Influence of an Extreme Saharan Dust Event on the Air Quality of the West Region of Portugal
Abstract
:1. Introduction
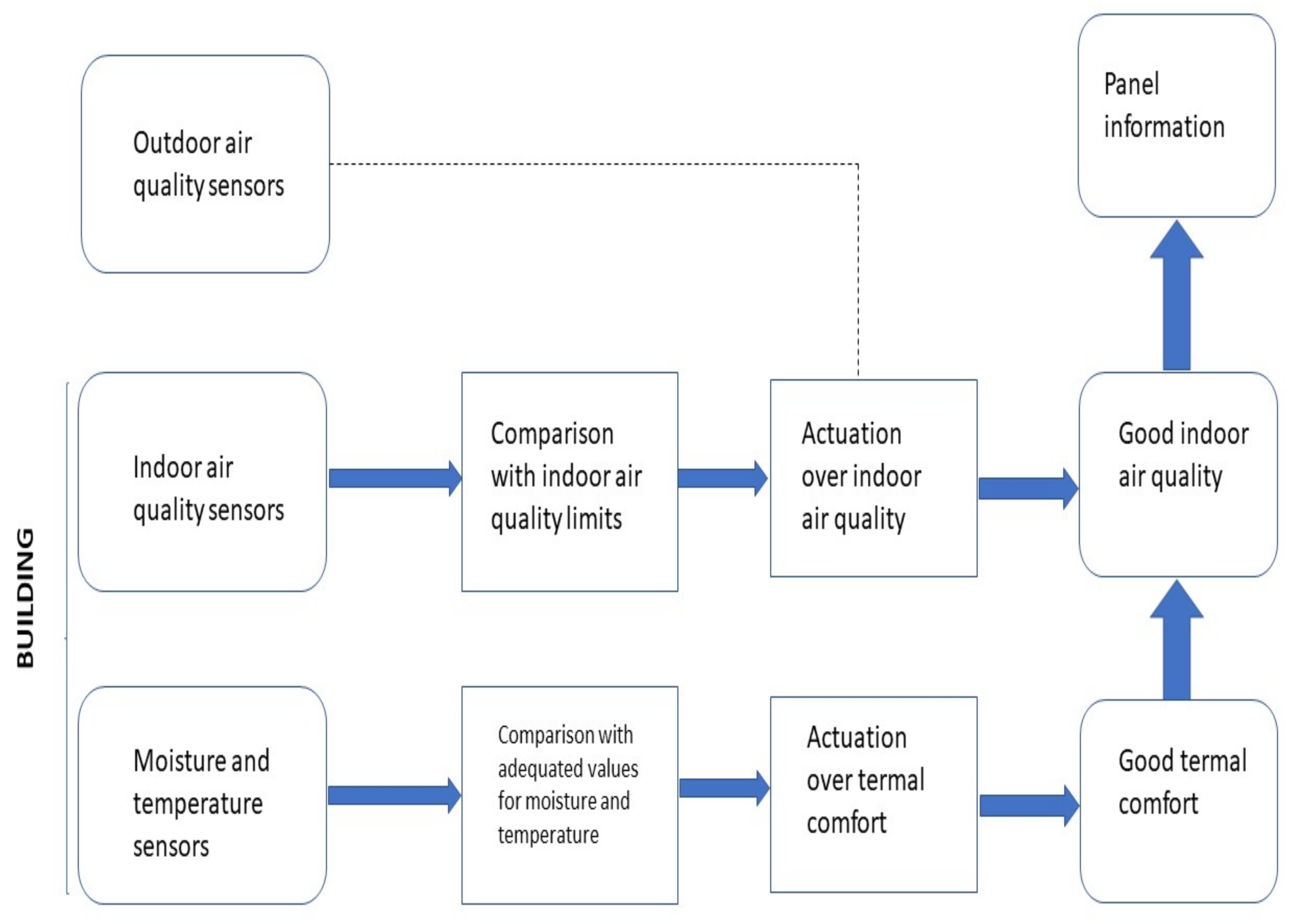
2. Materials and Methods
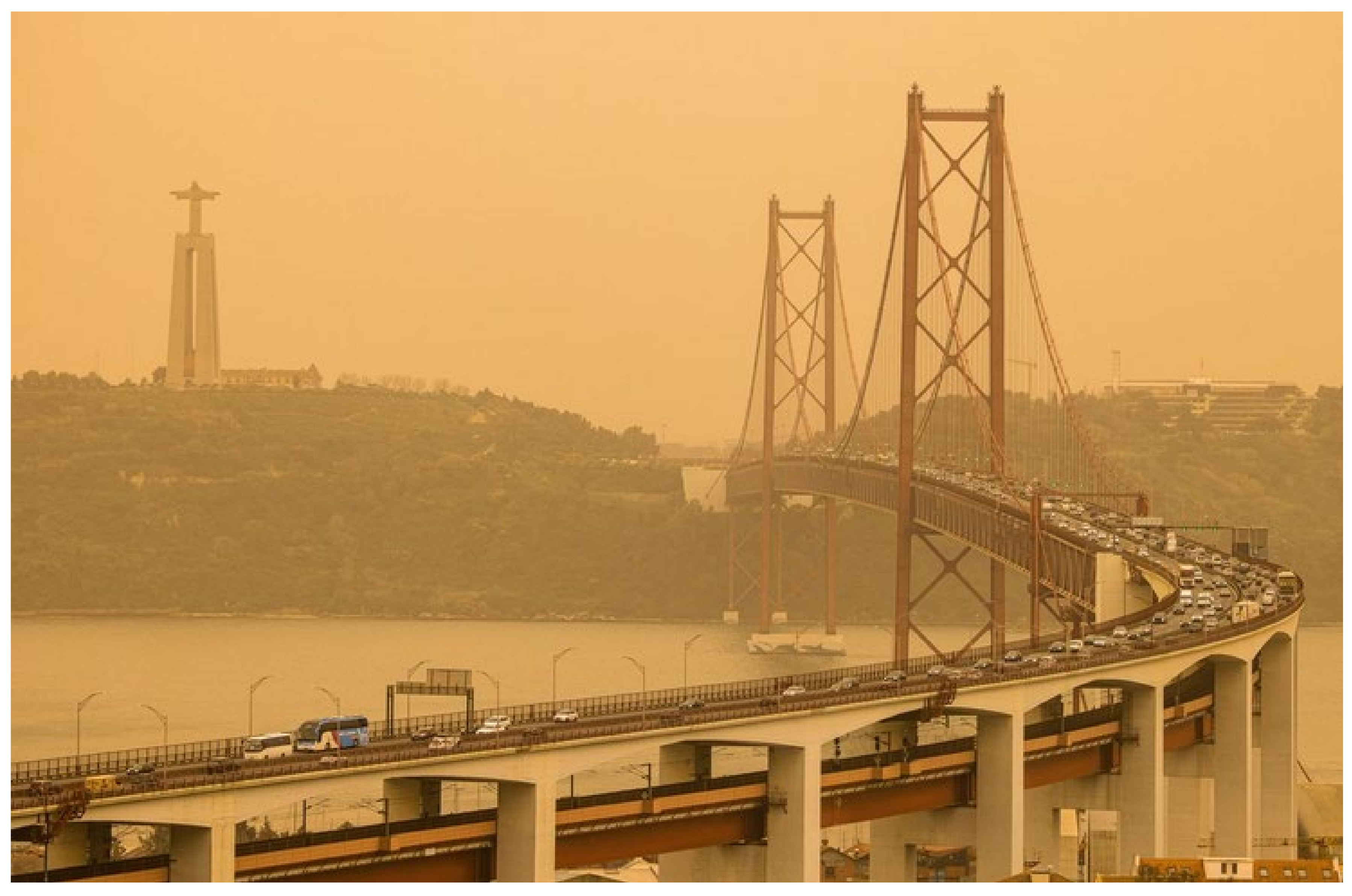
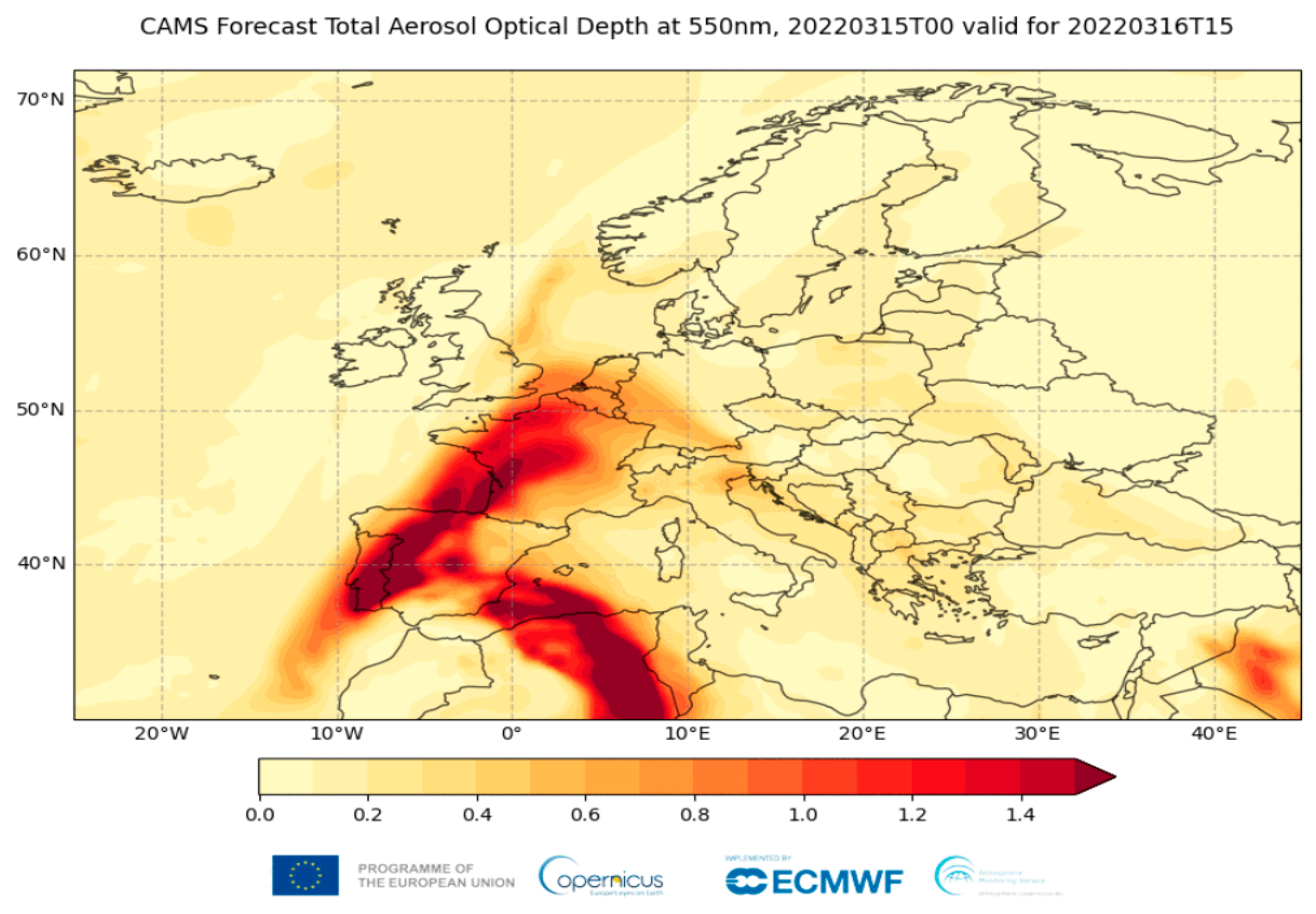
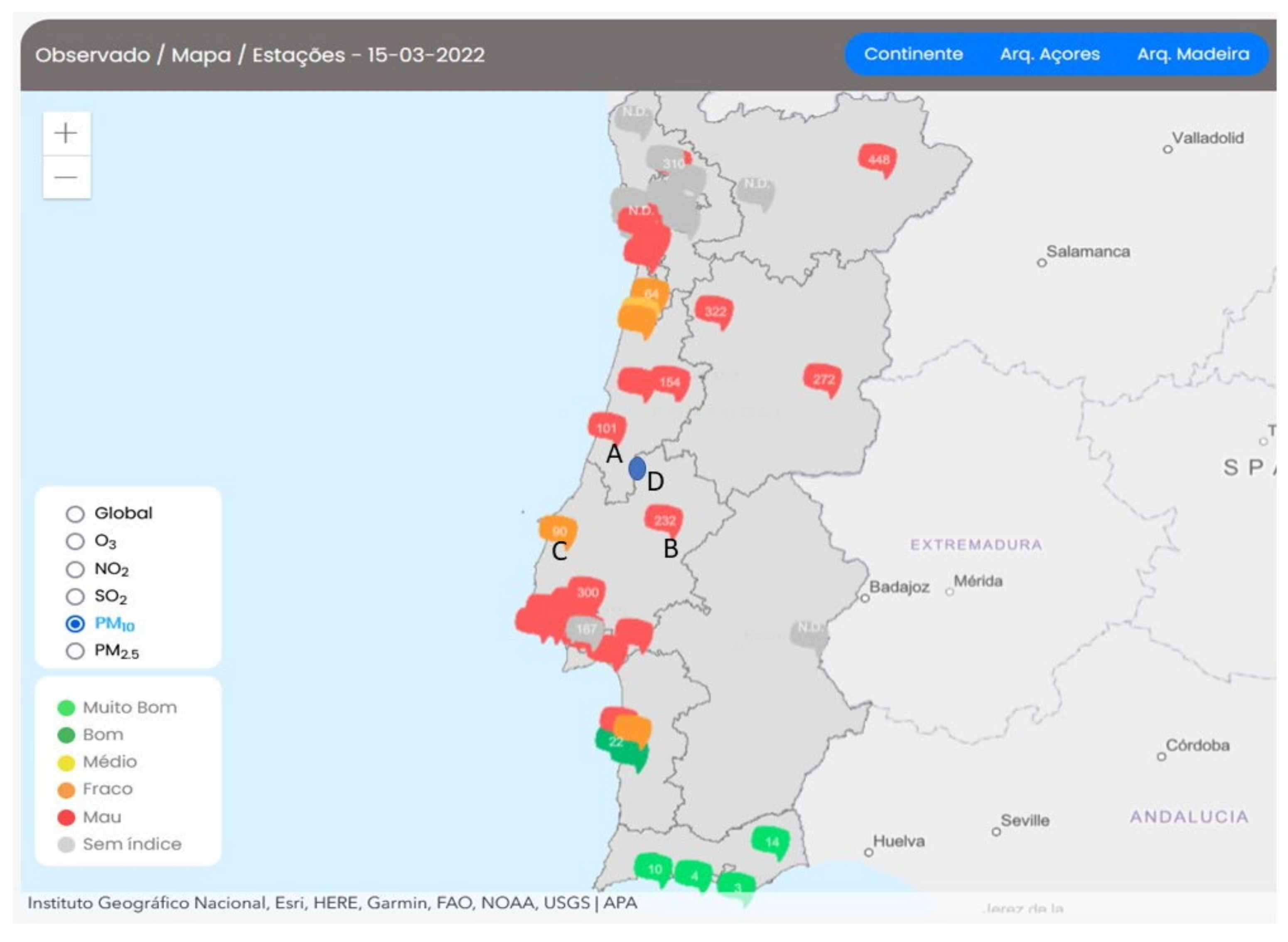
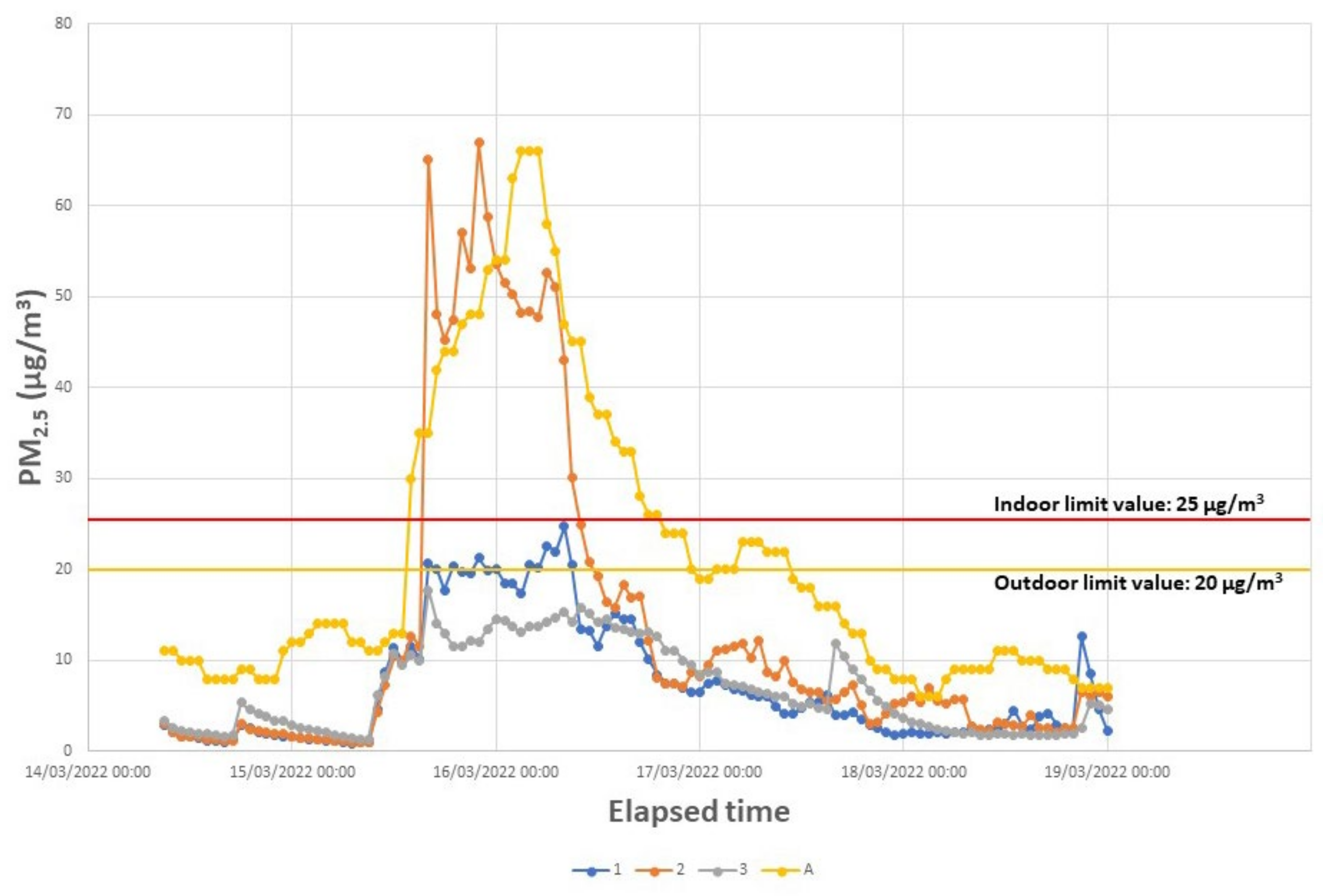
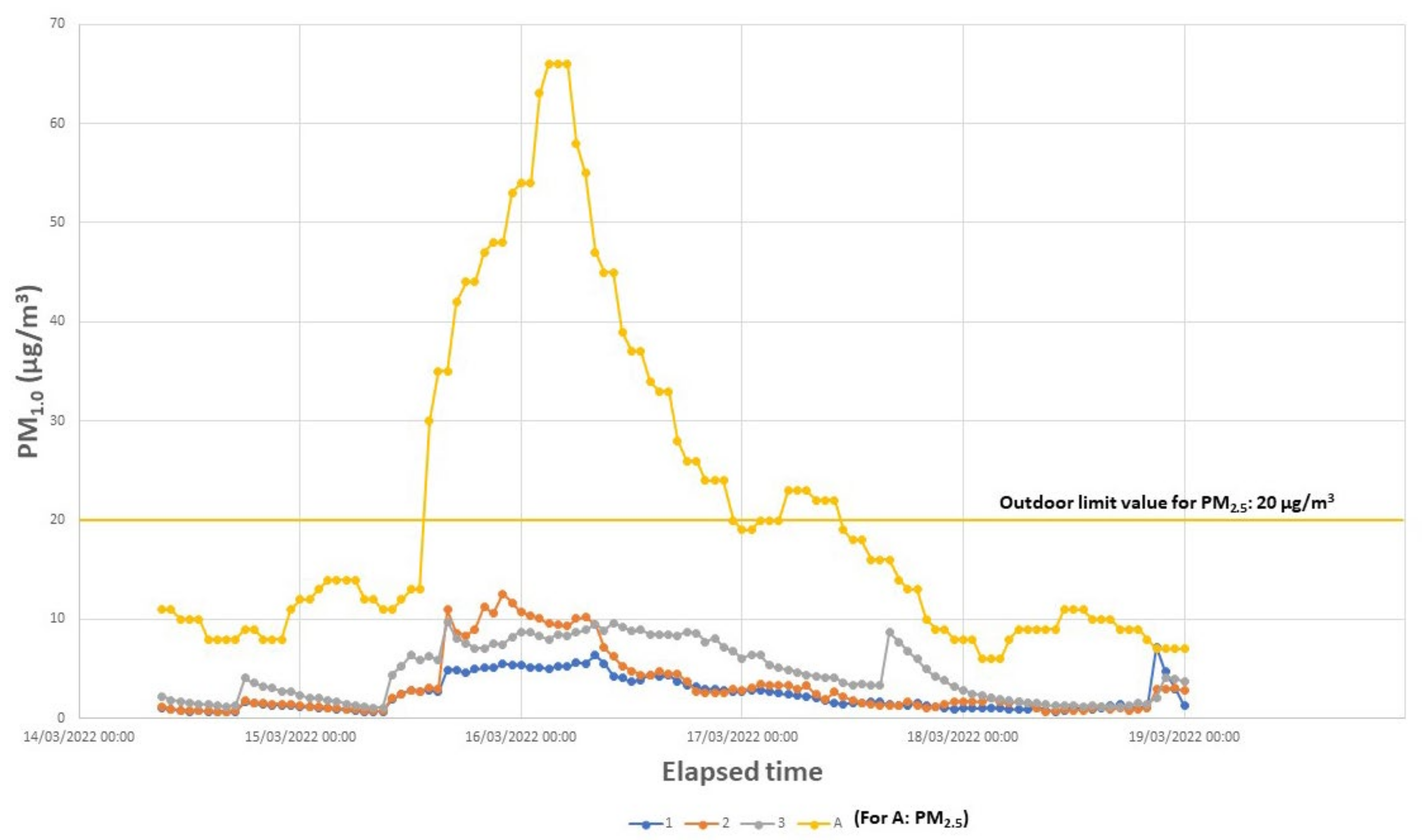
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fernandez, A.; Sicard, M.; Costa, M.J.; Guerrero-Rascado, J.L.; Gómez-Amo, J.L.; Molero, F.; Barragán, R.; Basart, S.; Bortoli, D.; Bedoya-Velásquez, A.E.; et al. Extreme, wintertime Saharan dust intrusion in the Iberian Peninsula: Lidar monitoring and evaluation of dust forecast models during the February 2017 event. Atmos. Res. 2019, 228, 223–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, D.; Costa, M.J.; Silva, A.M.; Salgado, R. Modeling Saharan desert dust radiative effects on clouds. Atmos. Res. 2013, 127, 178–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreae, M. Climate effects of changing atmospheric aerosol levels. In World Survey of Climatology, 16, Future Climate of the World; Henderson-Sellers, A., Ed.; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 1995; pp. 341–392. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2001: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability, Contribution of Working Group II to the Third Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; McCarthy, J.J., Canziani, O.F., Leary, N.A., Dokken, D.J., White, K.S., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2001; p. 1032. ISBN 0-521-01500-6. [Google Scholar]
- Salvador, P.; Alonso-Perez, S.; Pey, J.; Artinano, B.; de Bustos, J.; Alastuey, A.; Querol, X. African dust outbreaks over the western Mediterranean Basin: 11-year characterization of atmospheric circulation patterns and dust source areas. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 6759–6775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prospero, J.; Ginoux, P.; Torres, O.; Nicholson, S.; Gill, T. Environmental characterization of global sources of atmospheric soil dust identified with the Nimbus 7 Total Ozone Mapping Spectrometer (TOMS) absorbing aerosol product. Rev. Geophys. 2002, 40, 2-1–2-31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahowald, N.; Baker, A.; Bergametti, G.; Brooks, N.; Duce, R.; Jickells, T.; Kubilay, N.; Prospero, J.; Tegen, I. Atmospheric global dust cycle and iron inputs to the ocean. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2005, 19, GB4025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, F.; Bortoli, D.; Pereira, S.; Costa, M.J.; Silva, A.; Weinzierl, B.; Esselborn, M.; Petzold, A.; Rasp, K.; Heinold, B. Properties of dust aerosol particles transported to Portugal from the Sahara desert. Tellus B 2009, 61, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salvador, P.; Almeida, S.M.; Cardoso, J.; Almeida-Silva, M.; Nunes, T.; Cerqueira, M.; Alves, C.; Reis, M.A.; Chaves, P.C.; Artinano, B.; et al. Composition and origin of PM10 in Cape Verde: Characterization of long-range transport episodes. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 127, 326–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafontaine, C.; Bryson, R.; Wendland, W. Airstream regions of North-Africa and the Mediterranean. J. Clim. 1990, 3, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Obregón, M.; Pereira, S.; Salgueiro, V.; Costa, M.J.; Silva, A.M.; Serrano, A.; Bortoli, D. Aerosol radiative effects during two desert dust events in August 2012 over the Southwestern Iberian Peninsula. Atmos. Res. 2015, 153, 404–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, B.; Stenchikov, G.; Weinzierl, B.; Kalenderski, S.; Osipov, S. Dust plume formation in the free troposphere and aerosol size distribution during the Saharan Mineral Dust Experiment in North Africa. Tellus B Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2015, 67, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cuevas, E.; Gómez-Peláez, A.J.; Rodríguez, S.; Terradellas, E.; Basart, S.; Garcia, R.D.; Garcia, O.E.; Alonso-Perez, S. The pulsating nature of large-scale Saharan dust transport as a result of interplays between mid-latitude Rossby waves and the North African Dipole Intensity. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 167, 586–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pey, J.; Querol, X.; Alastuey, A.; Forastiere, F.; Stafoggia, M. African dust outbreaks over the Mediterranean Basin during 2001–2011: PM 10 concentrations, phenomenology and trends, and its relation with synoptic and mesoscale meteorology. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 1395–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Directive 2008/50/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 21 May 2008 on ambient air quality and cleaner air for Europe. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/en/ALL/?uri=CELEX%3A32008L0050 (accessed on 23 June 2022).
- Querol, X.; Pey, J.; Pandolfi, M.; Alastuey, A.; Cusack, M.; Pérez, N.; Moreno, T.; Viana, M.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Kallos, G. African dust contributions to mean ambient PM10 mass-levels across the Mediterranean Basin. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 4266–4277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvador, P.; Artíñano, B.; Molero, F.; Viana, M.; Pey, J.; Alastuey, A.; Querol, X. African dust contribution to ambient aerosol levels across central Spain: Characterization of long-range transport episodes of desert dust. Atmos. Res. 2013, 127, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agência Portuguesa do Ambiente, 2022 (in Portuguese). Available online: http://www.arsalentejo.min-saude.pt/arsalentejo/novidades/Documents/PREVISAO_EN_2022_03_15.pdf (accessed on 23 June 2022).
- Diapouli, E.; Manousakas, M.I.; Vratolis, S.; Vasilatou, V.; Pateraki, S.; Bairachtari, K.A.; Querol, X.; Amato, F.; Alastuey, A.; Karanasiou, A.A.; et al. AIRUSE-LIFE+: Estimation of natural source contributions to urban ambient air PM10 and PM2.5 concentrations in sourthern Europe—Implications to compliance with limit values. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 3673–3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Basart, S.; Peréz, C.; Nickovic, S.; Cuevas, E.; Baldasano, J. Development and evolution of the BSC-DREAM8b dust regional model over Northern Africa, the Mediterranean and the Middle East. Tellus B 2012, 64, 18539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Almeida, S.; Freitas, M.; Pio, C. Neutron activation analysis for identification of African mineral dust transport. J. Radionuclid Chem. 2008, 276, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Rascado, J. Extreme Saharan dust event over the Southern Iberian Peninsula in September 2007: Active and passive remote sensing from surface and satellite. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 8453–8469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wyche, K.; Ricketts, H.; Brolly, M.; Smallbone, K. Emerging investigator series: The red sky: Investigating the hurricane Ophelia Saharan dust and biomass burning aerosol event. Environ. Sci. Atmos. 2022, 2, 165–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. WHO Global Air Quality Guidelines: Particulate Matter (Pm2.5 and Pm10), Ozone, Nitrogen Dioxide, Sulfur Dioxide, and Carbon Monoxide; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Duarte, R.; Gomes, J.F.P.; Querol, X.; Cattaneo, A.; Bergmans, B.; Saraga, D.; Maggos, T.; Di Gilio, A.; Rovelli, S.; Villanueva, F. Advanced instrumental approaches for chemical characterization of indoor particulate matter. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmans, B.; Cattaneo, A.; Duarte, R.M.B.O.; Gomes, J.F.P.; Saraga, D.; García, M.R.; Querol, X.; Liotta, L.F.; Safell, J.; Spinazzé, A.; et al. Particulate matter indoors: A strategy to sample and monitor size-selective fractions. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portaria 353-A/2013—Regulamento de desempenho energético dos edifícios de comércio e serviços (RECS): Requisitos de ventilação e qualidade do ar interior. Diário da República, 1ª série, 235: 4/12/2013 (In Portuguese). Available online: https://dre.pt/dre/detalhe/portaria/353-a-2013-331868 (accessed on 23 June 2022).
- Munir, S. Analyzing temporal trends in the ratios of PM2.5/PM10 in the UK. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2017, 17, 34–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, H.; Wang, R.; Feng, X.; An, C.; Qeian, J. Spatial characteristics of the PM2.5/PM10 ratio and its indicative significance regarding air pollution in Hebei Province, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



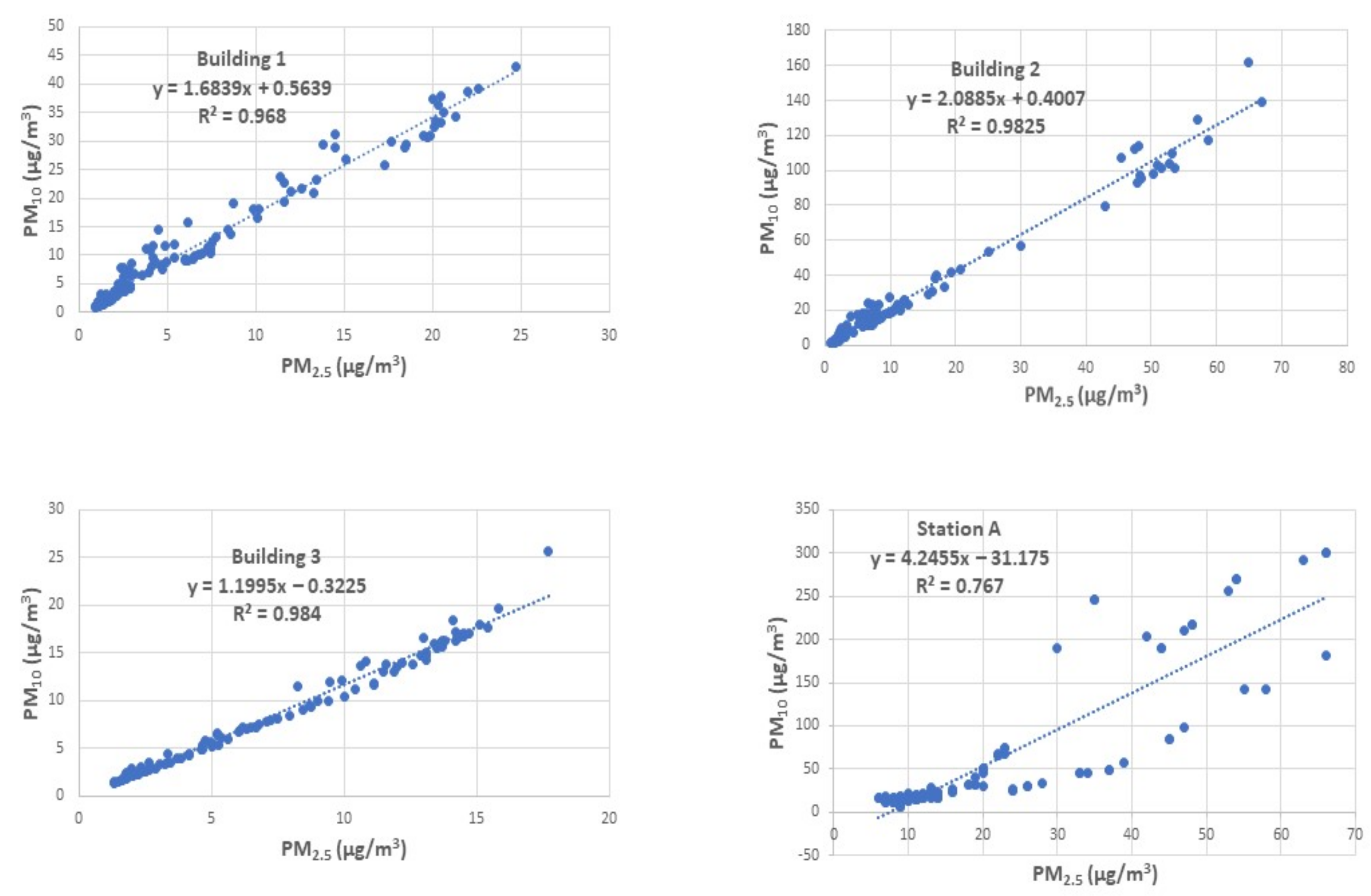
| PM | Stations | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fraction | Time Frame | A | B | C |
| 2.5 | Average 2021 | 8 | 6 | 6 |
| Average March 2021 | 9 | 8 | 9 | |
| 14 March 2022 | 10 | 1 | 4 | |
| 15 March 2022 | 25 | 32 | 32 | |
| 16 March 2022 | 41 | 54 | 33 | |
| 17 March 2022 | 17 | 19 | 16 | |
| 18 March 2022 | 9 | 5 | 6 | |
| 10 | Average 2021 | 17 | 12 | 14 |
| Average March 2021 | 19 | 18 | 20 | |
| 14 March 2022 | 16 | 8 | 9 | |
| 15 March 2022 | 101 | 232 | 90 | |
| 16 March 2022 | 111 | 203 | 88 | |
| 17 March 2022 | 40 | 61 | 43 | |
| 18 March 2022 | 14 | 16 | 17 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gomes, J.; Esteves, H.; Rente, L. Influence of an Extreme Saharan Dust Event on the Air Quality of the West Region of Portugal. Gases 2022, 2, 74-84. https://doi.org/10.3390/gases2030005
Gomes J, Esteves H, Rente L. Influence of an Extreme Saharan Dust Event on the Air Quality of the West Region of Portugal. Gases. 2022; 2(3):74-84. https://doi.org/10.3390/gases2030005
Chicago/Turabian StyleGomes, João, Helder Esteves, and Luis Rente. 2022. "Influence of an Extreme Saharan Dust Event on the Air Quality of the West Region of Portugal" Gases 2, no. 3: 74-84. https://doi.org/10.3390/gases2030005
APA StyleGomes, J., Esteves, H., & Rente, L. (2022). Influence of an Extreme Saharan Dust Event on the Air Quality of the West Region of Portugal. Gases, 2(3), 74-84. https://doi.org/10.3390/gases2030005







