Abstract
Nitric oxide (NO) is a proangiogenic factor acting through the soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC) pathway. However, angiogenic growth increases energy demand, which may be hampered by NO inhibition of cytochrome c oxidase (CcO). Then, NO activity would be the balanced result of sGC activation (pro-angiogenic) and CcO inhibition (anti-angiogenic). NO activity in a rat and eNOS−/− mice aortic ring angiogenic model and in a tube formation assay (human aortic endothelial cells) were analyzed in parallel with mitochondrial O2 consumption. Studies were performed with NO donor (DETA-NO), sGC inhibitor (ODQ), and NOS or nNOS inhibitors (L-NAME or SMTC, respectively). Experiments were performed under different O2 concentrations (0–21%). Key findings were: (i) eNOS-derived NO inhibits angiogenic growth by a mechanism independent on sGC pathway and related to inhibition of mitochondrial O2 consumption; (ii) NO inhibition of the angiogenic growth is more evident in hypoxic vessels; (iii) in the absence of eNOS-derived NO, the modulation of angiogenic growth, related to hypoxia, disappears. Therefore, NO, but not lower O2 levels, decreases the angiogenic response in hypoxia through competitive inhibition of CcO. This anti-angiogenic activity could be a promising target to impair pathological angiogenesis in hypoxic conditions, as it occurs in tumors or ischemic diseases.
1. Introduction
Blood vessels possess the capacity to rapidly form new sprouts (sprouting angiogenesis) in response to physiological demands or under pathological conditions requiring blood supply, as hypoxia or tumor growth. The surrounding tissues needed for O2 and nutrients incites the production of growth factors, such as the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), which acts as pro-angiogenic stimuli. The thin layer of ECs that lines the inner surface of blood vessels can rapidly switch from a quiescent to a highly proliferative state required for angiogenesis [1], and this change allows for new vessels to sprout from parental vessels. The EC exposed to the highest VEGF level, becomes the “tip cell” and migrates and guides new vessel sprouting. The sprout elongates by multiplying the number of “stalk cells” immediately behind the tip cell. This process involves some tightly coordinated events, including the degradation of the extracellular matrix, migration and proliferation of ECs, smooth muscle cells and pericytes to finally assemble new vessels [2]. ECs have long been considered to be metabolically inert and the angiogenic switch was thought to be solely regulated by growth factor signaling [3]. However, recent evidence indicates that ECs metabolism also modulates angiogenic fate by showing that angiogenesis requires both, an increase in glycolysis and mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation for a full ECs response [1]. In this respect, we must consider two different conditions; on the one hand, the no angiogenic quiescent ECs, involved in vascular maintenance, with low energy consumption and full abundance of metabolic substrates; on the other hand, the angiogenic sprouting ECs, which usually possess high energy demands and challenging nutrient conditions. In the low energy demand situation, ECs meet their energetic requirements largely by glycolysis. However, in the high energy demand condition related to angiogenic growth, ATP production through mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation becomes increasingly important [1].
Previous evidence indicates that nitric oxide (NO) may have proangiogenic or anti-angiogenic effects, depending on its concentration and/or duration of exposure, intrinsic sensitivity of cells to NO and distribution of NO [4,5,6,7,8]. The activity of NO as a proangiogenic factor has been extensively reviewed elsewhere [5,7,8], as well as the role of the sGC pathway in this process [9]. Moreover, the effects of VEGF are coupled to up-regulation of eNOS, NO production and cGMP signaling [4,10]. However, NO can also inhibit oxidative phosphorylation in ECs by interaction with the cytochrome c oxidase (CcO), the terminal enzyme of the mitochondrial electron transport chain [11]. As NO and O2 compete for binding to CcO, the inhibitory effect of NO may increase when O2 concentration decreases and vice versa, which makes this NO pleiotropic effect highly relevant in hypoxic conditions [12]. In a scenario of reduced O2 availability, the higher affinity of NO for CcO impairs oxidative phosphorylation [13,14,15] and ATP supply. However, when O2 supply diminishes, the ECs switch from a quiescent to a proliferative state and becomes more dependent on oxidative phosphorylation. In these circumstances, NO, through CcO inhibition, may impair the increased energy demand of ECs and may exhibit anti-angiogenic activity.
To delineate the exact role of NO on angiogenesis, the in vitro angiogenic activity of endogenously released or exogenously added NO and its relationship with sGC and mitochondrial O2 consumption were studied. Our data provide evidence that, under hypoxic conditions, the increased inhibitory activity of NO on mitochondrial respiration, decreases O2 consumption and inhibits angiogenic growth, an effect that is independent of sGC activation. According to this, a therapeutic approach based on the local administration of NO donors could be useful in scenarios characterized by pathological angiogenesis such as tumor growth or ischemic disease.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Tissues
The study was performed in male Wistar rats (250–300 g, bred in our faculty’s animal facility) or wild-type (WT) and eNOS knockout (eNOS−/− mice (C57BL/6Jx129, 20–25 g, UCL, London, UK), housed (5 animals per cage) under a 12 h light/dark cycle at 22 °C and 60% humidity, and maintained on standard chow and water ad libitum until they were used for the study. Animals were decapitated under brief anesthesia with inhaled isoflurane. Segments of the thoracic aorta were aseptically removed and cleaned from the adipose tissue as previously described [15]. All of the experimental procedures complied with guidelines established in Spanish legislation (Royal Decree RD 1201/2005) and were approved by the Experimental Animal Ethics Committee of the University of Valencia, Spain (protocol code 2014/VSC/PEA/00117, date of approval 25 July 2014).
2.2. Arterial Ring Model of Angiogenesis
Rats or mice arterial rings (1 mm) were sectioned and prepared, as previously described [16], in a Petri dish on ice and rinsed with 5 consecutive washes of Krebs solution mM) (NaCl 118, KCl 4.7, CaCl2 1.8, KH2PO4 1.2, NaHCO3 25.0, glucose 11.0). The periaortic fibroadipose tissue was removed with fine micro-dissecting forceps and scissors, carefully avoiding damage to the arterial wall. Matrigel® (BD Bioscience, San Jose, CA, USA) was kept on ice in cold chamber (4 °C) for at least 4 h before the experiment took place. A toal of 50 µL of Matrigel® per well was added, and the arterial rings were randomized into wells in 96-well plates (Costar, Corning, NY, USA), which were kept on ice until use. After 15 min at room temperature, Matrigel® polymerized, and 200 µL of 37 °C preheated Endothelial Basal Medium (EBM, Promocell (Heildelberg, Germany)) were added. EBM was enriched with Fetal Calf Serum (FCS, 50 µL/mL), human basic Fibroblast Growth Factor (hbFGF, 10 ng/mL), human Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (hVEGF, 0.5 ng/mL), human Epidermal Growth Factor (hEGF, 5 ng/mL), human Recombinant Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 (R3IGF-1, 20 ng/mL), ascorbic acid (1 µg/mL) and hydrocortisone (0.5 µg/mL) (EBM-MV2, Promocell (Heildelberg, Germany). Media were supplemented with 0.015 µg/mL Amphotericin B (Biowhittaker® Lonza Basel, Switzerland), and 30 µg/mL Gentamicin (Genta-gobens®, Laboratorios Normon SA, Tres Cantos, Madrid, Spain). Plates were incubated at 37 °C and 5% CO2 for 6 days, renewing the medium, as well as the stimuli required, the day after starting the experiment, and then every 2 days. In some experiments, the NO-donor [(Z)-1-[2-aminoethyl)-N-(2-ammonioethyl) amino* diazen-1-ium-1,2-diolate] (DETA-NO, 1–100 μM), the sGC inhibitor 1H-[1,2,4] oxadiazolo [4,3-a] quinoxaline-1-one (ODQ, 5 μM), the non-selective NOS inhibitor NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME, 100 µM), or the nNOS selective inhibitors S-Methyl-L-Thiocitrulline (SMTC, 1 µM), were added to the culture medium as indicated. All drugs from Sigma Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA) except DETA-NO (Alexis, Lausen, Switzerland). Experiments were performed in duplicate with at least 3 different animals. When indicated, experiments were performed at 0% O2, 1% O2, 3% O2, 12% O2 and 21% O2 in a hypoxic chamber Xvivo System Model X3 Cytocentric Cell Incubation and Handling Platform (BioSpherix, Ltd., RRID: SCR_021175, New York, NY, USA). At the beginning of the experiment, processing parameters were fixed, and all images were collected by the same researcher under the same observation conditions (light, contrast and magnification). The cultures were photographed daily from Day 3 to Day 6 in an inverted microscope Leica DM IL LED coupled to a Leica Digital Camera at appropriate magnifications (25×). On the 7th day, a final time fluorescence cell staining was performed. The length of the longest vessel sprouting from the rat aortic rings was measured as the distance in the x and y axis, (taking the outer surface of the ring as the starting point) using Leica Microsystems LAS Software V3.7.0 (Wetzlar, Germany) as has been described elsewhere [16].
2.3. Tube Formation Assay
The capacity of human aortic ECs (hAoECs, PromoCell, Heidelberg, Germany) to form capillary tubule-like networks was tested by seeding 60,000 cells, at passages 4–5, in 96-well plates (Costar, Corning, NY, USA) pre-coated with 50 mL growth factor reduced Matrigel ® (BD Biosciences Bedford, MA, USA) according to the experimental procedure previously described [17]. The cells were incubated 18 h at 37 °C and 5% CO2, in EBM enriched with Fetal Calf Serum (FCS, 50 µL/mL), human basic Fibroblast Growth Factor (hbFGF, 10 ng/mL), human Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (hVEGF, 0.5 ng/mL), human Epidermal Growth Factor (hEGF, 5 ng/mL), human Recombinant Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 (R3IGF-1, 20 ng/mL), ascorbic acid (1 µg/mL) and hydrocortisone (0.5 µg/mL) (EBM-MV2, Promocell (Heildelberg, Germany). Media were supplemented with 0.015 µg/mL Amphotericin B (Biowhittaker® Lonza Basel, Switzerland), and 30 µg/mL Gentamicin (Genta-gobens®, Laboratorios Normon SA, Tres Cantos, Madrid, Spain). In some cases, L-NAME (100 μM) was added to the medium. Experiments were performed at 0% O2, 1% O2, 3% O2, 12% O2 and 21% O2, in a hypoxic chamber Xvivo System Model X3 Cytocentric Cell Incubation and Handling Platform. At the end of the incubation time, cells were stained for 15 min with 5 μM calcein AM (Invitrogen, Molecular Probes Inc., Paisley, UK). The images were visualized using a Leica DM IL LED microscope coupled to a Leica Fluorescence Camera at appropriate magnification (25×). The total number of tubules in each visual field (four different fields for plate) was quantified using Image J (National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MA, USA) freeware. Each treatment was carried out in duplicate wells (duplicate data were averaged) with experimental “n” corresponding to independent experiments.
2.4. Functional Experiments
Rings obtained from rat vessels were suspended in a 5 mL organ bath (37 °C) containing Krebs solution and gassed with 12% O2, 5% CO2 and 83% N2, which produced an O2 concentration of about 130 μM, similar to that present in aortic blood [15]. The rings were monitored with a dissolved O2 m (ISO2, World Precision Instruments, Stevenage, Herts, UK). An initial load of 2 g was applied to each preparation and maintained throughout a 75–90 min equilibration period. Tension was recorded isometrically by Grass FTO3 force–displacement transducers and data were recorded on a disc (Power Lab). The rings were stimulated with KCl (80 mM) and phenylephrine (1 μM). The presence (>90%) of a relaxant response to acetylcholine (ACh, 10 μM) in phenylephrine precontracted preparations indicated the existence of a functional endothelium. All drugs were from Sigma Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). The vessels were then exposed to 1 μM phenylephrine which produces a sustained contractile response and cumulative dose response curves of relaxation were obtained by adding cumulative concentrations of DETA-NO (1 to 100 μM), or a single concentration of L-NAME (100 mM), SMTC (1 µM) or ODQ (1 µM). Changes in vascular tone induced by drugs were quantified as a percentage of the contractile response induced by KCl.
2.5. Oxygen Consumption Measurements
Aortic rings were placed in gas-tight chambers containing 1 mL of Krebs solution and gently agitated at 37 °C. O2 consumption by the tissue was measured with a Clark-type O2 electrode (Rank Brothers, Bottisham, UK) calibrated with an air-saturated Krebs solution, assuming an O2 concentration of 200 μM as previously described [15]. Sodium cyanide (1 mM) was employed to confirm that O2 consumption was mainly mitochondrial (approx. 95–99%). Measurements were obtained using the Duo18 data acquisition device (World Precision Instruments, Stevenage, UK). The rate of O2 consumption was expressed as nM O2/min/mg protein and was calculated at two specific concentrations of O2: 130 and 30 µM, which correspond with the concentration of O2 present in arterial blood and in tissues, respectively [15]. Proteins were determined with the BCA protein assay reagent kit® (Pierce, Rockford, MI, USA) using BSA as the standard.
2.6. qRT-PCR
Frozen samples of aortic rings and new branches obtained after 6 days of angiogenic growth were treated as previously described [18] in order to extract total RNA, which was quantified and analyzed by running 1 µg of each sample by microfluidic electrophoresis using the Experion TM automated electrophoresis system (BioRad, Madrid, Spain) following the manufacture’s conditions. The total RNA (500 ng) and oligo(dT)16 as a primer (250 ng) in DEPC-treated water were pre-heated to 70 °C and cooled on ice for cDNA synthesis. The reactions (20 μL) contained ImProm-II TM reaction buffer, 3 mM MgCl2, 20 U of Recombinant RNAsin® Ribonuclease Inhibitor (Promega Corp., Madison, WI, USA), 0.5 mM of each deoxynucleoside triphosphate, and 1 μL of ImProm-II TM Reverse Transcriptase (Promega Corp., Madison, WI, USA), and were incubated at 25 °C for 5 min (annealing step), following by an extension step at 42 °C for 60 min and a final step at 70 °C for 15 min (heat-inactivate). The mRNAs encoding the rat endothelial (eNOS, Nos3), neuronal (nNOS, Nos1) and inducible (iNOS, Nos2) nitric oxide synthases, and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (Gapdh) as internal standard, were quantified by TaqManTM real-time RT-PCR with a GeneAmp 7500 Fast System (Applied Biosystems, Carlsbad, CA, USA). We analyzed (in duplicate reactions) a 10-fold dilution of the RT reaction of each sample using the TaqManTM Gene Expression Assays (Applied Biosystems, USA). The specific primer-probes were Nos3 (Rn02132634_s1); Nos2 (Rn00561646_m1); Nos1 (Rn00583793_m1) and Gapdh (Rn99999916_s1), (Applied Biosystems, USA). Real-time PCR reactions were conducted in 25 μL with TaqMan Universal PCR Master Mix (Applied Biosystems, USA), including 5 μL of diluted RT reaction, and 1.25 μL of 20X TaqMan Gene Expression Assay Mix (250 nM for the probe and 900 nM for each primer). cDNA was amplified following the manufacturer’s instructions: 1 initial hold-step at 95 °C for 10 min, a second step with 40 cycles, 15 s at 95 °C (denaturation) and 1 min at 60 °C (annealing/extension). The targets and reference (Gapdh) were amplified in parallel reactions. The Ct values obtained for each gene were referenced with GAPDH and converted into the linear form using the term 2–ΔCt × 104 as a value directly proportional to the mRNA copy number.
2.7. Statistical Analysis
Data were expressed as mean ± standard error of the mean. Statistical differences between groups were determined by one-way ANOVA followed by Šídák’s multiple comparisons test (GraphPad Prism 9.2.0 Software, San Diego, CA, USA). A probability value of p < 0.05 was considered significant.
3. Results
3.1. The NO Donor DETA-NO Inhibits Angiogenic Growth by a Mechanism Independent of sGC Activation
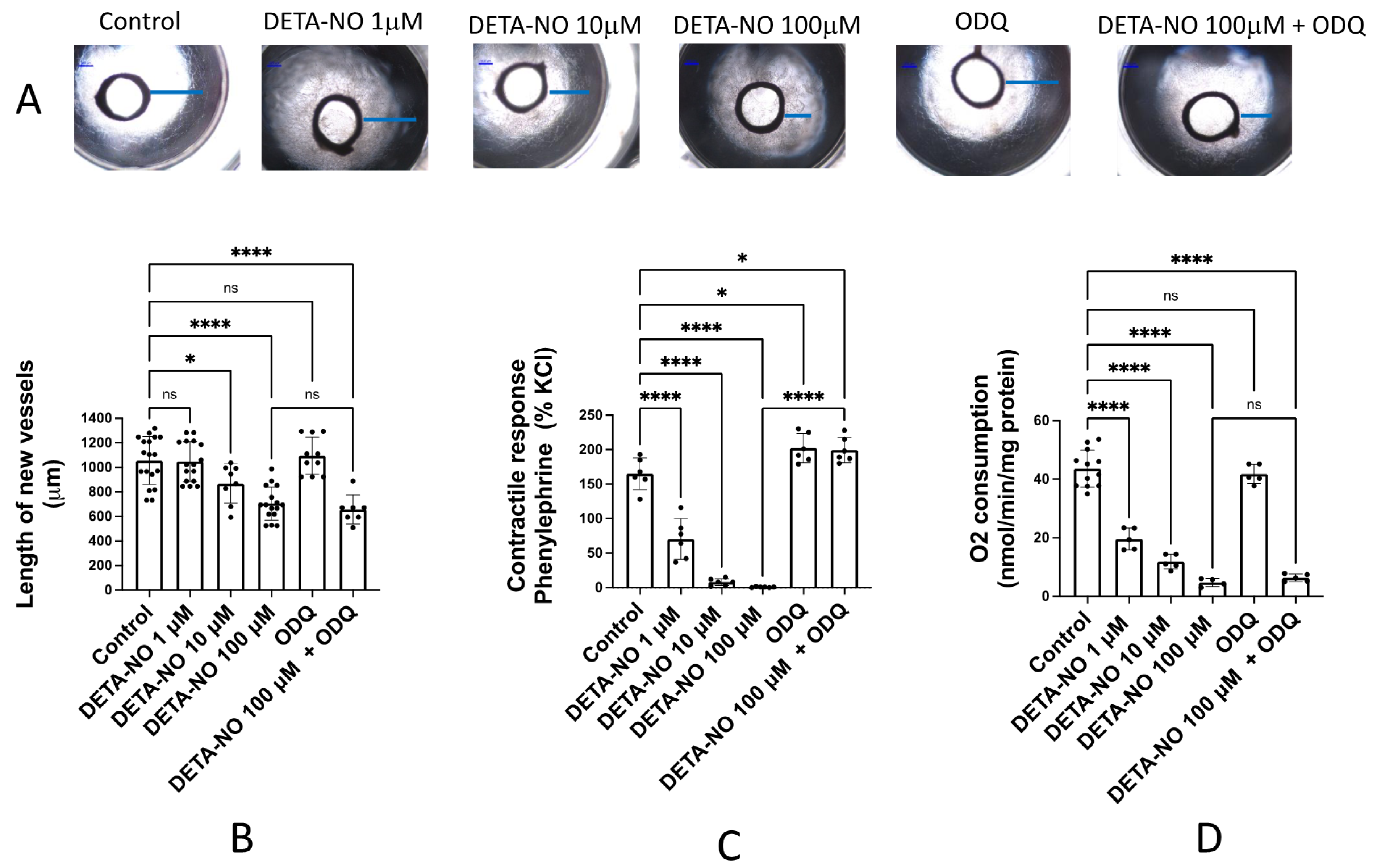
In order to investigate the activity of exogenous NO in the angiogenic process, rat aortic rings were incubated for 6 days in Matrigel® and endothelial cell medium enriched with growth factors and in the absence (control) or presence of different concentrations of DETA-NO, a NO donor. Figure 1A shows representative images of the angiogenic outgrowths. No significant changes were observed in vessels incubated with the sGC inhibitor ODQ (5 μM) or 1 μM DETA-NO. However, in the presence of 10 and 100 μM DETA-NO, the length of the new vessels formed was significantly lower (Figure 1B). This inhibitory effect remained when aortic rings were incubated with 100 μM DETA-NO + 5 μM ODQ (Figure 1B), indicating that inhibition of the angiogenic growth by DETA-NO was not mediated by sGC activation. The same results were observed when aortic rings were incubated in medium with FCS but without growing factors (results not shown).
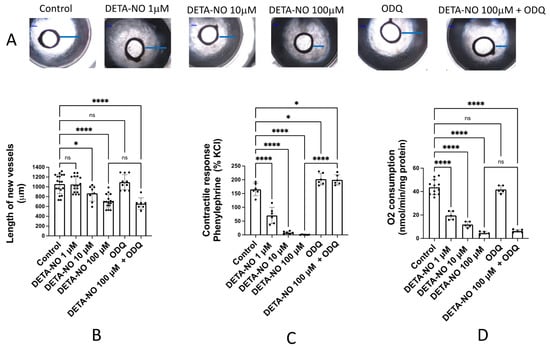
Figure 1.
DETA-NO inhibits angiogenic growth and O2 consumption in rat aorta by a mechanism independent of sGC activity. (A) Representative images of the explants obtained after 6 days of culture of rat aortic rings in Matrigel™ in the absence (control) and presence of different concentrations of the NO donor DETA-NO, and/or the sGC inhibitor ODQ. Blue lines represent the length of the longest vessel sprouting from the outer surface of the aortic ring (starting point). Quantification of the sprouting response (B), the contractile tone (C), and the rate of O2 consumption (D) in rat aorta, in the absence (control) or presence of DETA-NO (1, 10 and 100 µmoles/L), ODQ (5 µmoles/L) and DETA-NO 100 µM + ODQ 5 µmoles/L. The length of the longest neovessel formed was expressed as µm, taking the outer surface of the ring as the starting point. Changes in the contractile tone induced by phenylephrine 10 µM were expressed as a percentage of the KCl-induced contraction. The rate of O2 consumption was measured at 130 µM O2 and was expressed as nmol/min/mg protein. Dots represent individual data. Histograms and error bars show mean values ± SEM from n ≥ 5 independent experiments. ns = not significant, * p < 0.05, **** p < 0.0001 by one-way ANOVA followed by Šídák’s multiple comparisons test (GraphPad Prism 9.2.0 Software, San Diego, CA, USA).
As it is well known that NO-donors relax arterial smooth muscle through a sGC pathway, we assessed the vasodilator activity of the same concentrations of DETA-NO and ODQ assayed in the aortic ring angiogenesis. These experiments were performed in isolated organ baths and the experimental procedure includes addition of a pre-contractile agent, phenylephrine (1 μM), which provides a sustained contractile response. The subsequent addition of cumulative concentrations of DETA-NO (1–100 μM) produced a dose-dependent vasorelaxant response. The addition of the sGC inhibitor ODQ (5 μM) significantly increased vascular tone and completely inhibited DETA-NO induced vasodilatation, confirming the essential role of sGC in the vasodilator activity of NO and NO-donors (Figure 1C).
Finally, we assayed the action of 100 mM DETA-NO on aortic O2 consumption. The rate of O2 consumption was measured at the interval 130–120 μM, which constitutes the concentration of O2 present in arterial blood [15]. The results, summarized in Figure 1D, indicate that DETA-NO inhibits the rate of O2 consumption in a dose-dependent manner, and this inhibition is not prevented by the sGC inhibitor ODQ. Therefore, these results suggest that inhibition of O2 consumption mediated by DETA-NO is independent of sGC activity, as occurred with the inhibition of angiogenic growth.
3.2. NO Endogenously Released by eNOS Inhibits Angiogenic Growth and O2 Consumption
In order to determine the activity of endogenously released NO we performed experiments of angiogenesis in rat aortic rings incubated in the presence of the NO synthase inhibitor L-NAME.
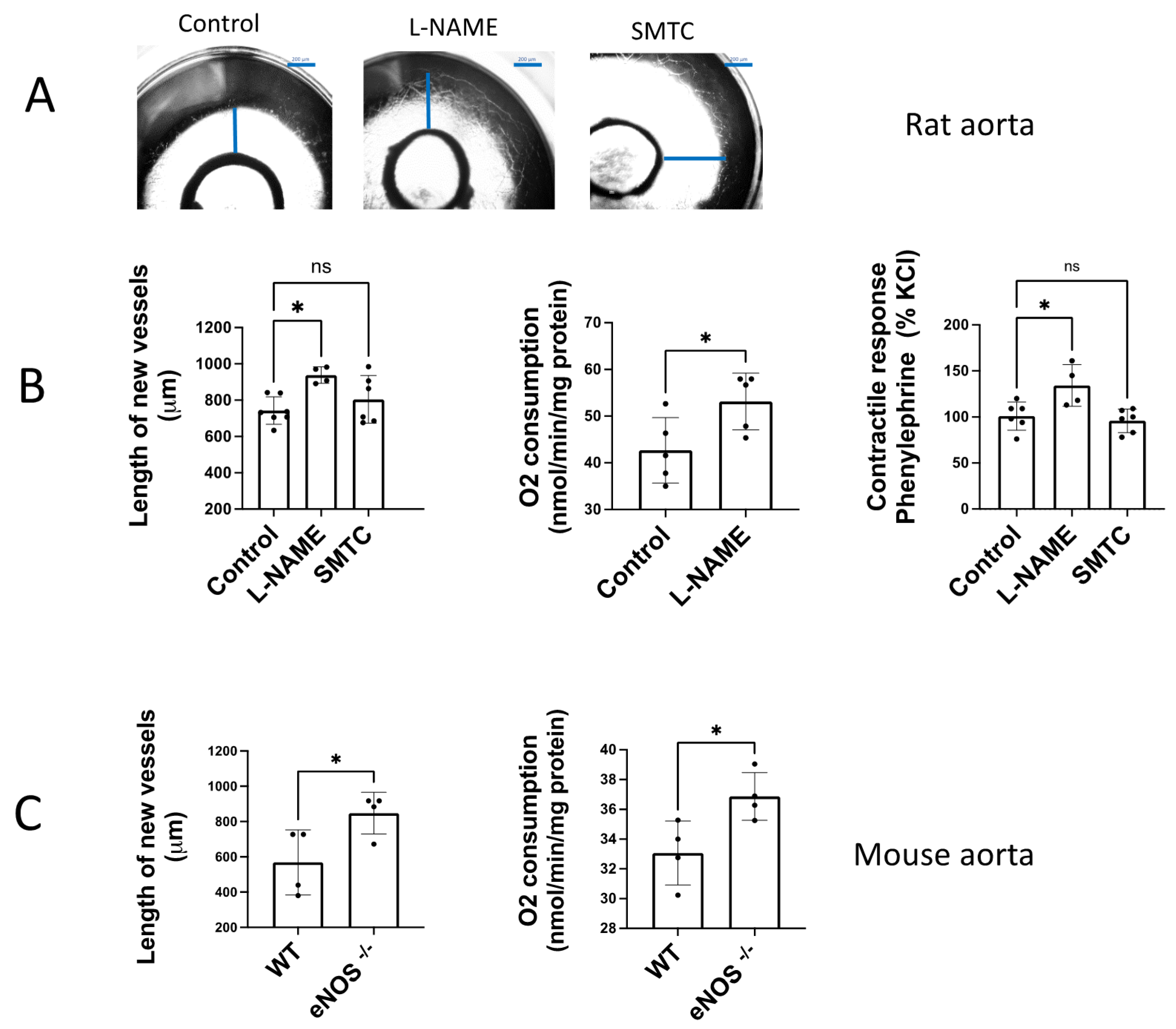
The angiogenic growth of rat aortic rings incubated in Matrigel ® was increased by addition of a non-selective NOS inhibitor, L-NAME (100 µM) (Figure 2A,B). In contrast, the selective nNOS inhibitor SMTC (1 µM) did not significantly modify the angiogenic growth, excluding the participation of nNOS. In the same way, we observed a significant increase in contractile tone in aortic rings incubated with L-NAME 100 µM, but not when SMTC 1 μM was added (Figure 2B).
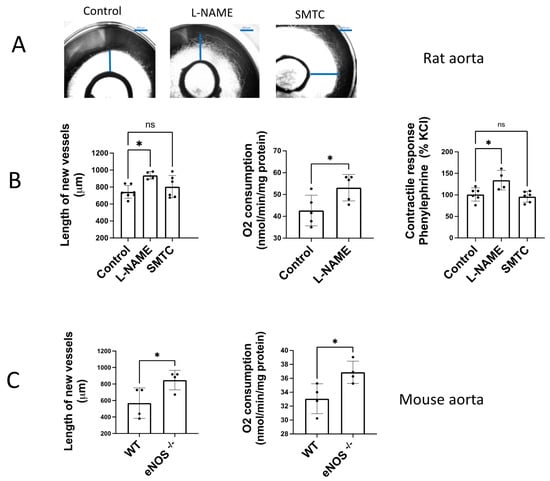
Figure 2.
Endogenously released NO inhibits angiogenic growth and O2 consumption. (A) Representative rat aortic ring explants in the absence (control) and presence of the non-selective NOS inhibitor L-NAME and the selective nNOS inhibitor SMTC (B) Quantification of the sprouting response, the contractile tone, and the rate of O2 consumption in rat aortas incubated in the absence (control) and presence of L-NAME (100 µM), and SMTC (1 µM). (C) Quantification of the sprouting response and the rate of O2 consumption in aorta from WT and eNOS−/− mice. The length of the longest neovessel formed, expressed as μm, was measured taking the outer surface of the ring as the starting point. Changes in the contractile tone induced by phenylephrine 10 µM were expressed as a percentage of the KCl-induced contraction. The rate of O2 consumption was measured at 130 µM O2 and was expressed as nmol/min/mg protein. Dots represent individual data. Histograms and error bars show mean values ± SEM from n ≥ 5 independent experiments. ns = not significant, * p < 0.05, by one-way ANOVA followed by Šídák’s multiple comparisons test (GraphPad Prism 9.2.0 Software, San Diego, CA, USA).
In aortic rings from eNOS−/− mice cultured in Matrigel ® for 6 days, we found an increased length of the new vessels formed compared to the angiogenic sprouting observed in aortas from wild type mice (WT, Figure 2C). The same occurs when the rate of O2 consumption was determined, which showed an increased rate in aorta from eNOS −/− vs. WT mice (Figure 2C). These results confirm that endogenous NO released by eNOS contributes to modulate angiogenic growth and O2 consumption in a similar way. This observation suggests that both processes could be linked, because of angiogenic growth may require a high energetic demand.
3.3. eNOS Expression Decreases in Sprouting Microvessels vs. the Aortic Ring
In addition to its well-known role as modulator of vascular tone, our present results suggest that NO released by eNOS plays an essential role in the regulation of angiogenesis and vascular O2 consumption. Therefore, our next objective was to determine the expression of eNOS but also the other two isoforms of NO synthase, nNOS and iNOS, in aorta and the new microvessels formed during the aortic angiogenic growth.
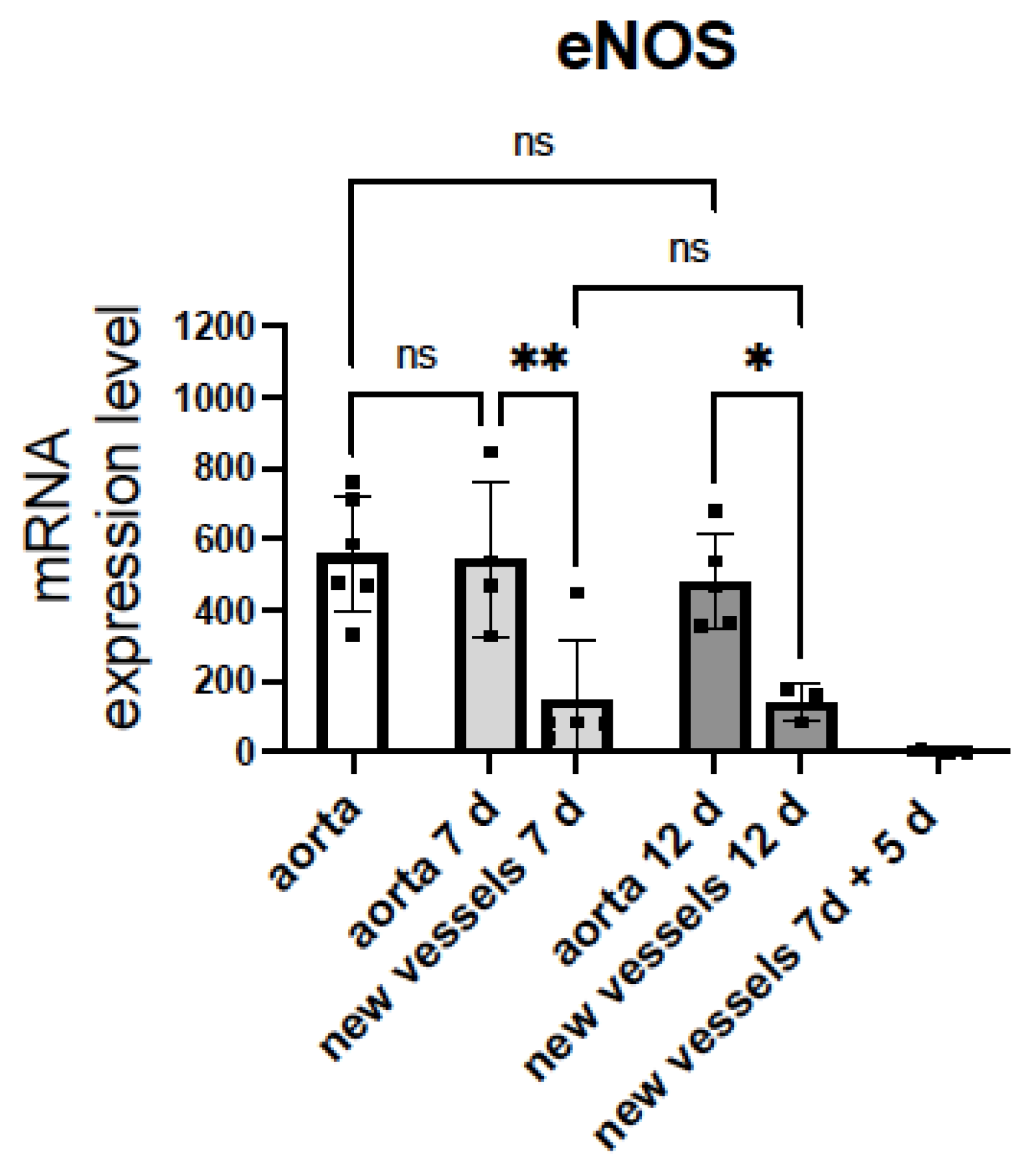
The mRNA levels of iNOS were undetectable in either aorta or new microvessels (n = 5). nNOS was detected in aorta but not in microvessels (n = 5, data not shown). Notably, eNOS was expressed in both aorta and microvessels (Figure 3). The eNOS expression in aorta did not change after 6 or 12 days of incubation with Matrigel® and medium enriched with FCS and growth factors.
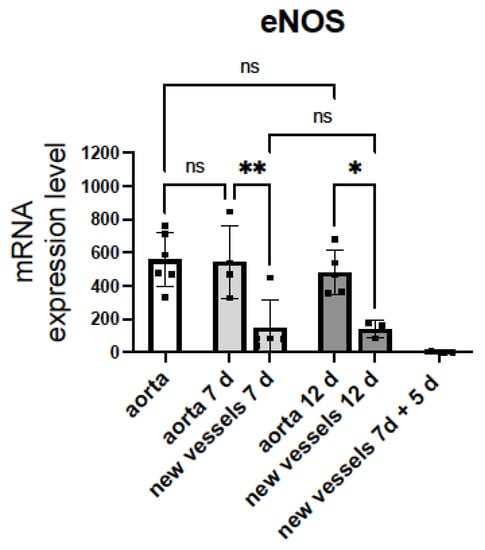
Figure 3.
mRNA levels of eNOS in sprouting microvessels are lower than in aortic rings. mRNA encoding the endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (Gapdh) were quantified by TaqManTM real-time RT-PCR before (white bar) and after (grey bars) 7 days or 12 days of angiogenic growth, in rat aortic rings and sprouting new vessels. Aorta 7 d = aortic ring incubated in Matrigel® with EGM-MV2 for 7 days. New vessels 7 d = sprouting microvessels obtained after incubation of rat aortic rings in Matrigel® with EGM-MV2 for 7 days. Aorta 12 d and new vessels 12 d = aortic ring and sprouting microvessels obtained after incubation of rat aortic rings in Matrigel® with EGM-MV2 for 7, extraction and posterior incubation for 5 days. New vessels 7 d + 5 d = sprouting microvessels obtained after incubation of rat aortic rings in Matrigel® with EGM-MV2 for 7 days, extraction, and posterior incubation for 5 days in Matrigel ® without the aortic ring. The Ct values obtained for each gene were referenced to Gapdh and expressed as 2−∆Ct × 10,000. Dots represent individual data. Histograms and error bars show mean values ± SEM from n ≥ 3 independent experiments. ns = not significant, * p < 0.05, ** p< 0.01, by one-way ANOVA followed by Šídák’s multiple comparisons test (GraphPad Prism 9.2.0 Software, San Diego, CA, USA).
Of note, the eNOS expression in the sprouting microvessels was significantly lower than in aorta and did not change after 7 or 12 days of angiogenic growth. However, when microvessels growing from the aortic ring for 7 days were isolated free of the aortic ring and re-seeded in Matrigel® for an additional 5 day incubation period, mRNA levels of eNOS dramatically decreased (Figure 3). These results suggest that reduced expression of eNOS facilitate the angiogenic growth of ECs. Moreover, the eNOS expression in the new branches appears to be controlled by the parent vessel and decreases when they grow in the absence of the aortic ring. This intriguing observation needs future work to be confirmed.
3.4. NO Inhibition of O2 Consumption and Angiogenic Growth Is More Pronounced in Hypoxic Vessels
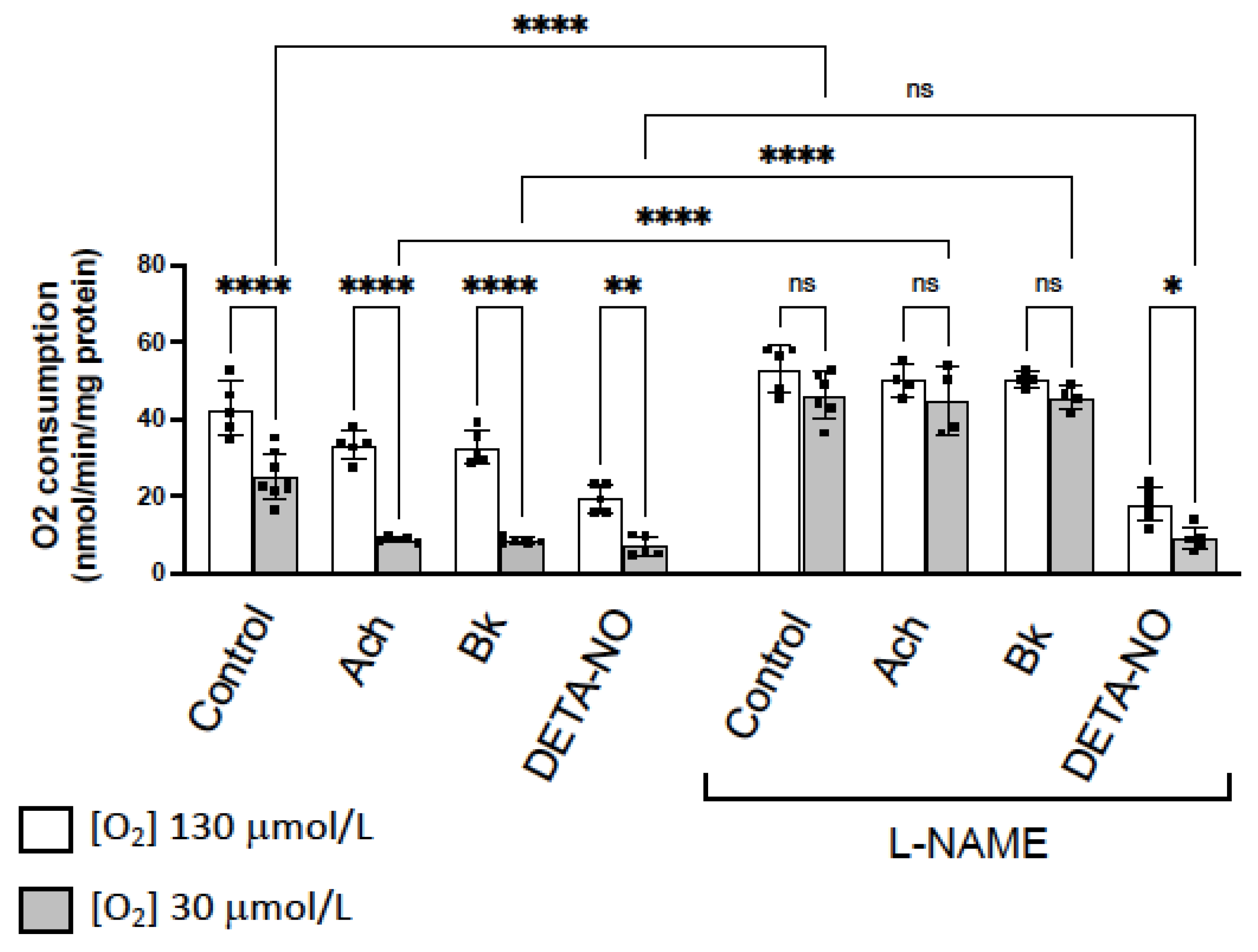
Our previous evidence indicates that NO decreases mitochondrial O2 consumption in vessels through competitive inhibition of cytochrome c oxidase (CcO) [13,14,15], being this activity more evident in hypoxic conditions. Similar results have been obtained in the present work, when we analyzed changes in O2 consumption induced by the NO-donor DETA-NO, and by eNOS activators as ACh and Bk.
Figure 4 shows that O2 consumption is lower at low O2 concentrations (30 μM) than in normoxia (130 μM O2). ACh, Bk and DETA-NO, which all inhibit O2 consumption at 130 and 30 μM O2, did not modify the different pattern rate of O2 consumption observed in hypoxia vs. normoxia. However, in the presence of L-NAME, the difference in the rate of O2 consumption at 130 or 30 mM O2 was abolished in control rings, in rings incubated with ACh or Bk plus L-NAME, but not in aorta incubated with DETA-NO plus L-NAME (Figure 4).
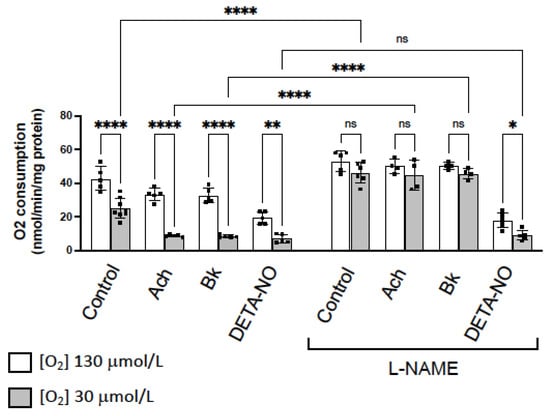
Figure 4.
NO inhibition of O2 consumption is more pronounced in hypoxic vessels. Rate of O2 consumption determined in normoxia (130 µM O2, white bars) and hypoxia (30 µM O2, grey bars) in basal conditions (control) and in the presence of two agents that activate eNOS, acetylcholine (ACh 10 µM) and bradykinin (Bk 10 µM), and the NO-donor DETA-NO (10 μM). In parallel, the same experiments were performed in the presence of the NOS inhibitor L-NAME (100 µM). The rate of O2 consumption was measured at 130 µM O2 and was expressed as nmol/min/mg protein. Dots represent individual data. Histograms and error bars show mean values ± SEM from n ≥ 5 independent experiments. ns = not significant, * p < 0.05, ** p< 0.01, **** p < 0.0001 by one-way ANOVA followed by Šídák’s multiple comparisons test (GraphPad Prism 9.2.0 Software, San Diego, CA, USA).
These results suggest that inhibition of eNOS activity and NO release, abolishes the differences in O2 consumption observed in hypoxic vs. normoxic conditions. However, in the presence of the exogenously added NO, L-NAME did not produce any effect. Therefore, differences in O2 consumption observed in hypoxia vs. normoxia, are due to the NO inhibitory activity on CcO, which is more pronounced in hypoxic conditions.
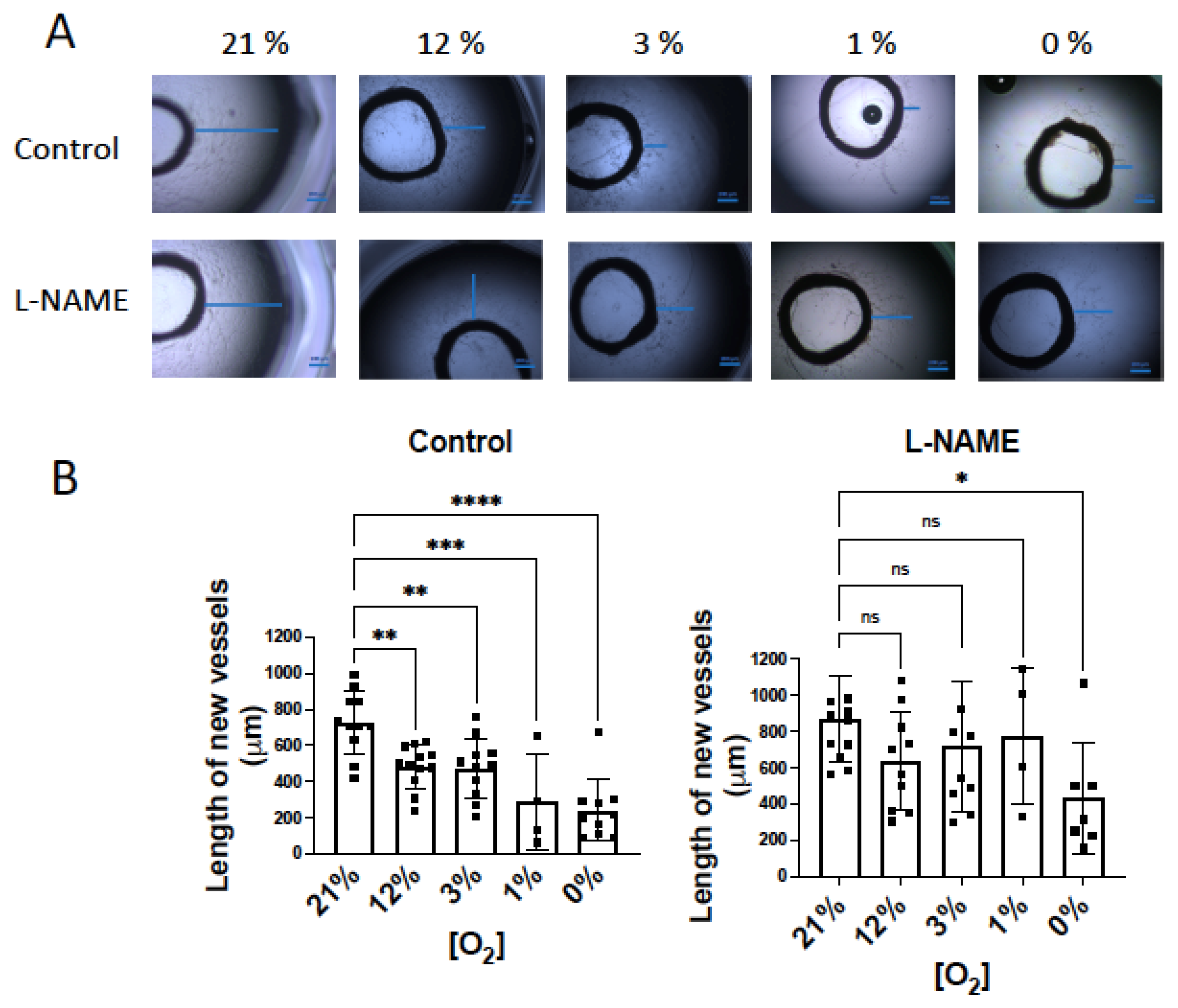
According to this, if NO inhibitory activity on O2 consumption is more evident in hypoxia, the NO inhibitor effect on angiogenesis may be, in turn, more marked. To confirm this hypothesis, our next objective was to analyze the influence of NO on angiogenic growth in hypoxic conditions. Aortic rings were incubated in a hypoxic chamber under different O2 concentrations: 21%, atmospheric concentration; 12%, concentration in vessels; 3% concentration in tissues; 1% and 0%, hypoxic conditions [15]. When aortic rings were incubated for 6 days in Matrigel®, the length of the largest new vessels diminished in parallel to decreased O2 concentration (Figure 5A). As expected, in the presence of L-NAME, the length of the sprouting vessels was similar in 21% to 1% O2 conditions, and it was only significantly lower at 0% O2 (Figure 5A).
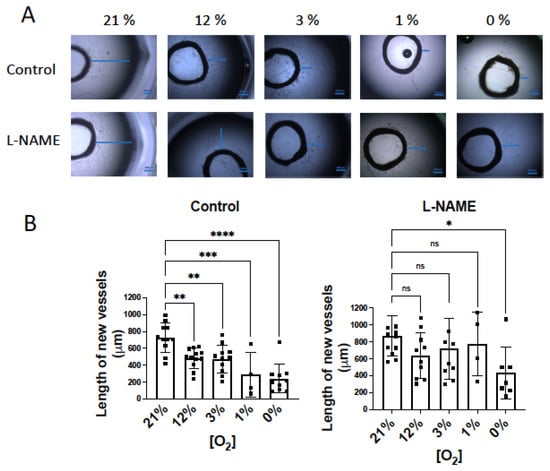
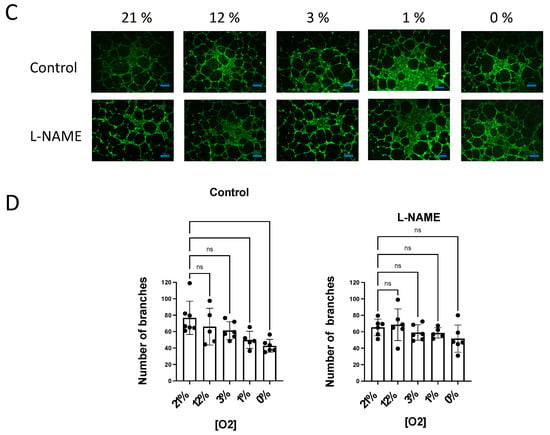
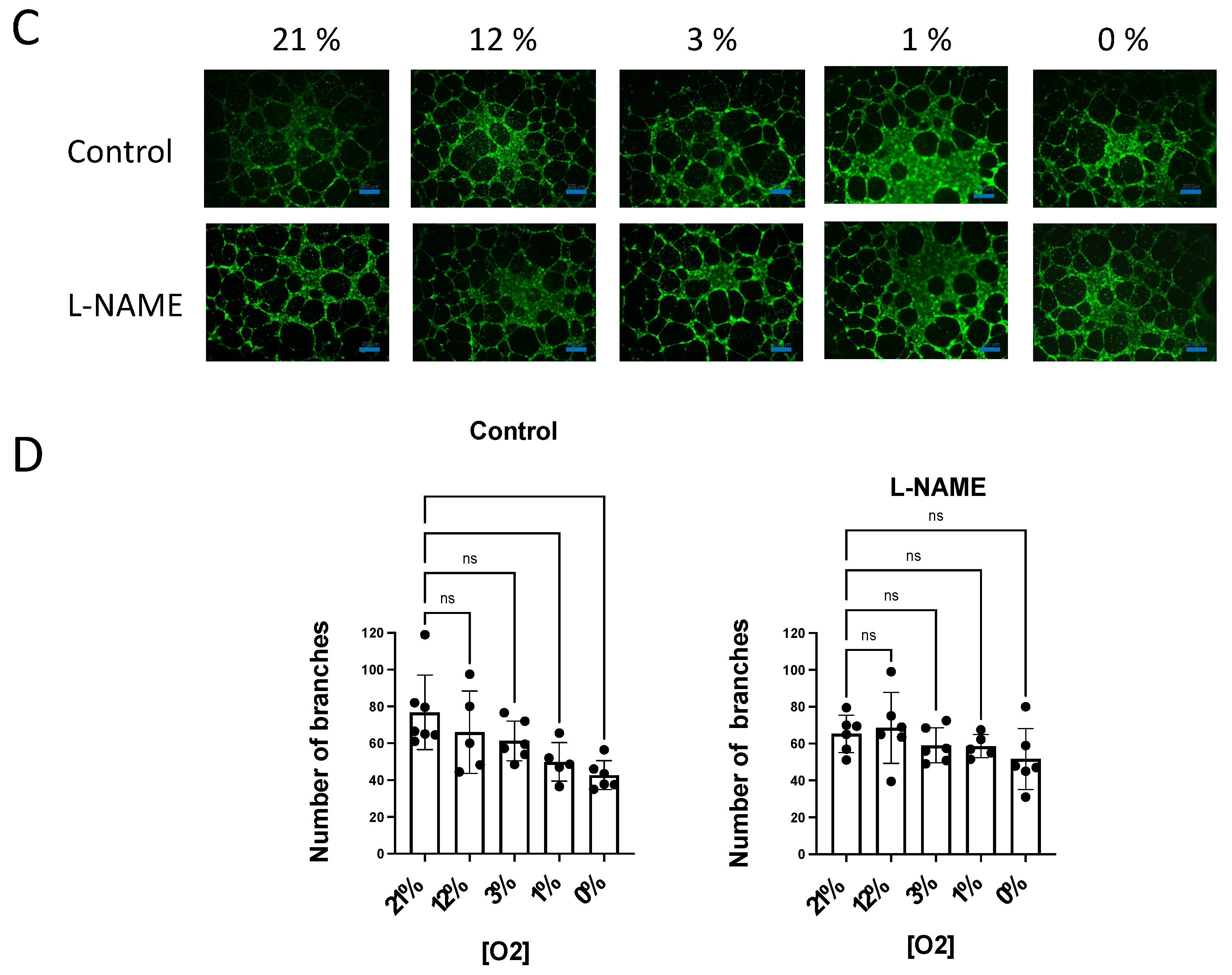
Figure 5.
NO inhibition of angiogenic growth is more evident in hypoxic vessels. (A) Representative rat aortic ring explants observed after 6 days of incubation in Matrigel ® in a hypoxic chamber under different concentrations of O2, (21%, 12%, 3%, 1%, 0%) in the absence and presence of L-NAME (100 µM). (B) Quantification of the sprouting response of rat aorta obtained under different concentrations of O2 in the absence and presence of L-NAME. The length of the longest neovessel formed, expressed as µm, was measured taking the outer surface of the ring as the starting point (blue lines). (C) Representative images of the tube formation obtained after 18 h of incubation of human aortic endothelial cells (hAoECs) in Matrigel ® in a hypoxic chamber under different concentrations of O2 (21%, 12%, 3%, 1%, 0%) in the absence and presence of L-NAME (100 µM). Fluorescence cell staining of each preparation was performed by incubation with 5 µM calcein AM. (D) Average number of branches obtained in the tube formation assay performed with human aortic endothelial cells (hAo EC) across different concentrations of O2 (21%, 12%, 3%, 1%, 0%) in the absence and presence of L-NAME (100 µM). Dots represent individual data. Histograms and error bars show mean values ± SEM from n ≥ 4 independent experiments. ns = not significant * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001 by one-way ANOVA followed by Šídák’s multiple comparisons test (GraphPad Prism 9.2.0 Software, San Diego, CA, USA).
Next, we performed similar experiments with human aortic ECs (hAo ECs) incubated in Matrigel® for 18 h. In these experiments, the number of new tubes was quantified as a measure of the angiogenic growth. Our results show that the number of new branches decreased in parallel with O2 availability, being significantly lower at 1% and 0% O2 concentrations. However, in the presence of L-NAME, the angiogenic growth was similar across the different O2 concentrations assayed (Figure 5B).
These results demonstrate that endogenous NO modulates angiogenesis in parallel with O2 consumption. These activities depend on O2 concentrations, being more marked at low O2 levels.
4. Discussion
Angiogenesis is an essential and complex biological response, facilitated by NO through the activation of the sGC pathway [5,7,8,9]. However, the angiogenic process requires an increase in the cellular energy demand under growth conditions [1], which could be hampered by the NO-dependent inhibition of CcO [13,14,15,19,20,21]. Therefore, the role of NO on the angiogenic process would be the balanced result of sGC activity and cellular energy availability; the latter dependent on CcO function. Present work analyzes these processes in parallel and key findings are presented under the following headings:
- (1)
- eNOS-derived NO inhibits angiogenic growth by a mechanism related to inhibition of CcO and independent of the sGC pathway
- (2)
- NO inhibition of the angiogenic growth and O2 consumption is more evident in hypoxic vessels
According to this, NO decreases angiogenic growth, an effect dependent on external O2 concentration. In the absence of eNOS-derived NO, the modulation of angiogenic growth, related to O2 concentration, disappears. Collectively, these observations support the notion that NO plays an essential role as modulator of the angiogenic growth in hypoxic vessels, by adjusting it to the O2 supply.
4.1. NO Inhibits Angiogenic Growth by a Mechanism Related to Inhibition of CcO and Independent of the sGC Pathway
It has been previously shown that NO significantly contributes to the proangiogenic program via the cGMP signaling pathway [9], which mediates the stimulatory effects of NO, particularly proliferation, adhesion, and chemotaxis at low NO concentrations. However, at high concentrations these processes are inhibited by mechanisms independent of cGMP [6].
NO, through the sGC pathway, can trigger EC migration by inducing angiogenic factors such as VEGF and/or inhibiting antiangiogenic factors [8]. Furthermore, NO has been reported both to promote and to inhibit the activity of the transcription factor hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1), which also plays a role in angiogenesis. High NO levels stabilize HIF-1alpha at all O2 concentrations. By contrast, lower NO concentrations decrease HIF-1alpha stabilized by hypoxia. This effect is dependent on the inhibition of mitochondrial respiration [22].
Controversial data has been obtained with NO-donors. An increased tube formation was observed in human ECs incubated with elevated concentrations of DETA-NO [23], which are higher that concentrations used in the present work. On the other hand, previous evidence has demonstrated a negative effect of NO donors on angiogenesis. Thus, different NO-releasing vasodilators inhibit angiogenesis, whereas the NOS inhibitor L-NMA promotes it [24]. The consequence of this anti-angiogenic activity was a reduction in the growth and metastatic properties of a Lewis lung carcinoma cells [25]. More recently, Ciccone et al. [26] described the antiangiogenic properties of DETA-NO and a new NO donor, and Yang et al. [27] found that DETA-NO inhibits angiogenic sprouting in the rat aortic ring assay. In our hands, DETA-NO, at the same concentration range that promotes sGC-induced vasodilation, also exhibited anti-angiogenic activity in the aortic ring model of angiogenesis. The contribution of our work is the observation that DETA-NO antiangiogenic activity was not mediated by the sGC pathway, since the sGC inhibitor ODQ did not affect it, despite it completely inhibited DETA-NO mediated vasodilatation. (Figure 1). Interestingly, the same range of concentrations that inhibits angiogenic sprouting also inhibits the rate of aortic O2 consumption in a sGC independent fashion. The parallelism observed between DETA-NO inhibition of mitochondrial O2 consumption and angiogenic growth suggest a close relationship between these two processes.
It is known that ECs meet their energetic requirements largely by glycolysis. However, for the full angiogenic response, ECs require both, an increase in glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation [1,28]. The conditional knockout of a subunit of the mitochondrial respiratory complex III, results in diminished EC proliferation [29], and specific deficiency of CcO slows wound healing-related vascularization and reduces angiogenesis and tumor growth [1]. According to this, the inhibition of mitochondrial O2 consumption by DETA-NO, through CcO inhibition [11,12,13,14,15], could be the mechanism involved in this anti-angiogenic activity.
To determine the role of endogenously released NO on the angiogenic sprouting, the activity of a NOS inhibitor, L-NAME, was assayed. In our hands, L-NAME inhibited sGC-induced vasodilation, exhibited pro-angiogenic activity and increased aortic O2 consumption (Figure 2), confirming for endogenous NO the same activity found with exogenously added NO. As the nNOS selective inhibitor SMTC does not affect these processes, eNOS or iNOS could be the isoforms responsible for the NO-release involved in the modulation of angiogenic growth. However, iNOS is least likely to participate in these effects since in our experimental conditions, mRNA levels of this isoform were not detected in the aorta ([18] and present results), nor in sprouting branches. Besides, nNOS was detected in the aorta, but not in the new vessels that sprout from the artery, while mRNA levels of eNOS were detected in both the aorta and new vessels and were maintained until the end of the angiogenic process that we assayed (Figure 3). Then, eNOS would be responsible of the endogenous NO release involved in the modulation of angiogenesis and the rate of O2 consumption. Results obtained in eNOS−/− mice confirm the role of eNOS as modulator of both processes, since an increase in angiogenic growth and in the rate of O2 consumption were observed in eNOS−/− mice vs. WT.
Interestingly, in rats, eNOS expression in the sprouting microvessels was significantly lower than in aorta, suggesting that this reduced expression of eNOS would facilitate the angiogenic growth. Moreover, eNOS expression in the new branches appears to be controlled by the parent vessel, as it dramatically decreased when they grew in the absence of the aortic ring. This intriguing observation needs future work to be confirmed.
4.2. NO-Induced Inhibition of Angiogenic Growth and O2 Consumption Depends on the O2 Concentration and Is More Pronounced in Hypoxic Vessels
It is well known that NO competes with O2 for binding to CcO and inhibits it, which makes this inhibition highly relevant in hypoxic conditions [19,20,21]. In fact, an immediate effect of the reduced supply of O2 during hypoxia is that endogenous NO becomes a more effective inhibitor of CcO and, consequently, the rate of O2 consumption is reduced [13,14,15]. Therefore, NO adjusts O2 consumption to O2 availability.
Present results confirm previous evidence and show that the rate of O2 consumption in the rat’s aorta was significantly lower at 30 μM than 130 μM O2, but in the presence of L-NAME, this difference was not observed and the rate of O2 consumption was similar at high and low O2 levels (Figure 4). Therefore, NO is responsible for the different rate of O2 consumption observed at low vs. high O2 concentrations.
A significant difference in the rate of O2 consumption at low or high levels was also observed when endogenous NO release was induced by ACh or Bk, two agents that activate eNOS in vessels [30], and differences were abolished by addition of L-NAME, confirming that endogenously released NO was responsible for the decreased rate of O2 consumption observed at low O2 levels. As expected, in the presence of DETA-NO, the lower rate of O2 consumption at 30 μM O2 was not increased by L-NAME, excluding a direct effect of L-NAME on O2 consumption.
Similar observations were reproduced in experiments with the aortic ring model of angiogenesis. When O2 concentration decreased (from 21% to 0%), lower neovessel growth was observed, suggesting that a lower O2 availability compromise vessel sprouting (Figure 5).
Hypoxia is a potent inducer of angiogenesis, through HIF-1 stabilization, leading to the activation of many target genes including VEGF [31,32]. Paradoxically, when the angiogenic process is triggered by growth factors, as occurs in our aortic ring model, hypoxia directly inhibits neo-vessels formation, as a previous work described [32]. Similar results were obtained when human ECs were incubated in Matrigel ® with growth factor at different O2 concentrations: the new tube formation was significantly decreased at O2 concentrations lower than 3%. Therefore, previous and present results demonstrate that changes in O2 levels profoundly affect the capacity of ECs to respond to angiogenic stimuli like growth factors, and these changes may be related to a lower mitochondrial ATP supply [1] derived from a lower O2 consumption in hypoxic conditions.
Interestingly, this lower O2 consumption adjusted to O2 availability was not observed in the presence of L-NAME, and, in parallel, no significant differences were found in the angiogenic growth between the low or high O2 levels. Only in anoxia (0% O2) was the aortic sprouting decreased and the L-NAME did not revert this inhibition. According to these observations, the lack of energy supply derived from a low rate of mitochondrial O2 consumption only affects angiogenic growth in the absence of O2. In the presence of low-to-high levels of O2 (1–21%), the control of O2 consumption and energy supply for the angiogenic growth depends on NO interaction with CcO. If NO release is inhibited by L-NAME, mitochondrial rate of O2 consumption was not affected by lower O2 levels, nor was angiogenic growth. Therefore, NO, but not lower O2 levels, is responsible for the decreased angiogenic response observed in hypoxia, and this activity could be attributed, at least partly, to competitive inhibition of CcO byNO, which decreases O2 consumption and is potentiated at low O2 concentrations. As NO becomes more effective as inhibitor of CcO, the mitochondrial respiration is impaired, and compromises the energetically demanding angiogenic growth.
In some circumstances, such as tumor progression or ischemic disease, where pro-angiogenic factors such as VEGF are highly expressed and co-exist with hypoxic conditions, the contribution of NO as modulator of the angiogenic growth could be a promising target to impair pathological angiogenesis.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.D.; Data curation, Victor Victor, F.J.-A. and P.D.; Investigation, C.A., D.V., F.M. and F.J.-A.; Methodology, C.A., D.V., F.M., C.N. and L.G.; Resources, V.M.V.; Supervision, P.D.; Validation, P.D.; Writing—original draft, F.J.-A. and P.D.; Writing—review & editing, C.A., V.M.V., F.J.-A. and P.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research has been supported by grants from the Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad (SAF2013-45362-R). PI19/00838, by Carlos III Health Institute and by the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF ‘‘A way to build Europe’’); PROMETEO/2019/027 by Ministry of Health of the Valencian Regional Government.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Ethics Committee of Universidad de Valencia (protocol code 2014/VSC/PEA/00117, date of approval 25 July 2014).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Schiffmann, L.M.; Werthenbach, J.P.; Heintges-Kleinhofer, F.; Seeger, J.M.; Fritsch, M.; Günther, S.D.; Willenborg, S.; Brodesser, S.; Lucas, C.; Jüngst, C.; et al. Mitochondrial respiration controls neoangiogenesis during wound healing and tumour growth. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eelen, G.; De Zeeuw, P.; Treps, L.; Harjes, U.; Wong, B.; Carmeliet, P. Endothelial Cell Metabolism. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 3–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, R.H.; Alitalo, K. Molecular regulation of angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 464–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burke, A.J.; Sullivan, F.J.; Giles, F.J.; Glynn, S.A. The yin and yang of nitric oxide in cancer progression. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mistry, R.K.; Brewer, A.C. Redox regulation of gasotransmission in the vascular system: A focus on angiogenesis. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 108, 500–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alsharabasy, A.M.; Glynn, S.A.; Pandit, A. The role of extracellular matrix in tumour angiogenesis: The throne has NOx servants. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2020, 48, 2539–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, S.; Shen, X.; Glawe, J.; Kolluru, G.K.; Kevil, C.G. Nitric Oxide and Hydrogen Sulfide Regulation of Ischemic Vascular Growth and Remodeling. Compr. Physiol. 2019, 9, 1213–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, F.H.; Dervan, E.; Bhattacharyya, D.D.; McAuliffe, J.D.; Miranda, K.M.; Glynn, S.A. The Role of Nitric Oxide in Cancer: Master Regulator or Not? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehners, M.; Dobrowinski, H.; Feil, S.; Feil, R. cGMP Signaling and Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Plasticity. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2018, 5, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ziche, M.; Morbidelli, L. Nitric Oxide and Angiogenesis. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2000, 50, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poderoso, J.J.; Helfenberger, K.; Poderoso, C. The effect of nitric oxide on mitochondrial respiration. Nitric Oxide 2019, 88, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, C.; Moncada, S. Nitric Oxide, Cytochrome C Oxidase, and the Cellular Response to Hypoxia. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2010, 30, 643–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Núnez, C.; Víctor, V.M.; Tur, R.; Alvarez-Barrientos, A.; Moncada, S.; Esplugues, J.V.; D’Ocón, P. Discrepancies Between Nitroglycerin and NO-Releasing Drugs on Mitochondrial Oxygen Consumption, Vasoactivity, and the Release of NO. Circ. Res. 2005, 97, 1063–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Victor, V.M.; Nuñez, C.; D’Ocón, P.; Taylor, C.T.; Esplugues, J.V.; Moncada, S. Regulation of oxygen distribution in tissues by endothelial nitric oxide. Circ. Res. 2009, 104, 1178–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nuñez, C.; Victor, V.M.; Martí, M.; D’Ocon, P. Role of endothelial nitric oxide in pulmonary and systemic arteries during hypoxia. Nitric Oxide 2014, 37, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, D.; Hernández, B.; Segura, V.; Pascual, D.; Fornaciari, G.; Monto, F.; Mirabet, V.; Montesinos, M.C.; D’Ocon, P. Methodological Approach to Use Fresh and Cryopreserved Vessels as Tools to Analyze Pharmacological Modulation of the Angiogenic Growth. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2016, 68, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muedra, V.; Moreno, L.; Rodilla, V.; Arce, C.; Montó, F.; Blázquez, Á.; Pérez, P.; D’Ocon, P. Dexamethasone Preconditioning in Cardiac Procedures Reduces Decreased Antithrombin Activity and Is Associated to Beneficial Outcomes: Role of Endothelium. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arce, C.; Vicente, D.; Segura, V.; Flacco, N.; Montó, F.; Almenar, L.; Agüero, J.; Rueda, J.; Jiménez-Altayó, F.; Vila, E.; et al. Activation of α1A-adrenoceptors desensitizes the rat aorta response to phenylephrine through a neuronal NOS pathway, A mechanism lost with ageing. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 174, 2015–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moncada, S.; Erusalimsky, J. Does nitric oxide modulate mitochondrial energy generation and apoptosis? Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2002, 3, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagen, T.; Taylor, C.T.; Lam, F.; Moncada, S. Redistribution of Intracellular Oxygen in Hypoxia by Nitric Oxide: Effect on HIF1alpha. Science 2003, 302, 1975–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, C.E.; Giulivi, C. Nitric oxide regulation of mitochondrial oxygen consumption II: Molecular mechanism and tissue physiology. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2007, 292, C1993–C2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mateo, J.; García-Lecea, M.; Cadenas, S.; Hernández, C.; Moncada, S. Regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha by nitric oxide through mitochondria-dependent and -independent pathways. Biochem. J. 2003, 376, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schwalm, S.; Pfeilschifter, J.; Huwiler, A. Sphingosine kinase 1 is critically involved in nitric oxide-mediated human endothelial cell migration and tube formation. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 160, 1641–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pipili-Synetos, E.; Sakkoula, E.; Haralabopoulos, G.; Andriopoulou, P.; Peristeris, P.; Maragoudakis, M. Evidence that nitric oxide is an endogenous antiangiogenic mediator. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1994, 111, 894–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pipili-Synetos, E.; Papageorgiou, A.; Sakkoula, E.; Sotiropoulou, G.; Fotsis, T.; Karakiulakis, G.; Maragoudakis, M. Inhibition of angiogenesis, tumour growth and metastasis by the NO-releasing vasodilators, isosorbide mononitrate and dinitrate. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1995, 116, 1829–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ciccone, V.; Monti, M.; Monzani, E.; Casella, L.; Morbidelli, L. The metal-nonoate Ni(SalPipNONO) inhibits in vitro tumor growth, invasiveness and angiogenesis. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 13353–13365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, C.; Hwang, H.H.; Jeong, S.; Seo, D.; Jeong, Y.; Lee, D.Y.; Lee, K. Inducing angiogenesis with the controlled release of nitric oxide from biodegradable and biocompatible copolymeric nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 6517–6530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Potente, M.; Carmeliet, P. The Link Between Angiogenesis and Endothelial Metabolism. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2017, 79, 43–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diebold, L.P.; Gil, H.J.; Gao, P.; Martinez, C.A.; Weinberg, S.; Chandel, N.S. Mitochondrial complex III is necessary for endothelial cell proliferation during angiogenesis. Nat. Metab. 2019, 1, 158–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moncada, S.; Higgs, E.A. Nitric Oxide and the Vascular Endothelium. In The Vascular Endothelium I. Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology; Moncada, S., Higgs, A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; Volume 176, pp. 213–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, P.H.; Ratcliffe, P. Oxygen sensors and angiogenesis. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2002, 13, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aplin, A.; Nicosia, R.F. Hypoxia paradoxically inhibits the angiogenic response of isolated vessel explants while inducing overexpression of vascular endothelial growth factor. Angiogenesis 2016, 19, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).