Hypobiosis and Development of Haemonchus contortus and Trichostrongylus colubriformis Infection in Lambs under Different Levels of Nutrition
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
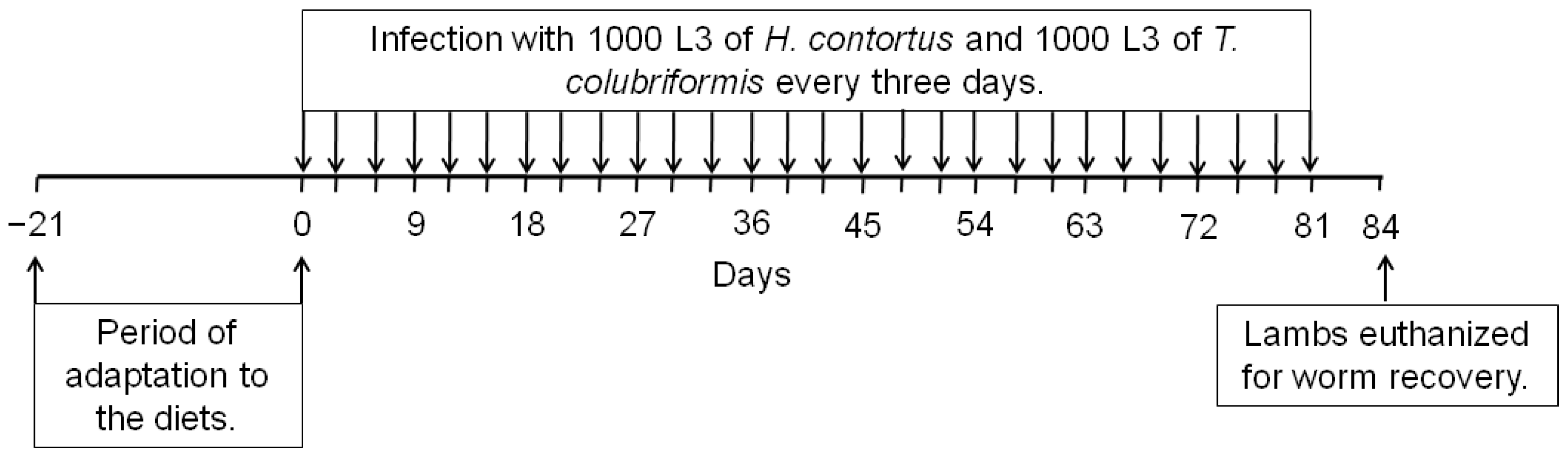
2.1. Description of the Experiment
- Diet 1—infected (n = 7) and control (n = 4);
- Diet 2—infected (n = 7) and control (n = 4);
- Diet 3—infected (n = 7) and control (n = 4);
- Diet 4—infected (n = 6) and control (n = 4).
2.2. Nematode Isolates, Production of L3, and Serial Infections
2.3. Blood Samples
2.4. Worm Examination
2.5. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
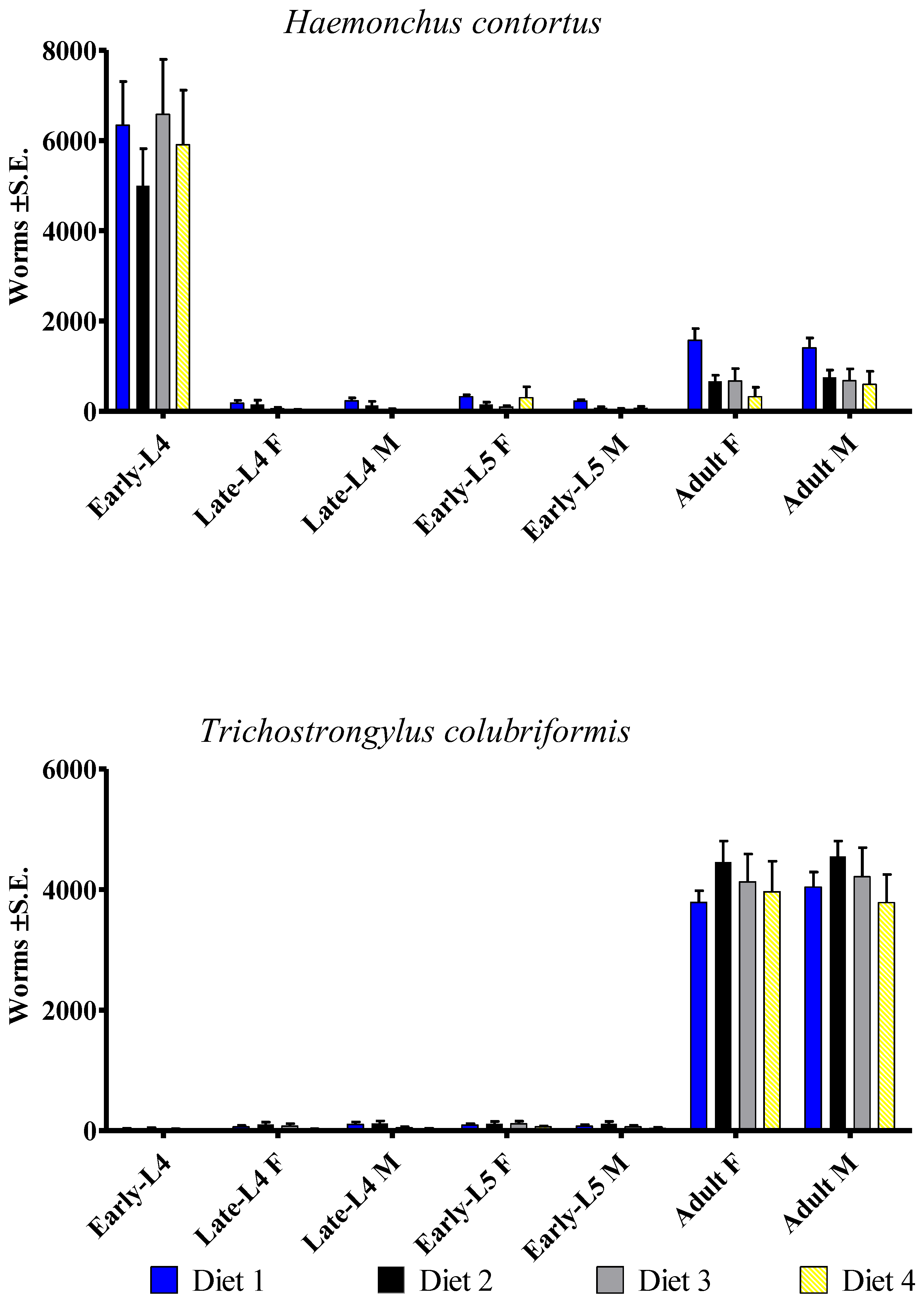
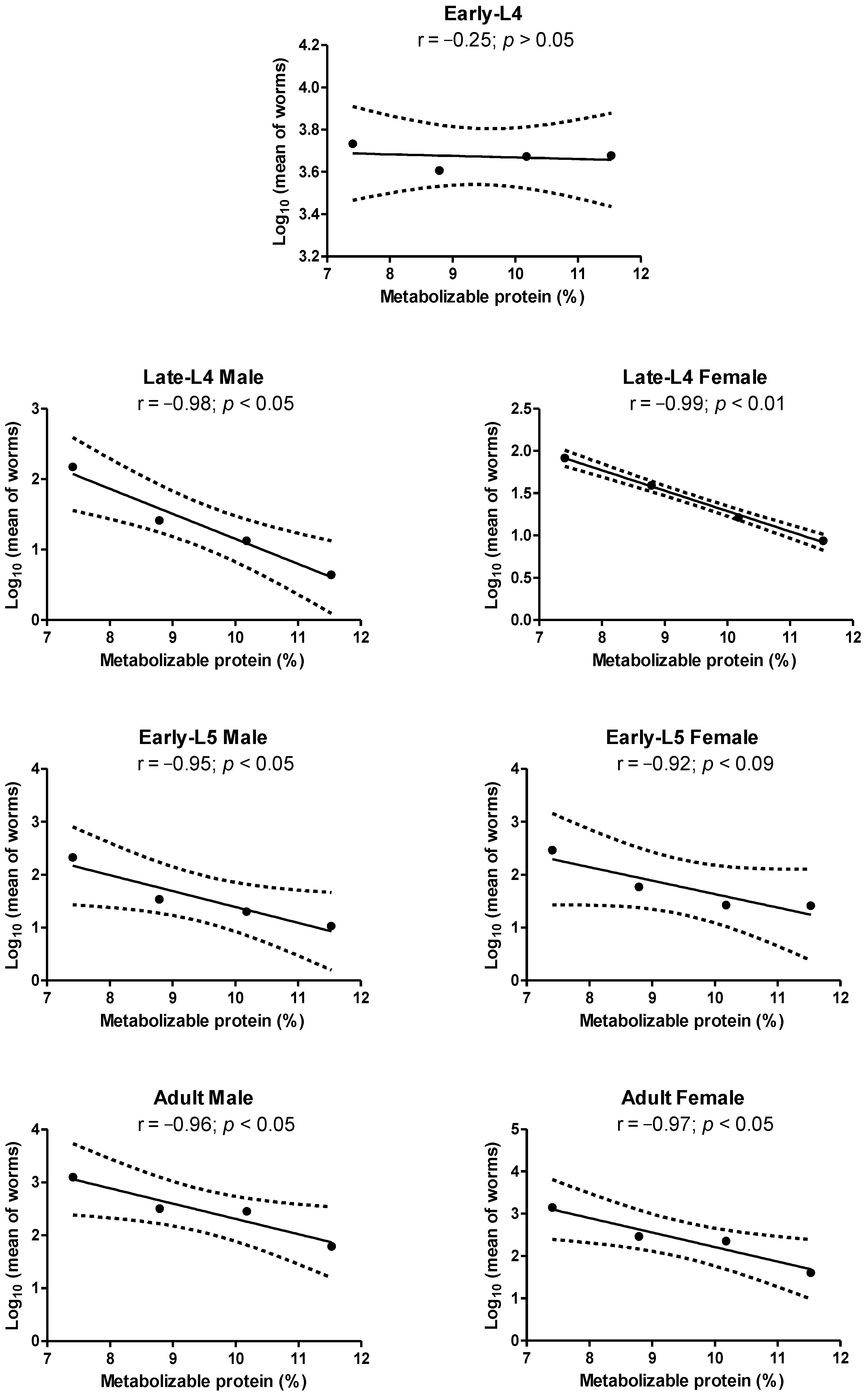
3.1. Haemonchus contortus
3.2. Trichostrongylus colubriformis
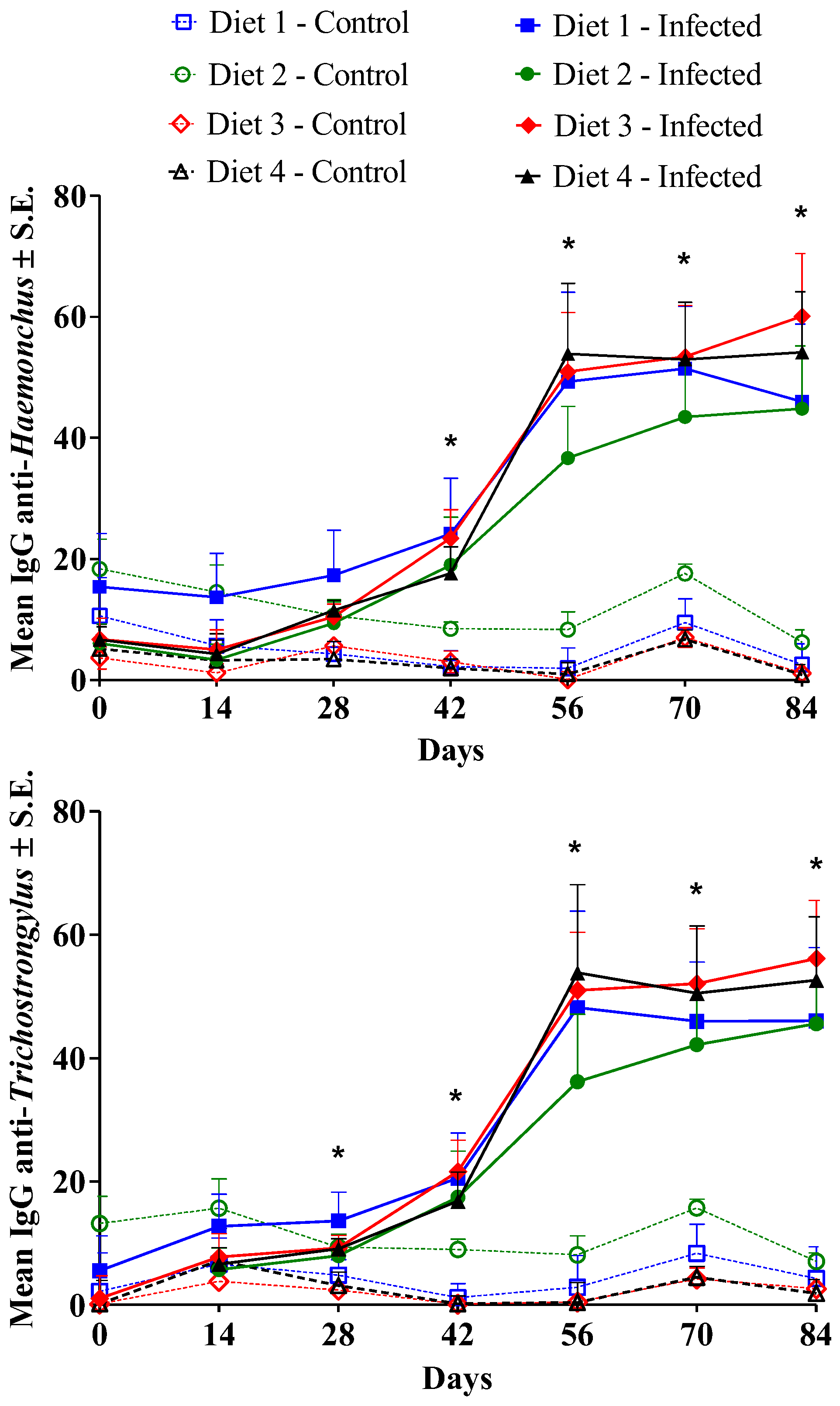
3.3. Immune Response
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wilmsen, M.O.; Silva, B.F.; Bassetto, C.C.; Amarante, A.F.T. Gastrointestinal nematode infections in sheep raised in Botucatu, State of São Paulo, Brazil. Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Vet. 2014, 23, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chagas, A.C.S.; Tupy, O.; Santos, I.B.; Esteves, S.N. Economic impact of gastrointestinal nematodes in Morada Nova sheep in Brazil. Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Vet. 2022, 31, e008722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardia, D.F.F.; Rocha-Oliveira, R.A.; Tsunemi, M.H.; Amarante, A.F.T. Immune response and performance of growing Santa Ines lambs to artificial Trichostrongylus colubriformis infections. Vet. Parasitol. 2011, 182, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriazakis, I.; Anderson, D.H.; Oldham, J.D.; Coop, R.L.; Jackson, F. Long-term subclinical infection with Trichostrongylus colubriformis: Effects on food intake, diet selection and performance of growing lambs. Vet. Parasitol. 1996, 61, 297–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, M.A.; Bompadre, T.F.V.; Fernandes, E.A.N.; Katiki, L.M.; Mui, T.S.; Abdalla, A.L.; Louvandini, H. Computed tomography and radioactive 32P detected phosphorus impairment in metabolism, reduced bones density and animal performance caused by mixed infection of Haemonchus contortus and Trichostrongylus colubriformis in sheep. Vet. Parasitol. 2023, 315, 109887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Sullivan, B.M.; Donald, A.D. Responses to infection with Haemonchus contortus and Trichostrongylus colubriformis in ewes of different reproductive status. Int. J. Parasitol. 1973, 3, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besier, R.B.; Kahn, L.P.; Sargison, N.D.; Van Wyk, J.A. The pathophysiology, ecology and epidemiology of Haemonchus contortus infection in small ruminants. Adv. Parasitol. 2016, 93, 95–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgado, J.A.; Santos, C.P. Overview of anthelmintic resistance of gastrointestinal nematodes of small ruminants in Brazil. Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Vet. 2016, 25, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cintra, M.C.R.; Teixeira, V.N.; Nascimento, L.V.; Sotomaior, C.S. Lack of efficacy of monepantel against Trichostrongylus colubriformis in sheep in Brazil. Vet. Parasitol. 2016, 216, 4–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gainza, Y.A.; Santos, I.B.; Figueiredo, A.; Santos, L.A.L.; Esteves, S.N.; Barioni-Junior, W.; Minho, A.P.; Chagas, A.C.S. Anthelmintic resistance of Haemonchus contortus from sheep flocks in Brazil: Concordance of in vivo and in vitro (RESISTA-Test©) methods. Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Vet. 2021, 30, 025120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, N.; Neves, J.H.; Pennacchi, C.S.; Castilhos, A.M.; Amarante, A.F.T. Performance of lambs under four levels of dietary supplementation and artificially mix-infected with Haemonchus contortus and Trichostrongylus colubriformis. Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Vet. 2021, 30, 025420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louvandini, H.; Veloso, C.F.M.; Paludo, G.R.; Dell’ Porto, A.; Gennari, S.M.; McManus, C.M. Influence of protein supplementation on the resistance and resilience on young hair sheep naturally infected with gastrointestinal nematodes during rainy and dry seasons. Vet. Parasitol. 2006, 137, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, L.J.; Walkden-Brown, S.W.; Kahn, L.P. Ecology of the free-living stages of major trichostrongylid parasites of sheep. Vet. Parasitol. 2006, 42, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, D.B. Observations on the self-cure reaction and other forms of immunological responsiveness against Haemonchus contortus in sheep. Int. J. Parasitol. 1983, 13, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, M.C.; Xavier, J.K.; Amarante, M.R.V.; Bassetto, C.C.; Amarante, A.F.T. Immune response to Haemonchus contortus and Haemonchus placei in sheep and its role on parasite specificity. Vet. Parasitol. 2014, 203, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés, A.; Muñoz-Antoli, C.; Esteban, J.G.; Toledo, R. Th2 and Th1 responses: Clear and hidden sides of immunity against intestinal helminths. Trends Parasitol. 2017, 33, 678–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatongi, P.M.; Prichard, R.K.; Ranjan, S.; Gathuma, J.M.; Munyua, W.K.; Cheruiyot, H.; Scott, M.E. Hypobiosis of Haemonchus contortus in natural infections of sheep and goats in a semi-arid area of Kenya. Vet. Parasitol. 1998, 77, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dineen, J.K.; Donald, A.D.; Wagland, B.M.; Offner, J. The dynamics of the host-parasite relationship: III. The response of sheep to primary infection with Haemonchus contortus. Parasitology 1965, 55, 515–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barger, I.A.; Le Jambre, L.F.; Georgi, J.R.; Davies, H.I. Regulation of Haemonchus contortus populations in sheep exposed to continuous infection. Int. J. Parasitol. 1985, 15, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eysker, M. Inhibition of the development of Trichostrongylus spp. as third stage larvae in sheep. Vet. Parasitol. 1978, 4, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobson, R.J.; Waller, P.J.; Donald, A.D. Population dynamics of Trichostrongylus colubriformis in sheep: The effect of host age on the establishment of infective larvae. Int. J. Parasitol. 1990, 20, 353–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueno, H.; Gonçalves, P.C. Manual Para Diagnóstico das Helmintoses de Ruminantes, 4th ed.; Japan International Cooperation Agency: Tokyo, Japan, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Rocha, R.A. Sobrevivência e Migração Vertical de Larvas Infectantes de Trichostrongylus colubriformis em Gramíneas, nas Diferentes Estações do ano. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade Estadual Paulista, Botucatu, SP, Brazil, 24 April 2006. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/11449/104111 (accessed on 24 July 2023).
- Silva, B.F. Migração Vertical das Larvas Infectantes de Haemonchus contortus em Capim Braquiária (Brachiaria decumbens). Master’s Dissertation, Universidade Estadual Paulista, Botucatu, SP, Brazil, 2007. Available online: https://www2.ibb.unesp.br/posgrad/teses/bga_me_2007_bruna_silva.pdf (accessed on 24 July 2023).
- Amarante, A.F.T.; Susin, I.; Rocha, R.A.; Silva, M.B.; Mendes, C.Q.; Pires, A.V. Resistance of Santa Ines and crossbred ewes to naturally acquired gastrointestinal nematode infections. Vet. Parasitol. 2009, 165, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, B.F.; Bassetto, C.C.; Amarante, A.F.T. Immune responses in sheep naturally infected with Oestrus ovis (Diptera: Oestridae) and gastrointestinal nematodes. Vet. Parasitol. 2012, 190, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanobana, K.; Vervelde, L.; Van Der Veer, M.; Eysker, M.; Ploeger, H. Characterization of host responder types after a single Cooperia oncophora infection: Kinetics of the systemic immune response. Parasite Immunol. 2001, 23, 641–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SAS Institute. SAS User’s Guide; Version 9.4 [Online]; SAS Institute Inc.: Cary, NC, USA, 2016; Available online: https://support.sas.com/ (accessed on 24 July 2023).
- Melo, G.K.A.; Ítavo, C.C.B.F.; Monteiro, K.L.S.; Silva, J.A.; Silva, P.C.G.; Ítavo, L.C.V.; Borges, D.G.L.; Borges, F.A. Effect of creep-fed supplement on the susceptibility of pasture-grazed suckling lambs to gastrointestinal helminthes. Vet. Parasitol. 2017, 239, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, E.M.; Parkins, J.J.; Holmes, P.H. The effect of dietary protein on the pathophysiology of acute ovine haemonchosis. Vet. Parasitol. 1986, 20, 291–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faz-López, B.; Morales-Montor, J.; Terrazas, L.I. Role of macrophages in the repair process during the tissue migrating and resident helminth infections. BioMed. Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 8634603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benavides, M.V.; Sonstegard, T.S.; Kemp, S.; Mugambi, J.M.; Gibson, J.P.; Baker, R.L.; Hanotte, O.; Marshall, K.; Van Tassell, C. Identification of novel loci associated with gastrointestinal parasite resistance in a Red Maasai x Dorper backcross population. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, 0122797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veglia, F. The Anatomy and Life-History of the Haemonchhus contortus (Rud). Rep. Dir. Vet. Res. 1915, 3–4, 347–500. Available online: https://repository.up.ac.za/handle/2263/10471 (accessed on 29 September 2023).
- Albuquerque, A.C.A.; Bassetto, C.C.; Almeida, F.A.; Hildersley, K.A.; McNeilly, T.N.; Britton, C.; Amarante, A.F.T. Differences in immune responses to Haemonchus contortus infection in the susceptible Ile de France and the resistant Santa Ines sheep under different anthelmintic treatments regimens. Vet. Res. 2019, 50, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtney, C.H.; Parker, C.F.; McClure, K.E.; Herd, R.P. Population dynamics of Haemonchus contortus and Trichostrongylus spp. in sheep. Int. J. Parasitol. 1983, 13, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michel, J.F. The phenomena of host resistance and the course of infection of Ostertagia ostertagi in calves. Parasitology 1963, 53, 63–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carvalho, N.; Neves, J.H.d.; Pennacchi, C.S.; Amarante, A.F.T.d. Hypobiosis and Development of Haemonchus contortus and Trichostrongylus colubriformis Infection in Lambs under Different Levels of Nutrition. Ruminants 2023, 3, 401-412. https://doi.org/10.3390/ruminants3040033
Carvalho N, Neves JHd, Pennacchi CS, Amarante AFTd. Hypobiosis and Development of Haemonchus contortus and Trichostrongylus colubriformis Infection in Lambs under Different Levels of Nutrition. Ruminants. 2023; 3(4):401-412. https://doi.org/10.3390/ruminants3040033
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarvalho, Nadino, José Henrique das Neves, Caio Santos Pennacchi, and Alessandro Francisco Talamini do Amarante. 2023. "Hypobiosis and Development of Haemonchus contortus and Trichostrongylus colubriformis Infection in Lambs under Different Levels of Nutrition" Ruminants 3, no. 4: 401-412. https://doi.org/10.3390/ruminants3040033
APA StyleCarvalho, N., Neves, J. H. d., Pennacchi, C. S., & Amarante, A. F. T. d. (2023). Hypobiosis and Development of Haemonchus contortus and Trichostrongylus colubriformis Infection in Lambs under Different Levels of Nutrition. Ruminants, 3(4), 401-412. https://doi.org/10.3390/ruminants3040033





