Formation, Characterization and SEM Microanalysis of Yeelimite †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
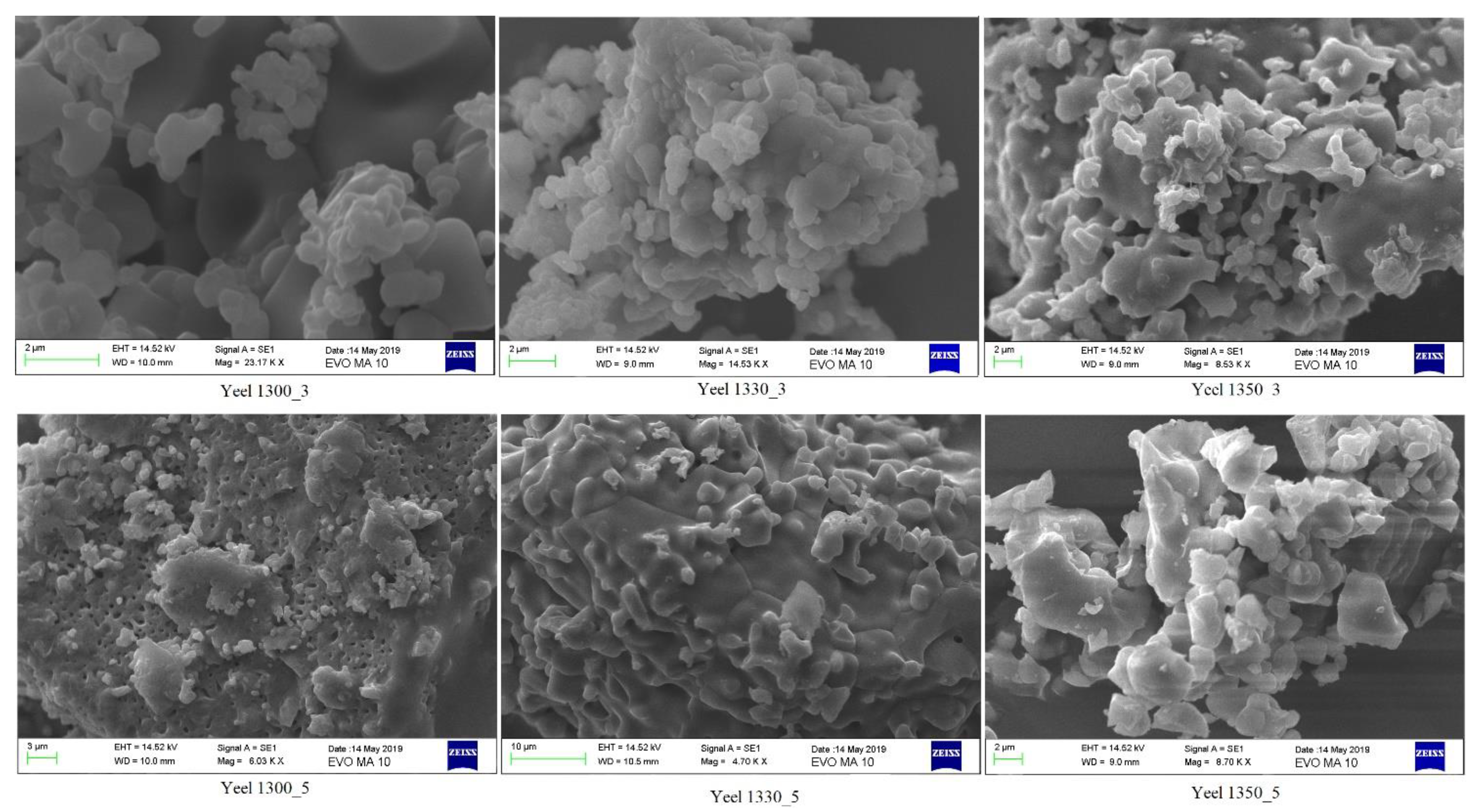
3.1. SEM Results
3.2. Characterization of the Samples
3.3. Compressive Strength of the Samples with and without Standard Sand
4. Conclusions
- Yeelimite, formed at temperatures ≥ 1300 °C, contains krotite (CaO·Al2O3), anhydrite (CaSO4) and mayenite ((CaO)12(Al2O3)7) as secondary phases.
- The shape of the produced yeelimite grains is polygonal.
- The crystals of the so-formed yeelimite are larger (30 nm) than the yeelimite crystals of the CSA cement (15 nm) [7]. This is because stoichiometric yeelimite is not 100 wt.% pure yeelimite, and secondary phases are formed.
- The formed stoichiometric yeelimite is brittle.
- By increasing the yeelimite content, the compressive strength increases.
- The compressive strength at the 28th day of hydration of yeelimite exceeds 95 MPa.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kamitsou, M.D.; Kanellopoulou, D.G.; Christogerou, A.; Kostagiannakopoulou, C.; Kostopoulos, V.; Angelopoulos, G.N. Valorization of FGD and Bauxite Residue in Sulfobelite Cement Production. Waste Biomass Valorization 2020, 11, 5445–5456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewlett, P.C. Lea’s Chemistry of Cement and Concrete, 4th ed.; Elsevier Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Londono-Zuluaga, D.; Tobon, J.I.; Aranda, M.A.G.; Santacruz, I.; De la Torre, A.G. Influence of fly ash blending on hydration and physical behavior of belite–alite–ye’elimite cements. Mater. Struct. 2018, 51, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortes, G.M.; Lourenço, R.R.; Montini, M.; Gallo, J.B.; de Anchieta, R.J. Synthesis and mechanical characterization of iron oxide rich sulfobelite cements prepared using bauxite residue. J. Mater. Res. 2016, 19, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gartner, E.; Sui, T. Alternative cement clinkers. Cem. Concr. Res. 2018, 114, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Khessaimi, Y.; El Hafiane, Y.; Smith, A.; Trauchessec, R.; Diliberto, C.; Lecomte, A. Solid-state synthesis of pure ye’elimite. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2018, 38, 3401–3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, J.W.; Bideaux, R.A.; Bladh, K.W.; Nichols, M.C. Handbook of Mineralogy; Mineralogical Society of America: Chantilly, VA, USA, 2003; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Winnefeld, F.; Barlag, S. Calorimetric and thermogravimetric study on the influence of calcium sulfate on the hydration of ye’elimite. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2010, 101, 949–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bullerjahn, F.; Boehm-Courjault, E.; Zajac, M.; Haha, M.B.; Scrivener, K. Hydration reactions and stages of clinker composed mainly of stoichiometric ye’elimite. Cem. Concr. Res. 2019, 116, 120–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuesta, A.; De la Torre, A.G.; Losilla, E.R.; Peterson, V.K.; Rejmak, P.; Ayuela, A.; Frontera, C.; Aranda, M.A. Structure, atomistic simulations, and phase transition of stoichiometric yeelimite. Chem. Mater. 2013, 25, 1680–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pöllmann, H.; Stöber, S. Investigations on commercial and synthetic calcium sulfoaluminate cements. In Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Cement Microscopy, Milan, Italy, 13–17 April 2014; International Cement Microscopy Association (ICMA): Milan, Italy, 2014; Volume 1, p. 471, ISBN 1-930787-09-X. [Google Scholar]

| Experiment | Yeel.1300_3 | Yeel.1300_5 | Yeel.1330_3 | Yeel.1330_5 | Yeel.1350_3 | Yeel.1350_5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TFinal (°C) | 1300 | 1300 | 1330 | 1330 | 1350 | 1350 |
| Total time (h/min) | 2:50 | 5:10 | 2:50 | 5:10 | 2:50 | 5:10 |
| Element. | Atomic wt.% of Experiment. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yeel.1300_3. | Yeel.1300_5 | Yeel.1330_3 | Yeel.1330_5 | Yeel.1350_3 | Yeel.1350_5 | |
| O * | 60.58 | 59.57 | 62.30 | 65.69 | 63.33 | 59.87 |
| Al | 18.43 | 20.23 | 17.89 | 16.79 | 18.71 | 19.71 |
| S | 4.02 | 2.67 | 2.98 | 2.30 | 2.09 | 1.82 |
| Ca | 16.97 | 17.53 | 16.83 | 15.21 | 15.87 | 18.60 |
| Crystal Phase (wt.%). | Yeelimite | Anhydrite | Krotite | Mayenite | SUM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yeel.1300_3 | 80.6 | 4.3 | 9.7 | 5.4 | 100 |
| Yeel.1330_3 | 86.1 | 2.5 | 5.9 | 5.5 | 100 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kamitsou, M.D.; Kostakopoulos, E.; Kanellopoulou, D.G.; Hallet, V.; Petrica, P.; Christogerou, A.; Angelopoulos, G.N. Formation, Characterization and SEM Microanalysis of Yeelimite. Mater. Proc. 2021, 5, 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/materproc2021005106
Kamitsou MD, Kostakopoulos E, Kanellopoulou DG, Hallet V, Petrica P, Christogerou A, Angelopoulos GN. Formation, Characterization and SEM Microanalysis of Yeelimite. Materials Proceedings. 2021; 5(1):106. https://doi.org/10.3390/materproc2021005106
Chicago/Turabian StyleKamitsou, Maria D., Elias Kostakopoulos, Dimitra G. Kanellopoulou, Vincent Hallet, Petrica Petrica, Angeliki Christogerou, and George N. Angelopoulos. 2021. "Formation, Characterization and SEM Microanalysis of Yeelimite" Materials Proceedings 5, no. 1: 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/materproc2021005106
APA StyleKamitsou, M. D., Kostakopoulos, E., Kanellopoulou, D. G., Hallet, V., Petrica, P., Christogerou, A., & Angelopoulos, G. N. (2021). Formation, Characterization and SEM Microanalysis of Yeelimite. Materials Proceedings, 5(1), 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/materproc2021005106







