Deep mtDNA Sequence Divergences and Possible Species Radiation of Whip Spiders (Arachnida, Amblypygi, Phrynidae, Phrynus/Paraphrynus) among Caribbean Oceanic and Cave Islands
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
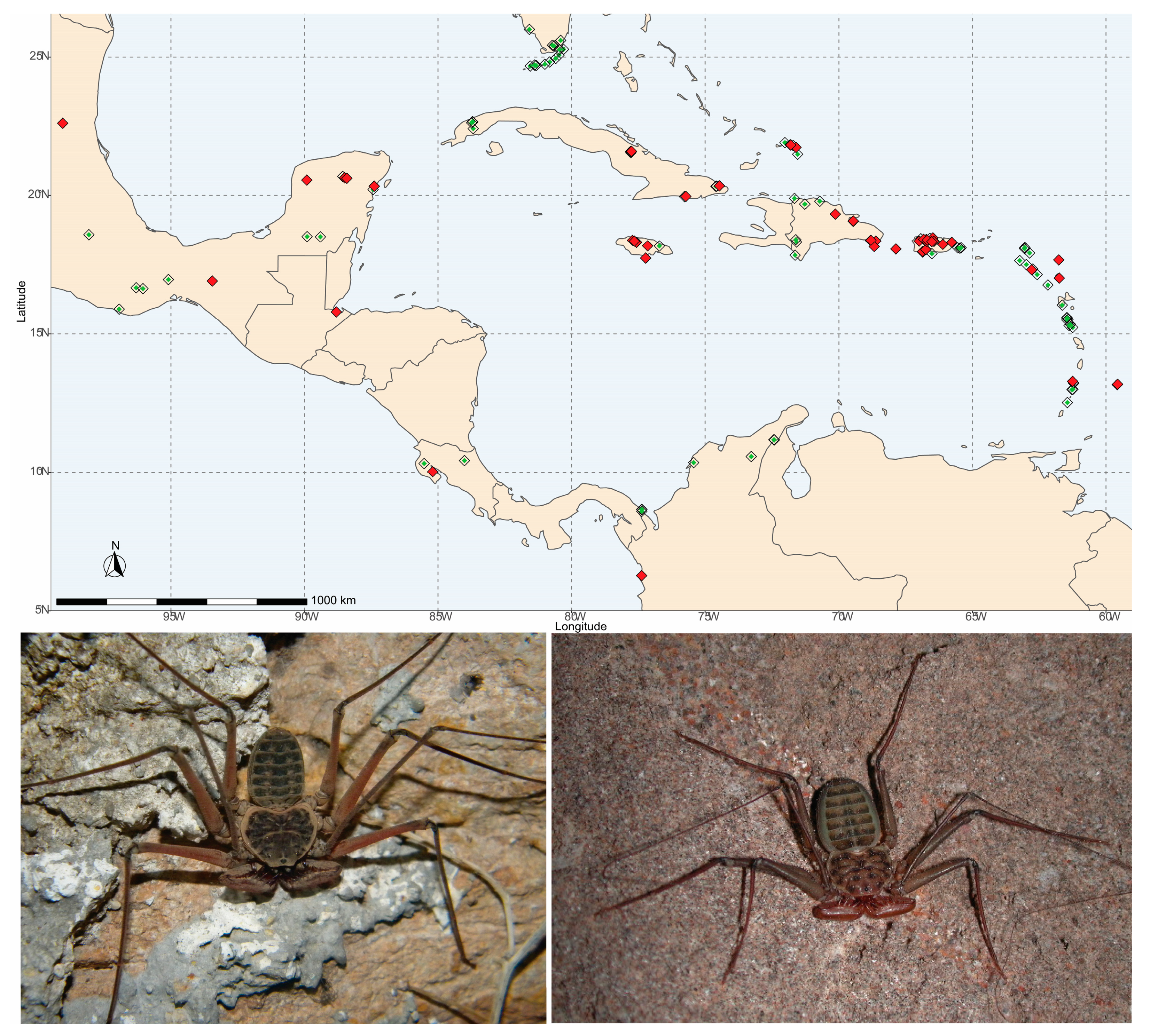
2.1. Study Organisms, Taxon Sampling, and Identification
2.2. Data
2.3. Species Delineation and Population Assignment
2.4. Genetic Distances and Isolation
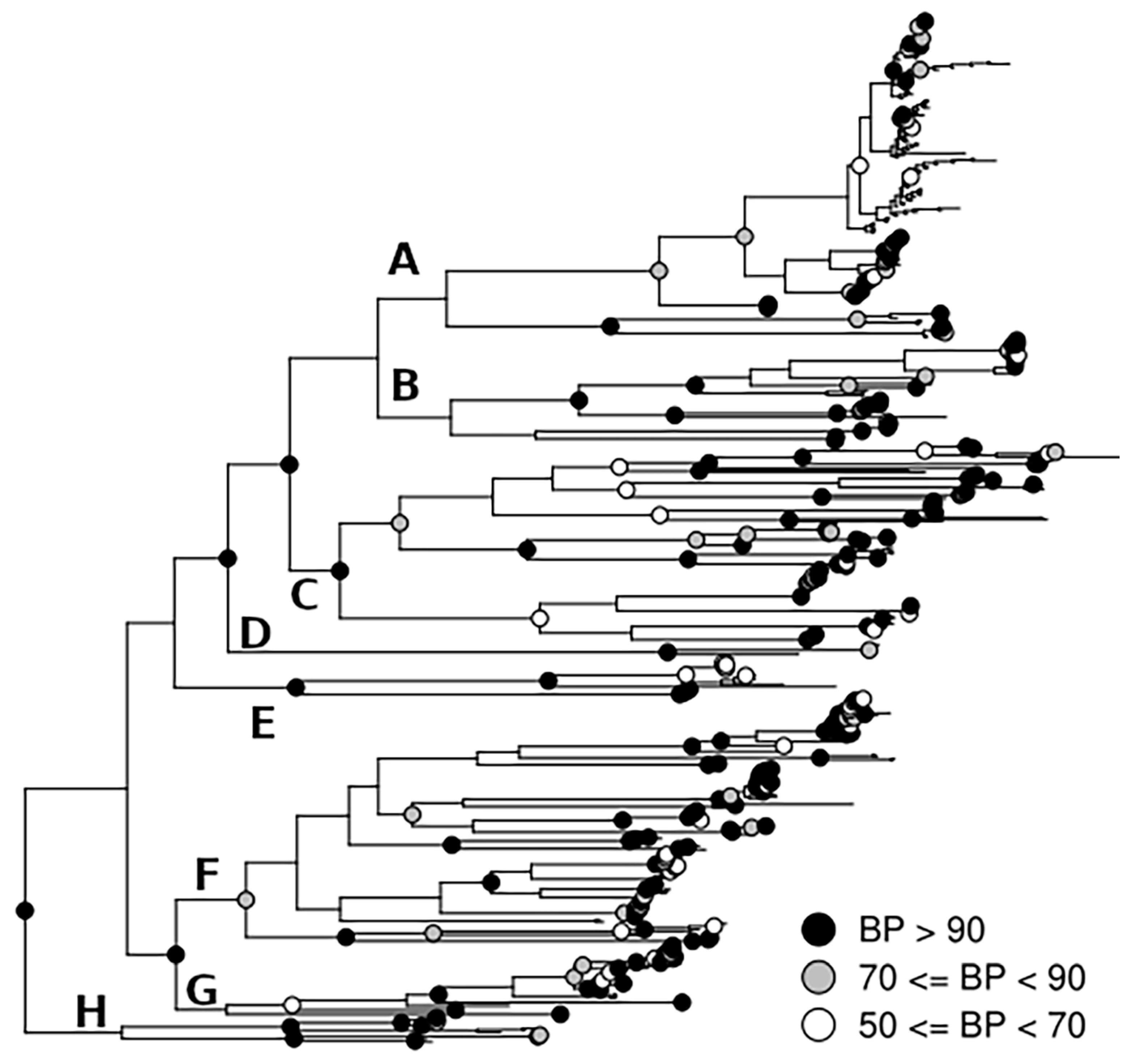
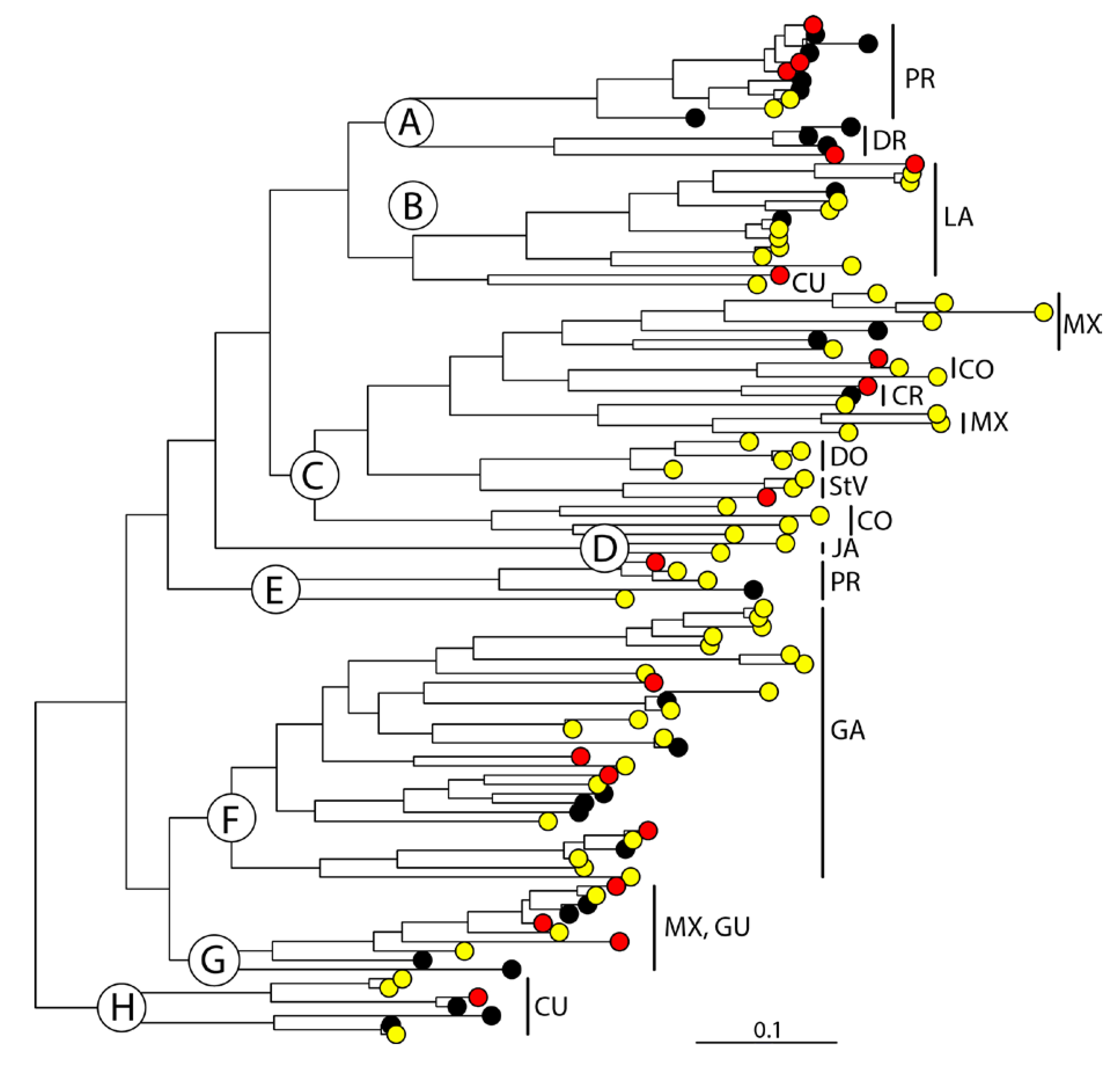
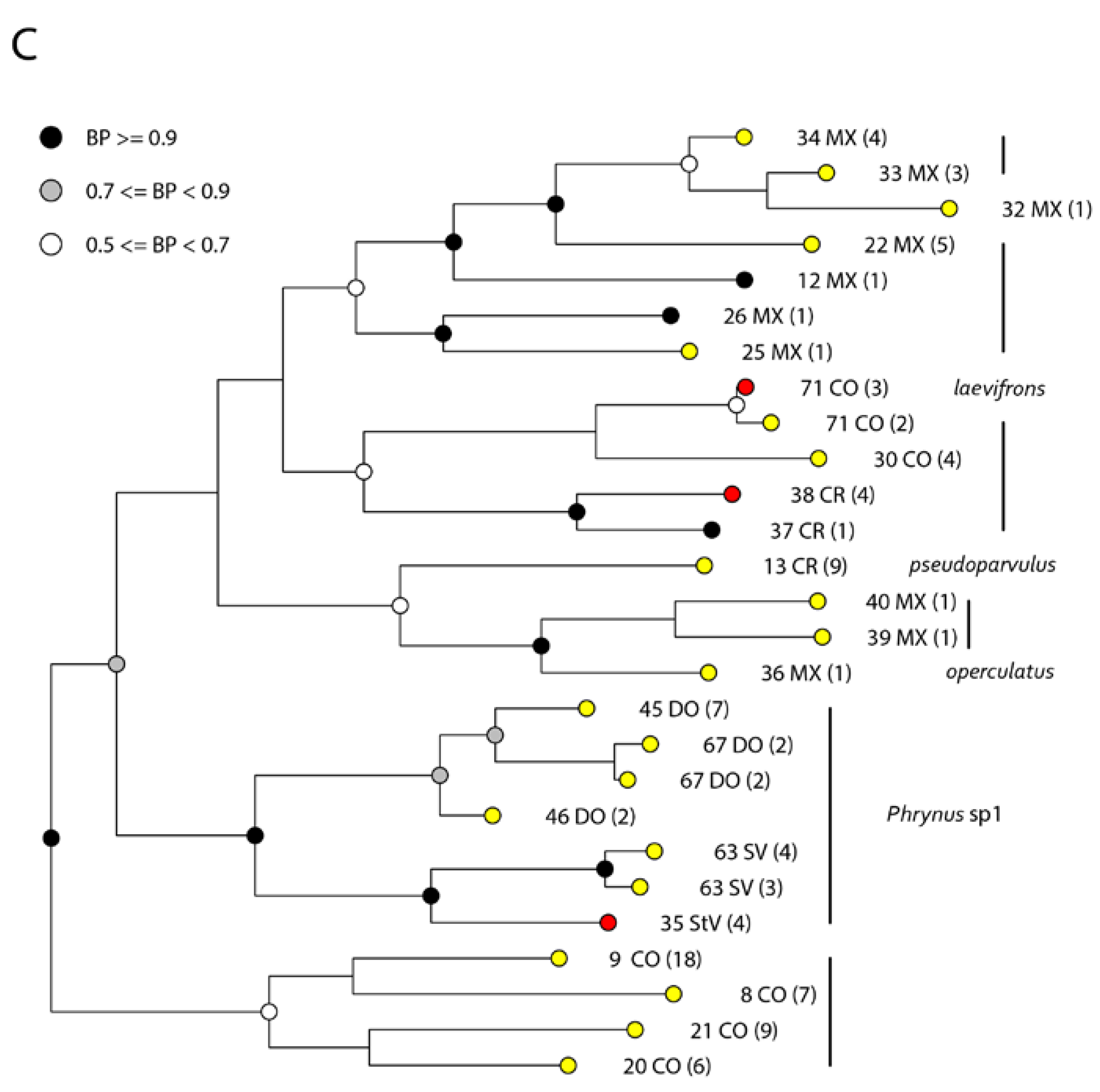
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Agnarsson, I.; Kuntner, M. The Generation of a Biodiversity Hotspot: Biogeography and Phylogeography of the Western Indian Ocean Islands. In Current Topics in Phylogenetics and Phylogeography of Terrestrial and Aquatic Systems; InTech: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, R.G.; Roderick, G.K. Arthropods on islands: Colonization, speciation, and conservation. Ann. Rev. Entomol. 2002, 47, 595–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warren, B.H.; Simberloff, D.; Ricklefs, R.E.; Aguilee, R.; Condamine, F.L.; Gravel, D.; Morlon, H.; Mouquet, N.; Rosindell, J.; Casquet, J.; et al. Islands as model systems in ecology and evolution: Prospects fifty years after MacArthur-Wilson. Ecol. Lett. 2015, 18, 200–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, P. Diversity and community assembly patterns of epigean vs. troglobiont spiders in the Iberian Peninsula. Int. J. Speleol. 2012, 41, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, R.; Clauge, D. Encyclopedia of Islands; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Juan, C.; Emerson, B.C. Evolution underground: Shedding light on the diversification of subterranean insects. J. Biol. 2010, 9, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juan, C.; Guzik, M.T.; Jaume, D.; Cooper, S.J.B. Evolution in caves: Darwin’s ‘wrecks of ancient life’ in the molecular era. Mol. Ecol. 2010, 19, 3865–3880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snowman, C.; Zigler, K.; Hedin, M. Caves as islands: Mitochondrial phylogeography of cave-obligate spider species Nesticus barri (Araneae: Nesticidae). J. Arachnol. 2010, 38, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, L.A.; Bloom, T.; Caicedo, L.; Alicea-Serrano, A.; Sánchez-Ruíz, J.; May-Collado, L.J.; Binford, G.; Agnarsson, I. Islands within islands: Diversification of tailless whip spiders (Amblypygi, Phrynus) in Caribbean caves. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2015, 93, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culver, D.; Deharveng, L.; Bedos, A.; Lewis, J.; Madden, M.; Reddell, J.; Sket, B.; Trontelj, P.; White, D. The mid-latitude biodiversity ridge in terrestrial cave fauna. Ecography 2006, 29, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, M. Subterannean Biogeography: Whate have we learned from molecular techniques? J. Cave Karst Stud. 2007, 69, 179–186. [Google Scholar]
- Hedin, M.; Thomas, S.M. Molecular systematics of eastern North American Phalangodidae (Arachnida: Opiliones: Laniatores), demonstrating convergent morphological evolution in caves. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2010, 54, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedin, M.C. Molecular phylogenetics at the population/species interface in cave spiders of the southern Appalachians (Araneae: Nesticidae: Nesticus). Mol. Biol. Evol. 1997, 14, 309–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weygoldt, P. Whip Spiders (Chelicerata: Amblypygi): Their Biology, Morphology and Systematics; Apollo Books: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Bond, J.E.; Stockman, A.K. An integrative method for delimiting cohesion species: Finding the population-species interface in a group of Californian trapdoor spiders with extreme genetic divergence and geographic structuring. Syst. Biol. 2008, 57, 628–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, M.S. Catalogue of the Smaller Arachnid Orders of the World: Amblypygi, Uropygi, Schizomida, Palpigradi, Ricinulei and Solifugae; Ciro Publishing: Melbourne, Australia, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Quintero, D. The amblypygid genus Phrynus in the Americas (Amblypygi, Phrynidae). J. Arachnol. 1981, 9, 117–166. [Google Scholar]
- Garwood, R.J.; Dunlop, J.A.; Knecht, B.J.; Hegna, T.A. The phylogeny of fossil whip spiders. BMC Ecol. Evol. 2017, 17, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natural History Museum Bern. World Amblypygi Catalog. 2022. Available online: http://wac.nmbe.ch (accessed on 15 February 2023).
- Hebert, P.D.N.; Cywinska, A.; Ball, S.L.; DeWaard, J.R. Biological identifications through DNA barcodes. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B-Biol. Sci. 2003, 270, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Čandek, K.; Kuntner, M. DNA barcoding gap: Reliable species identification over morphological and geographical scales. Mol. Ecol. Res. 2015, 15, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.L.; Yang, X.Q.; Wang, T.C.; Yu, X. Assessing the effectiveness of mitochondrial COI and 16S rRNA genes for DNA barcoding of farmland spiders in China. Mitochondr. DNA Part A 2018, 29, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolasco, S.; Valdez-Mondragón, A. To be or not to be… Integrative taxonomy and species delimitation in the daddy long-legs spiders of the genus Physocyclus (Araneae, Pholcidae) using DNA barcoding and morphology. Zookeys 2022, 1135, 93–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puillandre, N.; Achaz, G. ASAP: Assemble species by automatic partitioning. Mol. Ecol. Res. 2020, 21, 609–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujisawa, T.; Barraclough, T.G. Delimiting species using single-locus data and the generalized mixed yule coalescent approach: A revised method and evaluation on simulated data sets. Syst. Biol. 2013, 62, 707–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Kapli, P.; Pavlidis, P.; Stamatakis, A. A general species delimitation method with applications to phylogenetic placements. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 2869–2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flouri, T.; Rannala, B.; Yang, Z. A tutorial on the use of BPP for species tree estimation and species delimitation. In Phylogenetics in the Genomic Era; Authors open access book; HAL Open Science: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Rannala, B.; Yang, Z. Bayes estimation of species divergence times and ancestral population sizes using DNA sequences from multiple loci. Genetics 2002, 164, 1645–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Rannala, B. Unguided species delimitation using DNA sequence data from multiple loci. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2014, 31, 3125–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solovyeva, E.N.; Dunayev, E.A.; Nazarov, R.A.; Bondarenko, D.A.; Poyarkov, N.A. COI-Barcoding and species delimitation assessment of toad-headed agamas of the genus Phrynocephalus (Agamidae, Squamata) reveal unrecognized diversity in Central Eurasia. Diversity 2023, 15, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, C.A.; Formanowicz, D.R.; Bond, J.E. Species delimitation and phylogeography of Aphonopelma hentzi (Araneae, Mygalomorphae, Theraphosidae): Cryptic diversity in North American tarantulas. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmadi, C.; Harvey, M.S. The female of Phrynus exsul (Amblypygi, Phrynidae) from Indonesia. J. Arachnol. 2007, 35, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waygoldt, P. Evolutionary morphology of whip spiders: Towards a phylogenetic system (Chelicerata: Arachnida: Amblypygi). J. Zool. Syst. Ecol. Res. 1996, 34, 185–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnarsson, I.; Rayor, L.S. A molecular phylogeny of the Australian huntsman spiders (Sparassidae, Deleninae): Implications for taxonomy and social behaviour. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2013, 69, 895–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnarsson, I.; Maddison, W.P.; Avilés, L. The phylogeny of the social Anelosimus spiders (Araneae: Theridiidae) inferred from six molecular loci and morphology. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2007, 43, 833–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddison, D.R.; Maddison, W.P. Chromaseq: A Mesquite Module for Analyzing Sequence Chromatograms, version 1.0. Available online: https://chromaseq.mesquiteproject.org/ (accessed on 15 February 2023).
- Maddison, W.; Maddison, D. Mesquite: A Modular System for Evolutionary Analysis. 2021. Available online: http://mesquiteproject.org (accessed on 15 February 2023).
- Green, P. PHRAP. 1999. Available online: http://phrap.org/ (accessed on 15 February 2023).
- Green, P.; Ewing, B. PHRED. 2002. Available online: http://phrap.org/ (accessed on 15 February 2023).
- Katoh, S. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darriba, D.; Taboada, G.L.; Doallo, R.; Posada, D. jModelTest 2: More models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huelsenbeck, J.P.; Ronquist, R. MRBAYES: Bayesian inference of phylogenetic trees. Bioinfomatics 2001, 17, 754–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronquist, F.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 1572–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, M.; Pfeiffer, W.; Schwartz, T. Creating the CIPRES Science Gateway for inference of large phylogenetic trees. In Proceedings of the 2010 Gateway Computing Environments Workshop (GCE), New Orleans, LA, USA, 14 November 2010; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Nylander, J.; Wilgenbusch, J.; Warren, D.; Swofford, D. AWTY (are we there yet?): A system for graphical exploration of MCMC convergence in Bayesian phylogenetics. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezard, T.; Fujisawa, T.; Barraclough, T.G. SPLITS: SPecies’ LImits by Threshold Statistics. R Package, version 1.0-18/r45. 2009. Available online: http://R-Forge.R-project.org/projects/splits/ (accessed on 14 September 2021).
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2022; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 15 February 2023).
- Paradis, E.; Claude, J.; Strimmer, K. APE: Analyses of phylogenetics and evolution in R language. Bioinformatics 2004, 20, 289–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontaneto, D.; Herniou, E.A.; Boschetti, C.; Caprioli, M.; Melone, G.; Ricci, C.; Barraclough, T.G. Independently evolving species in asexual bdelloid rotifers. PLoS Biol. 2007, 5, e87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pons, J.; Barraclough, T.G.; Gomez-Zurita, J.; Cardoso, A.; Duran, D.P.; Hazell, S.; Kamoun, S.; Sumlin, W.D.; Vogler, A.P. Sequence-based species delimitation for the DNA taxonomy of undescribed insects. Syst. Biol. 2006, 55, 595–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monaghan, M.T.; Wild, R.; Elliot, M.; Fujisawa, T.; Balke, M.; Inward, D.J.G.; Lees, D.C.; Ranaivosolo, R.; Eggleton, P.; Barraclough, T.G.; et al. Accelerated species inventory on Madagascar using coalescent-based models of species delineation. Syst. Biol. 2009, 58, 298–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Friendly, M.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; McGlinn, D.; Minchin, P.R.; O’Hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.; et al. vegan: Community Ecology Package. R package, version 2.5-7. 2020. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan (accessed on 14 September 2021).
- Hijmans, R.J.; Williams, E.M.; Vennes, C. Geosphere: Spherical Trigonometry. R Package. 2021. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=geosphere (accessed on 14 September 2021).
- Hedin, M. High stakes species delimitation in eyeless cave spiders (Cicurina, Dictynidae, Araneae) from central Texas. Mol. Ecol. 2015, 24, 346–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Miranda, G.S.; Kulkarni, S.S.; Tagliatela, J.; Baker, C.M.; Giupponi, A.P.L.; Labarque, F.L.; Gavish-Regev, E.; Rix, M.E.; Carvalho, L.S.; Fusari, L.M.; et al. The rediscovery of a relict unlocks the first global phylogeny of whip spiders (Amblypygi). BioRxvi 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloom, T.; Binford, G.; Alayon, G.; Esposito, L.; Peterson, I.; Nishida, A.; Loubet-Senear, K.; Agnarsson, I. Discovery of two new species of eyeless spiders within a single Hispaniola cave. J. Arachnol. 2014, 42, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Armas, L.F. Arachnids of the Dominican Republic. Palpigradi, Schizomida, Solifugae, and Thelyphonida (Chelicerata: Arachnida). Rev. Iber. Aracnol. Vol. Espec. Monogr. 2004, 2, 1–63. [Google Scholar]
- de Armas, L.F. New arachnids from Puerto Rico (Arachnida: Amblypygi, Araneae, Opiliones, Parasitiformes, Schizomida, Scorpiones). Bol. De La SEA 2010, 47, 55–64. [Google Scholar]
- de Armas, L.F.; Arias, A.A.A. A new species Phrynus Lamarck, 1801 (Amblypygi: Phrynidae) from Colombia. Bol. De La SEA 2008, 43, 25–28. [Google Scholar]
- de Armas, L.F.; Gonzalez, A.P. Amblypygids of the Dominican Republic (Arachnida: Ambypygi). Rev. Iber. Aracnol. 2001, 3, 47–66. [Google Scholar]
- de Armas, L.F.; Teruel, R. A new species of Phrynus (Amblypygi: Phrynidae) from Puerto Rico. Bol. De La SEA 2010, 47, 127–130. [Google Scholar]
- de Armas, L.F.; Viquez, C. A new species of Phrynus (Amblypygi: Phrynidae) from Costa Rica. Rev. Iber. Aracnol. 2001, 4, 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, E.A.; Chain, F.J.J.; Crease, T.J.; MacIsaac, H.J.; Cristescu, M.E. Divergence thresholds and divergent biodiversity estimates: Can metabarcoding reliably describe zooplankton communities? Ecol. Evol. 2015, 5, 2234–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, J.E.; Godwin, R.L.; Colby, J.D.; Newton, L.G.; Zahnle, X.J.; Agnarsson, I.; Hamilton, C.A.; Kuntner, M. Improving taxonomic practices and enhancing its extensibility—An example from araneology. Diversity 2022, 14, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnarsson, I.; Van Patten, C.; Sargeant, L.; Chomitz, B.; Dziki, A.; Binford, G. A radiation of the ornate Caribbean ‘smiley-faced spiders’—With descriptions of 15 new species (Araneae, Theridiidae, Spintharus). Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2018, 182, 758–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coddington, J.A.; Agnarsson, I.; Miller, J.; Kuntner, M.; Hormiga, G. Undersampling bias: The null hypothesis for singleton species in tropical arthropod biodiversity surveys. J. Anim. Ecol. 2009, 78, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapin, K.J.; Winkler, D.E.; Wiencek, P.; Agnarsson, I. Island biogeography and ecological modeling of the amblypygid Phrynus marginemaculatus in the Florida Keys archipelago. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 8, 9139–9151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Country | Code | n | Number of Specimens in Caves | Number of Morpho-Species | Number of ASAP Species | Number of bPTP Species |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antigua * | AN | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 |
| Barbados * | BS | 8 | 6 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Barbuda * | BA | 3 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Guatemala | BE | 3 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Colombia | CO | 54 | 1 | 3 | 7 | 8 |
| Costa Rica | CR | 14 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| Cuba | CU | 34 | 7 | 6 | 11 | 13 |
| Dominica * | DO | 13 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 4 |
| Dominican Republic | DR | 53 | 22 | 5 | 13 | 21 |
| Guadeloupe * | GU | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Jamaica | JA | 42 | 29 | 3 | 8 | 8 |
| Mexico | MX | 54 | 21 | 3 | 15 | 19 |
| Monserrat * | MO | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Puerto Rico | PR | 184 | 139 | 5 | 7 | 20 |
| Saba * | SA | 3 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| St. Barts * | SB | 3 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| St. Eustatius * | SE | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| St. Kitts * | SK | 12 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| St. Martin * | SM | 2 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| St. Vincent * | SV | 11 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Turks and Caicos | TC | 19 | 9 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| USA, Florida | FL | 23 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Agnarsson, I.; Coddington, J.A.; Caicedo-Quiroga, L.; May-Collado, L.J.; Pálsson, S. Deep mtDNA Sequence Divergences and Possible Species Radiation of Whip Spiders (Arachnida, Amblypygi, Phrynidae, Phrynus/Paraphrynus) among Caribbean Oceanic and Cave Islands. Taxonomy 2023, 3, 133-147. https://doi.org/10.3390/taxonomy3010011
Agnarsson I, Coddington JA, Caicedo-Quiroga L, May-Collado LJ, Pálsson S. Deep mtDNA Sequence Divergences and Possible Species Radiation of Whip Spiders (Arachnida, Amblypygi, Phrynidae, Phrynus/Paraphrynus) among Caribbean Oceanic and Cave Islands. Taxonomy. 2023; 3(1):133-147. https://doi.org/10.3390/taxonomy3010011
Chicago/Turabian StyleAgnarsson, Ingi, Jonathan A. Coddington, Laura Caicedo-Quiroga, Laura J. May-Collado, and Snæbjörn Pálsson. 2023. "Deep mtDNA Sequence Divergences and Possible Species Radiation of Whip Spiders (Arachnida, Amblypygi, Phrynidae, Phrynus/Paraphrynus) among Caribbean Oceanic and Cave Islands" Taxonomy 3, no. 1: 133-147. https://doi.org/10.3390/taxonomy3010011
APA StyleAgnarsson, I., Coddington, J. A., Caicedo-Quiroga, L., May-Collado, L. J., & Pálsson, S. (2023). Deep mtDNA Sequence Divergences and Possible Species Radiation of Whip Spiders (Arachnida, Amblypygi, Phrynidae, Phrynus/Paraphrynus) among Caribbean Oceanic and Cave Islands. Taxonomy, 3(1), 133-147. https://doi.org/10.3390/taxonomy3010011







