Purification and Characterization of Antibodies Directed against the α-Gal Epitope
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Purification of Anti-α-Gal Antibodies
2.2. Conjugation of Anti-α-Gal Antibodies with Horseradish Peroxidase
2.3. Characterization of the Purified Anti-α-Gal Antibody
2.3.1. ELISA Binding Assays
2.3.2. Erythrocyte Agglutination Assay
2.3.3. Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR)
2.3.4. Western Blot
2.3.5. Determination of IgG Subclasses
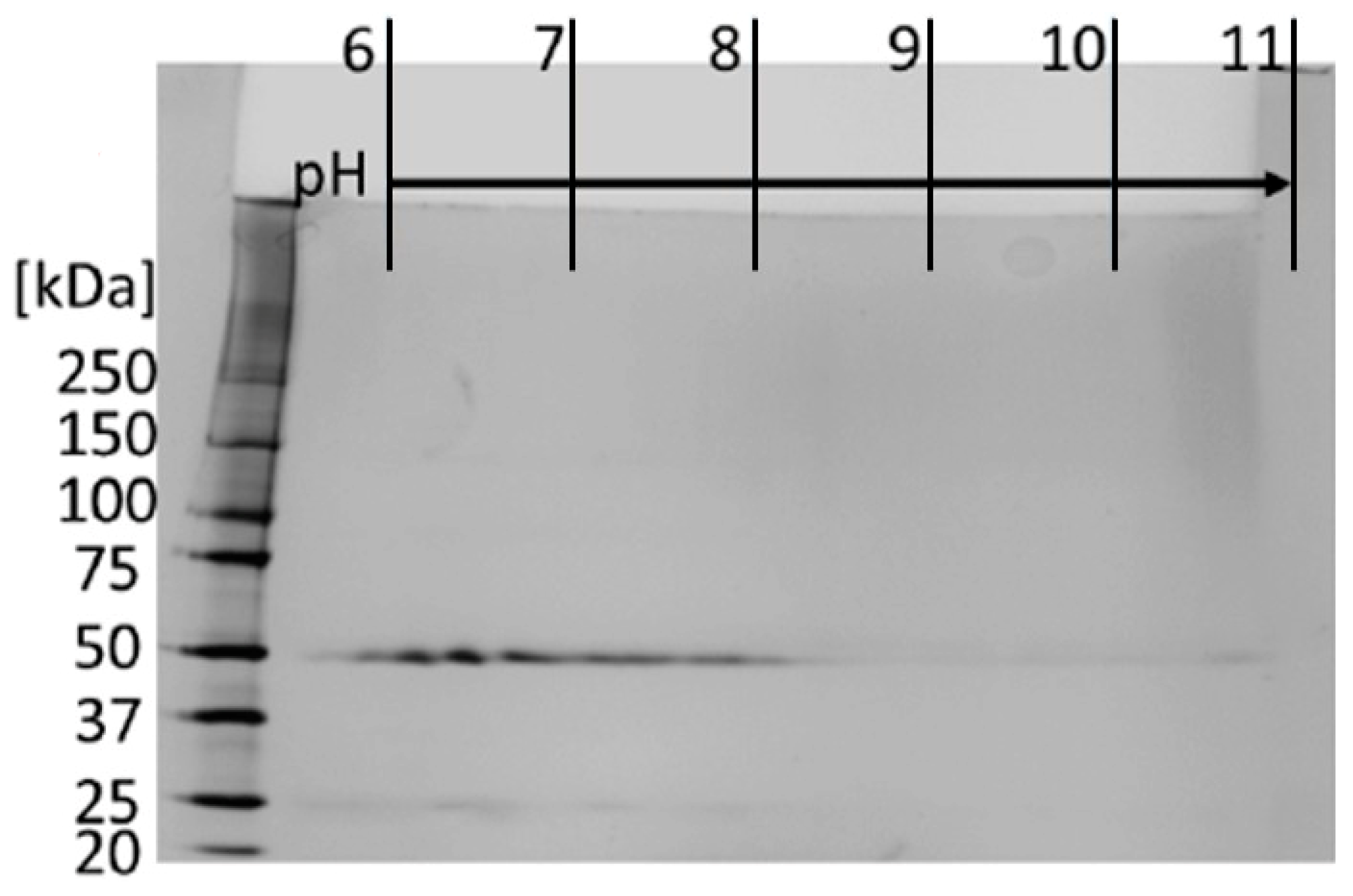
2.3.6. Two-Dimensional (2D) Gel Electrophoresis
2.3.7. N-Glycan Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
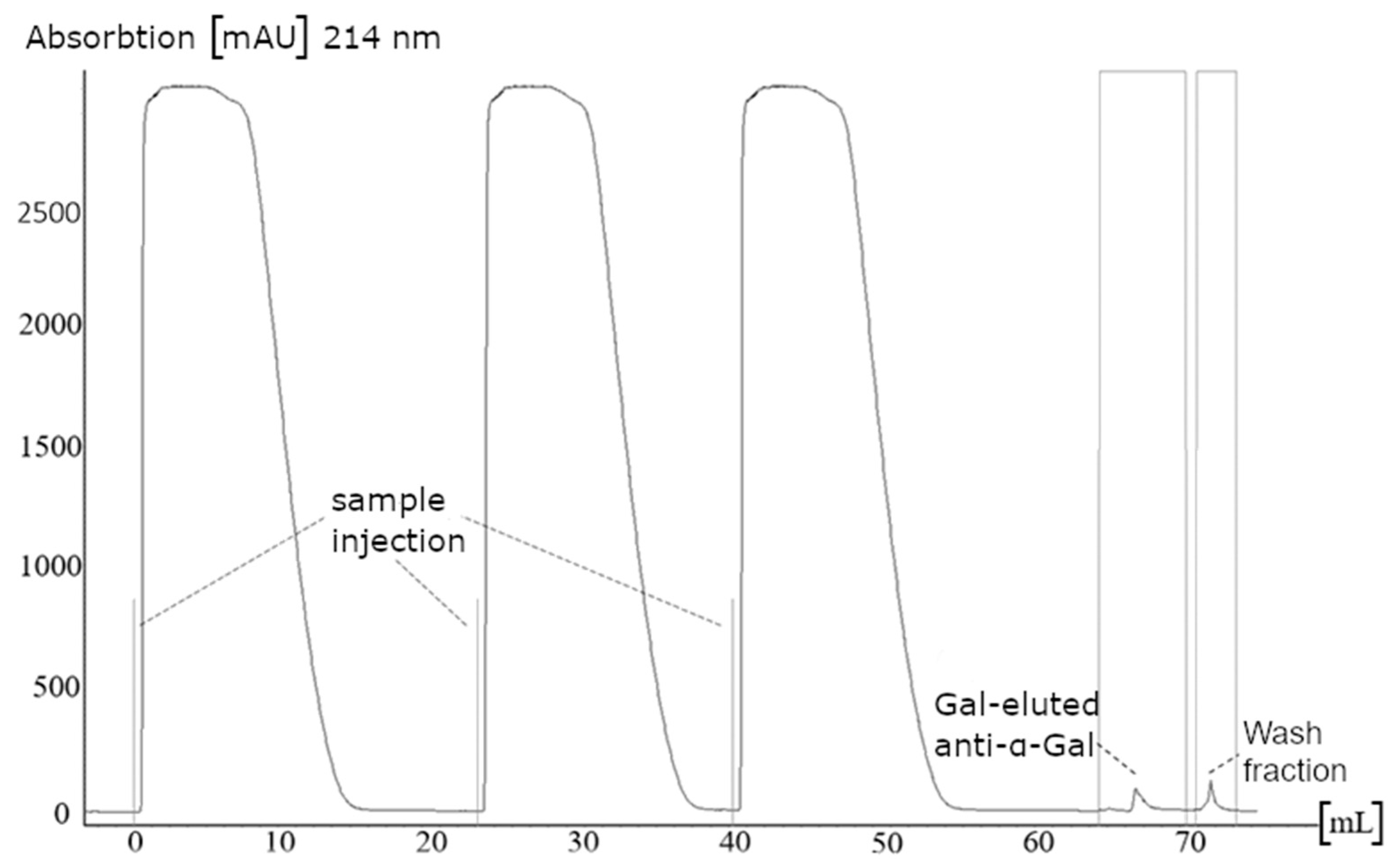
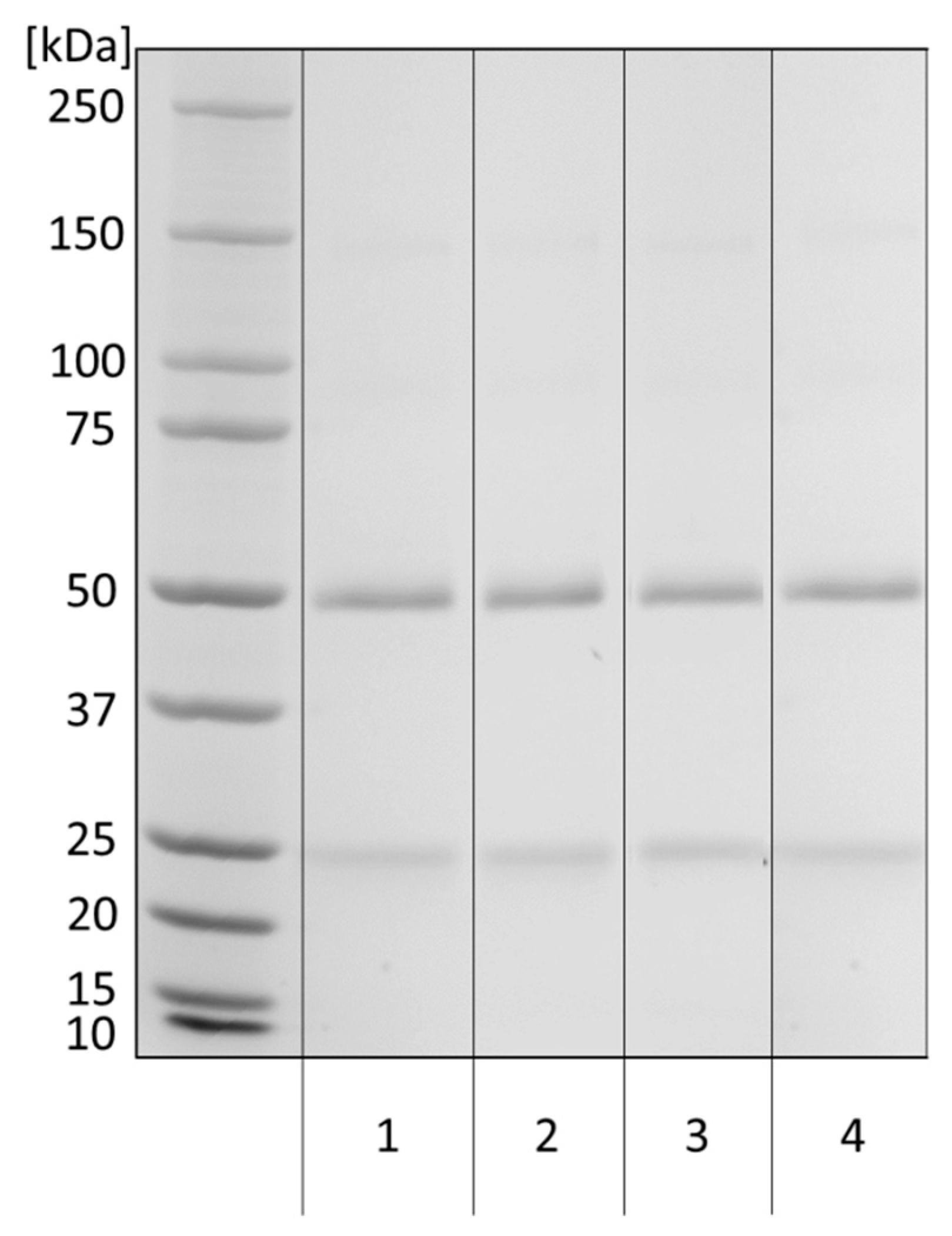
3.1. Purification of Anti-α-Gal Antibodies
3.2. Anti-α-Gal Antibody Characteristics
3.2.1. Subclass Determination
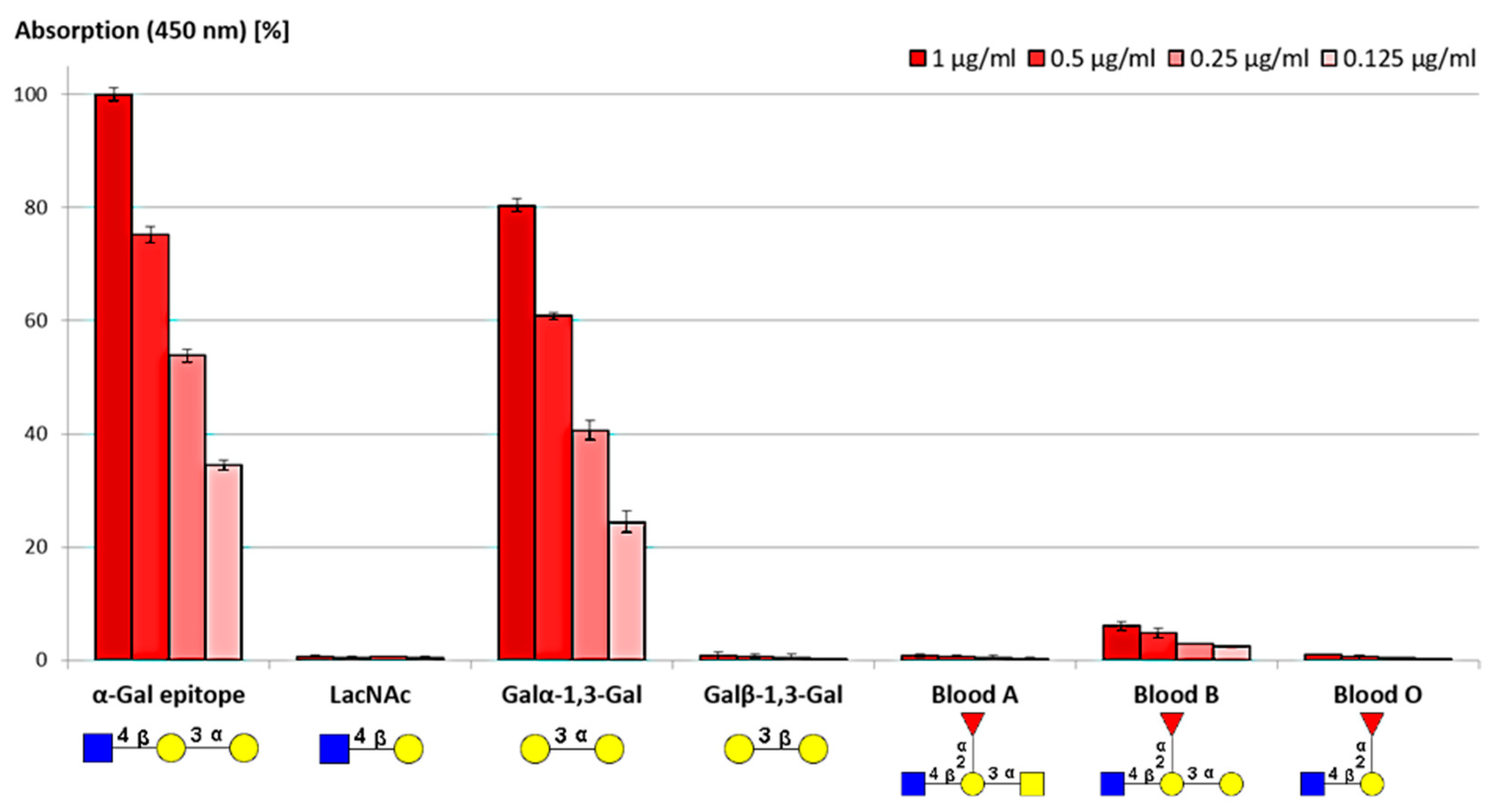
3.2.2. Selectivity and Binding Affinities of Anti-α-Gal Antibodies
ELISA Assay
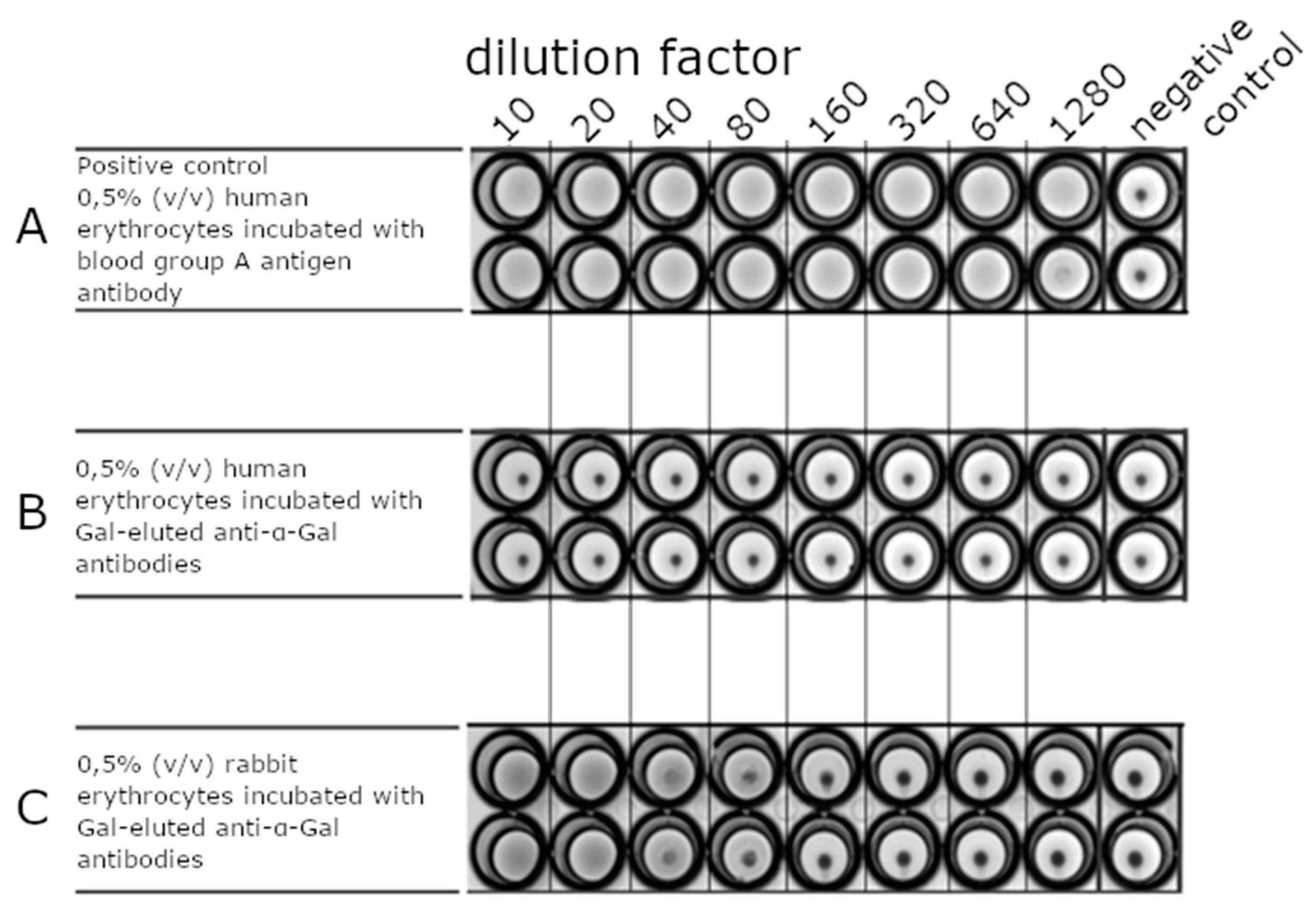
Erythrocyte Agglutination
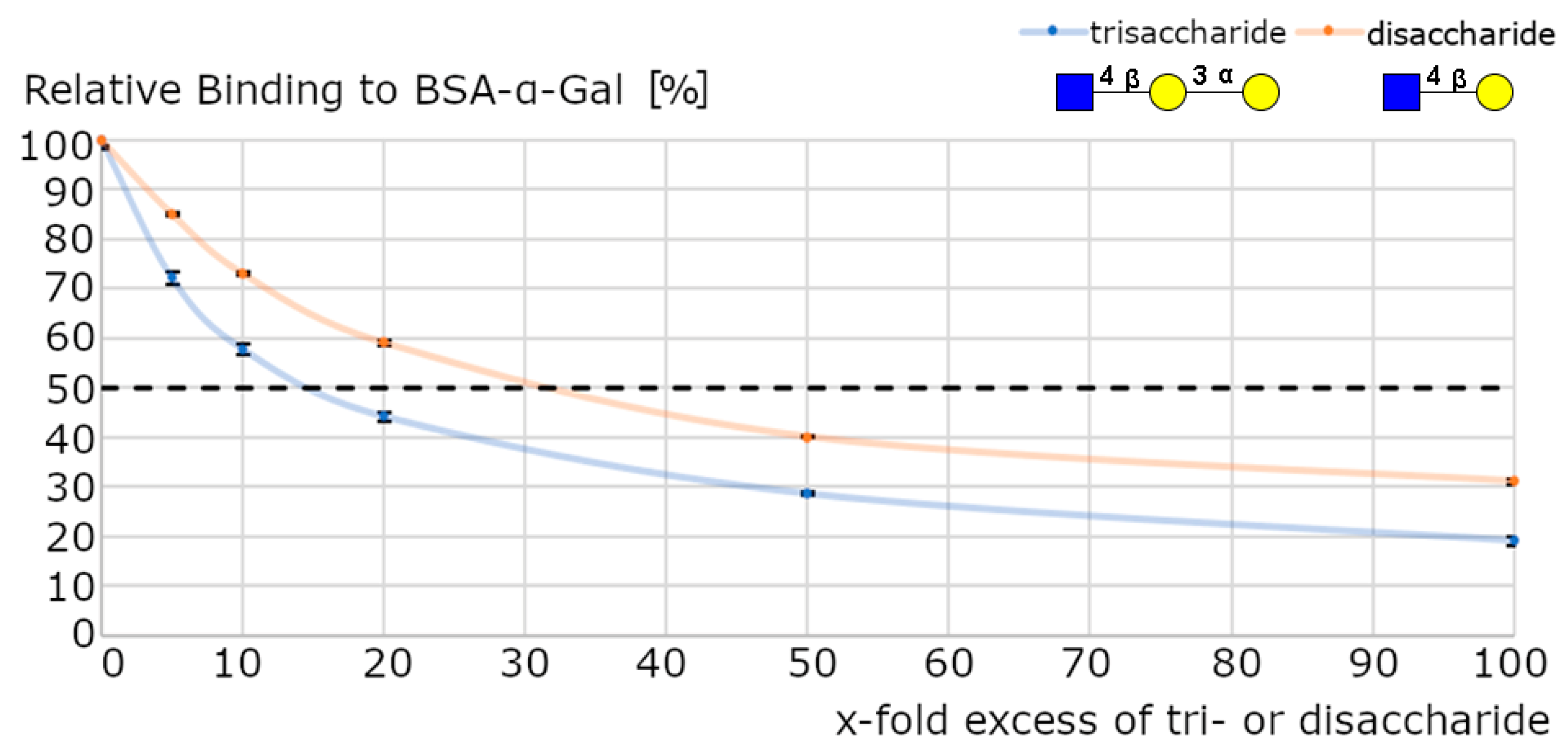
Binding Affinity
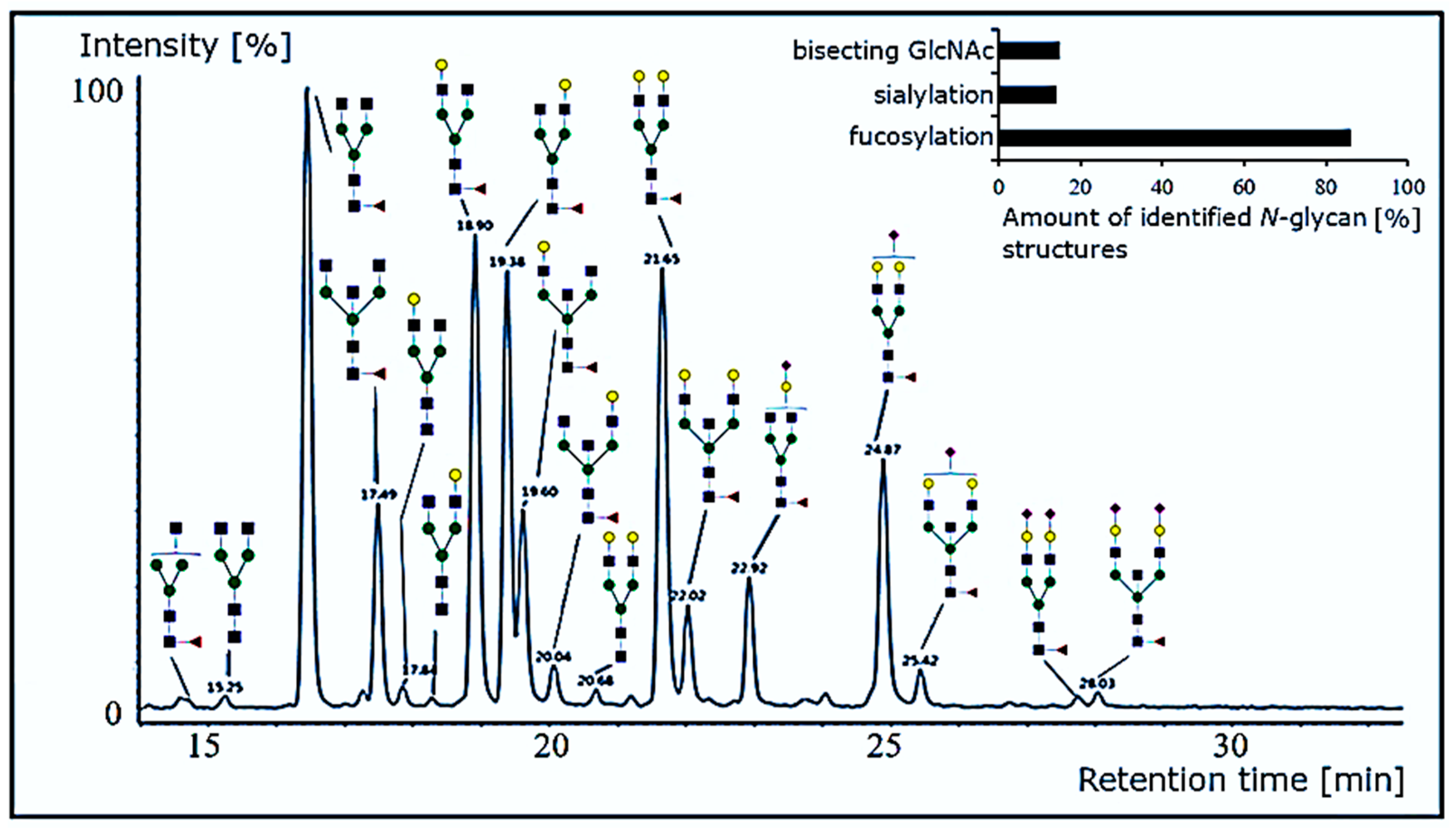
3.2.3. N-Glycosylation Profile of Anti-α-Gal Antibodies
3.3. Verification of the Anti-α-Gal Suitability as Detection Antibody
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Galili, U.; Rachmilewitz, E.A.; Peleg, A.; Flechner, I. A unique natural human IgG antibody with anti-alpha-galactosyl specificity. J. Exp. Med. 1984, 160, 1519–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huai, G.; Qi, P.; Yang, H.; Wang, Y. Characteristics of α-Gal epitope, anti-Gal antibody, α1,3 galactosyltransferase and its clinical exploitation (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 37, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galili, U.; Shohet, S.B.; Kobrin, E.; Stults, C.L.; Macher, B.A. Man, apes, and Old World monkeys differ from other mammals in the expression of alpha-galactosyl epitopes on nucleated cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1988, 263, 17755–17762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinke, J.W.; Platts-Mills, T.A.; Commins, S.P. The alpha-gal story: Lessons learned from connecting the dots. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 135, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, R.D.; Rivera-Marrero, C.A.; Ernst, L.K.; Cummings, R.D.; Lowe, J.B. Frameshift and nonsense mutations in a human genomic sequence homologous to a murine UDP-Gal:beta-D-Gal(1,4)-D-GlcNAc alpha(1,3)-galactosyltransferase cDNA. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 7055–7061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lantéri, M.; Giordanengo, V.; Vidal, F.; Gaudray, P.; Lefebvre, J.-C. A complete 1,3-galactosyltransferase gene is present in the human genome and partially transcribed. Glycobiology 2002, 12, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.C.; Tanemura, M.; Galili, U. Synthesis of -gal epitopes (Gal 1-3Gal 1-4GlcNAc-R) on human tumor cells by recombinant 1,3galactosyltransferase produced in Pichia pastoris. Glycobiology 2001, 11, 577–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanemura, M.; Miyoshi, E.; Nagano, H.; Eguchi, H.; Matsunami, K.; Taniyama, K.; Hatanaka, N.; Akamatsu, H.; Mori, M.; Doki, Y. Cancer immunotherapy for pancreatic cancer utilizing α-gal epitope/natural anti-Gal antibody reaction. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 11396–11410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanida, T.; Tanemura, M.; Miyoshi, E.; Nagano, H.; Furukawa, K.; Nonaka, Y.; Akita, H.; Hama, N.; Wada, H.; Kawamoto, K.; et al. Pancreatic cancer immunotherapy using a tumor lysate vaccine, engineered to express α-gal epitopes, targets pancreatic cancer stem cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 46, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galili, U.; Buehler, J.; Shohet, S.B.; Macher, B.A. The human natural anti-Gal IgG. III. The subtlety of immune tolerance in man as demonstrated by crossreactivity between natural anti-Gal and anti-B antibodies. J. Exp. Med. 1987, 165, 693–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galili, U. The α-gal epitope and the anti-Gal antibody in xenotransplantation and in cancer immunotherapy. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2005, 83, 674–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macher, B.A.; Galili, U. The Galalpha1,3Galbeta1,4GlcNAc-R (alpha-Gal) epitope: A carbohydrate of unique evolution and clinical relevance. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1780, 75–88. [Google Scholar]
- Galili, U. Anti-Gal: An abundant human natural antibody of multiple pathogeneses and clinical benefits. Immunology 2013, 140, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eto, T.; Ichikawa, Y.; Nishimura, K.; Ando, S.; Yamakawa, T. Chemistry of lipid of the posthemyolytic residue or stroma of erythrocytes. XVI. Occurrence of ceramide pentasaccharide in the membrane of erythrocytes and reticulocytes of rabbit. J. Biochem. 1968, 64, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egge, H.; Kordowicz, M.; Peter-Katalinić, J.; Hanfland, P. Immunochemistry of I/i-active oligo- and polyglycosylceramides from rabbit erythrocyte membranes. Characterization of linear, di-, and triantennary neolactoglycosphingolipids. J. Biol. Chem. 1985, 260, 4927–4935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, H.; Chinuki, Y.; Tanaka, A.; Morita, E. Laminin g-1 and collagen\alpha-1 (VI) chain are galactose-\alpha-1,3-galactose-bound allergens in beef. Allergy 2014, 69, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galili, U.; Mandrell, R.E.; Hamadeh, R.M.; Shohet, S.B.; Griffiss, J.M. Interaction between human natural anti-alpha-galactosyl immunoglobulin G and bacteria of the human flora. Infect. Immun. 1988, 56, 1730–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, B.; Portugal, S.; Tran, T.; Gozzelino, R.; Ramos, S.; Gomes, J.; Regalado, A.; Cowan, P.J.; D’Apice, A.J.; Chong, A.S.; et al. Gut Microbiota Elicits a Protective Immune Response against Malaria Transmission. Cell 2014, 159, 1277–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galili, U.; Anaraki, F.; Thall, A.; Hill-Black, C.; Radic, M. One percent of human circulating B lymphocytes are capable of producing the natural anti-Gal antibody. Blood 1993, 82, 2485–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anraku, K.; Sato, S.; Jacob, N.; Eubanks, L.M.; Ellis, B.A.; Janda, K.D. The design and synthesis of an α-Gal trisaccharide epitope that provides a highly specific anti-Gal immune response. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2017, 15, 2979–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, H.A.; Loveland, B.E.; Sandrin, M.S. Gal alpha(1,3)Gal is the major xenoepitope expressed on pig endothelial cells recognized by naturally occurring cytotoxic human antibodies. Transplantation 1994, 58, 879–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanemura, M.; Maruyama, S.; Galil, I.U. Differential expression of alpha-GAL epitopes (Galalpha1-3Galbeta1-4GlcNAc-R) on pig and mouse organs. Transplantation 2000, 69, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiro, R.G.; Bhoyroo, V.D. Occurrence of alpha-D-galactosyl residues in the thyroglobulins from several species. Localization in the saccharide chains of the complex carbohydrate units. J. Biol. Chem. 1984, 259, 9858–9866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanemura, M.; Yin, D.; Chong, A.S.; Galili, U. Differential immune responses to alpha-Gal epitopes on xenografts and allografts // Differential immune responses to alpha-gal epitopes on xenografts and allografts: Implications for accommodation in xenotransplantation. J. Clin. Investig. 2000, 105, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naso, F.; Gandaglia, A.; Iop, L.; Spina, M.; Gerosa, G. Alpha-Gal detectors in xenotransplantation research: A word of caution. Xenotransplantation 2012, 19, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.H.; Mirakhur, B.; Chan, E.; Le, Q.-T.; Berlin, J.; Morse, M.; Murphy, B.A.; Satinover, S.M.; Hosen, J.; Mauro, D.; et al. Cetuximab-Induced Anaphylaxis and IgE Specific for Galactose-α-1,3-Galactose. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 1109–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebo, D.G.; Faber, M.; Sabato, V.; Leysen, J.; Gadisseur, A.; Bridts, C.H.; de Clerck, L.S. Sensitization to the mammalian oligosaccharide galactose-alpha-1,3-galactose (alpha-gal): Experience in a Flemish case series. Acta Clin. Belg. 2013, 68, 206–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, S.; Scherer, K.; Heijnen, I.A.F.M.; Bircher, A.J. Skin prick test and basophil reactivity to cetuximab in patients with IgE to alpha-gal and allergy to red meat. Allergy 2013, 69, 403–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, E.A.; Platts-Mills, T.A.; Commins, S.P. Drug allergens and food—the cetuximab and galactose-α-1,3-galactose story. Ann. Allergy. Asthma Immunol. 2014, 112, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Platts-Mills, T.A.; Schuyler, A.J.; Tripathi, A.; Commins, S.P. Anaphylaxis to the Carbohydrate Side Chain Alpha-gal. Immunol. Allergy Clin. N. Am. 2015, 35, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jappe, U. “Update on meat allergy. alpha-Gal: A new epitope, a new entity?”. Der Hautarzt Zeitschrift Für Dermatologie Venerologie Und Verwandte Gebiete 2012, 63, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jappe, U.; Minge, S.; Kreft, B.; Ludwig, A.; Przybilla, B.; Walker, A.; Varga, R.; Seidel, P.; Biedermann, T.; Anemüller, W.; et al. Meat allergy associated with galactosyl-α-(1,3)-galactose (α-Gal)-Closing diagnostic gaps by anti-α-Gal IgE immune profiling. Allergy 2017, 73, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolver, S.E.; Sun, D.R.; Commins, S.P.; Schwartz, L.B. A peculiar cause of anaphylaxis: No more steak? The journey to discovery of a newly recognized allergy to galactose-alpha-1,3-galactose found in mammalian meat. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2013, 28, 322–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flaherty, M.G.; Kaplan, S.J.; Jerath, M.R. Diagnosis of Life-Threatening Alpha-Gal Food Allergy Appears to Be Patient Driven. J. Prim. Care Community Health 2017, 8, 345–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commins, S.P.; James, H.R.; Kelly, L.A.; Pochan, S.L.; Workman, L.J.; Perzanowski, M.S.; Kocan, K.M.; Fahy, J.V.; Nganga, L.W.; Ronmark, E.; et al. The relevance of tick bites to the production of IgE antibodies to the mammalian oligosaccharide galactose-α-1,3-galactose. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 127, 1286–1293.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamsten, C.; Tran, T.A.T.; Starkhammar, M.; Brauner, A.; Commins, S.P.; Platts-Mills, T.A.; van Hage, M. Red meat allergy in Sweden: Association with tick sensitization and B-negative blood groups. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 132, 1431–1434.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan, L.G. Red meat allergy induced by tick bites: A Norwegian case report. Eur. Ann. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 49, 186–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoury, J.K.; Khoury, N.C.; Schaefer, D.; Chitnis, A.; Hassen, G.W. A tick-acquired red meat allergy: A case series. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2017. [CrossRef]
- Mateos-Hernández, L.; Villar, M.; Moral, A.; Rodríguez, C.G.; Arias, T.A.; De La Osa, V.; Brito, F.F.; De Mera, I.G.F.; Alberdi, P.; Ruiz-Fons, F.; et al. Tick-host conflict: Immunoglobulin E antibodies to tick proteins in patients with anaphylaxis to tick bite. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 20630–20644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Motal, U.M.; Guay, H.M.; Wigglesworth, K.; Welsh, R.M.; Galili, U. Immunogenicity of Influenza Virus Vaccine Is Increased by Anti-Gal-Mediated Targeting to Antigen-Presenting Cells. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 9131–9141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varki, A.; Cummings, R.D.; Esko, J.D.; Freeze, H.; Stanley, P.; Marth, J.D.; Bertozzi, C.R.; Hart, G.; Etzler, M.E. Symbol nomenclature for glycan representation. Proteomics 2009, 9, 5398–5399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Towbin, H.; Staehelin, T.; Gordon, J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: Procedure and some applications. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1979, 76, 4350–4354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, A.; Duffy, C.; Gordon, A.; Morrison, S.; Arguello, A.; Welsh, M.; Earley, B. Comparison of single radial immunodiffusion and ELISA for the quantification of immunoglobulin G in bovine colostrum, milk and calf sera. J. Appl. Anim. Res. 2018, 46, 758–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevallet, M.; Luche, S.; Rabilloud, T. Silver staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 1852–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieben, R.; Allmen, E.; Korchagina, E.Y.; Nydegger, U.E.; Neethling, F.A.; Kujundžić, M.; Koren, E.; Bovin, N.V.; Cooper, D.K. Detection, immunoabsorption, and inhibition of cytotoxic activity of anti-αGal antibodies using newly developed substances with synthetic Gal α1-3Gal disaccharide epitopes. Xenotransplantation 1995, 2, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obukhova, P.; Rieben, R.; Bovin, N. Normal human serum contains high levels of anti-Gal alpha 1-4GlcNAc antibodies. Xenotransplantation 2007, 14, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Holzknecht, E.Z.; Bruno, D.; Parker, W.; Platt, J.L. Modulation of natural IgM binding and complement activation by natural IgG antibodies: A role for IgG anti-Gal alpha1-3Gal antibodies. J. Immunol. 1996, 157, 5163–5168. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tomlinson, S.; Nussenzweig, V. Human alternative complement pathway-mediated lysis of rabbit erythrocytes is enhanced by natural anti-Galalpha1-3Gal antibodies. J. Immunol. 1997, 159, 5606–5609. [Google Scholar]
- Rispens, T.; Derksen, N.I.L.; Commins, S.P.; Platts-Mills, T.A.; Aalberse, R.C. IgE Production to α-Gal Is Accompanied by Elevated Levels of Specific IgG1 Antibodies and Low Amounts of IgE to Blood Group, B. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidarsson, G.; Dekkers, G.; Rispens, T. IgG Subclasses and Allotypes: From Structure to Effector Functions. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Germann, T.; Bongartz, M.; Dlugonska, H.; Hess, H.; Schmitt, E.; Kolbe, L.; Kölsch, E.; Podlaski, F.J.; Gately, M.K.; Rüde, E. Interleukin-12 profoundly up-regulates the synthesis of antigen-specific complement-fixing IgG2a, IgG2b and IgG3 antibody subclasses in vivo. Eur. J. Immunol. 1995, 25, 823–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, S.C.; Shaulov, A.; Wang, R.; Balk, S.P.; Exley, M.A. CD1d ligation on human monocytes directly signals rapid NF-kappaB activation and production of bioactive IL-12. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 11811–11816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Kandeva, T.; Tchervenkov, J. CD1d-Mediated Interaction Between Activated T Cells and B Cells Is Essential to B-Cell Proliferation and Anti-α-Gal Antibody Production. Transplant. Proc. 2009, 41, 398–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.-S.; Subramaniam, S.; Narang, V.; Srinivasan, K.; Saunders, S.P.; Carbajo, D.; Wen-Shan, T.; Hamadee, N.H.; Lum, J.; Lee, A.; et al. IgG1 memory B cells keep the memory of IgE responses. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Lee, S.; Kwon, S.Y.; Lee, Y.; Park, Y.K.; Ban, S.J. Analysis of the proficiency of single radial immunodiffusion assays for quality control of influenza vaccines in Korea. Biologicals. 2017, 50, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williamson, A.R. Antibody isoelectric spectra. Analysis of the heterogeneity of antibody molecules in serum by isoelectric focusing in gel and specific detection with hapten. Eur. J. Immunol. 1971, 1, 390–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prin, C.; Bene, M.C.; Gobert, B.; Montagne, P.; Faure, G.C. Isoelectric restriction of human immunoglobulin isotypes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Gen. Subj. 1995, 1243, 287–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milland, J.; Yuriev, E.; Xing, P.-X.; McKenzie, I.F.C.; Ramsland, P.A.; Sandrin, M.S. Carbohydrate residues downstream of the terminal Galα(1,3)Gal epitope modulate the specificity of xenoreactive antibodies. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2007, 85, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galili, U.; LaTemple, D.C.; Radic, M.Z. A sensitive assay for measuring α-gal epitope expression on cells by a monoclonal anti-gal antibody1. Transplantation 1998, 65, 1129–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabezas-Cruz, A.; de la Fuente, J. Immunity to α-Gal: Toward a Single-Antigen Pan-Vaccine To Control Major Infectious Diseases. ACS Cent. Sci. 2017, 3, 1140–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brestoff, J.R.; Tesfazghi, M.T.; Zaydman, M.A.; Jackups, R.; Kim, B.S.; Scott, M.G.; Gronowski, A.M.; Grossman, B.J. The B antigen protects against the development of red meat allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2018, 6, 1790–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galili, U.; Swanson, K. Gene sequences suggest inactivation of alpha-1,3-galactosyltransferase in catarrhines after the divergence of apes from monkeys. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 7401–7404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galili, U. Significance of the Evolutionary α1,3-Galactosyltransferase (GGTA1) Gene Inactivation in Preventing Extinction of Apes and Old World Monkeys. J. Mol. Evol. 2014, 80, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plum, M.; Michel, Y.; Wallach, K.; Raiber, T.; Blank, S.; Bantleon, F.I.; Diethers, A.; Greunke, K.; Braren, I.; Hackl, T.; et al. Close-up of the Immunogenic α1,3-Galactose Epitope as Defined by a Monoclonal Chimeric Immunoglobulin E and Human Serum Using Saturation Transfer Difference (STD) NMR. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 43103–43111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pourazar, A. Red cell antigens: Structure and function. Asian J. Transfus. Sci. 2007, 1, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller-Loennies, S.; MacKenzie, C.; Patenaude, S.I.; Evans, S.; Kosma, P.; Brade, H.; Brade, L.; Narang, S. Characterization of high affinity monoclonal antibodies specific for chlamydial lipopolysaccharide. Glycobiology 2000, 10, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Rispens, T.; Heer, P.O.-D.; Derksen, N.I.; Wolbink, G.; Van Schouwenburg, P.A.; Kruithof, S.; Aalberse, R.C. Nanomolar to sub-picomolar affinity measurements of antibody–antigen interactions and protein multimerizations: Fluorescence-assisted high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal. Biochem. 2013, 437, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.K. Generation of Recombinant Anti-N-Glycolylneuraminic Acid (Neu5Gc) Scfv and Its Applications for Detection and Quantitation of Neu5Gc. Ph.D. Thesis, National University of Ireland, Galway, Ireland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Galili, U.; Basbaum, C.; Shohet, S.; Buehler, J.; Macher, B. Identification of erythrocyte Gal alpha 1-3Gal glycosphingolipids with a mouse monoclonal antibody, Gal-13. J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 4683–4688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.-W.; Li, S.-B.; Sun, W.Q.; Yun, Z.-M.; Zhang, X.; Song, J.-W.; Zhang, S.-K.; Leng, L.; Ji, S.-P.; Tan, Y.-X.; et al. Quantification of α-Gal Antigen Removal in the Porcine Dermal Tissue by α-Galactosidase. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods 2015, 21, 1197–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buehler, J.; Galili, U.; Macher, B.A. Use of the enzyme-linked immunoadsorbent assay to monitor the purification of glycosphingolipid antigens by high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal. Biochem. 1987, 164, 521–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; Bantog, C.; Bayer, R. The impact of glycosylation on monoclonal antibody conformation and stability. mAbs 2011, 3, 568–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higel, F.; Seidl, A.; Sörgel, F.; Friess, W. N-glycosylation heterogeneity and the influence on structure, function and pharmacokinetics of monoclonal antibodies and Fc fusion proteins. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2016, 100, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; DiLillo, D.J.; Bournazos, S.; Giddens, J.; Ravetch, J.V.; Wang, L.-X. Modulating IgG effector function by Fc glycan engineering. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 3485–3490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Woen, S.; Wang, T.; Liau, B.; Zhao, S.; Chen, C.; Yang, Y.; Song, Z.; Wormald, M.R.; Yu, C.; et al. Challenges of glycosylation analysis and control: An integrated approach to producing optimal and consistent therapeutic drugs. Drug Discov. Today 2016, 21, 740–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakae, Y.; Satoh, T.; Yagi, H.; Yanaka, S.; Yamaguchi, T.; Isoda, Y.; Iida, S.; Okamoto, Y.; Kato, K. Conformational effects of N-glycan core fucosylation of immunoglobulin G Fc region on its interaction with Fc\gamma receptor IIIa. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cymer, F.; Beck, H.; Rohde, A.; Reusch, D. Therapeutic monoclonal antibody N-glycosylation–Structure, function and therapeutic potential. Biologicals 2018, 52, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolovic, D.; Krstic, M.; Mihailovic, J.; Starkhammar, M.; Cirkovic, V.T.; Hamsten, C.; van Hage, M. Peptidomics of an in vitro digested \alpha-Gal carrying protein revealed IgE-reactive peptides. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; Liu, T.; Yang, L.; Daus, A.; Crowley, R.; Zhou, Q. Structural characterization of N-linked oligosaccharides on monoclonal antibody cetuximab by the combination of orthogonal matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization hybrid quadrupole–quadrupole time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry and sequential enzymatic digestion. Anal. Biochem. 2007, 364, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalpathado, D.S.; Desaire, H. Glycopeptide analysis by mass spectrometry. Analyst 2008, 133, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Qu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Prytkova, I.; Wu, S. Intact glycopeptide characterization using mass spectrometry. Expert Rev. Proteom. 2016, 13, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y. New Approaches for Quantitative Analysis of Glycopeptides Using Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Georgia, Athens, Greece, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lalonde, M.-E.; Durocher, Y. Therapeutic glycoprotein production in mammalian cells. J. Biotechnol. 2017, 251, 128–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Subclass | Calibrator Concentration [µg/mL] | Squared Diameter [cm2] | Sample Concentration [µg/mL] | Relative Part [%] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calibrator | Sample | ||||
| IgG1 | 1400 | 0.81 | 0.36 ± 0.06 | 492 ± 111 | 24 ± 6 |
| 840 | 0.64 | ||||
| 350 | 0.25 | ||||
| 140 | 0.16 | ||||
| IgG2 | 800 | 0.64 | 0.55 ± 0.05 | 1422 ± 137 | 76 ± 7 |
| 480 | 0.36 | ||||
| 200 | 0.16 | ||||
| 80 | 0.09 | ||||
| IgG3 | - | - | n.d. | - | - |
| IgG4 | - | - | n.d. | - | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zappe, A.; Rosenlöcher, J.; Kohla, G.; Hinderlich, S.; Parr, M.K. Purification and Characterization of Antibodies Directed against the α-Gal Epitope. BioChem 2021, 1, 81-97. https://doi.org/10.3390/biochem1020008
Zappe A, Rosenlöcher J, Kohla G, Hinderlich S, Parr MK. Purification and Characterization of Antibodies Directed against the α-Gal Epitope. BioChem. 2021; 1(2):81-97. https://doi.org/10.3390/biochem1020008
Chicago/Turabian StyleZappe, Andreas, Julia Rosenlöcher, Guido Kohla, Stephan Hinderlich, and Maria Kristina Parr. 2021. "Purification and Characterization of Antibodies Directed against the α-Gal Epitope" BioChem 1, no. 2: 81-97. https://doi.org/10.3390/biochem1020008
APA StyleZappe, A., Rosenlöcher, J., Kohla, G., Hinderlich, S., & Parr, M. K. (2021). Purification and Characterization of Antibodies Directed against the α-Gal Epitope. BioChem, 1(2), 81-97. https://doi.org/10.3390/biochem1020008






