iBTA-Induced Biotube® Blood Vessels: 2020 Update
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Development Process of the Molds for Biotube Preparation (Biotube Makers)
2.1. Development of Original Straight Mold
2.2. First-in-Man (FIM) Study of Straight Mold
2.3. Development of Plastic Spiral Biotube Maker for Long Length Biotube
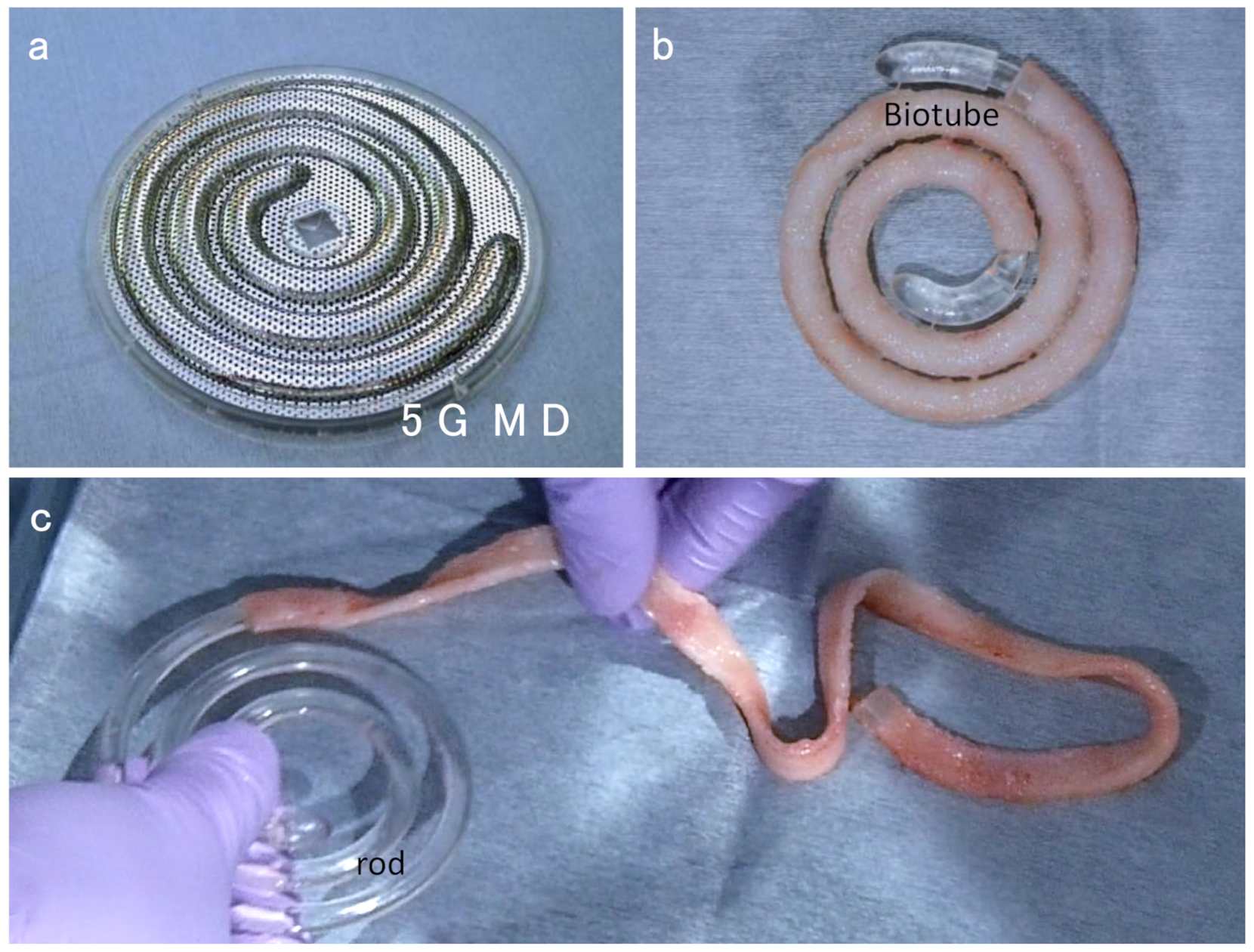
2.4. Development of Stainless Steel Spiral Biotube Maker
3. Progress of Preclinical Tests
3.1. Biotube Formation Test
3.2. Biotube Implantation Test
4. Future Plan
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Komura, M.; Komura, H.; Satake, R.; Suzuki, K.; Yonekawa, H.; Ikebukuro, K.; Komuro, H.; Hoshi, K.; Takato, T.; Moriwaki, T.; et al. Fabrication of an anatomy-mimicking BIO-AIR-TUBE with engineered cartilage. Regen. Ther. 2019, 11, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umeda, S.; Nakayama, Y.; Terazawa, T.; Iwai, R.; Hiwatashi, S.; Nakahata, K.; Takama, Y.; Okuyama, H. Long-term outcomes of patch tracheoplasty using collagenous tissue membranes (biosheets) produced by in-body tissue architecture in a beagle model. Surg. Today 2019, 49, 958–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiwatashi, S.; Nakayama, Y.; Umeda, S.; Takama, Y.; Terazawa, T.; Okuyama, H. Tracheal Replacement Using an In-Body Tissue-Engineered Collagenous Tube “BIOTUBE” with a Biodegradable Stent in a Beagle Model: A Preliminary Report on a New Technique. Eur. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2019, 29, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Okuyama, H.; Umeda, S.; Takama, Y.; Terasawa, T.; Nakayama, Y. Patch esophagoplasty using an in-body-tissue-engineered collagenous connective tissue membrane. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2018, 53, 223–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takiyama, N.; Mizuno, T.; Iwai, R.; Uechi, M.; Nakayama, Y. In-body tissue-engineered collagenous connective tissue membranes (BIOSHEETs) for potential corneal stromal substitution. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2016, 10, E518–E526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, K.; Komura, M.; Terawaki, K.; Kodaka, T.; Gohara, T.; Komura, H.; Nakayama, Y. Engineering and repair of diaphragm using biosheet (a collagenous connective tissue membrane) in rabbits. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2018, 53, 330–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iimori, Y.; Iwai, R.; Nagatani, K.; Inoue, Y.; Funayama-Iwai, M.; Okamoto, M.; Nakata, M.; Mie, K.; Nishida, H.; Nakayama, Y.; et al. Urinary bladder reconstruction using autologous collagenous connective tissue membrane “Biosheet®” induced by in-body tissue architecture: A pilot study. Regen. Ther. 2020, 15, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terazawa, T.; Furukoshi, M.; Nakayama, Y. One-year follow-up study of iBTA-induced allogenic biosheet for repair of abdominal wall defects in a beagle model: A pilot study. Hernia 2019, 23, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, Y.; Oshima, N.; Tatsumi, E.; Ichii, O.; Nishimura, T. iBTA-induced bovine Biosheet for repair of abdominal wall defects in a beagle model: Proof of concept. Hernia 2018, 22, 1033–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terazawa, T.; Kawashima, T.; Umeno, T.; Wada, T.; Ozaki, S.; Miyamoto, S.; Nakayama, Y. Mechanical characterization of an in-body tissue-engineered autologous collagenous sheet for application as an aortic valve reconstruction material. J. Biomech. 2020, 99, 109528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawashima, T.; Umeno, T.; Terazawa, T.; Wada, T.; Shuto, T.; Nishida, H.; Anai, H.; Nakayama, Y.; Miyamoto, S. Aortic valve neocuspidization with in-body tissue-engineered autologous membranes: Preliminary results in a long-term goat model. Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2021, ivab015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, Y.; Ishibashi-Ueda, H.; Takamizawa, K. In vivo tissue-engineered small- caliber arterial graft prosthesis consisting of autologous tissue (biotube). Cell Transplant. 2004, 13, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, T.; Kanda, K.; Ishibashi-Ueda, H.; Yaku, H.; Nakayama, Y. Development of biotube vascular grafts incorporating cuffs for easy implantation. J. Artif. Organs 2007, 10, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai, O.; Kanda, K.; Ishibashi-Ueda, H.; Takamizawa, K.; Ametani, A.; Yaku, H.; Nakayama, Y. Development of the wing-attached rod for acceleration of “Biotube” vascular grafts fabrication in vivo. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2007, 83, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, T.; Kanda, K.; Ishibashi-Ueda, H.; Yaku, H.; Nakayama, Y. Autologous small-caliber “biotube” vascular grafts with argatroban loading: A histomorphological examination after implantation to rabbits. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2010, 92, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, T.; Kanda, K.; Yamanami, M.; Ishibashi-Ueda, H.; Yaku, H.; Nakayama, Y. Long-term animal implantation study of biotube-autologous small-caliber vascular graft fabricated by in-body tissue architecture. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2011, 98, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanami, M.; Ishibashi-Ueda, H.; Yamamoto, A.; Iida, H.; Watanabe, T.; Kanda, K.; Yaku, H.; Nakayama, Y. Implantation study of small-caliber “biotube” vascular grafts in a rat model. J. Artif. Organs 2013, 16, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, D.; Enmi, J.I.; Iwai, R.; Kurisu, K.; Tatsumi, E.; Nakayama, Y. One year Rat Study of iBTA-induced “Microbiotube” Microvascular Grafts with an Ultra-Small Diameter of 0.6 mm. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2018, 55, 882–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, D.; Enmi, J.; Moriwaki, T.; Ishibashi-Ueda, H.; Kobayashi, M.; Iwana, S.; Iida, H.; Satow, T.; Takahashi, J.C.; Kurisu, K.; et al. Development of in vivo tissue-engineered microvascular grafts with an ultra small diameter of 0.6 mm (MicroBiotubes): Acute phase evaluation by optical coherence tomography and magnetic resonance angiography. J. Artif. Organs 2016, 19, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, Y.; Kaneko, Y.; Takewa, Y.; Okumura, N. Mechanical properties of human autologous tubular connective tissues (human biotubes) obtained from patients undergoing peritoneal dialysis. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2016, 104, 1431–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, J.H.; Efendy, J.L.; Campbell, G.R. Novel vascular graft grown within recipient’s own peritoneal cavity. Circ. Res. 1999, 85, 1173–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geelhoed, W.J.; Moroni, L.; Rotmans, J.I. Utilizing the Foreign Body Response to Grow Tissue Engineered Blood Vessels in Vivo. J. Cardiovasc. Transl. Res. 2017, 10, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geelhoed, W.J.; van der Bogt, K.E.A.; Rothuizen, T.C.; Damanik, F.F.R.; Hamming, J.F.; Mota, C.D.; van Agen, M.S.; de Boer, H.C.; Restrepo, M.T.; Hinz, B.; et al. A novel method for engineering autologous non-thrombogenic in situ tissue-engineered blood vessels for arteriovenous grafting. Biomaterials 2020, 229, 119577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai, O.; Kanda, K.; Takamizawa, K.; Sato, T.; Yaku, H.; Nakayama, Y. Faster and stronger vascular “Biotube” graft fabrication in vivo using a novel nicotine-containing mold. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2009, 90, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, Y.; Tsujinaka, T. Acceleration of robust “biotube” vascular graft fabrication by in-body tissue architecture technology using a novel eosin Y-releasing mold. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2014, 102, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwai, R.; Tsujinaka, T.; Nakayama, Y. Preparation of Biotubes with vascular cells component by in vivo incubation using adipose-derived stromal cell-exuding multi-microporous molds. J. Artif. Organs 2015, 18, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oie, T.; Yamanami, M.; Ishibashi-Ueda, H.; Kanda, K.; Yaku, H.; Nakayama, Y. In-body optical stimulation formed connective tissue vascular grafts, “biotubes,” with many capillaries and elastic fibers. J. Artif. Organs 2010, 13, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Zhou, Y.M.; Ishibashi-Ueda, H.; Takamizawa, K.; Ando, J.; Kanda, K.; Yaku, H.; Nakayama, Y. In vitro maturation of “biotube” vascular grafts induced by a 2-day pulsatile flow loading. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2009, 91, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukoshi, M.; Moriwaki, T.; Nakayama, Y. Development of an in vivo tissue-engineered vascular graft with designed wall thickness (biotube type C) based on a novel caged mold. J. Artif. Organs 2016, 19, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, Y.; Furukoshi, M.; Tatsumi, E. Shape memory of in-body tissue-engineered Biotube® vascular grafts and the preliminary evaluation in animal implantation experiments. J. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2020, 61, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukoshi, M.; Tatsumi, E.; Nakayama, Y. Application of in-body tissue architecture-induced Biotube vascular grafts for vascular access: Proof of concept in a beagle dog model. J. Vasc. Access 2020, 21, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terazawa, T.; Nishimura, T.; Mitani, T.; Ichii, O.; Ikeda, T.; Kosenda, K.; Tatsumi, E.; Nakayama, Y. Wall thickness control in biotubes prepared using type-C mold. J. Artif. Organs 2018, 21, 387–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Introduction of Biotube®. Available online: http://www.medical-biotube.com. (In Japanese).
- Sakigake Designation Scheme. Available online: https://www.mhlw.go.jp/file/05-Shingikai-11121000-Iyakushokuhinkyoku-Soumuka/0000123357.pdf (accessed on 24 June 2014). (In Japanese)
- Nakayama, Y.; Kaneko, Y.; Okumura, N.; Terazawa, T. Initial 3-year results of first human use of an in-body tissue-engineered autologous “Biotube” vascular graft for hemodialysis. J. Vasc. Access 2020, 21, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, Y.; Furukoshi, M.; Terazawa, T.; Iwai, R. Development of long in vivo tissue-engineered “Biotube” vascular grafts. Biomaterials 2018, 185, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higashita, R.; Nakayama, Y.; Shiraishi, Y.; Iwai, R.; Inoue, Y.; Yamada, A.; Terazawa, T.; Tajikawa, T.; Miyazaki, M.; Ohara, M.; et al. Acute phase evaluation of small-diameter long iBTA-induced vascular graft “Biotube” in a goat model. unpublished in preparation.
- Niklason, L.E.; Lawson, J.H. Bioengineered human blood vessels. Science 2020, 9, 6513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutowski, P.; Gage, S.M.; Guziewicz, M.; Ilzecki, M.; Kazimierczak, A.; Kirkton, R.D.; Niklason, L.E.; Pilgrim, A.; Prichard, H.L.; Przywara, S.; et al. Arterial reconstruction with human bioengineered acellular blood vessels in patients with peripheral arterial disease. J. Vasc. Surg. 2020, 72, 1247–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nakayama, Y.; Higashita, R.; Shiraishi, Y.; Umeno, T.; Tajikawa, T.; Yamada, A.; Mori, K.; Miyazaki, M.; Ohara, M.; Iwai, R.; et al. iBTA-Induced Biotube® Blood Vessels: 2020 Update. Kidney Dial. 2021, 1, 3-13. https://doi.org/10.3390/kidneydial1010002
Nakayama Y, Higashita R, Shiraishi Y, Umeno T, Tajikawa T, Yamada A, Mori K, Miyazaki M, Ohara M, Iwai R, et al. iBTA-Induced Biotube® Blood Vessels: 2020 Update. Kidney and Dialysis. 2021; 1(1):3-13. https://doi.org/10.3390/kidneydial1010002
Chicago/Turabian StyleNakayama, Yasuhide, Ryuji Higashita, Yasuyuki Shiraishi, Tadashi Umeno, Tsutomu Tajikawa, Akihiro Yamada, Kazuki Mori, Manami Miyazaki, Mamiko Ohara, Ryosuke Iwai, and et al. 2021. "iBTA-Induced Biotube® Blood Vessels: 2020 Update" Kidney and Dialysis 1, no. 1: 3-13. https://doi.org/10.3390/kidneydial1010002
APA StyleNakayama, Y., Higashita, R., Shiraishi, Y., Umeno, T., Tajikawa, T., Yamada, A., Mori, K., Miyazaki, M., Ohara, M., Iwai, R., Terazawa, T., Oie, T., Yambe, T., & Miyamoto, S. (2021). iBTA-Induced Biotube® Blood Vessels: 2020 Update. Kidney and Dialysis, 1(1), 3-13. https://doi.org/10.3390/kidneydial1010002






