BRIDE v2: A Validated Collection of Genes Involved in the Mammalian Brain Response to Low-Dose Ionizing Radiation
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design and Content Overview
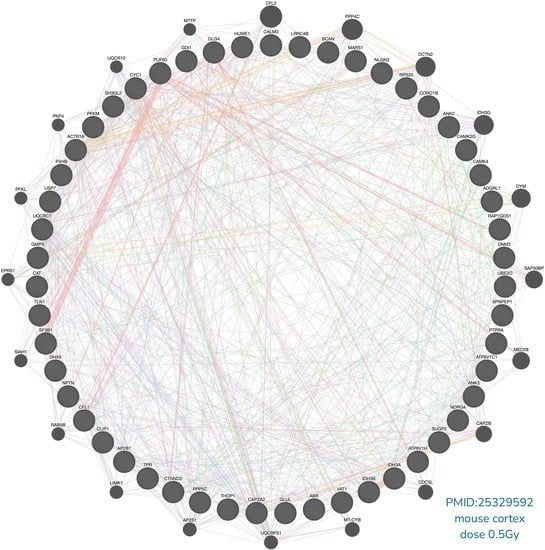
2.1.1. Design Details
2.1.2. Content Details
2.2. System Architecture
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Data Consumption
3.2. Utility and Discussion
3.3. Availability and Requirements
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mullenders, L.; Atkinson, M.; Paretzke, H.; Sabatier, L.; Bouffler, S. Assessing cancer risks of low-dose radiation. Nat. Cancer 2009, 9, 596–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einstein, A.J. Medical imaging: The radiation issue. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2009, 6, 436–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Angelis, G.; Caldora, M.; Santaquilani, M.; Scipione, R.; Verdecchia, A. Radiation exposure of civilian airline crew members and associated biological effects due to the atmospheric ionizing radiation environment. Phys. Med. 2001, 17 (Suppl. 1), 258–260. [Google Scholar]
- Bonner, W.M. Low-dose radiation: Thresholds, bystander effects, and adaptive responses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 4973–4975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thompson, G. Unmasking the truth: The science and policy of low-dose ionizing radiation. Bull. At. Sci. 2012, 68, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feinendegen, L.E.; Pollycove, M.; Sondhaus, C.A. Responses to Low Doses of Ionizing Radiation in Biological Systems. Nonlinearity Biol. Toxicol. Med. 2004, 2, 143–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kempf, S.J.; Azimzadeh, O.; Atkinson, M.J.; Tapio, S. Long-term effects of ionising radiation on the brain: Cause for concern? Radiat. Environ. Biophys. 2013, 52, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nussbaum, R.H.; Kohnlein, W. Inconsistencies and open questions regarding low-dose health effects of ionizing radiation. Environ. Health Perspect. 1994, 102, 656–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucinotta, F.A.; Schimmerling, W.; Wilson, J.W.; Peterson, L.E.; Badhwar, G.D.; Saganti, P.B.; Dicello, J.F. Space Radiation Cancer Risks and Uncertainties for Mars Missions. Radiat. Res. 2001, 156 Pt 2, 682–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, Z.; Schwietert, C.W.; Lehnert, B.; Stern, R.; Nami, I. Effects of low-dose ionizing radiation on gene expression in human skin biopsies. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2004, 58, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azimzadeh, O.; Scherthan, H.; Sarioglu, H.; Barjaktarovic, Z.; Conrad, M.; Vogt, A.; Calzada-Wack, J.; Neff, F.; Aubele, M.; Buske, C.; et al. Rapid proteomic remodeling of cardiac tissue caused by total body ionizing radiation. Proteomics 2011, 11, 3299–3311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Squillaro, T.; Galano, G.; De Rosa, R.; Peluso, G.; Galderisi, U. The effect of low-dose ionizing radiation on stem cell biology: A contribution to radiation risk. Stem Cells 2018, 36, 1146–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loganovsky, K. Do low doses of ionizing radiation affect the human brain? Data Sci. J. 2009, 8, BR13–BR35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verheyde, J.; Benotmane, M.A. Unraveling the fundamental molecular mechanisms of morphological and cognitive de-fects in the irradiated brain. Brain Res. Rev. 2007, 53, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.-S.; Won, Y.J.; Kim, B.-C.; Park, D.; Bae, J.-H.; Park, S.-J.; Noh, S.J.; Kang, Y.-R.; Choi, S.H.; Yoon, J.-H.; et al. Low-dose irradiation promotes Rad51 expression by down-regulating miR-193b-3p in hepatocytes. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tharmalingam, S.; Sreetharan, S.; Kulesza, A.V.; Boreham, D.R.; Tai, T.C. Low-Dose Ionizing Radiation Exposure, Oxidative Stress and Epigenetic Programming of Health and Disease. Radiat. Res. 2017, 188, 525–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolov, M.; Neumann, R. Global Gene Expression Alterations as a Crucial Constituent of Human Cell Response to Low Doses of Ionizing Radiation Exposure. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 17, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karapiperis, C.; Kempf, S.J.; Quintens, R.; Azimzadeh, O.; Vidal, V.L.; Pazzaglia, S.; Bazyka, D.; Mastroberardino, P.G.; Scouras, Z.G.; Tapio, S.; et al. Brain Radiation Information Data Exchange (BRIDE): Integration of experimental data from low-dose ionising radiation research for pathway discovery. BMC Bioinform. 2016, 17, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Warde-Farley, D.; Donaldson, S.L.; Comes, O.; Zuberi, K.; Badrawi, R.; Chao, P.; Franz, M.; Grouios, C.; Kazi, F.; Lopes, C.T.; et al. The GeneMANIA prediction server: Biological network integration for gene prioritization and predicting gene function. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38 (Suppl. 2), W214–W220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Philippi, S. Light-weight integration of molecular biological databases. Bioinformatics 2003, 20, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marx, V. Biology: The big challenges of big data. Nature 2013, 498, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karp, P.D. Database links are a foundation for interoperability. Trends Biotechnol. 1996, 14, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippi, S.; Köhler, J. Addressing the problems with life-science databases for traditional uses and systems biology. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2006, 7, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UniProt Consortium. UniProt: A hub for protein information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D204–D212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- NCBI Resource Coordinators. Database resources of the National Center for Biotechnology Information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D7–D17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Orchard, S.; Ammari, M.; Aranda, B.; Breuza, L.; Briganti, L.; Broackes-Carter, F.; Campbell, N.H.; Chavali, G.; Chen, C.; Del-Toro, N.; et al. The MIntAct project—IntAct as a common curation platform for 11 molecular interaction databases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D358–D363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, A.R.; Overly, C.C.; Sunkin, S.M. The Allen Brain Atlas: 5 years and beyond. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2009, 10, 821–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.L.; Eppig, J.T. The mammalian phenotype ontology: Enabling robust annotation and comparative analysis. WIREs Syst. Biol. Med. 2009, 1, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drysdale, R.; Cook, C.E.; Petryszak, R.; Baillie-Gerritsen, V.; Barlow, M.; Gasteiger, E.; Gruhl, F.; Haas, J.; Lanfear, J.; Lopez, R.; et al. The ELIXIR Core Data Resources: Fundamental infrastructure for the life sciences. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 2636–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Provider | Section | Type | Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| NCBI | Graph | Unification Link | web page |
| Fasta | Unification Link | web page | |
| Biosystems | Unification Link | web page | |
| Pathway | Unification Link | web page | |
| Protein | Unification Link | web page | |
| Geo Profile | Unification Link | web page | |
| PIE | Unification Link | web page | |
| IntAct | PSICQUIC | Unification Link | web page |
| Alzheimer db | Unification Link | web page | |
| Interactions | Unification Link | web page | |
| Genemania | Network Visualizer | Relationship Link | web page |
| Rb Store | Organism | Unification Link | web page |
| Allen Mouse Brain | Mouse Brain Experiments | Unification Link | web page |
| Developing Mouse Brain Experiments | Unification Link | web page | |
| Expression Mask Image | Unification Link | image file | |
| MGI Phenotypes | Phenotypes | Unification Link | web page |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Karapiperis, C.; Vasileiou, D.; Angelis, L.; Ouzounis, C.A. BRIDE v2: A Validated Collection of Genes Involved in the Mammalian Brain Response to Low-Dose Ionizing Radiation. Radiation 2022, 2, 311-317. https://doi.org/10.3390/radiation2040024
Karapiperis C, Vasileiou D, Angelis L, Ouzounis CA. BRIDE v2: A Validated Collection of Genes Involved in the Mammalian Brain Response to Low-Dose Ionizing Radiation. Radiation. 2022; 2(4):311-317. https://doi.org/10.3390/radiation2040024
Chicago/Turabian StyleKarapiperis, Christos, Dimitrios Vasileiou, Lefteris Angelis, and Christos A. Ouzounis. 2022. "BRIDE v2: A Validated Collection of Genes Involved in the Mammalian Brain Response to Low-Dose Ionizing Radiation" Radiation 2, no. 4: 311-317. https://doi.org/10.3390/radiation2040024
APA StyleKarapiperis, C., Vasileiou, D., Angelis, L., & Ouzounis, C. A. (2022). BRIDE v2: A Validated Collection of Genes Involved in the Mammalian Brain Response to Low-Dose Ionizing Radiation. Radiation, 2(4), 311-317. https://doi.org/10.3390/radiation2040024