Cerebral Hemodynamic Alterations in Dialysis COVID-19 Survivors: A Transcranial Doppler Ultrasound Study on Intracranial Pressure Dynamics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Design
2.2. Measurement
2.3. Statistical Analyses
2.4. Ethical Approval and Consent to Participate
2.5. Data Availability Statement
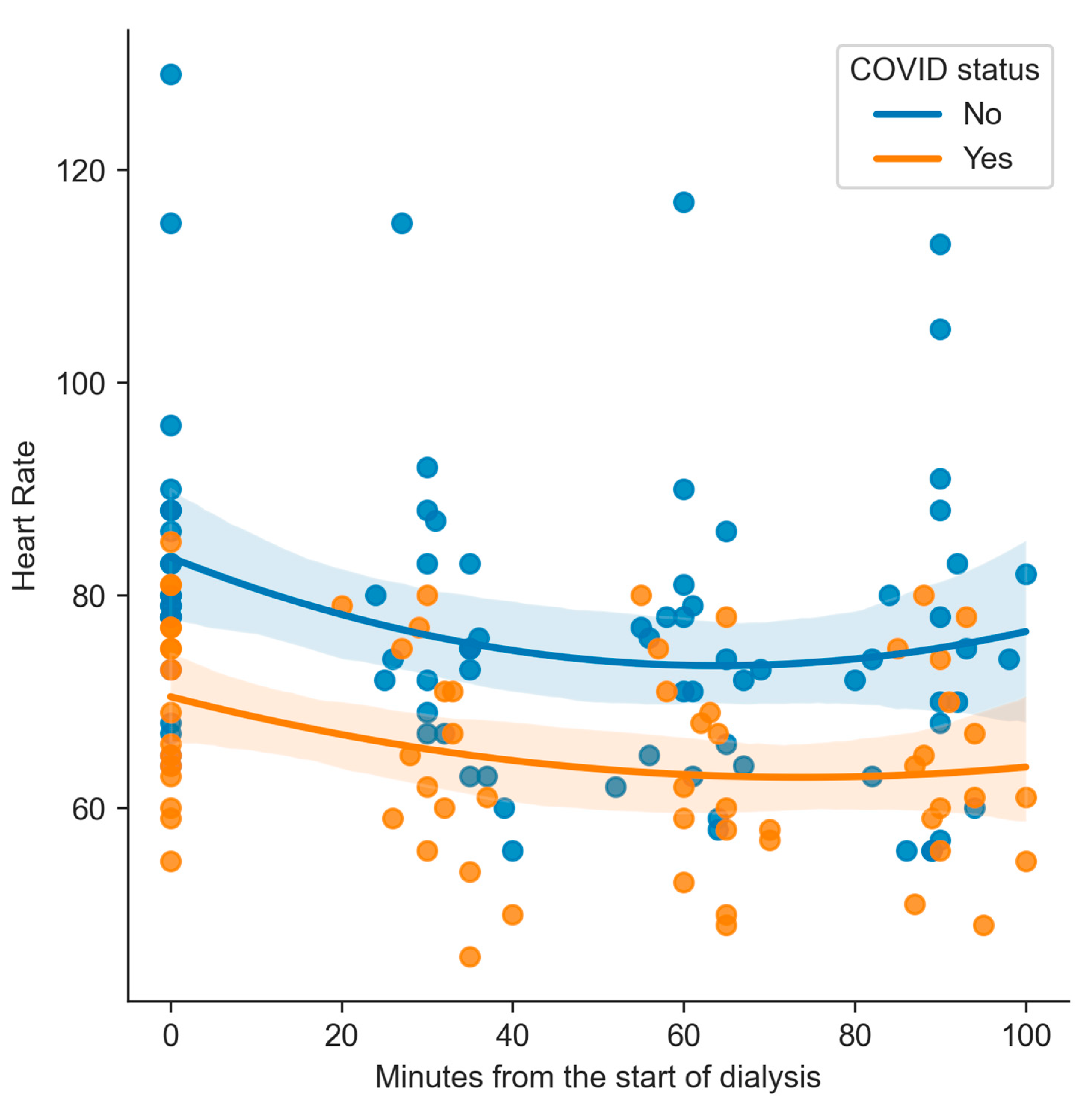
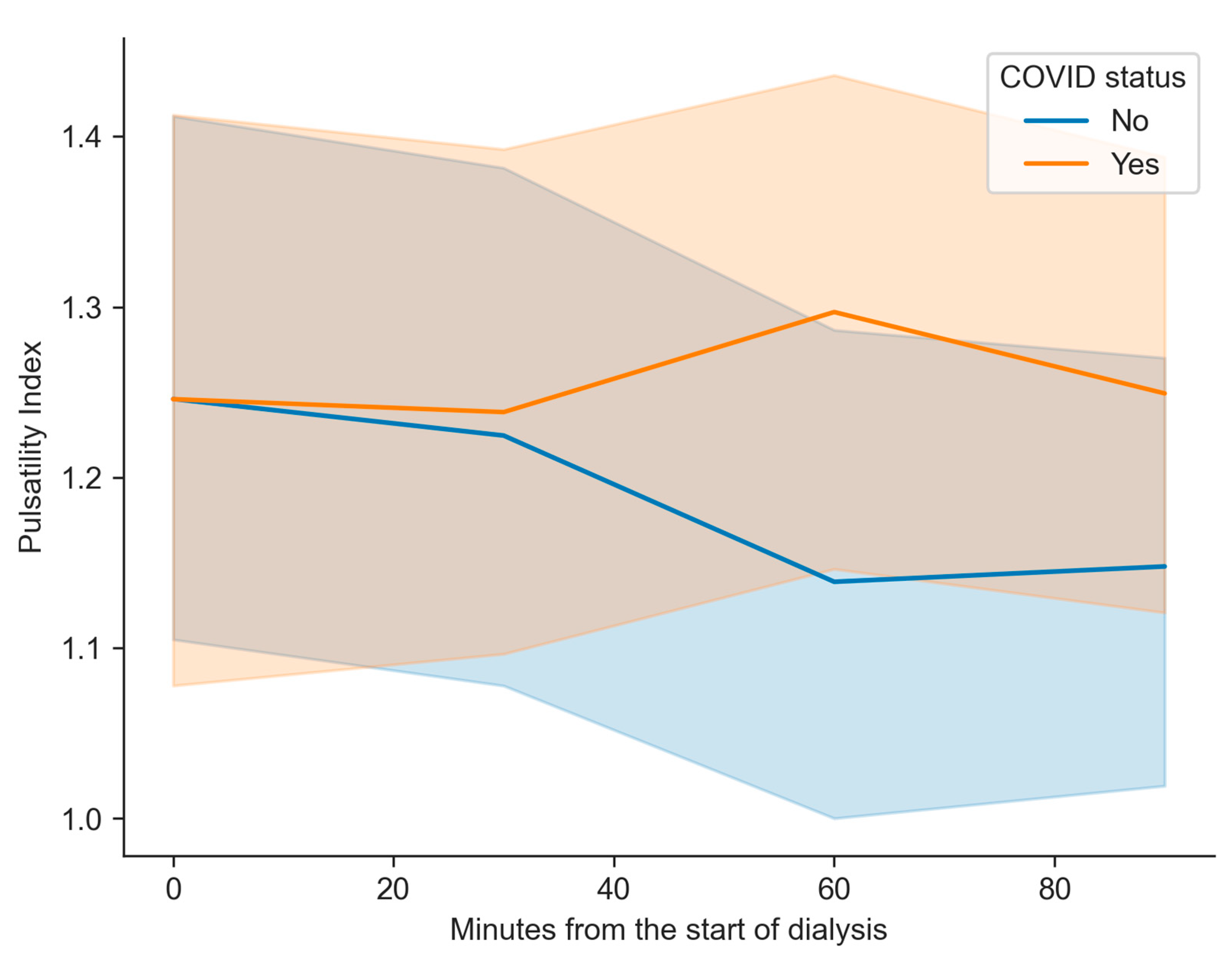
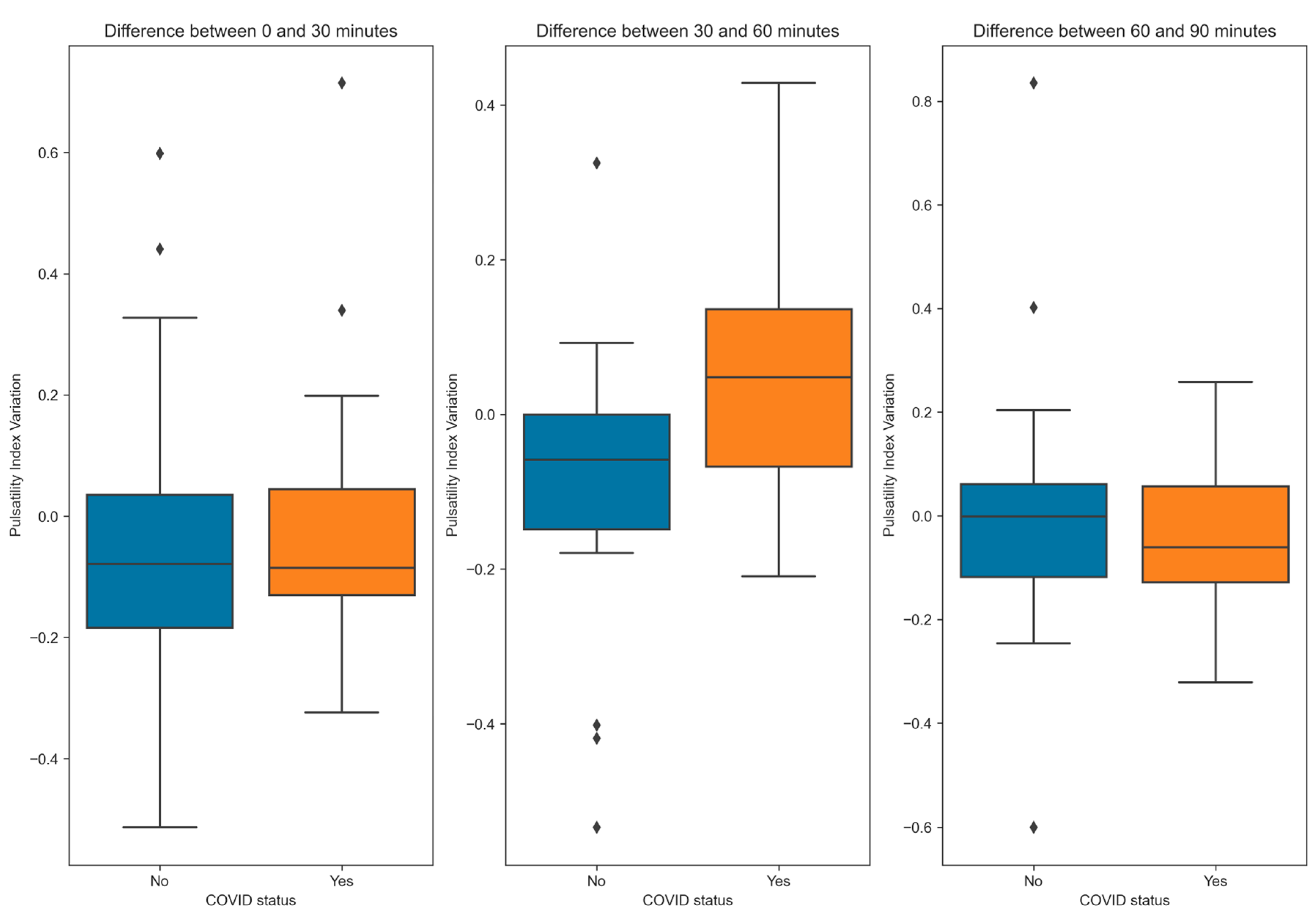
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Hoffmann, M.; Kleine-Weber, H.; Schroeder, S.; Krüger, N.; Herrler, T.; Erichsen, S.; Schiergens, T.S.; Herrler, G.; Wu, N.H.; Nitsche, A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor. Cell 2020, 181, 271–280.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oikonomou, E.; Souvaliotis, N.; Lampsas, S.; Siasos, G.; Poulakou, G.; Theofilis, P.; Papaioannou, T.G.; Haidich, A.B.; Tsaousi, G.; Ntousopoulos, V.; et al. Endothelial Dysfunction in Acute and Long Standing COVID-19: A Prospective Cohort Study. Vascul. Pharmacol. 2022, 144, 106975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libby, P.; Lüscher, T. COVID-19 Is, in the End, an Endothelial Disease. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 3038–3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrints, C.J.M.; Krychtiuk, K.A.; Van Craenenbroeck, E.M.; Segers, V.F.; Price, S.; Heidbuchel, H. Endothelialitis Plays a Central Role in the Pathophysiology of Severe COVID-19 and Its Cardiovascular Complications. Acta Cardiol. 2021, 76, 109–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, W.J.; Liang, W.H.; He, J.X.; Zhong, N.S. Cardiovascular Comorbidity and Its Impact on Patients with COVID-19. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 55, 2001227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackermann, M.; Verleden, S.E.; Kuehnel, M.; Haverich, A.; Welte, T.; Laenger, F.; Vanstapel, A.; Werlein, C.; Stark, H.; Tzankov, A.; et al. Pulmonary Vascular Endothelialitis, Thrombosis, and Angiogenesis in COVID-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robles, J.P.; Zamora, M.; Adan-Castro, E.; Siqueiros-Marquez, L.; de la Escalera, G.M.; Clapp, C. The Spike Protein of SARS-CoV-2 Induces Endothelial Inflammation through Integrin A5β1 and NF-ΚB Signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 101695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haffke, M.; Freitag, H.; Rudolf, G.; Seifert, M.; Doehner, W.; Scherbakov, N.; Hanitsch, L.; Wittke, K.; Bauer, S.; Konietschke, F.; et al. Endothelial Dysfunction and Altered Endothelial Biomarkers in Patients with Post-COVID-19 Syndrome and Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (ME/CFS). J. Transl. Med. 2022, 20, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapeña-Motilva, J.; Gómez-Enjuto, S.; Hernándo-Requejo, V.; Huertas-González, N. Síndrome de Desequilibrio Sintomático Tras Infección Por SARS-CoV-2, a Propósito de Un Caso. Neurología 2023, 38, 712–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcic, M.; Marcic, L.; Marcic, B.; Capkun, V.; Vukojevic, K. Cerebral Vasoreactivity Evaluated by Transcranial Color Doppler and Breath-Holding Test in Patients after SARS-CoV-2 Infection. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaloria, N.; Panda, N.B.; Bhagat, H.; Kaloria, N.; Soni, S.L.; Chauhan, R.; Chhabra, R.; Jangra, K. Pulsatility Index Reflects Intracranial Pressure Better than Resistive Index in Patients with Clinical Features of Intracranial Hypertension. J. Neurosci. Rural Pract. 2020, 11, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’brien, N.F.; Lovett, M.E.; Chung, M.; Maa, T. Non-Invasive Estimation of Cerebral Perfusion Pressure Using Transcranial Doppler Ultrasonography in Children with Severe Traumatic Brain Injury. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2020, 36, 2063–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollard, T.J.; Johnson, A.E.W.; Raffa, J.D.; Mark, R.G. Tableone: An Open Source Python Package for Producing Summary Statistics for Research Papers. JAMIA Open 2018, 1, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellner, J.; Romner, B.; Reinstrup, P.; Kristiansson, K.A.; Ryding, E.; Brandt, L. Transcranial Doppler Sonography Pulsatility Index (PI) Reflects Intracranial Pressure (ICP). Surg. Neurol. 2004, 62, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esnault, P.; Lacroix, G.; Cungi, P.J.; D’Aranda, E.; Cotte, J.; Goutorbe, P. Dialysis Disequilibrium Syndrome in Neurointensive Care Unit: The Benefit of Intracranial Pressure Monitoring. Crit. Care 2012, 16, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, W.; Chen, F.; Cui, L. COVID-19 and Cognitive Impairment: Neuroinvasive and Blood-Brain Barrier Dysfunction. J. Neuroinflamm. 2022, 19, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greene, C.; Connolly, R.; Brennan, D.; Laffan, A.; O’Keeffe, E.; Zaporojan, L.; O’Callaghan, J.; Thomson, B.; Connolly, E.; Argue, R.; et al. Blood–Brain Barrier Disruption and Sustained Systemic Inflammation in Individuals with Long COVID-Associated Cognitive Impairment. Nat. Neurosci. 2024, 27, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silver, S.M.; Desimone, J.A.; Smith, D.A.; Sterns, R.H. Dialysis Disequilibrium Syndrome (DDS) in the Rat: Role of the “Reverse Urea Effect”. Kidney Int. 1992, 42, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, B.; Komanduri, S. Dialysis Disequilibrium Syndrome. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Mistry, K. Dialysis Disequilibrium Syndrome Prevention and Management. Int. J. Nephrol. Renovasc. Dis. 2019, 12, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platten, M.; Wick, W. Blood-Brain Barrier and Brain Edema. In Handbook of Clinical Neurology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; Volume 104, pp. 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiyatkin, E.A.; Sharma, H.S. Leakage of the Blood-Brain Barrier Followed by Vasogenic Edema as the Ultimate Cause of Death Induced by Acute Methamphetamine Overdose. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2019, 146, 189–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cash, A.; Theus, M.H. Mechanisms of Blood-Brain Barrier Dysfunction in Traumatic Brain Injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krasemann, S.; Haferkamp, U.; Pfefferle, S.; Woo, M.S.; Heinrich, F.; Schweizer, M.; Appelt-Menzel, A.; Cubukova, A.; Barenberg, J.; Leu, J.; et al. The Blood-Brain Barrier Is Dysregulated in COVID-19 and Serves as a CNS Entry Route for SARS-CoV-2. Stem Cell Rep. 2022, 17, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrini, L.; Albecka, A.; Mallery, D.L.; Kellner, M.J.; Paul, D.; Carter, A.P.; James, L.C.; Lancaster, M.A. SARS-CoV-2 Infects the Brain Choroid Plexus and Disrupts the Blood-CSF Barrier in Human Brain Organoids. Cell Stem Cell 2020, 27, 951–961.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nägele, M.P.; Haubner, B.; Tanner, F.C.; Ruschitzka, F.; Flammer, A.J. Endothelial Dysfunction in COVID-19: Current Findings and Therapeutic Implications. Atherosclerosis 2020, 314, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcic, M.; Marcic, L.; Lovric Kojundzic, S.; Marinovic Guic, M.; Marcic, B.; Caljkusic, K. Chronic Endothelial Dysfunction after COVID-19 Infection Shown by Transcranial Color-Coded Doppler: A Cross-Sectional Study. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehboob, R.; von Kries, J.P.; Ehsan, K.; Almansouri, M.; Bamaga, A.K. Role of Endothelial Cells and Angiotensin Converting Enzyme-II in COVID-19 and Brain Damages Post-Infection. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1210194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigen, T.; Ihle-Hansen, H.; Lyngbakken, M.N.; Berge, T.; Thommessen, B.; Ihle-Hansen, H.; Orstad, E.B.; Enger, S.; Røsjø, H.; Tveit, A.; et al. Carotid Atherosclerosis Is Associated with Middle Cerebral Artery Pulsatility Index. J. Neuroimaging 2020, 30, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asarcikli, L.D.; Hayiroglu, M.İ.; Osken, A.; Keskin, K.; Kolak, Z.; Aksu, T. Heart Rate Variability and Cardiac Autonomic Functions in Post-COVID Period. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 2022, 63, 715–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visco, V.; Vitale, C.; Rispoli, A.; Izzo, C.; Virtuoso, N.; Ferruzzi, G.J.; Santopietro, M.; Melfi, A.; Rusciano, M.R.; Maglio, A.; et al. Post-COVID-19 Syndrome: Involvement and Interactions between Respiratory, Cardiovascular and Nervous Systems. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dani, M.; Dirksen, A.; Taraborrelli, P.; Torocastro, M.; Panagopoulos, D.; Sutton, R.; Lim, P.B. Autonomic Dysfunction in ‘Long COVID’: Rationale, Physiology and Management Strategies. Clin. Med. 2021, 21, e63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, B.P.; Khoury, J.A.; Blair, J.E.; Grill, M.F. COVID-19 Dysautonomia. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrero, J.J.; Chen, J.; Kovesdy, C.P.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Critical Appraisal of Biomarkers of Dietary Intake and Nutritional Status in Patients Undergoing Dialysis. Semin. Dial. 2014, 27, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameter | Formula |
|---|---|
| Pulsatility index | |
| Resistance index | |
| Estimated cerebral perfusion pressure (mmHg) | |
| Mean blood pressure (mmHg) |
| Variable | Non-COVID-19 | COVID-19 Survivors | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of participants | 21 | 16 | |
| Men (n, %) | 12 (57.1%) | 13 (81.2%) | 0.231 a |
| Women (n, %) | 9 (42.9%) | 3 (20.0%) | |
| Age (mean ± SD) | 66.8 ± 11.9 years | 67.5 ± 15.1 years | 0.869 c |
| Hemodialysis duration (mean ± SD) | 60.2 ± 72.9 months | 98.2 ± 135.0 months | 0.322 c |
| Time since COVID-19 infection (mean ± SD) | - | 13.3 ± 4.3 months | - |
| Arterial hypertension (n, %) | 19 (90.5%) | 15 (93.8%) | 1.000 b |
| Dyslipidemia (n, %) | 14 (70.0%) | 7 (43.8%) | 0.212 a |
| Diabetes mellitus (n, %) | 10 (47.6%) | 4 (25.0%) | 0.288 a |
| Atrial fibrillation (n, %) | 6 (28.6%) | 3 (18.8%) | 0.702 b |
| Heart failure (n, %) | 6 (28.6%) | 3 (18.8%) | 0.702 b |
| Β-blockers or diltiazem use | 6 (28.6%) | 2 (12.5%) | 0.423 b |
| Limb ischemia (n, %) | 5 (20.8%) | 4 (15.4%) | 0.721 b |
| COPD (n, %) | 1 (4.8%) | 2 (5.4%) | 1.000 b |
| Cancer (n, %) | 5 (23.8%) | 6 (16.2%) | 0.206 b |
| Liver disease (n, %) | 5 (23.8%) | 8 (22.2%) | 1.000 b |
| Autoimmune diseases (n, %) | 3 (14.3%) | 4 (10.8%) | 0.618 b |
| Ischemic heart disease (n, %) | 4 (19.0%) | 6 (16.2%) | 0.680 b |
| Stroke (n, %) | 1 (4.8%) | 2 (5.4%) | 1.000 b |
| Intracranial interventions (n, %) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 1.000 b |
| Intracranial hypertension (n, %) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 1.000 b |
| Intracranial hypotension (n, %) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 1.000 b |
| Tobacco use (n, %) | 6 (31.6%) | 10 (32.3%) | 1.000 b |
| Variable | Non-COVID-19 | COVID-19 Survivors | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dialysis time (mean ± SD) | 245.7 ± 13.2 min | 244.8 ± 13.9 min | 0.624 c |
| Ultrafiltration volume (mean ± SD) | 2493.9 ± 864.5 mL | 2535.2 ± 771.4 mL | 0.751 c |
| QB (median [IQR]) | 350.0 [350.0, 400.0] mL/min | 350.0 [350.0, 385.0] mL/min | 0.588 d |
| Sodium bath (mean ± SD) | 137.4 ± 1.0 mEq/L | 137.4 ± 1.2 mEq/L | 0.794 c |
| Potassium bath (median [IQR]) | 2.0 [2.0, 2.0] mEq/L | 2.0 [2.0, 2.0] mEq/L | 0.329 d |
| Calcium bath (mean ± SD) | 1.6 ± 0.1 mEq/L | 1.6 ± 0.1 mEq/L | 0.160 c |
| Bicarbonate bath (mean ± SD) | 33.2 ± 2.7 mEq/L | 33.4 ± 2.5 mEq/L | 0.555 c |
| Glucose bath (median [IQR]) | 1.0 [1.0, 5.5] g/dL | 1.0 [1.0, 5.5] g/dL | 0.869 d |
| Creatinine (mean ± SD) | 7.8 ± 1.7 mg/dL | 8.2 ± 1.7 mg/dL | 0.458 c |
| Difference in creatinine (mean ± SD) | −5.7 ± 1.4 mg/dL | −5.5 ± 1.9 mg/dL | 0.744 c |
| Hematocrit (mean ± SD) | 34.9 ± 3.7% | 33.7 ± 6.4% | 0.503 c |
| Difference in hematocrit (mean ± SD) | 3.9 ± 2.7% | 4.5 ± 7.2% | 0.751 c |
| Carbon dioxide (mean ± SD) | 39.7 ± 5.1 mmHg | 40.5 ± 6.0 mmHg | 0.676 c |
| Difference in carbon dioxide (mean ± SD) | 0.9 ± 2.8 mmHg | 1.6 ± 4.1 mmHg | 0.572 c |
| Sodium (mean ± SD) | 139.0 ± 2.3 mEq/L | 139.8 ± 3.2 mEq/L | 0.436 c |
| Difference in sodium (mean ± SD) | 0.1 ± 2.9 mEq/L | −9.6 ± 34.7 mEq/L | 0.297 c |
| Potassium (mean ± SD) | 5.0 ± 0.6 mEq/L | 5.5 ± 0.8 mEq/L | 0.051 c |
| Difference in potassium (mean ± SD) | −1.6 ± 0.6 mEq/L | 6.3 ± 33.4 mEq/L | 0.355 c |
| Calcium (mean ± SD) | 8.9 ± 0.6 mg/dL | 9.0 ± 0.4 mg/dL | 0.781 c |
| Difference in calcium (mean ± SD) | 1.1 ± 0.7 mg/dL | 0.7 ± 1.7 mg/dL | 0.340 c |
| Magnesium (mean ± SD) | 2.1 ± 0.3 mg/dL | 2.4 ± 0.4 mg/dL | 0.023 c |
| Difference in magnesium (mean ± SD) | −0.2 ± 0.2 mg/dL | −0.5 ± 0.4 mg/dL | 0.016 c |
| Variable | Coefficient | Std. Error | t | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| COVID-19 | 0.1481 | 0.065 | 2.273 | 0.032 |
| Age | 0.0041 | 0.002 | 2.583 | 0.016 |
| Hemodialysis duration | 0.0005 | 0.000 | 1.303 | 0.205 |
| Sex | −0.1263 | 0.067 | −1.877 | 0.073 |
| DBP difference | −0.0010 | 0.003 | −0.291 | 0.773 |
| HR difference | −0.0030 | 0.009 | −0.352 | 0.728 |
| Creatinine difference | −0.0388 | 0.016 | −2.490 | 0.020 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lapeña-Motilva, J.; Fouz-Ruiz, D.; Ruiz-Ortiz, M.; Sanpedro-Murillo, E.; Gómez-Enjuto, S.; Hernando-Jimenez, I.; Frias-González, A.; Suso, A.S.; Merida-Herrero, E.; Benito-León, J. Cerebral Hemodynamic Alterations in Dialysis COVID-19 Survivors: A Transcranial Doppler Ultrasound Study on Intracranial Pressure Dynamics. Kidney Dial. 2025, 5, 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/kidneydial5020012
Lapeña-Motilva J, Fouz-Ruiz D, Ruiz-Ortiz M, Sanpedro-Murillo E, Gómez-Enjuto S, Hernando-Jimenez I, Frias-González A, Suso AS, Merida-Herrero E, Benito-León J. Cerebral Hemodynamic Alterations in Dialysis COVID-19 Survivors: A Transcranial Doppler Ultrasound Study on Intracranial Pressure Dynamics. Kidney and Dialysis. 2025; 5(2):12. https://doi.org/10.3390/kidneydial5020012
Chicago/Turabian StyleLapeña-Motilva, José, Daniel Fouz-Ruiz, Mariano Ruiz-Ortiz, Eduardo Sanpedro-Murillo, Sara Gómez-Enjuto, Inés Hernando-Jimenez, Aida Frias-González, Andrea Soledad Suso, Evangelina Merida-Herrero, and Julián Benito-León. 2025. "Cerebral Hemodynamic Alterations in Dialysis COVID-19 Survivors: A Transcranial Doppler Ultrasound Study on Intracranial Pressure Dynamics" Kidney and Dialysis 5, no. 2: 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/kidneydial5020012
APA StyleLapeña-Motilva, J., Fouz-Ruiz, D., Ruiz-Ortiz, M., Sanpedro-Murillo, E., Gómez-Enjuto, S., Hernando-Jimenez, I., Frias-González, A., Suso, A. S., Merida-Herrero, E., & Benito-León, J. (2025). Cerebral Hemodynamic Alterations in Dialysis COVID-19 Survivors: A Transcranial Doppler Ultrasound Study on Intracranial Pressure Dynamics. Kidney and Dialysis, 5(2), 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/kidneydial5020012






