Influence of the Chromium Content on the Characteristics of the Matrix, the Tantalum Carbides Population, and the Hardness of Cast Co(Cr)-0.4C-6Ta Alloys
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design of the Alloys for the Study
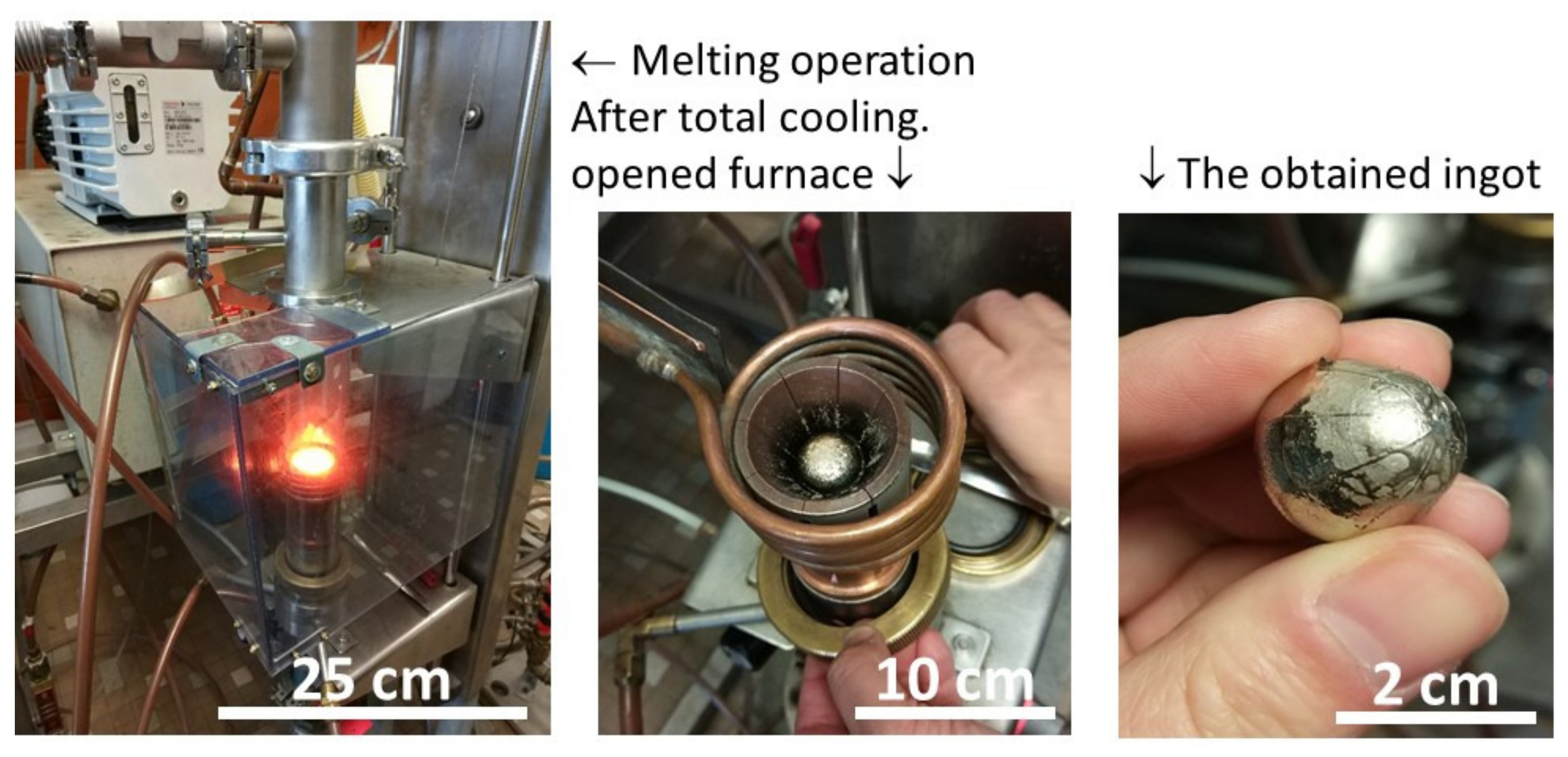
2.2. Elaboration Details
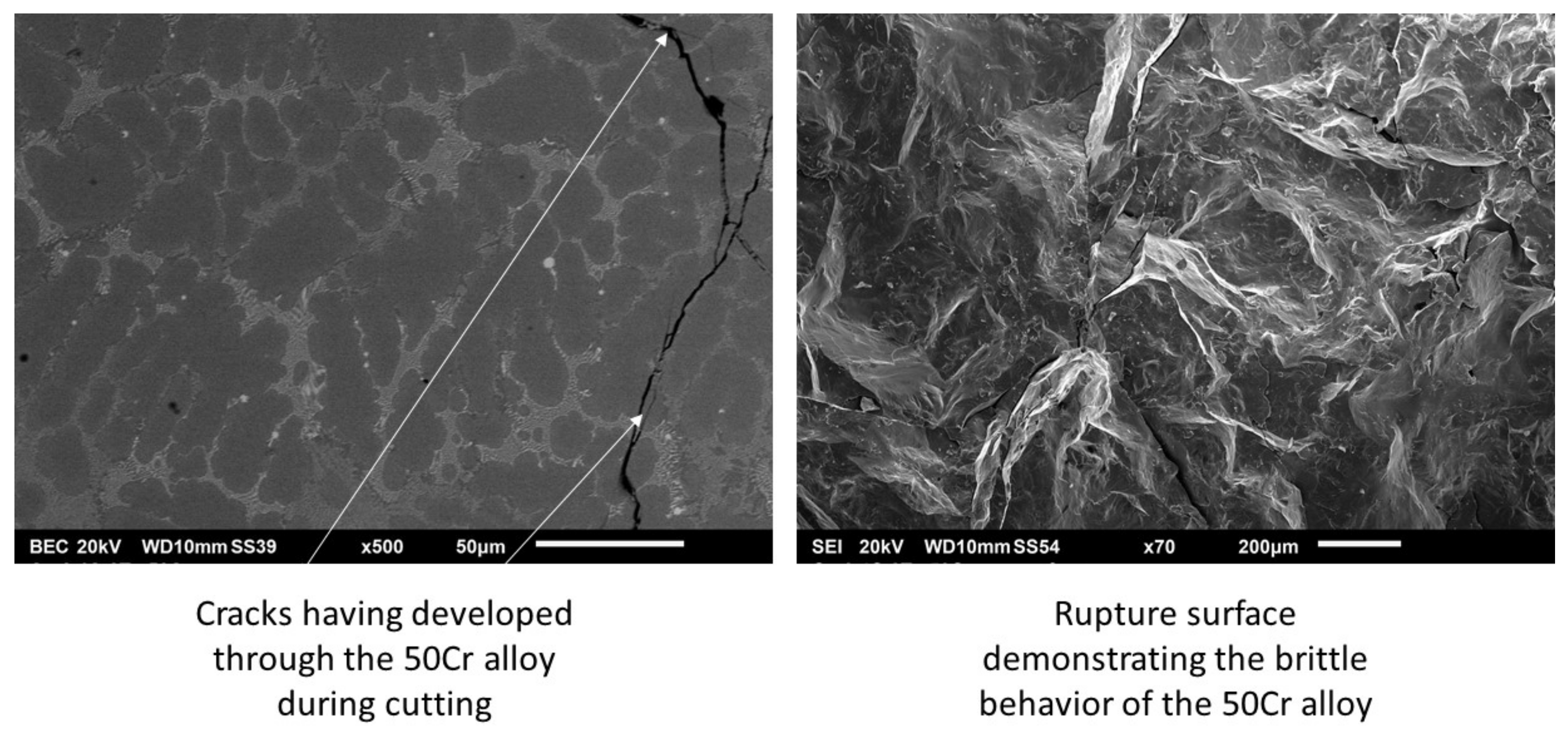
2.3. Sample Preparation, Exposure to High Temperatures, and Metallographic Characterization and Indentation
2.4. Thermodynamic Calculations
3. Results and Discussion
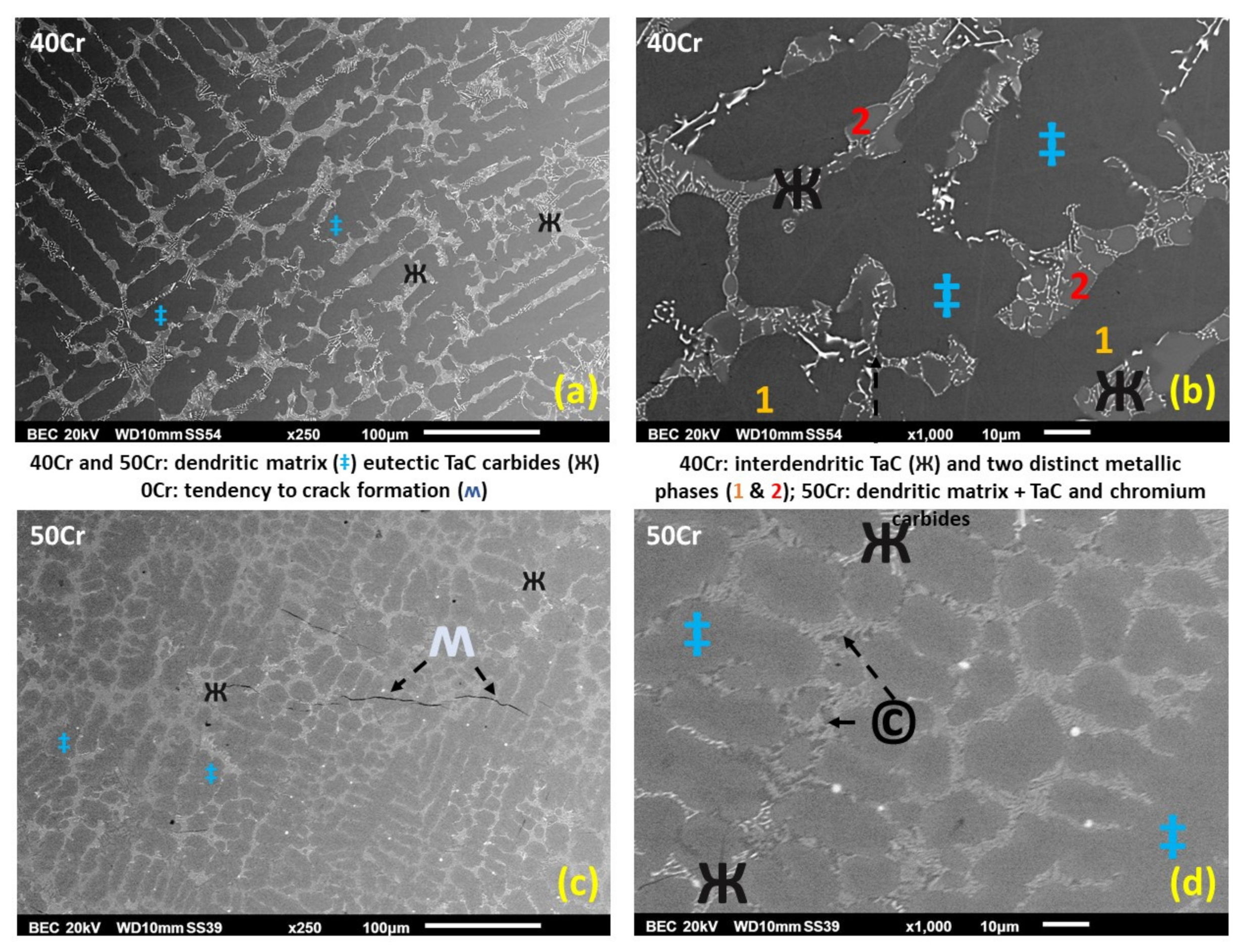
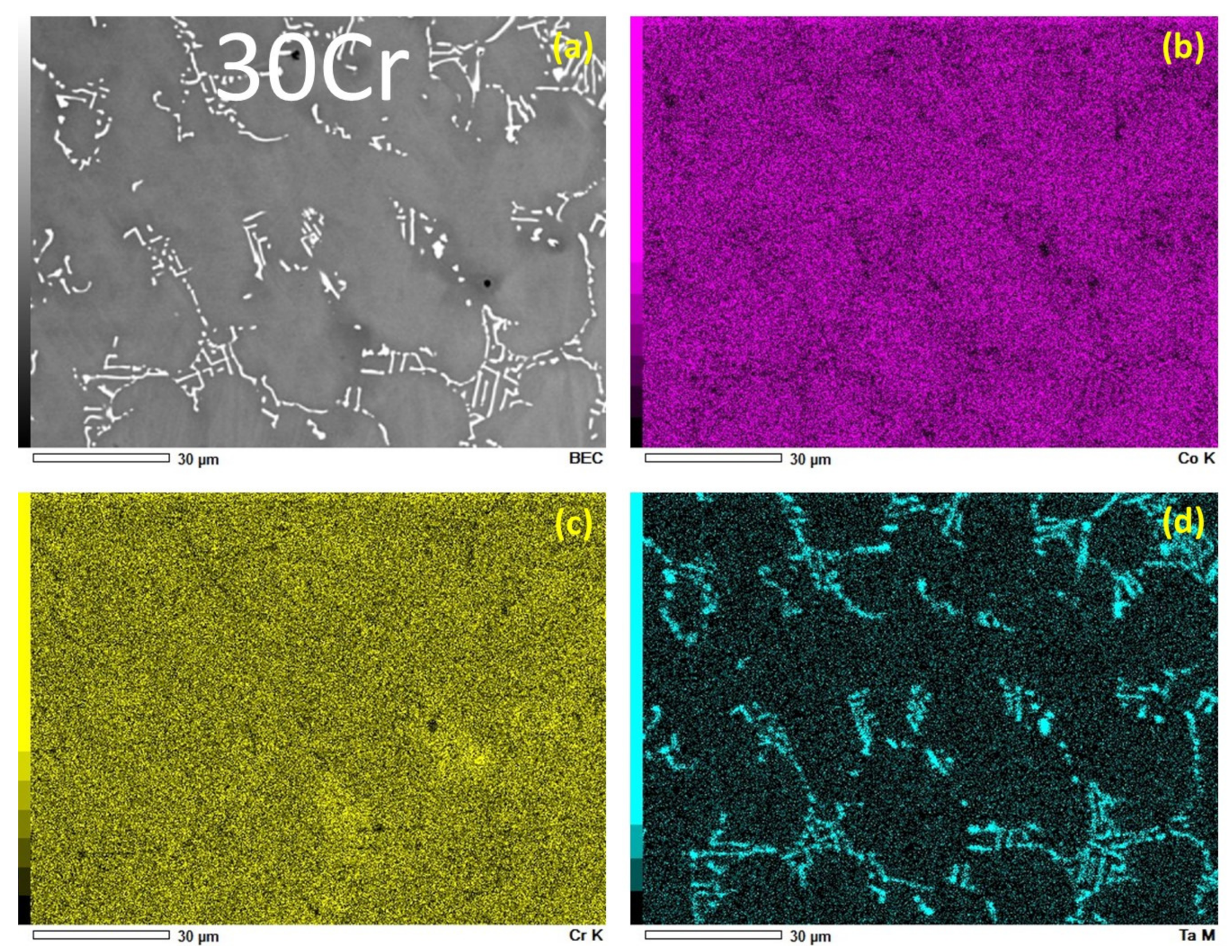
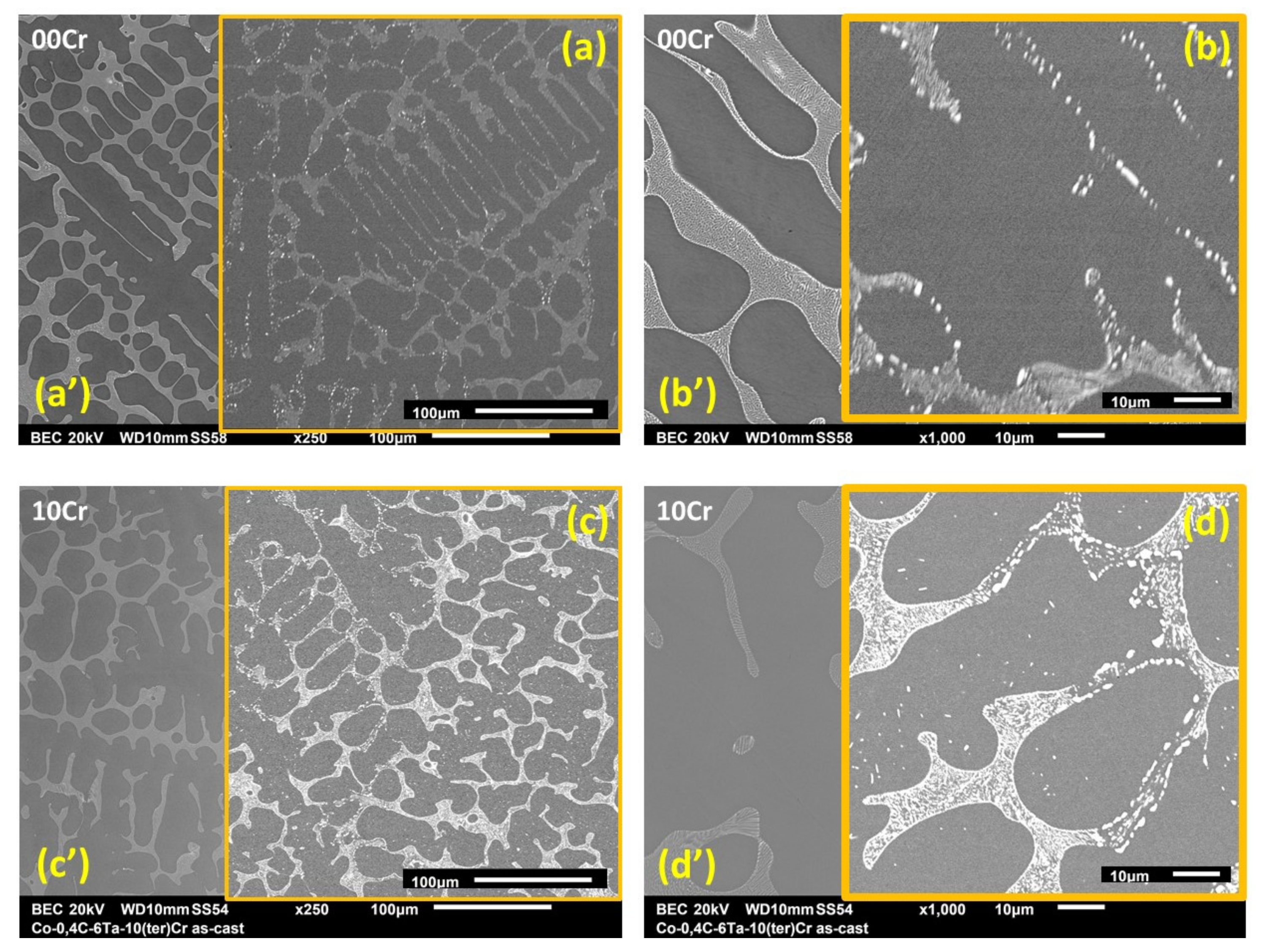
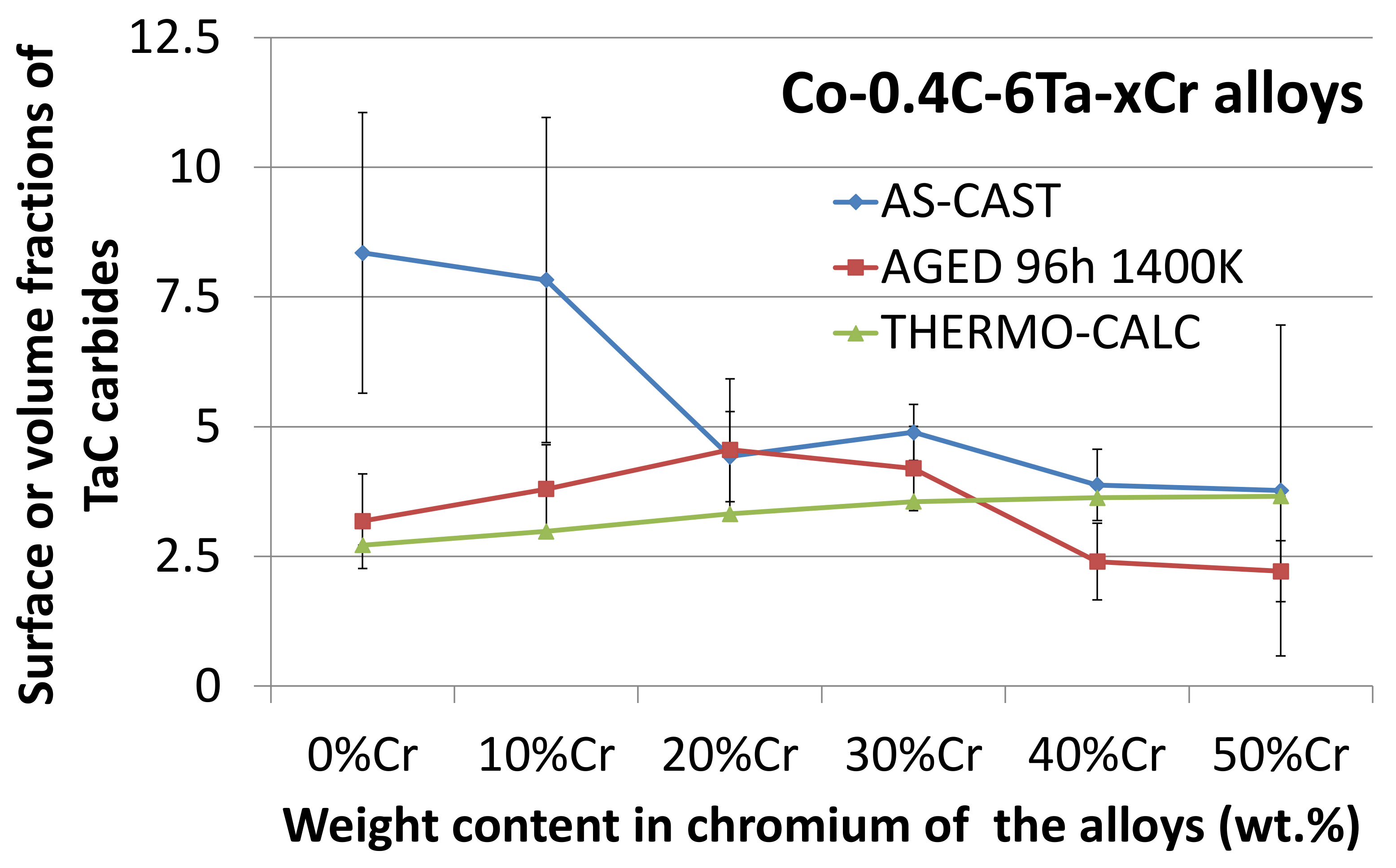
3.1. Chemical Composition and Microstructures of the Alloys in Their As-Cast States
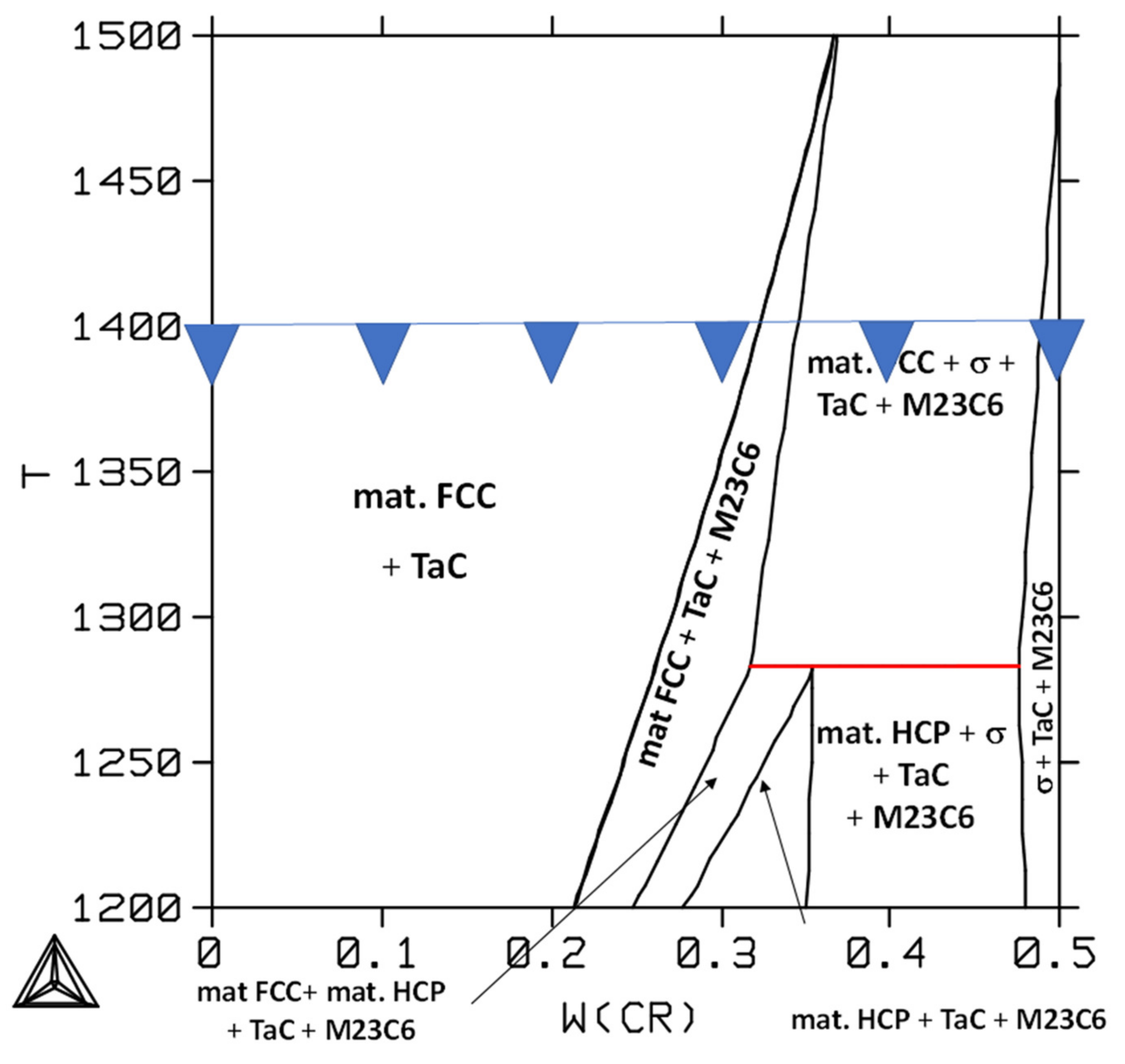
3.2. Microstructures of the Alloys after Aging at 1400 K
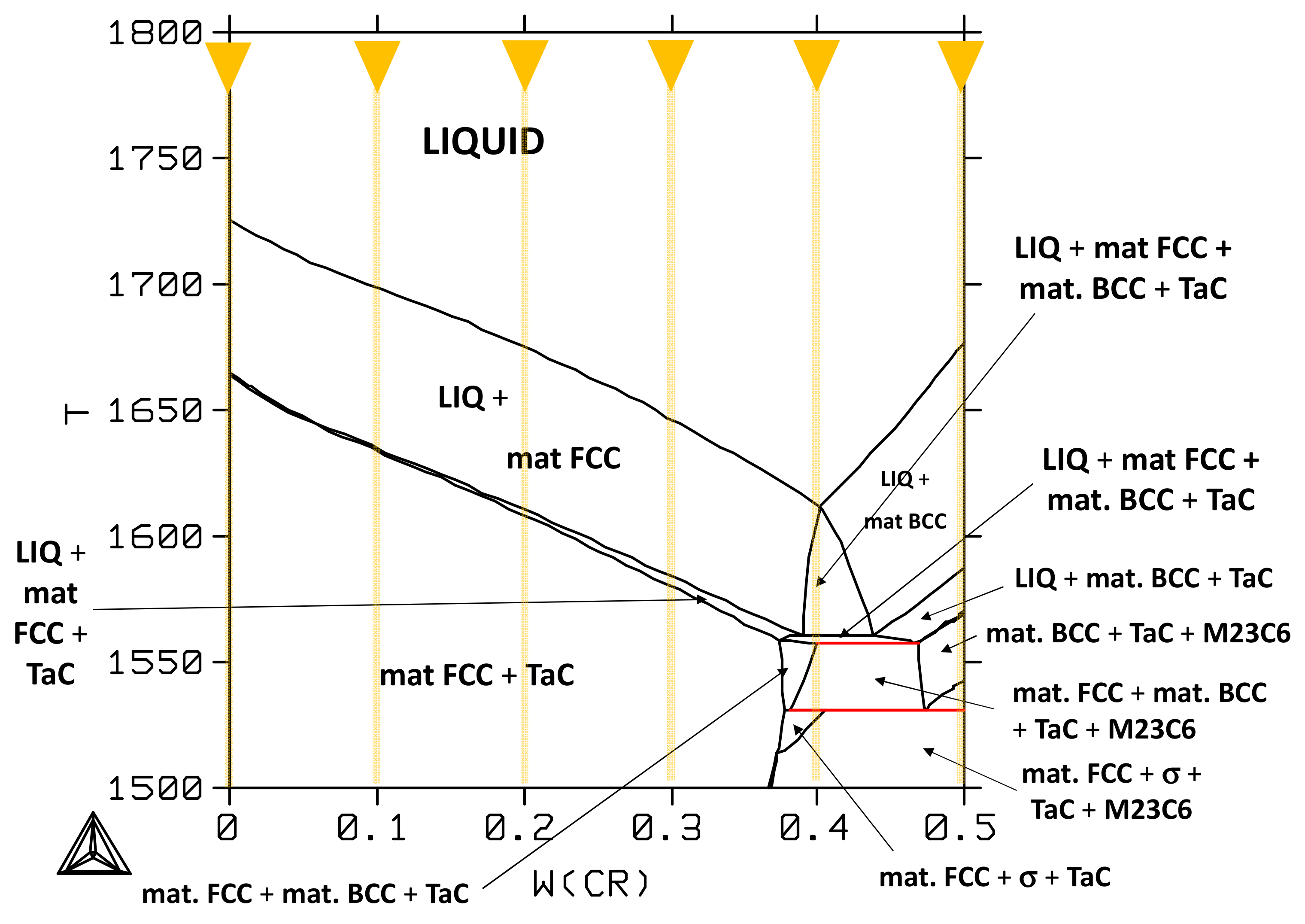
3.3. Interpretation of the As-Cast States and Aged States Using Thermodynamic Calculations
3.4. Comparison of Thermodynamic Calculations and Metallographic Observations
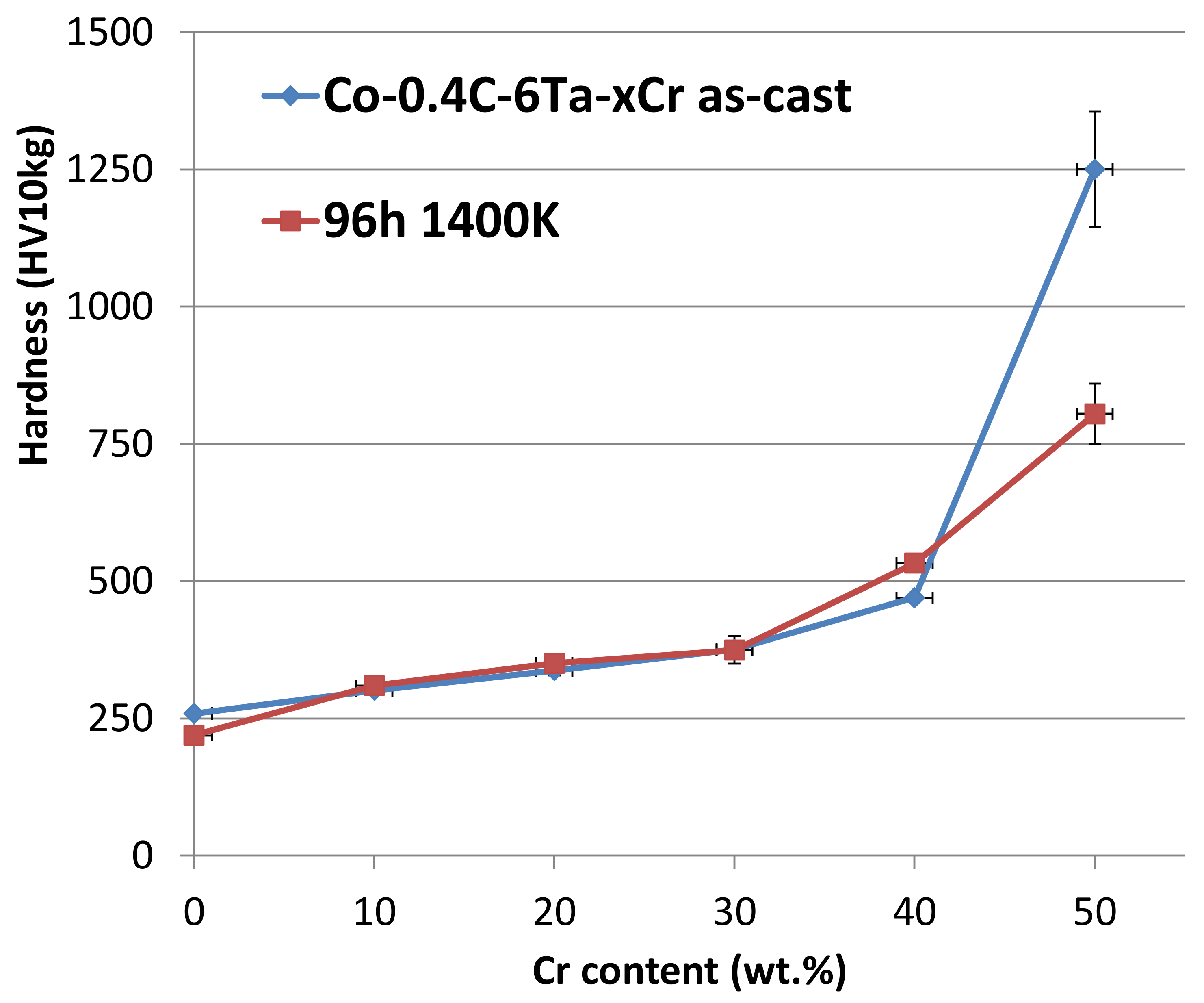
3.5. Indentation Results
3.6. Discussion
4. Conclusions
- Decreasing the Cr content down to 10 wt.% refines the eutectic TaC;
- 20 to 30 wt.%Cr keeps the script-like shaped TaC, which is known to be favorable against creep resistance;
- Cr contents beyond 40 wt.% decrease TaC stability and favor the minor presence of chromium carbides;
- Cr contents beyond 40 wt.% induce matrix changes from FCC to HCP, and the CoCr sigma phase enhances hardness and brittleness and decreases toughness;
- A Cr content close to 30 wt.% is best for good general high-temperature behavior.
5. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sims, C.T.; Hagel, W.C. The Superalloys; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, C.; Pan, F.; Qu, X.; Duan, B.; Wang, T.; He, X. Novel cobalt base superalloy and its high-temperature flow behavior. Rare Met. 2008, 27, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.H.; Yao, X.D.; Guan, H.R.; Hu, Z.Q. Relationship between degeneration of M7C3 and precipitation of M23C6 in a cobalt base superalloy. Mater. Sci. Technol. 1999, 15, 596–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, E.F. Superalloys: A Technical Guide; ASM International: Metals Park, OH, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Woulds, M.J.; Cass, T.R. Developments in Mar-M alloy 509. Cobalt 1969, 42, 3–13. [Google Scholar]
- Berthod, P. High temperature properties of several chromium-containing Co-based alloys reinforced by different types of MC carbides (M = Ta, Nb, Hf and/or Zr). J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 481, 746–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michon, S.; Aranda, L.; Berthod, P.; Steinmetz, P. High temperature evolution of the microstructure of a cast cobalt base superalloy—Consequences on its thermomechanical properties. Metall. Res. Technol. 2004, 101, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthod, P. As-Cast microstructures of high entropy alloys designed to be TaC-strengthened. J. Met. Mater. Res. 2022, 5, 4685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthod, P. Strengthening Against Creep at Elevated Temperature of HEA Alloys of the CoNiFeMnCr Type Using MC-Carbides. In Proceedings of the 152nd TMS Annual Meeting and Exhibition, San Diego, CA, USA, 19—23 March 2023. accepted paper. [Google Scholar]
- Berthod, P.; Aranda, L.; Vébert, C.; Michon, S. Experimental and thermodynamic study of the high temperature microstructure of tantalum containing nickel-based alloys. Calphad 2004, 28, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Buchanan, E.R.; Tarshis, L.A. Strengths and failure mechanisms of a cobalt-chromium-tantalum carbide (Co-15Cr-13TaC) directionally solidified eutectic alloy. Metall. Trans. 1974, 5, 1413–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, E.R.; Lemkey, F.D. Directionally solidified eutectic superalloys. Compos. Mater. 1974, 4, 101–157. [Google Scholar]
- Karge, L.; Gilles, R.; Mukherji, D.; Beran, P.; Strunz, P.; Hoelzel, M.; Roesler, J. Beyond Ni-base superalloys: Influence of Cr addition on Co-Re base alloys strengthened by nano-sized TaC precipitates. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2018, 551, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurz, W.; Fisher, D.J. Fundamentals of Solidification; Trans. Tech. Publication: Stafa-Zurich, Switzerland, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Beck, C.G.; Santhanam, A.T. Effect of microstructure on the thermal fatigue resistance of a cast cobalt-base alloy, Mar-M509. Therm. Fatigue Mater. Compon. 1976, 612, 123–140. [Google Scholar]
- Michon, S.; Berthod, P.; Aranda, L.; Rapin, C.; Podor, R.; Steinmetz, P. Application of thermodynamic calculations to study high temperature behavior of TaC-strengthened Co-base superalloys. Calphad 2003, 27, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesoult, G. Traité des Matériaux 5. Thermodynamique des Matériaux: De L’elaboration des Matériaux à la Genèse des Microstructures; Presses Polytechniques et Universitaires Romandes: Lausanne, Switzerland, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Michel, G.M.; Berthod, P.; Vilasi, M.; Mathieu, S.; Steinmetz, P. Protection of cobalt-based refractory alloys by chromium deposition on surface. Part I: Sub-surface enrichment in chromium by pack-cementation and diffusion. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2011, 205, 3708–3715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Michel, G.M.; Berthod, P.; Vilasi, M.; Mathieu, S.; Steinmetz, P. Protection of cobalt-based refractory alloys by chromium deposition on surface. Part II: Behaviour of the coated alloys in oxidation at high temperature. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2011, 205, 5241–5247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Total Weight: 40 g | Co Contents and Masses | C Contents and Masses | Ta Contents and Masses | Cr Contents and Masses | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 00Cr | 93.6 wt.% | 37.44 g | 0.4 wt.% | 0.16 g | 6 wt.% | 2.4 g | 0 wt.% | / |
| 10Cr | 83.6 wt.% | 33.44 g | 0.4 wt.% | 0.16 g | 6 wt.% | 2.4 g | 10 wt.% | 4 g |
| 20Cr | 73.6 wt.% | 29.44 g | 0.4 wt.% | 0.16 g | 6 wt.% | 2.4 g | 20 wt.% | 8 g |
| 30Cr | 63.6 wt.% | 25.44 g | 0.4 wt.% | 0.16 g | 6 wt.% | 2.4 g | 30 wt.% | 12 g |
| 40Cr | 53.6 wt.% | 21.44 g | 0.4 wt.% | 0.16 g | 6 wt.% | 2.4 g | 40 wt.% | 16 g |
| 50Cr | 43.6 wt.% | 17.44 g | 0.4 wt.% | 0.16 g | 6 wt.% | 2.4 g | 50 wt.% | 20 g |
| Alloy | 00Cr | 10Cr | 20Cr | 30Cr | 40Cr | 50Cr | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cr | AVERAGE CONTENT | / | 10.26 wt.% | 21.11 wt.% | 30.60 wt.% | 40.26 wt.% | 50.06 wt.% |
| Standard deviation | / | 0.22 wt.% | 0.18 wt.% | 0.39 wt.% | 0.14 wt.% | 0.67 wt.% | |
| Ta | AVERAGE CONTENT | 6.86 wt.% | 5.84 wt.% | 7.18 wt.% | 7.15 wt.% | 6.77 wt.% | 6.65 wt.% |
| Standard deviation | 0.04 wt.% | 1.38 wt.% | 0.68 wt.% | 0.24 wt.% | 0.18 wt.% | 1.04 wt.% | |
| Alloy | 0Cr | 10Cr | 20Cr | 30Cr | 40Cr | 50Cr | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cr | AVERAGE CONTENT | / | 10.42 wt.% | 20.32 wt.% | 30.01 wt.% | m1 (38.77) m2 (46.61) | 55.17 wt.% |
| Standard deviation | / | 0.26 wt.% | 0.27 wt.% | 0.19 wt.% | m1 (0.12) m2 (1.77) | 1.24 wt.% | |
| Ta | AVERAGE CONTENT | 2.48 wt.% | 2.59 wt.% | 2.17 wt.% | 2.30 wt.% | m1 (2.13) m2 (5.53) | 1.52 wt.% |
| Standard deviation | 0.24 wt.% | 0.76 wt.% | 0.11 wt.% | 0.29 wt.% | m1 (0.22) m2 (0.34) | 0.37 wt.% | |
| Alloy | 0Cr | 10Cr | 20Cr | 30Cr | 40Cr | 50Cr | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cr | AVERAGE CONTENT | / | 10.60 | 21.94 | 31.92 | 39.41 | 51.21 |
| Standard deviation | / | 0.12 | 0.48 | 0.90 | 2.04 | 1.19 | |
| Ta | AVERAGE CONTENT | 2.47 | 2.51 | 1.37 | 1.60 | 3.91 | 2.89 |
| Standard deviation | 0.72 | 0.68 | 0.11 | 0.12 | 3.76 | 0.74 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Berthod, P.; Bouaraba, M.; Cai, J. Influence of the Chromium Content on the Characteristics of the Matrix, the Tantalum Carbides Population, and the Hardness of Cast Co(Cr)-0.4C-6Ta Alloys. Micro 2023, 3, 239-255. https://doi.org/10.3390/micro3010017
Berthod P, Bouaraba M, Cai J. Influence of the Chromium Content on the Characteristics of the Matrix, the Tantalum Carbides Population, and the Hardness of Cast Co(Cr)-0.4C-6Ta Alloys. Micro. 2023; 3(1):239-255. https://doi.org/10.3390/micro3010017
Chicago/Turabian StyleBerthod, Patrice, Merzouk Bouaraba, and Junfu Cai. 2023. "Influence of the Chromium Content on the Characteristics of the Matrix, the Tantalum Carbides Population, and the Hardness of Cast Co(Cr)-0.4C-6Ta Alloys" Micro 3, no. 1: 239-255. https://doi.org/10.3390/micro3010017
APA StyleBerthod, P., Bouaraba, M., & Cai, J. (2023). Influence of the Chromium Content on the Characteristics of the Matrix, the Tantalum Carbides Population, and the Hardness of Cast Co(Cr)-0.4C-6Ta Alloys. Micro, 3(1), 239-255. https://doi.org/10.3390/micro3010017







