Exploring the Effect of Prolonged Ankle Plantar-Flexed Standing on Postural Control, Balance Confidence, Falls Efficacy, and Perceived Balance in Older Adults
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| A-P | Anterior–posterior |
| M-L | Medio-lateral |
| RMS | Root mean square |
| GRC | Generalised Rating of Change |
| ICC | Intraclass Correlation Coefficient |
| SStotal | Sum of squares total |
| MDC | Minimal Detectable Change |
References
- Winter, D.A. Human balance and posture control during standing and walking. Gait Posture 1995, 3, 193–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, D.A.; Patla, A.E.; Rietdyk, S.; Ishac, M.G. Ankle muscle stiffness in the control of balance during quiet standing. J. Neurophysiol. 2001, 85, 2630–2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyas, S.; Medd, E.R.; Beaulieu, S.; Boileau, A.; Lajoie, Y.; Bilodeau, M. Older and young adults adopt different postural strategies during quiet bipedal stance after ankle plantarflexor fatigue. Neurosci. Lett. 2019, 701, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howcroft, J.; Lemaire, E.D.; Kofman, J.; McIlroy, W.E. Elderly fall risk prediction using static posturography. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlo, A.; Zemp, D.; Zanda, E.; Rocchi, S.; Meroni, F.; Tettamanti, M.; Recchia, A.; Lucca, U.; Quadri, P. Postural stability and history of falls in cognitively able older adults: The Canton Ticino study. Gait Posture 2012, 36, 662–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.A.; Stergiou, N.; Ulrich, B.D. Lyapunov exponent and surrogation analysis of patterns of variability: Profiles in new walkers with and without down syndrome. Motor Control 2010, 14, 126–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiefer, A.W.; Armitano-Lago, C.N.; Cone, B.L.; Bonnette, S.; Rhea, C.K.; Cummins-Sebree, S.; Riley, M.A. Postural control development from late childhood through young adulthood. Gait Posture 2021, 86, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, T.L.; Newton, R.U.; Burnett, A.F. Reliability of traditional and fractal dimension measures of quiet stance center of pressure in young, healthy people. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2005, 86, 2034–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhea, C.K.; Silver, T.A.; Hong, S.L.; Ryu, J.H.; Studenka, B.E.; Hughes, C.M.; Haddad, J.M. Noise and complexity in human postural control: Interpreting the different estimations of entropy. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafond, D.; Corriveau, H.; Herbert, R.; Prince, F. Intrasession reliability of center of pressure measures of postural steadiness in healthy elderly people. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2004, 85, 896–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, R.; Ebrahimi, T.I.; Esteki, A.; Maroufi, N.; Parnianpour, M. Test-retest reliability and minimal detectable change for center of pressure measures of postural stability in elderly subjects. Med. J. Islam. Repub. Iran 2010, 23, 224–232. [Google Scholar]
- Myers, A.M.; Fletcher, P.C.; Myers, A.H.; Sherk, W. Discriminative and evaluative properties of the activities-specific balance confidence (ABC) scale. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 1998, 53, M287–M294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yardley, L.; Beyer, N.; Hauer, K.; Kempen, G.; Piot-Ziegler, C.; Todd, C. Development and initial validation of the Falls Efficacy Scale International (FES-I). Age Ageing 2005, 34, 614–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legters, K.; Verbus, N.B.; Kitchen, S.; Tomecsko, J.; Urban, N. Fear of falling, balance confidence and health-related quality of life in individuals with postpolio syndrome. Physiother. Theory Pract. 2006, 22, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioural Sciences, 2nd ed.; Erlbaum: Hillsdale, NJ, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Brydges, C.R. Effect size guidelines, sample size calculations, and statistical power in gerontology. Innov. Aging 2019, 3, igz036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuillerme, N.; Forestier, N.; Nougier, V. Attentional demands and postural sway: The effect of the calf muscles fatigue. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2002, 34, 1907–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quijoux, F.; Nicolaï, A.; Chairi, I.; Bargiotas, I.; Ricard, D.; Yelnik, A.; Oudre, L.; Bertin-Hugault, F.; Vidal, P.P.; Vayatis, N.; et al. A review of center of pressure (COP) variables to quantify standing balance in elderly people: Algorithms and open-access code. Physiol. Rep. 2021, 9, e15067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, T.L.; Dugan, E.L.; Humphries, B.; Newton, R.U. Discriminating between elderly and young using a fractal dimension analysis of centre of pressure. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2004, 1, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauer, K.A.; Kempen, G.I.; Schwenk, M.; Yardley, L.; Beyer, N.; Todd, C.; Oster, P.; Zijlstra, G.A. Validity and sensitivity to change of the Falls Efficacy Scales International to assess fear of falling in older adults with and without cognitive impairment. Gerontology 2011, 57, 462–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McColl, L.; McMeekin, P.; Poole, M.; Parry, S.W. Is fear of falling key to identifying gait and balance abnormalities in community-dwelling older adults? Protocol of a mixed-methods approach. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e067040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delbaere, K.; Close, J.C.; Mikolaizak, A.S.; Sachdev, P.S.; Brodaty, H.; Lord, S.R. The Falls Efficacy Scale International (FES-I). A comprehensive longitudinal validation study. Age Ageing 2010, 39, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schepens, S.; Goldberg, A.; Wallace, M. The short version of the Activities-specific Balance Confidence (ABC) scale: Its validity, reliability, and relationship to balance impairment and falls in older adults. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2010, 51, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peretz, C.; Herman, T.; Hausdorff, J.M.; Giladi, N. Assessing fear of falling: Can a short version of the Activities-specific Balance Confidence scale be useful? Mov. Disord. 2006, 21, 2101–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, A.A.; Abbott, J.H.; Baxter, D.; Cook, C. The ability of a sustained within-session finding of pain reduction during traction to dictate improved outcomes from a manual therapy approach on patients with osteoarthritis of the hip. J. Man. Manip. Ther. 2010, 18, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamper, S.J.; Maher, C.G.; Mackay, G. Global rating of change scales: A review of strengths and weaknesses and considerations for design. J. Man. Manip. Ther. 2009, 17, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, D.C.; Walsh, G.S. The minimal important change for measures of balance and postural control in older adults: A systematic review. Age Ageing 2022, 51, afac284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafał, S.; Janusz, M.; Wiesław, O.; Robert, S. Test-retest reliability of measurements of the center of pressure displacement in quiet standing and during maximal voluntary body leaning among healthy elderly men. J. Hum. Kinet. 2011, 28, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratner, B. The correlation coefficient: Its values range between +1/−1, or do they? J. Target. Meas. Anal. Mark. 2009, 17, 139–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, T.K.; Li, M.Y. A guideline of selecting and reporting intraclass correlation coefficients for reliability research. J. Chiropr. Med. 2016, 15, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weir, J.P. Quantifying test-retest reliability using the intraclass correlation coefficient and the SEM. J. Strength. Cond. Res. 2005, 19, 231–240. [Google Scholar]
- Freitas, S.M.; Wieczorek, S.A.; Marchetti, P.H.; Duarte, M. Age-related changes in human postural control of prolonged standing. Gait Posture 2005, 22, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sozzi, S.; Ghai, S.; Schieppati, M. Incongruity of geometric and spectral markers in the assessment of body sway. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 929132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waters, T.R.; Dick, R.B. Evidence of health risks associated with prolonged standing at work and intervention effectiveness. Rehabil. Nurs. 2015, 40, 148–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, D.G.; Lamb, G.D.; Westerblad, H. Skeletal muscle fatigue: Cellular mechanisms. Physiol. Rev. 2008, 88, 287–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hody, S.; Croisier, J.L.; Bury, T.; Rogister, B.; Leprince, P. Eccentric Muscle Contractions: Risks and Benefits. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acaster, S.; Dickerhoof, R.; DeBusk, K.; Bernard, K.; Strauss, W.; Allen, L.F. Qualitative and quantitative validation of the FACIT-fatigue scale in iron deficiency anemia. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2015, 13, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hepple, R.T. The Role of O2 Supply in Muscle Fatigue. Can. J. Appl. Physiol. 2002, 27, 56–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nocella, M.; Colombini, B.; Benelli, G.; Cecchi, G.; Bagni, M.A.; Bruton, J. Force decline during fatigue is due to both a decrease in the force per individual cross-bridge and the number of cross-bridges. J. Physiol. 2011, 589, 3371–3381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penedo, T.; Polastri, P.F.; Rodrigues, S.T.; Santinelli, F.B.; Costa, E.C.; Imaizumi, L.F.I.; Barbieri, R.A.; Barbieri, F.A. Motor strategy during postural control is not muscle fatigue joint-dependent, but muscle fatigue increases postural asymmetry. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0247395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Park, J.S. The Correlation between Proprioception and Postural Control in Healthy Adults. Iran. J. Public Health 2022, 51, 2360–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adkin, A.; Frank, J.S.; Jog, M.S. Fear of falling and postural control in Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2003, 18, 496–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisson, E.J.; Remaud, A.; Boyas, S.; Lajoie, Y.; Bilodeau, M. Effects of fatiguing isometric and isokinetic ankle exercises on postural control while standing on firm and compliant surfaces. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2012, 9, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doherty, C.; Bleakley, C.; Hertel, J.; Caulfield, B.; Ryan, J.; Delahunt, E. Postural control strategies during single limb stance following acute lateral ankle sprain. Clin. Biomech. 2014, 29, 643–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyas, S.; Hajj, M.; Bilodeau, M. Influence of ankle plantarflexor fatigue on postural sway, lower limb articular angles, and postural strategies during unipedal quiet standing. Gait Posture 2013, 37, 547–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horak, F.B.; Shupert, C.L.; Mirka, A. Components of postural dyscontrol in the elderly: A review. Neurobiol. Aging 1989, 10, 727–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terwee, C.B.; Peipert, J.D.; Chapman, R.; Lai, J.S.; Terluin, B.; Cella, D.; Griffiths, P.; Mokkink, L.B. Minimal important change (MIC): A conceptual clarification and systematic review of MIC estimates of PROMIS measures. Quality Life Res. 2021, 30, 2729–2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Seol, H.; Nussbaum, M.A.; Madigan, M.L. Reliability of COP-based postural sway measures and age-related differences. Gait Posture 2008, 28, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanenburg, J.; de Bruin, E.D.; Favero, K.; Uebelhart, D.; Mulder, T. The reliability of postural balance measures in single and dual tasking in elderly fallers and non-fallers. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2008, 9, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, P.X.; Abu Osman, N.A.; Yusof, A.; Wan Abas, W.A. Biomechanical evaluation of the relationship between postural control and body mass index. J. Biomech. 2012, 45, 1638–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, D.; Bilodeau, M. Rating of perceived exertion (RPE) in studies of fatigue-induced postural control alterations in healthy adults: Scoping review of quantitative evidence. Gait Posture 2021, 90, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallenberg, L.A.C.; Schulte, E.; Disselhorst-Klug, C.; Hermens, H.J. Myoelectric manifestations of fatigue at low contraction levels in subjects with and without chronic pain. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2007, 17, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
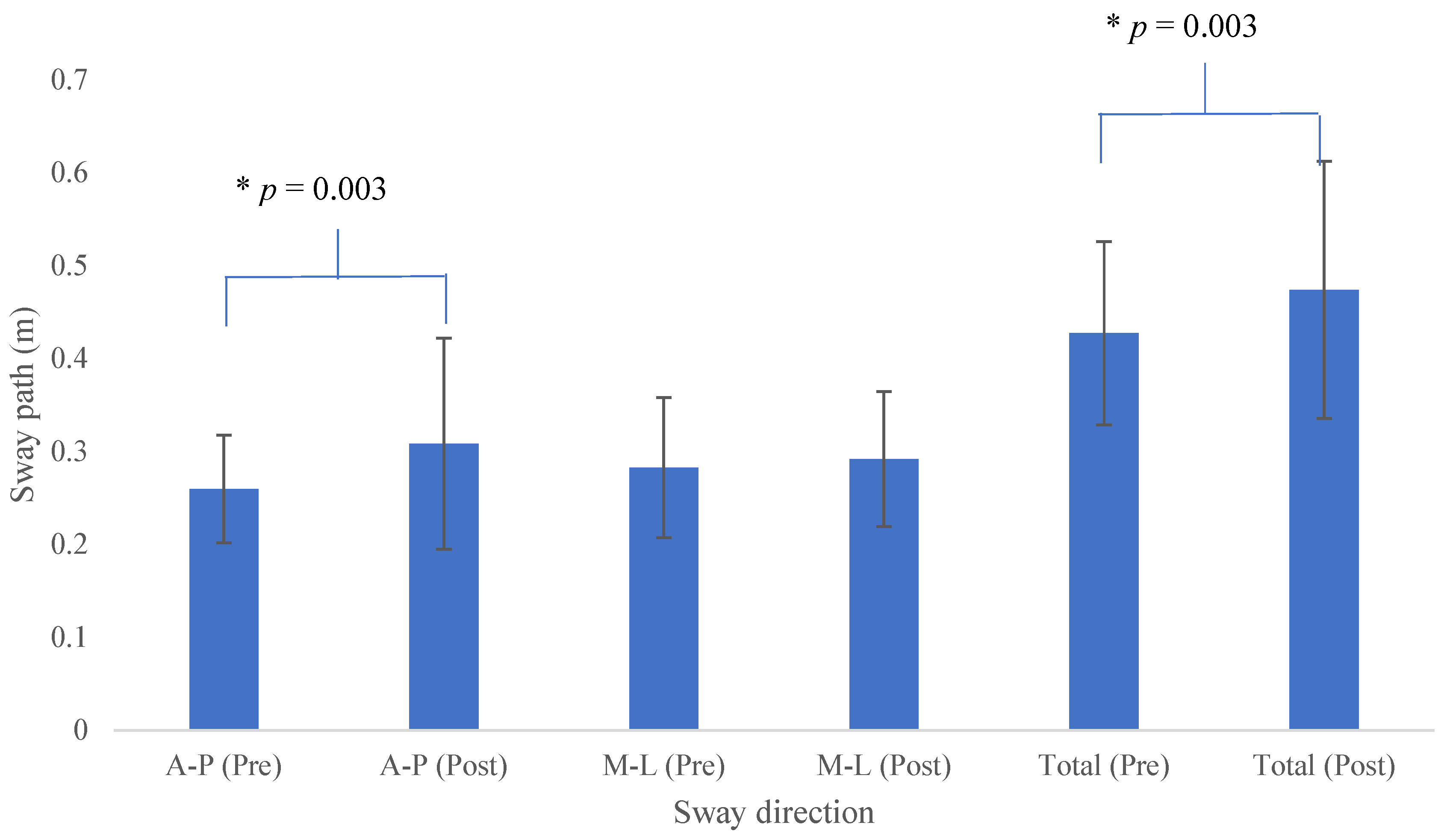
| Pre-Mean (SD) | Post-Mean (SD) | Cohen’s d | |
|---|---|---|---|
| RMS A-P (m) * | 0.049 (±0.0009) | 0.058 (±0.0021) | 5.6 |
| RMS M-L (m) | 0.059 (±0.0009) | 0.035 (±0.0012) | 0.9 |
| RMS radius (m) * | 0.009 (±0.0124) | 0.011 (±0.0141) | 0.2 |
| 95% ellipse area (m2) | 0.0003 (±0.0001) | 0.0004 (±0.0002) | 0.6 |
| Fractal dimension | 1.72 (0.08) | 1.73 (0.09) | 0.1 |
| A-P Sway Length | M-L Sway Length | Total Sway Length | RMS A-P | RMS M-L | RMS Radius | Sway Area | Fractal Dimension | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GRC | R | 0.59 | 0.25 | 0.61 | 0.42 | 0.28 | 0.35 | 0.32 | −0.13 |
| P | <0.01 * | 0.25 | <0.01 * | 0.04 * | 0.19 | 0.10 | 0.12 | 0.55 | |
| FES-I | R | 0.02 | 0.18 | 0.07 | −0.07 | −0.08 | −0.15 | −0.02 | 0.05 |
| P | 0.92 | 0.41 | 0.77 | 0.76 | 0.73 | 0.50 | 0.93 | 0.82 | |
| ABC | R | −0.31 | −0.15 | −0.32 | 0.14 | −0.06 | 0.19 | 0.002 | −0.16 |
| P | 0.15 | 0.48 | 0.13 | 0.51 | 0.79 | 0.36 | 0.99 | 0.47 |
| ICC2,5 | SSTotal | SD | SEM | MDC95 | %MDC95 | Participants Exceeding MDC95 (n) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A-P sway path length | 0.92 * | 0.516 | 0.07 | 0.2 | 0.05 | 19.3% | 9 |
| M-L sway path length | 0.98 * | 0.685 | 0.08 | 0.1 | 0.03 | 10.6% | 2 |
| Total sway path length | 0.96 * | 1.265 | 0.10 | 0.2 | 0.06 | 14.0% | 9 |
| A-P RMS | 0.27 | 0.0004 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.004 | 8.2% | 9 |
| M-L RMS | 0.68 * | 0.0002 | 0.001 | 0.0008 | 0.002 | 5.9% | 10 |
| RMS radius | 0.95 * | 0.21 | 0.013 | 0.003 | 0.008 | 88.9% | 10 |
| Sway area | 0.69 * | 0.000005 | 0.0002 | 0.0001 | 0.0003 | 100% | 0 |
| Fractal dimension | 0.80 * | 1.29 | 0.10 | 0.05 | 0.13 | 7.6% | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Low, D.C. Exploring the Effect of Prolonged Ankle Plantar-Flexed Standing on Postural Control, Balance Confidence, Falls Efficacy, and Perceived Balance in Older Adults. Biomechanics 2025, 5, 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomechanics5020019
Low DC. Exploring the Effect of Prolonged Ankle Plantar-Flexed Standing on Postural Control, Balance Confidence, Falls Efficacy, and Perceived Balance in Older Adults. Biomechanics. 2025; 5(2):19. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomechanics5020019
Chicago/Turabian StyleLow, Daniel Craig. 2025. "Exploring the Effect of Prolonged Ankle Plantar-Flexed Standing on Postural Control, Balance Confidence, Falls Efficacy, and Perceived Balance in Older Adults" Biomechanics 5, no. 2: 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomechanics5020019
APA StyleLow, D. C. (2025). Exploring the Effect of Prolonged Ankle Plantar-Flexed Standing on Postural Control, Balance Confidence, Falls Efficacy, and Perceived Balance in Older Adults. Biomechanics, 5(2), 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomechanics5020019






