Revisit of the Photoirradiation of ?-Lipoic Acid—Role of Hydrogen Sulfide Produced in the Reaction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
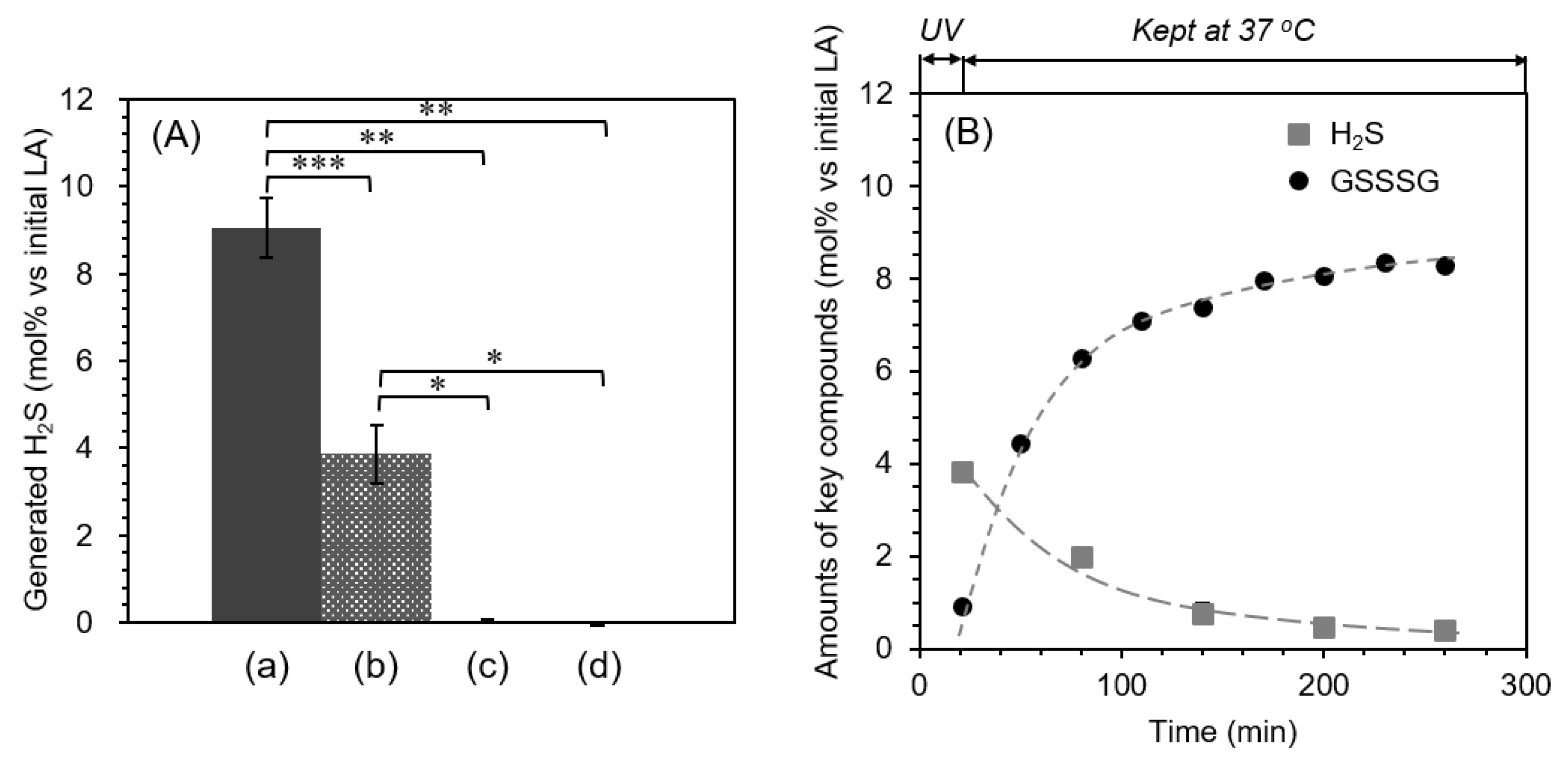
2.1. Generation of Glutathione Trisulfide (GSSSG) by Ultra-Violet Light (UVL) Irradiation of α-Lipoic Acid (LA) in the Presence of Oxidized Glutathione (GSSG)
2.2. UVL Irradiation of LA in the Presence of Cystine (CysSSCys) and Dimethyldisulfide (DMDS)
2.3. Quantification of Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S)
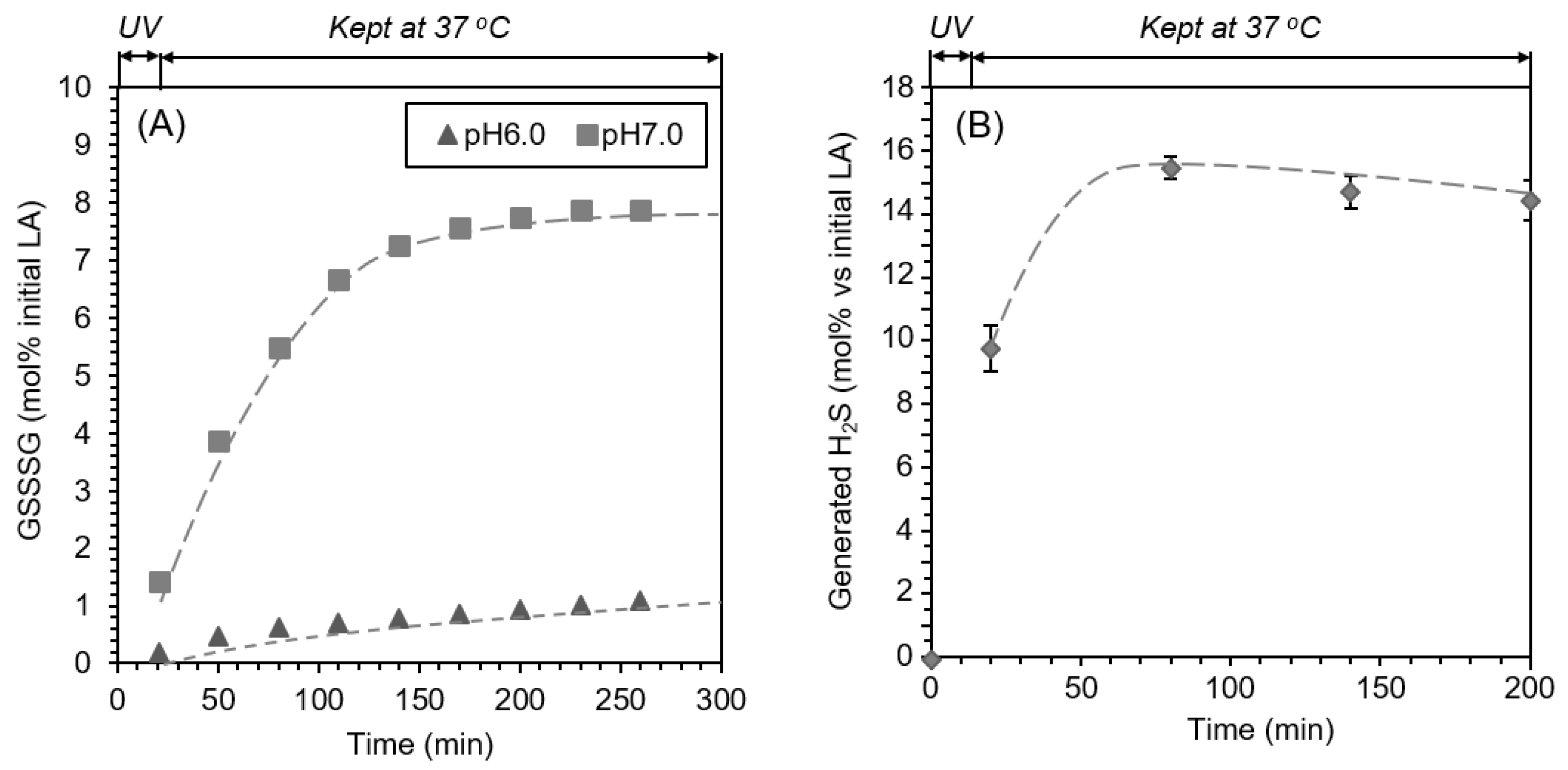
2.4. pH-Dependent Formation of GSSSG
2.5. Reaction of GSSG with Na2S
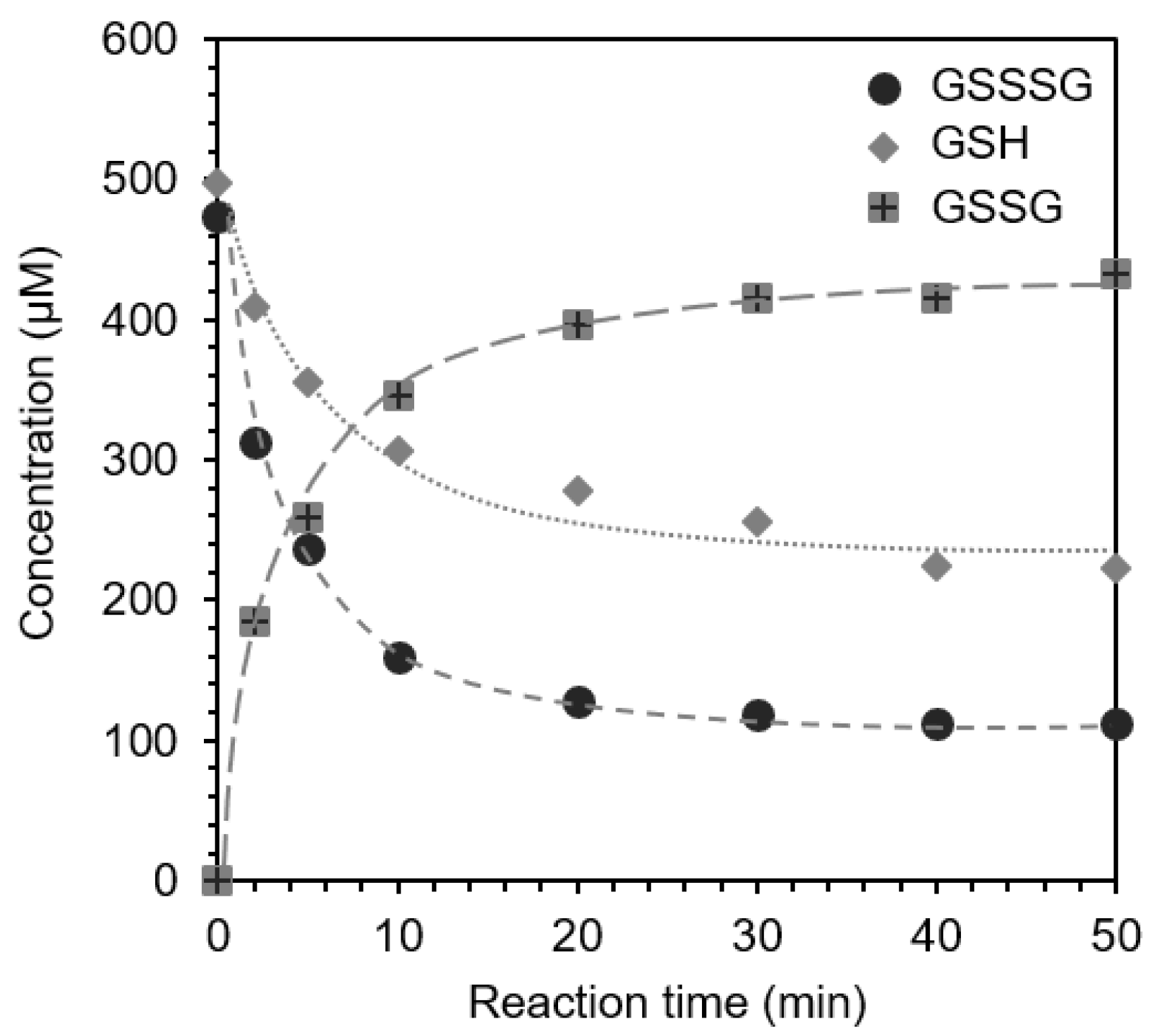
2.6. Reaction of GSSSG with Glutathione (GSH) (Interaction and Cross-Talk of Biothiols)
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Photoreaction of LA in the Presence of Disulfides (GSSG, CysSSCys, DMDS)
4.3. Quantification of H2S Using a Methylene Blue Method
4.4. GSSSG Formation at Different pH Conditions
4.5. The Reaction of GSSG with Na2S at Air-Saturated and Degassed Conditions
4.6. The Reaction of GSSSG with GSH
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Han, D.; Tritschler, H.J.; Packer, L. Alpha-lipoic acid increases the intracellular glutathione in a human T-lymphocyte in Jurkat cell line. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1995, 207, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packer, L.; Wutt, H.H.; Tritschler, H.J. Alpha-lipoic acid as a biological antioxidant. Free Rad. Biol. Med. 1995, 19, 227–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.P. Redefining oxidative stress. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2006, 8, 1865–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, M.; Go, Y.M.; Jones, D.P. Nonequilibrium thermodynamics of thiol/disulfide redox systems: A perspective on redox system biology. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2008, 44, 921–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamada, T.; Hashida, K.; Takarada-Iemata, M.; Matsugo, S.; Hori, O. a-Lipoic acid enantiomers protect SH-SY5Y cells against glutathione depletion. Neurochem. Int. 2011, 59, 1003–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moni, H.; Packer, L.; Saris, N.E.L. Antioxidant and prooxidant activities of alpha-lipoic acid and dihydrolipoic acid. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2002, 182, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Packer, L.; Cadenas, E. Lipoic acid: Energy metabolism and redox regulation of transcription and cell signaling. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2011, 48, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dorsam, B.; Fahrer, J. The disulfide compound a-lipoic acid and its derivatives: A novel class of anticancer agents targeting mitochondria. Cancer Lett. 2016, 371, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsugo, S.; Han, D.; Tritschler, H.J.; Packer, L. Decomposition of alpha-lipoic acid derivatives by photoirradiation- formation of dihydrolipoic acid from alpha-lipoic acid-. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Int. 1996, 38, 51–59. [Google Scholar]
- Ikuta, N.; Sugiyama, H.; Shimosegawa, H.; Nakane, R.; Ishida, Y.; Uekaji, Y.; Nakata, D.; Pallauf, K.; Rimbach, G.; Terao, K.; et al. Analysis of the enhanced stability of R(+)-alpha lipoic acid by the complex formation with cyclodextrins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 3639–3655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ikuta, N.; Tanaka, A.; Otsubo, A.; Ogawa, N.; Yamamoto, H.; Mizukami, T.; Arai, S.; Okuno, M.; Terao, K.; Matsugo, S. Spectroscopic studies of R(+)-alpha-lipoic acid complexes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 20469–20485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ikuta, N.; Endo, T.; Hosomi, S.; Setou, K.; Tanaka, S.; Ogawa, N.; Yamamoto, H.; Mizukami, T.; Arai, S.; Okuno, M.; et al. Structural analysis of crystalline R(+)-alpha-lipoic acid-alpha-cyclodextrin complex based on microscopic and spectroscopic studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 24614–24628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wada, N.; Wakami, H.; Konishi, T.; Matsugo, S. The effect of biothiol on UV irradiated α–lipoic acid. Biofactors 2008, 34, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, N.; Wakami, H.; Konishi, T.; Matsugo, S. The degradation and regeneration of α–lipoic acid under the irradiation of UV light in the existence of Homocysteine. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2009, 44, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Calvin, M.; Barltrop, J.A. A possible primary quantum conversion act of photosynthesis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1952, 74, 6153–6154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brown, P.R.; Edwards, J.O. Effect of solvent on the photolysis of α–lipoic acid. J. Org. Chem. 1969, 34, 3131–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida, M.; Sawa, T.; Kitajima, N.; Ono, K.; Inoue, H.; Ihara, H.; Motohashi, N.; Yamamoto, M.; Suematsu, M.; Kurose, H. Hydrogen sulfide anion regulates redox signaling via electrophile sulfhydration. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2012, 8, 714–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, K.; Akaike, T.; Sawa, T.; Kumagai, Y.; Wink, D.A.; Tantillo, D.J.; Hobbs, A.J.; Nagy, P.; Xian, M.; Lin, J.; et al. Redox chemistry and chemical biology of H2S, hydropersulfides, and derived species: Implications of their possible biological activity and utility. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2014, 77, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wallace, J.L. Hydrogen sulfide-releasing anti-inflammatory drugs. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2007, 28, 501–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Bhatia, M.; Zhu, Y.Z.; Zhu, Y.C.; Ramnath, R.D.; Wang, Z.J.; Mohammed Anuar, F.B.; Whiteman, M.; Salto-Tellez, M.; Moore, P.K. Hydrogen sulfide is a novel mediator of lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in the mouse. FASEB J. 2005, 19, 1196–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ida, T.; Sawa, T.; Ihara, H.; Tsuchiya, Y.; Watanabe, Y.; Kumagai, Y.; Suematsu, M.; Motohashi, H.; Fujii, S.; Matsunaga, T.; et al. Reactive cysteine persulfides and S-polythiolation regulate oxidative stress and redox signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 7606–7611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tajc, S.G.; Tolbert, B.S.; Basavappa, R.; Miller, B.L. Direct determination of thiol pKa by isothermal titration microcalorimetry. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 10508–10509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevasanta, E.; Lange, M.; Bonanta, J.; Coitino, E.L.; Ferrer-Sueta, G.; Filipovic, M.R.; Alvarez, B. Reaction of hydrogen sulfide with disulfide and sulfenic acid to form the strongly nucleophilic persulfide. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 26866–26880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cotton, F.; Wilkinson, G. Advanced Inorganic Chemistry; John Wiley Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Self, W.T.; Tsai, L.; Stadtman, C. Synthesis and characterization of selenotrisulfide-derivatives of lipoic acid and lipoamide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 12481–12486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Munday, M.; Munday, J.S.; Munday, C.M. Comparative mono-, di-, tri-and tetrasulfides derived from plants of the Allium family: Redox cycling in vitro and hemolytic activity Phase 2 enzyme induction in vivo. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2003, 34, 1200–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-M.; Chang, H.J.; Kim, W.-K.; Chang, N.; Chun, H.S. Structure-activity relationship of neuroprotective and reactive oxygen species scavenging activities for allium organosulfur compounds. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 6547–6553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, J. Ascent of therapy: Pharmacological implications of natural products containing redox-active sulfur atoms. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2006, 23, 851–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panzella, L.; Verotta, L.; Goya, L.; Ramos, S.; Martin, M.A.; Bravo, L.; Napolitano, A.; d’Lschia, M. Synthesis and bioactivity profile of 5-s-lipoylhydroxytyrosol-based multidefense antioxidants with sizable(poly)sulfide chain. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 1710–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iciek, M.; Włodek, L. Biosynthesis and biological properties of compounds containing highly reactive, reduced sulfate sulfur. Pol. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 53, 215–225. [Google Scholar]
- Park, C.M.; Weerasinghe, L.; Day, J.J.; Fukuto, J.M.; Xian, M. Persulfides: Current knowledge and challenges in chemistry and chemical biology. Mol. Biosyst. 2015, 11, 1775–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bilska, A.; Dudek, M.; Iciek, M.; Kwiecien, I.; Sokotowska-Jezewicz, M.; Filipek, B.; Wtodek, L. Biological actions of lipoic associated with sulfane sulfur metabolism. Pharmacol. Rep. 2008, 60, 225–232. [Google Scholar]
- Bilska-Wilkosz, A.; Iciek, M.; KowalczykpPachel, D.; Gorny, M.; Sokolowska-Jezewicz, M.; Wlodek, L. Lipoic acid as a possible pharmacological source of hydrogen sulfide/sulfane sulfur. Molecules 2017, 22, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| pH | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HS−/H2S | 1/100 | 1/10 | 1/1 | 10/1 | 100/1 |
| GS−/GSH | 1/10,000 | 1/1000 | 1/100 | 1/10 | 1/1 |
| GSS−/GSSH | 1/1 | 10/1 | 100/1 | 1000/1 | 10,000/1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wada, N.; Matsugo, S. Revisit of the Photoirradiation of ?-Lipoic Acid—Role of Hydrogen Sulfide Produced in the Reaction. BioChem 2021, 1, 148-158. https://doi.org/10.3390/biochem1030012
Wada N, Matsugo S. Revisit of the Photoirradiation of ?-Lipoic Acid—Role of Hydrogen Sulfide Produced in the Reaction. BioChem. 2021; 1(3):148-158. https://doi.org/10.3390/biochem1030012
Chicago/Turabian StyleWada, Naoki, and Seiichi Matsugo. 2021. "Revisit of the Photoirradiation of ?-Lipoic Acid—Role of Hydrogen Sulfide Produced in the Reaction" BioChem 1, no. 3: 148-158. https://doi.org/10.3390/biochem1030012
APA StyleWada, N., & Matsugo, S. (2021). Revisit of the Photoirradiation of ?-Lipoic Acid—Role of Hydrogen Sulfide Produced in the Reaction. BioChem, 1(3), 148-158. https://doi.org/10.3390/biochem1030012






