Predisposing Factors, Clinical Picture, and Outcome of B-Cell Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma in Sjögren’s Syndrome
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Predisposing Factors
2.1. Demographic Features
2.2. Clinical Predisposing Factors
2.3. Serological Predisposing Factors
2.4. Hematological Predisposing Factors
2.5. Histological Predisposing Factors
2.6. Disease Activity as a Predisposing Factor
2.7. Molecular and Genetic Predisposing Factors
2.7.1. Genetics
2.7.2. Epigenetics
2.7.3. Gene Expression
2.7.4. Proteins
2.8. Imaging-Defined Predisposing Factors
2.9. Predictive Models for Lymphoma Development
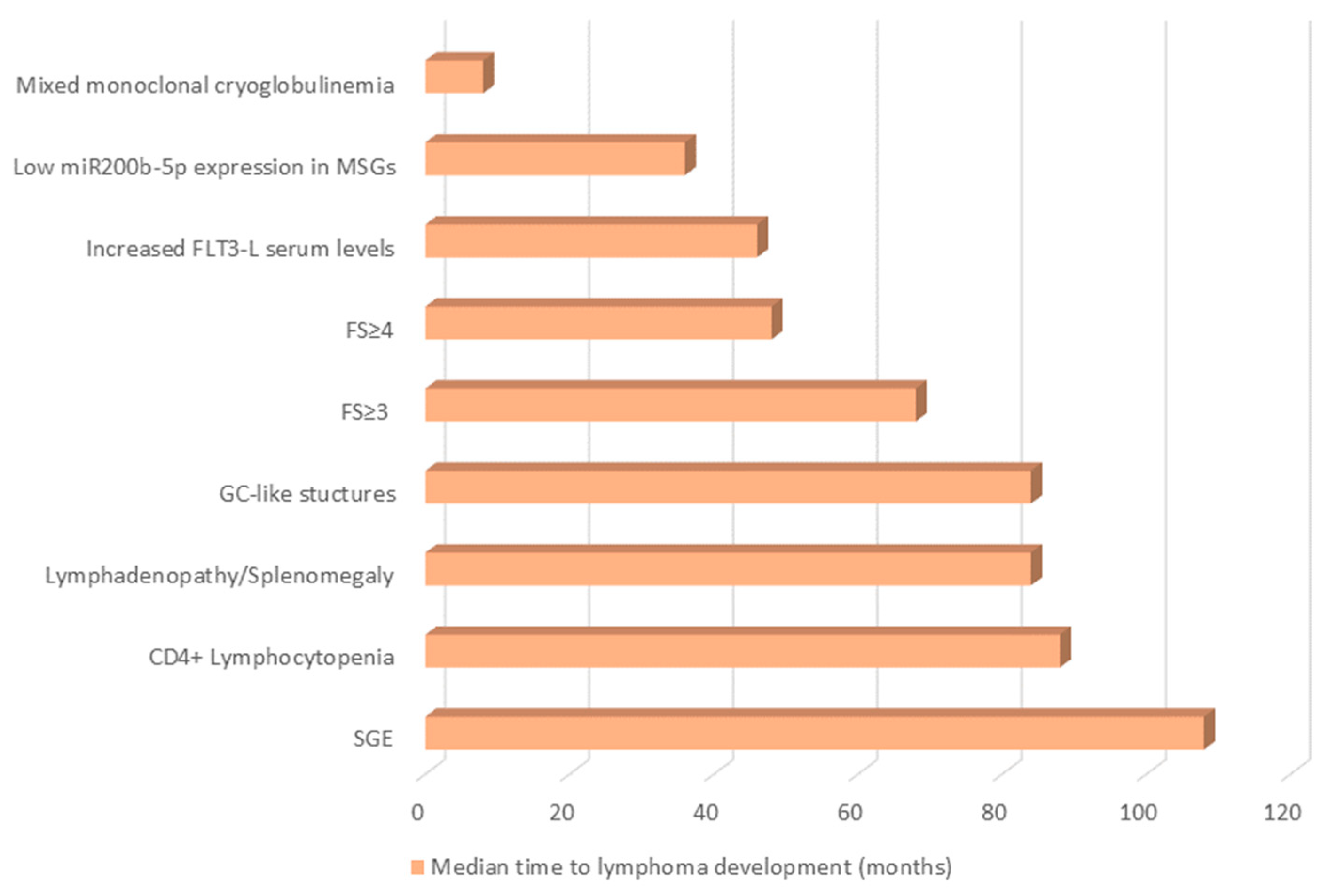
2.10. “One Size Fits All?”: Distinct Predisposing Factors for Different Patient Subgroups and Lymphoma Subtypes, Predisposing Factors Detected at Different Time-Points before Lymphoma Development
3. Clinical Picture
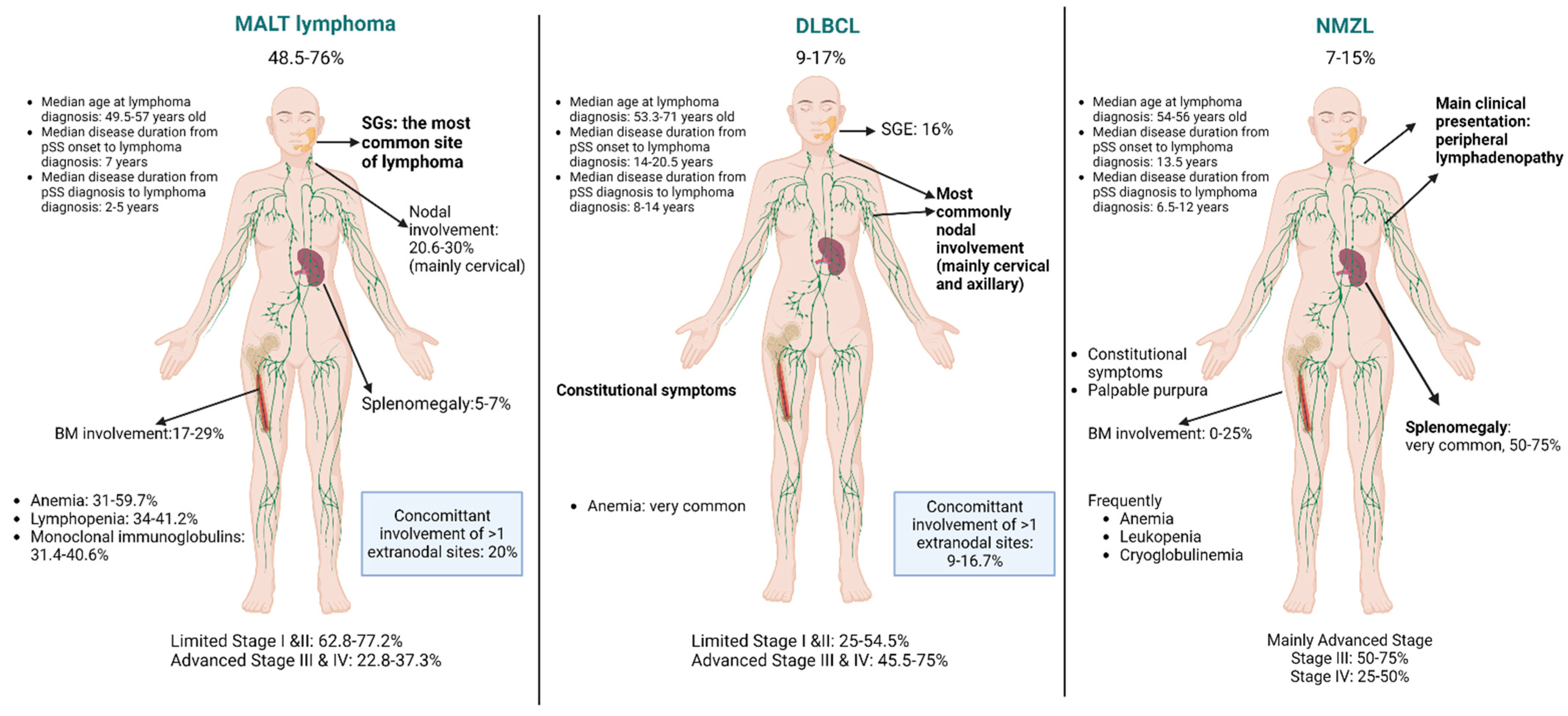
3.1. MALT Lymphomas
3.2. DLBCL
3.3. Nodal Marginal Zone Lymphomas
3.4. Other B-Cell NHLs
4. Outcome
4.1. Response to Treatment
4.2. Survival
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goules, A.V.; Tzioufas, A.G. Lymphomagenesis in Sjögren’s syndrome: Predictive biomarkers towards precision medicine. Autoimmun. Rev. 2019, 18, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stergiou, I.E.; Poulaki, A.; Voulgarelis, M. Pathogenetic Mechanisms Implicated in Sjögren’s Syndrome Lymphomagenesis: A Review of the Literature. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christodoulou, M.I.; Kapsogeorgou, E.K.; Moutsopoulos, H.M. Characteristics of the minor salivary gland infiltrates in Sjögren’s syndrome. J. Autoimmun. 2010, 34, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goules, A.V.; Tzioufas, A.G. Primary Sjӧgren’s syndrome: Clinical phenotypes, outcome and the development of biomarkers. Autoimmun. Rev. 2016, 15, 695–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Molina, G.; Kostov, B.; Brito-Zerón, P.; Vissink, A.; Mandl, T.; Hinrichs, A.C.; Quartuccio, L.; Baldini, C.; Seror, R.; Szántó, A.; et al. Characterization and outcomes of 414 patients with primary SS who developed hematological malignancies. Rheumatology 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theander, E.; Henriksson, G.; Ljungberg, O.; Mandl, T.; Manthorpe, R.; Jacobsson, L.T. Lymphoma and other malignancies in primary Sjögren’s syndrome: A cohort study on cancer incidence and lymphoma predictors. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2006, 65, 796–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stergiou, I.E.; Papageorgiou, A.; Chatzis, L.G.; Tzioufas, A.G.; Voulgarelis, M.; Goules, A. T cell lymphoma in the setting of Sjögren’s syndrome: T cells gone bad? Report of five cases from a single centre cohort. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2020, 38 (Suppl. 126), 125–129. [Google Scholar]
- Swerdlow, S.H.C.E.; Harris, N.L.; Jaffe, E.S.; Pileri, S.A.; Stein, H.; Thiele, J. World Health Organization Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues, 4th ed.; IARC: Lyon, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Baimpa, E.; Dahabreh, I.J.; Voulgarelis, M.; Moutsopoulos, H.M. Hematologic manifestations and predictors of lymphoma development in primary Sjögren syndrome: Clinical and pathophysiologic aspects. Medicine 2009, 88, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito-Zerón, P.; Kostov, B.; Fraile, G.; Caravia-Durán, D.; Maure, B.; Rascón, F.-J.; Zamora, M.; Casanovas, A.; Lopez-Dupla, M.; Ripoll, M.; et al. Characterization and risk estimate of cancer in patients with primary Sjögren syndrome. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2017, 10, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chatzis, L.G.; Stergiou, I.E.; Goules, A.V.; Pezoulas, V.; Tsourouflis, G.; Fotiadis, D.; Tzioufas, A.G.; Voulgarelis, M. Clinical picture, outcome and predictive factors of lymphoma in primary Sjögren’s syndrome: Results from a harmonized dataset (1981–2021). Rheumatology 2022, 61, 3576–3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papageorgiou, A.; Ziogas, D.C.; Mavragani, C.P.; Zintzaras, E.; Tzioufas, A.G.; Moutsopoulos, H.M.; Voulgarelis, M. Predicting the outcome of Sjogren’s syndrome-associated non-hodgkin’s lymphoma patients. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schenone, L.N.; Pellet, A.C.; Mamani, M.; Melo, F.; Adrover, M.; Barreira, J.; Dermarchi, J.; Escobar, C.S.; Santiago, L.; Salvatierra, G.; et al. Development of lymphoma in patients with primary Sjögren Syndrome OMICS Publishing Group. Int. J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2019, 14, 69–74. [Google Scholar]
- Voulgarelis, M.; Dafni, U.G.; Isenberg, D.A.; Moutsopoulos, H.M. Malignant lymphoma in primary Sjögren’s syndrome: A multicenter, retrospective, clinical study by the European Concerted Action on Sjögren’s Syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 1999, 42, 1765–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voulgarelis, M.; Ziakas, P.D.; Papageorgiou, A.; Baimpa, E.; Tzioufas, A.G.; Moutsopoulos, H.M. Prognosis and outcome of non-Hodgkin lymphoma in primary Sjögren syndrome. Medicine 2012, 91, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Royer, B.; Cazals-Hatem, D.; Sibilia, J.; Agbalika, F.; Cayuela, J.-M.; Soussi, T.; Maloisel, F.d.r.; Clauvel, J.-P.; Brouet, J.-C.; Mariette, X. Lymphomas in Patients with Sjögren’s Syndrome Are Marginal Zone B-Cell Neoplasms, Arise in Diverse Extranodal and Nodal Sites, and Are Not Associated with Viruses. Blood 1997, 90, 766–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vasaitis, L.; Nordmark, G.; Theander, E.; Backlin, C.; Smedby, K.E.; Askling, J.; Rönnblom, L.; Sundström, C.; Baecklund, E. Population-based study of patients with primary Sjögren’s syndrome and lymphoma: Lymphoma subtypes, clinical characteristics, and gender differences. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2020, 49, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solans-Laqué, R.; López-Hernandez, A.; Bosch-Gil, J.A.; Palacios, A.; Campillo, M.; Vilardell-Tarres, M. Risk, predictors, and clinical characteristics of lymphoma development in primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 41, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapinos, N.I.; Polihronis, M.; Moutsopoulos, H.M. Lymphoma development in Sjögren’s syndrome: Novel p53 mutations. Arthritis Rheum. 1999, 42, 1466–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisa, E.K.; Pisa, P.; Kang, H.I.; Fox, R.I. High frequency of t(14;18) translocation in salivary gland lymphomas from Sjögren’s syndrome patients. J. Exp. Med. 1991, 174, 1245–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ihrler, S.; Baretton, G.B.; Menauer, F.; Blasenbreu-Vogt, S.; Löhrs, U. Sjögren’s Syndrome and MALT Lymphomas of Salivary Glands: A DNA-Cytometric and Interphase-Cytogenetic Study. Mod. Pathol. 2000, 13, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alamanos, Y.; Tsifetaki, N.; Voulgari, P.V.; Venetsanopoulou, A.I.; Siozos, C.; Drosos, A.A. Epidemiology of primary Sjögren’s syndrome in north-west Greece, 1982–2003. Rheumatology 2006, 45, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brito-Zerón, P.; Kostov, B.; Solans, R.; Fraile, G.; Suárez-Cuervo, C.; Casanovas, A.; Rascón, F.J.; Qanneta, R.; Pérez-Alvarez, R.; Ripoll, M.; et al. Systemic activity and mortality in primary Sjögren syndrome: Predicting survival using the EULAR-SS Disease Activity Index (ESSDAI) in 1045 patients. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ioannidis, J.P.; Vassiliou, V.A.; Moutsopoulos, H.M. Long-term risk of mortality and lymphoproliferative disease and predictive classification of primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 2002, 46, 741–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skopouli, F.N.; Dafni, U.; Ioannidis, J.P.; Moutsopoulos, H.M. Clinical evolution, and morbidity and mortality of primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2000, 29, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theander, E.; Manthorpe, R.; Jacobsson, L.T. Mortality and causes of death in primary Sjögren’s syndrome: A prospective cohort study. Arthritis Rheum. 2004, 50, 1262–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos-Casals, M.; Cervera, R.; Font, J.; Garcóa-Carrasco, M.; Espinosa, G.; Reino, S.; Pallarés, L.; Ingelmo, M. Young Onset of Primary Sjögren’s syndrome: Clinical and immunological characteristics. Lupus 1998, 7, 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito-Zerón, P.; Ramos-Casals, M.; Bove, A.; Sentis, J.; Font, J. Predicting adverse outcomes in primary Sjogren’s syndrome: Identification of prognostic factors. Rheumatology 2007, 46, 1359–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fragkioudaki, S.; Mavragani, C.P.; Moutsopoulos, H.M. Predicting the risk for lymphoma development in Sjogren syndrome: An easy tool for clinical use. Medicine 2016, 95, e3766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnsen, S.J.; Brun, J.G.; Gøransson, L.G.; Småstuen, M.C.; Johannesen, T.B.; Haldorsen, K.; Harboe, E.; Jonsson, R.; Meyer, P.A.; Omdal, R. Risk of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma in primary Sjögren’s syndrome: A population-based study. Arthritis Care Res. 2013, 65, 816–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goules, A.V.; Argyropoulou, O.D.; Pezoulas, V.C.; Chatzis, L.; Critselis, E.; Gandolfo, S.; Ferro, F.; Binutti, M.; Donati, V.; Zandonella Callegher, S.; et al. Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome of Early and Late Onset: Distinct Clinical Phenotypes and Lymphoma Development. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 594096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldini, C.; Pepe, P.; Luciano, N.; Ferro, F.; Talarico, R.; Grossi, S.; Tavoni, A.; Bombardieri, S. A clinical prediction rule for lymphoma development in primary Sjögren’s syndrome. J. Rheumatol. 2012, 39, 804–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatzis, L.; Pezoulas, V.C.; Ferro, F.; Gandolfo, S.; Donati, V.; Binutti, M.; Callegher, S.Z.; Venetsanopoulou, A.; Zampeli, E.; Mavrommati, M.; et al. Sjögren’s Syndrome: The Clinical Spectrum of Male Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramírez Sepúlveda, J.I.; Kvarnström, M.; Eriksson, P.; Mandl, T.; Norheim, K.B.; Johnsen, S.J.; Hammenfors, D.; Jonsson, M.V.; Skarstein, K.; Brun, J.G.; et al. Long-term follow-up in primary Sjögren’s syndrome reveals differences in clinical presentation between female and male patients. Biol. Sex Differ. 2017, 8, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, M.Y.; Huang, Y.T.; Liu, M.F.; Lu, T.H. Incidence of cancer in a nationwide population cohort of 7852 patients with primary Sjogren’s syndrome in Taiwan. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2012, 71, 524–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thandra, K.C.; Barsouk, A.; Saginala, K.; Padala, S.A.; Barsouk, A.; Rawla, P. Epidemiology of Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. Med. Sci. 2021, 9, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gondran, G.; Fauchais, A.; Lambert, M.; Ly, K.; Launay, D.; Queyrel, V.; Benazahari, H.; Liozon, E.; Loustaud-Ratti, V.; Hachulla, E.; et al. Primary Sjogren’s syndrome in men. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2008, 37, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassan, S.S.; Thomas, T.L.; Moutsopoulos, H.M.; Hoover, R.; Kimberly, R.P.; Budman, D.R.; Costa, J.; Decker, J.L.; Chused, T.M. Increased risk of lymphoma in sicca syndrome. Ann. Intern. Med. 1978, 89, 888–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrol, E.; González-Pulido, C.; Praena-Fernández, J.M.; Isenberg, D.A. A retrospective study of long-term outcomes in 152 patients with primary Sjogren’s syndrome: 25-year experience. Clin. Med. 2014, 14, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vita, S.; Gandolfo, S.; Zandonella Callegher, S.; Zabotti, A.; Quartuccio, L. The evaluation of disease activity in Sjögren’s syndrome based on the degree of MALT involvement: Glandular swelling and cryoglobulinaemia compared to ESSDAI in a cohort study. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2018, 36 (Suppl. 112), 150–156. [Google Scholar]
- Nocturne, G.; Virone, A.; Ng, W.F.; Le Guern, V.; Hachulla, E.; Cornec, D.; Daien, C.; Vittecoq, O.; Bienvenu, B.; Marcelli, C.; et al. Rheumatoid Factor and Disease Activity Are Independent Predictors of Lymphoma in Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016, 68, 977–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quartuccio, L.; Isola, M.; Baldini, C.; Priori, R.; Bartoloni Bocci, E.; Carubbi, F.; Maset, M.; Gregoraci, G.; Della Mea, V.; Salvin, S.; et al. Biomarkers of lymphoma in Sjögren’s syndrome and evaluation of the lymphoma risk in prelymphomatous conditions: Results of a multicenter study. J. Autoimmun. 2014, 51, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Risselada, A.P.; Kruize, A.A.; Bijlsma, J.W. Clinical features distinguishing lymphoma development in primary Sjögren’s Syndrome--a retrospective cohort study. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 43, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutcliffe, N.; Inanc, M.; Speight, P.; Isenberg, D. Predictors of lymphoma development in primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 1998, 28, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Feng, S.; Yan, S.; Zhao, Y.; Li, M.; Sun, J.; Zhang, F.C.; Cui, Q.; Dong, Y. Incidence of malignancy in primary Sjogren’s syndrome in a Chinese cohort. Rheumatology 2010, 49, 571–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Vita, S.; Isola, M.; Baldini, C.; Goules, A.V.; Chatzis, L.G.; Quartuccio, L.; Zabotti, A.; Giovannini, I.; Donati, V.; Ferro, F.; et al. Predicting lymphoma in Sjögren’s syndrome and the pathogenetic role of parotid microenvironment through precise parotid swelling recording. Rheumatology 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goules, A.; Masouridi, S.; Tzioufas, A.G.; Ioannidis, J.P.; Skopouli, F.N.; Moutsopoulos, H.M. Clinically significant and biopsy-documented renal involvement in primary Sjögren syndrome. Medicine 2000, 79, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzioufas, A.G.; Manoussakis, M.N.; Costello, R.; Silis, M.; Papadopoulos, N.M.; Moutsopoulos, H.M. Cryoglobulinemia in autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Evidence of circulating monoclonal cryoglobulins in patients with primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 1986, 29, 1098–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzioufas, A.G.; Boumba, D.S.; Skopouli, F.N.; Moutsopoulos, H.M. Mixed monoclonal cryoglobulinemia and monoclonal rheumatoid factor cross-reactive idiotypes as predictive factors for the development of lymphoma in primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 1996, 39, 767–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldini, C.; Pepe, P.; Quartuccio, L.; Priori, R.; Bartoloni, E.; Alunno, A.; Gattamelata, A.; Maset, M.; Modesti, M.; Tavoni, A.; et al. Primary Sjogren’s syndrome as a multi-organ disease: Impact of the serological profile on the clinical presentation of the disease in a large cohort of Italian patients. Rheumatology 2014, 53, 839–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martel, C.; Gondran, G.; Launay, D.; Lalloué, F.; Palat, S.; Lambert, M.; Ly, K.; Loustaud-Ratti, V.; Bezanahary, H.; Hachulla, E.; et al. Active immunological profile is associated with systemic Sjögren’s syndrome. J. Clin. Immunol. 2011, 31, 840–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nocturne, G.; Seror, R.; Fogel, O.; Belkhir, R.; Boudaoud, S.; Saraux, A.; Larroche, C.; Le Guern, V.; Gottenberg, J.E.; Mariette, X. CXCL13 and CCL11 Serum Levels and Lymphoma and Disease Activity in Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 3226–3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Argyropoulou, O.D.; Pezoulas, V.; Chatzis, L.; Critselis, E.; Gandolfo, S.; Ferro, F.; Quartuccio, L.; Donati, V.; Treppo, E.; Bassoli, C.R.; et al. Cryoglobulinemic vasculitis in primary Sjögren’s Syndrome: Clinical presentation, association with lymphoma and comparison with Hepatitis C-related disease. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2020, 50, 846–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theander, E.; Vasaitis, L.; Baecklund, E.; Nordmark, G.; Warfvinge, G.; Liedholm, R.; Brokstad, K.; Jonsson, R.; Jonsson, M.V. Lymphoid organisation in labial salivary gland biopsies is a possible predictor for the development of malignant lymphoma in primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2011, 70, 1363–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottenberg, J.E.; Seror, R.; Miceli-Richard, C.; Benessiano, J.; Devauchelle-Pensec, V.; Dieude, P.; Dubost, J.J.; Fauchais, A.L.; Goeb, V.; Hachulla, E.; et al. Serum levels of beta2-microglobulin and free light chains of immunoglobulins are associated with systemic disease activity in primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Data at enrollment in the prospective ASSESS cohort. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walters, M.T.; Stevenson, F.K.; Herbert, A.; Cawley, M.I.; Smith, J.L. Urinary monoclonal free light chains in primary Sjögren’s syndrome: An aid to the diagnosis of malignant lymphoma. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1986, 45, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chatzis, L.G.; Pezoulas, V.; Voulgari, P.V.; Baldini, C.; Exarchos, T.P.; Fotiadis, D.I.; Mavragani, C.P.; Skopouli, F.N.; Moutsopoulos, H.M.; Tzioufas, A.G.; et al. Combined seronegativity in Sjögren’s syndrome. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2021, 39 (Suppl. 133), 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quartuccio, L.; Baldini, C.; Bartoloni, E.; Priori, R.; Carubbi, F.; Corazza, L.; Alunno, A.; Colafrancesco, S.; Luciano, N.; Giacomelli, R.; et al. Anti-SSA/SSB-negative Sjögren’s syndrome shows a lower prevalence of lymphoproliferative manifestations, and a lower risk of lymphoma evolution. Autoimmun. Rev. 2015, 14, 1019–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pertovaara, M.; Pukkala, E.; Laippala, P.; Miettinen, A.; Pasternack, A. A longitudinal cohort study of Finnish patients with primary Sjögren’s syndrome: Clinical, immunological, and epidemiological aspects. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2001, 60, 467–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agmon-Levin, N.; Kivity, S.; Tzioufas, A.G.; López Hoyos, M.; Rozman, B.; Efes, I.; Shapira, Y.; Shamis, A.; Amital, H.; Youinou, P.; et al. Low levels of vitamin-D are associated with neuropathy and lymphoma among patients with Sjögren’s syndrome. J. Autoimmun. 2012, 39, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerli, R.; Muscat, C.; Giansanti, M.; Danieli, M.G.; Sciuto, M.; Gabrielli, A.; Fiandra, E.; Vitali, C. Quantitative assessment of salivary gland inflammatory infiltration in primary Sjögren’s syndrome: Its relationship to different demographic, clinical and serological features of the disorder. Br. J. Rheumatol. 1997, 36, 969–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brito-Zerón, P.; Retamozo, S.; Ramos-Casals, M. Phenotyping Sjögren’s syndrome: Towards a personalised management of the disease. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2018, 36 (Suppl. 112), 198–209. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Carubbi, F.; Alunno, A.; Cipriani, P.; Bartoloni, E.; Baldini, C.; Quartuccio, L.; Priori, R.; Valesini, G.; De Vita, S.; Bombardieri, S.; et al. A retrospective, multicenter study evaluating the prognostic value of minor salivary gland histology in a large cohort of patients with primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Lupus 2015, 24, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Risselada, A.P.; Kruize, A.A.; Goldschmeding, R.; Lafeber, F.P.; Bijlsma, J.W.; van Roon, J.A. The prognostic value of routinely performed minor salivary gland assessments in primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 73, 1537–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzis, L.; Goules, A.V.; Pezoulas, V.; Baldini, C.; Gandolfo, S.; Skopouli, F.N.; Exarchos, T.P.; Kapsogeorgou, E.K.; Donati, V.; Voulgari, P.V.; et al. A biomarker for lymphoma development in Sjogren’s syndrome: Salivary gland focus score. J. Autoimmun. 2021, 121, 102648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haacke, E.A.; van der Vegt, B.; Vissink, A.; Spijkervet, F.K.L.; Bootsma, H.; Kroese, F.G.M. Germinal centres in diagnostic labial gland biopsies of patients with primary Sjögren’s syndrome are not predictive for parotid MALT lymphoma development. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 1781–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mossel, E.; Delli, K.; van Nimwegen, J.F.; Stel, A.J.; Kroese, F.G.M.; Spijkervet, F.K.L.; Vissink, A.; Arends, S.; Bootsma, H. Ultrasonography of major salivary glands compared with parotid and labial gland biopsy and classification criteria in patients with clinically suspected primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 1883–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pijpe, J.; Kalk, W.W.I.; van der Wal, J.E.; Vissink, A.; Kluin, P.M.; Roodenburg, J.L.N.; Bootsma, H.; Kallenberg, C.G.M.; Spijkervet, F.K.L. Parotid gland biopsy compared with labial biopsy in the diagnosis of patients with primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Rheumatology 2007, 46, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Nimwegen, J.F.; van Ginkel, M.S.; Arends, S.; Haacke, E.A.; van der Vegt, B.; Sillevis Smitt-Kamminga, N.; Spijkervet, F.K.L.; Kroese, F.G.M.; Stel, A.J.; Brouwer, E.; et al. Validation of the ACR-EULAR criteria for primary Sjögren’s syndrome in a Dutch prospective diagnostic cohort. Rheumatology 2018, 57, 818–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Voulgarelis, M.; Moutsopoulos, H.M. Lymphoproliferation in autoimmunity and Sjögren’s syndrome. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2003, 5, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stott, D.I.; Hiepe, F.; Hummel, M.; Steinhauser, G.; Berek, C. Antigen-driven clonal proliferation of B cells within the target tissue of an autoimmune disease. The salivary glands of patients with Sjögren’s syndrome. J. Clin. Investig. 1998, 102, 938–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jordan, R.C.; Masaki, Y.; Takeshita, S.; Speight, P.M.; Sugai, S. High prevalence of B-cell monoclonality in labial gland biopsies of Japanese Sjögren’s syndrome patients. Int. J. Hematol. 1996, 64, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miklos, J.A.; Swerdlow, S.H.; Bahler, D.W. Salivary gland mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma immunoglobulin VH genes show frequent use of V1-69 with distinctive CDR3 features. Blood 2000, 95, 3878–3884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visser, A.; Verstappen, G.M.; van der Vegt, B.; Vissink, A.; Bende, R.J.; Bootsma, H.; Bos, N.A.; Kroese, F.G.M. Repertoire Analysis of B-Cells Located in Striated Ducts of Salivary Glands of Patients with Sjögren’s Syndrome. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bende, R.J.; Janssen, J.; Beentjes, A.; Wormhoudt, T.A.M.; Wagner, K.; Haacke, E.A.; Kroese, F.G.M.; Guikema, J.E.J.; van Noesel, C.J.M. Salivary Gland Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue-Type Lymphoma From Sjögren’s Syndrome Patients in the Majority Express Rheumatoid Factors Affinity-Selected for IgG. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020, 72, 1330–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bende, R.J.; Aarts, W.M.; Riedl, R.G.; de Jong, D.; Pals, S.T.; van Noesel, C.J. Among B cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas, MALT lymphomas express a unique antibody repertoire with frequent rheumatoid factor reactivity. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 201, 1229–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broeren, M.G.A.; Wang, J.J.; Balzaretti, G.; Groenen, P.; van Schaik, B.D.C.; Chataway, T.; Kaffa, C.; Bervoets, S.; Hebeda, K.M.; Bounova, G.; et al. Proteogenomic analysis of the autoreactive B cell repertoire in blood and tissues of patients with Sjögren’s syndrome. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2022, 81, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bende, R.J.; Slot, L.M.; Hoogeboom, R.; Wormhoudt, T.A.; Adeoye, A.O.; Guikema, J.E.; van Noesel, C.J. Stereotypic rheumatoid factors that are frequently expressed in mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue-type lymphomas are rare in the labial salivary glands of patients with Sjögren’s syndrome. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 1074–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Jackson, K.J.L.; Wang, J.J.; Schofield, P.; Field, M.A.; Koppstein, D.; Peters, T.J.; Burnett, D.L.; Rizzetto, S.; Nevoltris, D.; et al. Lymphoma Driver Mutations in the Pathogenic Evolution of an Iconic Human Autoantibody. Cell 2020, 180, 878–894.e819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vita, S.; Boiocchi, M.; Sorrentino, D.; Carbone, A.; Avellini, C.; Dolcetti, R.; Marzotto, A.; Gloghini, A.; Bartoli, E.; Beltrami, C.A.; et al. Characterization of prelymphomatous stages of B cell lymphoproliferation in Sjögren’s syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 1997, 40, 318–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Re, V.; De Vita, S.; Gasparotto, D.; Marzotto, A.; Carbone, A.; Ferraccioli, G.; Boiocchi, M. Salivary gland B cell lymphoproliferative disorders in Sjögren’s syndrome present a restricted use of antigen receptor gene segments similar to those used by hepatitis C virus-associated non-Hodgkins’s lymphomas. Eur. J. Immunol. 2002, 32, 903–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, A.; Gloghini, A.; Ferlito, A. Pathological features of lymphoid proliferations of the salivary glands: Lymphoepithelial sialadenitis versus low-grade B-cell lymphoma of the malt type. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2000, 109, 1170–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haacke, E.A.; van der Vegt, B.; Vissink, A.; Spijkervet, F.K.L.; Bootsma, H.; Kroese, F.G.M. Germinal Centers in Diagnostic Biopsies of Patients with Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome Are Not a Risk Factor for Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma but a Reflection of High Disease Activity: Comment on the Article by Sène et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 170–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Risselada, A.P.; Looije, M.F.; Kruize, A.A.; Bijlsma, J.W.; van Roon, J.A. The role of ectopic germinal centers in the immunopathology of primary Sjögren’s syndrome: A systematic review. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 42, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sène, D.; Ismael, S.; Forien, M.; Charlotte, F.; Kaci, R.; Cacoub, P.; Diallo, A.; Dieudé, P.; Lioté, F. Ectopic Germinal Center-Like Structures in Minor Salivary Gland Biopsy Tissue Predict Lymphoma Occurrence in Patients with Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018, 70, 1481–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnsen, S.J.; Berget, E.; Jonsson, M.V.; Helgeland, L.; Omdal, R.; Jonsson, R. Evaluation of germinal center-like structures and B cell clonality in patients with primary Sjögren syndrome with and without lymphoma. J. Rheumatol. 2014, 41, 2214–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakshbandi, U.; Haacke, E.A.; Bootsma, H.; Vissink, A.; Spijkervet, F.K.L.; van der Vegt, B.; Kroese, F.G.M. Bcl6 for identification of germinal centres in salivary gland biopsies in primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Oral Dis. 2020, 26, 707–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barone, F.; Bombardieri, M.; Manzo, A.; Blades, M.C.; Morgan, P.R.; Challacombe, S.J.; Valesini, G.; Pitzalis, C. Association of CXCL13 and CCL21 expression with the progressive organization of lymphoid-like structures in Sjögren’s syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 2005, 52, 1773–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bombardieri, M.; Barone, F.; Humby, F.; Kelly, S.; McGurk, M.; Morgan, P.; Challacombe, S.; De Vita, S.; Valesini, G.; Spencer, J.; et al. Activation-induced cytidine deaminase expression in follicular dendritic cell networks and interfollicular large B cells supports functionality of ectopic lymphoid neogenesis in autoimmune sialoadenitis and MALT lymphoma in Sjögren’s syndrome. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 4929–4938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delli, K.; Haacke, E.A.; Ihrler, S.; van der Vegt, B.; Vissink, A.; Bootsma, H.; Spijkervet, F.K.; Kroese, F.G. Need for consensus guidelines to standardise the assessment of germinal centres and other histopathological parameters in salivary gland tissue of patients with primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, e32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jonsson, M.V.; Skarstein, K. Follicular dendritic cells confirm lymphoid organization in the minor salivary glands of primary Sjögren’s syndrome. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2008, 37, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, B.A.; Jonsson, R.; Daniels, T.; Bombardieri, M.; Brown, R.M.; Morgan, P.; Bombardieri, S.; Ng, W.-F.; Tzioufas, A.G.; Vitali, C.; et al. Standardisation of labial salivary gland histopathology in clinical trials in primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 1161–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barone, F.; Bombardieri, M.; Rosado, M.M.; Morgan, P.R.; Challacombe, S.J.; De Vita, S.; Carsetti, R.; Spencer, J.; Valesini, G.; Pitzalis, C. CXCL13, CCL21, and CXCL12 expression in salivary glands of patients with Sjogren’s syndrome and MALT lymphoma: Association with reactive and malignant areas of lymphoid organization. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 5130–5140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Quartuccio, L.; Baldini, C.; Bartoloni, E.; Priori, R.; Carubbi, F.; Alunno, A.; Gandolfo, S.; Gattamelata, A.; Giacomelli, R.; Gerli, R.; et al. Correlation between ESSDAI and ClinESSDAI in a real-life cohort of patients with Sjögren’s syndrome. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2017, 35, 546–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackay, F.; Groom, J.R.; Tangye, S.G. An important role for B-cell activation factor and B cells in the pathogenesis of Sjögren’s syndrome. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2007, 19, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nezos, A.; Papageorgiou, A.; Fragoulis, G.; Ioakeimidis, D.; Koutsilieris, M.; Tzioufas, A.G.; Moutsopoulos, H.M.; Voulgarelis, M.; Mavragani, C.P. B-cell activating factor genetic variants in lymphomagenesis associated with primary Sjogren’s syndrome. J. Autoimmun. 2014, 51, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papageorgiou, A.; Mavragani, C.P.; Nezos, A.; Zintzaras, E.; Quartuccio, L.; De Vita, S.; Koutsilieris, M.; Tzioufas, A.G.; Moutsopoulos, H.M.; Voulgarelis, M. A BAFF receptor His159Tyr mutation in Sjögren’s syndrome-related lymphoproliferation. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 2732–2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildebrand, J.M.; Luo, Z.; Manske, M.K.; Price-Troska, T.; Ziesmer, S.C.; Lin, W.; Hostager, B.S.; Slager, S.L.; Witzig, T.E.; Ansell, S.M.; et al. A BAFF-R mutation associated with non-Hodgkin lymphoma alters TRAF recruitment and reveals new insights into BAFF-R signaling. J. Exp. Med. 2010, 207, 2569–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nocturne, G.; Boudaoud, S.; Miceli-Richard, C.; Viengchareun, S.; Lazure, T.; Nititham, J.; Taylor, K.E.; Ma, A.; Busato, F.; Melki, J.; et al. Germline and somatic genetic variations of TNFAIP3 in lymphoma complicating primary Sjogren’s syndrome. Blood 2013, 122, 4068–4076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nezos, A.; Gkioka, E.; Koutsilieris, M.; Voulgarelis, M.; Tzioufas, A.G.; Mavragani, C.P. TNFAIP3 F127C Coding Variation in Greek Primary Sjogren’s Syndrome Patients. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018, 6923213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Korona, B.; Korona, D.; Zhao, W.; Wotherspoon, A.C.; Du, M.Q. GPR34 activation potentially bridges lymphoepithelial lesions to genesis of salivary gland MALT lymphoma. Blood 2022, 139, 2186–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintanilla-Martinez, L.; Fend, F. Turning up the heat on salivary gland MALT lymphoma. Blood 2022, 139, 2094–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathijs, B.; Julio Finalet, F.; Thomas, T.; Helena, U.; Lucienne, M.; de Laurence, L.; Daan, D.; Pascal, W.; Xavier, S.; Peter, V.; et al. t(X;14)(p11.4;q32.33) is recurrent in marginal zone lymphoma and up-regulates GPR34. Haematologica 2012, 97, 184–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moody, S.; Thompson, J.S.; Chuang, S.S.; Liu, H.; Raderer, M.; Vassiliou, G.; Wlodarska, I.; Wu, F.; Cogliatti, S.; Robson, A.; et al. Novel GPR34 and CCR6 mutation and distinct genetic profiles in MALT lymphomas of different sites. Haematologica 2018, 103, 1329–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nezos, A.; Makri, P.; Gandolfo, S.; De Vita, S.; Voulgarelis, M.; Crow, M.K.; Mavragani, C.P. TREX1 variants in Sjogren’s syndrome related lymphomagenesis. Cytokine 2020, 132, 154781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argyriou, E.; Nezos, A.; Roussos, P.; Venetsanopoulou, A.; Voulgarelis, M.; Boki, K.; Tzioufas, A.G.; Moutsopoulos, H.M.; Mavragani, C.P. Leukocyte Immunoglobulin-Like Receptor A3 (LILRA3): A Novel Marker for Lymphoma Development among Patients with Young Onset Sjogren’s Syndrome. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colafrancesco, S.; Ciccacci, C.; Priori, R.; Latini, A.; Picarelli, G.; Arienzo, F.; Novelli, G.; Valesini, G.; Perricone, C.; Borgiani, P. STAT4, TRAF3IP2, IL10, and HCP5 Polymorphisms in Sjögren’s Syndrome: Association with Disease Susceptibility and Clinical Aspects. J. Immunol. Res. 2019, 2019, 7682827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gourzi, V.C.; Kapsogeorgou, E.K.; Kyriakidis, N.C.; Tzioufas, A.G. Study of microRNAs (miRNAs) that are predicted to target the autoantigens Ro/SSA and La/SSB in primary Sjögren’s Syndrome. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2015, 182, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kapsogeorgou, E.K.; Gourzi, V.C.; Manoussakis, M.N.; Moutsopoulos, H.M.; Tzioufas, A.G. Cellular microRNAs (miRNAs) and Sjögren’s syndrome: Candidate regulators of autoimmune response and autoantigen expression. J. Autoimmun. 2011, 37, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapsogeorgou, E.K.; Papageorgiou, A.; Protogerou, A.D.; Voulgarelis, M.; Tzioufas, A.G. Low miR200b-5p levels in minor salivary glands: A novel molecular marker predicting lymphoma development in patients with Sjögren’s syndrome. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 77, 1200–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fragkioudaki, S.; Nezos, A.; Souliotis, V.L.; Chatziandreou, I.; Saetta, A.A.; Drakoulis, N.; Tzioufas, A.G.; Voulgarelis, M.; Sfikakis, P.P.; Koutsilieris, M.; et al. MTHFR gene variants and non-MALT lymphoma development in primary Sjogren’s syndrome. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mavragani, C.P.; Nezos, A.; Sagalovskiy, I.; Seshan, S.; Kirou, K.A.; Crow, M.K. Defective regulation of L1 endogenous retroelements in primary Sjogren’s syndrome and systemic lupus erythematosus: Role of methylating enzymes. J. Autoimmun. 2018, 88, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sisto, M.; Lisi, S.; Lofrumento, D.D.; Ingravallo, G.; Maiorano, E.; D’Amore, M. A failure of TNFAIP3 negative regulation maintains sustained NF-κB activation in Sjögren’s syndrome. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2011, 135, 615–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnsen, S.J.; Gudlaugsson, E.; Skaland, I.; Janssen, E.A.; Jonsson, M.V.; Helgeland, L.; Berget, E.; Jonsson, R.; Omdal, R. Low Protein A20 in Minor Salivary Glands is Associated with Lymphoma in Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome. Scand. J. Immunol. 2016, 83, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nezos, A.; Gravani, F.; Tassidou, A.; Kapsogeorgou, E.K.; Voulgarelis, M.; Koutsilieris, M.; Crow, M.K.; Mavragani, C.P. Type I and II interferon signatures in Sjogren’s syndrome pathogenesis: Contributions in distinct clinical phenotypes and Sjogren’s related lymphomagenesis. J. Autoimmun. 2015, 63, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cinoku, I.I.; Verrou, K.M.; Piperi, E.; Voulgarelis, M.; Moutsopoulos, H.M.; Mavragani, C.P. Interferon (IFN)-stimulated gene 15: A novel biomarker for lymphoma development in Sjögren’s syndrome. J. Autoimmun. 2021, 123, 102704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldini, C.; Santini, E.; Rossi, C.; Donati, V.; Solini, A. The P2X7 receptor-NLRP3 inflammasome complex predicts the development of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma in Sjogren’s syndrome: A prospective, observational, single-centre study. J. Intern. Med. 2017, 282, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakrakou, A.G.; Boiu, S.; Ziakas, P.D.; Xingi, E.; Boleti, H.; Manoussakis, M.N. Systemic activation of NLRP3 inflammasome in patients with severe primary Sjögren’s syndrome fueled by inflammagenic DNA accumulations. J. Autoimmun. 2018, 91, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoussakis, M.N.; Boiu, S.; Korkolopoulou, P.; Kapsogeorgou, E.K.; Kavantzas, N.; Ziakas, P.; Patsouris, E.; Moutsopoulos, H.M. Rates of infiltration by macrophages and dendritic cells and expression of interleukin-18 and interleukin-12 in the chronic inflammatory lesions of Sjögren’s syndrome: Correlation with certain features of immune hyperactivity and factors associated with high risk of lymphoma development. Arthritis Rheum. 2007, 56, 3977–3988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nezos, A.; Skarlis, C.; Psarrou, A.; Markakis, K.; Garantziotis, P.; Papanikolaou, A.; Gravani, F.; Voulgarelis, M.; Tzioufas, A.G.; Koutsilieris, M.; et al. Lipoprotein-Associated Phospholipase A2: A Novel Contributor in Sjögren’s Syndrome-Related Lymphoma? Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 683623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quartuccio, L.; Salvin, S.; Fabris, M.; Maset, M.; Pontarini, E.; Isola, M.; De Vita, S. BLyS upregulation in Sjogren’s syndrome associated with lymphoproliferative disorders, higher ESSDAI score and B-cell clonal expansion in the salivary glands. Rheumatology 2013, 52, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Antonysamy, M.A.; Thomson, A.W. Flt3 ligand (FL) and its influence on immune reactivity. Cytokine 2000, 12, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobón, G.J.; Renaudineau, Y.; Hillion, S.; Cornec, D.; Devauchelle-Pensec, V.; Youinou, P.; Pers, J.O. The Fms-like tyrosine kinase 3 ligand, a mediator of B cell survival, is also a marker of lymphoma in primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 3447–3456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobón, G.J.; Saraux, A.; Gottenberg, J.E.; Quartuccio, L.; Fabris, M.; Seror, R.; Devauchelle-Pensec, V.; Morel, J.; Rist, S.; Mariette, X.; et al. Role of Fms-like tyrosine kinase 3 ligand as a potential biologic marker of lymphoma in primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 65, 3218–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traianos, E.Y.; Locke, J.; Lendrem, D.; Bowman, S.; Hargreaves, B.; Macrae, V.; Tarn, J.R.; Ng, W.F. Serum CXCL13 levels are associated with lymphoma risk and lymphoma occurrence in primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Rheumatol. Int. 2020, 40, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allen, C.D.; Ansel, K.M.; Low, C.; Lesley, R.; Tamamura, H.; Fujii, N.; Cyster, J.G. Germinal center dark and light zone organization is mediated by CXCR4 and CXCR5. Nat. Immunol. 2004, 5, 943–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzis, L.; Goules, A.V.; Stergiou, I.E.; Voulgarelis, M.; Tzioufas, A.G.; Kapsogeorgou, E.K. Serum, but Not Saliva, CXCL13 Levels Associate with Infiltrating CXCL13+ Cells in the Minor Salivary Gland Lesions and Other Histologic Parameters in Patients with Sjögren’s Syndrome. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 705079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, S.F.; Artis, D. Sensing the outside world: TSLP regulates barrier immunity. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandolfo, S.; Bulfoni, M.; Fabro, C.; Russi, S.; Sansonno, D.; Di Loreto, C.; Cesselli, D.; De Vita, S. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin expression from benign lymphoproliferation to malignant B-cell lymphoma in primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2019, 37 (Suppl. 118), 55–64. [Google Scholar]
- Gandolfo, S.; Fabro, C.; Kapsogeorgou, E.; Colafrancesco, S.; Ferro, F.; Bartoloni, E.; Quartuccio, L.; Goules, A.; Priori, R.; Alunno, A.; et al. Validation of thymic stromal lymphopoietin as a biomarker of primary Sjögren’s syndrome and related lymphoproliferation: Results in independent cohorts. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2020, 38 (Suppl. 126), 189–194. [Google Scholar]
- Devauchelle-Pensec, V.; Zabotti, A.; Carvajal-Alegria, G.; Filipovic, N.; Jousse-Joulin, S.; De Vita, S. Salivary gland ultrasonography in primary Sjögren’s syndrome: Opportunities and challenges. Rheumatology 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coiffier, G.; Martel, A.; Albert, J.D.; Lescoat, A.; Bleuzen, A.; Perdriger, A.; De Bandt, M.; Maillot, F. Ultrasonographic damages of major salivary glands are associated with cryoglobulinemic vasculitis and lymphoma in primary Sjogren’s syndrome: Are the ultrasonographic features of the salivary glands new prognostic markers in Sjogren’s syndrome? Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, e111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Theander, E.; Mandl, T. Primary Sjögren’s syndrome: Diagnostic and prognostic value of salivary gland ultrasonography using a simplified scoring system. Arthritis Care Res. 2014, 66, 1102–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzon, M.; Tulipano Di Franco, F.; Zabotti, A.; Pegolo, E.; Giovannini, I.; Manfrè, V.; Mansutti, E.; De Vita, S.; Zuiani, C.; Girometti, R. Sonographic features of lymphoma of the major salivary glands diagnosed with ultrasound-guided core needle biopsy in Sjögren’s syndrome. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2021, 39 (Suppl. 133), 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzon, M.; Spina, E.; Tulipano Di Franco, F.; Giovannini, I.; De Vita, S.; Zabotti, A. Salivary Gland Ultrasound in Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome: Current and Future Perspectives. Open Access Rheumatol. 2022, 14, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldini, C.; Zabotti, A.; Filipovic, N.; Vukicevic, A.; Luciano, N.; Ferro, F.; Lorenzon, M.; De Vita, S. Imaging in primary Sjögren’s syndrome: The ‘obsolete and the new’. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2018, 36 (Suppl. 112), 215–221. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Grevers, G.; Ihrler, S.; Vogl, T.J.; Weiss, M. A comparison of clinical, pathological and radiological findings with magnetic resonance imaging studies of lymphomas in patients with Sjögren’s syndrome. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 1994, 251, 214–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Wang, P.; Yang, J.; Yu, Q. Non-Hodgkin lymphoma involving the parotid gland: CT and MR imaging findings. Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. 2013, 42, 20130046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bădărînză, M.; Serban, O.; Maghear, L.; Bocsa, C.; Micu, M.; Damian, L.; Felea, I.; Fodor, D. Shear wave elastography as a new method to identify parotid lymphoma in primary Sjögren Syndrome patients: An observational study. Rheumatol. Int. 2020, 40, 1275–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, C.; Mekinian, A.; Uzunhan, Y.; Fauchais, A.L.; Dhote, R.; Pop, G.; Eder, V.; Nunes, H.; Brillet, P.Y.; Valeyre, D.; et al. 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computer tomography as an objective tool for assessing disease activity in Sjögren’s syndrome. Autoimmun. Rev. 2013, 12, 1109–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keraen, J.; Blanc, E.; Besson, F.L.; Leguern, V.; Meyer, C.; Henry, J.; Belkhir, R.; Nocturne, G.; Mariette, X.; Seror, R. Usefulness of (18) F-Labeled Fluorodeoxyglucose-Positron Emission Tomography for the Diagnosis of Lymphoma in Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 1147–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorodetskiy, V.; Probatova, N.; Obukhova, T.; Vasilyev, V. Analysis of prognostic factors in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma associated with rheumatic diseases. Lupus Sci. Med. 2021, 8, e000561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorodetskiy, V.R.; Probatova, N.A.; Radenska-Lopovok, S.G.; Ryzhikova, N.V.; Sidorova, Y.V.; Sudarikov, A.B. Clonal relationship of marginal zone lymphoma and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in Sjogren’s syndrome patients: Case series study and review of the literature. Rheumatol. Int. 2020, 40, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kourou, K.D.; Pezoulas, V.C.; Georga, E.I.; Exarchos, T.; Papaloukas, C.; Voulgarelis, M.; Goules, A.; Nezos, A.; Tzioufas, A.G.; Moutsopoulos, E.M.; et al. Predicting Lymphoma Development by Exploiting Genetic Variants and Clinical Findings in a Machine Learning-Based Methodology with Ensemble Classifiers in a Cohort of Sjögren’s Syndrome Patients. IEEE Open J. Eng. Med. Biol. 2020, 1, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorodetskiy, V.R.; Probatova, N.A.; Vasilyev, V.I. Characteristics of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in patients with primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 23, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vasaitis, L.; Nordmark, G.; Theander, E.; Backlin, C.; Smedby, K.E.; Askling, J.; Rönnblom, L.; Sundström, C.; Baecklund, E. Comparison of patients with and without pre-existing lymphoma at diagnosis of primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2019, 48, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Classical | Newly Proposed | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical | SGE [11,18,24,28,29,32,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45] Skin vasculitis/Palpable purpura [6,14,18,24,25,39,43,44] Lymphadenopathy [9,14,29,38,44,45] Splenomegaly [9,38] Raynaud [29] Peripheral nerve involvement [14,43] Glomerulonephritis [25,43,47] | Disease activity | ESSDAI [11,23,41] |
| Serological | Cryoglobulinemia [9,10,11,25,40,41,42,49,50,51] RF positivity [29,41,49,50] Anti-Ro/SSA [29,142] Anti-La/SSB [29,42,142] Low serum C4 levels [6,9,10,18,24,25,29,32,41,42,43,50] Low serum C3 levels [6,10,18,32,50] Monoclonal Igs [10,29,43,45] Hypergammaglobulinemia [18,45,50] Serum and urine Ig light chains and their kappa/lamda ratio [143] β2 microglobulin [55,59] | Genetics | BAFF polymorphisms [96] BAFF-R His159Tyr mutation [97,98] TNFAIP3 variants [99,100] GPR34 translocations/mutations [103,104] TREX variants [105] LILRA3 variant [106] HCP5 rs3099844 variant [107] |
| Epigenetics | Low miR200b-5p levels in MSGs [110] MTHFR SNPs [111] LINE1-retroelements [112] | ||
| Hematological | Anemia [10,14,18] Leukopenia [18,42] Lymphopenia [9,14,18,41] Neutropenia [9] CD4+ T lymphopenia [6] Low CD4+/CD8+ ratio ≤ 0.8 [6] | Gene expression | Decreased A20 expression in MSGs [113,114] High IFNγ/IFNα mRNA ratio in MSGs [115] High ISG-15 expression [116] P2X7R-inflammasome complex [117] Increased Lp-PLA2 [120] |
| Histological | Ectopic GCs [54,85] MSG FS [11,64,65] AID distribution in ectopic GCs [89] | Proteins | Increased BAFF serum levels [52,55,121] Increased FLT-3L serum levels [123,124] Increased CXCL13 serum levels [52,125] Increased serum TSLP levels [130] |
| Imaging | SGUS: OMERACT score, hypoechoic lesions [132,133,134,135] PET/CT: SUVmax of ≥4.7 and/or focal lung lesions [141] | ||
| MALT Lymphoma | DLBCL |
|---|---|
| Cryoglobulinemia [9,11] FS [11] ESSDAI at pSS diagnosis [11] Neutropenia [9] Low serum C4 levels [9,18] Low serum C3 levels [10,18] Lymphadenopathy/Splenomegaly [9] | Lymphocytopenia [9,18] CD4+/CD8+ T-cell ratio ≤ 0.8 [6] Anemia [10] Low serum C4 levels [10] |
| Median OS | ||
| Pre-Rituximab era | Low-risk lymphomas: 6.33 years Intermediate/High-risk lymphomas: 1.83 years | [14] |
| Post-Rituximab era | MALT lymphomas: 13 years DLBCLs: 6 years | [17] |
| 5-year OS | ||
| Pre-Rituximab era | Low-risk lymphomas: 70% Intermediate/High-risk lymphomas: 48% | [14] |
| Post-Rituximab era | All lymphoma subtypes: 90.91% | [12] |
| All lymphoma subtypes: 86.5% | [5] | |
| MALT lymphomas: 94.1% DLBCLs: 75% NMZLs: 87.5% | [12] | |
| MALT lymphomas: 91% DLBCL: 54.5% NMZLs: 62.5% | [11] | |
| 5-year EFS | ||
| Post-Rituximab era | MALT lymphomas: 86.2% DLBCLs: 50% NMZL: 62.5% | [12] |
| MALT lymphomas: 63.6% DLBCLs: 45.4% NMZL: 62.5% | [11] | |
| 10-year OS | ||
| Post-Rituximab era | MALT lymphomas: 79% DLBCLs: 40.9% NMZLs: 46% | [11] |
| 10-year EFS | ||
| Post-Rituximab era | MALT lymphomas: 45.5% DLBCLs: 24.2% NMZLs: 31% | [11] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stergiou, I.E.; Goules, A.V.; Voulgarelis, M.; Tzioufas, A.G. Predisposing Factors, Clinical Picture, and Outcome of B-Cell Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma in Sjögren’s Syndrome. Immuno 2022, 2, 584-608. https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno2040037
Stergiou IE, Goules AV, Voulgarelis M, Tzioufas AG. Predisposing Factors, Clinical Picture, and Outcome of B-Cell Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma in Sjögren’s Syndrome. Immuno. 2022; 2(4):584-608. https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno2040037
Chicago/Turabian StyleStergiou, Ioanna E., Andreas V. Goules, Michael Voulgarelis, and Athanasios G. Tzioufas. 2022. "Predisposing Factors, Clinical Picture, and Outcome of B-Cell Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma in Sjögren’s Syndrome" Immuno 2, no. 4: 584-608. https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno2040037
APA StyleStergiou, I. E., Goules, A. V., Voulgarelis, M., & Tzioufas, A. G. (2022). Predisposing Factors, Clinical Picture, and Outcome of B-Cell Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma in Sjögren’s Syndrome. Immuno, 2(4), 584-608. https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno2040037







