Re-Supplying Autonomous Mobile Parcel Lockers in Last-Mile Distribution
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. The Generalized Vehicle Routing Problem with Time Windows
2.2. The VRP with Multiple Time Windows
2.3. Mobile Parcel Lockers
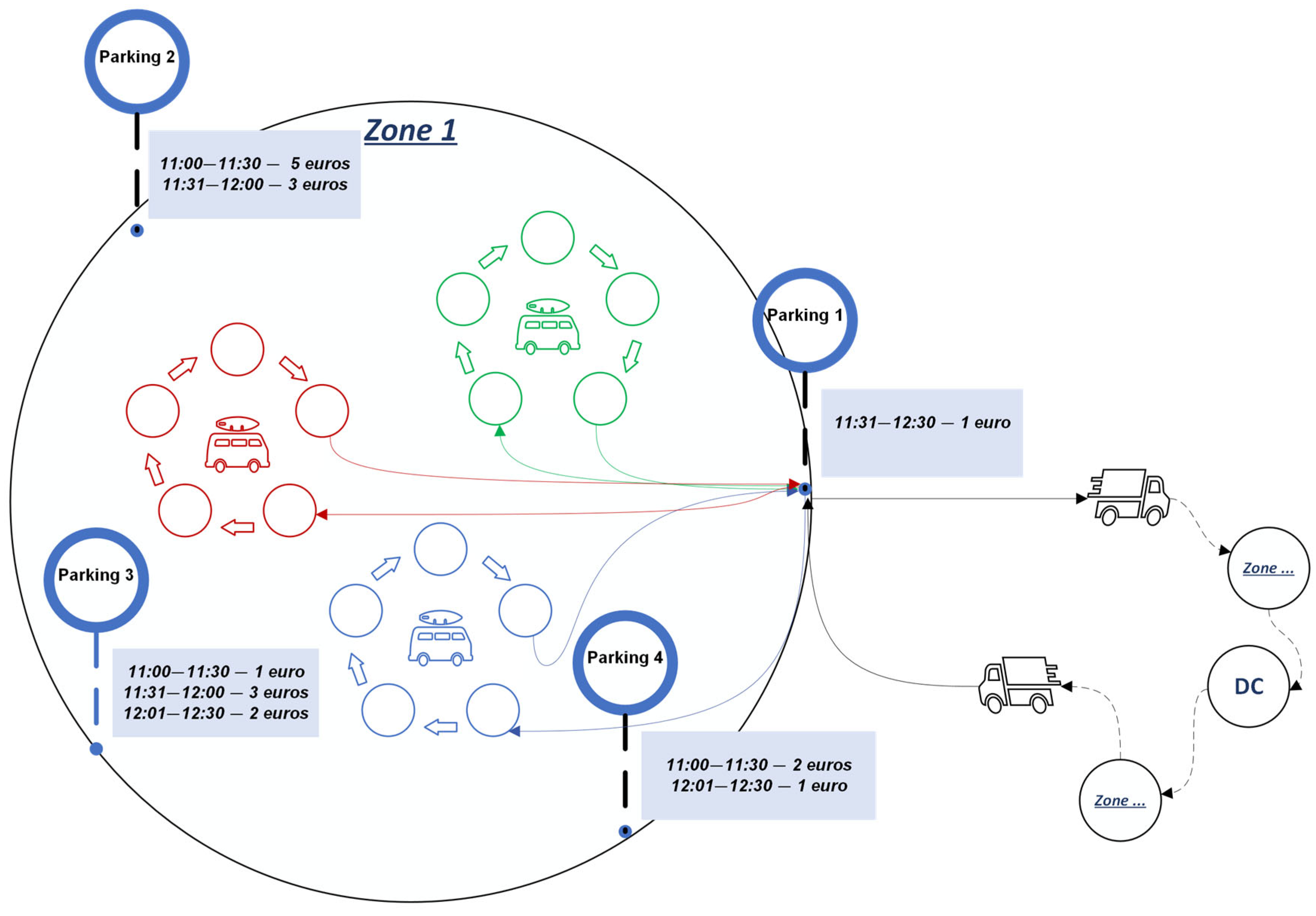
3. Problem Description
Mixed-Integer Linear Programming Model
4. The Solution Approach
4.1. Cost Functions
4.1.1. Total Traveling Cost Formula
4.1.2. Capacity Violation and Penalty Cost Formula
4.1.3. Time Window Violation and Its Penalty Cost Formula
4.1.4. Parking Slot Cost Formula
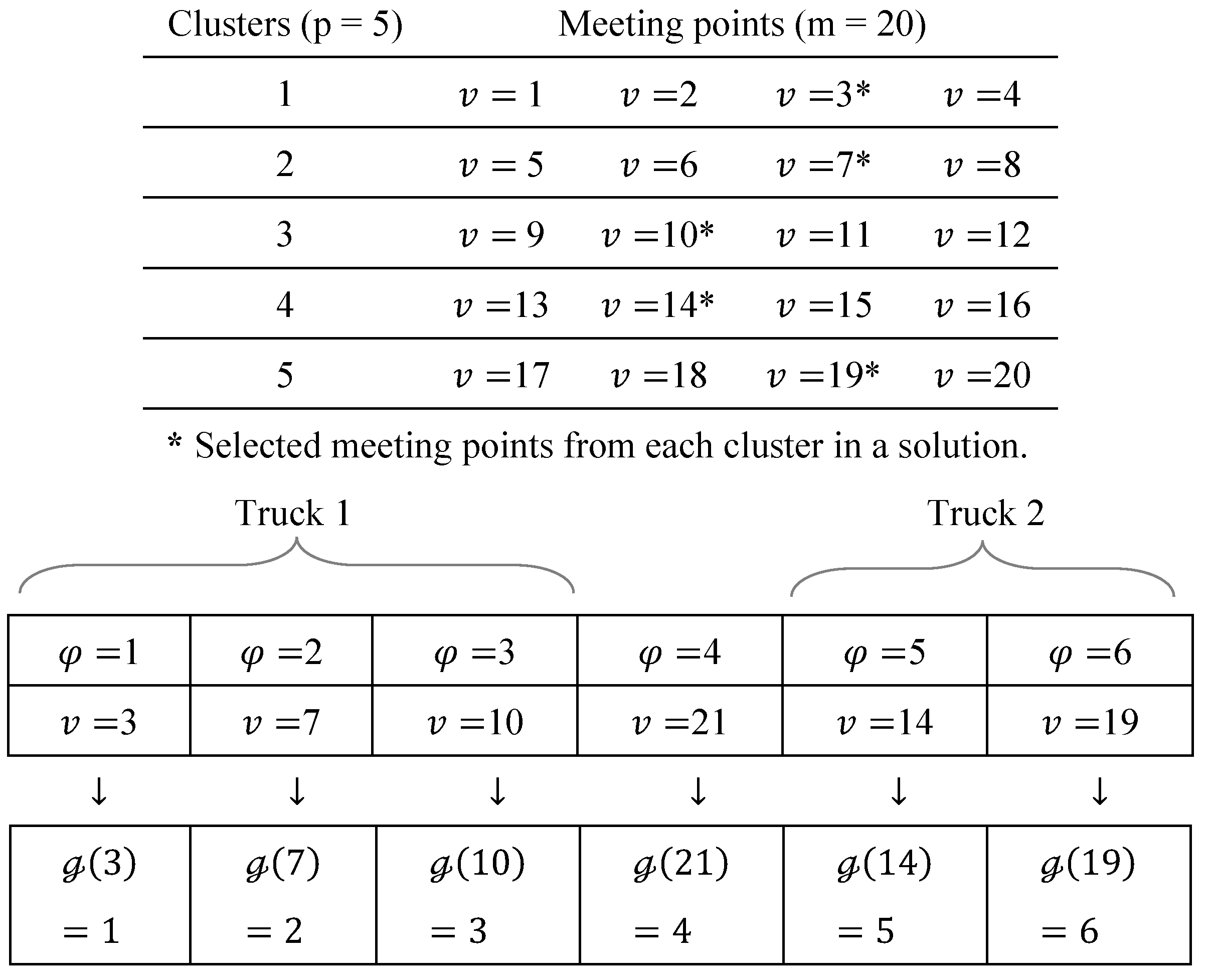
4.2. A Cluster-Based Simulated Annealing Algorithm
| Algorithm 1. The cluster-based simulated annealing algorithm (CSA) |
| //Initialization phase creates an initial solution (instance) by calling Algorithm 3; ωbest ← ω; calculate the fitness value (ω); F(ωbest) ← F(ω); T ← T0; Tf ← 0; //improvement phase for externaliteration = 1 to EImax do if T > Tf then for internaliteration = 1 to IImax do ωnew ←createnighborhoodsolutions(ω); F(ωnew) ← calculatethefitnessvalue(ωnew); if F(ωnew) <= F(ω) then ω ← ωnew; else Δ = T0 − Tf; η = e(Δ/T); if random(0,1) <= η then ω← ωnew; end end end end if F(ω) <= F(ωbest) then ωnew ← ω; end T = εT; end |
| Algorithm 2. Clustering algorithm. |
| Input: Nodes’ coordinates, nodes’ labels |
| Output: A set of H clusters, |
| Step 1: Call data to extract horizontal and vertical coordinates. |
| Step 2: Analyze the maximum number of distinct clusters by calling the silhouette method. |
| Step 3: Select p based on the silhouette method. |
| Step 4: Apply the K-means method for clustering. |
| Step 5: Print zones (clusters) with memberships. |
| Algorithm 3. Initial random solution algorithm. |
| Input: An instance Output: An initial solution, ω function create initial solution (instance) N ← Ninstance; p ← pinstance; k ← kinstance; |ω| ← p + k − 1; ω ← 0; for g = 1 to p do cluster(g) ← random_sampling(g,1); end ω ← [permutation([p+1:p+k−1],[cluster(g) from 1 to p])]; |
| Algorithm 4. Create neighborhoods algorithm. |
| Input: An initial solution, ω Output: A new solution, ωnew function create neighborhoods (ω) r ← random_integer_number[1, 6] switch r do case 1 do ωnew ←2_opt(ω); end case 2 do ωnew ← remove_insert1(ω); end case 3 do ωnew ← shake_cluster(ω); end case 4 do ωnew ← 3_opt(ω); end case 5 do ωnew ← remove_insert_2(ω); end case 6 do ωnew ←reverse(ω); end end |
5. Computational Experiments
5.1. Dataset and Strategy Definition
5.2. Performance Metrics and Parameters
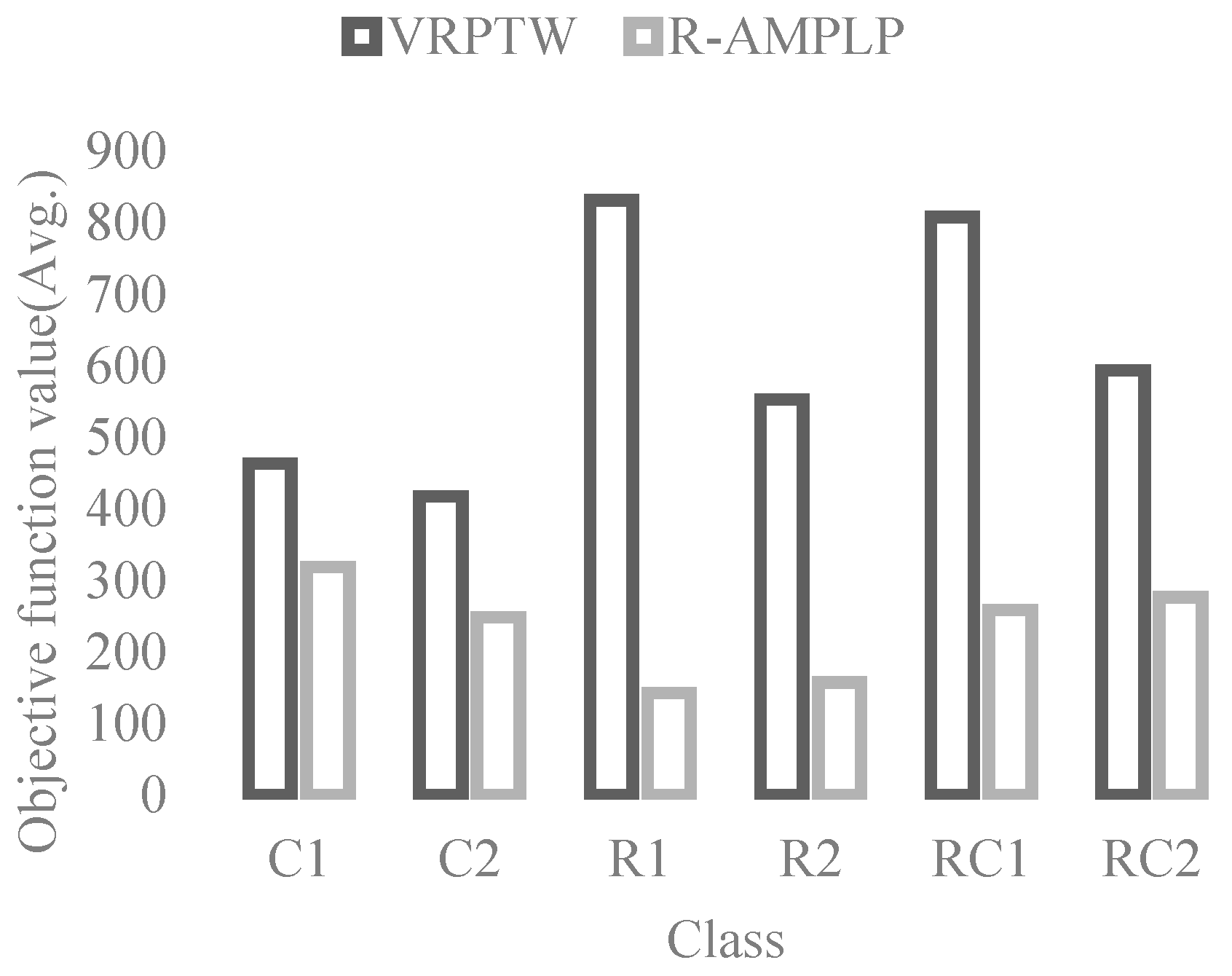
5.3. Results of the R-AMPLP and VRPTW
5.4. Comparison with CPLEX Solutions
5.5. Summary of Findings
5.6. Managarial Insights
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Algorithm A1. 2_opt algorithm. |
| Input: An initial solution, ω Output: A new solution, ωnew function 2_opt (ω) S ← |ω|; g(v) ← 0; g(u) ← 0; [list(1),list(2)] ← random sampling((1,S),2); g(v) ← list(1); g(u) ← list(2); update(ω) ← ω([g(u) g(v)]); ωnew ← ω; |

| Algorithm A2. remove_insert_1 algorithm. |
| Input: An initial solution, ω Output: A new solution, ωnew function remove_insert_1 (ω) S ← |ω|; g(v) ← 0; g(u) ← 0; [list(1),list(2)] ← random sampling((1,S),2); g(v) ← list(1); g(u) ← list(2); if g(v)<g(u) then update (ω) ← ω([[1:g(v)−1][g(v)+1:g(u)][g(v)][g(u)+1:|ω|])]); else update (ω) ← ω([[1:g(u)][g(v)][g(u)+1:g(v)−1][g(v)+1:|ω|])]); end ωnew ← ω; |
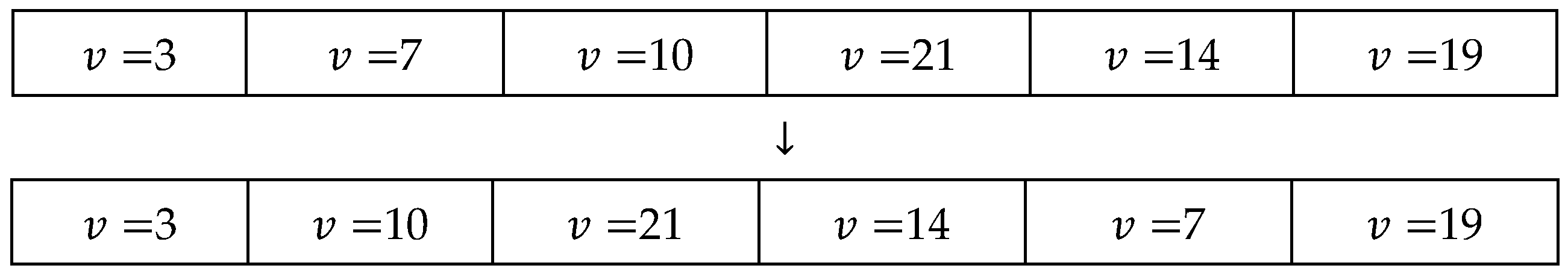
| Algorithm A3. shake_cluster algorithm. |
| Input: An initial solution, ω Output: A new solution, ωnew function shake-cluster (ω) S ← |ω|; L ← Linstance; C← Cinstance; for g(v) do if v\∈ L then update (ω) ← ω([random_sampling(g(g(v)).1)}); end end ωnew ← ω; |

| Algorithm A4. 3_opt algorithm. |
| Input: An initial solution, ω Output: A new solution, ωnew function 3_opt (ω) S ← |ω|; g(v) ← 0; g(u) ← 0; g(w) ← 0; [list(1),list(2),list(3)] ← random sampling((1,S),3); g(v) ← list(1); g(u) ← list(2); g(w) ← list(3); update (ω) ← ω([[g(u)] [g(w)] [g(v)]]); ωnew ← ω; |
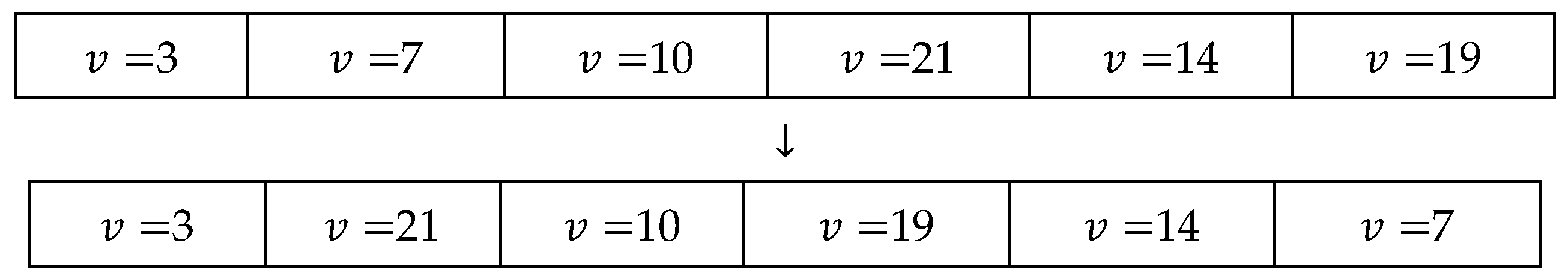
| Algorithm A5. remove_insert_2 algorithm. |
| Input: An initial solution, ω Output: A new solution, ωnew function remove_insert_2 (ω) S ← |ω|; g(v) ← 0; g(u) ← 0; [list(v)] ← random sampling((1,S),1); [list(u)] ← find dummy(ω,1); g(v) ← list(v); g(u) ←list(u); if g(v) < g(u) then update (ω)←ω([[1:g(v)−1][g(v)+1:g(u)[g(v)][g(u)+1:|ω|]]); else update (ω)←ω([[g(v)][ 1:g(u)[g(u)+1:g(v)+1][g(v)+1:|ω|]]); end ωnew ← ω; |

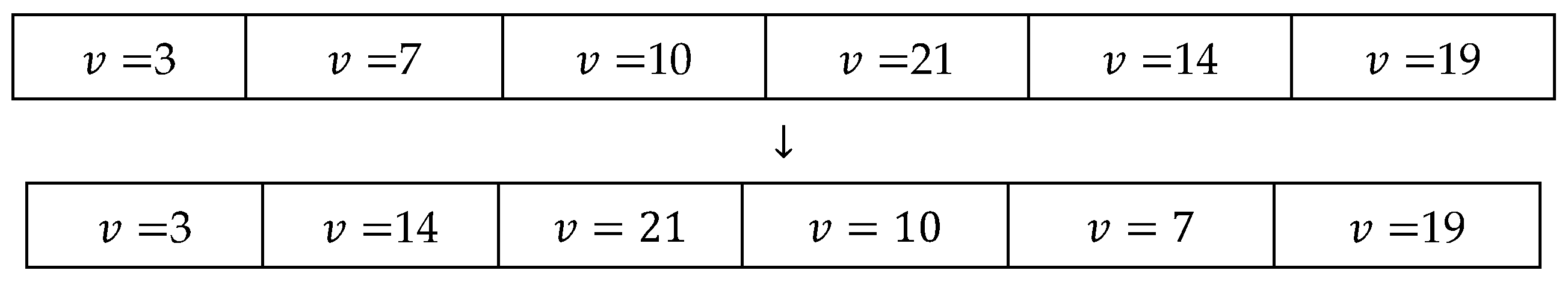
| Algorithm A6. reverse algorithm. |
| Input: An initial solution, ω Output: A new solution, ωnew function reverse (ω) S ← |ω|; g(v) ← 0; g(u) ← 0; g(w) ← 0; g(y) ← 0; [list(1),list(2)] ← random sampling((1,S),2); g(v) ← list(1); g(u) ← list(2); g(w) ← find min(g(v),g(u)); g(y) ← find max(g(v),g(u)); update (ω) ← ω(reverse([[g(y)] : [g(w)]])); ωnew ← ω; |
References
- Siegfried, P.; Zhang, J.J. Developing a Sustainable Concept for Urban Last-Mile Delivery. Open J. Bus. Manag. 2020, 9, 268–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, E.; Syntetos, A.; Van Woensel, T. Last mile logistics: Research trends and needs. IMA J. Manag. Math. 2022, 33, 549–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Q.; Fan, T.; Pan, F.; Zhang, C. A vehicle-UAV operation scheme for instant delivery. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2020, 149, 106809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alnaggar, A.; Gzara, F.; Bookbinder, J.H. Crowdsourced delivery: A review of platforms and academic literature. Omega 2021, 98, 102139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, D.; Savelsbergh, M.; Toriello, A. Vehicle routing with roaming delivery locations. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2017, 80, 71–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figliozzi, M.A. Carbon emissions reductions in last mile and grocery deliveries utilizing air and ground autonomous vehicles. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2020, 85, 102443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.H.; Wang, Y.; He, D.; Lee, L.H. Last-mile delivery: Optimal locker location under multinomial logit choice model. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2020, 142, 102059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Demir, E.; Huang, Y.; Qiu, R. The adoption of self-driving delivery robots in last mile logistics. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2021, 146, 102214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojas Viloria, D.; Solano-Charris, E.L.; Muñoz-Villamizar, A.; Montoya-Torres, J.R. Unmanned aerial vehicles/drones in vehicle routing problems: A literature review. Int. Trans. Oper. Res. 2021, 28, 1626–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savelsbergh, M.; Van Woensel, T. 50th anniversary invited article—City logistics: Challenges and opportunities. Transp. Sci. 2016, 50, 579–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwerdfeger, S.; Boysen, N. Optimizing the changing locations of mobile parcel lockers in last-mile distribution. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2020, 285, 1077–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwerdfeger, S.; Boysen, N. Who moves the locker? A benchmark study of alternative mobile parcel locker concepts. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2022, 142, 103780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boysen, N.; Fedtke, S.; Schwerdfeger, S. Last-mile delivery concepts: A survey from an operational research perspective. OR Spectr. 2021, 43, 1–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulmer, M.W.; Streng, S. Same-day delivery with pickup stations and autonomous vehicles. Comput. Oper. Res. 2019, 108, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desrochers, M.; Lenstra, J.K.; Savelsbergh, M.W.; Soumis, F. Vehicle Routing with Time Windows: Optimization and Approximation; (No. OS-R8715); CWI. Department of Operations Research and System Theory [BS]: Vancouver, BC, Canada, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Ghiani, G.; Improta, G. An efficient transformation of the generalized vehicle routing problem. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2000, 122, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedayati, S.; Setak, M.; Demir, E.; Van Woensel, T. A new approach to the joint order batching and picker routing problem with alternative locations. IMA J. Manag. Math. 2024, 35, 241–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moccia, L.; Cordeau, J.-F.; Laporte, G. An incremental tabu search heuristic for the generalized vehicle routing problem with time windows. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 2012, 63, 232–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozbaygin, G.; Karasan, O.E.; Savelsbergh, M.; Yaman, H. A branch-and-price algorithm for the vehicle routing problem with roaming delivery locations. Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 2017, 100, 115–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumez, D.; Lehuédé, F.; Péton, O. A large neighborhood search approach to the vehicle routing problem with delivery options. Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 2021, 144, 103–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilk, C.; Olkis, K.; Irnich, S. The last-mile vehicle routing problem with delivery options. OR Spectr. 2021, 43, 877–904. [Google Scholar]
- Lombard, A.; Tamayo-Giraldo, S.; Fontane, F. Vehicle routing problem with roaming delivery locations and stochastic travel times (VRPRDL-S). Transp. Res. Procedia 2018, 30, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favaretto, D.; Moretti, E.; Pellegrini, P. Ant colony system for a VRP with multiple time windows and multiple visits. J. Interdiscip. Math. 2007, 10, 263–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belhaiza, S.; Hansen, P.; Laporte, G. A hybrid variable neighborhood tabu search heuristic for the vehicle routing problem with multiple time windows. Comput. Oper. Res. 2014, 52, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belhaiza, S.; M’Hallah, R.; Brahim, G.B. A new hybrid genetic variable neighborhood search heuristic for the vehicle routing problem with multiple time windows. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC), San Sebastián, Spain, 5–8 June2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Beheshti, A.K.; Hejazi, S.R.; Alinaghian, M. The vehicle routing problem with multiple prioritized time windows: A case study. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2015, 90, 402–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoogeboom, M.; Dullaert, W.; Lai, D.; Vigo, D. Efficient neighborhood evaluations for the vehicle routing problem with multiple time windows. Transp. Sci. 2020, 54, 400–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Cattaruzza, D.; Ogier, M.; Rousselot, C.; Semet, F. Mixed integer programming formulations for the generalized traveling salesman problem with time windows. 4OR 2021, 19, 571–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, D.; Leung, S.C. A simulated annealing algorithm for the capacitated vehicle routing problem with two-dimensional loading constraints. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2018, 265, 843–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Mu, D.; Zhao, F.; Sutherland, J.W. A parallel simulated annealing method for the vehicle routing problem with simultaneous pickup–delivery and time windows. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2015, 83, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousseeuw, P.J. Silhouettes: A graphical aid to the interpretation and validation of cluster analysis. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 1987, 20, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, M.M. Algorithms for the vehicle routing and scheduling problems with time window constraints. Oper. Res. 1987, 35, 254–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilog. IBM ILOG CPLEX Optimization Studio [Online]. 2023. Available online: https://www.ibm.com/products/ilog-cplex-optimization-studio (accessed on 22 July 2024).


| Reference | Setting | GVRPTW | VRPMTW | MPLs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [11] | Alternative locations | * | * | |
| [24,25] | Alternative time windows | * | ||
| [11,20] | Sharing delivery locations | * | ||
| This paper | Alternative locations and alternative time windows | * | * | * |
| Reference | Model | Solution | Roaming/ GVRPTW | Multiple Time Windows | Parking Slot Fee | AMPL | Sharing Locations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [5] | IP a | GRASP d-VNS e | * | ||||
| [18] | - | TS f | * | ||||
| [21] | MIP b | GRASP | * | ||||
| [20] | MIP | LNS g | * | * | |||
| [21] | SP c | BPC h | * | * | |||
| This paper | MIP | CSA i | * | * | * | * |
| Notation | Description |
|---|---|
| Sets | |
| The set of nodes | |
| The set of meeting points | |
| The set of arcs | |
| The set of clusters corresponding to meeting points | |
| The complement set of clusters associated with AMPL paths | |
| The set of vehicles | |
| The depot | |
| Leaving point in cluster h | |
| Returning point in cluster h | |
| Parameters | |
| The traveling distance (cost) between meeting points and | |
| The demand of node | |
| The speed of vehicle | |
| The capacity of vehicle | |
| The earliest arriving time at a meeting point | |
| The latest arriving time at a meeting point | |
| The parking cost at a meeting point | |
| Decision variables | |
| The arrival time at a meeting point | |
| If the traveling path between node to node is traveled by a vehicle , it is equal to , and otherwise | |
| If the node in a cluster is visited by a vehicle , it is equal to , and otherwise |
| Class | Scenario | Strategy | ID | NTWs | Average of Solutions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | c101—c103 | 25nps | c101-c103:25nps | 75 | 3 | 20 | 60 | 3 | 83.48 |
| 50nps | c101-c103:50nps | 150 | 6 | 20 | 60 | 3 | 231.58 | ||
| 75nps | c101-c103:75nps | 225 | 9 | 20 | 60 | 3 | 466.84 | ||
| 100nps | c101-c103:100nps | 300 | 10 | 20 | 60 | 3 | 478.41 | ||
| c101—c106 | 25nps | c101-c106:25nps | 150 | 3 | 20 | 60 | 6 | 82.48 | |
| 50nps | c101-c106:50nps | 300 | 7 | 20 | 60 | 6 | 266.94 | ||
| 75nps | c101-c106:75nps | 450 | 10 | 20 | 60 | 6 | 495.03 | ||
| 100nps | c101-c106:100nps | 600 | 10 | 20 | 60 | 6 | 470.24 | ||
| c101—c109 | 25nps | c101-c109:25nps | 225 | 3 | 20 | 60 | 9 | 71.12 | |
| 50nps | c101-c109:50nps | 450 | 6 | 20 | 60 | 9 | 243.29 | ||
| 75nps | c101-c109:75nps | 675 | 8 | 20 | 60 | 9 | 446.26 | ||
| 100nps | c101-c109:100nps | 900 | 10 | 20 | 60 | 9 | 488.05 | ||
| Average | - | - | - | 375 | 8.5 | 20 | 60 | 6 | 318.64 |
| Dataset | Subset | Optimal (Benchmark) | CSA Solution | Gap% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | c101 | 25 | 25 | 191.3 | 191.81 | 0.27% |
| c101 | 50 | 50 | 362.4 | 363.24 | 0.23% | |
| c101 | 100 | 100 | 827.3 | 828.93 | 0.20% | |
| c102 | 25 | 25 | 190.3 | 190.73 | 0.23% | |
| c102 | 50 | 50 | 361.4 | 362.17 | 0.21% | |
| c102 | 100 | 100 | 827.3 | 828.93 | 0.20% | |
| c103 | 25 | 25 | 190.3 | 190.73 | 0.23% | |
| c103 | 50 | 50 | 361.4 | 362.17 | 0.21% | |
| c103 | 100 | 100 | 826.3 | 834.75 | 1.02% | |
| c104 | 25 | 25 | 186.9 | 187.45 | 0.29% | |
| c104 | 50 | 50 | 358 | 358.88 | 0.25% | |
| c104 | 100 | 100 | 822.9 | 834.94 | 1.46% | |
| c105 | 25 | 25 | 191.3 | 191.81 | 0.27% | |
| c105 | 50 | 50 | 362.4 | 363.24 | 0.23% | |
| c105 | 100 | 100 | 827.3 | 828.93 | 0.20% | |
| c106 | 25 | 25 | 191.3 | 191.81 | 0.27% | |
| c106 | 50 | 50 | 362.4 | 363.24 | 0.23% | |
| c106 | 100 | 100 | 827.3 | 828.93 | 0.20% | |
| c107 | 25 | 25 | 191.3 | 191.81 | 0.27% | |
| c107 | 50 | 50 | 362.4 | 363.24 | 0.23% | |
| c107 | 100 | 100 | 827.3 | 828.93 | 0.20% | |
| c108 | 25 | 25 | 191.3 | 191.81 | 0.27% | |
| c108 | 50 | 50 | 362.4 | 363.24 | 0.23% | |
| c108 | 100 | 100 | 827.3 | 828.94 | 0.20% | |
| c109 | 25 | 25 | 191.3 | 191.81 | 0.27% | |
| c109 | 50 | 50 | 362.4 | 363.92 | 0.42% | |
| c109 | 100 | 100 | 827.3 | 828.94 | 0.20% | |
| Average | 459.65 | 463.45 | 0.36% |
| Class | Scenario | Strategy | ID | NTWs | Average of Solutions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C2 | c201—c203 | 25nps | c201-c203:25nps | 75 | 8 | 20 | 60 | 3 | 173.50 |
| 50nps | c201-c203:50nps | 150 | 9 | 20 | 60 | 3 | 213.34 | ||
| 75nps | c201-c203:75nps | 225 | 10 | 20 | 60 | 3 | 373.65 | ||
| 100nps | c201-c203:100nps | 300 | 8 | 20 | 60 | 3 | 294.02 | ||
| c201—c206 | 25nps | c201-c206:25nps | 150 | 9 | 20 | 60 | 6 | 224.05 | |
| 50nps | c201-c206:50nps | 300 | 5 | 20 | 60 | 6 | 145.77 | ||
| 75nps | c201-c206:75nps | 450 | 8 | 20 | 60 | 6 | 221.37 | ||
| 100nps | c201-c206:100nps | 600 | 10 | 20 | 60 | 6 | 341.01 | ||
| c201—c208 | 25nps | c201-c208:25nps | 200 | 10 | 20 | 60 | 8 | 266.68 | |
| 50nps | c201-c208:50nps | 400 | 7 | 20 | 60 | 8 | 204.00 | ||
| 75nps | c201-c208:75nps | 600 | 10 | 20 | 60 | 8 | 306.95 | ||
| 100nps | c201-c208:100nps | 800 | 7 | 20 | 60 | 8 | 216.77 | ||
| Average | - | - | - | 354.16 | 8.41 | 20 | 60 | 5.66 | 248.42 |
| Dataset | Subset | Optimal (Benchmark) | CSA Solution | Gap% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C2 | c201 | 25 | 25 | 214.7 | 215.54 | 0.39% |
| c201 | 50 | 50 | 360.2 | 361.79 | 0.44% | |
| c201 | 100 | 100 | 589.1 | 673.16 | 14.27% | |
| c202 | 25 | 25 | 214.7 | 215.54 | 0.39% | |
| c202 | 50 | 50 | 360.2 | 395.81 | 9.89% | |
| c202 | 100 | 100 | 589.1 | 674.29 | 14.46% | |
| c203 | 25 | 25 | 214.7 | 215.54 | 0.39% | |
| c203 | 50 | 50 | 359.8 | 393.98 | 9.50% | |
| c203 | 100 | 100 | 588.7 | 674.95 | 14.65% | |
| c204 | 25 | 25 | 213.1 | 215.54 | 1.15% | |
| c204 | 50 | 50 | 350.1 | 393.37 | 12.36% | |
| c204 | 100 | 100 | 588.1 | 640.59 | 8.93% | |
| c205 | 25 | 25 | 214.7 | 215.54 | 0.39% | |
| c205 | 50 | 50 | 359.8 | 364.75 | 1.38% | |
| c205 | 100 | 100 | 586.4 | 652.41 | 11.26% | |
| c206 | 25 | 25 | 214.7 | 215.54 | 0.39% | |
| c206 | 50 | 50 | 359.8 | 361.41 | 0.45% | |
| c206 | 100 | 100 | 586 | 642.57 | 9.65% | |
| c207 | 25 | 25 | 214.5 | 215.54 | 0.48% | |
| c207 | 50 | 50 | 359.6 | 402.32 | 11.88% | |
| c207 | 100 | 100 | 585.5 | 675.75 | 15.41% | |
| c208 | 25 | 25 | 214.5 | 215.54 | 0.48% | |
| c208 | 50 | 50 | 350.5 | 352.12 | 0.46% | |
| c208 | 100 | 100 | 585.5 | 637.07 | 8.81% | |
| Average | - | - | - | 386.41 | 417.53 | 8.05% |
| Class | Scenario | Strategy | ID | NTWs | Average of Solutions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | r101–r103 | 25nps | r101-r103:25nps | 75 | 10 | 20 | 60 | 3 | 276.05 |
| 50nps | r101-r103:50nps | 150 | 4 | 20 | 60 | 3 | 88.46 | ||
| 75nps | r101-r103:75nps | 225 | 5 | 20 | 60 | 3 | 102.31 | ||
| 100nps | r101-r103:100nps | 300 | 4 | 20 | 60 | 3 | 78.92 | ||
| r101–r106 | 25nps | r101-r106:25nps | 150 | 9 | 20 | 60 | 6 | 253.62 | |
| 50nps | r101-r106:50nps | 300 | 10 | 20 | 60 | 6 | 264.91 | ||
| 75nps | r101-r106:75nps | 450 | 4 | 20 | 60 | 6 | 78.84 | ||
| 100nps | r101-r106:100nps | 600 | 4 | 20 | 60 | 6 | 78.81 | ||
| r101–r109 | 25nps | r101-r109:25nps | 225 | 9 | 20 | 60 | 9 | 284.7 | |
| 50nps | r101-r109:50nps | 450 | 8 | 20 | 60 | 9 | 240.79 | ||
| 75nps | r101-r109:75nps | 675 | 4 | 20 | 60 | 9 | 76.25 | ||
| 100nps | r101-r109:100nps | 900 | 4 | 20 | 60 | 9 | 65.59 | ||
| r101–r112 | 25nps | r101-r112:25nps | 300 | 8 | 20 | 60 | 12 | 207.54 | |
| 50nps | r101-r112:50nps | 600 | 4 | 20 | 60 | 12 | 77.25 | ||
| 75nps | r101-r112:75nps | 900 | 3 | 20 | 60 | 12 | 34.26 | ||
| 100nps | r101-r12:100nps | 1200 | 4 | 20 | 60 | 12 | 68.69 | ||
| Average | - | - | - | 468.75 | 5.87 | 20 | 60 | 7.5 | 142.31 |
| Dataset | Subset | Optimal (Benchmark) | CSA Solution | Gap% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | r101 | 25 | 25 | 617.1 | 627.13 | 1.63% |
| r101 | 50 | 50 | 1044 | 1065.9 | 2.10% | |
| r101 | 100 | 100 | 1637.7 | 1699.34 | 3.76% | |
| r102 | 25 | 25 | 547.1 | 550.20 | 0.57% | |
| r102 | 50 | 50 | 909 | 923.22 | 1.56% | |
| r102 | 100 | 100 | 1466.6 | 1523.34 | 3.87% | |
| r103 | 25 | 25 | 454.6 | 464.82 | 2.25% | |
| r103 | 50 | 50 | 772.9 | 813.05 | 5.19% | |
| r103 | 100 | 100 | 1208.7 | 1289.84 | 6.71% | |
| r104 | 25 | 25 | 416.9 | 437.08 | 4.84% | |
| r104 | 50 | 50 | 625.4 | 644.07 | 2.99% | |
| r104 | 100 | 100 | 971.5 | 1043.67 | 7.43% | |
| r105 | 25 | 25 | 530.5 | 531.53 | 0.19% | |
| r105 | 50 | 50 | 899.3 | 948.36 | 5.46% | |
| r105 | 100 | 100 | 1355.3 | 1462.89 | 7.94% | |
| r106 | 25 | 25 | 465.4 | 466.48 | 0.23% | |
| r106 | 50 | 50 | 793 | 830.78 | 4.76% | |
| r106 | 100 | 100 | 1234.6 | 1299.89 | 5.29% | |
| r107 | 25 | 25 | 424.3 | 437.67 | 3.15% | |
| r107 | 50 | 50 | 711.1 | 746.12 | 4.92% | |
| r107 | 100 | 100 | 1064.6 | 1127.83 | 5.94% | |
| r108 | 25 | 25 | 379.3 | 398.29 | 5.01% | |
| r108 | 50 | 50 | 617.87 | 630.53 | 2.05% | |
| r108 | 100 | 100 | - | 1001.17 | - | |
| r109 | 25 | 25 | 441.3 | 442.62 | 0.30% | |
| r109 | 50 | 50 | 786.8 | 819.21 | 4.12% | |
| r109 | 100 | 100 | 1146.9 | 1211.66 | 5.65% | |
| r110 | 25 | 25 | 444.1 | 447.47 | 0.76% | |
| r110 | 50 | 50 | 697 | 735.05 | 5.46% | |
| r110 | 100 | 100 | 1068 | 1150.07 | 7.68% | |
| r111 | 25 | 25 | 428.8 | 440.04 | 2.62% | |
| r111 | 50 | 50 | 707.2 | 740.56 | 4.72% | |
| r111 | 100 | 100 | 1048.7 | 1101.81 | 5.06% | |
| r112 | 25 | 25 | 393 | 413.44 | 5.20% | |
| r112 | 50 | 50 | 630.2 | 646.85 | 2.64% | |
| r112 | 100 | 100 | - | 999.19 | - | |
| Average | - | - | - | 792.31 * | 831.71 * | 4.97% |
| Class | Scenario | Strategy | ID | NTWs | Average of Solutions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | r201—r203 | 25nps | r201-r203:25nps | 75 | 10 | 20 | 60 | 3 | 271.9 |
| 50nps | r201-r203:50nps | 150 | 4 | 20 | 60 | 3 | 85.06 | ||
| 75nps | r201-r203:75nps | 225 | 5 | 20 | 60 | 3 | 100.42 | ||
| 100nps | r201-r203:100nps | 300 | 4 | 20 | 60 | 3 | 84.01 | ||
| r201—r206 | 25nps | r201-r206:25nps | 150 | 9 | 20 | 60 | 6 | 287.70 | |
| 50nps | r201-r206:50nps | 300 | 10 | 20 | 60 | 6 | 247.64 | ||
| 75nps | r201-r206:75nps | 450 | 4 | 20 | 60 | 6 | 79.52 | ||
| 100nps | r201-r206:100nps | 600 | 4 | 20 | 60 | 6 | 77.36 | ||
| r201—r209 | 25nps | r201-r209:25nps | 225 | 9 | 20 | 60 | 9 | 285.15 | |
| 50nps | r201-r209:50nps | 450 | 8 | 20 | 60 | 9 | 232.81 | ||
| 75nps | r201-r209:75nps | 675 | 4 | 20 | 60 | 9 | 81.04 | ||
| 100nps | r201-r209:100nps | 900 | 4 | 20 | 60 | 9 | 70.90 | ||
| r201—r211 | 25nps | r201-r211:25nps | 275 | 8 | 20 | 60 | 11 | 225.76 | |
| 50nps | r201-r211:50nps | 550 | 9 | 20 | 60 | 11 | 280.85 | ||
| 75nps | r201-r211:75nps | 825 | 3 | 20 | 60 | 11 | 34.30 | ||
| 100nps | r201-r211:100nps | 1100 | 4 | 20 | 60 | 11 | 72.23 | ||
| Average | - | - | - | 453.12 | 6.18 | 20 | 60 | 7.25 | 157.29 |
| Dataset | Subset | Optimal (Benchmark) | CSA Solution | Gap% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | r201 | 25 | 25 | 463.3 | 475.51 | 2.64% |
| r201 | 50 | 50 | 791.9 | 836.80 | 5.67% | |
| r201 | 100 | 100 | 1143.2 | 1271.95 | 11.26% | |
| r202 | 25 | 25 | 410.5 | 421.28 | 2.63% | |
| r202 | 50 | 50 | 698.5 | 765.80 | 9.63% | |
| r202 | 100 | 100 | - | 1265.5 | - | |
| r203 | 25 | 25 | 391.4 | 399.67 | 2.11% | |
| r203 | 50 | 50 | 605.3 | 618.98 | 2.26% | |
| r203 | 100 | 100 | - | 977.39 | - | |
| r204 | 25 | 25 | 355 | 358.57 | 1.01% | |
| r204 | 50 | 50 | 506.4 | 530.84 | 4.83% | |
| r204 | 100 | 100 | - | 824.16 | - | |
| r205 | 25 | 25 | 393 | 407.00 | 3.56% | |
| r205 | 50 | 50 | 690.1 | 723.90 | 4.90% | |
| r205 | 100 | 100 | - | 1074.42 | - | |
| r206 | 25 | 25 | 324.0 | 325.10 | 0.34% | |
| r206 | 50 | 50 | 632.4 | 692.00 | 9.42% | |
| r206 | 100 | 100 | - | 970.02 | - | |
| r207 | 25 | 25 | 361.6 | 392.32 | 8.50% | |
| r207 | 50 | 50 | - | 583.01 | - | |
| r207 | 100 | 100 | - | 914.83 | - | |
| r208 | 25 | 25 | 328.2 | 331.79 | 1.09% | |
| r208 | 50 | 50 | - | 510.88 | - | |
| r208 | 100 | 100 | - | 778.72 | - | |
| r209 | 25 | 25 | 370.7 | 399.21 | 7.69% | |
| r209 | 50 | 50 | 600.6 | 619.53 | 3.15% | |
| r209 | 100 | 100 | - | 954.34 | - | |
| r210 | 25 | 25 | 404.6 | 431.10 | 6.55% | |
| r210 | 50 | 50 | 645.6 | 679.01 | 5.18% | |
| r210 | 100 | 100 | - | 959.19 | - | |
| r211 | 25 | 25 | 350.9 | 351.9 | 0.28% | |
| r211 | 50 | 50 | 535.5 | 581.60 | 8.61% | |
| r211 | 100 | 100 | - | 817.02 | - | |
| Average | - | - | - | 526.33 * | 553.04 * | 5.07% * |
| Class | Scenario | Strategy | ID | NTWs | Average of Solutions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RC1 | rc101—rc103 | 25nps | rc101-rc103:25nps | 75 | 4 | 20 | 60 | 3 | 187.33 |
| 50nps | rc101-rc103:50nps | 150 | 5 | 20 | 60 | 3 | 235.24 | ||
| 75nps | rc101-rc103:75nps | 225 | 8 | 20 | 60 | 3 | 278.85 | ||
| 100nps | rc101-rc103:100nps | 300 | 10 | 20 | 60 | 3 | 350.11 | ||
| rc101—rc106 | 25nps | rc101-rc106:25nps | 150 | 3 | 20 | 60 | 6 | 124.08 | |
| 50nps | rc101-rc106:50nps | 300 | 4 | 20 | 60 | 6 | 201.48 | ||
| 75nps | rc101-rc106:75nps | 450 | 9 | 20 | 60 | 6 | 288.80 | ||
| 100nps | rc101-rc106:100nps | 600 | 10 | 20 | 60 | 6 | 316.13 | ||
| rc101—rc108 | 25nps | rc101-rc108:25nps | 200 | 7 | 20 | 60 | 8 | 235.24 | |
| 50nps | rc101-rc108:50nps | 400 | 5 | 20 | 60 | 8 | 255.85 | ||
| 75nps | rc101-rc108:75nps | 600 | 9 | 20 | 60 | 8 | 347.09 | ||
| 100nps | rc101-rc108:100nps | 800 | 9 | 20 | 60 | 8 | 284.67 | ||
| Average | - | - | - | 354.16 | 6.91 | 20 | 60 | 5.66 | 258.74 |
| Dataset | Subset | Optimal (Benchmark) | CSA Solution | Gap% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RC1 | rc101 | 25 | 25 | 461.1 | 464.57 | 0.75% |
| rc101 | 50 | 50 | 944 | 968.80 | 2.63% | |
| rc101 | 100 | 100 | 1619.8 | 1721.18 | 6.26% | |
| rc102 | 25 | 25 | 351.8 | 352.74 | 0.27% | |
| rc102 | 50 | 50 | 822.5 | 890.26 | 8.24% | |
| rc102 | 100 | 100 | 1457.4 | 1539.48 | 5.63% | |
| rc103 | 25 | 25 | 332.8 | 333.91 | 0.33% | |
| rc103 | 50 | 50 | 710.9 | 753.52 | 6.00% | |
| rc103 | 100 | 100 | 1258 | 1391.77 | 10.63% | |
| rc104 | 25 | 25 | 306.6 | 307.14 | 0.18% | |
| rc104 | 50 | 50 | 545.8 | 546.51 | 0.13% | |
| rc104 | 100 | 100 | - | 1191.07 | - | |
| rc105 | 25 | 25 | 411.3 | 434.29 | 5.59% | |
| rc105 | 50 | 50 | 855.3 | 894.08 | 4.53% | |
| rc105 | 100 | 100 | 1513.7 | 1649.14 | 8.95% | |
| rc106 | 25 | 25 | 345.5 | 347.26 | 0.51% | |
| rc106 | 50 | 50 | 723.2 | 814.49 | 12.62% | |
| rc106 | 100 | 100 | - | 1475.35 | - | |
| rc107 | 25 | 25 | 298.3 | 298.95 | 0.22% | |
| rc107 | 50 | 50 | 642.7 | 671.77 | 4.52% | |
| rc107 | 100 | 100 | 1207.8 | 1278.37 | 5.84% | |
| rc108 | 25 | 25 | 294.5 | 295.74 | 0.42% | |
| rc108 | 50 | 50 | 598.1 | 599.17 | 0.18% | |
| rc108 | 100 | 100 | 1114.2 | 1217.62 | 9.28% | |
| Average | - | - | - | 764.33 * | 807.76 * | 5.68% * |
| Class | Scenario | Strategy | ID | NTWs | Average of Solutions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RC2 | rc201—rc203 | 25nps | rc201-rc203:25nps | 75 | 4 | 20 | 60 | 3 | 187.33 |
| 50nps | rc201-rc203:50nps | 150 | 5 | 20 | 60 | 3 | 238.58 | ||
| 75nps | rc201-rc203:75nps | 225 | 8 | 20 | 60 | 3 | 297.67 | ||
| 100nps | rc201-rc203:100nps | 300 | 10 | 20 | 60 | 3 | 357.66 | ||
| rc201—rc206 | 25nps | rc201-rc206:25nps | 150 | 3 | 20 | 60 | 6 | 143.4 | |
| 50nps | rc201-rc206:50nps | 300 | 4 | 20 | 60 | 6 | 209.03 | ||
| 75nps | rc201-rc206:75nps | 450 | 9 | 20 | 60 | 6 | 313.10 | ||
| 100nps | rc201-rc206:100nps | 600 | 10 | 20 | 60 | 6 | 347.58 | ||
| rc201—rc208 | 25nps | rc201-rc208:25nps | 200 | 7 | 20 | 60 | 8 | 240.23 | |
| 50nps | rc201-rc208:50nps | 400 | 5 | 20 | 60 | 8 | 250.89 | ||
| 75nps | rc201-rc208:75nps | 600 | 9 | 20 | 60 | 8 | 359.58 | ||
| 100nps | rc201-rc208:100nps | 800 | 9 | 20 | 60 | 8 | 369.96 | ||
| Average | - | - | - | 354.16 | 6.91 | 20 | 60 | 5.66 | 276.25 |
| Class | Subset | Optimal (Benchmark) | CSA Solution | Gap% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RC2 | rc201 | 25 | 25 | 360.2 | 361.24 | 0.29% * |
| rc201 | 50 | 50 | 684.8 | 686.31 | 0.22% | |
| rc201 | 100 | 100 | 1261.8 | 1395.70 | 10.61% | |
| rc202 | 25 | 25 | 338 | 338.82 | 0.24% | |
| rc202 | 50 | 50 | 613.6 | 665.53 | 8.46% | |
| rc202 | 100 | 100 | 1092.3 | 1233.72 | 12.95% | |
| rc203 | 25 | 25 | 326.9 | 328.44 | 0.47% | |
| rc203 | 50 | 50 | 555.3 | 625.60 | 12.66% | |
| rc203 | 100 | 100 | - | 1082.26 | - | |
| rc204 | 25 | 25 | 299.7 | 315.95 | 5.42% | |
| rc204 | 50 | 50 | 444.2 | 462.98 | 4.23% | |
| rc204 | 100 | 100 | - | 847.32 | - | |
| rc205 | 25 | 25 | 338 | 338.93 | 0.28% | |
| rc205 | 50 | 50 | 630.2 | 631.98 | 0.28% | |
| rc205 | 100 | 100 | 1154 | 1241.2 | 7.56% | |
| rc206 | 25 | 25 | 324 | 325.10 | 0.34% | |
| rc206 | 50 | 50 | 610 | 611.75 | 0.29% | |
| rc206 | 100 | 100 | - | 1190.45 | - | |
| rc207 | 25 | 25 | 298.3 | 298.95 | 0.22% | |
| rc207 | 50 | 50 | 558.6 | 561.42 | 0.50% | |
| rc207 | 100 | 100 | - | 1081.70 | - | |
| rc208 | 25 | 25 | 269.1 | 269.56 | 0.17% | |
| rc208 | 50 | 50 | - | 491.46 | - | |
| rc208 | 100 | 100 | - | 810.35 | - | |
| Average | - | - | - | 564.38 * | 594.06 * | 5.26% * |
| Class | Scenario | Strategy | ID | NTWs | MIP Solution | CSA Solution | Gap% | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | c101-c103 | 25nps | c101-c103:25nps | 75 | 3 | 20 | 60 | 3 | 83.48 | 83.48 | 0.00% |
| C1 | c101-c106 | 25nps | c101-c106:25nps | 150 | 3 | 20 | 60 | 6 | 82.48 | 82.48 | 0.00% |
| C1 | c101-c109 | 25nps | c101-c109:25nps | 225 | 3 | 20 | 60 | 9 | 71.12 | 71.12 | 0.00% |
| C2 | c201-c203 | 25nps | c201-c203:25nps | 75 | 8 | 20 | 60 | 3 | 172.81 | 173.5 | 0.40% |
| C2 | c201-c206 | 25nps | c201-c206:25nps | 150 | 9 | 20 | 60 | 6 | 199.38 | 214.39 | 7.53% |
| C2 | c201-c208 | 25nps | c201-c208:25nps | 200 | 10 | 20 | 60 | 8 | 236.03 | 243.67 | 3.24% |
| R1 | r101-r103 | 25nps | r101-r103:25nps | 75 | 10 | 20 | 60 | 3 | 242.32 | 246.33 | 1.65% |
| R1 | r101-r106 | 25nps | r101-r106:25nps | 150 | 9 | 20 | 60 | 6 | 207.00 | 234.7 | 13.38% |
| R1 | r101-r109 | 25nps | r101-r109:25nps | 225 | 9 | 20 | 60 | 9 | 238.70 | 257.61 | 7.92% |
| R1 | r101-r112 | 25nps | r101-r112:25nps | 300 | 8 | 20 | 60 | 12 | 197.00 | 207.54 | 5.35% |
| R2 | r201-r203 | 25nps | r201-r203:25nps | 75 | 10 | 20 | 60 | 3 | 244.32 | 264.52 | 8.27% |
| R2 | r201-r206 | 25nps | r201-r206:25nps | 150 | 9 | 20 | 60 | 6 | 209.32 | 233.73 | 11.66% |
| R2 | r201-r209 | 25nps | r201-r209:25nps | 225 | 9 | 20 | 60 | 9 | 234.34 | 250.73 | 6.99% |
| R2 | r201-r211 | 25nps | r201-r211:25nps | 275 | 8 | 20 | 60 | 11 | 198.63 | 209 | 5.22% |
| RC1 | rc101-rc103 | 25nps | rc101-rc103:25nps | 75 | 4 | 20 | 60 | 3 | 187.33 | 187.33 | 0.00% |
| RC1 | rc101-rc106 | 25nps | rc101-rc106:25nps | 150 | 3 | 20 | 60 | 6 | 124.08 | 124.08 | 0.00% |
| RC1 | rc101-rc108 | 25nps | rc101-rc108:25nps | 200 | 7 | 20 | 60 | 8 | 231.23 | 235.24 | 1.73% |
| RC2 | rc201-rc203 | 25nps | rc201-rc203:25nps | 75 | 4 | 20 | 60 | 3 | 187.33 | 187.33 | 0.00% |
| RC2 | rc201-rc206 | 25nps | rc201-rc206:25nps | 150 | 3 | 20 | 60 | 6 | 143.39 | 143.39 | 0.00% |
| RC2 | rc201-rc208 | 25nps | rc201-rc208:25nps | 200 | 7 | 20 | 60 | 8 | 231.23 | 240.23 | 3.89% |
| Average | 186.07 | 194.52 | 4.54% | ||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hedayati, S.; Setak, M.; Van Woensel, T.; Demir, E. Re-Supplying Autonomous Mobile Parcel Lockers in Last-Mile Distribution. Future Transp. 2024, 4, 1266-1296. https://doi.org/10.3390/futuretransp4040061
Hedayati S, Setak M, Van Woensel T, Demir E. Re-Supplying Autonomous Mobile Parcel Lockers in Last-Mile Distribution. Future Transportation. 2024; 4(4):1266-1296. https://doi.org/10.3390/futuretransp4040061
Chicago/Turabian StyleHedayati, Sajjad, Mostafa Setak, Tom Van Woensel, and Emrah Demir. 2024. "Re-Supplying Autonomous Mobile Parcel Lockers in Last-Mile Distribution" Future Transportation 4, no. 4: 1266-1296. https://doi.org/10.3390/futuretransp4040061
APA StyleHedayati, S., Setak, M., Van Woensel, T., & Demir, E. (2024). Re-Supplying Autonomous Mobile Parcel Lockers in Last-Mile Distribution. Future Transportation, 4(4), 1266-1296. https://doi.org/10.3390/futuretransp4040061








