Abstract
In recent years, the ubiquitous occurrence of plastic debris has become a significant environmental concern, posing considerable harm to our ecosystems. Microplastics (MPs) (1 μm–5 mm) and nanoplastics (NPs) (<1 μm) are noticeable in diverse forms, spreading throughout the environment. Notably, wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) emerge as major contributors to the generation of MP and NP. Within these treatment plants, water influx from domestic and commercial sources carries a considerable load of MPs derived from items like fiber clothing, personal care products, and toothpaste. Lacking dedicated removal mechanisms, these MPs persist through the wastewater treatment process, ultimately entering natural water bodies and the soil environment. The novelty of this review lies in its detailed examination of contemporary methodologies for sampling, detecting, and eliminating MPs specifically from WWTPs. By critically assessing the efficacy of current removal techniques at various treatment stages, the review offers targeted insights into practical aspects of MP management in these facilities. As the study of micro/nano plastics is still in its early stages, this article aims to contribute by offering a comprehensive review of the methods utilized for plastic debris removal in both WWTPs and drinking water treatment plants (DWTPs). Furthermore, the article provides a comprehensive overview of the existing rules, regulations, and policies concerning MPs in the United States. This inclusion not only broadens the scope of the review but also establishes it as a valuable reference for understanding the regulatory framework related to MPs. This review uniquely combines a focused evaluation of WWTPs/DWTPs, an exploration of removal methods, and an examination of regulatory framework, making a different contribution to the review article. Through this review, we aim to enhance understanding and awareness of the multi-layered challenges posed by MPs, offering insights that can inform future research directions and policy initiatives.
1. Introduction
We are in the era of plastics, using them extensively in our daily lives. Plastics offer numerous advantages, including being lightweight, flexible, durable, adaptable, and affordable. These merits have led to widespread usage, contributing to a significant increase in global production and consumption [1,2,3]. Plastics are made up of smaller molecular units called monomers and different polymeric materials categorized by polymeric species such as polyethylene (PE), polystyrene (PS), low-density polyethylene (LDPE), polypropylene (PP), polyvinylchloride (PVC), nylon, polyethylene terephthalate (PET), polyamide (PA), and high-density polyethylene (HDPE). In 1950, the global production of plastic was 1.5 million tons, and it is expected to reach 483.19 million tons by 2030 [4]. As per recent reports, 12% of plastic waste is incinerated for energy recovery, 8% is buried in landfills, and 71% is released into the environment [5]. Internationally, a total of 353 million tons of plastic waste was generated in 2019 and only 9% was recycled. Approximately 1.7 million tons of plastic waste enter the oceans, while an additional 6.1 million tons are discharged into various aquatic bodies [6]. Small-sized plastic particles with a range of 1 μm–5 mm are known as microplastics (MPs) [1], and tiny-sized plastic particles smaller than 1 μm are known as nanoplastics (NPs) [7]. These particles are either intentionally manufactured or result from the destruction of large-size plastic debris. MPs smaller than 20 μm could enter the liver and kidneys [8]. In general, smaller-sized particles are more easily distributed. Notably, NPs exhibit even greater ease of distribution in human organs compared to MPs. Because of technical limitations in the identification of NPs in environmental samples, the research on NPs is limited, and general research is primarily focused on MPs with a size range of up to 1 mm.
Municipal WWTPs play an important role as the primary recipients of MPs and NPs originating from domestic wastewater, industrial effluents, and stormwater [9,10]. These plants stand out as important contributors to the introduction of MPs to the environment. As per the latest reports, it is estimated that the average American and Canadian household disposes of 533 million microfibers from laundry into wastewater systems yearly [11]. Around 25% of primary MPs in the oceans come from WWTPs [12]. Various research papers were published on MPs in WWTPs, focusing on the detection, characterization, and validation of new methods for MPs in wastewater samples [13], and others focused on characteristics, retention, and occurrence in WWTPs [14,15]. Several review papers have focused on MP concentrations and compositions in different wastewater treatment stages and the effect of treatment processes on MPs [10,16]. However, a comprehensive review that encompasses the generation, sources, analysis, fate, and current regulations on MPs is lacking. There is a gap in the systematic examination of the state of the art of MPs in WWTPs.
The goal of this review is to study current techniques employed for microplastic treatment and assess their efficiency in removing MPs from WWTPs. The review provides a summary of various MP detection and characterization methods, as well as treatment technologies used for the removal of MPs from wastewater and drinking water. The article also addresses the current regulatory framework regarding MPs. The primary objective is to examine the quantities of MPs entering and leaving different treatment plants. This study aims to delineate an understanding of the early stages of MP research, the existing regulatory frameworks, and proposed regulations for the future. Figure 1 illustrates the basic structure of this review.
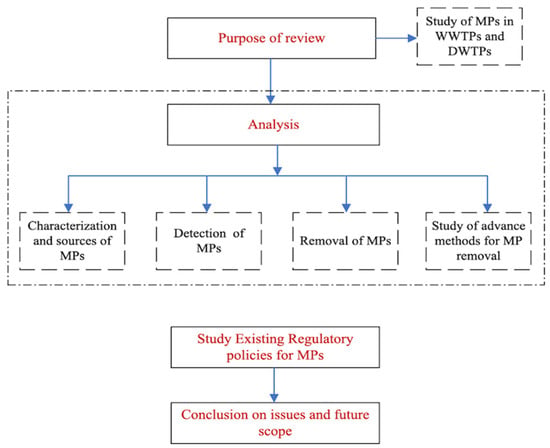
Figure 1.
Structure of the literature review.
2. Materials and Methods Study of MPs in Wastewater Treatment Plants
2.1. Sizes of MPs in WWTPs
The size of plastic debris can vary widely, but generally, they are segregated into different size ranges. Plastic particles with a size > 25 mm are known as macro-plastics, those with a size range of 5–25 mm are known as mesoplastics, those with a size < 5 mm are known as microplastics, and those with a size < 100 nm are known as nanoplastics. Degradation and fragmentation gradually cause large-size plastic items to break down into smaller particles in WWTPs [17]. Among all these size ranges, MPs and NPs are mostly studied in WWTPs. In this review, the emphasis is placed on the MPs in WWTPs due to the abundance of existing studies on MPs compared to the limited availability of research on NPs.
2.2. Sources of MPs in WWTPs
MPs have diverse origins. Two distinct sources contribute to the entry of MPs into WWTPs: primary and secondary. Probable primary sources include cosmetics and personal care products (face care, toothpaste, exfoliating agents), fibers from laundry washing (shredding of synthetic cloths, abrasion); accidental loss of pellets (during transportation, manufacturing, recycling, or processing); wear and tear of tires; debris from 3D printing, etc. [18,19]. Several countries including Canada, France, New Zealand, Sweden, and the United Kingdom have banned personal care products that contain MPs [20].
On the other hand, secondary sources of MPs in WWTPs often result from the breakdown of larger plastic items that have entered the environment. These can include the fragmentation of improperly discarded plastic such as plastic bottles, bags, or fragments from various sources into the environment, and the degradation of the primary plastics by ultraviolet (UV) light, temperature, or microbial degradation. Additionally, after the COVID-19 pandemic, inappropriately discarded facemasks were considered a secondary source in the WWTPs [21].
Across different WWTPs, the sources of MPs vary depending on the type of wastewater, area of sewer catchment, season, and population. These factors make each facility unique in terms of MP composition, posing challenges in sampling and analysis. However, recent studies have explored more methods for detecting and identifying MPs in WWTPs.
2.3. Detection, Sampling, and Analysis of MPs
This section discusses the essential aspects of the detection, sampling, and analysis of MPs. The detection process involves three stages: sample collection, sample pretreatment, and sample characterization. Figure 2 illustrates the general flowchart of MP detection in WWTPs. It is important to note that the selection of a specific method may vary depending on the sample characteristics.
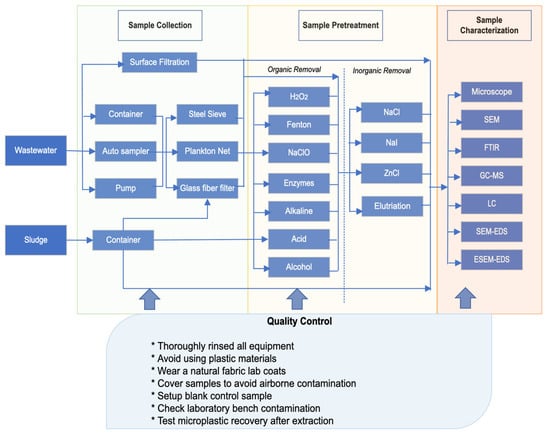
Figure 2.
Techniques used for MP detection in WWTPs adapted from Sun et al. [18], with permission from Elsevier, 2024.
2.3.1. Sample Collection
- Wastewater
In WWTPs, MPs are widely distributed in both wastewater and sludge. To date, no specific standardized method is available for sampling MPs in WWTPs. Various sampling methods are used for MP sampling from wastewater by different researchers, as illustrated in Table 1. In grab sampling, generally, 0.1–50 L of sample collection was reported from influent or biological treatment units [14,22,23]. These grab samples could be used to find the fluctuations in MP concentrations over shorter periods.
Composite sampling is also widely used, involving the combination of multiple samples into a single sample. This technique yields an average sample and offers several benefits, including improved representativeness, increased precision, and cost-effectiveness.
Surface filtration is applicable primarily at the final outfall location [9]. While this method is useful for sampling treated effluent, small-sized MPs may be easily underestimated due to the relatively large mesh size to collect large-sized samples.
The separate pumping method finds extensive use in primary, secondary, and treatment units [21]. The minimum sieve size for on-field filtration can reach down to 10 μm [14], but a preferable sieve with a pore size of >20 μm is often used to collect sample effectively [13,24].
Autosampler collections are also widely used as they are fully automated, allowing samples to be collected at required time intervals [22,25]. These devices play an important role in enhancing the precision of sample collection. To address the changes in MP concentration levels over time, automated samplers can be used for either grab sampling or composite sampling. This helps to reduce fluctuations in MP concentrations. Autosamplers can collect MPs down to 1 μm. These devices can also collect time and flow-proportional wastewater samples [21]. Specialized equipment is required for the auto-sampling method.
- Sludge
For sludge sampling, a commonly used technique is grab sampling by on-site filtration [18]. Composite sampling is also a potential method for sludge sampling, although it is not universally adopted [26]. In some cases, grab sampling along with an autosampler can be used, providing a fully automated approach [27]. More details on sludge sampling are provided in Table 1.

Table 1.
Various sampling methods for MPs in WWTPs.
Table 1.
Various sampling methods for MPs in WWTPs.
| Sampling Method | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Container collection (Grab sampling) | Manually collects water samples in containers. |
|
| [15,27,28] |
| Surface filtration | It employs a filtration system to capture microplastics present on the water’s surface. |
|
| [9,29] |
| Autosampler collection | Autosamplers are automated devices that collect water samples at specified time intervals. |
|
| [13,22] |
| Separate pumping and filtration | It involves using specialized equipment to pump water and then filter it to collect microplastics. |
|
| [14,24,25,30,31] |
| Manual grab sampling | Manually collects the sludge sample for analysis. |
|
| [21] |
| Grabbing with autosampler | Automated devices are used to collect the sludge samples. |
|
| [21,26,32] |
2.3.2. Sample Pretreatment
To ensure the robustness and cleanliness of the MP sample, it is essential to implement effective pretreatment of the water sample. Proper pretreatment procedures contribute significantly to the accuracy and reliability of subsequent MP analysis. Various methodologies have been documented for the extraction of MPs. Extraction typically involves removing natural organic and inorganic materials from samples through chemical and/or enzymatic digestion. Inorganic material separation by density separation or centrifugation follows, enabling the separation of MPs from other solids.
Normally, physical, and chemical extraction methods are applied to extract MPs. In the chemical extraction method, several digestion protocols are applied, such as 15–35% hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), Fenton’s reagents, acid-based (35–60% HNO3, 20–37% HCl), [33], and alkaline based methods (10 M NaOH) [34]. A common chemical method to remove organic matter in WWTP samples is catalytic wet peroxidation (WPO). This method, employing chemicals like H2O2, NaClO, and Fenton reagents, is widely used to pre-treat samples from different environments, such as freshwater, sediments, seawater, and organisms [33,35,36]. It is considered that major plastic debris remained unchanged during the WPO process, apart from a minor change in the size and shape of polypropylene particles and polyethylene [37].
Fenton reagents are proficient in rapidly breaking down organic compounds without affecting the MPs [38]. In the marine environment, the use of Fenton reagents is recommended by the US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) for MP analysis [36]. Another method to cleanse MPs from organic matter is enzymatic degradation. In this approach, MP samples are submerged in a mixture of enzymes such as amylase, chitinase, lipase, and cellulase [34]. In the wastewater and sludge samples, an alternate method for the removal of organic matter is alkaline treatment and acid treatment [24]. In one of the research papers, they found that the harsh condition (10 M of NaOH) would damage the MPs or their structure [34]. Additionally, the low pH intolerant polymers would be damaged by strong oxidizing agents such as nitric acid and sulfuric acids.
In the physical extraction method, the density-based separation method is widely used. Sodium chloride solution (1.2 g/cm3 NaCl) has been the most preferred salt for density separation as it can achieve higher extraction for bulkier MPs [39]. Additionally, 1.5–1.8 g/cm3 of brine ZnCl2 and 1.6–1.8 g/cm3 NaI solution can be used for the density separation [33,39,40]; moreover, oil-based separation and magnetic separation methods are used to extract MPs [41].
2.3.3. Sample Characterization
Diverse techniques are used to characterize MPs, encompassing methods such as microscopy, thermo-techniques, and spectroscopy. Table 2 offers a comprehensive summary of various characterizations. MP characterization is generally classified into two types, physical and chemical. Physical characterization mainly refers to assessing parameters like size distribution, shape, and color. The stereomicroscope is a widely used tool for physical characterization, enabling measurements of size, counts, and morphology. However, visual analysis of MPs has certain limitations due to lower magnification, leading to variations in results, and not all the MPs can be identified. It has been reported that up to 70% error could be detected and this error increased with tiny particles [42]. To reduce the overestimation of suspected MPs, a staining method has been used [24]. Nile red dye was used to stain MPs, but the efficiency can be affected by the dye used in plastic manufacturing. For example, when tire wear particles were stained with Nile red, they did not show fluorescence [43,44]. A Rose Bengal solution known for its effectiveness in staining natural and non-plastic particles [24,45]. This dye helps to differentiate MPs from other particles. However, non-plastic particles are challenging to identify, and therefore further investigation on the staining efficiency of the Rose Bengal solution, particularly on colored non-plastic debris, is crucial [21].

Table 2.
Characterization methods on MPs.
Chemical characterization, on the other hand, involves identifying the composition of MPs. Various chemical analysis methods include Raman spectroscopy [35,46,47], liquid chromatography (LC) [48], FTIR spectroscopy [14], and gas chromatography combined with mass spectrometry (GC-MS), including pyrolysis-GC-MS and thermal extraction desorption-GC-MS [49,50]. Among these, the spectroscopic technique is the most widely used to analyze MPs. The most frequently reported method for MP analysis collected from WWTPs is FTIR. Another frequently used spectroscopic method to detect MPs is Raman spectroscopy [31]. Compared with FTIR, Raman spectroscopy showed better spatial resolution (down to 1 mm) [51]. MPs can also be studied by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) based techniques. For the fast identification of plastics in the sample, GC-MS and LC-based techniques can be used. Researchers often use GC-MS methods along with thermal analysis for MP identification. This technique recognizes them through mass spectrometry analysis of the substances produced during the heating [52]. However, chemical characterization of MPs poses several challenges, including the need to examine individual molecules and difficulties arising from the addictive’s presence. The smaller size of MPs adds complication to the extraction and isolation process [53]. MPs are often found in complex matrices (sediments, biological tissues, etc.) where the surrounding environment can impact their chemical properties [54] and this matrix effect interferes with the analysis. The presence of additives (dyes and fillers) adds another layer of complexity to MP’s chemical characterization [55].
2.4. Occurrence of MPs in WWTPs
A comprehensive exploration of the presence of MPs in WWTPs is covered in this section. A study explores the pathway of MPs within treatment systems, assessing their potential effects on water quality and the ecosystem. Summarizing the concentration of MPs in various WWTPs proves challenging due to insufficient particle concentration in some facilities, making it difficult to fully grasp the extent of MP presence. Nonetheless, this section aims to present an overview of the current situation regarding MPs in WWTPs.
Primary treatment units, such as screening, grit removal, primary clarifiers, and sedimentation with flocculation aim to remove MPs with different densities. The secondary treatment units, which involve processes like the activated sludge process, membrane reactors, or other biological treatments along with secondary clarifiers, contribute to a substantial reduction in MPs. In the primary treatment phase, MPs that have different densities can be removed via grit removal and a primary clarifier [56]. Plastics are non-degradable in a shorter time frame; therefore, in a limited timeframe, secondary biological treatment is unable to degrade MP. Although the primary objective of WWTPs is not MP removal, approximately 0.2–14% of MPs may be disposed of with sludge and extracellular substances generated by micro-organisms [18,56].
Many WWTPs implement tertiary treatment to further remove MPs, employing methods such as coagulation, flocculation, sedimentation, filtration, and membrane bioreactor (MBR). However, these technologies have disadvantages, including limitations in the removal of polyethylene by coagulation, flocculation, and sedimentation (CFS), variations in MP removal efficiency by CFS techniques, and the exclusive removal of MPs larger than 20 μm by filtration and MBR [57,58].
Despite daily treatment of large water volumes in WWTPs, a significant number of MPs can escape, making these treatment plants major contributions to MPs pollution in the aquatic environment [59,60,61]. Various shapes and sizes of MPs, including granules, film, fibers, and spherical, are found in aquatic ecosystems. Fibers, characterized by their thin structure, smooth surface, and ease of passing through membranes [18,62,63], exhibit lower removal efficiency in WWTPs than other shapes but can be addressed through coagulation or the activated sludge process [56,63]. More details on MP removal in primary, secondary, and tertiary treatment are discussed in Section 2.6.
Fragmentation of MPs in WWTPs
In WWTPs, MP fragmentation and NP generation take place due to stirring, mixing, and pumping at various stages [64]. In the same study, it was found that the release of smaller-sized plastic particles into the environment after wastewater treatment is 40 times higher than the initial levels of MPs. This increase is credited to the fragmentation of MPs during various stages of treatment in WWTPs. Several mechanisms contribute to the fragmentation of MPs into NPs during the water treatment process including sand abrasion, UV irradiation, mechanical breakdown, crack formation, stress, hydrolysis, bio-assimilation by micro-organisms, and water shear forces [65].
The likely reason for fragmentation is the mechanically induced water shear force on the MP surface, resulting in abrasion, collision, crack propagation, and friction with impeller blades. However, secondary MPs may be produced at each treatment stage. Initially, larger particles over 5 mm may be present in the liquid at the treatment’s outset, typically removed during the initial stages through processes like screening and grit removal. Subsequently, actions like mixing, pumping, or bubbling generate forces in the water, breaking down larger particles into smaller MPs [18,30].
In the secondary treatment stage, MPs encounter the activated sludge process. Some studies report that a few microbes could fragment MPs into smaller MPs or NPs, indicating negligible biodegradation of MPs [66]. However, other studies suggest that biofilm formation by microorganisms during biological processes may cause MP fragmentation. For example, one of the researchers examined that biofilm may interrupt MP structure by altering its surface properties, and leaching enzymes ultimately enhance MP’s brittleness [67]. Specific chemical structures in polymers can be recognized by microorganism enzymes, expediting the biodegradation process [68].
During tertiary treatment, which involves processes like disinfection in WWTPs, certain MPs like polyethylene, polystyrene, and polypropylene tend to degrade or fragment [69,70]. Disinfection can indirectly impact the structure of these plastic particles. Ozonation in wastewater treatment, using ozone as a strong oxidizing agent, breaks down the chemical double bonds in polymers, causing MPs degradation [71]. Therefore, it can be concluded that MP fragmentation to NP takes place in WWTPs during various treatment stages. However, further scientific investigation is required to precisely determine the mechanisms involved.
2.5. MP Characteristics and Concentrations in WWTPs
WWTPs are recognized as significant sources of MP release into the aquatic environment [15,72]. In typical WWTPs, MPs are observed in both influent and effluent, displaying their characteristic appearances. Microbeads from personal care products and small-sized plastic fragments originating from larger plastics and synthetic fibers are sometimes visibly present. Several studies have identified over 45 types of MP polymers in WWTPs. These polymers include polyether sulfone (PES) and polyacrylamides (PAM), primarily produced in textile industries and medical devices, as well as PET among others. Polymers like PS, PE, and PP originate from personal care products, cosmetics, and the food packaging industry [73].
As shown in Table 3, different types of plastic particles are detected in different stages of WWTPs. The enormous variations in MP concentrations in these WWTPs may be attributed, in part, to differences in sample collection techniques, pretreatment methods, and analysis methods in various studies. Standardizing methods for MP sampling and analysis is crucial for establishing a more direct comparison of concentrations across different studies. In WWTPs, a large portion of the entering MP originates from diverse human activities, such as wearing synthetic clothing, using various plastic products, and household discharges, all of which directly affect the concentration of MPs. A statistical analysis conducted on 17 different wastewater treatment plants in the U.S. revealed a positive association between population size and total MP concentration in wastewater [30]. Information from different areas with varying economic levels and living standards underscores the significance of understanding MPs, as it impacts their concentration levels.

Table 3.
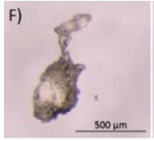
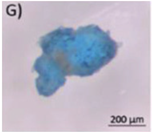
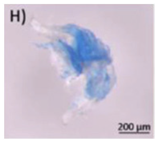
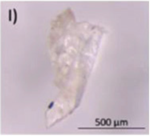
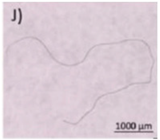
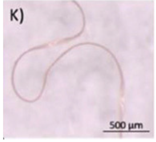
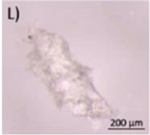
Typical appearance of different polymers detected in WWTP identified by μ-FTIR and/or μ-Raman, reproduced from [47], with permission from Elsevier, 2024. (A–E) Polyester, (F–I) Polyethylene, (J–K) Polyamide, and (L) Polypropylene.
Generally, tertiary treatment processes exhibit lower MP concentrations (0–51 particle/L) in the effluent of WWTPs compared to primary or secondary treatment processes (0–447 particle/L). However, studies showed that tertiary treatments may not further reduce MP concentrations in the effluent of WWTPs [14,30].
2.6. MP Removal in Various Stages of WWTPs
The calculation of MP removal in WWTPs is based on their concentrations in the influent and effluent streams. The concentration in each treatment plant is different depending on various factors such as the nature of the influent, the lifestyle of people, the season, and the level of treatment. Figure 3 presents values from existing literature to estimate how MPs flow through different stages of treatments, including preliminary, primary, secondary, and tertiary treatments, each with its efficiency in removing MPs. The removal rate of MPs varies based on the physicochemical characteristics of plastic particles, the treatments used in WWTPs, and the operating conditions during treatment. Generally, WWTPs operate on primary, secondary, and occasionally tertiary treatment [74]. Various mechanisms contribute to the removal of MPs, including the interception of MPs by screens, accumulation of suspended plastic particles through skimming, and the separation of heavy particles by adhering to solid particles, followed by removal through gravity sedimentation.
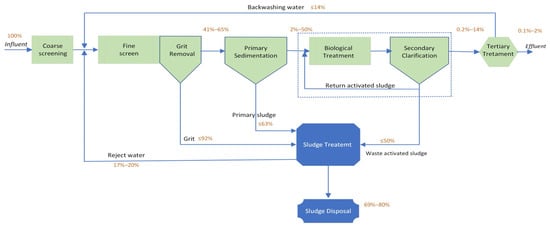
Figure 3.
Estimated MPs flow in WWTPs with primary, secondary, and tertiary treatment processes adapted from Sun et al. [18], with permission from Elsevier, 2024.
2.6.1. Removal during Preliminary and Primary Treatment
Maximum efficiency in MP removal is typically achieved during the preliminary and primary treatment stages. The main mechanism responsible for the removal of MPs during the pre-treatment stages is skimming. Light-floating MPs are efficiently removed through grease-skimming or surface-skimming in primary clarifiers, while heavy MPs settle or become trapped in solid flocs during gravity separation and grit removal [31]. Several studies have shown that pre-treatment is particularly effective in removing fibers compared to fragments in terms of shapes, with the relative numbers of fibers decreasing after pretreatment [24,25]. Microbeads, for instance, can be effectively removed during the skimming process [14]. A survey conducted in New York, USA showed that 4 out of 10 WWTPs still release microbeads after preliminary and primary treatment [75].
In the primary stage, aluminum and ferric salts are added as coagulants to disturb the surface charge of pollutants and facilitate flocs formation with MPs in wastewater. These flocs are subsequently removed through the skimming or settling process. The efficiency of coagulation in removing MPs can reach as high as 90%, depending on factors such as pH, the physical–chemical characteristics of MPs, coagulant dosages, and the specific chemical composition of coagulants [63]. In the primary treatment process, the absorption of MPs onto the lipid fraction of primary sludge through hydrophobic interactions, as well as their adsorption on the surface of the sludge particles via electrostatic interactions, collectively referred to as “sorption”, represents a significant and predominant mechanism for MP removal. This means that MP transitions from the liquid phase (wastewater) to the solid phase (sludge) [76]. However, MP retained within the sludge can leach out during sludge disposal, posing a significant challenge. Addressing this issue requires the implementation of supplementary treatment technologies or the adoption of sludge disposal methods designed to effectively remove MPs from the various environmental metrics. In Korean WWTPs, high MP removal efficiencies (57–64%) were observed during the primary treatment stage [71]. Similarly, 92% of removal in Canada [23], 74% of removal in Spain [77], and 78% of removal in Scotland [15] have been reported. The high removal efficiencies (>90%) were only reported for fibrous MPs during primary steps [47].
2.6.2. Removal during Secondary Treatment
In the secondary treatment stage of WWTPs, MP levels undergo further reduction during the biological treatment and clarification process. During the aeration process, tiny air bubbles attached to floating MPs, resulting in them rising to the surface and being removed through skimming. Approximately 95% of MPs have been removed by dissolved air floatation (DAF) [78]. Throughout the secondary treatment in the aeration tank, extracellular bacterial polymers, or sludge flocs play an important role in collecting remaining MPs. These small MPs are then separated and settled in the secondary clarifier. MPs can also become trapped within sludge flocs due to ingestion by protozoa or metazoans [79].
Additionally, chemicals used during flocculation, such as ferric sulfate, or other chemicals, can have a beneficial effect on MP removal, as flocculants encourage suspended particles to come together and form larger aggregates known as “flocs” [15]. Another important factor during this stage is the contact time of MPs in wastewater. Prolonged contact time has been linked to a higher possibility of surface biofilm coating on MPs, possibly functioning as wetting agents and altering the relative densities or surface properties of MPs [9]. This change significantly affects the removal efficiencies, with more fragments being removed than fibers in the secondary treatment [24,25]. Research has also shown that MPs larger than 500 μm are nearly absent from the secondary effluent [14,24].
Commonly used secondary treatment technologies in WWTPs involve biological processes, with activated sludge processes (ASP) being particularly frequent. These processes depend on the activated microorganisms present in the sludge to degrade or transform, as noted by these authors [80,81]. The key mechanism of MP biodegradation involves a series of stages, comprising integration and mineralization [82]. Small-sized plastic particles are consumed by microorganisms and hydrolyzed into simpler units through intracellular degradation [16].
Different biodegradation mechanisms can be identified based on the chemical structure and polymer types of MP. For example, the bacterium Ideonella sakaiensis can degrade PET in ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid through enzymes like PETase and MHETase [83]. Similarly, Azotobacter beijerinckii can degrade PS, and enzymes like esterase, protease, and lipase efficiently degrade polyester polyurethane [84]. MPs can serve as attachment surfaces for bacterial growth, which leads to the formation of biofilms. During biofilm formation, biomass may produce extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) that fasten the breakdown of MPs [85]. Studies have shown that biofilms provide higher degradation efficiency, with some strains actively engaged in degradation [86,87,88]. MP biodegradation is influenced by temperature, humidity, sunlight, and microbial enzymes. MPs also adsorb EPS or the secondary sludge and head toward their accumulation and sedimentation [89]. From the perspective of the activated sludge process, MP removal efficiency varies, ranging from 42% to 98%, depending on factors such as operational parameters and wastewater characteristics [15,47,71,77,90].
2.6.3. Removal during Tertiary Treatment
Tertiary treatments are specially designed to target recalcitrant solids, nutrients, and pathogens. In a study by [78], different tertiary treatment processes, such as disc filters (DF), rapid sand filtration (RSF), dissolved air flotation (DAF) for treating secondary effluent, and membrane bioreactor (MBR), for treating primary effluent, were compared. MBR showed the highest removal efficiency at 99.9%, followed by RSF at 97% and DAF at 95%. Therefore, tertiary treatment can significantly enhance the removal of MPs.
The removal efficiency of DF ranged from 40 to 98.5% [31]. Additionally, another study observed that MP concentrations decreased after ultrafiltration and RO treatments [24]. However, granular advanced filtration (GAF) did not reduce the MP discharges from WWTPs [30]. After tertiary treatment, the smallest size fractions, ranging from 20–100 µm and 100–190 µm, were found to be most abundant [24]. Additionally, it was found that, through filtration and activated carbon-based adsorption, MPs can be efficiently removed during tertiary treatment [91].
One of the research projects reported that 56% of MPs can be removed using a sand filter in Italy [40]. In one of the WWTPs in China, it was found that using sand filters an overall MPs removal efficiency ranged from 29–44% with higher retention, 31–49% removal for pellets, and 24–51% removal for fibers, and 19–28% removal for fragments observed. Rapid sand filters, which consist of various media layers such as gravel, anthracite, silica, sand, etc., have been shown to have good MP removal efficiency [63]. A report [71] mentioned that 74% of MP removal efficiency was found after passing wastewater with an influent concentration of 215 MPs/L through a rapid sand filter (RSF). Likewise, another research achieved 97% removal efficiency from w/w with an initial concentration of 0.7 ± 0.1 ppm by passing through RSF [13]. Thus, it can be concluded that sand filters can efficiently remove MPs in a low concentration range. A study demonstrated that the use of granular-activated carbon (GAC) filters has also shown 60.9% of MP removal [92].
It is important to note that MPs can experience further fragmentation due to physical (mixing, aeration) or chemical (disinfectant addition) tensions induced in WWTPs during different processes. For instance, the hardness of the silica sand filter is much higher (14.10 GPa) than polypropylene (PE) based MPs (0.9 GPa), which results in further fragmentation of MPs in sand filters. These small MPs may then disperse rather than cluster due to turbulent conditions in WWTPs, leading to the release of more MPs in the treated effluent compared to the influent concentration.
Various assessments have reported MP concentrations in the influent of WWTPs ranging from 0.14 to 3.14 × 104 particles per liter (particles/L). These concentrations decreased to a range of 0.001 to 297 particles/L in the effluent. The actual values can vary depending on factors such as the source of wastewater, daily and seasonal variations, temperature, sampling techniques, and plant operational parameters. In several studies from different countries, they investigated influent and effluent concentration as well as the efficiency of MPs in wastewater treatment plants [63,65,93]. Their findings are summarized in Table 4 below.

Table 4.
Concentration and removal efficiencies of MPs in different countries WWTPs (reproduced from [94]).
2.7. Potential Advanced Treatment Technologies MP Removal
Several advanced methods could be used for the removal of MPs from the WWTPs. Research developed a gravity-powered filtration system aimed at removing MP from secondary effluent in WWTPs [99]. The system can operate in two modes: filtration mode to filter MPs out of wastewater and backflush mode to wash the MPs out of the system. The feasibility of MP removal using dynamic membranes suggests that this technology could be further developed to remove MPs in an energy-efficient manner, but the construction and operational costs need evaluation [100].
An economical approach to developing targeted MP treatment technology is to adjust the relevant operational parameters of existing wastewater treatment processes. For instance, the impact of operational conditions like hydraulic retention time (HRT) on MP removal can be investigated in the skimming and sedimentation units in the future for potential improvement, as indicated by [31]. Improvements in flocculation and coagulation techniques could also play an important role in MP removal. Al-based coagulants exhibited better MP removal efficiency than Fe-based coagulants [101]. Polyacrylamide (PAM) can enhance MP removal efficiency in drinking water systems. For the removal of MPs in activated sludge, the ideal solution is to enhance the MP removal during the grease removal stage and treat grease separately to prevent MPs from entering the sludge waste.
The pyrolysis technique is an efficient method for treating MPs, breaking down long-chain polymers into oligomers as documented by Juiastuti et al. [102]. The calorific value of plastic is comparable to hydrocarbon fuels, making pyrolysis a cost-effective way to convert plastic into fuels, as indicated by Wong et al. [103]. Some other advanced methods are discussed here.
2.7.1. Electrocoagulation
In the electrocoagulation (EC) process, during the anodic reaction, metal ions are generated through the electrochemical dissolution of metal electrodes such as iron (Fe), manganese (Mn), aluminum (Al), etc. These metal ions generated at the anode react with OH− ions produced in a cathodic reaction to create metal hydroxide coagulants [104]. These metal hydroxide coagulants are effective at removing MPs by disrupting their surface charges and encouraging flocs formation. There is a generation of hydrogen gas bubbles at the cathode, which is a result of the electrolysis of water. This causes the flocs to rise to the top of the reactor. These flocs can later be removed through skimming or overflow [105]. A high MP removal efficiency of around 99.24% was observed at a current density of 11 A/m2, 7.5 pH, NaCl (0–2 g/L) was used as an electrolyte, and liquid soap was added as a surfactant [59]. The addition of the surfactant helps to develop the surface charge of the polyethylene, encouraging higher coagulation and flocculation; thus, electrocoagulation enhances the removal of MPs.
2.7.2. Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOP)
Advanced oxidation processes are chemical oxidation reactions that use various reactive oxygen species (ROS) to break down persistent contaminants. Hydroxyl and sulfate radicals are commonly used ROS to degrade wide-ranging contaminants in aquatic environments [106]. In the WWTPs, chlorine is often used as a disinfectant, but MP is not fully resistant to chlorine. Chlorination can alter the physical and chemical properties of MPs due to its strong oxidizing nature. UV oxidation also affects the topography and chemical characteristics of plastic particles. Under UV radiation, peroxy free radicals are generated from the breaking of C-C and C-H bonds and formed cross-linking compounds through secondary reactions. This leads to a reduction in the relative molecular mass of MPs [70].
Likewise, ozonation can break down the polymer structure of MPs into oxygen-containing functional groups, which effectively remove plastic particles and change their physicochemical properties including hydrophobicity, surface tension, adhesive properties. [63]. Several studies showed that around 90% of MPs could be removed with just 30 min of ozonation [71]. Moreover, approximately 90% decomposition of MPs could be achieved after 60 min of ozonation at 35 to 45 °C as highlighted by [71]. Thus, it can be concluded that AOPs are a promising alternative to MP removal from the environment because of their ability to break down and alter the properties of plastic particles.
2.7.3. Membrane Technologies
Researchers have tried different membranes that can trap these tiny particles. A study by Liu et al. [95], found that ultra-filtration (UF) membranes remove up to 96% of MPs while microfiltration (MF) membranes can remove 91% of tiny plastic particles [64]. Another study showed that electro-spun membranes removed 90% of MPs that were 50 nm in size. A specialty of these membranes is that they work well and are not easily clogged [92]. The only trouble with this membrane is as water passes through it, a layer of pollutants builds up on the membrane’s surface and that makes the membrane less effective as MPs become stuck on this layer. This process is called fouling, which reduces the membrane’s ability to filtrate. To overcome this issue, it is important to have a proper system to clean the membranes regularly (by backwashing). This aids in keeping the membranes working efficiently.
2.7.4. Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology offers a potential possibility to remove MPs from the environment. It can be a powerful tool not only for the removal of plastic particles but also for the detection and treatment of toxic pollutants. Engineered nanomaterials (ENMs) have similarities with NPs in terms of size and colloidal properties, making them a valuable source [107]. ENMs could be a reference point to understand the MP’s behavior and their environmental impacts [108]. For example, recent research showed that silver nanoparticles could interact with MPs in water and shed light on the nanomaterials and microplastic relationship [109]. Thus, various nanomaterials need to be developed to assist in breaking down plastic materials. For example, the presence of SiO2 nanoparticles can reduce the lag phase of plastic-degrading bacteria and enhance biodegradation [110]. In summary, nanotechnologies have a great ability to address the challenge of MPs in the environment and they can play an important role in removing and understanding the impact of these pollutants on the ecosystem.
The challenges associated with MPs are well-acknowledged, primarily due to their diverse characteristics. Beyond variations in sizes, shapes, and polymer types, MPs can also contain additional elements such as dyes, fillers, and plasticizers. Consequently, the efficacy of a specific separation technique is contingent upon the composition of the MPs being treated. It is crucial for the researchers to exercise caution and consider this diversity when interpreting results regarding the percentage of MPs removed by a particular method. A single approach may not be universally optimal, emphasizing the need for a nuanced selection of methods based on the unique characteristics of the MPs in question.
3. Study of MPs in Drinking Water Treatment Facilities
Drinking water treatment plants have an important role in enhancing water quality and making it safer for consumption. Traditional drinking water treatment aims to ensure that water is free from physical, chemical, and biological contaminants, including heavy metals, suspended particles, and microorganisms. Hence, DWTPs play a very important role in safeguarding public health by preventing MPs from transferring drinking water from its source. Different countries and regions have different standards for drinking water treatment, but presently, there are no specific techniques or governmental regulations in place to monitor the presence of MPs in drinking water [111,112,113]. However, several methods and techniques have been discovered to remove MPs from drinking water, which redirects ongoing efforts to address this concern [114]. These actions are essential for ensuring the safety and quality of drinking water for societies around the world.
3.1. Occurrence of MPs in Drinking Water
There are various ways through which MPs could enter the drinking water such as shaking the plastic bottles, wearing, and washing them, degradation of bottles, and direct contamination and there are also indirect ways of contamination such as washing synthetic fiber-based fabrics. The microfibers shed during the washing process, enter wastewater, and may not be captured by WWTPs. As a result, they accumulate in water bodies and probably reach drinking water sources. This kind of contamination can bypass traditional filtration methods and make the removal of MPs challenging [114]. For the accurate analysis and identification of the type of plastics in drinking water, several techniques were employed such as Raman spectroscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), flow cytometry, gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC-MS), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and pyrolysis [115,116,117].
The presence of MPs in food products and seawater has been widely studied in the past decade; however, studies examining the MP level in tap water is relatively limited [114]. However, tap water samples from various countries concluded that 83% of samples have microplastics fragments and fibers (0.1 to 5 mm length) [111]. A study found that smaller-sized plastic particles (50 μm) were present in tap water samples from different provinces of China [118]. It is important to note that WWTPs may not be able to remove all the MPs from wastewater, which increases the concerns about potential toxicological effects on humans and other organisms [119]. This emphasizes the need for improved techniques to address plastic contamination in drinking water systems.
3.2. Treatment Processes to Remove MPs from Drinking Water
Treatment processes to remove MPs from drinking water are essential to mitigate their harmful impacts on human health. There are several harmful effects such as oxidative stress, inflammation, necrosis, genotoxicity, cytotoxicity, and effects on cells and tissues due to MPs entering the drinking water [120,121]. Therefore, proper treatment technology is required to treat and remove MPs from drinking water. Traditional techniques used for the treatment of MPs such as flocculation, rely on interactions like hydrogen bonds, van der Waals forces, and electrostatic forces [95]. Hydrophilic polysulfone membranes have shown a high capability to absorb MPs within or onto the membrane surface [95]. Additionally, magnetic nanoparticle mixtures have been employed to remove various pollutants such as inorganic, organic, microbial, and microplastics pollutants as well [107]. These techniques provide a potential approach to mitigate the adverse impact of microplastics pollution in drinking water and safeguarding human health.
Strategies to Remove MPs from Drinking Water
Conventional drinking water treatment processes, which cover coagulation, sedimentation, sand filtration, and clarification, have shown potential to reduce the abundance of MPs in treated water [113]. The presence of MPs with sizes less than 1 mm was investigated in both raw and treated water [113]. Their results determined that traditional methods were effective in reducing MP levels in treated water when compared to raw water. Specifically, the removal efficiency was found around 70% for the treatment process that utilized coagulation/flocculation and sand filtration, 81% for a method that included coagulation/flocculation, sedimentation, sand filtration, and activated carbon filtration, and 83% for a treatment process involving coagulation/ flocculation, flotation, sand, filtration, and carbon filtration. These findings highlight the substantial reduction in MP achieved by employing these methods. Another study revealed the presence of MPs throughout the drinking water supply chain and supported the conventional method’s effectiveness in the removal of MPs [122]. In particular, small-sized MPs (less than 1 mm) can be more efficiently removed from raw water by these traditional methods. Therefore, it can be concluded that conventional treatment methods are very important for mitigating microplastic contamination in drinking water.
- Electrocoagulation
Electrocoagulation is a process that uses metal electrodes to produce coagulants through electricity to simplify and strengthen the coagulation process [105]. In electrocoagulation, metal electrodes produce cations when exposed to an electric field. There are three stages in electrocoagulation (see Figure 4A). (1) An electric field produces electrons at the anode, forming “micro-coagulants” such as Fe3+ or Al3+ hydroxides. (2) Coagulants trigger suspended particles and colloidal pollutants to lose their stability in the water (3) Once they destabilize, micro-coagulants and pollutants collide and form micro-flocs [112].
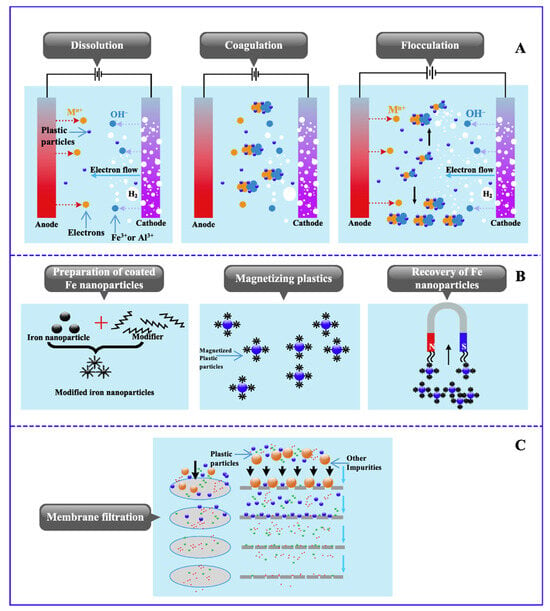
Figure 4.
Various strategies and methods to remove MPs from drinking water, adapted from Shen et al. [112], with permission from Elsevier, 2024. (A) MP removal by Electrocoagulation (B) MP removal by magnetic extraction (C) MP removal by membrane separation.
This method offers several advantages including environmental compatibility, automation ease, minimum sludge production, low capital costs, and energy efficiency. It has been also utilized to remove other contaminants from drinking water [123]. Remarkably, researchers conducted a study to examine the performance of electrocoagulation in removing MPs from wastewater under lab conditions and they found it to be an effective method [59]. The removal efficiency of over 90% was observed for polyethylene. At a pH level of 7.5, the highest removal was detected around 99.24%. This makes electrocoagulation a feasible option for removing MPs from drinking water. Despite certain limitations related to removal efficiency and operational costs, electrocoagulation proves to be a transferable and reproducible technique, making it suitable for transitioning from lab-scale to industrial levels [124].
- Magnetic extraction
In [41], the efficiency and effectiveness of magnetic extraction for the removal of MPs from water were examined. Magnetic extraction is a separation method that uses magnetic seeds and acid along with an external magnetic field to improve the separation practice. To make the process hydrophobic, iron (Fe) nanoparticles needed to be coated with hexadecyltrimethoxysilane which helps to enable the isolation of MPs from water. Figure 4B illustrates the process of preparing coated Fe nanoparticles and the removal of MPs by magnetic extraction. The study found that medium-sized (200 μm–1 mm) MPs had recovery rates of 84% in fresh water and 78% in sludge/sediment. For smaller MPs (<20 μm), 92% of polyethylene and polystyrene were easily recovered from seawater. Therefore, the researchers suggested that magnetic extraction might be particularly well-fitted for drinking water treatment [41].
- Membrane separation
Membrane separation is a commonly used technology for the advanced treatment of drinking water due to its advantages, including consistent effluent quality and simple operation [125]. This technology can be categorized based on the membrane size, which includes reverse osmosis, ultrafiltration, and nanofiltration. The functioning principle of membrane separation for water purification is shown in Figure 4C. By applying a pressure difference, the membrane’s pores are employed to capture MPs present in raw water. Although membrane separation is not specifically designed to remove MPs, its membrane pore size range aligns with that of the microplastics [126]. This alignment allows membranes to effectively serve as a physical barrier against MPs in drinking water treatment, offering a practical method to reduce MP contamination [13].
- Treatment using microorganisms.
Microbes have proven to be consistent in degrading pollutants, including heavy metals, oil spills, organic pesticides, polychlorinated biphenyls, and polycyclic aromatic Hydrocarbons (HCs), owing to their diverse metabolic capabilities [127]. Hydrolytic enzymes, such as CMCase, chitinase, xylanase, lipase, keratinase, and protease, which are secreted by bacteria, have been identified for their ability to degrade microplastics [128]. The biodegradation of plastics by microbes involves the release of extracellular enzymes, attachment to plastic surface, and consequent hydrolysis resulting in the formation of shorter polymeric intermediates. These intermediates contribute as a carbon source for microbial cells which leads to the production of CO2 [129].
- Treatment using membrane bioreactors.
Membrane bioreactors have demonstrated remarkable efficiency in removing microplastic during water treatment, reducing the microplastic concentration from 6.9 to 0.005 MPs/L (99.9% removal). Similarly, sand filters show a substantial removal capacity, reducing the MP concentration from 2 to 0.1 MPs/L. In comparison, disc filters have a wide range of performance with removal capability from 0.5 to 0.03–0.3 MPs/L (40–98.5%) [78]. Notably, membrane bioreactors stand out as a promising technique for effectively treating MP compared to conventional techniques [130].
- Treatment using ultrafiltration.
Ultrafiltration represents a newer MP treatment approach and offers advantages over conventional techniques. In this method, the water is passed through a special filter with small pores that catch the MPs, but the removal efficiency depends on the type and structure of MPs in the water [131]. Previous studies suggested that MPs can be eliminated by using a combination of aluminum (Al) or iron (Fe) salt coagulation along with UF [101]. Also, the UF process of MP removal was more efficient than the carbon filtration [132]. This method proves superior performance and contributes to cost reduction through better process automation and control. Apart from removing MPs efficiently, UF is also effective in eliminating suspended solids, algae, and cyanobacteria to a greater extent (up to six times higher) compared to traditional methods. Furthermore, this method can efficiently remove viruses and bacteria from water [133].
3.3. Status of MPs in the United States Drinking Water Treatment Plant Facilities
Microplastics in drinking water have attracted increased attention globally, but research on this may be comparatively limited in the United States. As MPs in water and drinking water are a relatively new and emerging field, it takes time for scientific studies to develop methods for the treatment. Currently, as discussed in previous sections, MPs are found in various water samples including river water or any other natural freshwater bodies, influent and effluent of WWTPs, and raw and treated water at drinking water treatment plants, as well as bottled filtered water. The concentration of MPs varies, ranging from negligible to several thousand items per liter, depending on sample types, sampling technique, sample preparation, and analysis methods.
Research on the MP levels in drinking water in the United States is limited, reflecting a relatively understudied aspect of assessing the quality of drinking water. The absence of legislative limits for MP content in drinking water makes it challenging to assess whether the concentration is too high or low. Further research is crucial in the field of MP detection and treatment in drinking water. There is a need to investigate the number and types of MPs present in drinking water, explore effective removal methods during treatment, and monitor the fate of MPs after removal, considering their non-degradable nature. Additional studies in this area will contribute to a better understanding of the potential risks associated with MPs in drinking water and aid in the development of appropriate regulatory measures and treatment strategies.
4. Current Regulations and Policies on MPs in the United States
In the United States, legislative authority is distributed across different levels, including city/town, county, state, and federal levels. Typically, county laws supersede city laws, and state laws take precedence over both county and city laws, while federal laws override all state laws. Various regulatory agencies, established by the US Congress, play a crucial role in formulating rules and regulations to facilitate the implementation of diverse laws [134]. In the context of toxicological issues, key agencies include the US Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA), the US Department of Agriculture, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), the Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC), and the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA). Plastic regulation falls under the purview of OSHA, FDA, USEPA, and CPSC.
As of now, the USEPA has not set specific criteria for plastic waste in water, leaving individual states responsible for such determinations [135]. The Safe Drinking Water Act (SDWA) focuses on ensuring safe drinking water in the USA, establishing permissible limits for natural and anthropogenic contaminants. However, plastic polymers are not currently classified as anthropogenic contaminants under SDWA [136].
A significant milestone in addressing MPs in the USA was the Microbead-Free Waters Act, signed into law by former President Barack Obama in 2015. This legislation, an amendment to the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FFDCA), prohibits the use of plastic microbeads in cosmetics’ packaging, manufacturing, and distribution [20,137]. This marked the first legal initiative specifically targeting MPs in the country. The law led to the cessation of microbead manufacturing for rinse-off cosmetics, and, as of 2019, products containing microbeads are no longer permitted in interstate trade [137]. In 2018, the Save Our Seas Act, focusing on marine debris, became law, and in 2020, former President Donald Trump signed the Save Our Seas 2.0 Act, which further addresses plastic particles and debris in US aquatic environments.
While there is no national ban on single-use plastic in the USA, some cities and states have implemented local laws. For instance, California became the first state to ban plastic bag usage in retail stores in 2017. Other states, including New York, Delaware, Connecticut, Oregon, Vermont, Maine, Puerto Rico, and the US Virgin Islands, have also imposed bans on single-use plastic bags [138,139,140]. Additionally, individual cities, such as San Francisco in California, have taken measures like proposing a tax on plastic bags, and some have implemented bans [141]. Various regions have extended bans to other plastic items, such as plastic straws, with examples like Williamstown, Massachusetts, banning plastic straws in 2015, and Washington DC initiating a ban in 2019 [142]
In 2018, California began enforcing standards on the levels of MPs in drinking water, requiring a formal definition of MPs and a standardized testing methodology for measuring contamination levels [143]. However, establishing robust policies on MPs remains challenging due to the widespread presence of MPs, the relatively early stage of research in microplastics analysis, and the associated costs of developing standardized measurement methods.
Moreover, MPs removed from effluent water often end up in sludge. The disposal of sludge varies, including methods such as sending it to landfills, using it in agriculture, adding it to compost, and incineration. Addressing the environmental impact of the fate of sludge and its contained MPs is crucial for future studies, providing a comprehensive understanding of the problem of MPs.
5. Conclusions
The state-of-art review on MPs reveals numerous challenges and concerns that, if left unaddressed, could pose significant threats to humans, aquatic ecosystems, soils, organisms, and the atmosphere in the future. Several key issues underscore the urgency of comprehensive action:
- Lack of Standardized Techniques: The absence of standardized techniques for the detection and analysis of MPs hinders accurate assessment. It is imperative for future studies to establish uniform procedures, ensuring the generation of reliable and comparable data for effective analysis.
- Need for Risk Assessment: A critical aspect involves conducting a thorough risk assessment of MPs, considering factors such as toxicity, exposure routes, and concentration. This holistic evaluation is essential for understanding and mitigating potential hazards associated with microplastic pollution.
- Limited Research on NPs: The existing body of research on NPs is notably limited, emphasizing the necessity for more extensive studies to comprehend their implications fully. This is crucial for developing informed strategies to manage and mitigate nanoplastic-related challenges.
- Public Awareness and Policy Gaps: The lack of public awareness, coupled with gaps in policies addressing MP pollution, poses a significant challenge. Delays in creating effective mitigation strategies may result from this insufficient understanding and regulatory framework.
- Challenges in Water Treatment Plants: Existing water treatment processes, such as skimming, sedimentation, and tertiary filtration, are not specifically designed for the removal of MPs. Consequently, a substantial quantity of microplastics can still be discharged with the effluent into aquatic systems, emphasizing the need for targeted interventions.
- Lack of Dedicated Treatment Processes: At present, full-scale wastewater treatment plants lack comprehensive processes exclusively dedicated to MP removal. The technology addressing microplastics in treatment is still in the early stages of research and development, requiring further exploration for practical and scalable solutions.
In light of these challenges, proactive measures are essential to prevent future problems for both humans and the environment. This includes ongoing research efforts, the development of effective and economical treatment technologies, raising public awareness, and the formulation of robust policies. Only through a multifaceted approach can we hope to mitigate the potential negative impacts of MP pollution.
Key future perspectives include conducting thorough risk assessments for MPs, establishing standardized detection techniques, expanding NP research, addressing public awareness and policy gaps, developing dedicated treatment methods, and improving water treatment processes. These steps are crucial to prevent potential negative impacts on ecosystems and human health. They underscore the need for ongoing research, technological innovation, and comprehensive policies.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.W. and K.V.; methodology, S.W.; validation, V.J. and S.W.; formal analysis, V.J. and S.W.; investigation, V.J.; resources, V.J.; data curation, V.J.; writing—original draft preparation, V.J.; writing—review and editing, S.W. and K.V.; visualization, V.J.; supervision, S.W.; project administration, S.W.; funding acquisition, S.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by NOAA, grant number NA23OAR4170169.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) for their support in this study, as well as the Mississippi-Alabama Sea Grant Consortium.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Andrady, A.L. Microplastics in the marine environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 1596–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monira, S.; Bhuiyan, M.A.; Haque, N.; Pramanik, B.K. Assess the performance of chemical coagulation process for microplastics removal from stormwater. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 155, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshewy, A.; El Hariri El Nokab, M.; Sayed, J.; Alassmy, Y.A.; Abduljawad, M.M.; D’hooge, D.R.; Van Steenberge, P.H.M.; Habib, M.H.; Sebakhy, K.O. Surfactant-free peroxidase-mediated enzymatic polymerization of a biorenewable butyrolactone monomer via a green approach: Synthesis of sustainable biobased latexes. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2024, 6, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhumitha, J. Production Forecast of Thermoplastics Worldwide from 2025 to 2050. 2024. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/664906/plastics-production-volume-forecastworldwide/ (accessed on 10 January 2024).
- United Nations Environment Programme. An Assessment Report on Issues of Concern: Chemicals and Waste Issues Posing Risks to Human Health and the Environment. 2020. Available online: https://wedocs.unep.org/20.500.11822/33807 (accessed on 1 September 2020).
- Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development. Global Plastics Outlook: Economic Drivers, Environmental Impacts and Policy Options; OECD Publishing, Paris, Europe: 2022. Available online: https://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/environment/global-plastics-outlook_de747aef-en (accessed on 1 December 2023).
- Gigault, J.; Ter Halle, A.; Baudrimont, M.; Pascal, P.Y.; Gauffre, F.; Phi, T.L.; Reynaud, S. Current opinion: What is a nanoplastic? Environ. Pollut. 2018, 235, 1030–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Microplastics in Drinking-Water. 2019. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/rest/bitstreams/1243269/retrieve (accessed on 1 December 2023).
- Carr, S.A.; Liu, J.; Tesoro, A.G. Transport and fate of microplastic particles in wastewater treatment plants. Water Res. 2016, 91, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, P.L.; Pramanik, B.K.; Shah, K.; Roychand, R. Pathway, classification, and removal efficiency of microplastics in wastewater treatment plants. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 255, 113326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vassilenko, E.; Watkins, M.; Chastain, S.; Mertens, J.; Posacka, A.M.; Patankar, S.; Ross, P.S. Domestic laundry and microfiber pollution: Exploring fiber shedding from consumer apparel textiles. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0250346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucher, J.; Friot, D. Primary Microplastics in the Oceans: Global Evaluation of Sources. 2017; p.5. Available online: https://holdnorgerent.no/wp-content/uploads/2020/03/IUCN-report-Primary-microplastics-in-the-oceans.pdf (accessed on 1 December 2023).
- Talvitie, J.; Mikola, A.; Koistinen, A.; Setälä, O. Solutions to microplastic pollution–Removal of microplastics from wastewater effluent with advanced wastewater treatment technologies. Water Res. 2017, 123, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mintenig, S.M.; Int-Veen, I.; Loder, M.G.; Primpke, S.; Gerdts, G. Identification of microplastic in effluents of wastewater treatment plants using focal plane array-based micro-Fourier-transform infrared imaging. Water Res. 2017, 108, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, F.; Ewins, C.; Carbonnier, F.; Quinn, B. Wastewater treatment works (WwTW) as a source of microplastics in the aquatic environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 5800–5808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyare, P.U.; Ouki, S.K.; Bond, T. Microplastics removal in wastewater treatment plants: A critical review. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2020, 6, 2664–2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okoffo, E.D.; O’Brien, S.; O’Brien, J.W.; Tscharke, B.J.; Thomas, K.V. Wastewater treatment plants as a source of plastics in the environment: A review of occurrence, methods for identification, quantification, and fate. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2019, 5, 1908–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Dai, X.; Wang, Q.; Van Loosdrecht, M.C.; Ni, B.J. Microplastics in wastewater treatment plants: Detection, occurrence, and removal. Water Res. 2019, 152, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kole, P.J.; Löhr, A.J.; Van Belleghem, F.G.; Ragas, A.M. Wear and tear of tyres: A stealthy source of microplastics in the environment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDevitt, J.P.; Criddle, C.S.; Morse, M.; Hale, R.C.; Bott, C.B.; Rochman, C.M. Addressing the Issue of Microplastics in the Wake of the Microbead-Free Waters Act a New Standard Can Facilitate Improved Policy. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 6611–6617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Z.; Chen, L.; Cizdziel, J.; Huang, Y. Research progress on microplastics in wastewater treatment plants: A holistic review. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 325, 116411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michielssen, M.R.; Michielssen, E.R.; Ni, J.; Duhaime, M. Fate of microplastics and other small anthropogenic litter (SAL) in wastewater treatment plants depends on unit processes employed. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2016, 2, 1064–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gies, E.A.; LeNoble, J.L.; Noël, M.; Etemadifar, A.; Bishay, F.; Hall, E.R.; Ross, P.S. Retention of microplastics in a major secondary wastewater treatment plant in Vancouver, Canada. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 133, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziajahromi, S.; Neale, P.A.; Rintoul, L.; Leusch, F.D.L. Wastewater treatment plants as a pathway for microplastics: Development of a new approach to sample wastewater-based microplastics. Water Res. 2017, 112, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talvitie, J.; Heinonen, M.; Paakkonen, J.P.; Vahtera, E.; Mikola, A.; Setala, O.; Vahala, R. Do wastewater treatment plants act as a potential point source of microplastics? Preliminary study in the coastal Gulf of Finland, Baltic Sea. Water Sci. Technol. 2015, 72, 1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittura, L.; Foglia, A.; Akyol, Ç.; Cipolletta, G.; Benedetti, M.; Regoli, F.; Fatone, F. Microplastics in real wastewater treatment schemes: Comparative assessment and relevant inhibition effects on anaerobic processes. Chemosphere 2021, 262, 128415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tagg, A.S.; Sapp, M.; Harrison, J.P.; Ojeda, J.J. Identification and quantification of microplastics in wastewater using focal plane array-based reflectance micro- FT-IR imaging. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 6032–6040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grab Sampling Image. Available online: https://news-network.rice.edu/news/files/2022/12/1219_WASTEWATER-1-WEB.jpg (accessed on 1 December 2023).
- Campanale, C.; Savino, I.; Pojar, I.; Massarelli, C.; Uricchio, V.F. A Practical Overview of Methodologies for Sampling and Analysis of Microplastics in Riverine Environments. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, S.A.; Garneau, D.; Sutton, R.; Chu, Y.; Ehmann, K.; Barnes, J.; Rogers, D.L. Microplastic pollution is widely detected in US municipal wastewater treatment plant effluent. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 218, 1045–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Liang, J.; Zhu, M.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, B. Microplastics in seawater and zooplankton from the Yellow Sea. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 242, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Autosampler Image. Available online: https://www.environmental-expert.com/products/model-sludge-sampler-special-automatic-water-samplers-213881 (accessed on 1 December 2023).
- Karami, A.; Golieskardi, A.; Choo, C.K.; Romano, N.; Ho, Y.B.; Salamatinia, B. A high-performance protocol for extraction of microplastics in fish. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 578, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, M.; Webb, H.; Lindeque, P.K.; Fileman, E.S.; Halsband, C.; Galloway, T.S. Isolation of microplastics in biota-rich seawater samples and marine organisms. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erni-Cassola, G.; Gibson, M.I.; Thompson, R.C.; Christie-Oleza, J.A. Lost, but found with nile red: A novel method for detecting and quantifying small microplastics (1 mm to 20 mm) in environmental samples. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 13641–13648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masura, J.; Baker, J.; Foster, G.; Arthur, C. Laboratory methods for the analysis of microplastics in the marine environment: Recommendations for quantifying synthetic particles in waters and sediments. NOAA Tech. Memo. 2015. Available online: https://marinedebris.noaa.gov/sites/default/files/publications-files/noaa_microplastics_methods_manual.pdf (accessed on 10 January 2024).
- McCormick, A.; Hoellein, T.J.; Mason, S.A.; Schluep, J.; Kelly, J.J. Microplastic is an abundant and distinct microbial habitat in an urban river. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 11863–11871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tagg, A.S.; Harrison, J.P.; Junam, Y.; Sapp, M.; Bradley, E.L.; Sinclair, C.J.; Ojeda, J.J. Fenton’s reagent for the rapid and efficient isolation of microplastics from wastewater. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 372–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinn, B.; Murphy, F.; Ewins, C. Validation of density separation for the rapid recovery of microplastics from sediment. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 1491–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magni, S.; Binelli, A.; Pittura, L.; Avio, C.G.; Della Torre, C.; Parenti, C.C.; Gorbi, S.; Regoli, F. The fate of microplastics in an Italian Wastewater Treatment Plant. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 652, 602–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grbic, J.; Nguyen, B.; Guo, E.; You, J.B.; Sinton, D.; Rochman, C.M. Magnetic extraction of microplastics from environmental samples. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2019, 6, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgoruz, V.; Gutow, L.; Thompson, R.C.; Thiel, M. Microplastics in the marine environment: A review of the methods used for identification and quantification. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 3060–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shim, W.J.; Song, Y.K.; Hong, S.H.; Jang, M. Identification and quantification of microplastics using Nile Red staining. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 113, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanton, T.; Johnson, M.; Nathanail, P.; MacNaughtan, W.; Gomes, R.L. Freshwater and airborne textile fibre populations are dominated by ‘natural’, not microplastic, fibres. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 666, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raju, S.; Carbery, M.; Kuttykattil, A.; Senthirajah, K.; Lundmark, A.; Rogers, Z.; Palanisami, T. Improved methodology to determine the fate and transport of microplastics in a secondary wastewater treatment plant. Water Res. 2020, 173, 115549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araujo, C.F.; Nolasco, M.M.; Ribeiro, A.M.P.; Ribeiro-Claro, P.J.A. Identification of microplastics using Raman spectroscopy: Latest developments and future prospects. Water Res. 2018, 142, 426–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lares, M.; Ncibi, M.C.; Sillanpää, M.; Sillanpää, M. Occurrence, identification, and removal of microplastic particles and fibers in conventional activated sludge process and advanced MBR technology. Water Res. 2018, 133, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elert, A.M.; Becker, R.; Duemichen, E.; Eisentraut, P.; Falkenhagen, J.; Sturm, H.; Braun, U. Comparison of different methods for MP detection: What can we learn from them, and why asking the right question before measurements matters? Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 1256–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekiff, J.H.; Remy, D.; Klasmeier, J.; Fries, E. Occurrence and spatial distribution of microplastics in sediments from Norderney. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 186, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dümichen, E.; Eisentraut, P.; Bannick, C.G.; Barthel, A.K.; Senz, R.; Braun, U. Fast identification of microplastics in complex environmental samples by a thermal degradation method. Chemosphere 2017, 174, 572–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro-Claro, P.J.; Nolasco, M.M.; Araujo, C.F. Chapter 5—Characterization of Microplastics by Raman Spectroscopy. Compr. Anal. Chem. 2017, 75, 119–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dümichen, E.; Barthel, A.-K.; Braun, U.; Bannick, C.G.; Brand, K.; Jekel, M.; Senz, R. Analysis of polyethylene microplastics in environmental samples, using a thermal decomposition method. Water Res. 2015, 85, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koelmans, A.A.; Bakir, A.; Burton, G.A.; Janssen, C.R. Microplastic as a vector for chemicals in the aquatic environment: Critical review and model-supported reinterpretation of empirical studies. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 3315–3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prata, J.C. Airborne microplastics: Consequences to human health? Environ. Pollut. 2018, 234, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avio, C.G.; Gorbi, S.; Regoli, F. Plastics and microplastics in the oceans: From emerging pollutants to emerged threat. Mar. Environ. Res. 2017, 128, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Kannan, K. MPs in house dust from 12 countries and associated human exposure. Environ. Int. 2020, 134, 105314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Lee, J.G.; Yun, H.; Deng, S.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, J.E.; Kwak, S.K.; Lee, K.B. Solving two environmental issues simultaneously: Waste polyethylene terephthalate plastic bottle-derived microporous carbons for capturing CO2. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 397, 125350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xie, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhong, S.; Qian, Y.; Gao, P. An overlooked entry pathway of microplastics into agricultural soils from application of sludge-based fertilizers. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 4248–4255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perren, W.; Wojtasik, A.; Cai, Q. Removal of microbeads from wastewater using electrocoagulation. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 3357–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Lin, T.; Chen, W. Occurrence and removal of microplastics in an advanced drinking water treatment plant (ADWTP). Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 700, 134520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zheng, H.; Zhao, J.; Luo, X.; Wang, Z.; Xing, B. Photodegradation elevated the toxicity of polystyrene microplastics to grouper (Epinephelus moara) through disrupting hepatic lipid homeostasis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 6202–6212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Luo, H.; Zou, J.; Chen, J.; Pan, X.; Rousseau, D.P.; Li, J. Characteristics and removal of microplastics in rural domestic wastewater treatment facilities of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 739, 139935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, X.T.; Nguyen, P.T.; Nguyen, V.T.; Dao, T.S.; Nguyen, P.D. Microplastics pollution in wastewater: Characteristics, occurrence, and removal technologies. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 19, 101013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramanik, B.K.; Pramanik, S.K.; Monira, S. Understanding the fragmentation of microplastics into nano-plastics and removal of nano/microplastics from wastewater using membrane, air flotation and nano-ferrofluid processes. Chemosphere 2021, 282, 131053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohana, A.A.; Farhad, S.M.; Haque, N.; Pramanik, B.K. Understanding the fate of nano-plastics in wastewater treatment plants and their removal using membrane processes. Chemosphere 2021, 284, 131430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkes, R.A.; Aristilde, L. Degradation and metabolism of synthetic plastics and associated products by Pseudomonas sp.: Capabilities and challenges. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 123, 582–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, L.; Yu, Y.; Adyel, T.M.; Wang, C.; Liu, Z.; Liu, S.; Hou, J. Distinct microbial metabolic activities of biofilms colonizing microplastics in three freshwater ecosystems. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 123577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monira, S.; Roychand, R.; Hai, F.I.; Bhuiyan, M.; Dhar, B.R.; Pramanik, B.K. Nano and microplastics occurrence in wastewater treatment plants: A comprehensive understanding of microplastics fragmentation and their removal. Chemosphere 2023, 334, 139011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gewert, B.; Plassmann, M.M.; MacLeod, M. Pathways for degradation of plastic polymers floating in the marine environment. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2015, 17, 1513–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; He, H.; Liu, M.; Li, S.; Tang, G.; Wang, W.; Cen, Z. Lost but can’t be neglected: Huge quantities of small microplastics hide in the South China Sea. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 633, 1206–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidayaturrahman, H.; Lee, T.G. A study on characteristics of microplastic in wastewater of South Korea: Identification, quantification, and fate of microplastics during treatment process. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 146, 696–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turan, N.B.; Erkan, H.S.; Engin, G.O. Microplastics in wastewater treatment plants: Occurrence, fate and identification. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 146, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, A.; Mankoti, M.; Rout, P.R.; Meena, S.S.; Dewan, S.; Kalia, B.; Banu, J.R. Sustainable utilization of food waste for bioenergy production: A step towards circular bioeconomy. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2022, 365, 109538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rout, P.R.; Shahid, M.K.; Dash, R.R.; Bhunia, P.; Liu, D.; Varjani, S.; Zhang, T.C.; Surampalli, R.Y. Nutrient removal from domestic wastewater: A comprehensive review on conventional and advanced technologies. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 296, 113246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneiderman, E.T. Discharging Microbeads to Our Waters: An Examination of Wastewater Treatment Plants in New York. New York State Office of the Attorney General 2015, pp. 1–11. Available online: https://ag.ny.gov/sites/default/files/reports/2015_Microbeads_Report_FINAL.pdf (accessed on 1 December 2023).
- Gaur, V.K.; Gupta, S.; Sharma, P.; Gupta, P.; Varjani, S.; Srivastava, J.K.; Chang, J.S.; Bui, X.T. Metabolic cascade for remediation of plastic waste: A case study on microplastic degradation. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2022, 8, 30–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayo, J.; Olmos, S.; López-Castellanos, J. Microplastics in an urban wastewater treatment plant: The influence of physicochemical parameters and environmental factors. Chemosphere 2020, 238, 124593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talvitie, J.; Mikola, A.; Setälä, O.; Heinonen, M.; Koistinen, A. How well is microlitter purified from wastewater?—A detailed study on the stepwise removal of microlitter in a tertiary level wastewater treatment plant. Water Res. 2017, 109, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherer, C.; Weber, A.; Lambert, S.; Wagner, M. Interactions of Microplastics with Freshwater Biota. 2018. Available online: https://library.oapen.org/bitstream/handle/20.500.12657/42902/1/2018_Book_FreshwaterMicroplastics.pdf#page=161 (accessed on 1 December 2023).
- Lee, E.; Rout, P.R.; Bae, J. The applicability of anaerobically treated domestic wastewater as a nutrient medium in hydroponic lettuce cultivation: Nitrogen toxicity and health risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 780, 146482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varjani, S.J. Microbial degradation of petroleum hydrocarbons. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 223, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, N.; Santhiya, D.; Sharma, J.G. Microbial remediation of micro-nano plastics: Current knowledge and future trends. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 115044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palm, G.J.; Reisky, L.; Böttcher, D.; Müller, H.; Michels, E.A.; Walczak, M.C.; Weber, G. Structure of the plastic-degrading Ideonella sakaiensis MHETase bound to a substrate. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.S.; Elsamahy, T.; Al-Tohamy, R.; Zhu, D.; Mahmoud, Y.A.G.; Koutra, E.; Sun, J. Plastic wastes biodegradation: Mechanisms, challenges, and future prospects. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 780, 146590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rout, P.R.; Mohanty, A.; Sharma, A.; Miglani, M.; Liu, D.; Varjani, S. Micro-and nanoplastics removal mechanisms in wastewater treatment plants: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2022, 6, 100070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, B.; Varjani, S.; Iragavarapu, G.P.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Vishal, B. Microbial fingerprinting of potential biodegrading organisms. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2019, 5, 181–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rout, P.R.; Dash, R.R.; Bhunia, P.; Lee, E.; Bae, J. Comparison between a single unit bioreactor and an integrated bioreactor for nutrient removal from domestic wastewater. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2021, 48, 101620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varjani, S.; Upasani, V.N.; Pandey, A. Bioremediation of oily sludge polluted soil employing a novel strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and phytotoxicity of petroleum hydrocarbons for seed germination. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 737, 139766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, N.; Liu, X.; Xing, W. Microplastics in wastewater treatment plants of Wuhan, Central China: Abundance, removal, and potential source in household wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 745, 141026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edo, C.; González-Pleiter, M.; Leganés, F.; Fernández-Piñas, F.; Rosal, R. Fate of microplastics in wastewater treatment plants and their environmental dispersion with effluent and sludge. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 259, 113837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.; Rout, P.R.; Kyun, Y.; Bae, J. Process optimization and energy analysis of vacuum degasifier systems for the simultaneous removal of dissolved methane and hydrogen sulfide from anaerobically treated wastewater. Water Res. 2020, 182, 115965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhang, L.; Chen, B.; Zhu, X. Low-pressure driven electrospun membrane with tuned surface charge for efficient removal of polystyrene nanoplastics from water. J. Memb. Sci. 2020, 614, 118470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Ding, T.; Peng, C.; Naz, I.; Sun, H.; Li, J.; Liu, J. Micro-and nanoplastics in wastewater treatment plants: Occurrence, removal, fate, impacts and remediation technologies-a critical review. Chem. Eng. 2021, 423, 130205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rout, P.R.; Goel, M.; Mohanty, A.; Pandey, D.S.; Halder, N.; Mukherjee, S.; Bhatia, S.K.; Sahoo, N.K.; Varjani, S. Recent advancements in microalgal mediated valorisation of wastewater from hydrothermal liquefaction of biomass. Bioenergy Res. 2022, 15, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhang, J.; Liu, H.; Guo, X.; Zhang, X.; Yao, X.; Cao, Z.; Zhang, T. A review of the removal of microplastics in global wastewater treatment plants: Characteristics and mechanisms. Environ. Int. 2021, 146, 106277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Liu, Q.; Yan, C.; Mancl, K.; Gong, D.; He, J.; Mei, X. Macro-and/or microplastics as an emerging threat effect crop growth and soil health. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 186, 106549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conley, K.; Clum, A.; Deepe, J.; Lane, H.; Beckingham, B. Wastewater treatment plants as a source of microplastics to an urban estuary: Removal efficiencies and loading per capita over one year. Water Res. X 2019, 3, 100030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyachenko, A.; Mitchell, J.; Arsem, N. Extraction and identification of microplastic particles from secondary wastewater treatment plant (WWTP) effluent. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 1412–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beljanski, A.; Cole, C.; Fuxa, F.; Setiawan, E.; Singh, H. Efficiency and Effectiveness of a Low-Cost, Self-Cleaning Microplastic Filtering System for Wastewater Treatment Plants. 2016. Available online: http://libjournals.unca.edu/ncur/wp-content/uploads/2021/06/2064-Beljanski-Alec.pdf (accessed on 1 December 2023).
- Li, L.; Xu, G.; Yu, H.; Xing, J. Dynamic membrane for micro-particle removal in wastewater treatment: Performance and influencing factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 627, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, B.; Xue, W.; Hu, C.; Liu, H.; Qu, J.; Li, L. Characteristics of microplastic removal via coagulation and ultrafiltration during drinking water treatment. Chem. Eng. 2019, 359, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juliastuti, S.R.; Hisbullah, M.I.; Abdillah, M. High density Polyethylene plastic waste treatment with microwave heating pyrolysis method using coconut-shell activated carbon to produce alternative fuels. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 334, 012015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.L.; Ngadi, N.; Abdullah, T.A.T.; Inuwa, I.M. Current state and future prospects of plastic waste as source of fuel: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 50, 1167–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkhatib, D.; Oyanedel-Craver, V.; Carissimi, E. Electrocoagulation applied for the removal of microplastics from wastewater treatment facilities. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 276, 118877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussa, D.T.; El-Naas, M.H.; Nasser, M.; Al-Marri, M.J. A comprehensive review of electrocoagulation for water treatment: Potentials and challenges. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 186, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiang, H.; Bian, K.; Wang, H.; Wang, C. A critical review of control and removal strategies for microplastics from aquatic environments. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Singh, R.P.; Rath, C.C.; Das, A.P. Synthetic microfibers: Source, transport, and their remediation. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 38, 101612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besseling, E.; Quik, J.T.; Sun, M.; Koelmans, A.A. Fate of nano-and microplastic in freshwater systems: A modeling study. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 220, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zou, X.; Wang, X.; Su, M.; Chen, C.; Sun, X.; Zhang, H. A preliminary study of the interactions between microplastics and citrate-coated silver nanoparticles in aquatic environments. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 385, 121601.10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, V.M. Review on the current status of polymer degradation: A microbial approach. Bioresour. Bioprocess 2017, 4, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosuth, M.; Mason, S.A.; Wattenberg, E.V. Anthropogenic contamination of tap water, beer, and seasalt. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0194970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, M.; Song, B.; Zhu, Y.; Zeng, G.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yi, H. Removal of microplastics via drinking water treatment: Current knowledge and future directions. Chemosphere 2020, 251, 126612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pivokonsky, M.; Cermakova, L.; Novotna, K.; Peer, P.; Cajthaml, T.; Janda, V. Occurrence of microplastics in raw and treated drinking water. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 643, 1644–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koelmans, A.A.; Nor, N.H.M.; Hermsen, E.; Kooi, M.; Mintenig, S.M.; De France, J. Microplastics in freshwaters and drinking water: Critical review and assessment of data quality. Water Res. 2019, 155, 410–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danopoulos, E.; Twiddy, M.; Rotchell, J.M. Microplastic contamination of drinking water: A systematic review. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0236838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Liu, H.; Chen, J.P. Microplastics in freshwater systems: A review on occurrence, environmental effects, and methods for microplastics detection. Water Res. 2018, 137, 362–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schymanski, D.; Oßmann, B.E.; Benismail, N.; Boukerma, K.; Dallmann, G.; Von der Esch, E.E.; Fischer, D.; Fischer, F.; Gilliland, D.; Glas, K.; et al. Analysis of microplastics in drinking water and other clean water samples with micro-Raman and micro-infrared spectroscopy: Minimum requirements and best practice guidelines. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2021, 413, 5969–5994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, H.; Jiang, Q.; Hu, X.; Zhong, X. Occurrence and identification of microplastics in tap water from China. Chemosphere 2020, 252, 126493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westphalen, H.; Abdelrasoul, A. Challenges and treatment of microplastics in water. Water Challenges an Urban. World 2018, 5, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecchiotti, G.; Colafarina, S.; Aloisi, M.; Zarivi, O.; Di Carlo, P.; Poma, A. Genotoxicity and oxidative stress induction by polystyrene nanoparticles in the colorectal cancer cell line HCT116. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0255120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yee, M.S.-L.; Hii, L.-W.; Looi, C.K.; Lim, W.-M.; Wong, S.-F.; Kok, Y.-Y.; Tan, B.-K.; Wong, C.-Y.; Leong, C.-O. Impact of microplastics and nanoplastics on human health. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mintenig, S.M.; Löder, M.G.J.; Primpke, S.; Gerdts, G. Low numbers of microplastics detected in drinking water from ground water sources. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 648, 631–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millar, G.J.; Lin, J.; Arshad, A.; Couperthwaite, S.J. Evaluation of electrocoagulation for the pre-treatment of coal seam water. J. Water Process Eng. 2014, 4, 166–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pico, Y.; Barcelo, D. Analysis and prevention of microplastics pollution in water: Current perspectives and future directions. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 6709–6719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.B.; Kamcev, J.; Robeson, L.M.; Elimelech, M.; Freeman, B.D. Maximizing the right stuff: The trade-off between membrane permeability and selectivity. Science 2017, 356, 1138–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, R.W. Membrane Technology and Applications, 3rd ed.; 2012. Available online: https://www.eng.uc.edu/~beaucag/Classes/Properties/Books/Richard%20W.%20Baker(auth.)%20-%20Membrane%20Technology%20and%20Applications,%20Third%20Edition%20(2012).pdf (accessed on 1 December 2023).
- Webb, H.K.; Arnott, J.; Crawford, R.J.; Ivanova, E.P. Plastic degradation and its environmental implications with special reference to poly(ethylene terephthalate). Polymers 2012, 5, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, P.; Singh, D.P. Microplastic degradation by bacteria in aquatic ecosystem. In Microorganisms for Sustainable Environment and Health; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 431–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanan, N.; Montazer, Z.; Sharma, P.K.; Levin, D.B. Microbial and enzymatic degradation of synthetic plastics. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 580709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menon, V.; Sharma, S.; Gupta, S.; Ghosal, A.; Nadda, A.K.; Jose, R.; Raizada, P. Prevalence and implications of microplastics in potable water system: An update. Chemosphere 2023, 317, 137848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Kumari, S.; Chopade, R.L.; Pandit, P.P.; Rai, A.R.; Nagar, V.; Awasthi, G.; Singh, A.; Awasthi, K.K.; Sankhla, M.S. An assessment of the impact of structure and type of microplastics on ultrafiltration technology for microplastic remediation. Sci. Prog. 2023, 106, 00368504231176399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalmau-Soler, J.; Ballesteros-Cano, R.; Boleda, M.R.; Paraira, M.; Ferrer, N.; Lacorte, S. Microplastics from headwaters to tap water: Occurrence and removal in a drinking water treatment plant in Barcelona Metropolitan area (Catalonia, NE Spain). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 59462–59472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuartucci, M. Ultrafiltration, a cost-effective solution for treating surface water to potable standard. Water Pract. Technol. 2020, 15, 426–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federal Reserve. FAQs: What Is a Regulation and How Is It Made? 2018. Retrieved 1 June 2022. Available online: https://www.federalreserve.gov/faqs/what-is-a-regulation.htm (accessed on 1 December 2023).
- USEPA. Trash-Free Waters. 2021. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/trash-free-waters (accessed on 2 December 2023).
- USEPA. Overview of the Safe Drinking Water Act. 2021. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sdwa/overview-safe-drinking-water-act (accessed on 4 October 2023).
- FDA, Supporting Document for Action Level for Inorganic Arsenic in Rice Cereals for Infants. 2020. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/97121/download (accessed on 1 December 2023).
- Rosengren, C. US Virgin Islands Plastic Bag Ban to Take Effect in 2017. Waste Dive. 2016. Retrieved 1 June 2022. Available online: https://www.wastedive.com/news/us-virgin-islands-plastic-bag-ban-to-take-effect-in-2017/427972/ (accessed on 1 December 2023).
- National Conference of State Legislatures (NCSL). State Plastic Bag Legislation. 2021. Retrieved 1 February 2022. Available online: https://www.ncsl.org/environment-and-natural-resources/state-plastic-bag-legislation (accessed on 1 December 2023).
- Coto, D. Puerto Rico to Ban Use of Plastic Bags through Executive Order after Legislators Opposed Bill. US News. 2015. Available online: https://www.foxnews.com/politics/after-legislation-fails-puerto-ricos-governor-bans-plastic-bags-in-executive-order (accessed on 1 December 2023).
- Romer, J.R. The evolution of San Francisco’s plastic-bag ban. Gold. Gate Univ. Environ. Law J. 2010, 1, 439–465. Available online: https://heinonline.org/HOL/LandingPage?handle=hein.journals/gguelr1&div=23&id=&page= (accessed on 1 December 2023).
- Gibbens, S. A Brief History of How Plastic Straws Took over the World. National Geographic. 2019. Retrieved 1 February 2022. Available online: https://www.nationalgeographic.com/environment/article/news-plastic-drinking-straw-history-ban (accessed on 1 December 2023).
- Maddela, N.R.; Ramakrishnan, B.; Kadiyala, T.; Venkateswarlu, K.; Megharaj, M. Do Microplastics and Nanoplastics Pose Risks to Biota in Agricultural Ecosystems? Soil Syst. 2023, 7, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).