Primary Resistance to EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors (TKIs): Contexts and Comparisons in EGFR-Mutated Lung Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
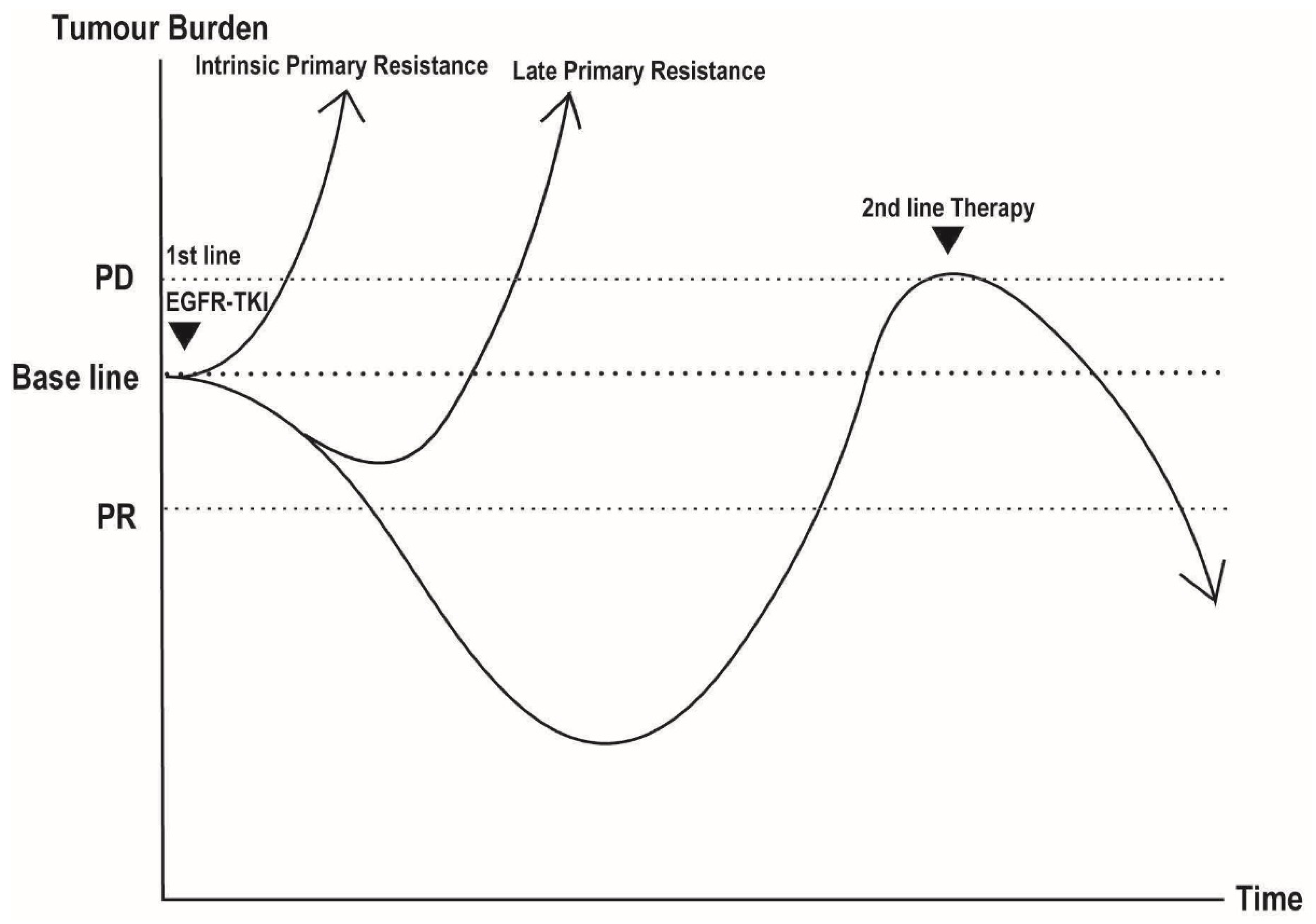
2. Overview of Drug-Induced Cancer Dynamics
3. Drug-Related Factors
3.1. Pharmacokinetic Mechanisms
3.2. Pharmacodynamic Mechanisms
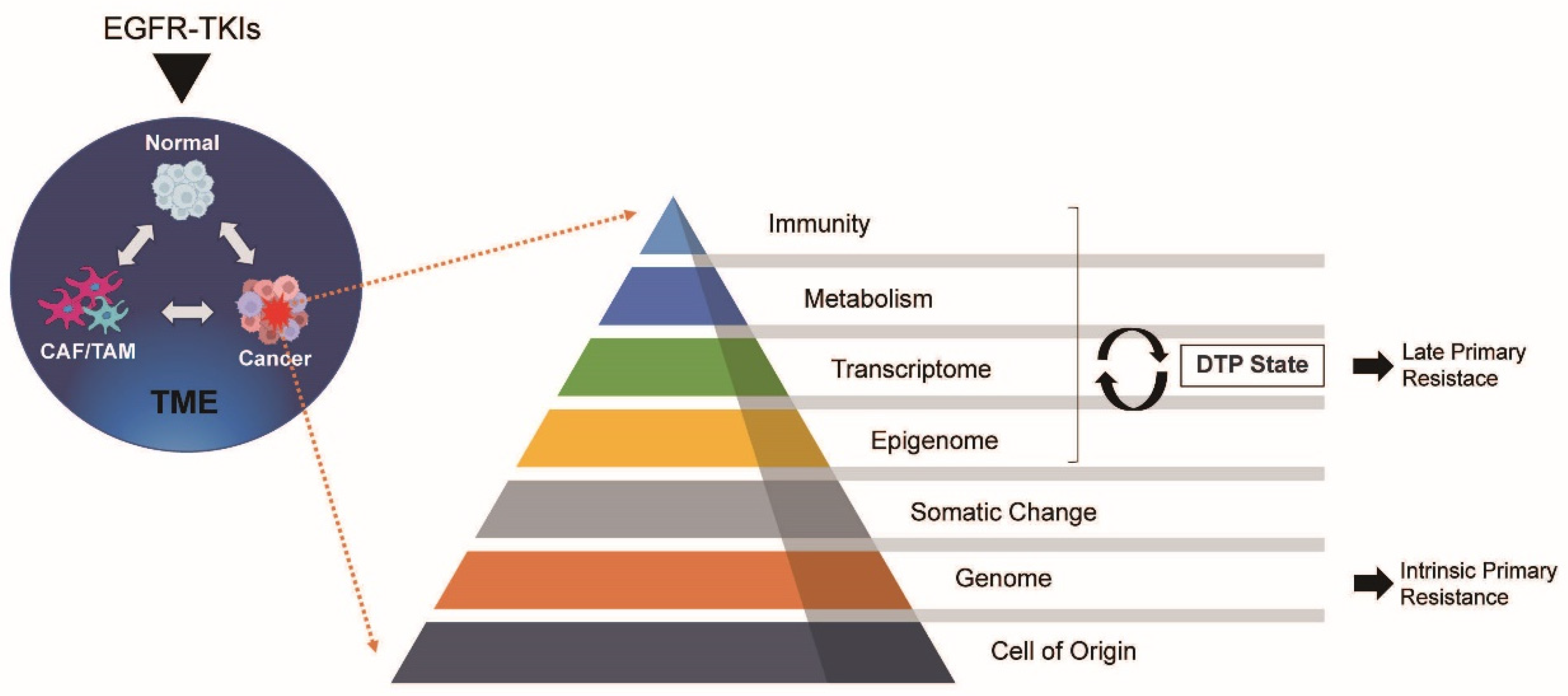
4. Tumor-Related Factors
4.1. Metabolism
4.1.1. DTP Cells and Late Primary Resistance
4.1.2. Lipid Metabolism and Autophagy
4.2. Transcriptome and Epigenome
4.3. Somatic and Genomic Changes
4.3.1. TP53
4.3.2. PIK3CA Mutation
4.3.3. PTEN Alterations
4.4. Cell of Origin
4.4.1. Lineage Plasticity
4.4.2. BIM Deletion Polymorphism
5. Tumour Microenvironment (TME)
Immunity
6. Discussion
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fitzmaurice, C.; Abate, D.; Abbasi, N.; Abbastabar, H.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abdel-Rahman, O.; Abdelalim, A.; Abdoli, A.; Abdollahpour, I.; Abdulle, A.S.M.; et al. Global, Regional, and National Cancer Incidence, Mortality, Years of Life Lost, Years Lived With Disability, and Disability-Adjusted Life-Years for 29 Cancer Groups, 1990 to 2017: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, 1749–1768. [Google Scholar]
- Lynch, T.J.; Bell, D.W.; Sordella, R.; Gurubhagavatula, S.; Okimoto, R.A.; Brannigan, B.W.; Harris, P.L.; Haserlat, S.M.; Supko, J.G.; Haluska, F.G.; et al. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 2129–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paez, J.G.; Jänne, P.A.; Lee, J.C.; Tracy, S.; Greulich, H.; Gabriel, S.; Herman, P.; Kaye, F.J.; Lindeman, N.; Boggon, T.J.; et al. EGFR mutations in lung cancer: Correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science 2004, 304, 1497–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mok, T.S.; Wu, Y.L.; Thongprasert, S.; Yang, C.H.; Chu, D.T.; Saijo, N.; Sunpaweravong, P.; Han, B.; Margono, B.; Ichinose, Y.; et al. Gefitinib or carboplatin-paclitaxel in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 947–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maemondo, M.; Inoue, A.; Kobayashi, K.; Sugawara, S.; Oizumi, S.; Isobe, H.; Gemma, A.; Harada, M.; Yoshizawa, H.; Kinoshita, I.; et al. Gefitinib or chemotherapy for non-small-cell lung cancer with mutated EGFR. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 2380–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosell, R.; Moran, T.; Queralt, C.; Porta, R.; Cardenal, F.; Camps, C.; Majem, M.; Lopez-Vivanco, G.; Isla, D.; Provencio, M.; et al. Screening for epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 958–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Hao, X.; Hu, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Ying, J. Clinical characteristics and response to tyrosine kinase inhibitors of patients with non-small cell lung cancer harboring uncommon epidermal growth factor receptor mutations. Chin. J. Cancer Res. 2017, 29, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosell, R.; Carcereny, E.; Gervais, R.; Vergnenegre, A.; Massuti, B.; Felip, E.; Palmero, R.; Garcia-Gomez, R.; Pallares, C.; Sanchez, J.M.; et al. Erlotinib versus standard chemotherapy as first-line treatment for European patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (EURTAC): A multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Wu, Y.L.; Chen, G.; Feng, J.; Liu, X.Q.; Wang, C.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Zhou, S.; Ren, S.; et al. Erlotinib versus chemotherapy as first-line treatment for patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (OPTIMAL, CTONG-0802): A multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2011, 12, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.; Tan, E.H.; O’Byrne, K.; Zhang, L.; Boyer, M.; Mok, T.; Hirsh, V.; Yang, J.C.; Lee, K.H.; Lu, S.; et al. Afatinib versus gefitinib as first-line treatment of patients with EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (LUX-Lung 7): A phase 2B, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.L.; Cheng, Y.; Zhou, X.; Lee, K.H.; Nakagawa, K.; Niho, S.; Tsuji, F.; Linke, R.; Rosell, R.; Corral, J.; et al. Dacomitinib versus gefitinib as first-line treatment for patients with EGFR-mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (ARCHER 1050): A randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 1454–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soria, J.C.; Ohe, Y.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Reungwetwattana, T.; Chewaskulyong, B.; Lee, K.H.; Dechaphunkul, A.; Imamura, F.; Nogami, N.; Kurata, T.; et al. Osimertinib in Untreated EGFR-Mutated Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.A.; Arcila, M.E.; Rekhtman, N.; Sima, C.S.; Zakowski, M.F.; Pao, W.; Kris, M.G.; Miller, V.A.; Ladanyi, M.; Riely, G.J. Analysis of tumor specimens at the time of acquired resistance to EGFR-TKI therapy in 155 patients with EGFR-mutant lung cancers. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 2240–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oxnard, G.R.; Hu, Y.; Mileham, K.F.; Husain, H.; Costa, D.B.; Tracy, P.; Feeney, N.; Sholl, L.M.; Dahlberg, S.E.; Redig, A.J.; et al. Assessment of Resistance Mechanisms and Clinical Implications in Patients with EGFR T790M-Positive Lung Cancer and Acquired Resistance to Osimertinib. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 1527–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chua, K.P.; Teng, Y.H.F.; Tan, A.C.; Takano, A.; Alvarez, J.J.S.; Nahar, R.; Rohatgi, N.; Lai, G.G.Y.; Aung, Z.W.; Yeong, J.P.S.; et al. Integrative Profiling of T790M-Negative EGFR-Mutated NSCLC Reveals Pervasive Lineage Transition and Therapeutic Opportunities. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 5939–5950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelhardt, H.; Böse, D.; Petronczki, M.; Scharn, D.; Bader, G.; Baum, A.; Bergner, A.; Chong, E.; Döbel, S.; Egger, G.; et al. Start Selective and Rigidify: The Discovery Path toward a Next Generation of EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 10272–10293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackman, D.; Pao, W.; Riely, G.J.; Engelman, J.A.; Kris, M.G.; Jänne, P.A.; Lynch, T.; Johnson, B.E.; Miller, V.A. Clinical definition of acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcoux, N.; Gettinger, S.N.; O’Kane, G.; Arbour, K.C.; Neal, J.W.; Husain, H.; Evans, T.L.; Brahmer, J.R.; Muzikansky, A.; Bonomi, P.D.; et al. EGFR-Mutant Adenocarcinomas That Transform to Small-Cell Lung Cancer and Other Neuroendocrine Carcinomas: Clinical Outcomes. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.V.; Lee, D.Y.; Li, B.; Quinlan, M.P.; Takahashi, F.; Maheswaran, S.; McDermott, U.; Azizian, N.; Zou, L.; Fischbach, M.A.; et al. A chromatin-mediated reversible drug-tolerant state in cancer cell subpopulations. Cell 2010, 141, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hata, A.N.; Niederst, M.J.; Archibald, H.L.; Gomez-Caraballo, M.; Siddiqui, F.M.; Mulvey, H.E.; Maruvka, Y.E.; Ji, F.; Bhang, H.E.; Krishnamurthy Radhakrishna, V.; et al. Tumor cells can follow distinct evolutionary paths to become resistant to epidermal growth factor receptor inhibition. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raha, D.; Wilson, T.R.; Peng, J.; Peterson, D.; Yue, P.; Evangelista, M.; Wilson, C.; Merchant, M.; Settleman, J. The cancer stem cell marker aldehyde dehydrogenase is required to maintain a drug-tolerant tumor cell subpopulation. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 3579–3590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez, M.; Rajaram, S.; Steininger, R.J.; Osipchuk, D.; Roth, M.A.; Morinishi, L.S.; Evans, L.; Ji, W.; Hsu, C.H.; Thurley, K.; et al. Diverse drug-resistance mechanisms can emerge from drug-tolerant cancer persister cells. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikubo, M.; Inoue, Y.; Liu, G.; Tsao, M.S. Mechanism of Drug Tolerant Persister Cancer Cells: The Landscape and Clinical Implication for Therapy. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, 1798–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeken, J.F.; Beumer, J.H.; Anders, N.M.; Wanjiku, T.; Rusnak, M.; Rudek, M.A. Preclinical assessment of the interactions between the antiretroviral drugs, ritonavir and efavirenz, and the tyrosine kinase inhibitor erlotinib. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2015, 76, 813–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chhun, S.; Verstuyft, C.; Rizzo-Padoin, N.; Simoneau, G.; Becquemont, L.; Peretti, I.; Swaisland, A.; Wortelboer, R.; Bergmann, J.F.; Mouly, S. Gefitinib-phenytoin interaction is not correlated with the C-erythromycin breath test in healthy male volunteers. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2009, 68, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swaisland, H.C.; Ranson, M.; Smith, R.P.; Leadbetter, J.; Laight, A.; McKillop, D.; Wild, M.J. Pharmacokinetic drug interactions of gefitinib with rifampicin, itraconazole and metoprolol. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2005, 44, 1067–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, Y.; Chiba, M. The role of extrahepatic metabolism in the pharmacokinetics of the targeted covalent inhibitors afatinib, ibrutinib, and neratinib. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2015, 43, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stopfer, P.; Marzin, K.; Narjes, H.; Gansser, D.; Shahidi, M.; Uttereuther-Fischer, M.; Ebner, T. Afatinib pharmacokinetics and metabolism after oral administration to healthy male volunteers. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2012, 69, 1051–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wind, S.; Giessmann, T.; Jungnik, A.; Brand, T.; Marzin, K.; Bertulis, J.; Hocke, J.; Gansser, D.; Stopfer, P. Pharmacokinetic drug interactions of afatinib with rifampicin and ritonavir. Clin. Drug Investig. 2014, 34, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahluwalia, M.S.; Becker, K.; Levy, B.P. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors for Central Nervous System Metastases from Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Oncologist 2018, 23, 1199–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosaka, T.; Tanizaki, J.; Paranal, R.M.; Endoh, H.; Lydon, C.; Capelletti, M.; Repellin, C.E.; Choi, J.; Ogino, A.; Calles, A.; et al. Response Heterogeneity of EGFR and HER2 Exon 20 Insertions to Covalent EGFR and HER2 Inhibitors. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 2712–2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robichaux, J.P.; Elamin, Y.Y.; Tan, Z.; Carter, B.W.; Zhang, S.; Liu, S.; Li, S.; Chen, T.; Poteete, A.; Estrada-Bernal, A.; et al. Mechanisms and clinical activity of an EGFR and HER2 exon 20-selective kinase inhibitor in non-small cell lung cancer. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 638–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robichaux, J.P.; Le, X.; Vijayan, R.S.K.; Hicks, J.K.; Heeke, S.; Elamin, Y.Y.; Lin, H.Y.; Udagawa, H.; Skoulidis, F.; Tran, H.; et al. Structure-based classification predicts drug response in EGFR-mutant NSCLC. Nature 2021, 597, 732–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warburg, O. On the origin of cancer cells. Science 1956, 123, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina, J.R.; Sun, Y.; Protopopova, M.; Gera, S.; Bandi, M.; Bristow, C.; McAfoos, T.; Morlacchi, P.; Ackroyd, J.; Agip, A.A.; et al. An inhibitor of oxidative phosphorylation exploits cancer vulnerability. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1036–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hangauer, M.J.; Viswanathan, V.S.; Ryan, M.J.; Bole, D.; Eaton, J.K.; Matov, A.; Galeas, J.; Dhruv, H.D.; Berens, M.E.; Schreiber, S.L.; et al. Drug-tolerant persister cancer cells are vulnerable to GPX4 inhibition. Nature 2017, 551, 247–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viswanathan, V.S.; Ryan, M.J.; Dhruv, H.D.; Gill, S.; Eichhoff, O.M.; Seashore-Ludlow, B.; Kaffenberger, S.D.; Eaton, J.K.; Shimada, K.; Aguirre, A.J.; et al. Dependency of a therapy-resistant state of cancer cells on a lipid peroxidase pathway. Nature 2017, 547, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nechushtan, H.; Hamamreh, Y.; Nidal, S.; Gotfried, M.; Baron, A.; Shalev, Y.I.; Nisman, B.; Peretz, T.; Peylan-Ramu, N. A phase IIb trial assessing the addition of disulfiram to chemotherapy for the treatment of metastatic non-small cell lung cancer. Oncologist 2015, 20, 366–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Zhang, W.; Wang, L.; Guo, F.; Song, D.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, D.; Fan, Y.; Wang, J. Hypermethylated CD36 gene affected the progression of lung cancer. Gene 2018, 678, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.Y.; Teng, X.; Laddha, S.V.; Ma, S.; Van Nostrand, S.C.; Yang, Y.; Khor, S.; Chan, C.S.; Rabinowitz, J.D.; White, E. Autophagy provides metabolic substrates to maintain energy charge and nucleotide pools in Ras-driven lung cancer cells. Genes Dev. 2016, 30, 1704–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strohecker, A.M.; Guo, J.Y.; Karsli-Uzunbas, G.; Price, S.M.; Chen, G.J.; Mathew, R.; McMahon, M.; White, E. Autophagy sustains mitochondrial glutamine metabolism and growth of BrafV600E-driven lung tumors. Cancer Discov. 2013, 3, 1272–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramilowski, J.A.; Yip, C.W.; Agrawal, S.; Chang, J.C.; Ciani, Y.; Kulakovskiy, I.V.; Mendez, M.; Ooi, J.L.C.; Ouyang, J.F.; Parkinson, N.; et al. Functional annotation of human long noncoding RNAs via molecular phenotyping. Genome Res. 2020, 30, 1060–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinogradova, M.; Gehling, V.S.; Gustafson, A.; Arora, S.; Tindell, C.A.; Wilson, C.; Williamson, K.E.; Guler, G.D.; Gangurde, P.; Manieri, W.; et al. An inhibitor of KDM5 demethylases reduces survival of drug-tolerant cancer cells. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2016, 12, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tetsu, O.; Hangauer, M.J.; Phuchareon, J.; Eisele, D.W.; McCormick, F. Drug Resistance to EGFR Inhibitors in Lung Cancer. Chemotherapy 2016, 61, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.; Gao, F.; Fu, S.; Wang, Y.; Fang, W.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, L. Concomitant Genetic Alterations with Response to Treatment and Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Patients With EGFR-Mutant Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 739–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blakely, C.M.; Watkins, T.B.K.; Wu, W.; Gini, B.; Chabon, J.J.; McCoach, C.E.; McGranahan, N.; Wilson, G.A.; Birkbak, N.J.; Olivas, V.R.; et al. Evolution and clinical impact of co-occurring genetic alterations in advanced-stage EGFR-mutant lung cancers. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 1693–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnet, M.B.; O’Toole, S.; Horvath, L.G.; Selinger, C.; Yu, B.; Ng, C.C.; Boyer, M.; Cooper, W.A.; Kao, S. EGFR-Co-Mutated Advanced NSCLC and Response to EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, 585–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zilfou, J.T.; Lowe, S.W. Tumor suppressive functions of p53. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2009, 1, a001883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Le Teuff, G.; Lacas, B.; Tsao, M.S.; Graziano, S.; Pignon, J.P.; Douillard, J.Y.; Le Chevalier, T.; Seymour, L.; Filipits, M.; et al. Prognostic and Predictive Effect of TP53 Mutations in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer from Adjuvant Cisplatin-Based Therapy Randomized Trials: A LACE-Bio Pooled Analysis. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 850–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Lee, B.; Shim, J.H.; Lee, S.H.; Park, W.Y.; Choi, Y.L.; Sun, J.M.; Ahn, J.S.; Ahn, M.J.; Park, K. Concurrent Genetic Alterations Predict the Progression to Target Therapy in EGFR-Mutated Advanced NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahar, R.; Zhai, W.; Zhang, T.; Takano, A.; Khng, A.J.; Lee, Y.Y.; Liu, X.; Lim, C.H.; Koh, T.P.T.; Aung, Z.W.; et al. Elucidating the genomic architecture of Asian EGFR-mutant lung adenocarcinoma through multi-region exome sequencing. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rho, J.K.; Choi, Y.J.; Ryoo, B.Y.; Na, I.I.; Yang, S.H.; Kim, C.H.; Lee, J.C. p53 enhances gefitinib-induced growth inhibition and apoptosis by regulation of Fas in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 1163–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabapathy, K.; Lane, D.P. Therapeutic targeting of p53: All mutants are equal, but some mutants are more equal than others. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Bader, A.G.; Vogt, P.K. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase mutations identified in human cancer are oncogenic. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 802–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawano, O.; Sasaki, H.; Endo, K.; Suzuki, E.; Haneda, H.; Yukiue, H.; Kobayashi, Y.; Yano, M.; Fujii, Y. PIK3CA mutation status in Japanese lung cancer patients. Lung Cancer 2006, 54, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, H.; Shigematsu, H.; Nomura, M.; Lockwood, W.W.; Sato, M.; Okumura, N.; Soh, J.; Suzuki, M.; Wistuba, I.I.; Fong, K.M.; et al. PIK3CA mutations and copy number gains in human lung cancers. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 6913–6921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spoerke, J.M.; O’Brien, C.; Huw, L.; Koeppen, H.; Fridlyand, J.; Brachmann, R.K.; Haverty, P.M.; Pandita, A.; Mohan, S.; Sampath, D.; et al. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) pathway alterations are associated with histologic subtypes and are predictive of sensitivity to PI3K inhibitors in lung cancer preclinical models. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 6771–6783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaft, J.E.; Arcila, M.E.; Paik, P.K.; Lau, C.; Riely, G.J.; Pietanza, M.C.; Zakowski, M.F.; Rusch, V.; Sima, C.S.; Ladanyi, M.; et al. Coexistence of PIK3CA and other oncogene mutations in lung adenocarcinoma-rationale for comprehensive mutation profiling. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2012, 11, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffler, M.; Bos, M.; Gardizi, M.; König, K.; Michels, S.; Fassunke, J.; Heydt, C.; Künstlinger, H.; Ihle, M.; Ueckeroth, F.; et al. PIK3CA mutations in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): Genetic heterogeneity, prognostic impact and incidence of prior malignancies. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 1315–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, L.; Zhu, Y.; Huang, C.; Qin, Y.; Liu, H.; Ren-Heidenreich, L.; Shi, B.; Ren, H.; Chu, X.; et al. Coexistence of EGFR with KRAS, or BRAF, or PIK3CA somatic mutations in lung cancer: A comprehensive mutation profiling from 5125 Chinese cohorts. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 110, 2812–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludovini, V.; Bianconi, F.; Pistola, L.; Chiari, R.; Minotti, V.; Colella, R.; Giuffrida, D.; Tofanetti, F.R.; Siggillino, A.; Flacco, A.; et al. Phosphoinositide-3-kinase catalytic alpha and KRAS mutations are important predictors of resistance to therapy with epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2011, 6, 707–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelman, J.A.; Mukohara, T.; Zejnullahu, K.; Lifshits, E.; Borrás, A.M.; Gale, C.M.; Naumov, G.N.; Yeap, B.Y.; Jarrell, E.; Sun, J.; et al. Allelic dilution obscures detection of a biologically significant resistance mutation in EGFR-amplified lung cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 2695–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Bao, H.; Le, X.; Fan, X.; Tang, M.; Shi, X.; Zhao, J.; Yan, J.; Xu, Y.; Quek, K.; et al. Distinct co-acquired alterations and genomic evolution during TKI treatment in non-small-cell lung cancer patients with or without acquired T790M mutation. Oncogene 2020, 39, 1846–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Cristofano, A.; Pandolfi, P.P. The multiple roles of PTEN in tumor suppression. Cell 2000, 100, 387–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Yen, C.; Liaw, D.; Podsypanina, K.; Bose, S.; Wang, S.I.; Puc, J.; Miliaresis, C.; Rodgers, L.; McCombie, R.; et al. PTEN, a putative protein tyrosine phosphatase gene mutated in human brain, breast, and prostate cancer. Science 1997, 275, 1943–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myers, M.P.; Stolarov, J.P.; Eng, C.; Li, J.; Wang, S.I.; Wigler, M.H.; Parsons, R.; Tonks, N.K. P-TEN, the tumor suppressor from human chromosome 10q23, is a dual-specificity phosphatase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 9052–9057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balsara, B.R.; Pei, J.; Mitsuuchi, Y.; Page, R.; Klein-Szanto, A.; Wang, H.; Unger, M.; Testa, J.R. Frequent activation of AKT in non-small cell lung carcinomas and preneoplastic bronchial lesions. Carcinogenesis 2004, 25, 2053–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vazquez, F.; Sellers, W.R. The PTEN tumor suppressor protein: An antagonist of phosphoinositide 3-kinase signaling. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2000, 1470, M21–M35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, C.; Basaki, Y.; Kawahara, A.; Nakashima, K.; Kage, M.; Izumi, H.; Kohno, K.; Uramoto, H.; Yasumoto, K.; Kuwano, M.; et al. Loss of PTEN expression by blocking nuclear translocation of EGR1 in gefitinib-resistant lung cancer cells harboring epidermal growth factor receptor-activating mutations. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 8715–8725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sos, M.L.; Koker, M.; Weir, B.A.; Heynck, S.; Rabinovsky, R.; Zander, T.; Seeger, J.M.; Weiss, J.; Fischer, F.; Frommolt, P.; et al. PTEN loss contributes to erlotinib resistance in EGFR-mutant lung cancer by activation of Akt and EGFR. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 3256–3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Diao, X.Y.; Zhang, X.; Shao, Q.; Feng, Y.F.; An, X.; Wang, H.Y. Identification of genetic alterations associated with primary resistance to EGFR-TKIs in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer patients with EGFR sensitive mutations. Cancer Commun. 2019, 39, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.G.; Chang, Y.L.; Hsu, Y.C.; Wu, J.Y.; Yang, C.H.; Yu, C.J.; Tsai, M.F.; Shih, J.Y.; Yang, P.C. Good response to gefitinib in lung adenocarcinoma of complex epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations with the classical mutation pattern. Oncologist 2008, 13, 1276–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomas, A.; Futter, C.E.; Eden, E.R. EGF receptor trafficking: Consequences for signaling and cancer. Trends Cell Biol. 2014, 24, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, A.V.; Lamaze, C.; Schmid, S.L. Control of EGF receptor signaling by clathrin-mediated endocytosis. Science 1996, 274, 2086–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goh, L.K.; Huang, F.; Kim, W.; Gygi, S.; Sorkin, A. Multiple mechanisms collectively regulate clathrin-mediated endocytosis of the epidermal growth factor receptor. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 189, 871–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brankatschk, B.; Wichert, S.P.; Johnson, S.D.; Schaad, O.; Rossner, M.J.; Gruenberg, J. Regulation of the EGF transcriptional response by endocytic sorting. Sci. Signal. 2012, 5, ra21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Futter, C.E.; Pearse, A.; Hewlett, L.J.; Hopkins, C.R. Multivesicular endosomes containing internalized EGF-EGF receptor complexes mature and then fuse directly with lysosomes. J. Cell Biol. 1996, 132, 1011–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinde, S.R.; Maddika, S. PTEN modulates EGFR late endocytic trafficking and degradation by dephosphorylating Rab7. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oser, M.G.; Niederst, M.J.; Sequist, L.V.; Engelman, J.A. Transformation from non-small-cell lung cancer to small-cell lung cancer: Molecular drivers and cells of origin. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, e165–e172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sequist, L.V.; Waltman, B.A.; Dias-Santagata, D.; Digumarthy, S.; Turke, A.B.; Fidias, P.; Bergethon, K.; Shaw, A.T.; Gettinger, S.; Cosper, A.K.; et al. Genotypic and histological evolution of lung cancers acquiring resistance to EGFR inhibitors. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3, 75ra26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youle, R.J.; Strasser, A. The BCL-2 protein family: Opposing activities that mediate cell death. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, K.P.; Hillmer, A.M.; Chuah, C.T.; Juan, W.C.; Ko, T.K.; Teo, A.S.; Ariyaratne, P.N.; Takahashi, N.; Sawada, K.; Fei, Y.; et al. A common BIM deletion polymorphism mediates intrinsic resistance and inferior responses to tyrosine kinase inhibitors in cancer. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, D.B.; Halmos, B.; Kumar, A.; Schumer, S.T.; Huberman, M.S.; Boggon, T.J.; Tenen, D.G.; Kobayashi, S. BIM mediates EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor-induced apoptosis in lung cancers with oncogenic EGFR mutations. PLoS Med. 2007, 4, 1669–1679, discussion 1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cragg, M.S.; Kuroda, J.; Puthalakath, H.; Huang, D.C.; Strasser, A. Gefitinib-induced killing of NSCLC cell lines expressing mutant EGFR requires BIM and can be enhanced by BH3 mimetics. PLoS Med. 2007, 4, 1681–1689, discussion 1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Somwar, R.; Politi, K.; Balak, M.; Chmielecki, J.; Jiang, X.; Pao, W. Induction of BIM is essential for apoptosis triggered by EGFR kinase inhibitors in mutant EGFR-dependent lung adenocarcinomas. PLoS Med. 2007, 4, e294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebi, H.; Oze, I.; Nakagawa, T.; Ito, H.; Hosono, S.; Matsuda, F.; Takahashi, M.; Takeuchi, S.; Sakao, Y.; Hida, T.; et al. Lack of association between the BIM deletion polymorphism and the risk of lung cancer with and without EGFR mutations. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, E.N.; Kim, E.Y.; Jung, J.Y.; Kim, A.; Oh, I.J.; Kim, Y.C.; Chang, Y.S. BCL2-like 11 intron 2 deletion polymorphism is not associated with non-small cell lung cancer risk and prognosis. Lung Cancer 2015, 90, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xargay-Torrent, S.; López-Guerra, M.; Saborit-Villarroya, I.; Rosich, L.; Campo, E.; Roué, G.; Colomer, D. Vorinostat-induced apoptosis in mantle cell lymphoma is mediated by acetylation of proapoptotic BH3-only gene promoters. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 3956–3968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, T.; Takeuchi, S.; Yamada, T.; Ebi, H.; Sano, T.; Nanjo, S.; Ishikawa, D.; Sato, M.; Hasegawa, Y.; Sekido, Y.; et al. EGFR-TKI resistance due to BIM polymorphism can be circumvented in combination with HDAC inhibition. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 2428–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, S.; Hase, T.; Shimizu, S.; Ando, M.; Hata, A.; Murakami, H.; Kawakami, T.; Nagase, K.; Yoshimura, K.; Fujiwara, T.; et al. Phase I study of vorinostat with gefitinib in BIM deletion polymorphism/epidermal growth factor receptor mutation double-positive lung cancer. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 561–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meador, C.B.; Hata, A.N. Acquired resistance to targeted therapies in NSCLC: Updates and evolving insights. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 210, 107522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, Q.; Yamada, T.; Matsumoto, K.; Matsumoto, I.; Oda, M.; Watanabe, G.; Kayano, Y.; Nishioka, Y.; Sone, S.; et al. Crosstalk to stromal fibroblasts induces resistance of lung cancer to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 6630–6638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straussman, R.; Morikawa, T.; Shee, K.; Barzily-Rokni, M.; Qian, Z.R.; Du, J.; Davis, A.; Mongare, M.M.; Gould, J.; Frederick, D.T.; et al. Tumour micro-environment elicits innate resistance to RAF inhibitors through HGF secretion. Nature 2012, 487, 500–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Z.; Wu, T.; Ou, W.; Wang, J.; Yang, B.; Zhao, Y.; Rao, Z.; et al. M2-polarized macrophages contribute to the decreased sensitivity of EGFR-TKIs treatment in patients with advanced lung adenocarcinoma. Med. Oncol. 2014, 31, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, A.K.; Han, S.; Tai, Y.; Ma, W.; Coker, C.; Quinn, S.A.; Shakri, A.R.; Zhong, T.J.; Scholze, H.; Lagos, G.G.; et al. Targeting S100A9-ALDH1A1-retinoic acid signaling to suppress brain relapse in EGFR-mutant lung cancer. Cancer Discov. 2022, 12, 1002–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azuma, K.; Ota, K.; Kawahara, A.; Hattori, S.; Iwama, E.; Harada, T.; Matsumoto, K.; Takayama, K.; Takamori, S.; Kage, M.; et al. Association of PD-L1 overexpression with activating EGFR mutations in surgically resected nonsmall-cell lung cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2014, 25, 1935–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, T.; Du, W.; Zhu, J.; Liu, Z.; Huang, J.A. The canonical TGF-β/Smad signalling pathway is involved in PD-L1-induced primary resistance to EGFR-TKIs in EGFR-mutant non-small-cell lung cancer. Respir. Res. 2019, 20, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terry, S.; Abdou, A.; Engelsen, A.S.T.; Buart, S.; Dessen, P.; Corgnac, S.; Collares, D.; Meurice, G.; Gausdal, G.; Baud, V.; et al. AXL Targeting Overcomes Human Lung Cancer Cell Resistance to NK- and CTL-Mediated Cytotoxicity. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2019, 7, 1789–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilera, T.A.; Rafat, M.; Castellini, L.; Shehade, H.; Kariolis, M.S.; Hui, A.B.; Stehr, H.; von Eyben, R.; Jiang, D.; Ellies, L.G.; et al. Reprogramming the immunological microenvironment through radiation and targeting Axl. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilera, T.A.; Giaccia, A.J. Molecular Pathways: Oncologic Pathways and Their Role in T-cell Exclusion and Immune Evasion-A New Role for the AXL Receptor Tyrosine Kinase. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 2928–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, K.G.; D’Arcangelo, E.; Tsao, M.S. Patient-derived cell line, xenograft and organoid models in lung cancer therapy. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2020, 9, 2214–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Study | EGFR-TKI | TKI-Generation | Overall Response Rate, % | Primary Resistance, % | Intrinsic Primary Resistance (PD), % | Late Primary Resistance (SD), % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IPASS | Gefitinib | 1 | 71.2 | 28.8 | 7.6 | 20.5 |
| NEJ003 | Gefitinib | 1 | 73.7 | 26.3 | 11 | 15.8 |
| WJTOG-3405 | Gefitinib | 1 | 62.1 | 37.9 | ||
| EURTAC | Erlotinib | 1 | 58 | 42 | ||
| OPTIMAL | Erlotinib | 1 | 83 | 17 | ||
| LUX-Lung-7 | Afatinib | 2 | 72.5 | 27.5 | 6 | 21 |
| ARCHER-1050 | Dacomitinib | 2 | 75 | 25 | 5 | 13 |
| FLAURA | Osimertinib | 3 | 80 | 20 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kobayashi, K. Primary Resistance to EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors (TKIs): Contexts and Comparisons in EGFR-Mutated Lung Cancer. J. Respir. 2023, 3, 223-236. https://doi.org/10.3390/jor3040021
Kobayashi K. Primary Resistance to EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors (TKIs): Contexts and Comparisons in EGFR-Mutated Lung Cancer. Journal of Respiration. 2023; 3(4):223-236. https://doi.org/10.3390/jor3040021
Chicago/Turabian StyleKobayashi, Keigo. 2023. "Primary Resistance to EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors (TKIs): Contexts and Comparisons in EGFR-Mutated Lung Cancer" Journal of Respiration 3, no. 4: 223-236. https://doi.org/10.3390/jor3040021
APA StyleKobayashi, K. (2023). Primary Resistance to EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors (TKIs): Contexts and Comparisons in EGFR-Mutated Lung Cancer. Journal of Respiration, 3(4), 223-236. https://doi.org/10.3390/jor3040021






