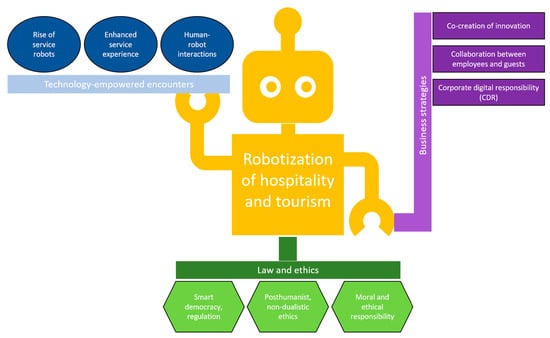
Co-Creating New Directions for Service Robots in Hospitality and Tourism
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Overview of Service Robots
2.1. The Rise of Service Robots in Hospitality and Tourism
Evolving Service Robot Roles in Tourism and Hospitality
2.2. Enhanced Service Experiences
Types of Service Robots that Enhance Experience
2.3. Transformative Changes in the Hospitality and Tourism Domain
Considering Employee Roles in Relation to Service Robots
3. Management and Ethical Issues in Service Robot Implementation
3.1. A Business Strategy to Increase Efficiency and Competitive Advantage
3.2. Structuring (Responsible) Service Experiences
3.2.1. Developing Diverse and Responsible Modes of Robotic Deliveries
3.2.2. Technological and Cultural Drivers
3.2.3. Anthropomorphism, Zoomorphism, and Robotic Embodiment
3.3. Ethical Considerations
4. Discussion and Directions Forward
Increasingly smartness and AmI support real-time service, empowering the co-creation of value for all stakeholders across multiple platforms. Interactions take place in real-time, at the exact moment when consumers are willing to engage with brands. […] Inevitably, smart environments transform industry structures, processes and practices, having disruptive impacts for service innovation, strategy, management, marketing and competitiveness [40] (pp.269-270).
4.1. Structural Transformations and “Just” Transitions
Digitalisation will not necessarily reduce, but rather transform jobs. Research finds that unemployment rates are generally lower in more digitalised economies, but it does typically lead to jobs being reallocated across industries. By one estimate, faster automation as a result of the pandemic will destroy 85 million jobs across 26 countries by 2025, but will also create 97 million new jobs—a net gain of 12 million [91].
4.2. Co-Creating Democracy and Regulatory Action through Collaborative Human-Robot Endeavors?
Co-creation is closely associated with contemporary ideas about innovation. Innovation in systems of production and consumption, in business ecosystems and supply chains, in processes and practices, have emerged as a result of collaborative ways of working together. Co-creation (sharing, collaboration, gifting, etc.) has redefined how we access resources such as knowledge expertise, capital, labour, and so on. […] We need to understand more about how co-creation may enhance innovation through inclusive thinking, or impeded it through exclusive (invitation only) cocreation practices [93] (p.295).
4.3. Blurring Human-Technological Dualisms towards Posthumanist Perspectives
How, and in what ways—competitively/collaboratively, hierarchically/horizontally—are capabilities, agency, and power distributed across human, machines, and natural systems?What new knowledge(s), questions, stakeholders, and partnerships are needed in order to adequately design for this problem?How are ethics, values, and responsibilities reflected and embedded throughout the design process? [97] (p.19).
- What constitutes a safe and “good” (ethical) robot-visitor encounter?
- How does increased automation and robotics, for example, service robots greeting you as you enter the hotel lobby or delivering food to your hotel room, affect the hospitality experience?
- Robots are increasingly being used to support and act as tour guides in museums and other destination settings. How can they facilitate cultural exchange by which visitors gain a rich experience of the local, facilitate learning about the destination, and challenges such as climate change and environmental literacy? What is gained and lost in the process? Will they significantly substitute meeting local residents?
- What additional questions and ethical issues arise as social-ecological systems turn increasing posthuman and transhuman?
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Buhalis, D.; Sinarta, Y. Real-time co-creation and nowness service: Lessons from tourism and hospitality. J. Travel Tour. Mark. 2019, 36, 563–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, S.; Webster, C. Adoption of robots, artificial intelligence and service automation by travel, tourism and hospitality companies—A cost-benefit analysis. In Artificial Intelligence and Service Automation by Travel, Tourism and Hospitality Companies—A Cost-Benefit Analysis; Prepared for the International Scientific Conference “Contemporary Tourism—Traditions and Innovations”; Sofia University: Sofia, Bulgaria, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Bowen, J.; Morosan, C. Beware hospitality industry: The robots are coming. Worldw. Hosp. Tour. Themes 2018, 10, 726–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pransky, J. Service robots—How we should define them? Serv. Robot Int. J. 1996, 2, 4–5. [Google Scholar]
- International Federation of Robotics: Service Robots. Available online: https://ifr.org/service-robots (accessed on 1 October 2020).
- Van Doorn, J.; Mende, M.; Noble, S.M.; Hulland, J.; Ostrom, A.L.; Grewal, D.; Petersen, J.A. Domo arigato Mr. Roboto: Emergence of automated social presence in organizational frontlines and customers’ service experiences. J. Serv. Res. 2017, 20, 43–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lobschat, L.; Mueller, B.; Eggers, F.; Brandimarte, L.; Diefenbach, S.; Kroschke, M.; Wirtz, J. Corporate digital responsibility. J. Bus. Res. 2019, 122, 875–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, J.; Hofacker, C.; Gretzel, U. Dawning of the age of robots in hospitality and tourism: Challenges for teaching and research. Eur. J. Tour. Res. 2017, 15, 104–111. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanov, S.; Webster, C.; Berezina, K. Robotics in tourism and hospitality. In Handbook of e-Tourism; Xiang, Z., Fuchs, M., Gretzel, U., Höpken, W., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Chi, O.H.; Denton, G.; Gursoy, D. Artificially intelligent device use in service delivery: A systematic review, synthesis, and research agenda. J. Hosp. Mark. Manag. 2020, 29, 757–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mende, M.; Scott, M.L.; van Doorn, J.; Grewal, D.; Shanks, I. Service robots rising: How humanoid robots influence service experiences and elicit compensatory consumer responses. J. Mark. Res. 2019, 56, 535–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.H.; Jeong, M. Guests’ perceptions of robot concierge and their adoption intentions. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2020, 32, 2613–2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, J.; Melão, N.; Salvadorinho, J.; Soares, B.; Rosete, A. Service robots in the hospitality industry: The case of Henn-na hotel, Japan. Technol. Soc. 2020, 63, 101423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Oh, M.; Choi, M.; Kim, S. Exploring the influence of culture on tourist experiences with robots in service delivery environment. Curr. Issues Tour. Available online: https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/13683500.2020.1735318 (accessed on 24 December 2020). [CrossRef]
- Tung, V.W.S.; Law, R. The potential for tourism and hospitality experience research in human-robot interactions. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2017, 29, 2498–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.M.; Chen, L.C.; Tseng, C.Y. Investigating an innovative service with hospitality robots. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2017, 29, 1305–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirtz, J.; Patterson, P.G.; Kunz, W.H.; Gruber, T.; Lu, V.N.; Paluch, S.; Martins, A. Brave new world: Service robots in the frontline. J. Serv. Manag. 2018, 29, 907–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Webster, C.; Ivanov, S. Robots in Travel, Tourism and Hospitality: Key Findings from A Global Study; Zangador: Varna, Bulgaria, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Neuhofer, B.; Magnus, B.; Celuch, K. The impact of artificial intelligence on event experiences: A scenario technique approach. Electron. Mark. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12525-020-00433-4 (accessed on 24 December 2020). [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, S.; Webster, C. Conceptual framework of the use of robots, artificial intelligence and service automation in travel, tourism, and hospitality companies. In Robots, Artificial Intelligence, and Service Automation in Travel, Tourism and Hospitality; Ivanov, S., Webster, C., Eds.; Emerald Publishing Limited: Bingley, UK, 2019; pp. 7–37. [Google Scholar]
- Tussyadiah, I. A review of research into automation in tourism: Launching the Annals of Tourism Research Curated Collection on Artificial Intelligence and Robotics in Tourism. Ann. Tour. Res. 2020, 81, 102883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuomi, A.; Tussyadiah, I.P.; Stienmetz, J. Applications and implications of service robots in hospitality. Cornell Hosp. Q. 2020, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Fusté-Forné, F. Robot chefs in gastronomy tourism: What’s on the menu? Tour. Manag. Perspect. 2021, 37, 100774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, S.; Gretzel, U.; Berezina, K.; Sigala, M.; Webster, C. Progress on robotics in hospitality and tourism: A review of the literature. J. Hosp. Tour. Technol. 2019, 10, 489–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, S.; Webster, C. Economic fundamentals of the use of robots, artificial intelligence, and service automation in travel, tourism, and hospitality. In Robots, Artificial Intelligence, and Service Automation in Travel, Tourism and Hospitality; Ivanov, S., Webster, C., Eds.; Emerald Publishing Limited: Bingley, UK, 2019; pp. 39–55. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Qi, S. User experience study: The service expectation of hotel guests to the utilization of ai-based service robot in full-service hotels. In International Conference on Human–Computer Interaction; Nah, F.H., Siau, K., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 350–366. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, L.; Cai, R.; Gursoy, D. Developing and validating a service robot integration willingness scale. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2019, 80, 36–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naumov, N. The impact of robots, artificial intelligence, and service automation on service quality and service experience in hospitality. In Robots, Artificial Intelligence, and Service Automation in Travel, Tourism and Hospitality; Ivanov, S., Webster, C., Eds.; Emerald Publishing Limited: Bingley, UK, 2019; pp. 123–133. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S. Multifaceted trust in tourism service robots. Ann. Tour. Res. 2020, 81, 102888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holley, P. The Boston restaurant where robots have replaced the chefs. The Washington Post, 17 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Belanche, D.; Casaló, L.V.; Flavián, C. Frontline robots in tourism and hospitality: Service enhancement or cost reduction? Electron. Mark. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12525-020-00432-5 (accessed on 24 December 2020). [CrossRef]
- Kabadayi, S.; Ali, F.; Choi, H.; Joosten, H.; Lu, C. Smart service experience in hospitality and tourism services. J. Serv. Manag. 2019, 30, 326–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Sun, S.; Law, R.; Zhang, X. Impact of robot hotel service on consumers’ purchase intention: A control experiment. Asia Pac. J. Tour. Res. 2020, 25, 780–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manthiou, A.; Klaus, P.; Kuppelwieser, V.G.; Reeves, W. Man vs. machine: Examining the three themes of service robotics in tourism and hospitality. Electron. Mark. 2020, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatan, A.; Dogan, S. What do hotel employees think about service robots? A qualitative study in Turkey. Touri. Manag. Perspect. 2021, 37, 100775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeoman, I. 2050-Tomorrow’s Tourism; Channel View Publications: Bristol, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- McCartney, G.; McCartney, A. Rise of the machines: Towards a conceptual service-robot research framework for the hospitality and tourism industry. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2020, 13, 3835–3851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, A.P.H.; Tung, V.W.S. Examining the effects of robotic service on brand experience: The moderating role of hotel segment. J. Travel Tour. Mark. 2019, 36, 458–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, T.; Nourbakhsh, I.; Dautenhahn, K. A survey of socially interactive robots. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2003, 42, 143–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buhalis, D. Technology in tourism-from information communication technologies to eTourism and smart tourism towards ambient intelligence tourism: A perspective article. Tour. Rev. 2019, 75, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christou, P.; Simillidou, A.; Stylianou, M.C. Tourists’ perceptions regarding the use of anthropomorphic robots in tourism and hospitality. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2020, 32, 3665–3683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigala, M. Tourism and COVID-19: Impacts and implications for advancing and resetting industry and research. J. Bus. Res. 2020, 117, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwok, A.O.; Koh, S.G. COVID-19 and Extended Reality (XR). Curr. Issues Tour. Available online: https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/citedby/10.1080/13683500.2020.1798896 (accessed on 24 December 2020). [CrossRef]
- Gretzel, U.; Sigala, M.; Xiang, Z.; Koo, C. Smart tourism: Foundations and developments. Electron. Mark. 2015, 25, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Talón-Ballestero, P.; García-Muiña, F.E.; Rienda-Gómez, J.J.; González-Serrano, L. Repeat Consumer Behavior on Smart P2P Tourism Platforms. Sustainability 2019, 11, 7082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cain, L.N.; Thomas, J.H.; Alonso, M., Jr. From sci-fi to sci-fact: The state of robotics and AI in the hospitality industry. J. Hosp. Tour. Technol. 2019, 10, 624–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuomi, A.; Tussyadiah, I.; Stienmetz, J. Leveraging LEGO® Serious Play® to embrace AI and robots in tourism. Ann. Tour. Res. 2020, 81, 102736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larivière, B.; Bowen, D.; Andreassen, T.W.; Kunz, W.; Sirianni, N.J.; Voss, C.; Wünderlich, N.V.; De Keyser, A. “Service Encounter 2.0”: An investigation into the roles of technology, employees and customers. J. Bus. Res. 2017, 79, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marinova, D.; de Ruyter, K.; Huang, M.H.; Meuter, M.L.; Challagalla, G. Getting smart: Learning from technology-empowered frontline interactions. J. Serv. Res. 2017, 20, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.J.; Bonn, M.A.; Ye, B.H. Hotel employee’s artificial intelligence and robotics awareness and its impact on turnover intention: The moderating roles of perceived organizational support and competitive psychological climate. Tour. Manag. 2019, 73, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, V.N.; Wirtz, J.; Kunz, W.H.; Paluch, S.; Gruber, T.; Martins, A.; Patterson, P.G. Service robots, customers and service employees: What can we learn from the academic literature and where are the gaps? J. Serv. Theory Pract. 2020, 30, 361–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes-Moraleda, L.; Díaz-Pérez, P.; Orea-Giner, A.; Muñoz-Mazón, A.; Villacé-Molinero, T. Interaction between hotel service robots and humans: A hotel-specific Service Robot Acceptance Model (sRAM). Tour. Manag. Perspect. 2020, 36, 100751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mingotto, E.; Montaguti, F.; Tamma, M. Challenges in re-designing operations and jobs to embody AI and robotics in services. Findings from a case in the hospitality industry. Electron. Mark. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12525-020-00439-y (accessed on 24 December 2020). [CrossRef]
- Weiss, A.; Bernhaupt, R.; Lankes, M.; Tscheligi, M. The USUS evaluation framework for human–robot interaction. In AISB2009: Proceedings of the Symposium on New Frontiers in Human–Robot Interaction; Dautenhahn, K., Ed.; AISB: Bath, UK, 2009; Volume 4, pp. 11–26. [Google Scholar]
- Amara, N.; Landry, R. Counting citations in the field of business and management: Why use Google Scholar rather than the Web of Science. Scientometrics 2012, 93, 553–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomezelj, D.O. A systematic review of research on innovation in hospitality and tourism. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2016, 28, 516–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harzing, A.W.; Alakangas, S. Google Scholar, Scopus and the Web of Science: A longitudinal and cross-disciplinary comparison. Scientometrics 2016, 106, 787–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.S.; Bai, B.H.; Kim, P.B.; Chon, K. Review of reviews: A systematic analysis of review papers in the hospitality and tourism literature. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2018, 70, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marasco, A.; De Martino, M.; Magnotti, F.; Morvillo, A. Collaborative innovation in tourism and hospitality: A systematic review of the literature. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2018, 30, 2364–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Martín, A.; Thelwall, M.; Orduna-Malea, E.; López-Cózar, E.D. Google Scholar, Microsoft Academic, Scopus, Dimensions, Web of Science, and OpenCitations’ COCI: A multidisciplinary comparison of coverage via citations. Scientometrics. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11192-020-03690-4 (accessed on 24 December 2020). [CrossRef]
- International Federation of Robotics. IFR Presents World Robotics Report 2020. Available online: https://ifr.org/ifr-press-releases/news/record-2.7-million-robots-work-in-factories-around-the-globe (accessed on 24 December 2020).
- International Federation of Robotics. Automation Strategies Drive 12% Increase in Number of Robots at Work Globally. Available online: https://ifr.org/post/automation-strategies-drive-12-increase-in-number-of-robots-at-work-globally (accessed on 24 December 2020).
- McLeay, F.; Osburg, V.S.; Yoganathan, V.; Patterson, A. Replaced by a Robot: Service Implications in the Age of the Machine. J. Serv. Res. Available online: https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/full/10.1177/1094670520933354 (accessed on 24 December 2020). [CrossRef]
- Belanche, D.; Casaló, L.V.; Flavián, C.; Schepers, J. Service robot implementation: A theoretical framework and research agenda. Serv. Ind. J. 2020, 40, 203–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, Y.; Choi, M.; Oh, M.; Kim, S. Service robots in hotels: Understanding the service quality perceptions of human-robot interaction. J. Hosp. Mark. Manag. 2019, 29, 613–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Lizundia, E.; Marcos, S.; Zalama, E.; Gómez-García-Bermejo, J.; Gordaliza, A. A bellboy robot: Study of the effects of robot behaviour on user engagement and comfort. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Stud. 2015, 82, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ivanov, S.; Seyitoğlu, F.; Markova, M. Hotel managers’ perceptions towards the use of robots: A mixed-methods approach. Inf. Technol. Tour. 2020, 22, 505–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Stienmetz, J.; Ashton, M. How will service robots redefine leadership in hotel management? A Delphi approach. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2020, 32, 2217–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tussyadiah, I.P.; Zach, F.J.; Wang, J. Do travelers trust intelligent service robots? Ann. Tour. Res. 2020, 81, 102886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuliano, L.; Lupetti, M.L.; Khan, S.; Germak, C. Ethic reflections about service robotics, from human protection to enhancement: Case study on cultural heritage. In Robotics-Legal, Ethical and Socioeconomic Impacts; Dekoulis, G., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2017; pp. 93–109. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanov, S.; Webster, C. Perceived appropriateness and intention to use service robots in tourism. In Information and Communication Technologies in Tourism; Pesonen, J., Neidhardt, J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 237–248. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; McGill, A.L. Gaming with Mr. Slot or gaming the slot machine? Power, anthropomorphism, and risk perception. J. Consum. Res. 2011, 38, 94–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, J.; Gretzel, U.; Pesonen, J. Marketing robot services in hospitality and tourism: The role of anthropomorphism. J. Travel Tour. Mark. 2019, 36, 784–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung, V.W.S.; Au, N. Exploring customer experiences with robotics in hospitality. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2018, 30, 2680–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.; Li, M.; Shu, B.; Bai, B. Enhancing hospitality experience with service robots: The mediating role of rapport building. J. Hosp. Mark. Manag. 2020, 29, 247–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, T.; Kanda, T. Rapport–expectation with a robot scale. Int. J. Soc. Robot. 2016, 8, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, T.; Oliveira, E. Understanding consumers’ acceptance of automated technologies in service encounters: Drivers of digital voice assistants adoption. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 122, 180–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, R.; Sivathanu, B. Adoption of AI-based chatbots for hospitality and tourism. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2020, 32, 3199–3226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grewal, D.; Kroschke, M.; Mende, M.; Roggeveen, A.L.; Scott, M.L. Frontline Cyborgs at Your Service: How Human Enhancement Technologies Affect Customer Experiences in Retail, Sales, and Service Settings. J. Interact. Mark. 2020, 51, 9–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, K.; Dutt, C.S.; Chathoth, P.; Daghfous, A.; Khan, M.S. The adoption of artificial intelligence and robotics in the hotel industry: Prospects and challenges. Electron. Mark. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12525-020-00442-3 (accessed on 24 December 2020). [CrossRef]
- Belk, R. Ethical issues in service robotics and artificial intelligence. Serv. Ind. J. Available online: https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/citedby/10.1080/02642069.2020.1727892 (accessed on 24 December 2020). [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jamal, T.; Higham, J. Justice and ethics: Towards a new platform for tourism and sustainability. J. Sustain. Tour. 2020, 29, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopacek, P.; Hersh, M. Roboethics. In Ethical Engineering for International Development and Environmental Sustainability; Hersh, M., Ed.; Springer: London, UK, 2015; pp. 65–102. [Google Scholar]
- Veruggio, G.; Operto, F.; Bekey, G. Roboethics: Social and ethical implications. In Springer Handbook of Robotics; Siciliano, B., Khatib, O., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 2135–2160. [Google Scholar]
- Riek, L.; Howard, D. A code of ethics for the human-robot interaction profession. Proc. We Robot. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=2757805 (accessed on 24 December 2020).
- Bulchand-Gidumal, J. Impact of Artificial Intelligence in Travel, Tourism, and Hospitality. In Handbook of e-Tourism; Xiang, Z., Fuchs, M., Gretzel, U., Höpken, W., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Heidegger, M. The Question Concerning Technology; Harper and Row: New York, NY, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Haraway, D. A Cyborg Manifesto: Science, Technology, and Socialist-Feminism in the Late 20th Century. In The International Handbook of Virtual Learning Environments; Weiss, J., Nolan, J., Hunsinger, J., Trifonas, P., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 117–158. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Z.; Chen, P.J.; Lew, A.A. From High-touch to high-tech: COVID-19 drives robotics adoption. Tour. Geogr. 2020, 22, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Wen, J. Effects of COVID-19 on hotel marketing and management: A perspective article. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2020, 32, 2563–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Economic Forum. The Future of Jobs Report 2020. Keynote speech by Christine Lagarde. Available online: https://www.ecb.europa.eu/press/key/date/2020/html/ecb.sp201120~e92d92352f.en.html (accessed on 1 December 2020).
- Gretzel, U.; Murphy, J. Making sense of robots: Consumer discourse on robots in tourism and hospitality service settings. In Robots, Artificial Intelligence, and Service Automation in Travel, Tourism and Hospitality; Ivanov, S., Webster, C., Eds.; Emerald Publishing Limited: Bingley, UK, 2019; pp. 93–104. [Google Scholar]
- Phi, G.T.; Dredge, D. Collaborative tourism-making: An interdisciplinary review of co-creation and a future research agenda. Tour. Recreat. Res. 2019, 44, 284–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamal, T. Justice and Ethics in Tourism; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Sigala, M. New technologies in tourism: From multi-disciplinary to anti-disciplinary advances and trajectories. Tour. Manag. Perspect. 2018, 25, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirtz, J.; So, K.K.F.; Mody, M.A.; Liu, S.Q.; Chun, H.H. Platforms in the peer-to-peer sharing economy. J. Serv. Manag. 2019, 30, 452–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forlano, L. Posthumanism and design. She Ji J. Des. Econ. Innov. 2017, 3, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, V.C. Ethics of artificial intelligence and robotics. In Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy; Zalta, E.N., Ed.; Stanford University: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 2020; pp. 1–70. [Google Scholar]
- Stankov, U.; Gretzel, U. Tourism 4.0 technologies and tourist experiences: A human-centered design perspective. Inf. Technol. Tour. 2020, 22, 477–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hacker, K.L.; Van Dijk, J. Digital Democracy: Issues of Theory and Practice; Sage: London, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Guia, J.; Jamal, T. A (Deleuzian) posthumanist paradigm for tourism research. Ann. Tour. Res. 2020, 84, 102982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fusté-Forné, F.; Jamal, T. Co-Creating New Directions for Service Robots in Hospitality and Tourism. Tour. Hosp. 2021, 2, 43-61. https://doi.org/10.3390/tourhosp2010003
Fusté-Forné F, Jamal T. Co-Creating New Directions for Service Robots in Hospitality and Tourism. Tourism and Hospitality. 2021; 2(1):43-61. https://doi.org/10.3390/tourhosp2010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleFusté-Forné, Francesc, and Tazim Jamal. 2021. "Co-Creating New Directions for Service Robots in Hospitality and Tourism" Tourism and Hospitality 2, no. 1: 43-61. https://doi.org/10.3390/tourhosp2010003
APA StyleFusté-Forné, F., & Jamal, T. (2021). Co-Creating New Directions for Service Robots in Hospitality and Tourism. Tourism and Hospitality, 2(1), 43-61. https://doi.org/10.3390/tourhosp2010003