freshwater lake. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2010, 60, 1358–1365. [Google Scholar]
- Bowman, J.P.; Nichols, C.M.; Gibson, J.A.E. Algoriphagus ratkowskyi gen. nov., sp. nov., Brumimicrobium glaciale gen. nov., sp. nov., Cryomorpha ignava gen. nov., sp. nov. and Crocinitomix catalasitica gen. nov., sp. nov., novel flavobacteria isolated from various polar habitats. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2003, 53, 1343–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heulin, T.; Barakat, M.; Christen, R.; Lesourd, M.; Sutra, L.; De Luca, G.; Achouak, W. Ramlibacter tataouinensis gen. nov., sp. nov., and Ramlibacter henchirensis sp. nov., cyst-producing bacteria isolated from subdesert soil in Tunisia. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2003, 53, 589–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, H.; Shinohara, A.; Fukui, M. Sulfurifustis variabilis gen. nov., sp. nov., a sulfur oxidizer isolated from a lake, and proposal of Acidiferrobacteraceae fam. nov. and Acidiferrobacterales ord. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2015, 65, 3709–3713. [Google Scholar]
- Emerson, D.; Rentz, J.A.; Lilburn, T.G.; Davis, R.E.; Aldrich, H.; Chan, C.; Moyer, C.L. A Novel Lineage of Proteobacteria Involved in Formation of Marine Fe-Oxidizing Microbial Mat Communities. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yee, B.; Oertli, G.E.; Fuerst, J.A.; Staley, J.E. Reclassification of the polyphyletic genus Prosthecomicrobium to form two novel genera, Vasilyevaea gen. nov. and Bauldia gen. nov. with four new combinations: Vasilyevaea enhydra comb. nov., Vasilyevaea mishustinii comb. nov., Bauldia consociata comb. nov. and Bauldia litoralis comb. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2010, 60, 2960–2966. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jung, M.-Y.; Islam, M.A.; Gwak, J.-H.; Kim, J.G.; Rhee, S.K. Nitrosarchaeum koreense gen. nov., sp. nov., an aerobic and mesophilic, ammonia-oxidizing archaeon member of the phylum Thaumarchaeota isolated from agricultural soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2018, 68, 3084–3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorokin, T.Y.; Lysenko, A.M.; Mityushina, L.L.; Tourova, T.P.; Jones, B.E.; Rainey, F.A.; Robertson, L.A.; Kuenen, G.J. Thioalkalimicrobium aerophilum gen. nov., sp. nov. and Thioalkalimicrobium sibericum sp. nov., and Thioalkalivibrio versutus gen. nov., sp. nov., Thioalkalivibrio nitratis sp.nov., novel and Thioalkalivibrio denitrificancs sp. nov., novel obligately alkaliphilic and obligately chemolithoautotrophic sulfur-oxidizing bacteria from soda lakes. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2001, 51, 565–580. [Google Scholar]
- Kuenen, J.G.; Veldkamp, H. Thiomicrospira pelophila, gen. n., sp. n., a new obligately chemolithotrophic colourless sulfur bacterium. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 1972, 38, 241–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miroshnichenko, M.L.; Kostrikina, N.A.; Chernyh, N.A.; Pimenov, N.V.; Tourova, T.P.; Antipov, A.N.; Spring, S.; Stackebrandt, E.; Bonch-Osmolovskaya, E.A. Caldithrix abyssi gen. nov., sp. nov., a nitrate-reducing, thermophilic, anaerobic bacterium isolated from a Mid-Atlantic Ridge hydrothermal vent, represents a novel bacterial lineage. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2003, 53, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, L.; Zhu, F.; Hong, X.; Gao, W.; Chen, J.; Sun, X. Sunxiuqinia elliptica gen. nov., sp. nov., a member of the phylum Bacteroidetes isolated from sediment in a sea cucumber farm. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2011, 61, 2885–2889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.-H.; Kang, S.-Y.; Schumann, P.; Oh, T.K. Yonghaparkia alkaliphila gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel member of the family Microbacteriaceae isolated from an alkaline soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2006, 56, 2415–2420. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.-F.; Liu, Y.L.; Dong, J.D.; Qu, L.Y.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Wang, F.-Z.; Tian, X.P.; Zhang, S. Mangrovibacterium diazotrophicum gen. nov., sp. nov., a nitrogen-fixing bacterium isolated from a mangrove sediment, and proposal of Prolixibacteraceae fam. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2014, 64, 875–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandecandelaere, I.; Nercessian, O.; Segaert, E.; Achouak, W.; Mollica, A.; Faimali, M.; De Vos, P.; Vandamme, P. Alteromonas genovensis sp. nov., isolated from a marine electroactive biofilm and emended description of Alteromonas macleodii. Baumann et al. 1972 (Approved Lists 1980). Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 1972, 58, 2589–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.; Schumann, P.; Chun, J. Demequina aestuarii gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel actinomycete of the suborder Micrococcineae, and reclassification of Cellulomonas fermentans Bagnara et al. 1985 as Actinotalea fermentans gen. nov., comb. Nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2007, 57, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.D. Labedella gwakjiensis gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel actinomycete of the family Microbacteriaceae. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2007, 57, 2498–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asker, D.; Beppu, T.; Ueda, K. Zeaxanthinibacter enoshimensis gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel zeaxanthin-producing marine bacterium of the family Flavobacteriaceae, isolated from seawater off Enoshima Island. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2007, 57, 837–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankratov, T.A.; Tindall, B.J.; Liesack, W.; Dedysh, S.N. Mucilaginibacter paludis gen. nov., sp. nov. and Mucilaginibacter gracilis sp. nov., pectin-, xylan- and laminarin-degrading members of the family Sphingobacteriaceae from acidic Sphagnum peat bog. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2007, 57, 2349–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irgens, R.L. Meniscus, a New Genus of Aerotolerant, Gas-Vacuolated Bacteria. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 1977, 27, 62829204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Niu, L.; Zhang, Y. Saccharofermentans acetigenes gen. nov., sp. nov., an anaerobic bacterium isolated from sludge treating brewery wastewater. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2010, 60, 2735–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.-L.; Xie, B.S.; Cai, M.; Tang, Y.-Q.; Wang, Y.-N.; Cui, H.-L.; Liu, X.-Y.; Tan, Y.; Wu, X.-L. Halodurantibacterium flavum gen. nov., sp. nov., a non-phototrophic bacterium isolated from an oil production mixture. Curr. Microbiol. 2015, 70, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanenko, L.A.; Tanaka, N.; Frolova, G.M.; Mikhailov, V.V. Arenicella xantha gen. nov., sp. nov., a gammaproteobacterium isolated from a marine sandy sediment. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2010, 60, 1832–1836. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, J.-M.; Jeon, C.O.; Lee, G.S.; Park, D.-J.; Kang, U.-G.; Park, C.-Y.; Kim, C.J. Leeia oryzae gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from a rice field in Korea. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2007, 57, 1204–1208. [Google Scholar]
- Hosoya, S.; Arunpairojana, V.; Suwannachart, C.; Kanjana-Opas, A.; Yokota, A. Aureispira marina gen. nov., sp. nov., a gliding, arachidonic acid-containing bacterium isolated from the southern coastline of Thailand. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2006, 56, 2931–2935. [Google Scholar]
- Higasjioka, Y.; Kojima, H.; Watanabe, M.; Fukui, M. Desulfatitalea tepidiphila gen. nov., sp. nov., a sulfate-reducing bacterium isolated from tidal flat sediment. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2013, 63, 761–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kojima, H.; Fukui, M. Sulfuriflexus mobilis gen. nov., sp. nov., a sulfur-oxidizing bacterium isolated from a brackish lake sediment. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 3515–3518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moe, W.M.; Yan, J.; Nobre, M.F.; DaCosta, M.S.; Rainey, F.A. Dehalogenimonas lykanthroporepellens gen. nov., sp. nov., a reductively dehalogenating bacterium isolated from chlorinated solvent-contaminated groundwater. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2009, 59, 2692–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.-H.; Kim, J.-G.; Jung, M.-Y.; Kim, S.J.; Gwak, J.-H.; Yu, W.-J.; Roh, S.W.; Kim, Y.H.; Rhee, S.-K. Ketobacter alkanivorans gen. nov., sp. nov., an n-alkane-degrading bacterium isolated from seawater. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2018, 68, 2258–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hania, W.B.; Joseph, M.; Schumann, P.; Bunk, B.; Fiebig, A.; Spröer, C.; Klenk, H.P.; Fardeau, M.-L.; Spring, S. Complete genome sequence and description of Salinispira pacifica gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel spirochaete isolated form a hypersaline microbial mat. Stand. Genom. Sci. 2015, 10, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorokin, D.Y.; Tourova, T.P.; Bezsoudnova, E.Y.; Pol, A.; Muyzer, G. Denitrification in a binary culture and thiocyanate metabolism in Thiohalophilus thiocyanoxidans gen. nov. sp. nov.—A moderately halophilic chemolithoautotrophic sulfur-oxidizing Gammaproteobacterium from hypersaline lakes. Arch. Microbiol. 2007, 187, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, S.; Waidner, B.; Itoh, T.; Schumann, P.; Spring, S.; Gescher, J. Metallibacterium scheffleri gen. nov., sp. nov., an alkalinizing gammaproteobacterium isolated from an acidic biofilm. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2013, 63, 1499–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, S.; Imachi, H.; Handa, S.; Ohashi, A.; Harada, H.; Kamagata, Y. Methanocella paludicola gen. nov., sp. nov., a methane-producing archaeon, the first isolate of the lineage ‘Rice Cluster I’, and proposal of the new archaeal order Methanocellales ord. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2008, 58, 929–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shieh, W.Y.; Jean, W.D. Alterococcus agarolyticus, gen.nov., sp.nov., a halophilic thermophilic bacterium capable of agar degradation. Can. J. Microbiol. 1998, 44, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M.; Kojima, H.; Fukui. M. Proposal of Effusibacillus lacus gen. nov., sp. nov., and reclassification of Alicyclobacillus pohliae as Effusibacillus pohliae comb. nov. and Alicyclobacillus consociatus as Effusibacillus consociatus comb. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2014, 64, 2770–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monciardini, P.; Cavaletti, L.; Rhangetti, A.; Schumann, P.; Rohde, M.; Bamonte, R.; Sosio, M.; Mezzelani, A.; Donadio, S. Novel members of the family Micromonosporaceae, Rugosimonospora acidiphila gen. nov., sp. nov. and Rugosimonospora africana sp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2009, 59, 2752–2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losey, N.A.; Stevenson, B.S.; Verbarg, S.; Rudd, S.; Moore, E.R.B.; Lawson, P.A. Fontimonas thermophila gen. nov., sp. nov., a moderately thermophilic bacterium isolated from a freshwater hot spring, and proposal of Solimonadaceae fam. nov. to replace Sinobacteraceae Zhou et al. 2008. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2013, 63, 254–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yordy, J.R.; Weaver, T.L. Methylobacillus: A new Genus of Obligately Methylotrophic Bacteria. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 1977, 27, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashefi, K.; Holmes, D.E.; Baross, J.A.; Lovely, D.R. Thermophily in the Geobacteraceae: Geothermobacter ehrlichii gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel thermophilic member of the Geobacteraceae from the “Bag City” hydrothermal vent. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 2985–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusube, M.; Sugihara, A.; Moriwaki, Y.; Ueoka, T.; Shimane, Y.; Minegishi, H. Alicyclobacillus cellulosilyticus sp. nov., a thermophilic, cellulolytic bacterium isolated from steamed Japanese cedar chips from a lumbermill. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2014, 64, 2257–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maaroufi, A.; Fardeau, M.-L.; BenAliGam, Z.; Cayol, J.-L.; Hamed, S.-B.; Labat, M. Anaerosalibacter bizertensis gen. nov., sp. nov., a halotolerant bacterium isolated from sludge. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2012, 62, 2469–2474. [Google Scholar]
- DeMeyer, S.E.; Coorevits, A.; Willems, A. Tardiphaga robiniae gen. nov., sp. nov., a new genus in the family Bradyrhizobiaceae isolated from Robinia pseudoacacia in Flanders (Belgium). Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 35, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.-H.; Yuan, H.-L.; Yang, J.-S.; Li, H.F.; Chen, N. Lacibacter cauensis gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel member of the phylum Bacteroidetes isolated from sediment of a eutrophic lake. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2009, 59, 1153–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inagaki, F.; Hideki, K.T.; Kobayashi, H.; Nealson, K.H.; Horikoshi, K. Sulfurimonas autotrophica gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel sulfur-oxidizing epsilon-proteobacterium isolated from hydrothermal sediments in the Mid-Okinawa Trough. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2003, 53, 1801–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, T.D.; Lawson, P.A.; Collins, M.D.; Falsen, E.; Tanner, R.S. Cloacibacterium normanense gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel bacterium in the family Flavobacteriaceae isolated from municipal wastewater. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2006, 56, 1311–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulichevskaya, I.S.; Ivanova, A.O.; Belova, S.E.; Baulina, O.I.; Baudelier, P.L.E.; Ripstra, W.I.C.; Damsté, J.S.S.; Zavarsin, G.A.; Dedysh, S.N. Schlesneria paludicola gen. nov., sp. nov., the first acidophilic member of the order Planctomycetales, from Sphagnum-dominated boreal wetland. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2007, 57, 2680–2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koops, H.-P.; Böttcher, B.; Möller, U.C.; Pommerening-Röser, A.; Stehr, G. Classification of eight new species of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria: Nitrosomonas communis sp. nov., Nitrosomonas ureae sp. nov., Nitrosomonas aestuarii sp. nov., Nitrosomonas marina sp. nov., Nitrosomonas nitrosa sp. nov., Nitrosomonas eutropha sp. nov., Nitrosomonas oligotropha sp. nov. and Nitrosomonas halophila sp. nov. J. General Microbiol. 1991, 137, 1689–1699. [Google Scholar]
- Köhler, J.M.; Ehrhardt, L.; Günther, P.M. Archaeal and Extremophilic Bacteria from Different Archaeological Excavation Sites. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araujo, A.S.F.; DePereira, A.P.D.; Antunes, J.E.L.; Oliveira, L.M.D.; DeMelo, W.J.; Rocha, S.M.B.; DoAmorim, M.R.; Ataujo, F.F.; Melo, V.M.M.; Mendes, L.W. Dynamics of bacterial and archaeal communities along composting of tannery sludge. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 64295–64306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, A.R.L.; Mendes, L.W.; Lemons, L.N.; Antunes, J.E.L.; Amorim, M.R.; Melo, V.M.M.; DeMelo, W.J.; VandenBrink, P.J.; Araujo, A.S. dynamics of archaeal community in soil with application of composted tannery sludge. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, A.S.F.; Lima, L.M.; Santos, V.M.; Schmidt, R. Repeated application of composted tannery sludge affects differently soil microbial biomass, enzymes activity, and ammonia-oxidizing organisms. Environ. Sci. Poll. Res. 2016, 23, 19193–19200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Feature/Area | Archaeological Situation | Sample | Coordinates | pH Values |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 58/V | Inside Vat | HB31 | 682091.3/5645202.8 | 7.41 |
| 58/Vref | Outside Vat | HB32-1, HB32-2 | 682091.3/5645202.8 | 8.09 |
| 60/V | Inside Vat | HB33 | 682088.5/5645201.9 | 7.71 |
| 60/Vref | Outside Vat | HB34-1, HB34-2 | 682088.5/5645201.9 | 8.37 |
| 61/V | Inside Vat | HB35-1, HB35-2 | 682087.5/5654201.3 | 8.1 |
| 61/Vref | Outside Vat | HB36-1, HB36-2 | 682087.5/5654201.3 | 8.29 |
| 70/Vref | Outside Vat | HB38-1, HB38-2 | 682088.4/5645197.8 | 8.6 |
| 57/V | Inside Vat | HB39-1, HB39-2 | 682088.4/5645197.8 | 7.65 |
| 57/Vref | Outside Vat | HB40-1, HB40-2 | 682092.0/5645192.7 | 8.18 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Köhler, J.M.; Ehrhardt, L.; Cao, J.; Möller, F.; Schüler, T.; Günther, P.M. Beta-Diversity Enhancement by Archaeological Structures: Bacterial Communities of an Historical Tannery Area of the City of Jena (Germany) Reflect the Ancient Human Impact. Ecologies 2023, 4, 325-343. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecologies4020021
Köhler JM, Ehrhardt L, Cao J, Möller F, Schüler T, Günther PM. Beta-Diversity Enhancement by Archaeological Structures: Bacterial Communities of an Historical Tannery Area of the City of Jena (Germany) Reflect the Ancient Human Impact. Ecologies. 2023; 4(2):325-343. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecologies4020021
Chicago/Turabian StyleKöhler, Johann Michael, Linda Ehrhardt, Jialan Cao, Frances Möller, Tim Schüler, and Peter Mike Günther. 2023. "Beta-Diversity Enhancement by Archaeological Structures: Bacterial Communities of an Historical Tannery Area of the City of Jena (Germany) Reflect the Ancient Human Impact" Ecologies 4, no. 2: 325-343. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecologies4020021
APA StyleKöhler, J. M., Ehrhardt, L., Cao, J., Möller, F., Schüler, T., & Günther, P. M. (2023). Beta-Diversity Enhancement by Archaeological Structures: Bacterial Communities of an Historical Tannery Area of the City of Jena (Germany) Reflect the Ancient Human Impact. Ecologies, 4(2), 325-343. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecologies4020021







