Evaluating the Bias of Two Point-of-Care Glucometers for Calves and Ewes: Awareness for Ruminant Practitioners
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
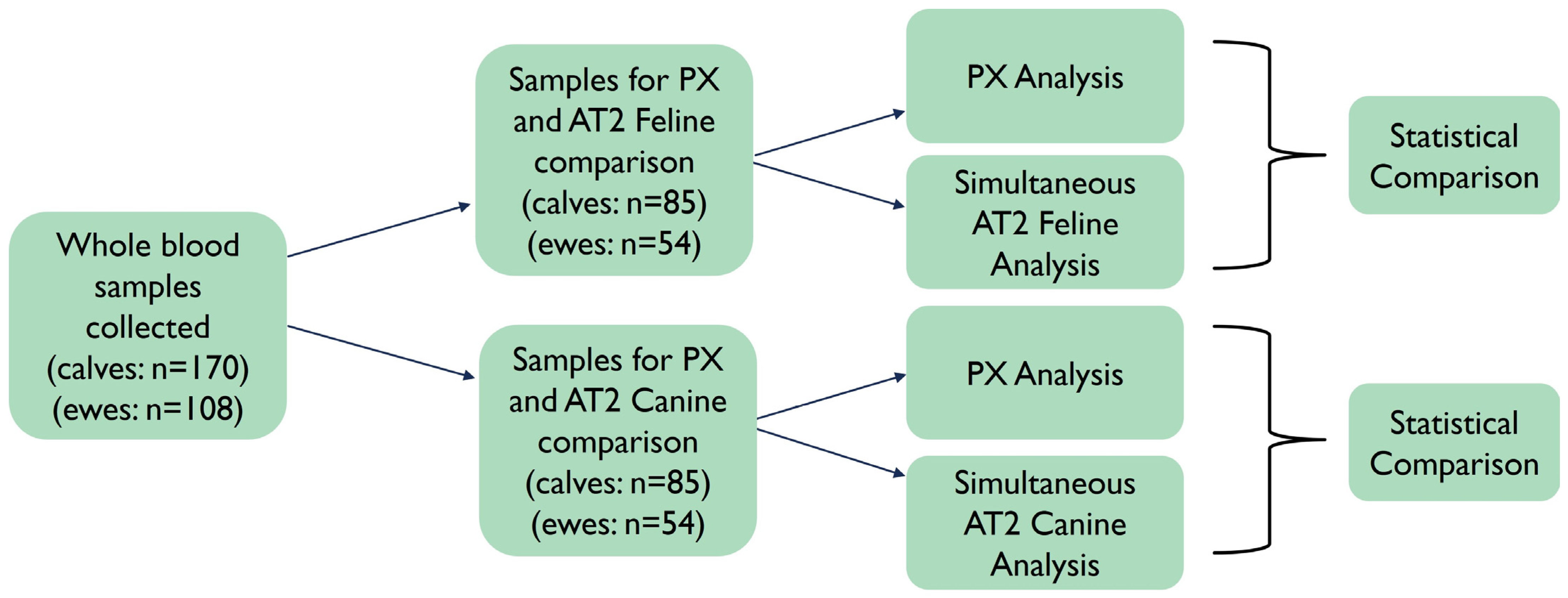
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Calf Study Group
2.2. Ewe Study Group
3. Results
3.1. Samples and Microvalidation
3.1.1. Calf Study Group
3.1.2. Ewe Study Group
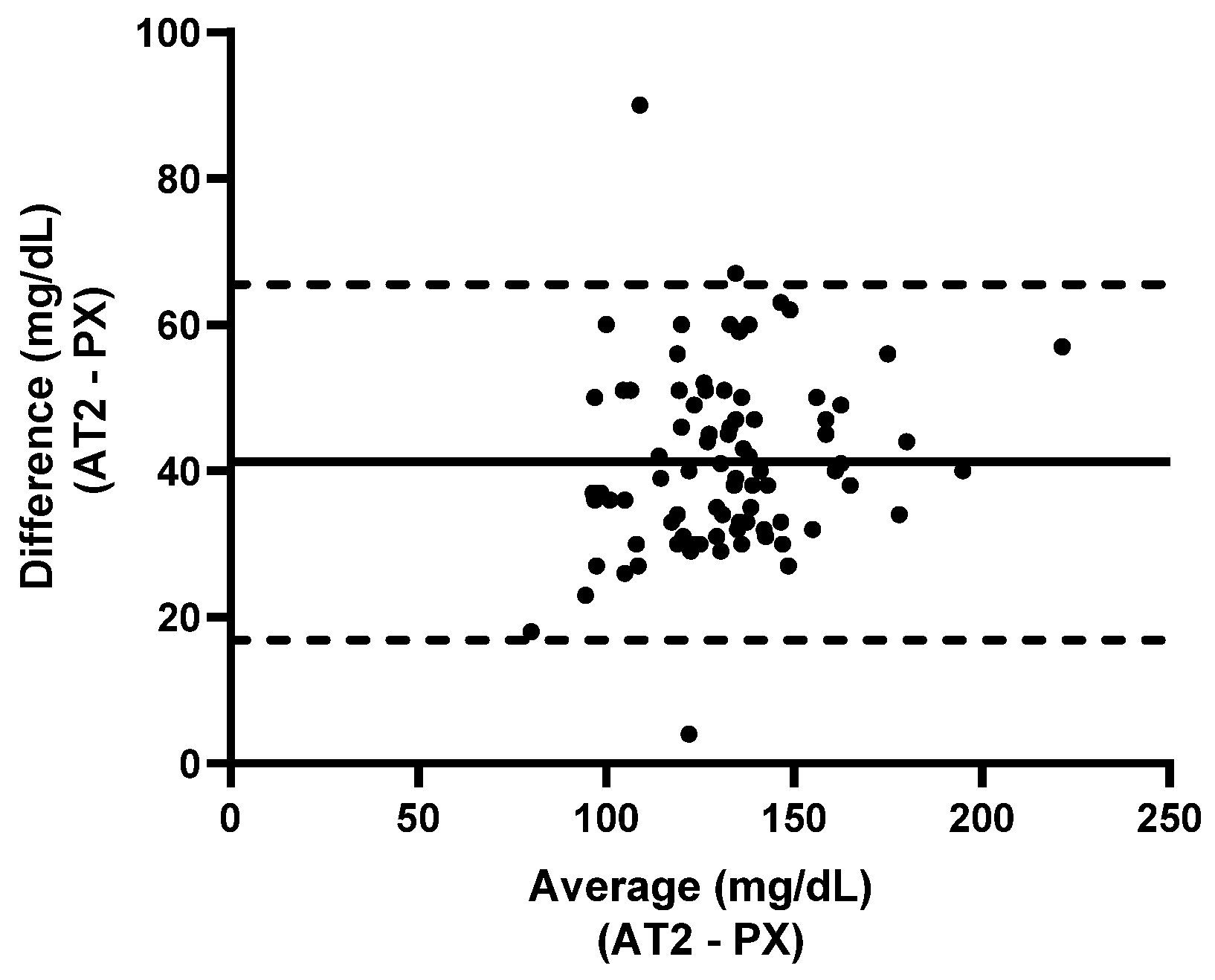
3.2. PX vs. AT2 Canine Setting
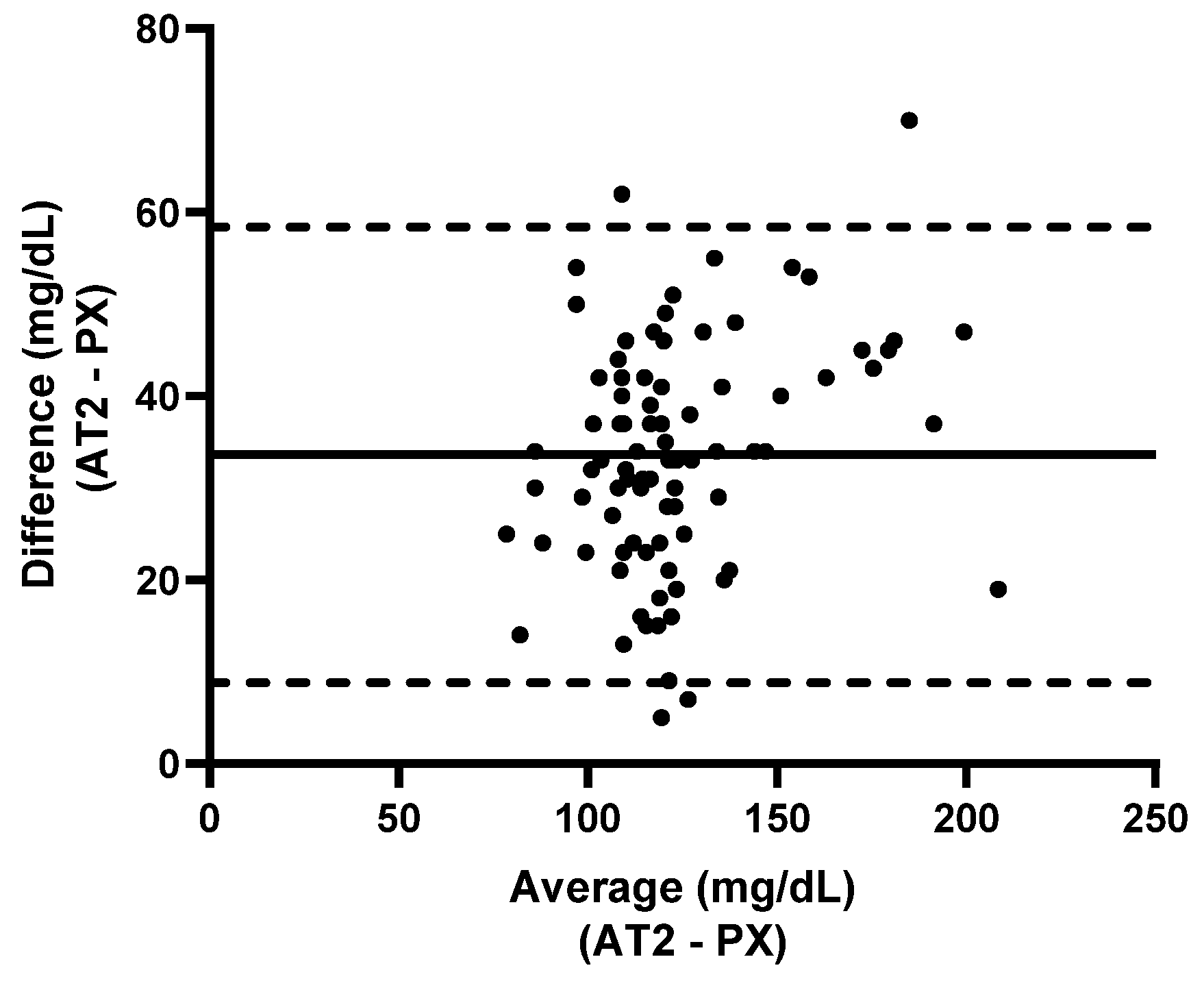
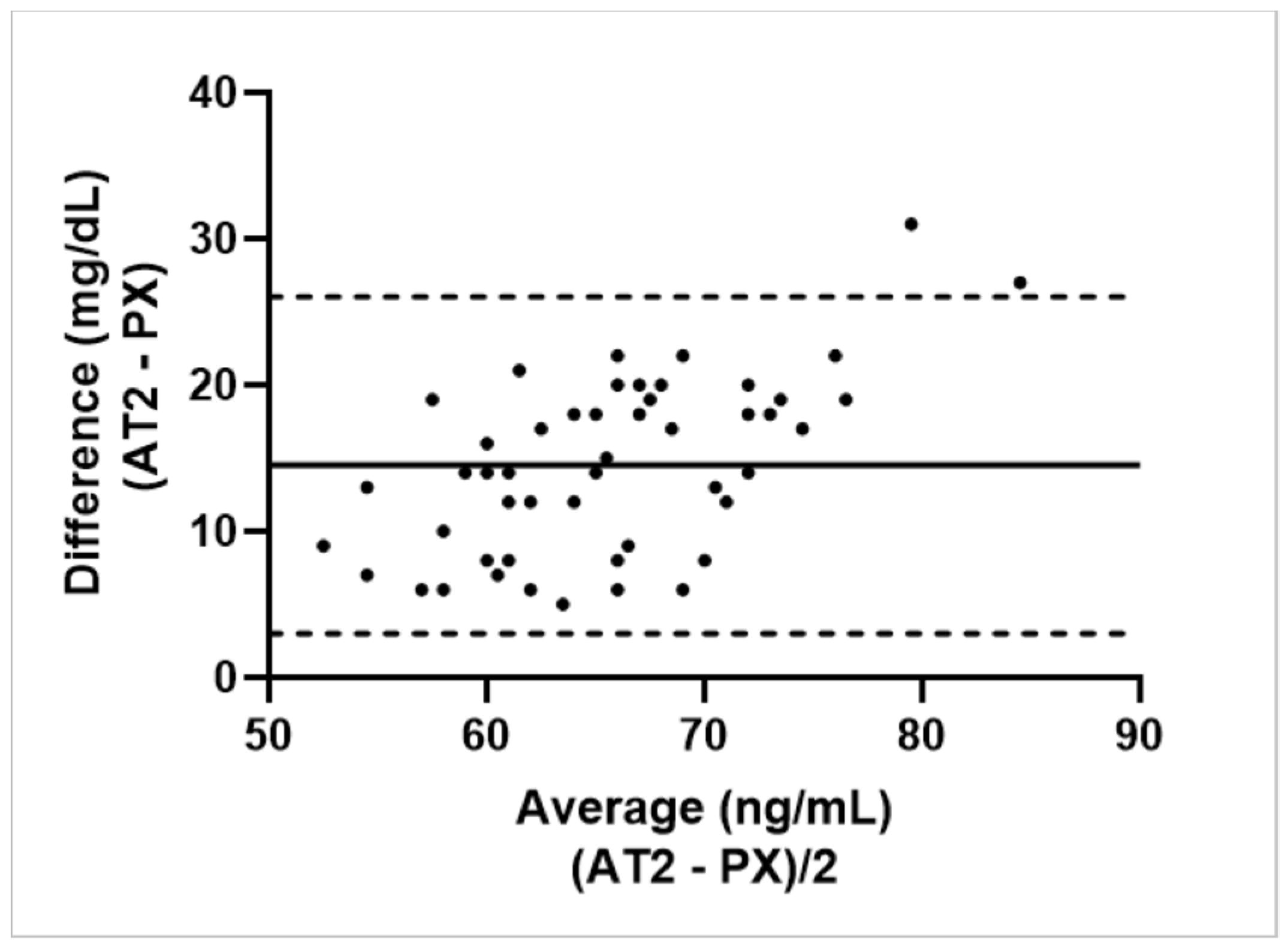
3.2.1. Calf Study Group
3.2.2. Ewe Study Group
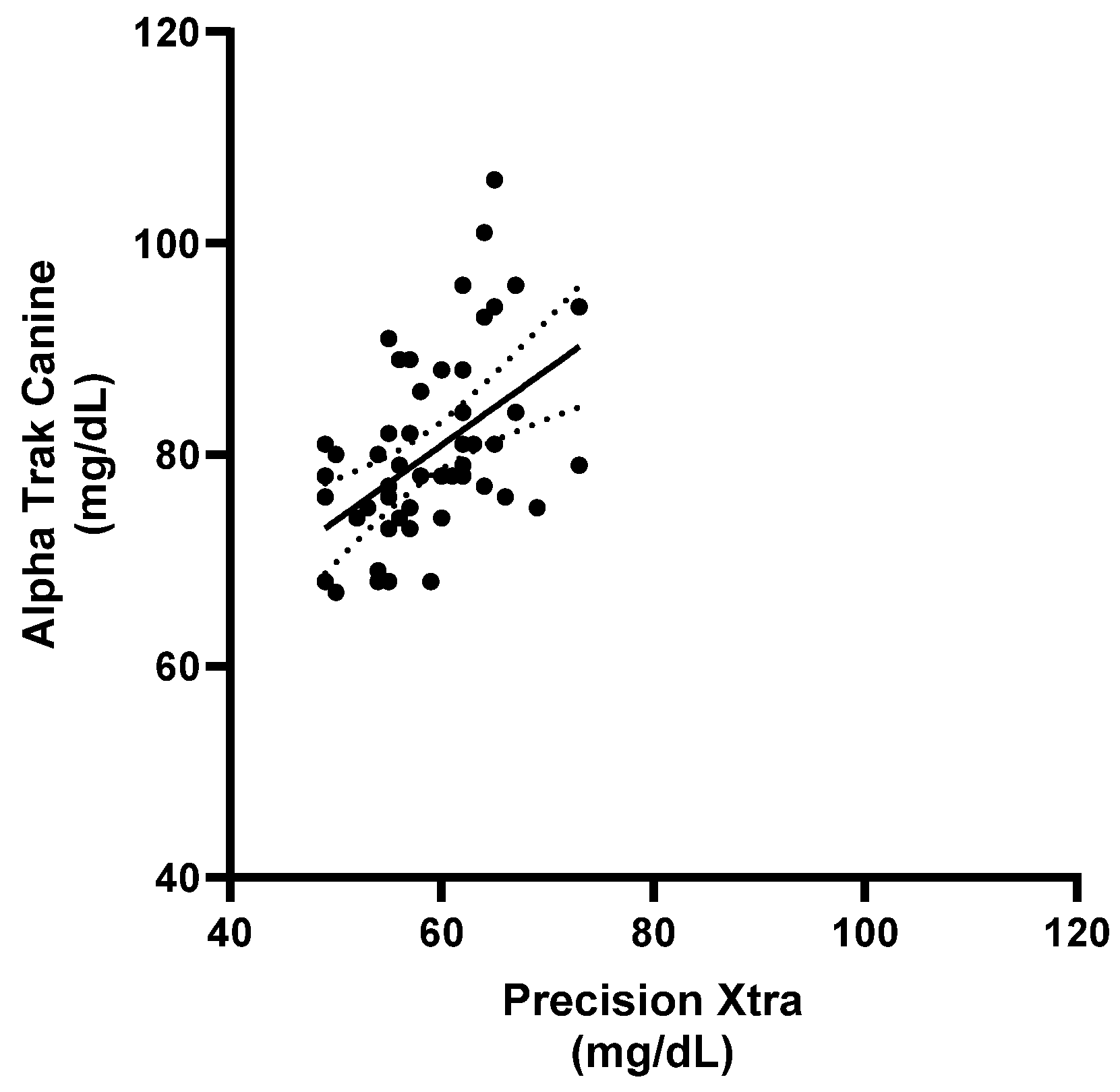
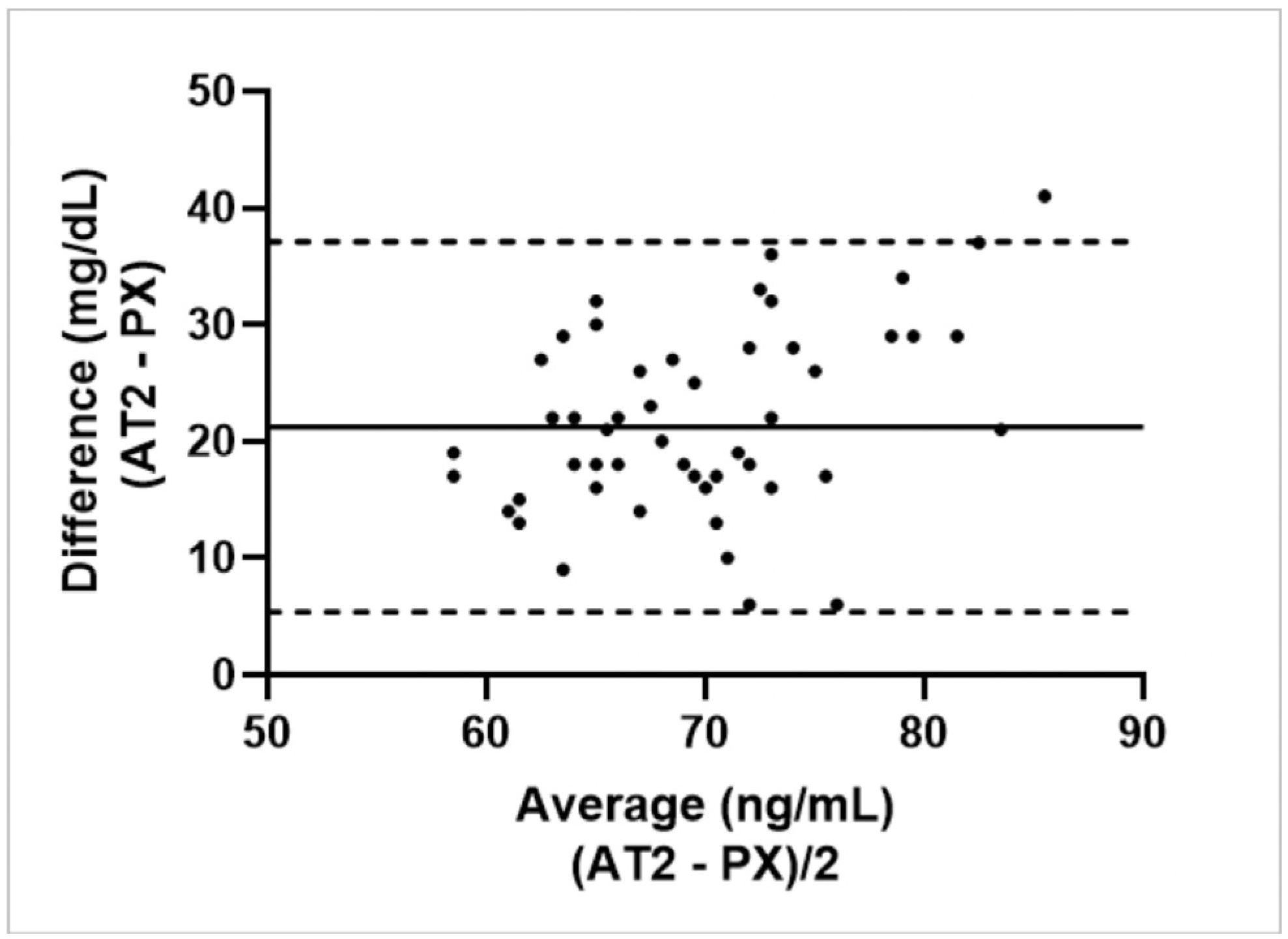
3.3. PX vs. AT2 Feline Setting
3.3.1. Calf Study Group
3.3.2. Ewe Study Group
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Digman, C.; Borto, D.; Nasraway, S.A., Jr. Hyperglycemia in the critically ill. Nutr. Clin. Care 2005, 8, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Radcliffe, R.M.; Buchanan, B.R.; Cook, V.L.; Divers, T.J. The clinical value of whole blood point-of-care biomarkers in large animal emergency and critical care medicine. J. Vet. Emerg. Crit. Care 2015, 25, 138–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wittrock, J.; Duffield, T.; LeBlanc, S. Validation of a point-of-care glucometer for use in dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 4514–4518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwersen, M.; Falkenberg, U.; Voigtsberger, R.; Forderung, D.; Heuwieser, W. Evaluation of an electronic cowside test to detect subclinical ketosis in dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2009, 92, 2618–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burke, C.; Rapheal, W.; Leslie, K.; Neuder, L. Test Comparison of Precision Xtra® and Ketostix® for Ketosis in Dairy Cows. In Proceedings of the American Association of Bovine Practitioners Proceedings of the Annual Conference, Charlotte, NC, USA, 25–27 September 2008; p. 187. [Google Scholar]
- Hornig, K.J.; Byers, S.R.; Callan, R.J.; Holt, T.; Field, M.; Han, H. Evaluation of a point-of-care glucose and β-hydroxybutyrate meter operated in various environmental conditions in prepartum and postpartum sheep. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2013, 74, 1059–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quandt, J.E.; Barletta, M.; Cornell, K.K.; Giguère, S.; Hofmeister, E.H. Evaluation of a point-of-care blood glucose monitor in healthy goats. J. Vet. Emerg. Crit. Care 2018, 28, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, V.L.; Hassel, D.M. Evaluation of the colic in horses: Decision for referral. Vet. Clin. Equine Pract. 2014, 30, 383–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ober, R.A.; Geist, G.E. Assessment of a Noninvasive Chronic Glucose Monitoring System in Euglycemic and Diabetic Swine (Sus scrofa). J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2020, 59, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selleri, P.; Di Girolamo, N.; Novari, G. Performance of two portable meters and a benchtop analyzer for blood glucose concentration measurement in rabbits. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2014, 245, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, L.M.; Gaines, D.W.; Babu, U.S.; Balan, K.V.; Reimschuessel, R.; Do, A.B.; Pereira, M.R.; Bigley, E.C., III; Ferguson, M.; Mehta, A. Diet-induced obesity precipitates kidney dysfunction and alters inflammatory mediators in mice treated with Shiga toxin 2. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 123, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCabe, K.A.; Rendle, M.; Harsch, S.; Lumbis, R. Prognostic Indicators of Avian Survival. J. Avian Med. Surg. 2020, 34, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivarez, J.D.; Mulon, P.-Y.; Ebner, L.S.; Cremerius, H.; Cantrell, C.; Rahn, R.; Soto-Gonzalez, W.; Bergman, J.; Cox, S.; Mochel, J.P.; et al. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties of pantoprazole in calves. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 9, 1101461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barr, C.A.; Gianotti, G.; Graffeo, C.E.; Drobatz, K.J.; Silverstein, D.C. Effect of blood collection by the push-pull technique from an indwelling catheter versus direct venipuncture on venous blood gas values before and after administration of alfaxalone or propofol in dogs. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2017, 251, 1166–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, G.Y. Confidence interval estimation for the Bland-Altman limits of agreement with multiple observations per individual. Stat. Methods Med. Res. 2013, 22, 630–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, A.L.; Kjelgaard-Hansen, M. Method comparison in the clinical laboratory. Vet. Clin. Pathol. 2006, 35, 276–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flatland, B.; Friedrichs, K.R.; Klenner, S. Differentiating between analytical and diagnostic performance evaluation with a focus on the method comparison study and identification of bias. Vet. Clin. Pathol. 2014, 43, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.S.; Bennett, K.; Flynn, R.; Gebert, J.; Mulon, P.-Y.; Garcia, J.D.; Harvill, L.; Escher, O.; Ebner, L.S.; Bergman, J.; et al. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of intravenously and subcutaneously administered pantoprazole in sheep (Ovis aries). PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0304533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.S.; Coetzee, J.F.; Fisher, I.W.G.; Borts, D.J.; Mochel, J.P. Pharmacokinetics of fentanyl citrate and norfentanyl in Holstein calves and effect of analytical performances on fentanyl parameter estimation. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 41, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trefz, F.M.; Feist, M.; Lorenz, I. Hypoglycaemia in hospitalised neonatal calves: Prevalence, associated conditions and impact on prognosis. Vet. J. 2016, 217, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coldman, M.; Good, W. The distribu-tion of sodium, potassium and glucose in the blood of some mammals. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 1967, 21, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, S.L.; Koenig, A.; Brainard, B.M. Formulation and validation of a predictive model to correct blood glucose concentrations obtained with a veterinary point-of-care glucometer in hemodiluted and hemoconcentrated canine blood samples. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2015, 246, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajendran, R.; Rayman, G. Point-of-care blood glucose testing for diabetes care in hospitalized patients: An evidence-based review. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2014, 8, 1081–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jangam, S.R.; Hayter, G.; Dunn, T.C. Impact of glucose measurement processing delays on clinical accuracy and relevance. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2013, 7, 660–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebel, A.; Rice, M.A.; Fahy, B.G. Accuracy of point-of-care glucose measurements. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2012, 6, 396–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Megahed, A.; Hiew, M.; Constable, P. The effects of sample temperature on the concentrations of glucose and β-OH butyrate measured by the Precision Xtra meter in plasma from periparturient dairy cattle. In Proceedings of the American Association of Bovine Practitioners Proceedings of the Annual Conference, New Orleans, LA, USA, 17–19 September 2015; p. 214. [Google Scholar]
- Tauk, B.S.; Drobatz, K.J.; Wallace, K.A.; Hess, R.S. Correlation between glucose concentrations in serum, plasma, and whole blood measured by a point-of-care glucometer and serum glucose concentration measured by an automated biochemical analyzer for canine and feline blood samples. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2015, 246, 1327–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Flynn, R.; Cremerius, H.; Ebner, L.; Mulon, P.-Y.; Garcia, J.; Bennett, K.; Gerbert, J.; Harvill, L.; Escher, O.; Cantrell, C.; et al. Evaluating the Bias of Two Point-of-Care Glucometers for Calves and Ewes: Awareness for Ruminant Practitioners. Ruminants 2024, 4, 304-315. https://doi.org/10.3390/ruminants4030022
Flynn R, Cremerius H, Ebner L, Mulon P-Y, Garcia J, Bennett K, Gerbert J, Harvill L, Escher O, Cantrell C, et al. Evaluating the Bias of Two Point-of-Care Glucometers for Calves and Ewes: Awareness for Ruminant Practitioners. Ruminants. 2024; 4(3):304-315. https://doi.org/10.3390/ruminants4030022
Chicago/Turabian StyleFlynn, Ryan, Haley Cremerius, Lisa Ebner, Pierre-Yves Mulon, Jessica Garcia, Kailee Bennett, Jessica Gerbert, Lainey Harvill, Olivia Escher, Channing Cantrell, and et al. 2024. "Evaluating the Bias of Two Point-of-Care Glucometers for Calves and Ewes: Awareness for Ruminant Practitioners" Ruminants 4, no. 3: 304-315. https://doi.org/10.3390/ruminants4030022
APA StyleFlynn, R., Cremerius, H., Ebner, L., Mulon, P.-Y., Garcia, J., Bennett, K., Gerbert, J., Harvill, L., Escher, O., Cantrell, C., Soto-Gonzalez, W., Rahn, R. R., Olivarez, J. D., Yuan, L., Mochel, J. P., Kreuder, A. J., & Smith, J. (2024). Evaluating the Bias of Two Point-of-Care Glucometers for Calves and Ewes: Awareness for Ruminant Practitioners. Ruminants, 4(3), 304-315. https://doi.org/10.3390/ruminants4030022





