Combining Geographic Information Systems and Hydraulic Modeling to Analyze the Hydraulic Response of an Urban Area Under Different Conditions: A Case Study to Assist Engineering Practice
Abstract
1. Introduction
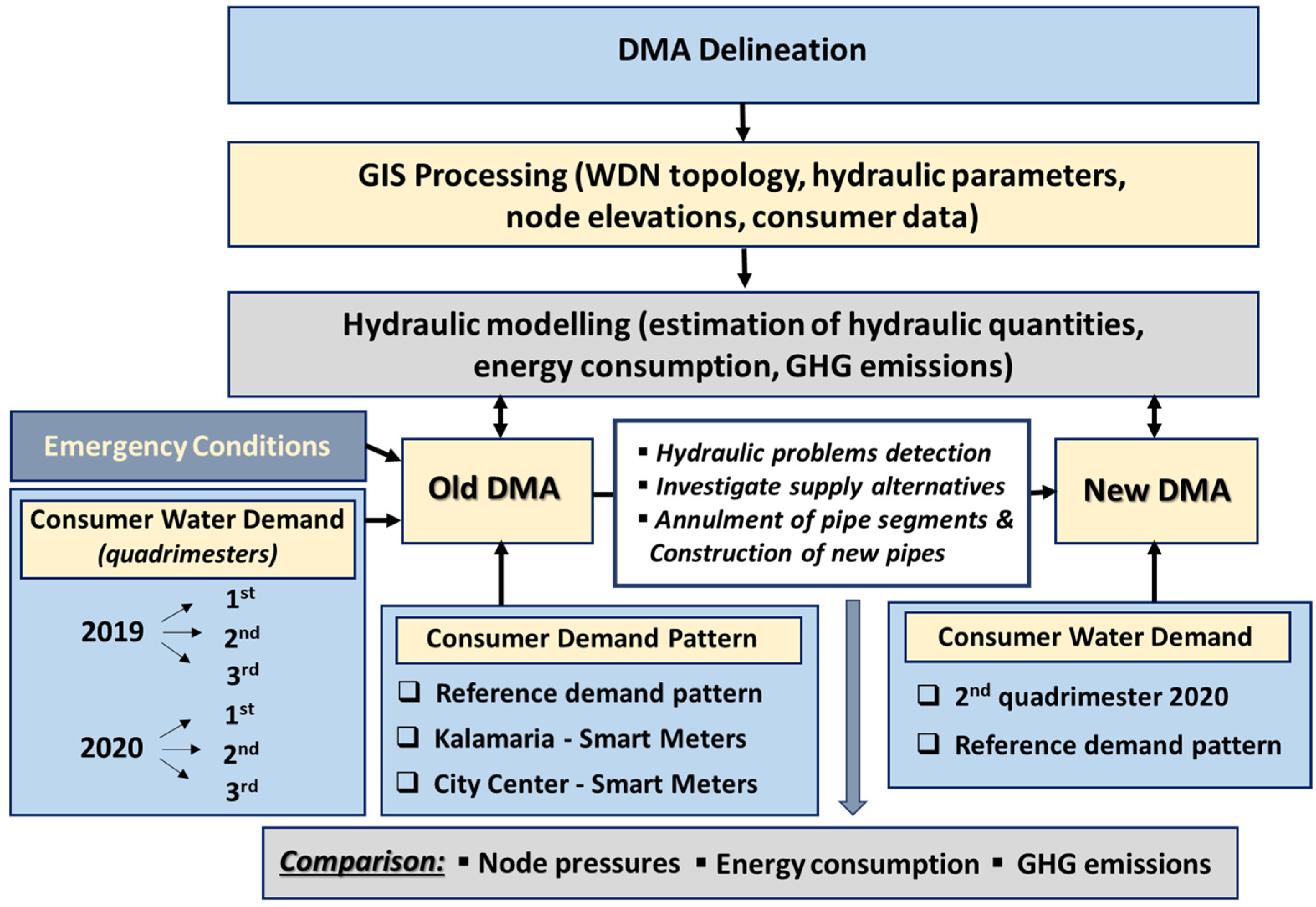
2. Materials and Methods
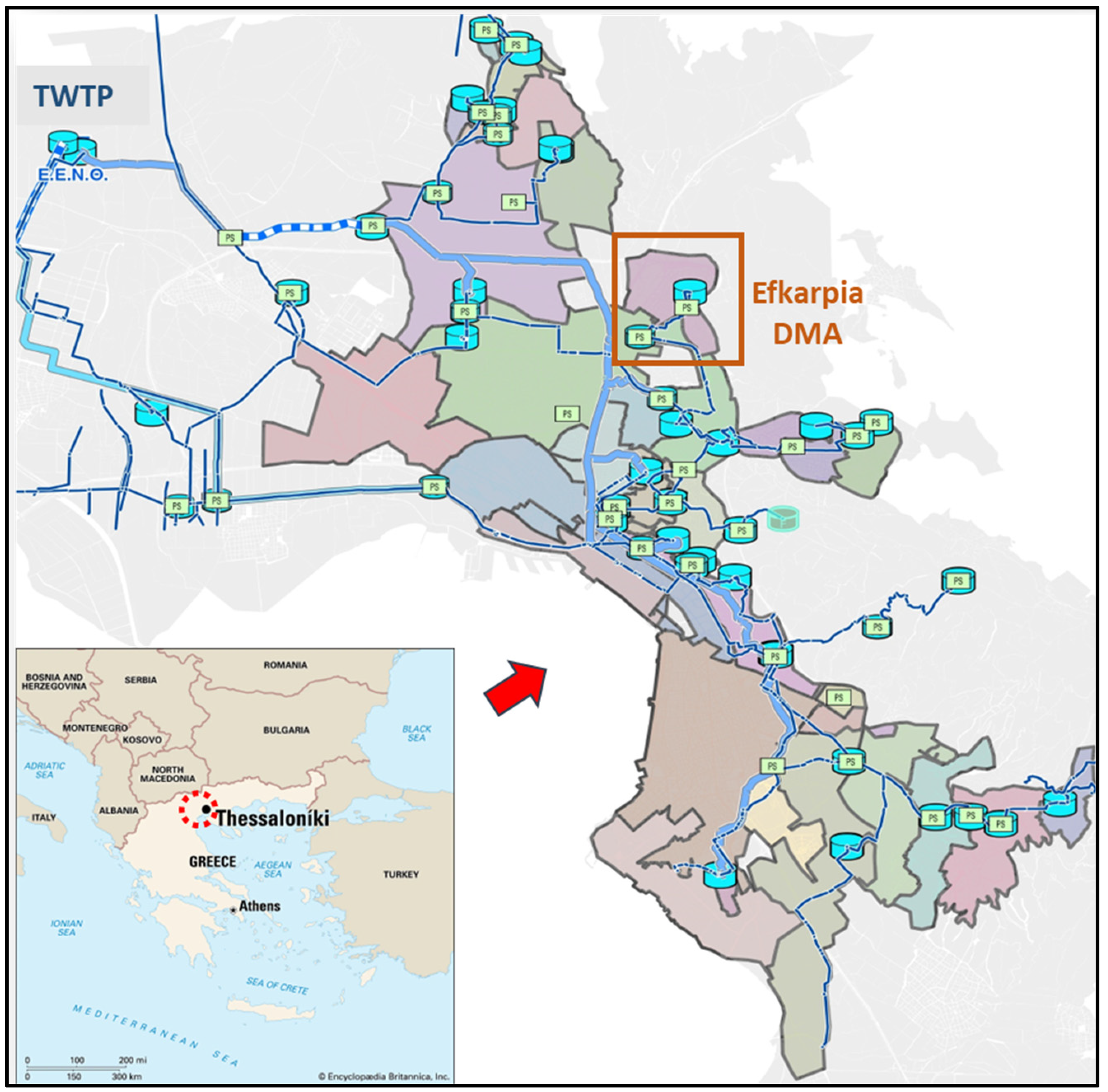
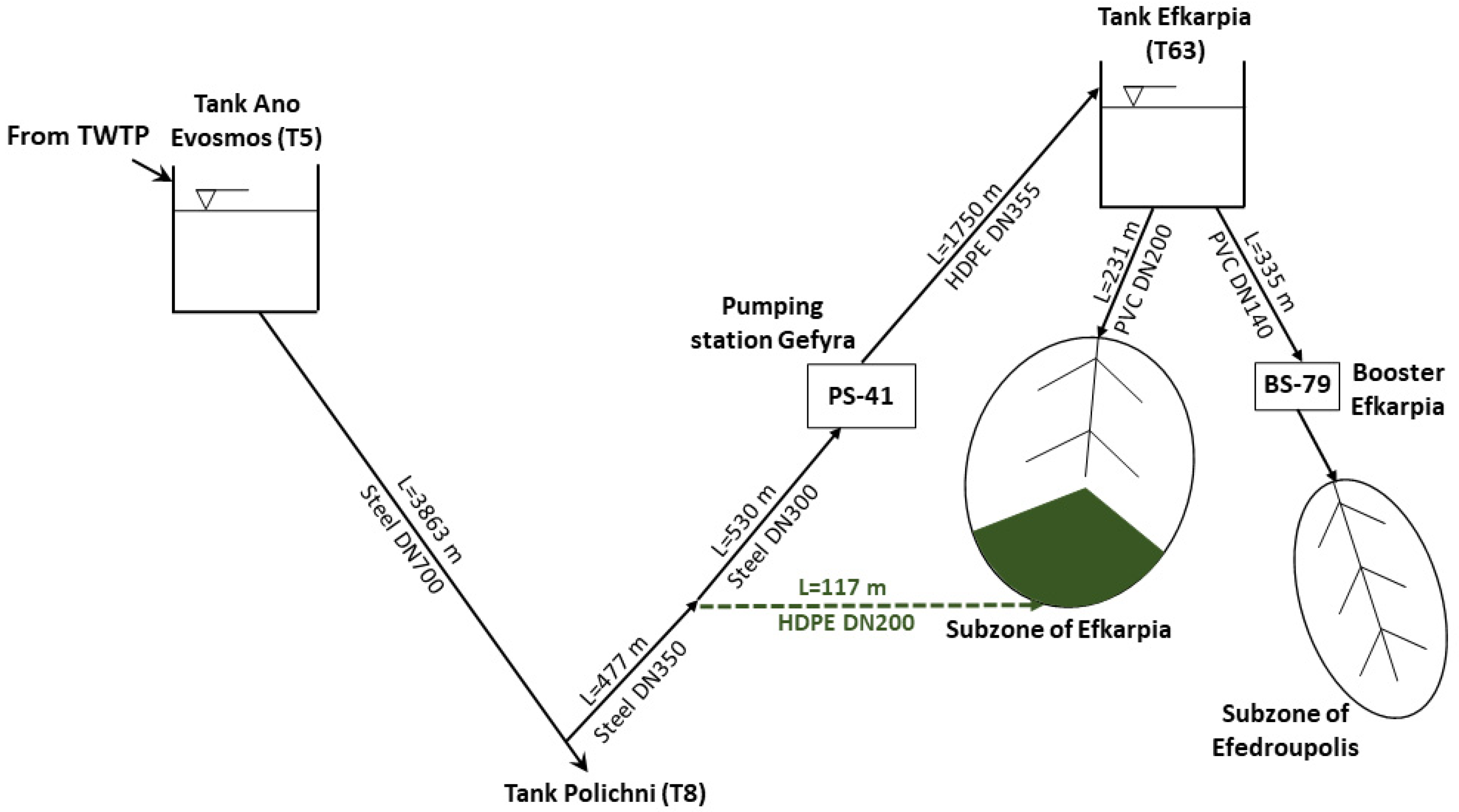
2.1. Study Area
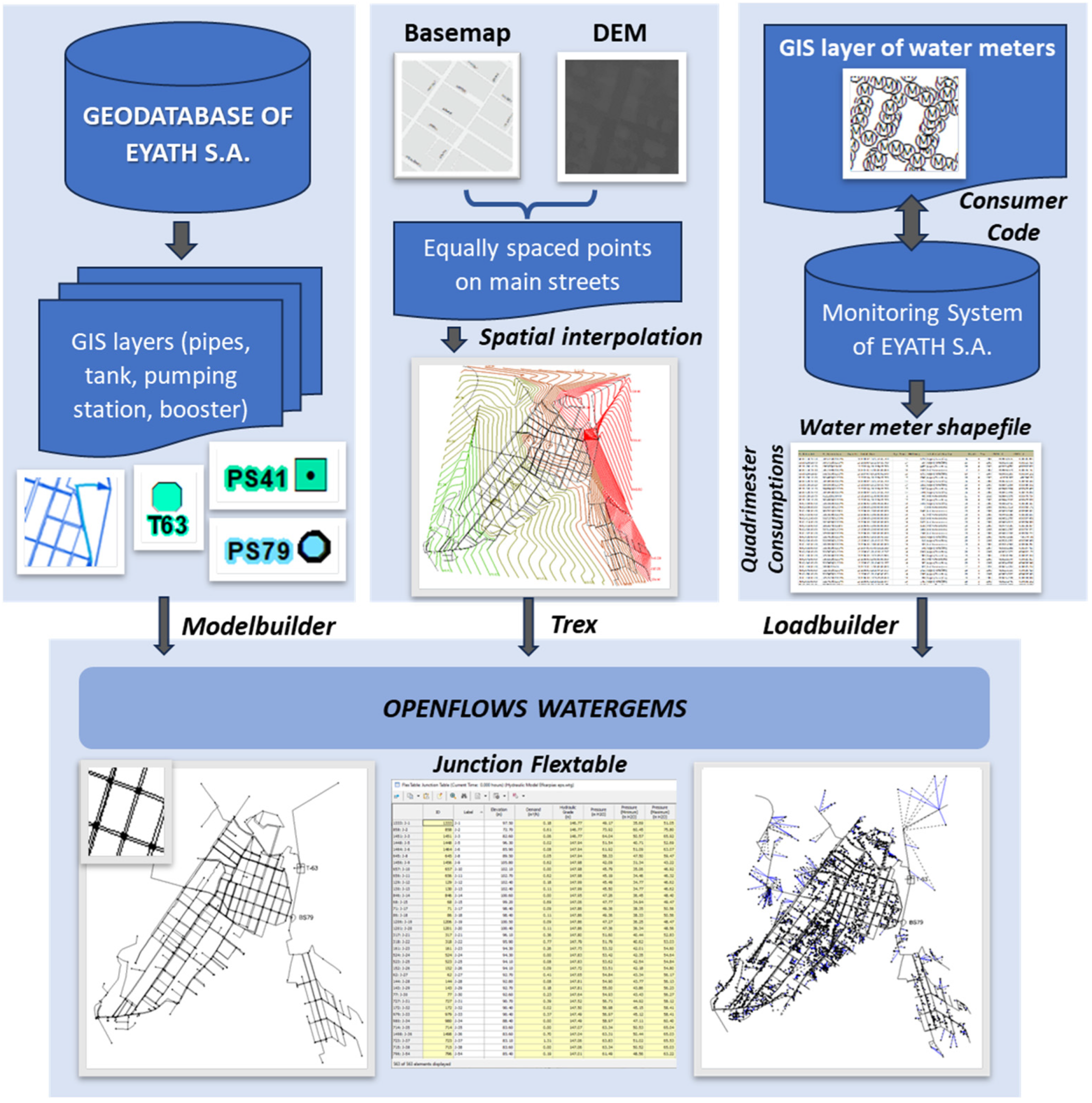
2.2. GIS Processing
2.3. Hydraulic Simulation and Analysis
2.3.1. Hydraulic Model Set-Up and Calibration
2.3.2. Hydraulic Simulation Using Consumption Data from Smart Meters
2.3.3. Energy Consumption and Savings
3. Results
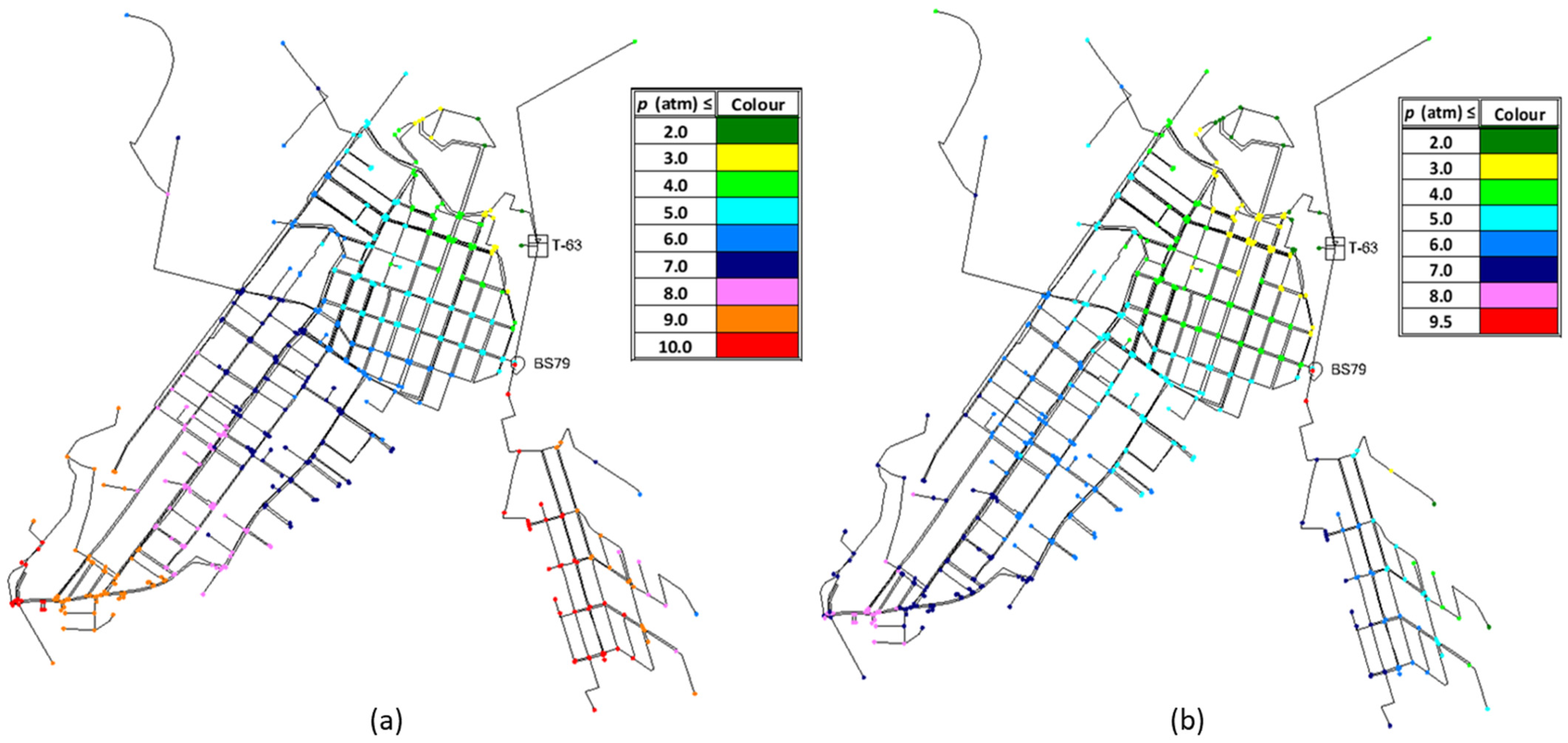
3.1. Hydraulic Model Results for Different Consumer Demands
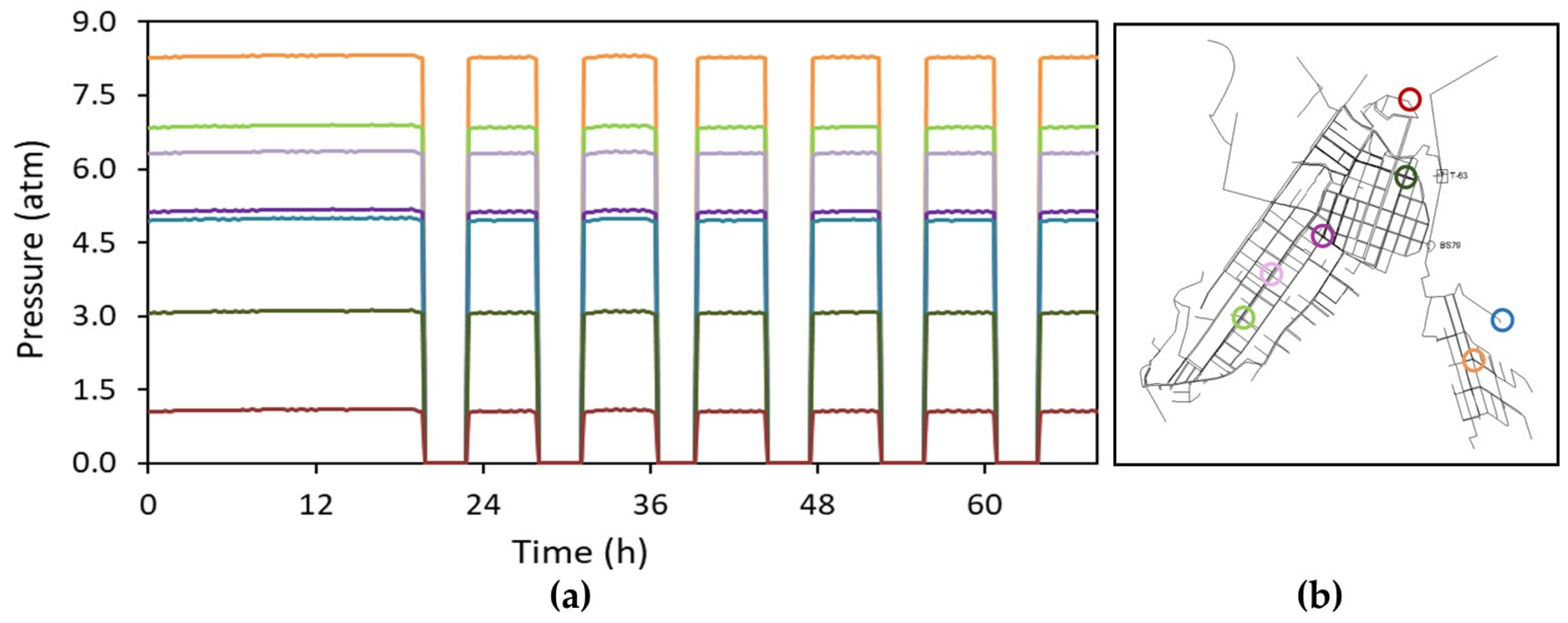
3.2. Hydraulic Model Results for Different Demand Patterns
3.3. Hydraulic Model Results for an Emergency Scenario
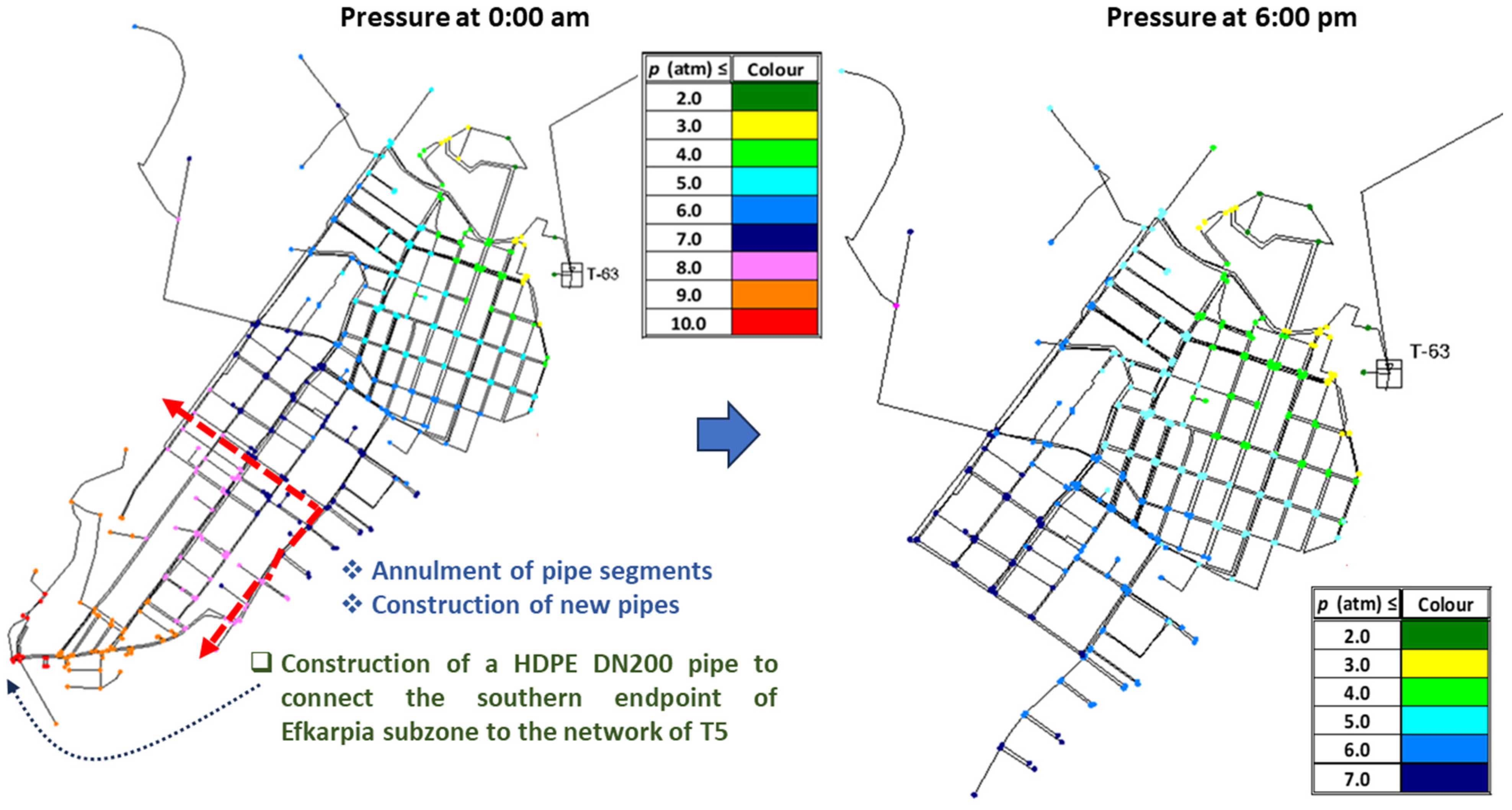
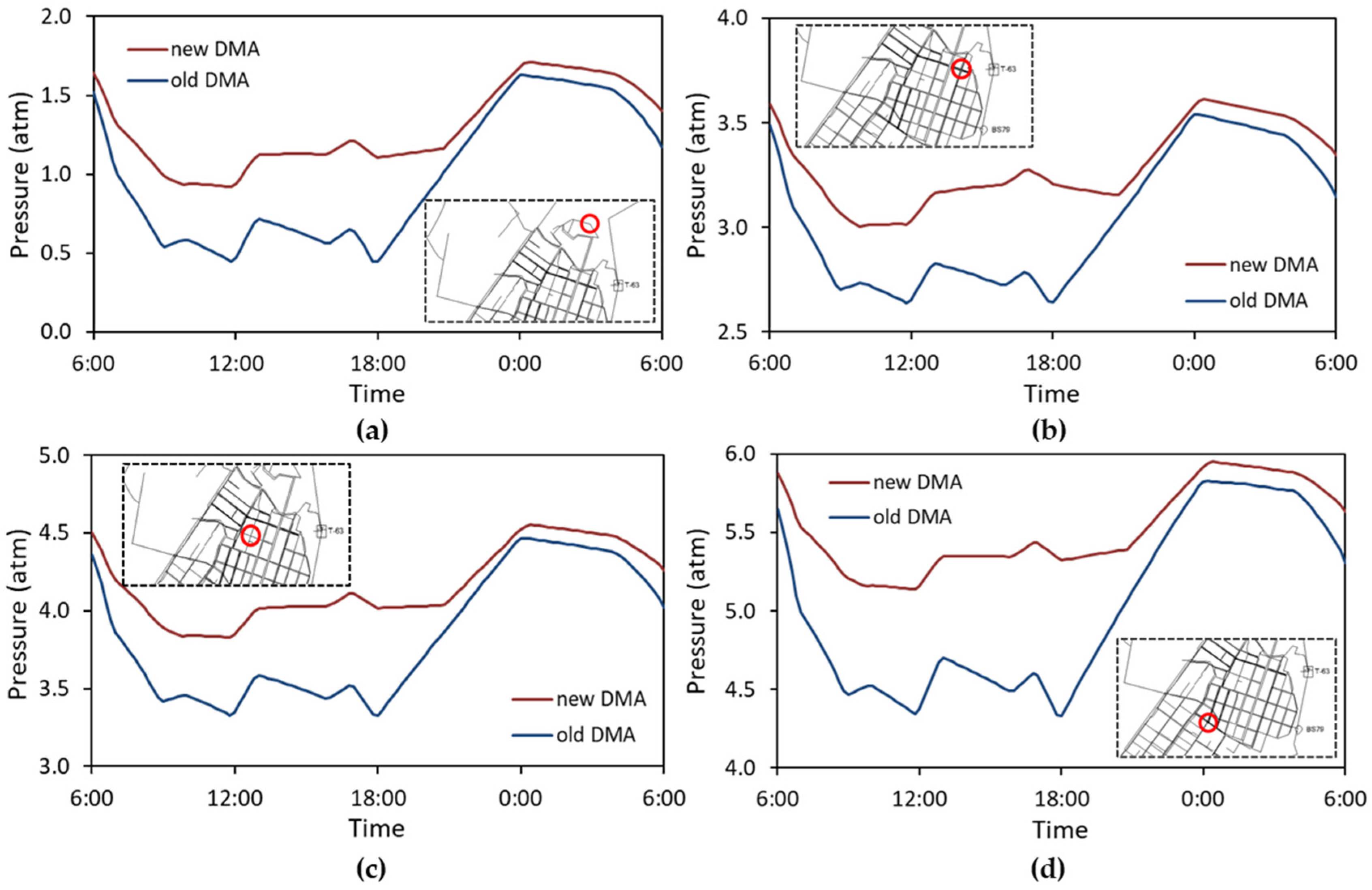
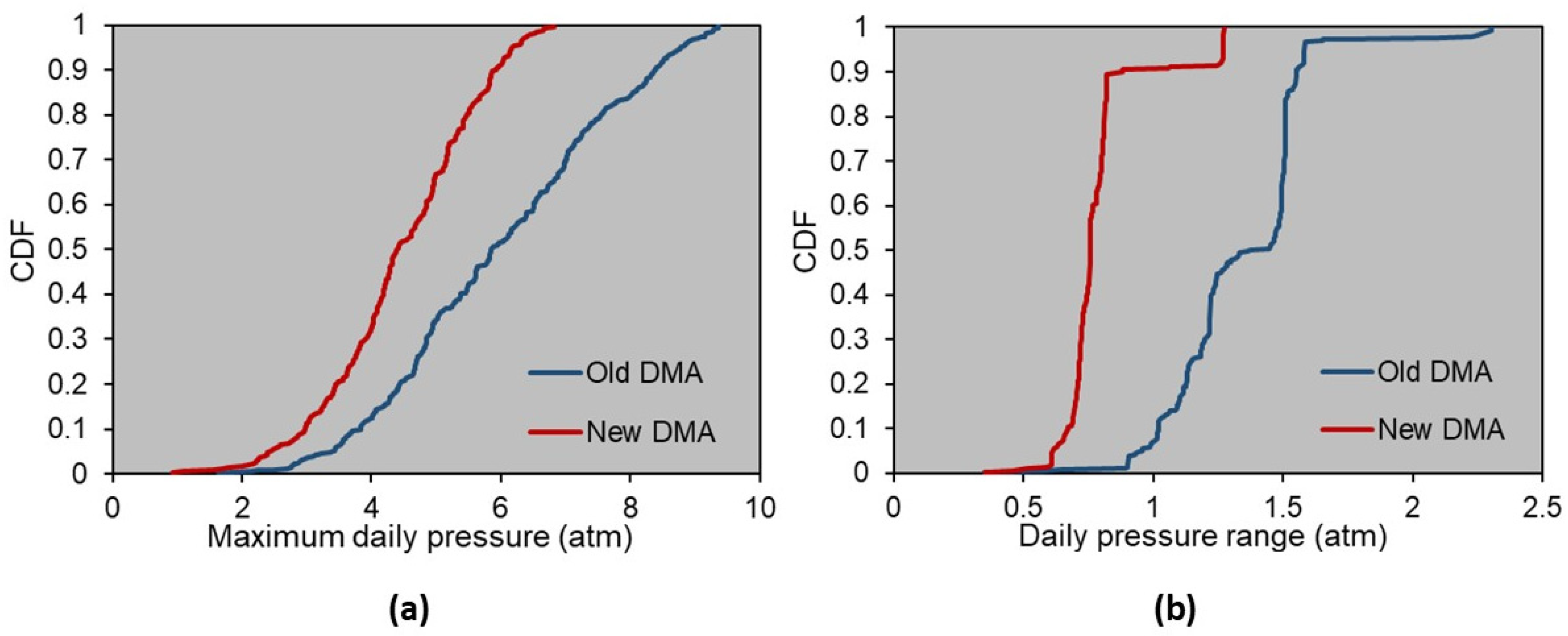
3.4. Transition to the New DMA of the Efkarpia District
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kanakoudis, V.; Tsitsifli, S. Integrated Management of Urban Water Distribution Networks; Open Academic Editions; Kallipos: Athens, Greece, 2015; Available online: https://repository.kallipos.gr/handle/11419/3415 (accessed on 13 December 2023). (In Greek)
- Morrison, J.; Tooms, S.; Rogers, D. District Metered Areas Guidance Notes; Specialist group on efficient operation and management of urban water distribution systems, Water Loss Task Force; International Water Association (IWA): London, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Thornton, J.; Sturm, R.; Kunkel, G. Water Loss Control; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Marzola, I.; Alvisi, S.; Franchini, M. Analysis of MNF and FAVAD model for leakage characterization by exploiting smart-metered data: The case of the Gorino Ferrarese (FE-Italy) district. Water 2021, 13, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, R.; Sousa, J.; Muranho, J.; Marques, A.S. Different design criteria for district metered areas in water distribution networks. Procedia Eng. 2015, 119, 1221–1230. [Google Scholar]
- Han, R.; Liu, J. Spectral Clustering and Genetic Algorithm for Design of District Metered Areas in Water Distribution Systems. Procedia Eng. 2017, 186, 152–159. [Google Scholar]
- Pesantez, J.E.; Berglund, E.Z.; Mahinthakumar, G. Geospatial and Hydraulic Simulation to Design District Metered Areas for Large Water Distribution Networks. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2020, 146, 06020010. [Google Scholar]
- Chatzivasili, S.; Papadimitriou KKanakoudis, V. Optimizing the formation of DMAs in a water distribution network through advanced modelling. Water 2019, 11, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brentan, B.M.; Campbell, E.; Meirelles, G.L.; Luvizotto, E.; Izquierdo, J. Social network community detection for DMA creation: Criteria analysis through multilevel optimization. Math. Probl. Eng. 2017, 2017, 9053238. [Google Scholar]
- Brentan, B.M.; Carpitella, S.; Izquierdo, J.; Luvizotto Jr, E.; Meirelles, G. District metered area design through multicriteria and multiobjective optimization. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 2022, 45, 3254–3271. [Google Scholar]
- Kowalska, B.; Suchorab, P.; Kowalski, D. Division of district metered areas (DMAs) in a part of water supply network using WaterGEMS (Bentley) software: A case study. Appl. Water Sci. 2022, 12, 166. [Google Scholar]
- Machell, J.; Mounce, S.R.; Boxall, J.B. Online modelling of water distribution systems: A UK case study. Drink Water Eng. Sci. 2010, 3, 21–27. [Google Scholar]
- Yu-Kun, H.; Chun-Hui, Z.; Yu-Chung, H. A GIS-based water distribution model for Zhengzhou city, China. Water Supply 2011, 11, 497–503. [Google Scholar]
- Alves, Z.; Muranho, J.; Albuquerque, T.; Ferreira, A. Water distribution network’s modeling and calibration. A case study based on scarce inventory data. Procedia Eng. 2014, 70, 31–40. [Google Scholar]
- Soldi, D.; Candelieri, A.; Archetti, F. Resilience and vulnerability in urban water distribution networks through network theory and hydraulic simulation. Procedia Eng. 2015, 119, 1259–1268. [Google Scholar]
- Kara, S.; Karadirek, I.E.; Muhammetoglu, A.; Muhammetoglu, H. Hydraulic Modeling of a Water Distribution Network in a Tourism Area with Highly Varying Characteristics. Procedia Eng. 2016, 162, 521–529. [Google Scholar]
- Galiatsatou, P.; Ganoulis, P.; Malamataris, D.; Prinos, P. Estimating and reducing leakages in the water distribution networks of small settlements: The case of Agios Germanos in the Prespes Municipality. Water 2024, 16, 2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mentes, A.; Galiatsatou, P.; Spyrou, D.; Samaras, A.; Stournara, P. Hydraulic simulation and analysis of an urban center’s aqueducts using emergency scenarios for network operation: The case of Thessaloniki City in Greece. Water 2020, 12, 1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekonnen, Y.A. Evaluation of hydraulic performances modeling of water distribution systems and physicochemical water quality analysis, in the case of Dangila town, Amhara region, Ethiopia. Water Conserv. Sci. Eng. 2022, 7, 247–265. [Google Scholar]
- Kuma, T.; Abate, B. Evaluation of hydraulic performance of water distribution system for sustainable management. Water Resour. Manag. 2021, 35, 5259–5273. [Google Scholar]
- Obura, D.; Kimera, D.; Dadebo, D. Application of GIS and hydraulic modeling for sustainable management of water supply networks: A pathway for achieving sustainable development goal (SDG) 6. Process Integr. Optim. Sustain. 2024, 8, 1017–1034. [Google Scholar]
- Dongare, P.; Sharma, K.V.; Kumar, V.; Mathew, A. Water distribution system modelling of GIS-remote sensing and EPANET for the integrated efficient design. J. Hydroinform. 2024, 26, 567–588. [Google Scholar]
- Boulos, P.F.; Jacobsen, L.B.; Heath, J.E.; Kamojjala, S.R.I. Real-time modeling of water distribution systems: A case study. J. Am. Water Works Assoc. 2014, 106, E391–E401. [Google Scholar]
- Shafiee, M.E.; Rasekh, A.; Sela, L.; Preis, A. Streaming smart meter data integration to enable dynamic demand assignment for real-time hydraulic simulation. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2020, 146, 06020008. [Google Scholar]
- Song, R.; Liu, X.; Zhu, B.; Guo, S. Modeling of Water Distribution System Based on Ten-Minute Accuracy Remote Smart Demand Meters. Water 2022, 14, 1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spedaletti, S.; Rossi, M.; Comodi, G.; Cioccolanti, L.; Salvi, D.; Lorenzetti, M. Improvement of the energy efficiency in water systems through water losses reduction using the district metered area (DMA) approach. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 77, 103525. [Google Scholar]
- Bentley WaterGEMS. Bentley WaterGEMS V8i Help-Software Manual; Bentley Systems: Watertown, MA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Childs, C. Interpolating surfaces in ArcGIS Spatial Analyst. ArcUser 2004, 32–35, 32–35. [Google Scholar]
- Murayama, Y.; Estoque, R.C. Creating a Digital Elevation Model (DEM): A GIS Lecture Tutorial. Division of Spatial Information Science, Graduate School of Life and Environmental Sciences; National University of Tsukuba: Japan. 2011. Available online: https://giswin.geo.tsukuba.ac.jp/sis/tutorial/Creating%20a%20DEM%20from%20a%20Topographic%20Map_RCEstoque.pdf (accessed on 22 November 2024).
- Paluszczyszyn, D. Advanced Modelling and Simulation of Water Distribution Systems with Discontinuous Control Elements. Ph.D. Thesis, Faculty of Technology, School of Engineering and Sustainable Development, De Montfort University, Leicester, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, D.; Lansey, K. Demand and roughness estimation in water distribution systems. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2011, 137, 20–30. [Google Scholar]
- Do, N.C.; Simpson, A.R.; Deuerlein, J.W.; Piller, O. Calibration of water demand multipliers in water distribution systems using genetic algorithms. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2016, 142, 04016044. [Google Scholar]
- Bhave, P.R. Calibrating water distribution network models. J. Environ. Eng. 1988, 114, 120–136. [Google Scholar]
- Boulos, P.F.; Wood, D.J. Explicit calculation of pipe-network parameters. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1990, 116, 1329–1344. [Google Scholar]
- Ormsbee, L.E. Implicit network calibration. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 1989, 115, 243–257. [Google Scholar]
- Kapelan, Z.S.; Savic, D.A.; Walters, G.A. Calibration of water distribution hydraulic models using a Bayesian-type procedure. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2007, 133, 927–936. [Google Scholar]
- Koppel, T.; Vassiljev, A. Calibration of a model of an operational water distribution system containing pipes of different age. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2009, 40, 659–664. [Google Scholar]
- Dini, M.; Tabesh, M. A new method for simultaneous calibration of demand pattern and Hazen-Williams coefficients in water distribution systems. Water Resour. Manag. 2014, 28, 2021–2034. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Zheng, F.; Duan, H.F.; Jia, Y.; Zhang, T.; Guo, X. Efficient numerical approach for simultaneous calibration of pipe roughness coefficients and nodal demands for water distribution systems. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2018, 144, 04018063. [Google Scholar]
- Beal, C.; Stewart, R.; Giurco, D.; Panuwatwanich, K. Intelligent metering for urban water planning and management. In Water Efficiency in Buildings: Theory and Practice; Adeyeye, K., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: West Sussex, UK, 2014; pp. 129–146. [Google Scholar]
- Mourtzios, C.; Kourtesis, D.; Papadimitriou, N.; Antzoulatos, G.; Kouloglou, I.O.; Vrochidis, S.; Kompatsiaris, I. Work- In-Progress: SMART-WATER, a Νovel Τelemetry and Remote Control System Infrastructure for the Management of Water Consumption in Thessaloniki. Internet of Things, Infrastructures and Mobile Applications. In Interactive Mobile Communication, Technologies and Learning, Proceedings of the 13th IMCL Conference, Thessaloniki, Greece, 31 October–1 November 2019; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 962–970. [Google Scholar]
- Antzoulatos, G.; Mourtzios, C.; Stournara, P.; Kouloglou, I.O.; Papadimitriou, N.; Spyrou, D.; Mentes, A.; Nikolaidis, E.; Karakostas, A.; Kourtesis, D.; et al. Making urban water smart: The SMART-WATER solution. Water Sci. Technol. 2020, 82, 2691–2710. [Google Scholar]
- Mentes, A.; Stournara, P.; Spyrou, D. Towards smart infrastructure: A case study in the water supply system of Thessaloniki. In Proceedings of the 11th European Young Water Professionals Conference IWA YWP, Prague, Czech Republic, 1–5 October 2019; pp. 513–519. [Google Scholar]
- Mentes, A.; Stournara, P.; Spyrou, D.; Samaras, A.; Galiatsatou, P. The Smart-Water project: Smart metering in the city of Thessaloniki. In Proceedings of the 11th European Young Water Professionals Conference IWA YWP, Prague, Czech Republic, 1–5 October 2019; pp. 505–512. [Google Scholar]
- Mentes, A.; Spyrou, D.; Stournara, P.; Galiatsatou, P. Smart-Water project: Software design for processing and managing water metering data. In Proceedings of the 39th IAHR World Congress, Granada, Spain, 19–24 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Hyndman, R.J.; Athanasopoulos, G. Forecasting: Principles and Practice, 2nd ed.; OTexts: Melbourne, Australia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Olsson, G. Water and Energy: Threats and Opportunities; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Tsanov, E.; Ribarova, I.; Dimova, G.; Ninov, P.; Kossida, M.; Makropoulos, C. Water stress mitigation in the Vit River Basin based on WEAP and MatLab simulation. Civ. Eng. J. 2020, 6, 2058–2071. [Google Scholar]
- Muhammetoglu, A.; Al-Omari, A.; Al-Houri, Z.; Topkaya, B.; Tumbul, T.; Muhammetoglu, H. Assessment of energy performance and GHG emissions for the urban water cycle toward sustainability. J. Water Clim. Change 2023, 14, 223–238. [Google Scholar]
- Wiedmann, T.; Minx, J.A. Definition of ‘Carbon Footprint’. In Ecological Economics Research Trends; Pertsova, C.C., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Boulos, P.F.; Bros, C.M. Assessing the carbon footprint of water supply and distribution systems. J. Am. Water Work Assoc. 2010, 102, 47–54. [Google Scholar]
- Sambito, M.; Freni, G. LCA methodology for the quantification of the carbon footprint of the integrated urban water system. Water 2017, 9, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO/TS 14067; Greenhouse Gases-Carbon Footprint of Products-Requirements and Guidelines for Quantification and Communication. International Organization for Standardization, ISO Central Secretariat: Geneve, Switzerland, 2013.
- Del Borghi, A.; Strazza, C.; Gallo, M.; Messineo, S.; Naso, M. Water supply and sustainability: Life cycle assessment of water collection, treatment and distribution service. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2013, 18, 1158–1168. [Google Scholar]
- Barjoveanu, G.; Comandaru, I.M.; Rodriguez-Garcia, G.; Hospido, A.; Teodosiu, C. Evaluation of water services system through LCA. A case study for Iasi City, Romania. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2014, 19, 449–462. [Google Scholar]
- Lane, J.L.; De Haas, D.W.; Lant, P.A. The diverse environmental burden of city-scale urban water systems. Water Res. 2015, 81, 398–415. [Google Scholar]
- Delre, A.; ten Hoeve, M.; Scheutz, C. Site-specific carbon footprints of Scandinavian wastewater treatment plants, using the life cycle assessment approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 211, 1001–1014. [Google Scholar]
- Zib, L., III; Byrne, D.M.; Marston, L.T.; Chini, C.M. Operational carbon footprint of the US water and wastewater sector’s energy consumption. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 321, 128815. [Google Scholar]
- Ortíz-Rodriguez, O.O.; Sonnemann, G.; Villamizar-G, R.A. The carbon footprint of water treatment as well as sewer and sanitation utilities of Pamplona in Colombia. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2022, 24, 3982–3999. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Wang, D.; Xiang, C.; Xia, L.; Zhang, K.; Shao, W.; Luan, Q. Assessment of the energy use for water supply in Beijing. Energy Procedia 2018, 152, 271–280. [Google Scholar]
- Samuelsson, J.; Delre, A.; Tumlin, S.; Hadi, S.; Offerle, B.; Scheutz, C. Optical technologies applied alongside on-site and remote approaches for climate gas emission quantification at a wastewater treatment plant. Water Res. 2018, 131, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stokes, J.R.; Horvath, A. Energy and air emission effects of water supply. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 2680–2687. [Google Scholar]
- ECAM. Energy, Performance and Carbon Emissions Assessment and Monitoring Tool. Water and Wastewater Companies for Climate Mitigation. Available online: https://climatesmartwater.org/ecam/ (accessed on 1 January 2024).
- Fighir, D.; Teodosiu, C.; Fiore, S. Environmental and energy assessment of municipal wastewater treatment plants in Italy and Romania: A comparative study. Water 2019, 11, 1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EIB Project Carbon Footprint Methodologies. Methodologies for the Assessment of Project Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Emission Variations. European Investment Bank. Available online: https://www.eib.org/en/publications/20220215-eib-project-carbon-footprint-methodologies (accessed on 1 January 2024).
- Lin, J.L.; Kang, S.F. Analysis of carbon emission hot spot and pumping energy efficiency in water supply system. Water Supply 2019, 19, 200–206. [Google Scholar]
- Greyvenstein, B.; Van Zyl, J.E. An experimental investigation into the pressure-leakage relationship of some failed water pipes. J. Water Supply Res. Technol. AQUA 2007, 56, 117–124. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Q.; Chen, Q.; Ma, J.; Blanckaert, K.; Wan, Z. Water saving and energy reduction through pressure management in urban water distribution networks. Water Resour. Manag. 2014, 28, 3715–3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Galiatsatou, P.; Stournara, P.; Kavouras, I.; Raouzaios, M.; Anastasiadis, C.; Iosifidis, F.; Spyrou, D.; Mentes, A. Combining Geographic Information Systems and Hydraulic Modeling to Analyze the Hydraulic Response of an Urban Area Under Different Conditions: A Case Study to Assist Engineering Practice. Geographies 2025, 5, 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/geographies5020017
Galiatsatou P, Stournara P, Kavouras I, Raouzaios M, Anastasiadis C, Iosifidis F, Spyrou D, Mentes A. Combining Geographic Information Systems and Hydraulic Modeling to Analyze the Hydraulic Response of an Urban Area Under Different Conditions: A Case Study to Assist Engineering Practice. Geographies. 2025; 5(2):17. https://doi.org/10.3390/geographies5020017
Chicago/Turabian StyleGaliatsatou, Panagiota, Panagiota Stournara, Ioannis Kavouras, Michail Raouzaios, Christos Anastasiadis, Filippos Iosifidis, Dimitrios Spyrou, and Alexandros Mentes. 2025. "Combining Geographic Information Systems and Hydraulic Modeling to Analyze the Hydraulic Response of an Urban Area Under Different Conditions: A Case Study to Assist Engineering Practice" Geographies 5, no. 2: 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/geographies5020017
APA StyleGaliatsatou, P., Stournara, P., Kavouras, I., Raouzaios, M., Anastasiadis, C., Iosifidis, F., Spyrou, D., & Mentes, A. (2025). Combining Geographic Information Systems and Hydraulic Modeling to Analyze the Hydraulic Response of an Urban Area Under Different Conditions: A Case Study to Assist Engineering Practice. Geographies, 5(2), 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/geographies5020017






