Deposition of Potentially Toxic Metals in the Soil from Surrounding Cement Plants in a Karst Area of Southeastern Brazil
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
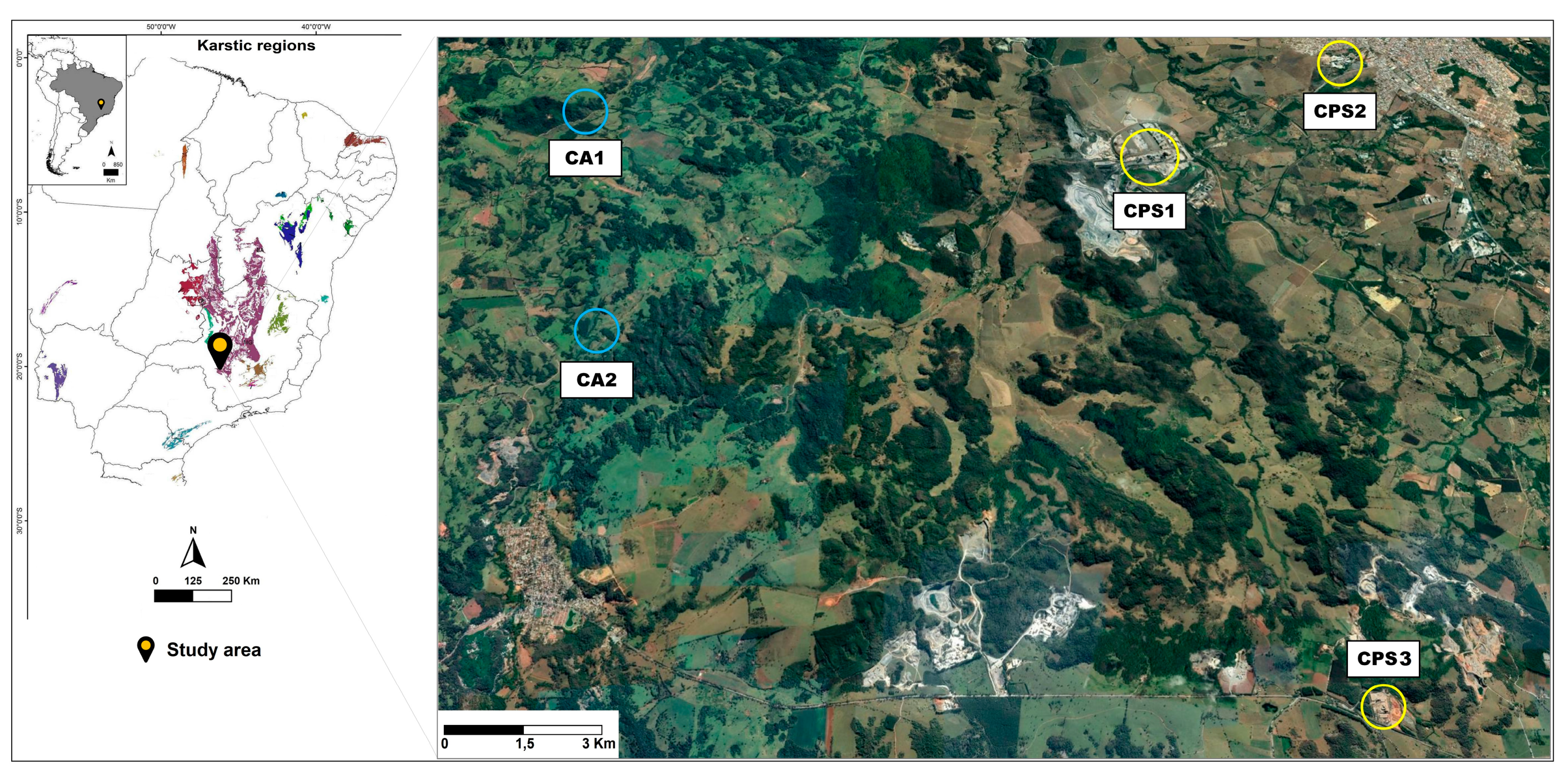
2.1. Sampling and Quantification of Potentially Toxic Metals in the Soil
2.2. Analysis of Potentially Toxic Metals Concentrations in the Soil
2.3. Health Risk Assessment
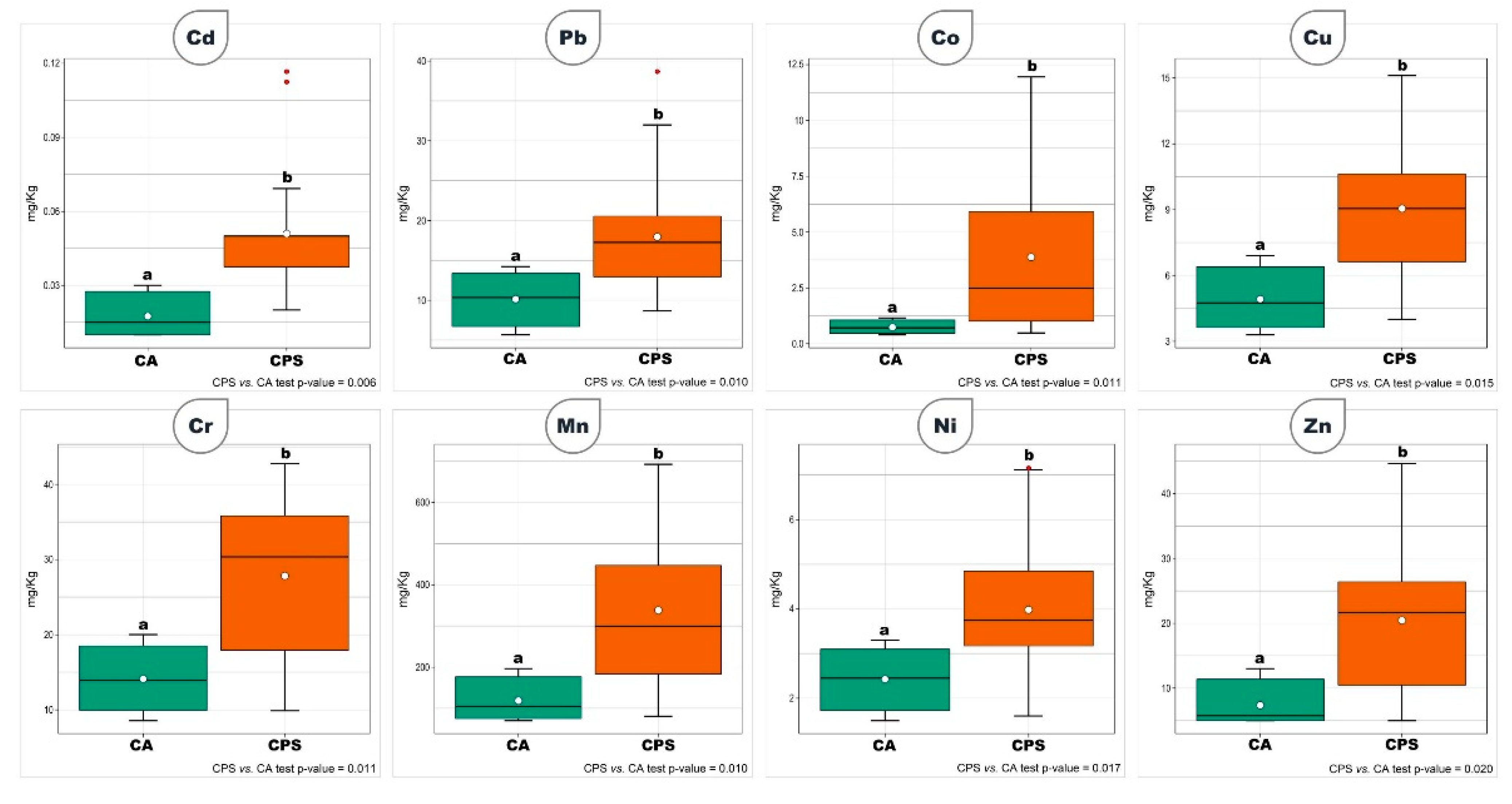
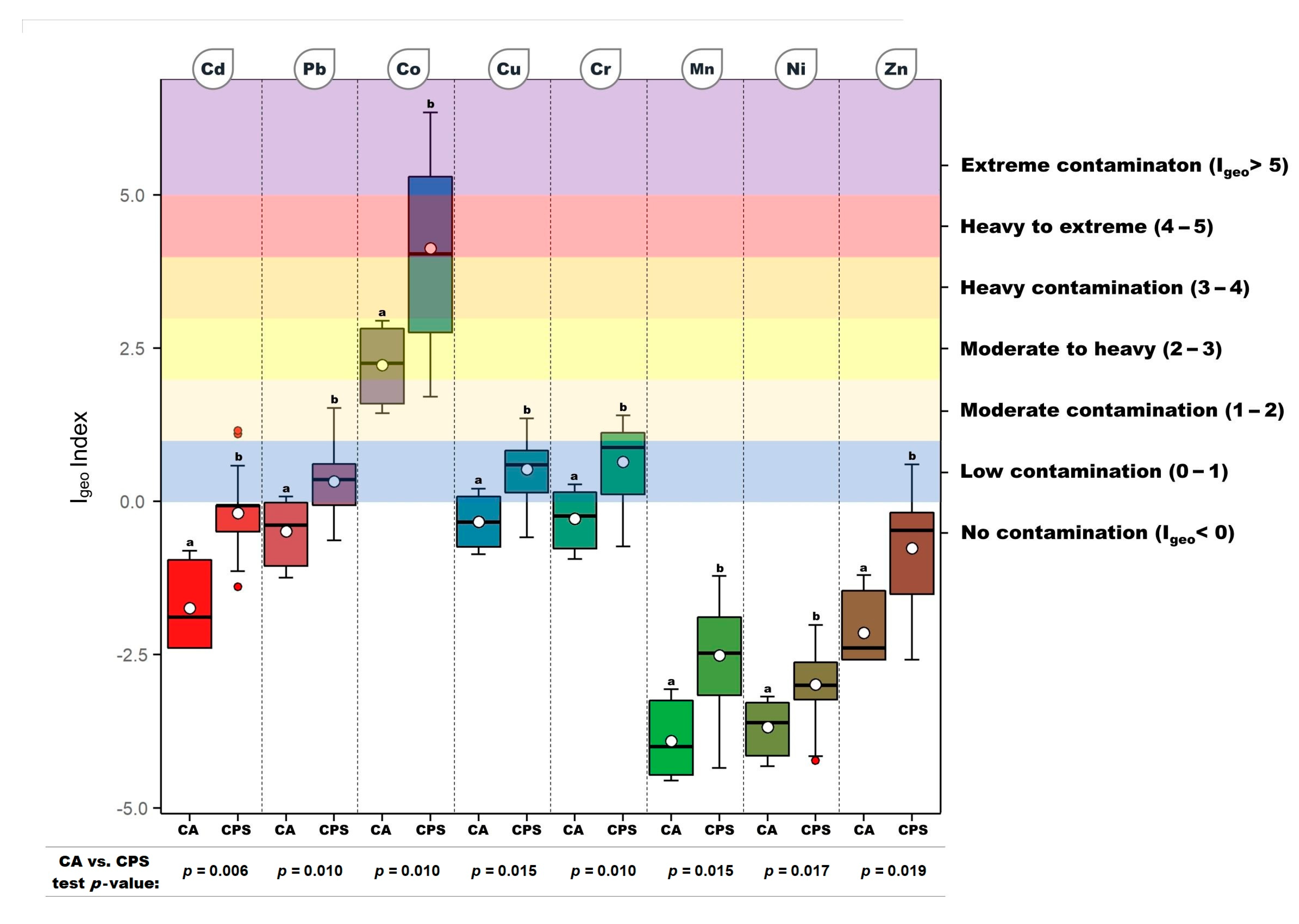
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Keesstra, S.D.; Bouma, J.; Wallinga, J.; Tittonell, P.; Smith, P.; Cerdà, A.; Montanarella, L.; Quinton, J.N.; Pachepsky, Y.; van der Putten, W.H.; et al. The significance of soils and soil science towards realization of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals. Soil 2016, 2, 111–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wall, D.H.; Behan-Pelletier, V.; Ritz, K.; Jones, T.H.; Six, J.; Strong, D.R.; van der Putten, W.H. Soil Ecology and Ecosystem Services; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Adhikari, K.; Hartemink, A.E. Linking soils to ecosystem services—A global review. Geoderma 2016, 262, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, M.J.; Dobos, R.; Peaslee, S.; Smith, D.W.; Seybold, C. Soil capability for the USA now and into the future. In Global Soil Security; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 63–76. [Google Scholar]
- Naila, A.; Meerdink, G.; Jayasena, V.; Sulaiman, A.Z.; Ajit, A.B.; Berta, G. A review on global metal accumulators—Mechanism, enhancement, commercial application, and research trend. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 26449–26471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, I.C.; Devi, N.L.; Singh, V.K.; Li, J.; Zhang, G. Spatial distribution, source analysis, and health risk assessment of heavy metals contamination in house dust and surface soil from four major cities of Nepal. Chemosphere 2019, 218, 1100–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimi, A.; Naghizadeh, A.; Biglari, H.; Peirovi, R.; Ghasemi, A.; Zarei, A. Assessment of human health risks and pollution index for heavy metals in farmlands irrigated by effluents of stabilization ponds. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 10317–10327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsezos, M. Metal-microbes interactions: Beyond environmental protection. Adv. Mater. Res. 2009, 71, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sherbiny, M.M.; Ismail, A.I.; EL-Hefnawy, M.E. A preliminary assessment of potential ecological risk and soil contamination by heavy metals around a cement factory, western Saudi Arabia. Open Chem. 2019, 17, 671–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabata-Pendias, A.; Mukherjee, A.B. Trace Elements from Soil to Human; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Qasemi, M.; Afsharnia, M.; Farhang, M.; Bakhshizadeh, A.; Allahdadi, M.; Zarei, A. Health risk assessment of nitrate exposure in groundwater of rural areas of Gonabad and Bajestan, Iran. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Feng, L. Multivariate and geostatistical analyzes of metals in urban soil of Weinan industrial areas, Northwest of China. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 47, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, A.; Ghaderpoori, M.; Kamarehi, B.; Abdipour, H. Soil pollution evaluation and health risk assessment of heavy metals around Douroud cement factory, Iran. Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadegarnia, N.F.; Azimzadeh, H.; Mosleh, A.A.; Ahad, S.; Bahman, K. Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals from cement factory dust. Environ. Health Eng. Manag. J. 2019, 6, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Hong, J.; Xu, C. Pollutants generated by cement production in China, their impacts, and the potential for environmental improvement. J. Clean Prod. 2015, 103, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermudez, G.M.; Moreno, M.; Invernizzi, R.; Plá, R.; Pignata, M.L. Heavy metal pollution in topsoils near a cement plant: The role of organic matter and distance to the source to predict total and HCl-extracted heavy metal concentrations. Chemosphere 2010, 78, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunkunle, C.O.; Fatoba, P.O. Contamination and spatial distribution of heavy metals in topsoil surrounding a mega cement factory. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2014, 5, 270–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yahaya, T.; Okpuzor, J.; Ajayi, T. The protective efficacy of selected phytonutrients on liver enzymes of albino rats exposed to cement dust. IOSR J. Pharm. Biol. Sci. 2013, 8, 38–44. [Google Scholar]
- Mandal, A.; Voutchkov, M. Heavy metals in soils around the cement factory in Rockfort, Kingston, Jamaica. Int. J. Geosci. 2011, 2, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ogunkunle, C.O.; Fatoba, P.O. Pollution Loads and the Ecological Risk Assessment of Soil Heavy Metals around a Mega Cement Factory in Southwest Nigeria. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2013, 22, 487–493. [Google Scholar]
- Travassos, L.E.P. Princípios de Carstologia e Geomorfologia Cárstica; ICMBio: Brasília, Brazil, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- IBGE—Instituto Brasileiro De Geografia E Estatística. Censo cidades. 2010. Available online: https://cidades.ibge.gov.br/ (accessed on 10 April 2021).
- Pacchioni, R.G.; Carvalho, F.M.; Thompson, C.E.; Faustino, A.L.; Nicolini, F.; Pereira, T.S.; Silva, R.C.B.; Cantão, M.E.; Gerber, A.; Vasconcelos, A.T.R.; et al. Taxonomic and functional profiles of soil samples from Atlantic forest and Caatinga biomes in northeastern Brazil. MicrobiologyOpen 2014, 3, 299–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA/U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Method 3050B. 1998. Available online: http://www.epa.gov/SW-846/pdfs/3050b.pdf (accessed on 18 March 2021).
- USEPA/U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Method 3050A. 1998. Available online: http://www.epa.gov/SW-846/3051a.pdf (accessed on 18 March 2021).
- BRASIL; Conselho Nacional do Meio Ambiente—CONAMA. Resolução no 420, de 28 de Dezembro de 2009; Diário Oficial da República Federativa do Brasil, Poder Executivo: Brasília, Brazil, 2009; p. 20. [Google Scholar]
- MINAS GERAIS; Conselho Estadual de Política Ambiental—COPAM. Deliberação Normativa COPAM nº 166, de 29 de Junho de 2011; Conselho Estadual de Política Ambiental: Belo Horizonte, Brazil, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Barbieri, M. The importance of enrichment factor (EF) and geoaccumulation index (Igeo) to evaluate the soil contamination. J. Geol. Geophys. 2016, 5, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, G. Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. Geojournal 1969, 2, 108–118. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammadi, A.A.; Zarei, A.; Esmaeilzadeh, M.; Taghavi, M.; Yousefi, M.; Yousefi, Z.; Sedighi, F.; Javan, S. Assessment of heavy metal pollution and human health risks assessment in soils around an industrial zone in Neyshabur, Iran. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2020, 195, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turekian, K.K.; Wedepohl, K.H. Distribution of the elements in some major units of the earth’s crust. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1961, 72, 175–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA/U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Indicators of the Environmental Impacts of Transportation; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Duan, X.; Wang, L. Spatial distribution and source analysis of heavy metals in soils influenced by industrial enterprise distribution: Case study in Jiangsu Province. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 710, 134953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization—WHO. Standard Maxima for Metals in Agricultural Soils; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Kolo, M.T.; Khandaker, M.U.; Amin, Y.M.; Abdullah, W.H.B.; Bradley, D.A.; Alzimami, K.S. Assessment of health risk due to the exposure of heavy metals in soil around mega coal-fired cement factory in Nigeria. Results Phys. 2018, 11, 755–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khashman, O.A.; Shawabkeh, R.A. Metals distribution in soils around the cement factory in southern Jordan. Environ. Pollut. 2006, 140, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, F.B.V.; Nascimento, C.W.A.; Araújo, P.R.M.; Silva, L.H.V.; Silva, R.F. Assessing heavy metal sources in sugarcane Brazilian soils: An approach using multivariate analysis. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brito, A.C.C.; Boechat, C.L.; Sena, A.F.S.; Duarte, L.D.S.L.; Nascimento, C.W.A.; Silva, Y.J.A.B.; Saraiva, P.C. Assessing the Distribution and Concentration of Heavy Metals in Soils of an Agricultural Frontier in the Brazilian Cerrado. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2020, 231, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, V.F.; Buschle, B.; Souza, L.C.P.; Bonfleur, E.J. Reference values for potentially harmful elements in soils from Atlantic Rainforest, Brazil. J. Geochem. Explor. 2017, 181, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Liu, Y.; Feng, X.; Mao, P.; Sun, A.; Wang, M.; Wang, M. Pollution effect assessment of industrial activities on potentially toxic metal distribution in windowsill dust and surface soil in central China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 759, 144023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masto, R.E.; George, J.; Rout, T.K.; Ram, L.C. Multi element exposure risk from soil and dust in a coal industrial area. J. Geochem. Explor. 2017, 176, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabarrón, M.; Faz, A.; Acosta, J.A. Use of multivariable and redundancy analysis to assess the behavior of metals and arsenic in urban soil and road dust affected by metallic mining as a base for risk assessment. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 206, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Wang, M.; Cao, J.; Gui, C.; Liu, Y.; He, X.; He, Y.; Liu, Y. Health risk assessment and bioaccessibilities of heavy metals for children in soil and dust from urban parks and schools of Jiaozuo, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 191, 110157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeaba, W.; Prasad, S.; Chandra, S. First assessment of metals contamination in road dust and roadside soil of Suva City, Fiji. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2019, 77, 249–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smidt, G.A.; Koschinsky, A.; Carvalho, L.M.; Monserrat, J.; Schnug, E. Heavy metal concentrations in soils in the vicinity of a fertilizer factory in Southern Brazil. Agric. Res. 2011, 61, 353–364. [Google Scholar]
- Antoniadis, V.; Shaheen, S.M.; Levizou, E.; Shahid, M.; Niazi, N.K.; Vithanage, M.; Ok, Y.S.; Bolan, N.; Rinklebe, J. A critical prospective analysis of the potential toxicity of trace element regulation limits in soils worldwide: Are they protective concerning health risk assessment?—A review. Environ. Int. 2019, 127, 819–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissmannová, H.D.; Pavlovský, J. Indices of soil contamination by heavy metals–methodology of calculation for pollution assessment (minireview). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okereafor, U.; Makhatha, M.; Mekuto, L.; Uche-Okereafor, N.; Sebola, T.; Mavumengwana, V. Toxic metal implications on agricultural soils, plants, animals, aquatic life and human health. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abdu, N.; Abdullahi, A.A.; Abdulkadir, A. Heavy metals and soil microbes. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2017, 15, 65–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giller, K.E.; Witter, E.; McGrath, S.P. Heavy metals and soil microbes. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2009, 41, 2031–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Xi, S. The effects of heavy metals on human metabolism. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2020, 30, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briffa, J.; Sinagra, E.; Blundell, R. Heavy metal pollution in the environment and their toxicological effects on humans. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabata-Pendias, A. Trace Elements in Soils and Plants; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton, E.I. Environmental variables in a holistic evaluation of land contaminated by historic mine wastes: A study of multi-element mine wastes in West Devon, England using arsenic as an element of potential concern to human health. Sci. Total Environ. 2000, 249, 171–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.F.; Gray, C.; Mico, C.; Zhao, F.J.; McGrath, S.P. Phytotoxicity and bioavailability of cobalt to plants in a range of soils. Chemosphere 2009, 75, 979–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaheen, S.M.; Rinklebe, J.; Frohne, T.; White, J.R.; DeLaune, R.D. Redox effects on release kinetics of arsenic, cadmium, cobalt, and vanadium in Wax Lake Deltaic freshwater marsh soils. Chemosphere 2016, 150, 740–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaborowska, M.; Kucharski, J.; Wyszkowska, J. Biological activity of soil contaminated with cobalt, tin, and molybdenum. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gál, J.; Hursthouse, A.; Tatner, P.; Stewart, F.; Welton, R. Cobalt and secondary poisoning in the terrestrial food chain: Data review and research gaps to support risk assessment. Environ. Int. 2008, 34, 821–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyssens, L.; Vinck, B.; Van Der Straeten, C.; Wuyts, F.; Maes, L. Cobalt toxicity in humans—A review of the potential sources and systemic health effects. Toxicology 2017, 387, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonsen, L.O.; Harbak, H.; Bennekou, P. Cobalt metabolism and toxicology—a brief update. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 432, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valko, M.M.H.C.M.; Morris, H.; Cronin, M.T.D. Metals, toxicity and oxidative stress. Curr. Med. Chem. 2005, 12, 1161–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dayan, A.D.; Paine, A.J. Mechanisms of chromium toxicity, carcinogenicity and allergenicity: Review of the literature from 1985 to 2000. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2001, 20, 439–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, F.; Zhong, G.; Ning, Z.; Liao, J.; Yu, W.; Wang, C.; Han, Q.; Li, Y.; Pan, J.; Tang, Z.; et al. Long-term exposure to copper induces autophagy and apoptosis through oxidative stress in rat kidneys. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 190, 110158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.J.; Niu, Z.F.; Wang, X.R.; Zhao, H.P. How the Soil Microbial Communities and Activities Respond to Long-Term Heavy Metal Contamination in Electroplating Contaminated Site. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Shen, Q.; Shi, J.; Xu, J.; Brookes, P.C.; Liu, X. Changes in microbial community structure due to chronic trace element concentrations in different sizes of soil aggregates. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 268, 115933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Zhang, J.; Ren, L.; Zhou, Y.; Gao, J.; Luo, L.; Yang, Y.; Peng, Q.; Huang, H.; Chen, A. Diagnosis of soil contamination using microbiological indices: A review on heavy metal pollution. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 242, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Ye, Y.; Hu, Y.; Shi, H. The variation in microbial community structure under different heavy metal contamination levels in paddy soils. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 180, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fajardo, C.; Costa, G.; Nande, M.; Botías, P.; García-Cantalejo, J.; Martín, M. Pb, Cd, and Zn soil contamination: Monitoring functional and structural impacts on the microbiome. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 135, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, X.; Yutong, Z.; Shenggao, L. Assessment of heavy metal pollution and human health risk in urban soils of steel industrial city (Anshan), Liaoning, Northeast China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 120, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, D.; Zhan, C.; Yang, G.; Liu, X.; Yang, J. Preliminary assessment of health risks of potentially toxic elements in settled dust over Beijing urban area. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shams, M.; Nezhad, N.T.; Dehghan, A.; Alidadi, H.; Paydar, M.; Mohammadi, A.A.; Zarei, A. Heavy metals exposure, carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic human health risks assessment of groundwater around mines in Joghatai, Iran. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2020, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, C.; Song, Y.; Chen, L.; Ji, J.; Li, J.; Yuan, X.; Yang, Z.; Ayoko, G.A.; Frost, R.L.; Theiss, F. Human health risks of heavy metals in paddy rice based on transfer characteristics of heavy metals from soil to rice. Catena 2019, 175, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proshad, R.; Islam, M.S.; Kormoker, T.; Sayeed, A.; Khadka, S.; Idris, A.M. Potential toxic metals (PTMs) contamination in agricultural soils and foodstuffs with associated source identification and model uncertainty. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 789, 147962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kormoker, T.; Proshad, R.; Islam, S.; Ahmed, S.; Chandra, K.; Uddin, M.; Rahman, M. Toxic metals in agricultural soils near the industrial areas of Bangladesh: Ecological and human health risk assessment. Tox Rev. 2019, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Factor | Definition | Unit | Children | Adult | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | Heavy metal concentration | mg/kg | - | - | - |
| IngR | Ingestion rate | mg/day | 100 | 50 | [6] |
| EF | Exposure frequency | days/year | 320 | 320 | [6] |
| ED | Exposure duration | years | 6 | 24 | [6] |
| BW | Body weight | kg | 18.6 | 80 | [6] |
| AT | Average time | days | ED × 365 | ED × 365 | [6] |
| InhR | Inhalation rate | m3/kg | 5 | 20 | [6] |
| PEF | Particle emission factor | m3/kg | 1.36 × 109 | 1.36 × 109 | [6] |
| SA | Exposed skin surface area | cm2 | 2699 | 3950 | [6] |
| AF | Skin adherence factor | (mg/cm) day | 0.2 | 0.07 | [6] |
| ABS | Dermal absorption factor | unitless | 0.001 | 0.001 | [6] |
| CF | Conversion factor | kg/mg | 1 × 10−6 | 1 × 10−6 | [6] |
| Soil | Cd | Pb | Co | Cu | Cr | Mn | Ni | Zn | City/Region, Country | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CPS 1 | 0.06 | 19.25 | 3.86 | 9.26 | 28.33 | 318.33 | 4.07 | 21.13 | Arcos, Brazil | This study |
| CPS 2 | 0.05 | 13.59 | 1.85 | 7.03 | 19.64 | 205.51 | 3.12 | 13.23 | Arcos, Brazil | This study |
| CPS 3 | 0.06 | 21.04 | 5.92 | 10.87 | 35.53 | 490.76 | 4.77 | 27.02 | Pains, Brazil | This study |
| Control | 0.06 | 19.67 | 5.22 | 8.47 | 25.20 | 376.93 | 4.07 | 19.57 | Pains, Brazil | This study |
| CPS | - | 29.70 | - | 28.50 | 131.00 | - | 37.70 | 98.20 | Rabigh, South Arabia | [9] |
| CPS | 289.90 | 469.20 | - | 404.40 | 186.20 | - | - | 168.10 | Sagamu, Nigeria | [17] |
| CPS | 147.80 | 31.47 | - | - | 57.21 | - | - | 138.50 | Kingston, Jamaica | [19] |
| CPS | - | 19.30 | - | 5.03 | 76.40 | 466.00 | 29.10 | 10.10 | Gombe, Nigeria | [35] |
| CPS | 5.00 | 55.00 | - | 2.89 | 22.18 | - | - | 44.51 | Qadissiya, Jordan | [36] |
| Agricultural soil | 1.90 | 11.20 | - | 6.40 | 18.80 | - | 4.90 | 16.20 | Pernanbuco, Brazil | [37] |
| Agricultural soil | 0.06 | 2.69 | - | 2.14 | 55.66 | 6.86 | 0.91 | 3.56 | Piauí, Brazil | [38] |
| Forest soil | 0.05 | 1.79 | - | 0.96 | 28.17 | 6.20 | 0.62 | 0.35 | Piauí, Brazil | [38] |
| Forest soil | 0.60 | 10.40 | 0.20 | 12.10 | 44.20 | - | 13.50 | 30.40 | Paraná, Brazil | [39] |
| Industrial area soil | 0.70 | 41.00 | 19.00 | 25.00 | 60.00 | 546.00 | 24.00 | 70.00 | Anyang, China | [40] |
| Industrial area soil | 0.20 | 27.00 | 24.00 | 48.00 | 124.00 | - | 36.00 | 110.00 | Jharia, India | [41] |
| Urban area soil | 1.10 | 137.00 | 46.00 | 277.00 | 309.00 | 1870.00 | 121.00 | 1020.00 | Four cities, Nepal | [6] |
| Urban area soil | 1.50 | 803.00 | 11.00 | 34.00 | 31.00 | 803.00 | 21.00 | 331.00 | Mazarron Town, Spain | [42] |
| Urban area soil | 0.50 | 31.00 | 18.00 | 21.00 | 59.00 | 488.00 | 36.00 | 100.00 | Jiaozuo, China | [43] |
| Roadside soil | 3.10 | 59.00 | 33.00 | 266.00 | 34.00 | - | 32.00 | 507.00 | Suva, Fiji | [44] |
| PTM | CA | Soil Enrichment 1 | CPS | Soil Enrichment 1 | CA vs. CPS p-Value 2 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | Max | SD | Mean | Min | Max | SD | Mean | ||||
| Cd | 0.038 | 0.148 | 0.049 | 0.062 | No | 0.123 | 0.830 | 0.171 | 0.252 | No | 0.003 |
| Pb | 0.109 | 0.238 | 0.060 | 0.005 | No | 0.168 | 1.069 | 0.201 | 0.345 | No | 0.042 |
| Co | 0.698 | 1.523 | 0.395 | 0.006 | No | 0.878 | 30.33 3 | 6.745 | 6.207 | High | 0.007 |
| Cu | 0.142 | 0.253 | 0.049 | 0.018 | No | 0.180 | 0.952 | 0.180 | 0.386 | No | 0.019 |
| Cr | 0.134 | 0.280 | 0.062 | 0.223 | No | 0.162 | 0.987 | 0.198 | 0.424 | No | 0.010 |
| Mn | 0.011 | 0.023 | 0.005 | 0.018 | No | 0.013 | 0.161 | 0.031 | 0.050 | No | 0.003 |
| Ni | 0.013 | 0.026 | 0.006 | 0.021 | No | 0.014 | 0.092 | 0.017 | 0.034 | No | 0.042 |
| Zn | 0.045 | 0.085 | 0.018 | 0.061 | No | 0.045 | 0.567 | 0.115 | 0.170 | No | 0.003 |
| Sampling Site | PTM | HQing | HQinh | HQderm | HI | NCR 1 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Children | Adult | Children | Adult | Children | Adult | Children | Adult | |||
| CPS1 | Cd | 2.83 × 10−10 | 1.32 × 10−10 | 1.04 × 10−16 | 3.87 × 10−16 | 1.53 × 10−12 | 7.27 × 10−13 | 2.84 × 10−10 | 1.32 × 10−10 | No |
| Pb | 3.18 × 10−7 | 1.48 × 10−7 | 1.75 × 10−11 | 6.52 × 10−11 | 1.72 × 10−9 | 8.22 × 10−10 | 3.19 × 10−7 | 1.49 × 10−7 | No | |
| Co | 1.82 × 10−7 | 8.48 × 10−8 | 1.07 × 10−11 | 3.99 × 10−11 | 5.62 × 10−13 | 2.68 × 10−13 | 1.82 × 10−7 | 8.49 × 10−8 | No | |
| Cu | 1.75 × 10−6 | 8.13 × 10−7 | 1.93 × 10−11 | 7.17 × 10−11 | 9.43 × 10−9 | 4.49 × 10−9 | 1.76 × 10−6 | 8.17 × 10−7 | No | |
| Cr | 4.01 × 10−7 | 1.86 × 10−7 | 2.95 × 10−13 | 1.10 × 10−12 | 2.06 × 10−11 | 9.82 × 10−12 | 4.01 × 10−7 | 1.86 × 10−7 | No | |
| Mn | 6.90 × 10−5 | 3.21 × 10−5 | 1.02 × 10−10 | 3.78 × 10−10 | 1.16 × 10−10 | 5.52 × 10−11 | 6.90 × 10−5 | 3.21 × 10−5 | No | |
| Ni | 3.84 × 10−7 | 1.78 × 10−7 | 3.81 × 10−12 | 1.42 × 10−11 | 2.13 × 10−9 | 1.02 × 10−9 | 3.86 × 10−7 | 1.79 × 10−7 | No | |
| Zn | 2.99 × 10−5 | 1.39 × 10−5 | 2.20 × 10−10 | 8.17 × 10−10 | 1.61 × 10−7 | 7.68 × 10−8 | 3.00 × 10−5 | 1.40 × 10−5 | No | |
| CPS2 | Cd | 2.36 × 10−10 | 1.10 × 10−10 | 8.66 × 10−17 | 3.22 × 10−16 | 1.27 × 10−12 | 6.06 × 10−13 | 2.37 × 10−10 | 1.10 × 10−10 | No |
| Pb | 2.24 × 10−7 | 1.04 × 10−7 | 1.24 × 10−11 | 4.60 × 10−11 | 1.22 × 10−9 | 5.80 × 10−10 | 2.25 × 10−7 | 1.05 × 10−7 | No | |
| Co | 8.75 × 10−8 | 4.07 × 10−8 | 5.15 × 10−12 | 1.91 × 10−11 | 2.70 × 10−13 | 1.28 × 10−13 | 8.75 × 10−8 | 4.07 × 10−8 | No | |
| Cu | 1.33 × 10−6 | 6.17 × 10−7 | 1.46 × 10−11 | 5.44 × 10−11 | 7.16 × 10−9 | 3.41 × 10−9 | 1.33 × 10−6 | 6.20 × 10−7 | No | |
| Cr | 2.78 × 10−7 | 1.29 × 10−7 | 2.04 × 10−13 | 7.60 × 10−13 | 1.43 × 10−11 | 6.81 × 10−12 | 2.78 × 10−7 | 1.29 × 10−7 | No | |
| Mn | 4.46 × 10−5 | 2.07 × 10−5 | 6.55 × 10−11 | 2.44 × 10−10 | 7.48 × 10−11 | 3.56 × 10−11 | 4.46 × 10−5 | 2.07 × 10−5 | No | |
| Ni | 2.94 × 10−7 | 1.37 × 10−7 | 2.92 × 10−12 | 1.08 × 10−11 | 1.63 × 10−9 | 7.78 × 10−10 | 2.95 × 10−7 | 1.37 × 10−7 | No | |
| Zn | 1.87 × 10−5 | 8.70 × 10−6 | 1.38 × 10−10 | 5.12 × 10−10 | 1.01 × 10−7 | 4.81 × 10−8 | 1.88 × 10−5 | 8.75 × 10−6 | No | |
| CPS3 | Cd | 2.90 × 10−4 | 1.35 × 10−10 | 1.07 × 10−16 | 3.97 × 10−16 | 1.57 × 10−12 | 7.46 × 10−13 | 2.90 × 10−4 | 1.36 × 10−10 | No |
| Pb | 2.83 × 10−2 | 1.61 × 10−7 | 1.91 × 10−11 | 7.12 × 10−11 | 1.88 × 10−9 | 8.98 × 10−10 | 2.83 × 10−2 | 1.62 × 10−7 | No | |
| Co | 2.79 × 10−3 | 1.30 × 10−7 | 1.64 × 10−11 | 6.11 × 10−11 | 8.61 × 10−13 | 4.10 × 10−13 | 2.79 × 10−3 | 1.30 × 10−7 | No | |
| Cu | 1.28 × 10−3 | 9.53 × 10−7 | 2.26 × 10−11 | 8.41 × 10−11 | 1.11 × 10−8 | 5.27 × 10−9 | 1.28 × 10−3 | 9.58 × 10−7 | No | |
| Cr | 5.58 × 10−2 | 2.34 × 10−7 | 3.69 × 10−13 | 1.37 × 10−12 | 2.59 × 10−11 | 1.23 × 10−11 | 5.58 × 10−2 | 2.34 × 10−7 | No | |
| Mn | 5.03 × 10-2 | 4.95 × 10-5 | 1.56 × 10-10 | 5.82 × 10-10 | 1.79 × 10-10 | 8.51 × 10-11 | 5.03 × 10-2 | 4.95 × 10-5 | No | |
| Ni | 1.12 × 10-3 | 2.09 × 10-7 | 4.46 × 10-12 | 1.66 × 10-11 | 2.50 × 10-9 | 1.19 × 10-9 | 1.12 × 10-3 | 2.10 × 10-7 | No | |
| Zn | 4.24 × 10-4 | 1.78 × 10-5 | 2.81 × 10-10 | 1.04 × 10-9 | 2.06 × 10-7 | 9.82 × 10-8 | 4.25 × 10-4 | 1.79 × 10-5 | No | |
| CA | Cd | 4.83 × 10−10 | 2.24 × 10−10 | 1.77 × 10−16 | 6.60 × 10−16 | 2.60 × 10−12 | 1.24 × 10−12 | 4.85 × 10−10 | 2.26 × 10−10 | No |
| Pb | 4.50 × 10−7 | 2.09 × 10−7 | 2.48 × 10−11 | 9.23 × 10−11 | 2.44 × 10−9 | 1.16 × 10−9 | 4.52 × 10−7 | 2.10 × 10−7 | No | |
| Co | 3.32 × 10−7 | 1.54 × 10−7 | 1.95 × 10−11 | 7.26 × 10−11 | 1.02 × 10−12 | 4.87 × 10−13 | 3.32 × 10−7 | 1.54 × 10−7 | No | |
| Cu | 3.15 × 10−6 | 1.47 × 10−6 | 3.48 × 10−11 | 1.29 × 10−10 | 1.70 × 10−8 | 8.11 × 10−9 | 3.17 × 10−6 | 1.47 × 10−6 | No | |
| Cr | 4.28 × 10−7 | 1.99 × 10−7 | 3.15 × 10−13 | 1.17 × 10−12 | 2.20 × 10−11 | 1.05 × 10−11 | 4.28 × 10−7 | 1.99 × 10−7 | No | |
| Mn | 1.37 × 10−4 | 6.35 × 10−5 | 2.01 × 10−10 | 7.47 × 10−10 | 2.29 × 10−10 | 1.09 × 10−10 | 1.37 × 10−4 | 6.35 × 10−5 | No | |
| Ni | 6.06 × 10−7 | 2.82 × 10−7 | 6.01 × 10−12 | 2.24 × 10−11 | 3.37 × 10−9 | 1.60 × 10−9 | 6.09 × 10−7 | 2.83 × 10−7 | No | |
| Zn | 6.73 × 10−5 | 3.13 × 10−5 | 4.95 × 10−10 | 1.84 × 10−9 | 3.63 × 10−7 | 1.73 × 10−7 | 6.76 × 10−5 | 3.15 × 10−5 | No | |
| Sampling Site | PTM | ∑CR | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Children | Potential Risk 1 | Adult | Potential Risk 1 | ||
| CPS1 | Cd | 2.00 × 10−6 | Low | 9.33 × 10−7 | NS |
| Pb | 2.56 × 10−5 | Low | 1.19 × 10−5 | Low | |
| Co | 1.80 × 10−4 | High | 8.36 × 10−5 | Low | |
| Cr | 5.64 × 10−3 | High | 2.62 × 10−3 | High | |
| Ni | 1.62 × 10−5 | Low | 7.54 × 10−6 | Low | |
| CPS2 | Cd | 1.67 × 10−6 | Low | 7.77 × 10−7 | NS |
| Pb | 1.80 × 10−5 | Low | 8.39 × 10−6 | Low | |
| Co | 8.62 × 10−5 | Low | 4.01 × 10−5 | Low | |
| Cr | 3.91 × 10−3 | High | 1.82 × 10−3 | High | |
| Ni | 1.24 × 10−5 | Low | 5.77 × 10−6 | Low | |
| CPS3 | Cd | 2.06 × 10−6 | Low | 9.56 × 10−7 | NS |
| Pb | 2.79 × 10−5 | Low | 1.30 × 10−5 | Low | |
| Co | 2.75 × 10−4 | High | 1.28 × 10−4 | High | |
| Cr | 7.07 × 10−3 | Low | 3.29 × 10−3 | High | |
| Ni | 1.90 × 10−5 | Low | 8.83 × 10−6 | Low | |
| CA | Cd | 3.42 × 10−6 | Low | 1.59 × 10−6 | Low |
| Pb | 3.62 × 10−5 | Low | 1.68 × 10−5 | Low | |
| Co | 3.27 × 10−4 | High | 1.52 × 10−4 | High | |
| Cr | 6.03 × 10−3 | High | 2.80 × 10−3 | High | |
| Ni | 2.56 × 10−5 | Low | 1.19 × 10−5 | Low | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Silva, T.A.d.C.; Paula, M.d., Jr.; Silva, W.S.; Lacorte, G.A. Deposition of Potentially Toxic Metals in the Soil from Surrounding Cement Plants in a Karst Area of Southeastern Brazil. Conservation 2021, 1, 137-150. https://doi.org/10.3390/conservation1030012
Silva TAdC, Paula Md Jr., Silva WS, Lacorte GA. Deposition of Potentially Toxic Metals in the Soil from Surrounding Cement Plants in a Karst Area of Southeastern Brazil. Conservation. 2021; 1(3):137-150. https://doi.org/10.3390/conservation1030012
Chicago/Turabian StyleSilva, Thiago Augusto da Costa, Marcos de Paula, Jr., Washington Santos Silva, and Gustavo Augusto Lacorte. 2021. "Deposition of Potentially Toxic Metals in the Soil from Surrounding Cement Plants in a Karst Area of Southeastern Brazil" Conservation 1, no. 3: 137-150. https://doi.org/10.3390/conservation1030012
APA StyleSilva, T. A. d. C., Paula, M. d., Jr., Silva, W. S., & Lacorte, G. A. (2021). Deposition of Potentially Toxic Metals in the Soil from Surrounding Cement Plants in a Karst Area of Southeastern Brazil. Conservation, 1(3), 137-150. https://doi.org/10.3390/conservation1030012








