Hydrogels Made with Tilapia Fish Skin Increase Collagen Production and Have an Effect on MMP-2/MMP-9 Enzymes in Burn Treatment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
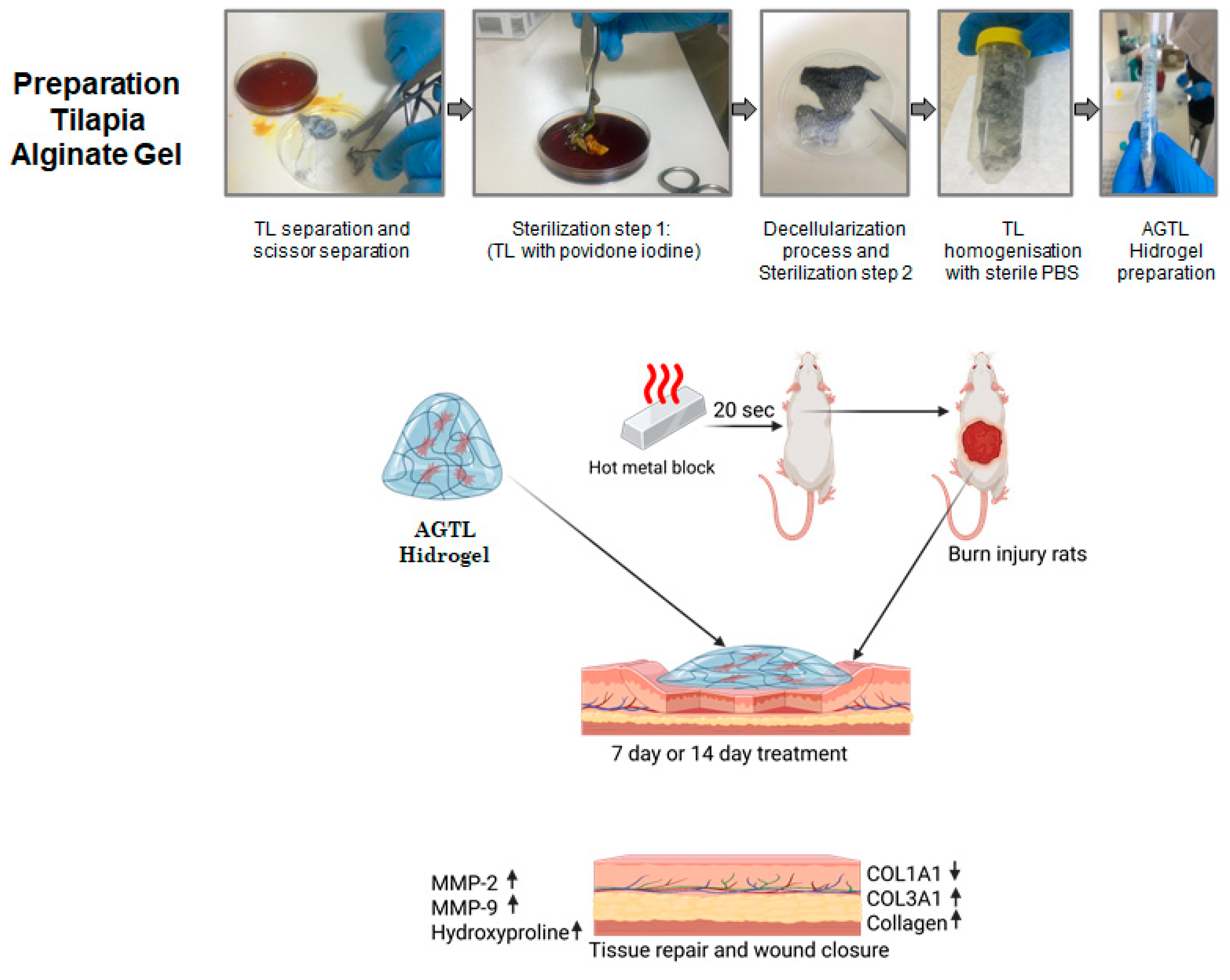
2.1. Preparation of Hydrogels from Tilapia and Alginate
2.2. Characterization of AGLT Hydrogels
2.3. Burn Model Creation and Treatment Groups
2.4. Gene Expression with qPCR
2.5. Protein Expression with Western Blotting
2.6. Hydroxyproline Assay
2.7. Histological Staining
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
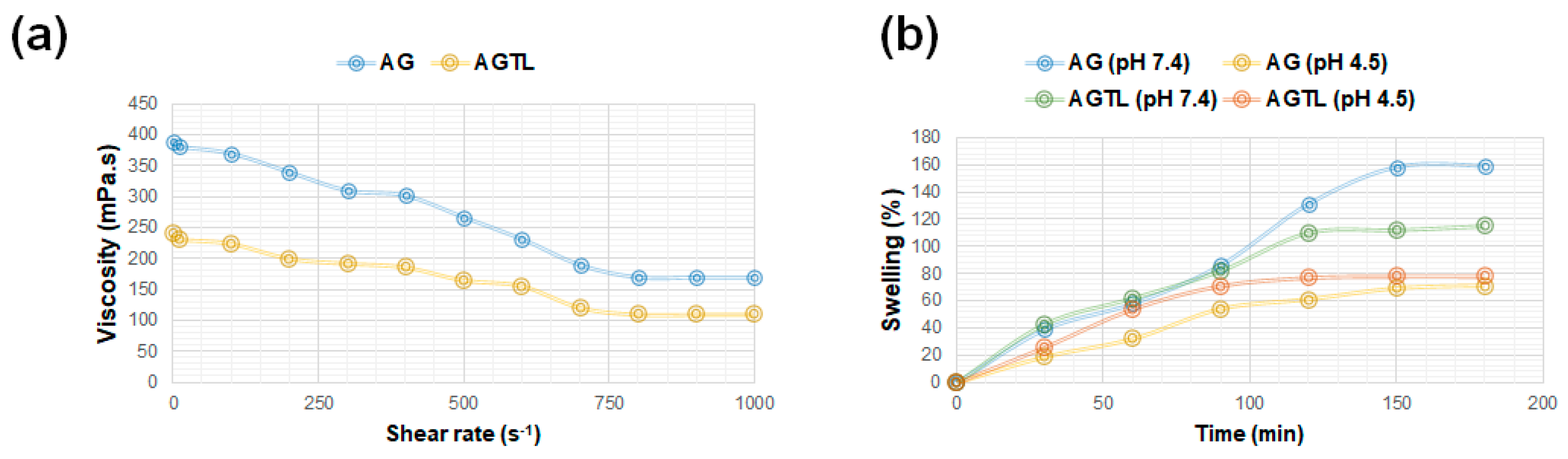
3.1. AG and AGTL Hydrogel Viscosity and Swelling Rate
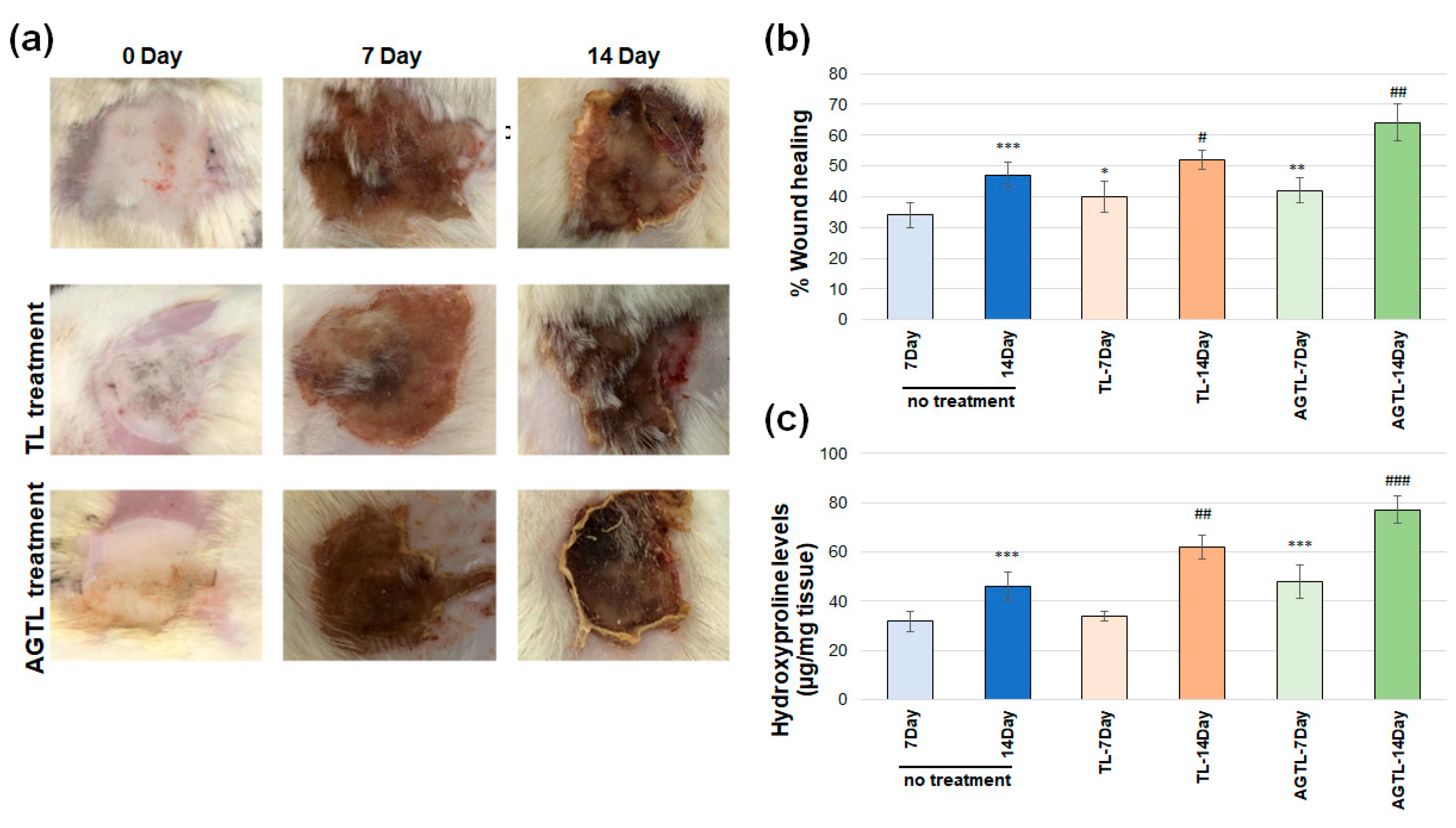
3.2. TL and AGTL Treatment Effects on Wound Closure
3.3. TL and AGTL Treatment Effects on Hydroxyproline
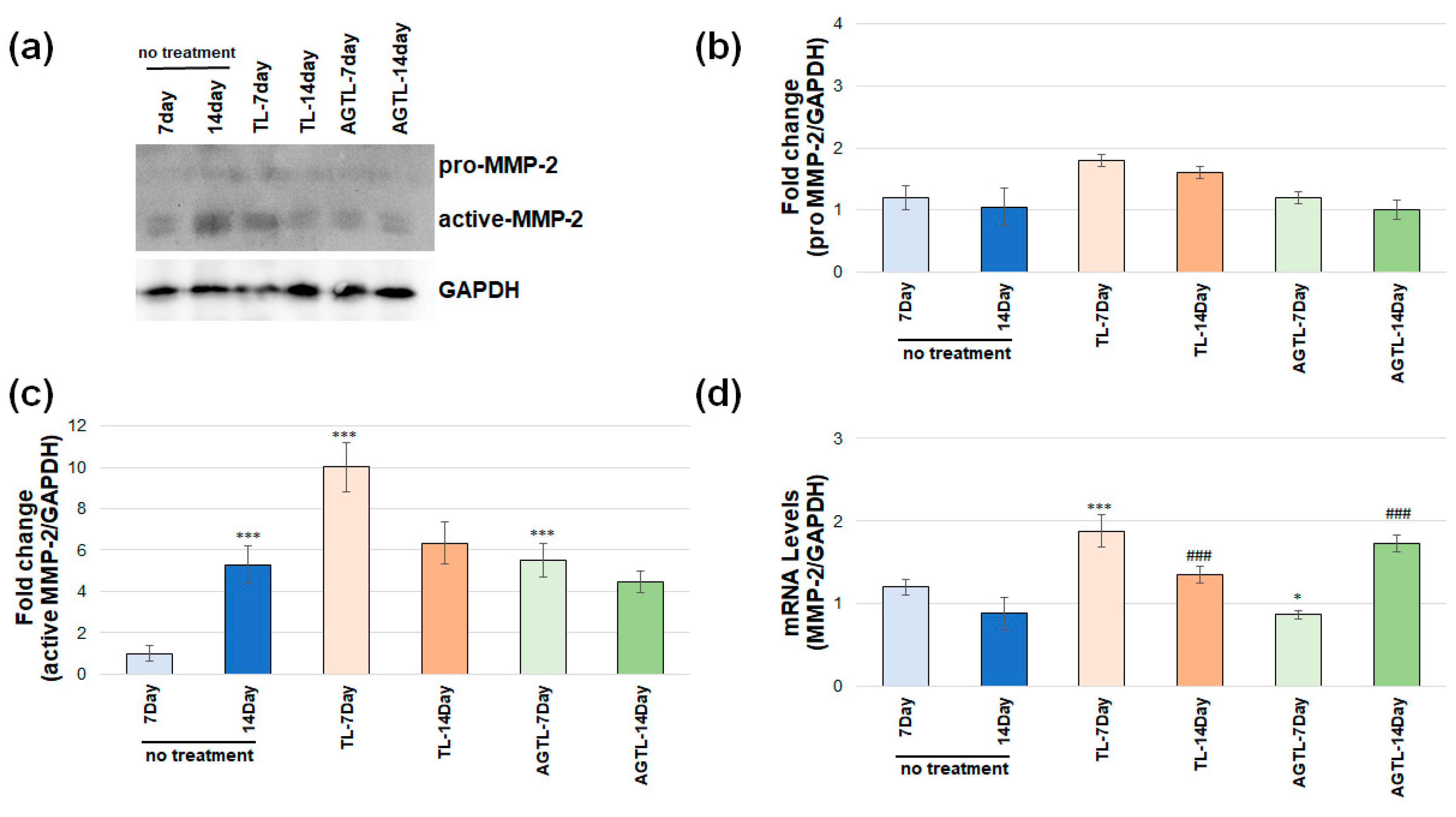
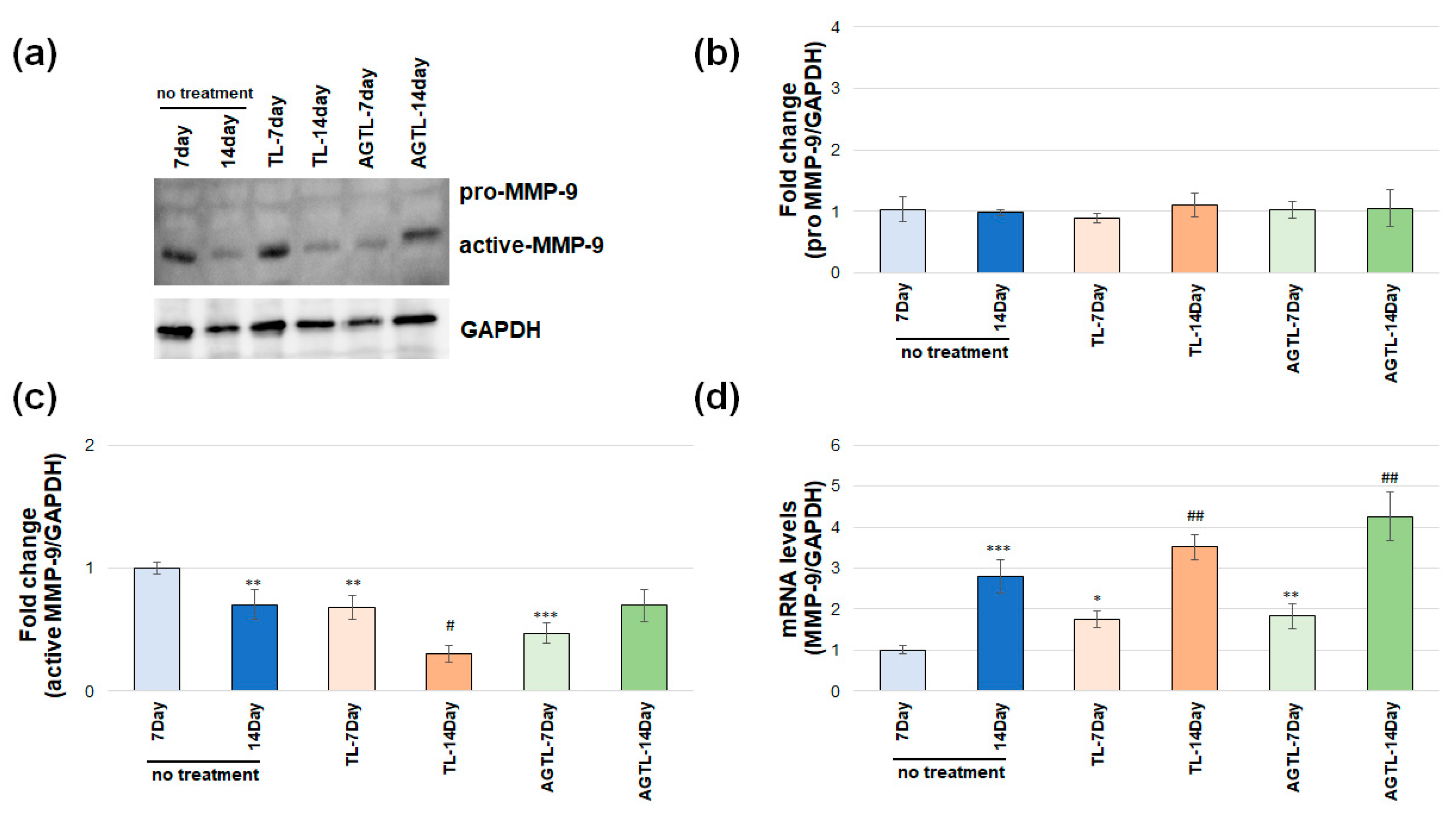
3.4. TL and AGTL Treatment Effects on MMP-2 and MMP-9 Gene and Protein Expression
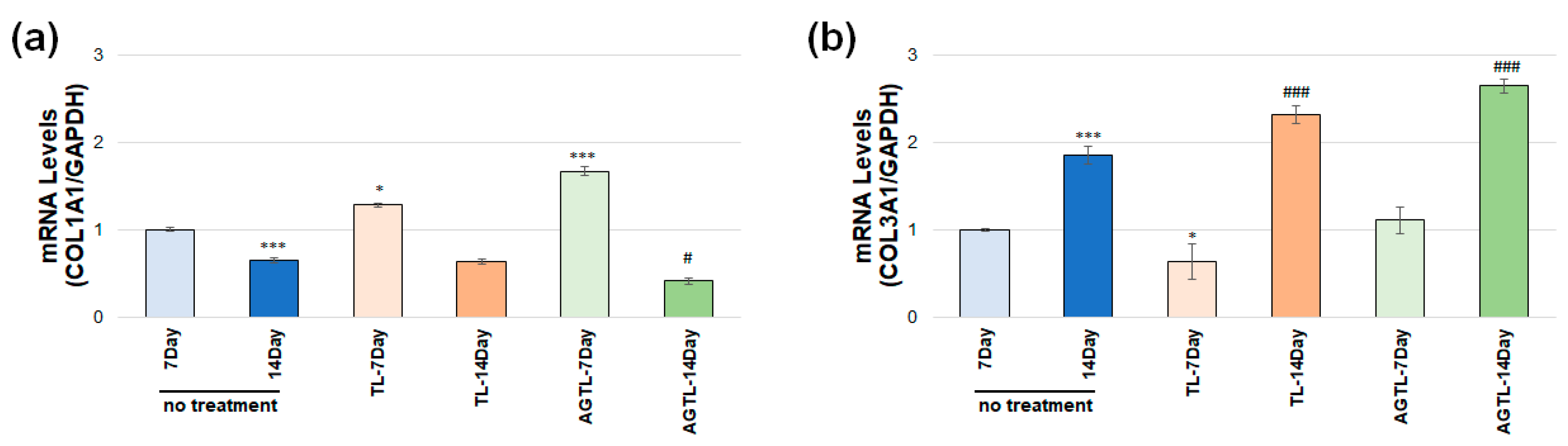
3.5. TL and AGTL Treatment Effects on COL1A1 and COL3A1 Gene Expression
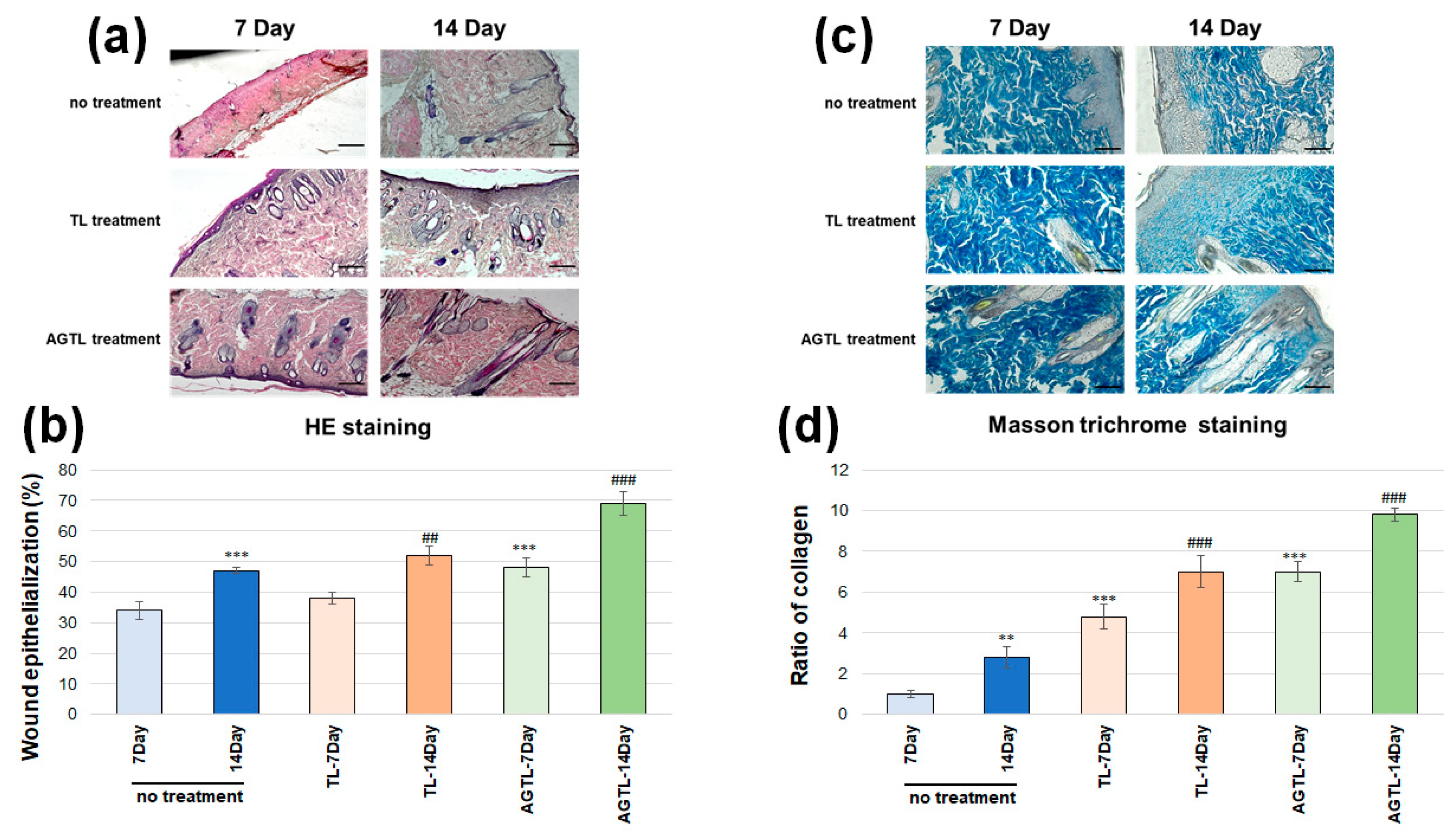
3.6. TL and AGTL Treatment Effects on Skin Tissue Epithelization and Collagen Fibers
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nişancı, M.; Öztürk, S. Yanık Fizyopatolojisi. Turk. Klin. Plast. Surg.-Spec. Top. 2010, 2, 8–14. [Google Scholar]
- Hankins, C.L.; Tang, X.Q.; Phipps, A. Hot Beverage Burns: An 11-Year Experience of the Yorkshire Regional Burns Centre. Burns 2006, 32, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elfawy, L.A.; Ng, C.Y.; Amirrah, I.N.; Mazlan, Z.; Wen, A.P.Y.; Fadilah, N.I.M.; Maarof, M.; Lokanathan, Y.; Fauzi, M.B. Sustainable Approach of Functional Biomaterials–Tissue Engineering for Skin Burn Treatment: A Comprehensive Review. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davison-Kotler, E.; Marshall, W.S.; García-Gareta, E. Sources of Collagen for Biomaterials in Skin Wound Healing. Bioengineering 2019, 6, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, B.A.; Júnior, E.M.L.; Filho, M.O.d.M.; Fechine, F.V.; de Moraes, M.E.A.; Júnior, F.R.S.; Soares, M.F.A.D.N.; Rocha, M.B.S. Use of Tilapia Skin as a Xenograft for Pediatric Burn Treatment: A Case Report. J. Burn Care Res. 2019, 40, 714–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Bhattacherjee, S.; Keswani, K.; Nath, P.; Paul, S. Application of Tilapia Fish Skin in Treatment of Burn Patients. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2024, 59, 103254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiakos, G.; Kuang, Z.; Lo, E. Improved Skin Regeneration with Acellular Fish Skin Grafts. Eng. Regen. 2020, 1, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.; Soliman, M.; Kotb, S.; Ali, M.M. Evaluation of Fish Skin as a Biological Dressing for Metacarpal Wounds in Donkeys. BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Yang, P.; Zhou, C.; Li, S.; Hong, P. Marine Collagen Peptides from the Skin of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus): Characterization and Wound Healing Evaluation. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, B.; Wang, H.; Li, J.; Liu, H.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, N.; Qin, S. Comprehensive Assessment of Nile Tilapia Skin (Oreochromis niloticus) Collagen Hydrogels for Wound Dressings. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, F.; Liu, J.; Wu, J.; Duan, Z.; Chen, M.; Meng, K.; Chen, S.; Shen, X.; Xia, G.; Zhao, M. Collagen Peptides Isolated from Salmo salar and Tilapia nilotica Skin Accelerate Wound Healing by Altering Cutaneous Microbiome Colonization via Upregulated NOD2 and BD14. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 1621–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, S.K.; Zhang, C.H.; Lin, H.; Yang, P.; Hong, P.Z.; Jiang, Z. Isolation and Characterisation of Acid-Solubilised Collagen from the Skin of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Food Chem. 2009, 116, 879–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalaby, M.; Agwa, M.; Saeed, H.; Khedr, S.M.; Morsy, O.; El-Demellawy, M.A. Fish Scale Collagen Preparation, Characterization and Its Application in Wound Healing. J. Polym. Environ. 2020, 28, 166–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, M.J.B.D.; Brandt, C.T. Nile Tilapia Skin Xenograft versus Silver-Based Hydrofiber Dressing in the Treatment of Second-Degree Burns in Adults. Rev. Bras. Cir. Plástica 2023, 34, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães, M.L.; da Silva, F.A.G.; de Souza, A.M.; da Costa, M.M.; de Oliveira, H.P. All-Green Wound Dressing Prototype Based on Nile Tilapia Skin Impregnated with Silver Nanoparticles Reduced by Essential Oil. Appl. Nanosci. 2022, 12, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães, M.L.; da Silva, F.A.G., Jr.; da Costa, M.M.; de Oliveira, H.P. Coating of Conducting Polymer-Silver Nanoparticles for Antibacterial Protection of Nile Tilapia Skin Xenografts. Synth. Met. 2022, 287, 117055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshahawy, A.M.; Mahmoud, G.A.E.; Mokhtar, D.M.; Ibrahim, A. The Optimal Concentration of Silver Nanoparticles in Sterilizing Fish Skin Grafts. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 19483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hingorani, D.V.; Lippert, C.N.; Crisp, J.L.; Savariar, E.N.; Hasselmann, J.P.C.; Kuo, C.; Nguyen, Q.T.; Tsien, R.Y.; Whitney, M.A.; Ellies, L.G. Impact of MMP-2 and MMP-9 Enzyme Activity on Wound Healing, Tumor Growth and RACPP Cleavage. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0198464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanjul-Fernández, M.; Folgueras, A.R.; Cabrera, S.; López-Otín, C. Matrix Metalloproteinases: Evolution, Gene Regulation and Functional Analysis in Mouse Models. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2010, 1803, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Chen, X.; Yin, X.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, C. Matrix Metalloproteinases on Skin Photoaging. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2024, 23, 3847–3862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Sapin-Minet, A.; Stefan, L.; Perrin, J.; Raeth-Fries, I.; Gaucher, C. Heparinized Collagen-Based Hydrogels for Tissue Engineering: Physical, Mechanical and Biological Properties. Int. J. Pharm. 2025, 670, 125126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardeazabal, L.; Izeta, A. Elastin and Collagen Fibres in Cutaneous Wound Healing. Exp. Dermatol. 2024, 33, e15052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Haldar, S.; Gupta, S.; Chauhan, S.; Mago, V.; Roy, P.; Lahiri, D. Single Unit Functionally Graded Bioresorbable Electrospun Scaffold for Scar-Free Full-Thickness Skin Wound Healing. Biomater. Adv. 2022, 139, 212980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.; Zhang, Z.; Yuan, D.; Yu, M.; Min, J. Tissue Engineering Applications of Recombinant Human Collagen: A Review of Recent Progress. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2024, 12, 1358246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adhikari, S.P.; Paudel, A.; Sharma, A.; Thapa, B.; Khanal, N.; Shastri, N.; Rai, S.; Adhikari, R. Development of Decellularized Fish Skin Scaffold Decorated with Biosynthesized Silver Nanoparticles for Accelerated Burn Wound Healing. Int. J. Biomater. 2023, 2023, 8541621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Council, N.R. Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, 8th ed.; The National Academic Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kilkenny, C.; Browne, W.J.; Cuthill, I.C.; Emerson, M.; Altman, D.G. Improving bioscience research reporting: The ARRIVE guidelines for reporting animal research. PLoS Biol. 2010, 8, e1000412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herndon, D.N. Total Burn Care; Elsevier Health Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Kocabiyik, B.; Gumus, E.; Abas, B.I.; Anik, A.; Cevik, O. Human Wharton-Jelly Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Reversed Apoptosis and Prevented Multi-Organ Damage in a Newborn Model of Experimental Asphyxia. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2022, 42, 3568–3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, E.J.; Gangadaran, P.; Rajendran, R.L.; Kim, H.M.; Oh, J.M.; Choi, K.Y.; Chung, H.Y.; Ahn, B.-C. Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Fibroblasts Promote Wound Healing by Optimizing Fibroblast and Endothelial Cellular Functions. Stem Cells 2021, 39, 266–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toriseva, M.; Kähäri, V.-M. Proteinases in Cutaneous Wound Healing. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2009, 66, 203–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, G.S.; Wysocki, A. Interactions Between Extracellular Matrix and Growth Factors in Wound Healing. Wound Repair Regen. 2009, 17, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erfan, G. Sıçanlarda ER: Yağ ile Oluşturulmuş Yarada Bitki Ekstrelerinin Karışımı Topikal Hemostatik Bir Ajanın Yara İyileşmesine Etkisi; İstanbul İl Sağlık Müdürlüğü: Istanbul, Turkey, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Y.-P.; Tuan, T.-L.; Hughes, M.; Wu, H.; Garner, W.L. Transforming Growth Factor-β- and Tumor Necrosis Factor-α-Mediated Induction and Proteolytic Activation of MMP-9 in Human Skin. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 22341–22350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parks, W.C.; Wilson, C.L.; López-Boado, Y.S. Matrix Metalloproteinases as Modulators of Inflammation and Innate Immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 4, 617–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eerola, L.M.; Alho, H.S.; Maasilta, P.K.; Inkinen, K.A.; Harjula, A.L.; Litmanen, S.H.; Salminen, U.-S. Matrix Metalloproteinase Induction in Post-Transplant Obliterative Bronchiolitis. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2005, 24, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullard, K.M.; Lund, L.; Mudgett, J.S.; Mellin, T.N.; Hunt, T.K.; Murphy, B.B.; Ronan, J.B.; Werb, Z.; Banda, M.J. Impaired Wound Contraction in Stromelysin-1–Deficient Mice. Ann. Surg. 1999, 230, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrilho, M.R.O.; Geraldeli, S.; Tay, F.; de Goes, M.; Carvalho, R.; Tjäderhane, L.; Reis, A.; Hebling, J.; Mazzoni, A.; Breschi, L.; et al. In Vivo Preservation of the Hybrid Layer by Chlorhexidine. J. Dent. Res. 2007, 86, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaco, J.L.; Lawrence, W.T. Acute Wound Healing: An Overview. Clin. Plast. Surg. 2003, 30, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niessen, F.B.; Spauwen, P.H.; Schalkwijk, J.; Kon, M. On the Nature of Hypertrophic Scars and Keloids: A Review. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1999, 104, 1435–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, A.; Tariq, A.; Khan, M.F.A.; Mirza, R.; Usman, M.; Nadir, A.; Khan, A. Multifunctional Tilapia Skin Based Smart Dressing of Silver Capped Allopurinol Nanoparticles for Treatment of Infectious Burn Wounds. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2025, 107, 106804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalaby, M.; Hamouda, D.; Khedr, S.M.; Mostafa, H.M.; Saeed, H.; Ghareeb, A.Z. Nanoparticles Fabricated from the Bioactive Tilapia Scale Collagen for Wound Healing: Experimental Approach. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0282557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbialy, Z.I.; Atiba, A.; Abdelnaby, A.; Al-Hawary, I.I.; Elsheshtawy, A.; El-Serehy, H.A.; Abdel-Daim, M.M.; Fadl, S.E.; Assar, D.H. Collagen Extract Obtained from Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus L.) Skin Accelerates Wound Healing in Rat Model via Up Regulating VEGF, bFGF, and α-SMA Genes Expression. BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Wang, N.; Xue, Y.; Ding, T.; Liu, X.; Mo, X.; Sun, J. Electrospun Tilapia Collagen Nanofibers Accelerating Wound Healing via Inducing Keratinocytes Proliferation and Differentiation. Colloids Surf. B 2016, 143, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, X.; Tian, M.; Yin, J.; Duan, H.; Tian, Y.; Wang, H.; Xia, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Y.; et al. Biofunctionalized Dissolvable Hydrogel Microbeads Enable Efficient Characterization of Native Protein Complexes. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 8633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, R.; Gruebele, M.; Leckband, D.E. Protein Folding Stability and Kinetics in Alginate Hydrogels. Biomacromolecules 2023, 24, 5245–5254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somsesta, N.; Jinnapat, A.; Fakpiam, S.; Suksanguan, C.; Wongsan, V.; Ouneam, W.; Wattanaeabpun, S.; Hongrattanavichit, I. Antimicrobial and Biodegradable Hydrogel Based on Nanocellulose/Alginate Incorporated with Silver Nanoparticles as Active Packaging for Poultry Products. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 27135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhao, X. Alginate Hydrogel Dressings for Advanced Wound Management. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 162, 1414–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumus, E.; Abas, B.I.; Cevik, E.; Kocabiyik, B.; Cenik, M.; Cevik, O. Alginate Encapsulation Induces Colony Formation with Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Exp. Biomed. Res. 2021, 4, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baydogan, B.; Kucuk, A.; Kozan, B.; Erdal, M.; Abas, B.I.; Cevik, O. Hydrogels Made with Tilapia Fish Skin Increase Collagen Production and Have an Effect on MMP-2/MMP-9 Enzymes in Burn Treatment. BioChem 2025, 5, 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/biochem5020008
Baydogan B, Kucuk A, Kozan B, Erdal M, Abas BI, Cevik O. Hydrogels Made with Tilapia Fish Skin Increase Collagen Production and Have an Effect on MMP-2/MMP-9 Enzymes in Burn Treatment. BioChem. 2025; 5(2):8. https://doi.org/10.3390/biochem5020008
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaydogan, Berkay, Aslihan Kucuk, Bensu Kozan, Merve Erdal, Burcin Irem Abas, and Ozge Cevik. 2025. "Hydrogels Made with Tilapia Fish Skin Increase Collagen Production and Have an Effect on MMP-2/MMP-9 Enzymes in Burn Treatment" BioChem 5, no. 2: 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/biochem5020008
APA StyleBaydogan, B., Kucuk, A., Kozan, B., Erdal, M., Abas, B. I., & Cevik, O. (2025). Hydrogels Made with Tilapia Fish Skin Increase Collagen Production and Have an Effect on MMP-2/MMP-9 Enzymes in Burn Treatment. BioChem, 5(2), 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/biochem5020008






