New Approaches in Electroanalytical Determination of Triazines-Based Pesticides in Natural Waters
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Instrumentation and Reagents
2.2. Electrochemical Cell
2.3. Experimental and Voltammetric Optimization
2.4. Analytical Parameters
2.5. Application of the Proposed Methodology
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of DAE
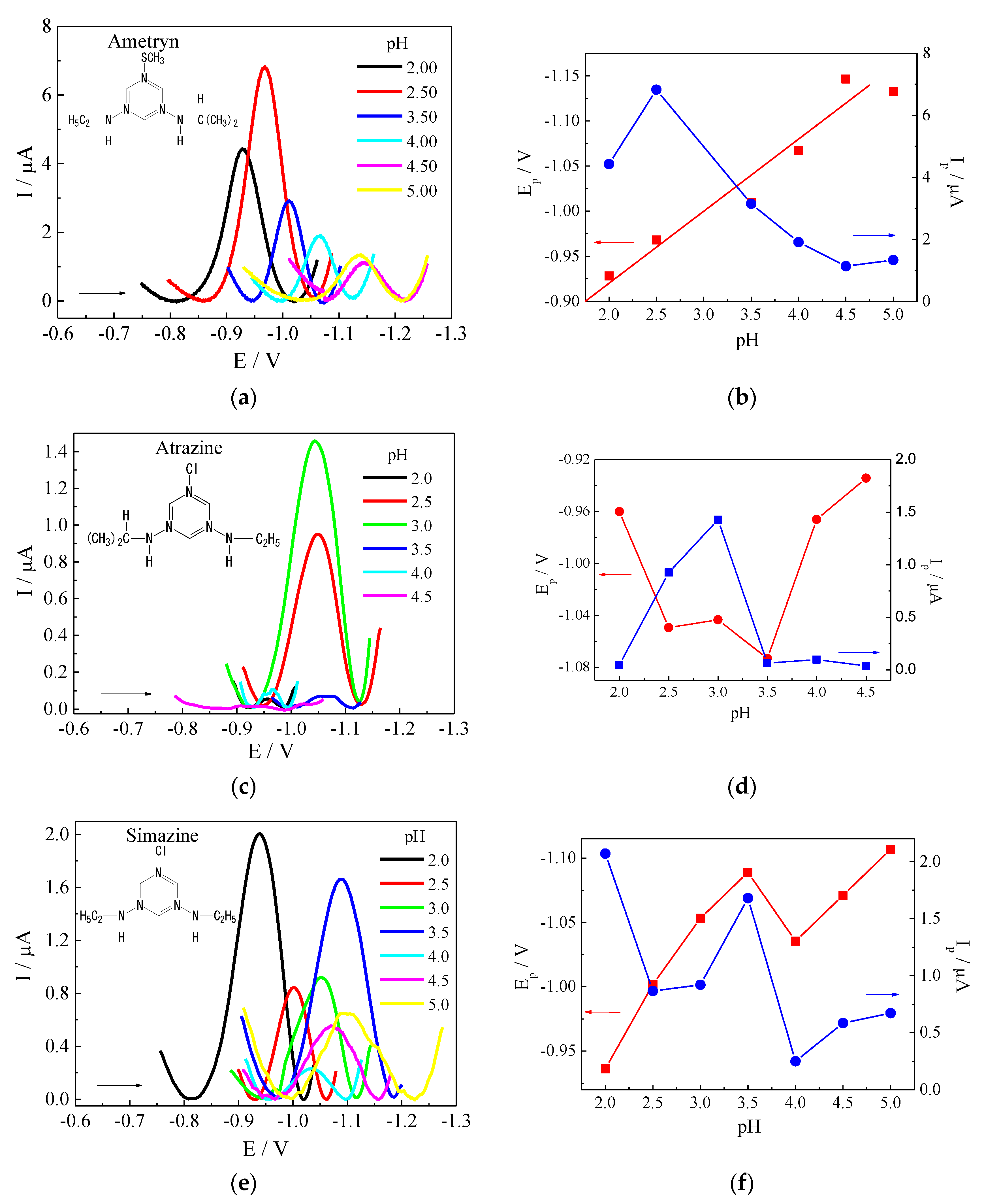
3.2. Experimental Optimization
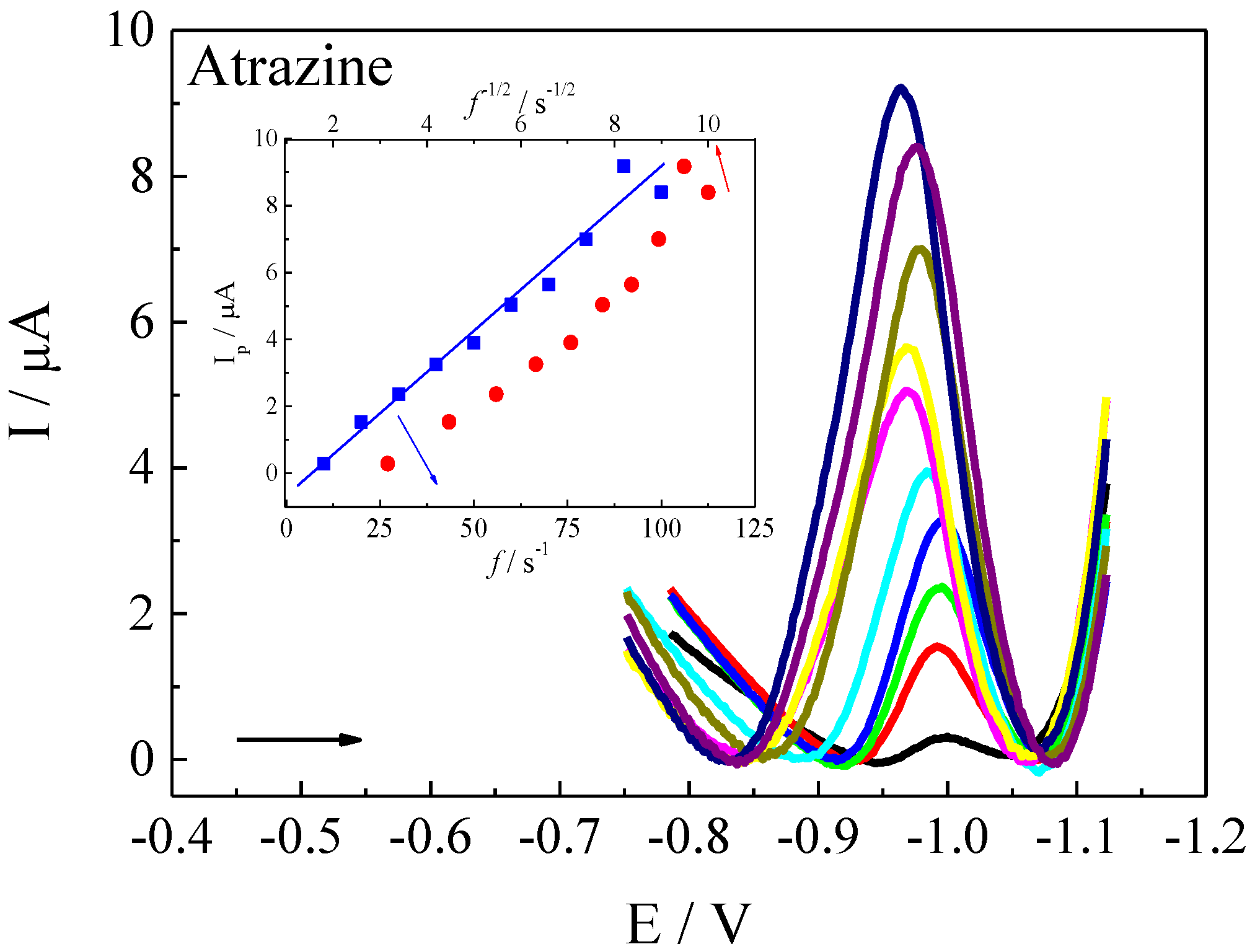
3.3. Voltammetric Parameters Optimization
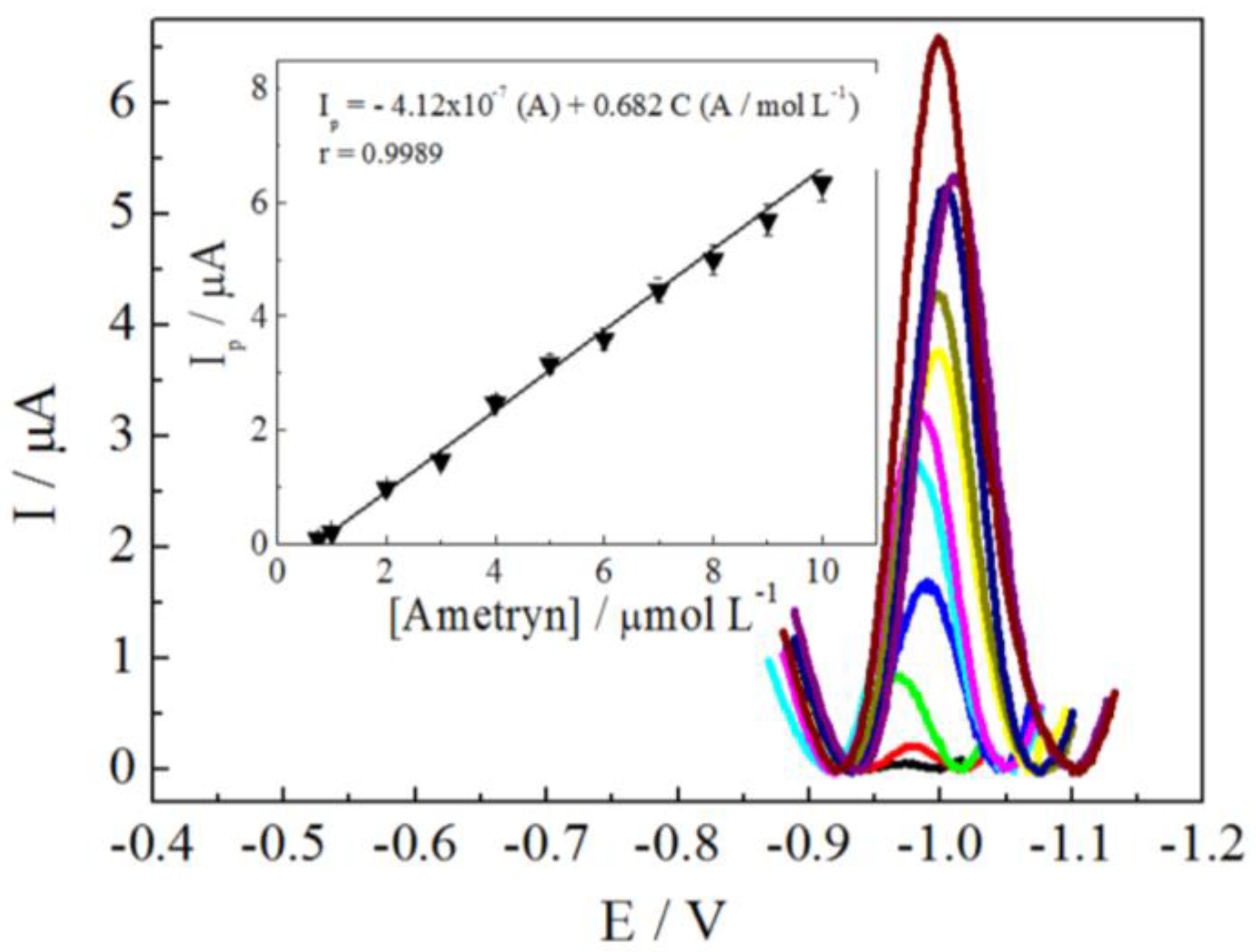
3.4. Analytical Parameters
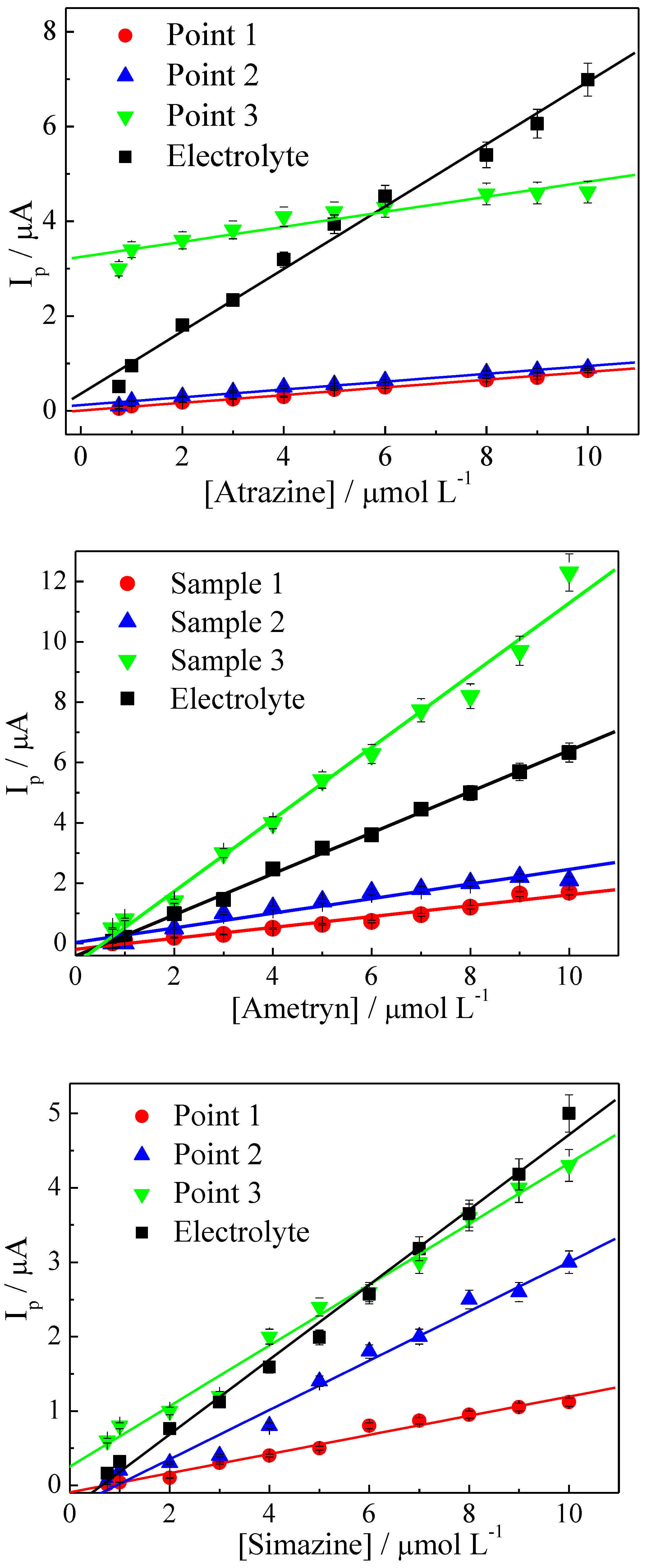
3.5. Analytical Applications
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- LeBarom, H.; McFarland, J.; Burvide, O. (Eds.) The Triazine Herbicides 50 Years Revolutionizing Agriculture, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Hornsboy, A.G.; Wauchope, R.D.; Herner, A.E. (Eds.) Pesticide Properties in the Environment; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- ANVISA. Regularização de Produtos—Agrotóxicos. Available online: http://portal.anvisa.gov.br/registros-e-autorizacoes/agrotoxicos/produtos/monografia-de-agrotoxicos/autorizadas (accessed on 19 June 2019).
- Reserved, A.R. Hayes Handbook of Pesticide Toxicology, 3rd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- FDA. Pesticide Analytical Manual Volume I (PAM) 3rd Edition. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/food/laboratory-methods-food-safety/pesticide-analytical-manual-volume-i-pam-3rd-edition (accessed on 20 January 2021).
- EU Commission. EU Pesticides Database. Available online: http://ec.europa.eu/food/plant/pesticides/eu-pesticides-database/public/?event=activesubstance.detail&language=EN&selectedID=972 (accessed on 20 January 2021).
- CONAMA. RESOLUÇÃO No 357, DE 17 DE MARÇO DE 2005. DOU. 2005. Available online: http://www2.mma.gov.br/port/conama/res/res05/res35705.pdf (accessed on 19 January 2021).
- Garbellini, G.S.; Pedrosa, V.A.; Salazar-Banda, G.R.; Avaca, L.A. Electroanalytical methodologies for the determination of triazine herbicides by square wave voltammetry and deconvolution techniques. Quim. Nova 2007, 30, 2025–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Ding, J.; Ni, L.; Yu, J.; Li, H.; Ding, H.; Chen, Y.; Ding, L. Preparation of magnetic superhydrophilic molecularly imprinted resins for detection of triazines in aqueous samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1497, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, K.; Kumar, S.; Chand, R.; Han, D.; Kim, Y. Fast detection of triazine herbicides on a microfluidic chip using capillary electrophoresis pulse amperometric detection. Microelectron. Eng. 2012, 97, 391–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Chen, B.; He, M.; Hu, B. Sensitive determination of seven triazine herbicide in honey, tomato and environmental water samples by hollow fiber based liquid-liquid-liquid microextraction combined with sweeping micellar electrokinetic capillary chromatography. Talanta 2018, 186, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Supraja, P.; Tripathy, S.; Vanjaria, S.R.K.; Singh, V.; Singhb, S.G. Electrospun tin (IV) oxide nanofiber based electrochemical sensor for ultrasensitive and selective detection of atrazine in water. Biosens. Bioelectron 2019, 141, 111441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Souza, D.; De Toledo, R.A.; Mazo, L.H.; Avaca, L.A.; Machado, S.A.S. Determination of triazine herbicides: Development of an electroanalytical method utilizing a solid amalgam electrode that minimizes toxic waste residues, and a comparative study between voltammetric and chromatographic technique. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 387, 2245–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. Stripping Analysis: Principles, Instrumentation, and Applications, 1st ed.; VCH Publishers Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Qinb, Z.; Liang, F.; Li, J.; Sun, Y.; Wang, X.; Ma, P.; Song, D. Vortex-assisted solid-phase extraction based on metal-organic framework/chitosan-functionalized hydrophilic sponge column for determination of triazine herbicides in environmental water by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chrom. A 2021, 1638, 461887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Chen, B.; You, L.; He, M.; Hu, B. Polydimethylsiloxane/MIL-100(Fe) coated stir bar sorptive extraction-high performance liquid chromatography for the determination of triazines in environmental water samples. Talanta 2017, 175, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-González, N.; Beceiro-González, E.; González-Castroa, M.J.; Alpendurada, M.F. On-line solid-phase extraction method for determination of triazine herbicides and degradation products in seawater by ultra-pressure liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chrom. A 2016, 1470, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing-Xiang Zhou, Q.X.; Gao, Y.Y. Combination of ionic liquid dispersive liquid-phase microextraction and high performance liquid chromatography for the determination of triazine herbicides in water samples. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2014, 25, 745–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roldán-Pijuán, M.; Lucena, R.; Cárdenas, S.; Valcárcel, M.; Kabir, A.; Furton, K.G. Stir fabric phase sorptive extraction for the determination of triazine herbicides in environmental waters by liquid chromatography. J. Chrom. A 2015, 1376, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svorc, L.; Rievaj, M.; Bustin, D. Green electrochemical sensor for environmental monitoring of pesticides: Determination of atrazine in river waters using a boron-doped diamond electrode. Sens. Act. B Chem. 2013, 181, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, C.; Niu, Y.; Li, S.; Luo, R. Electrochemical sensor based on molecularly imprinted composite membrane of poly(o-aminothiophenol) with gold nanoparticles for sensitive determination of herbicide simazine in environmental samples. Sens. Act. B Chem. 2017, 249, 747–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, D.; De Toledo, R.A.; Suffredini, H.B.; Mazo, L.H.; Machado, A.S. Characterization and Use of Copper Solid Amalgam Electrode for Electroanalytical Determination of Triazines-Based Herbicides. Electroanalysis 2006, 18, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirceski, V.; Komorsky-Lovric, S.; Lovric, M. Square-Ware Voltammetry Theory and Application, 1st ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Gonçalves-Filho, D.; Silva, C.G.; De Souza, D. Pesticides determination in foods and natural waters using solid amalgam-based electrodes: Challenges and trends. Talanta 2020, 212, 120756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yosypchuk, B.; Barek, J. Analytical Applications of Solid and Paste Amalgam Electrodes. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2009, 39, 189–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yosypchuk, B.; Novotný, L. Nontoxic Electrodes of Solid Amalgams. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2002, 32, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, D.; Melo, L.C.; Correia, A.N.; De Lima-Neto, P.; Fatibello-Filho, O.; Mascaro, L.H. Utilização de eletrodos sólidos de amálgama para a determinação analítica de compostos orgânicos e inorganicos. Quim. Nova 2011, 34, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, L.C.; Salazar-Banda, G.R.; Machado, S.A.S.; Lima-Neto, P.; De Souza, D.; Correia, A.N. A simple and sensitive detection of diquat herbicide using a dental amalgam electrode A comparison using the chromatographic technique. Talanta 2009, 79, 1216–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikkelsen, Ø.; Schrøder, K.H. Amalgam Electrode for Electroanalysis. Electroanalytical 2003, 15, 679–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cryosystems, O. Crystallographica. Available online: https://connect.oxcryo.com/software/cglegacy/ (accessed on 1 January 2019).
- Mocak, J.; Bond, A.M.; Mitchell, S.; Scollary, G. International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry Analytical Chemistry Division Commission on Electroanalytical Chemistry a Statistical Overview of Standard (Iupac and Acs) and New Procedures for Determining the Limits of Detection and Quantification: Ap. Pure Appl. Chern 1997, 69, 297–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Committee, A.M. Recommendations for the Definition, Estimation and Use of the Detection Limit. Analyst 1987, 112, 199–204. [Google Scholar]
- APHA. Standard Methods for examination of water and wastewater. An. Hidrol. Médica 2012, 21, 183–190. [Google Scholar]
- de la Guardia, M.; Garrigues, S. Handbook of Green Analytical Chemistry; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Grimshaw, J. Electrochemical Reactions and Mechanisms in Organic Chemistry, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Compton, R.G.; Banks, C.E. Understanding Voltammetry, 3rd ed.; World Scientific Publishing Europe: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Fry, A.J. Synthetic Organic Electrochemistry, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Scholz, F. (Ed.) Electroanalytical Methods: Guide to Experiments and Applications, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, J.N.; Miller, J.C. Statistics and Chemometrics for Analytical Chemistry, 6th ed.; Pearson: New York, NY, USA, 2010; Volume 46. [Google Scholar]
- Christian, G.D.; Dasgupta, P.K.; Schug, K.A. Analytical Chemistry, 7th ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-González, N.; González-Castro, M.J.; Beceiro-González, E.; Muniategui-Lorenzo, S. Development of a matrix solid phase dispersion methodology for the determination of triazine herbicides in marine sediments. Microchem. J. 2017, 133, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khana, S.; Hussain, S.; Wong, A.; Foguel, M.V.; Gonçalves, L.M.; Gurgoe, M.I.P.; Sotomayor, M.P.T. Synthesis and characterization of magnetic-molecularly imprinted polymersfor the HPLC-UV analysis of ametryn. React. Funct. Polym. 2018, 122, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Analytes | Method | Samples | LOD (µg L−1) | Precision | Recovery (%) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Triazines | HPLC-MS/MS | Drinking, tap, and environmental water | 0.014–0.045 | 0.4–14.5 | 78.9−118.6 | [15] |
| Triazines | HPLC-UV | Environmental water, East Lake water, and local pond water samples | 0.021–0.079 | 2.3–6.3 | 94.0–118 | [16] |
| Triazines and degradation products | UHPLC-MS/MS | Seawater | 0.008–0.217 | 0.0–3.9 | 80.3–99.8 | [17] |
| Triazines | HPLC-UV | Water | 0.05–0.06 | 3.2–8.9 | 85.1–100 | [18] |
| Triazines | UHPLC-DAD | Water | 0.08–0.47 | 1.4–11.8 | 75–126 | [19] |
| Atrazine | SWV coupled with BDDE | River water | 2.15 | 2.9 | 92–100 | [20] |
| Simazine | CV coupled to MIP/ATP@AuNPs/ATP/Au electrode | Soil, and tap and river water | 2.62 | 3.1 | 91–97 | [21] |
| Atrazine and ametryn | SWV coupled with CuSAE | Natural water | 3.02 | 3.4–3.9 | 93–94 | [22] |
| Parameter | Ametryn | Atrazine | Simazine |
|---|---|---|---|
| LR (µmol L−1) | 0.750–10.0 | 0.750–10.0 | 0.750–10.0 |
| r | 0.9989 | 0.9952 | 0.9963 |
| Intercept (A) | −4.12 × 10−7 | 3.62 × 10−7 | −3.19 × 10−7 |
| Slope (A/mol L−1) | 0.680 | 0.658 | 0.503 |
| CI of intercept (A) | ±4.51 × 10−7 | ±3.43 × 10−7 | ±1.01 × 10−6 |
| CI of slope (A/mol L−1) | ±0.197 | ±0.443 | ±0.418 |
| Sb (A) | 2.47 × 10−8 | 2.47 × 10−8 | 2.47 × 10−8 |
| LOD (mol L−1) | 1.20 × 10−7 (27.3 µg L−1) | 1.24 × 10−7 (26.8 µg L−1) | 1.62 × 10−7 (32.7 µg L−1) |
| LOQ (mol L−1) | 3.64 × 10−7 (82.7 µg L−1) | 3.76 × 10−7 (81.1 µg L−1) | 4.92 × 10−7 (99.2 µg L−1) |
| Error in repeatability (%) | 2.13 | 4.25 | 4.75 |
| Error in reproducibility (%) | 2.58 | 3.56 | 2.62 |
| Recovery (%) | 100.5 | 100.2 | 99.6 |
| Sample | LR (µmol L−1) | r | Slope (A/mol L−1) | DL (µmol L−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ametryn | ||||
| 1 | 0.7500–10.00 | 0.9824 | 0.1806 | 0.4522 (102.8 ppb) |
| 2 | 0.7500–10.00 | 0.9824 | 0.1806 | 0.4522 (102.8 ppb) |
| 3 | 0.7500–10.00 | 0.9824 | 0.1806 | 0.4522 (102.8 ppb) |
| Atrazine | ||||
| 1 | 0.7500–10.00 | 0.9959 | 0.08140 | 0.1003 (21.63 ppb) |
| 2 | 0.7500–10.00 | 0.9900 | 0.08249 | 0.9901 (213.5 ppb) |
| 3 | 0.7500–10.00 | 0.9474 | 0.1585 | 0.5153 (111.1 ppb) |
| Simazine | ||||
| 1 | 0.7500–10.00 | 0.9909 | 0.1288 | 0.6341 (127.9 ppb) |
| 2 | 0.7500–10.00 | 0.9903 | 0.3316 | 0.2462 (49.65 ppb) |
| 3 | 0.7500–10.00 | 0.9953 | 0.4078 | 0.2003 (40.39 ppb) |
| Ametryn | Atrazine | Simazine | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| Added (µmol L−1) | 2.000 | 2.000 | 2.000 | 2.000 | 2.000 | 2.000 | 2.000 | 2.000 | 2.000 |
| Recovered (µmol L−1) | 2.117 ± 0.130 | 2.196 ± 0.0627 | 1.952 ± 0.441 | 2.188 ± 0.0616 | 2.132 ± 0.193 | 2.044 ± 0.120 | 1.786 ± 0.232 | 2.060 ± 0.404 | 2.197 ± 0.112 |
| Recovery (%) | 106 | 110 | 98 | 109 | 107 | 102 | 89 | 103 | 110 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martins, F.C.O.L.; De Souza, D. New Approaches in Electroanalytical Determination of Triazines-Based Pesticides in Natural Waters. Analytica 2023, 4, 84-101. https://doi.org/10.3390/analytica4020008
Martins FCOL, De Souza D. New Approaches in Electroanalytical Determination of Triazines-Based Pesticides in Natural Waters. Analytica. 2023; 4(2):84-101. https://doi.org/10.3390/analytica4020008
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartins, Fernanda C. O. L., and Djenaine De Souza. 2023. "New Approaches in Electroanalytical Determination of Triazines-Based Pesticides in Natural Waters" Analytica 4, no. 2: 84-101. https://doi.org/10.3390/analytica4020008
APA StyleMartins, F. C. O. L., & De Souza, D. (2023). New Approaches in Electroanalytical Determination of Triazines-Based Pesticides in Natural Waters. Analytica, 4(2), 84-101. https://doi.org/10.3390/analytica4020008






