Blood Bacterial Microbiota of the American Bison (Bison bison) in Northern Mexico: A Reference for Health and Conservation
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Blood Sample Collection
2.3. Laboratory Work
2.4. Bioinformatic Analysis
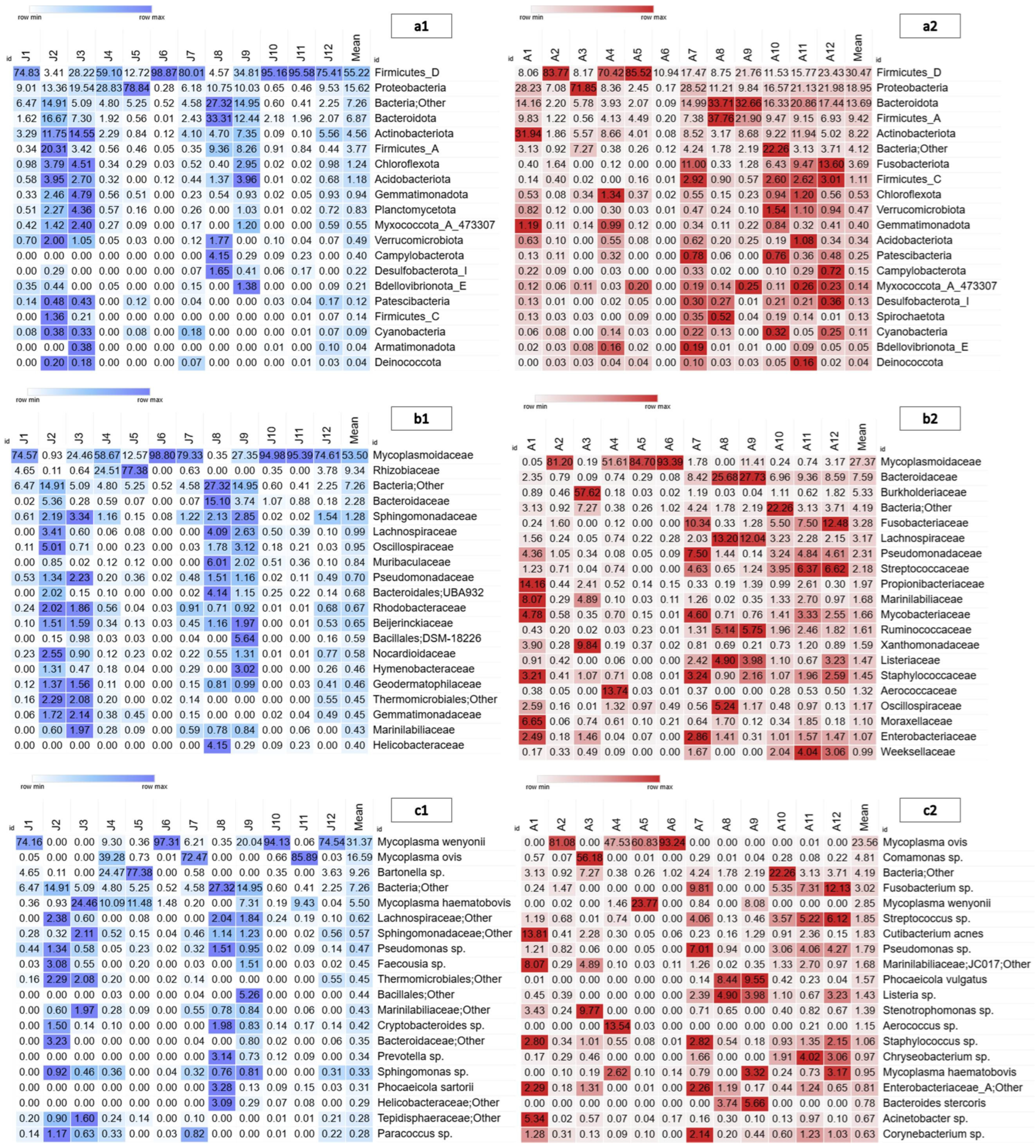
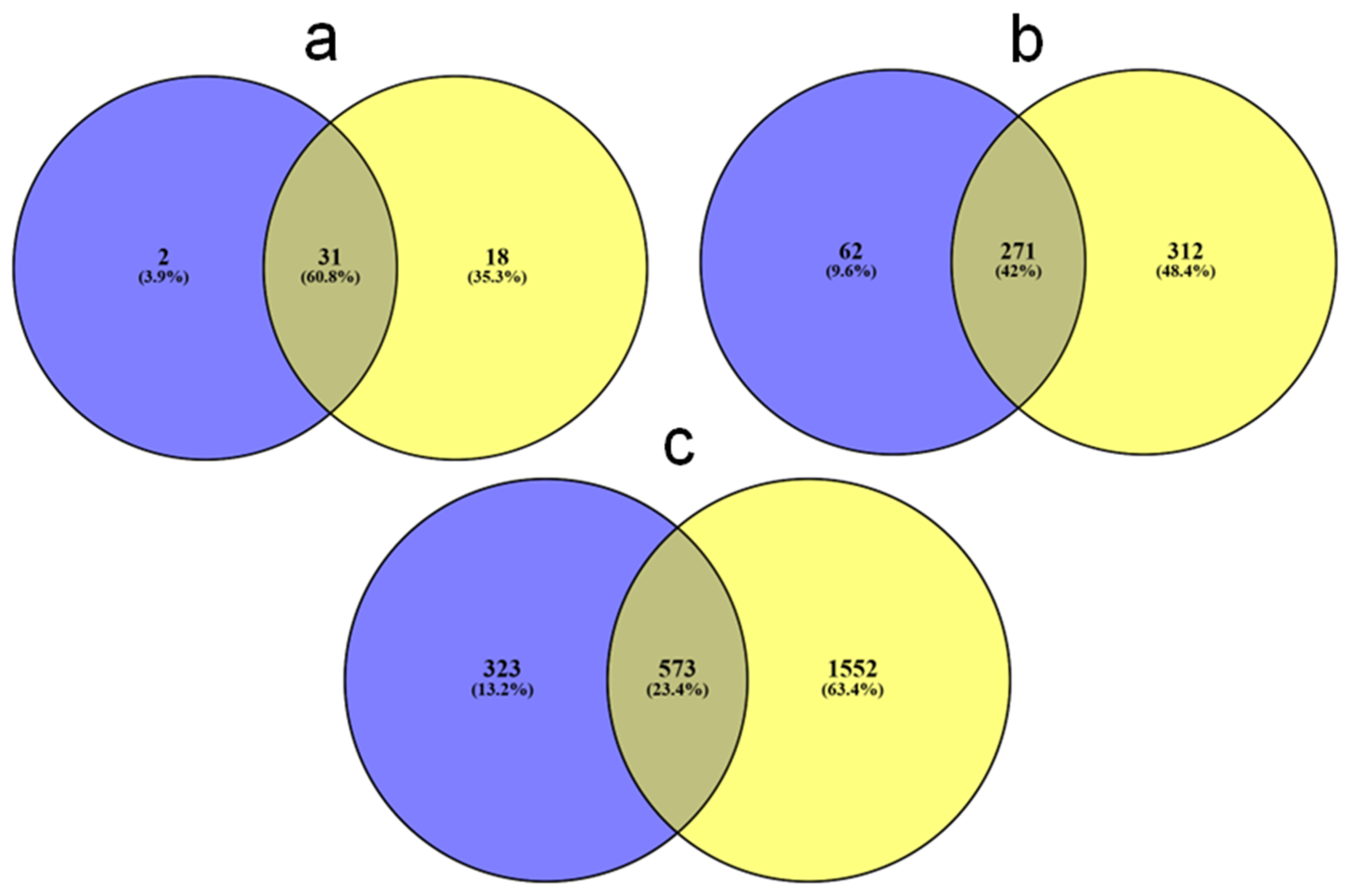
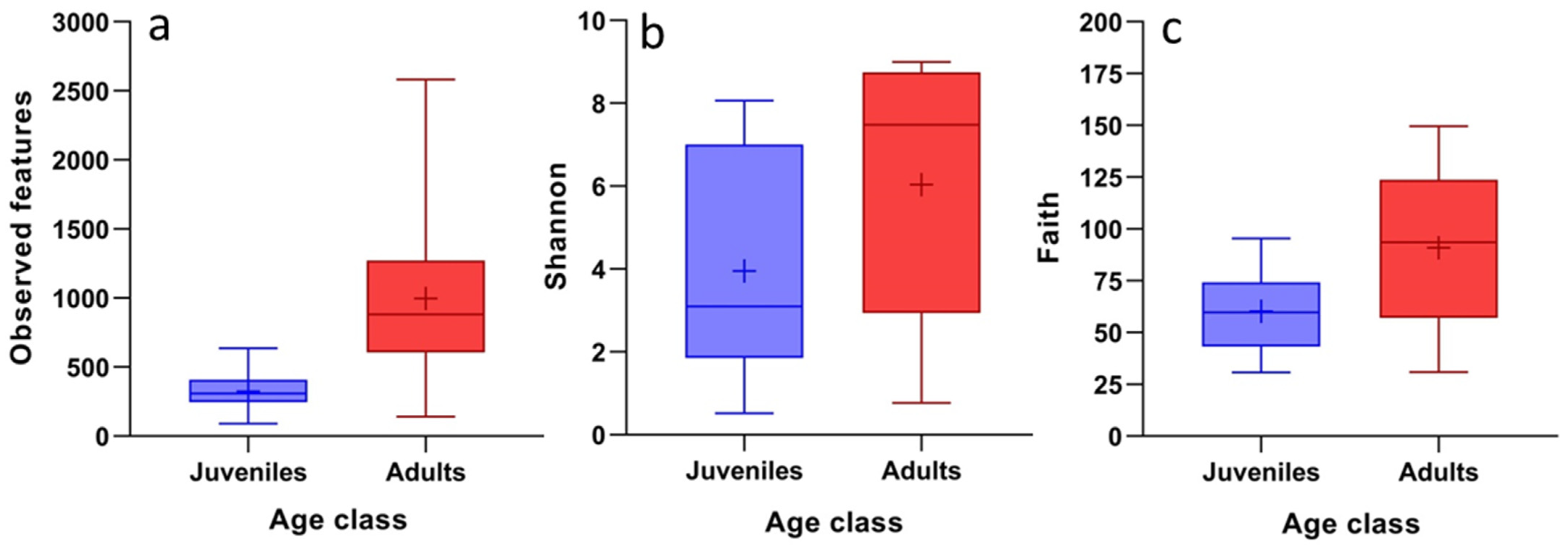
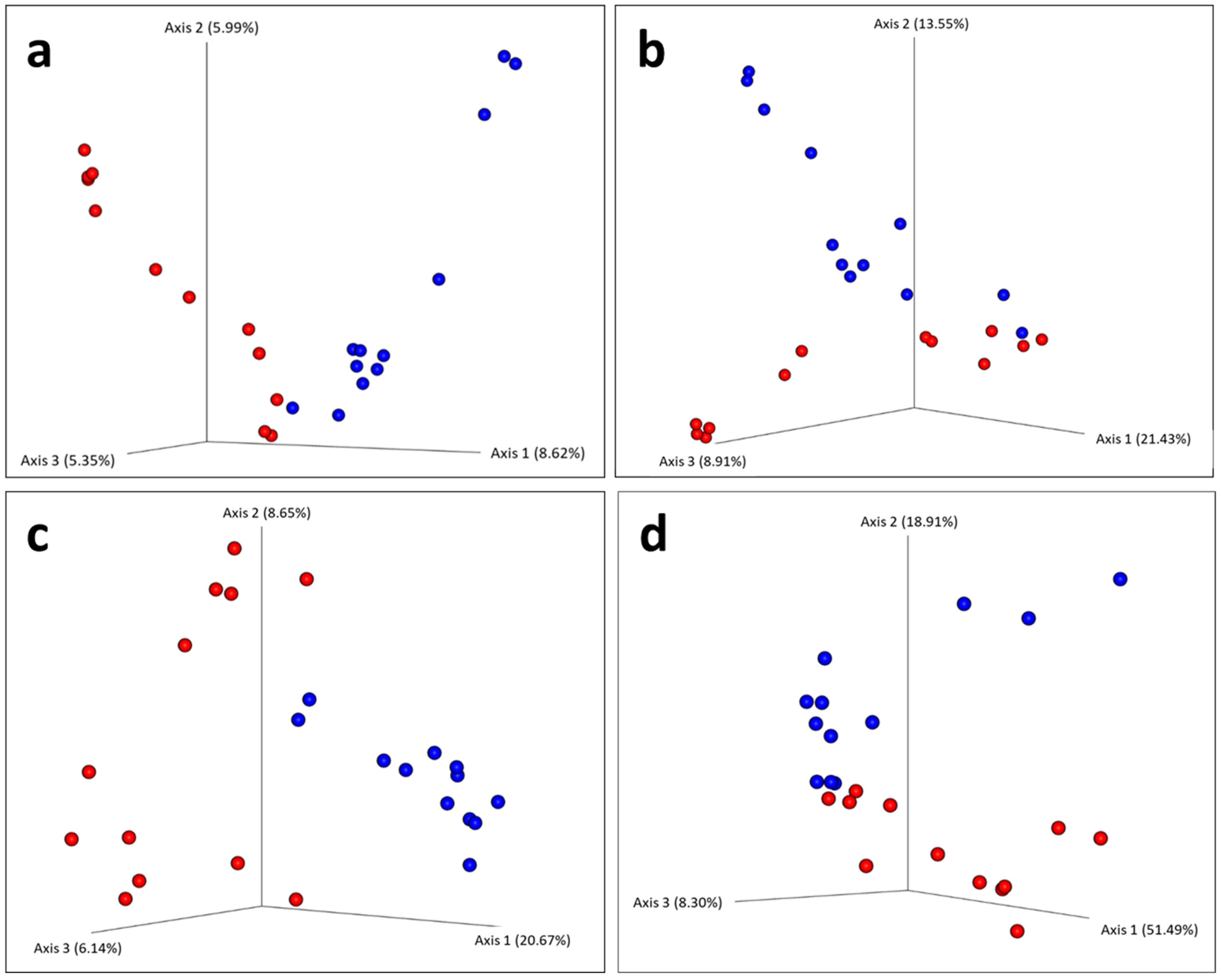
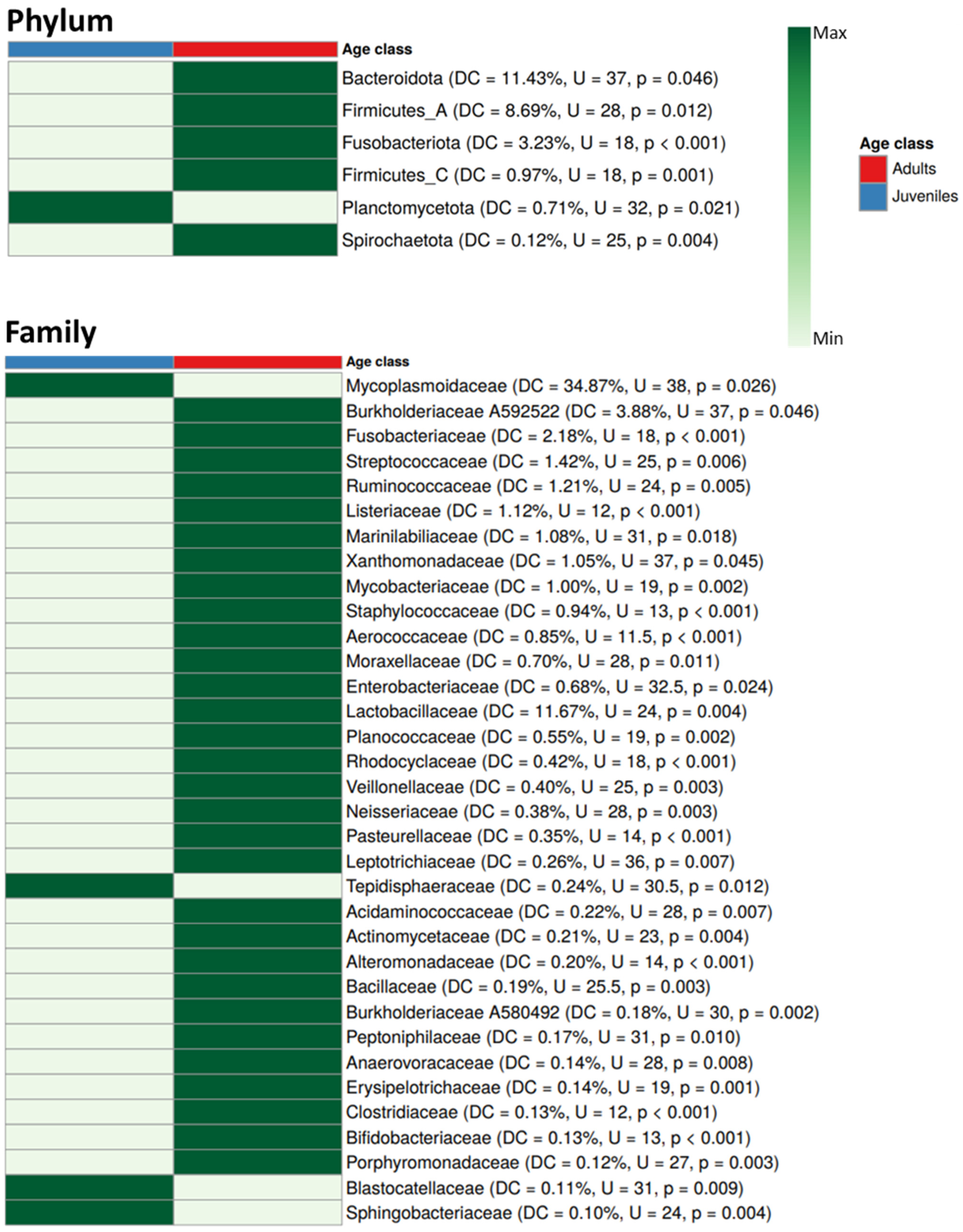
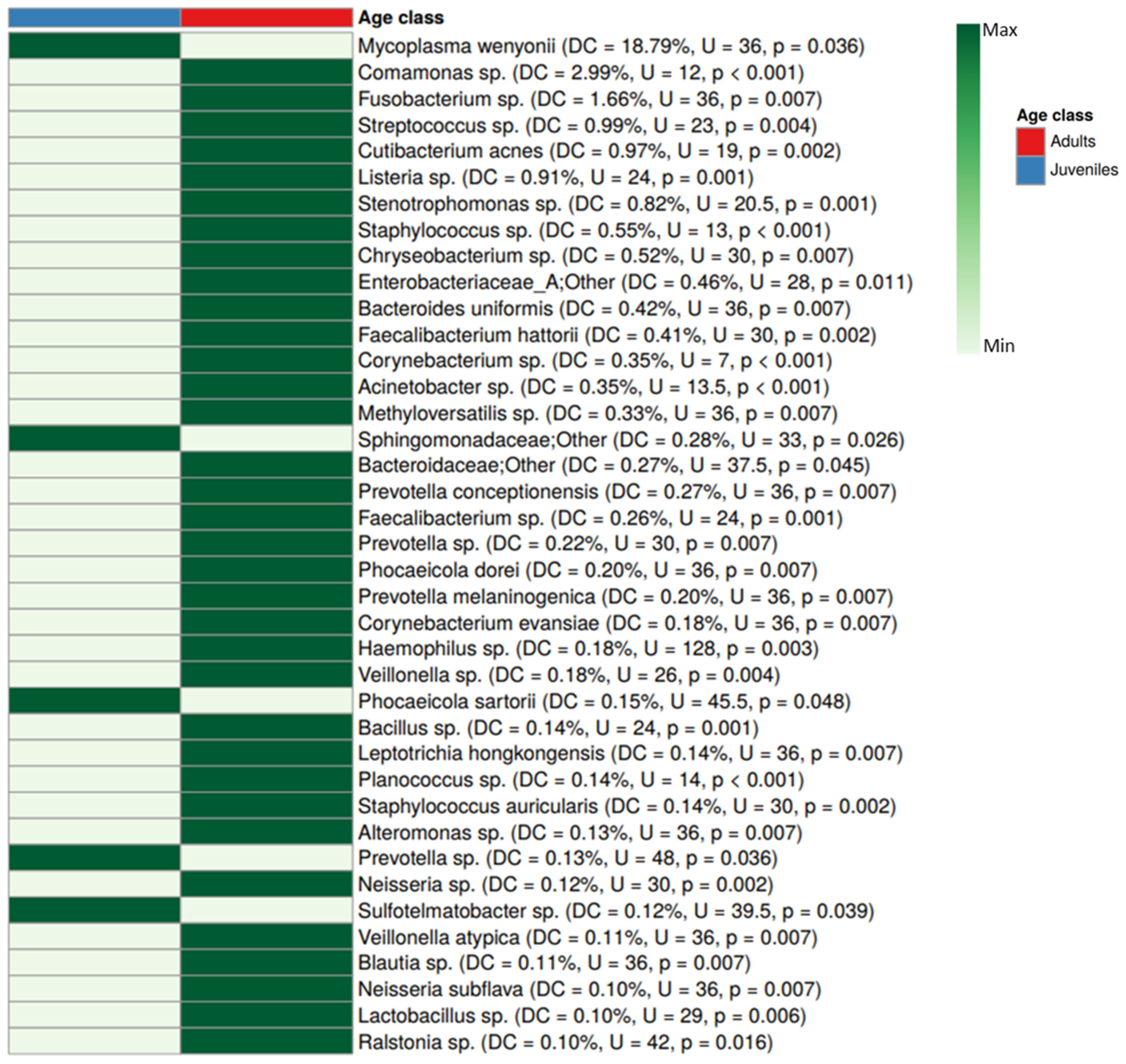
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Ecological Context of the American Bison Blood Microbiota
4.2. Differences in Blood Microbiota Between Age Classes
4.3. Health Context and Conservation of the American Bison Based on Its Blood Microbiota
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DNA | deoxyribonucleic acid |
| rRNA | ribosomal ribonucleic acid |
| NGS | next-generation sequencing |
| QIIME2 | Quantitative Insights into Microbial Ecology |
| ASVs | amplicon sequence variants |
| BLAST | Basic Local Alignment Search Tool |
| PCoA | principal coordinate analysis |
| PERMANOVA | permutational multivariate analysis of variance |
| SIMPER | similarity percentage analysis |
References
- Colston, T.J.; Jackson, C.R. Microbiome evolution along divergent branches of the vertebrate tree of life: What is known and unknown. Mol. Ecol. 2016, 25, 3776–3800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, M.C.; Arroyo, L.G.; Allen-Vercoe, E.; Stämpfli, H.R.; Kim, P.T.; Sturgeon, A.; Weese, J.S. Comparison of the fecal microbiota of healthy horses and horses with colitis by high throughput sequencing of the V3–V5 region of the 16S rRNA gene. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santoro, A.; Zhao, J.; Wu, L.; Carru, C.; Biagi, E.; Franceschi, C. Microbiomes other than the gut: Inflammaging and age-related diseases. Semin. Immunopathol. 2020, 42, 589–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Dela Peña, C.; Garduño-Niño, E.; Vaca-Paniagua, F.; Díaz-Velásquez, C.; Barrows, C.W.; Gomez-Gil, B.; Valenzuela-Núñez, L.M. Comparison of the fecal bacterial microbiota composition between wild and captive Bolson tortoises (Gopherus flavomarginatus). Herpetol. Conserv. Biol. 2019, 14, 587–600. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.; Wang, J.; Bahrndorff, S. Editorial: The wildlife gut microbiome and its implication for conservation biology. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 697499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, J.; Reese, A.T. Possibilities and limits for using the gut microbiome to improve captive animal health. Anim. Microbiome 2021, 3, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, D.J.; Rifkin, R.F.; Cowan, D.A.; Potgieter, M. The healthy human blood microbiome: Fact or fiction? Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.S.; Tan, S.P.; Wong, D.M.K.; Koo, W.L.Y.; Wong, S.H.; Tan, N.S. The blood microbiome and health: Current evidence, controversies, and challenges. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Païssé, S.; Valle, C.; Servant, F.; Courtney, M.; Burcelin, R.; Amar, J.; Lelouvier, B. Comprehensive description of blood microbiome from healthy donors assessed by 16S targeted metagenomic sequencing. Transfusion 2016, 56, 1138–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsafarova, B.; Hodzhev, Y.; Yordanov, G.; Tolchkov, V.; Kalfin, R.; Panaiotov, S. Morphology of blood microbiota in healthy individuals assessed by light and electron microscopy. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 12, 1091341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vientós-Plotts, A.I.; Ericsson, A.C.; Rindt, H.; Grobman, M.E.; Graham, A.; Bishop, K.; Cohn, L.A.; Reinero, C.R. Dynamic changes of the respiratory microbiota and its relationship to fecal and blood microbiota in healthy young cats. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0173818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Lang, T.; Shen, J.; Dai, J.; Tian, L.; Wang, X. Core gut bacteria analysis of healthy mice. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojas, C.A.; Park, B.; Scarsella, E.; Jospin, G.; Entrolezo, Z.; Jarett, J.K.; Martin, A.; Ganz, H.H. Species-level characterization of the core microbiome in healthy dogs using full-length 16S rRNA gene sequencing. Front. Veter-Sci. 2024, 11, 1405470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, R.D. Bacterial translocation from the gastrointestinal tract. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1999, 473, 11–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blekhman, R.; Goodrich, J.K.; Huang, K.; Sun, Q.; Bukowski, R.; Bell, J.T.; Spector, T.D.; Keinan, A.; Ley, R.E.; Gevers, D.; et al. Host genetic variation impacts microbiome composition across human body sites. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd-Price, J.; Abu-Ali, G.; Huttenhower, C. The healthy human microbiome. Genome Med. 2016, 8, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagpal, R.; Yadav, H. Bacterial translocation from the gut to the distant organs: An overview. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2017, 71 (Suppl. S1), 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laroche, M.; Raoult, D.; Parola, P. Insects and the transmission of bacterial agents. Microbiol. Spectr. 2018, 6, MTBP0017-2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittle, E.; Leonard, M.O.; Harrison, R.; Gant, T.W.; Tonge, D.P. Multi-method characterization of the human circulating microbiome. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarsella, E.; Sandri, M.; Monego, S.D.; Licastro, D.; Stefanon, B. Blood microbiome: A new marker of gut microbial population in dogs? Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Yang, X.; Xu, Z.; Li, J.; Sun, C.; Chen, R.; Wei, H.; Chen, L.; Du, H.; Li, G.; et al. The profile of blood microbiome in new-onset type 1 diabetes children. iScience 2024, 27, 110252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoza, B.L.; Byaruhanga, C.; Makgabo, S.M.; Nyangiwe, N.; Mnisi, T.; Nxumalo, S.; Oosthuizen, M.C.; Mnisi, Z.T.H. Tick distribution and comparative analysis of bovine blood microbiome in two provinces of South Africa using 16S rRNA PacBio sequencing approach. Front. Trop. Dis. 2024, 5, 1399364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapp, A.K.; Briggs, J.M.; Collins, S.L.; Hartnett, D.C.; Johnson, L.C.; Towne, E.G. The keystone role of Bison in North American Tallgrass Prairie. BioScience 1999, 49, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SEMARNAT. Programa de Acción Para la Conservación de la Especie Bisonte (Bison bison); SEMARNAT/CONANP: Ciudad de México, Mexico, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Shaw, J.H. How many bison originally populated western rangelands? Rangelands 1995, 17, 148–150. [Google Scholar]
- Potter, B.A.; Gerlach, S.C.; Gates, C.C.; Boyd, D.P.; Oetelaar, G.A.; Shaw, J.S. History of bison in North America. In American bison: Status Survey and Conservation Guidelines; International Union for Conservation of Nature: Gland, Switzerland, 2010; pp. 5–12. [Google Scholar]
- Redford, K.H.; Fearn, E. Ecological Future of Bison in North America: A Report from a Multi-Stakeholder, Transboundary Meeting; Wildlife Conservation Society: Bronx, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 2–4. [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson, E.W.; Redford, K.H.; Weber, B.; Aune, K.; Baldes, D.; Berger, J.; Carter, D.; Derr, J.; Dobrott, S.; Fearn, E.; et al. The ecological future of the North American bison: Conceiving long-term, large-scale conservation of wildlife. Conserv. Biol. 2008, 22, 252–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, L.R.; Ranglack, D.H.; Plumb, G. Bison bison (Green Status Assessment). The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2022, e.T2815A281520242. 2022. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org (accessed on 10 January 2025).
- List, R.; Ceballos, G.; Curtin, C.; Gogan, P.J.P.; Pacheco, J.; Truett, J. Historic distribution and challenges to bison recovery in the Northern Chihuahuan Desert. Conserv. Biol. 2007, 21, 1487–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SEMARNAT. Norma Oficial Mexicana NOM-059-SEMARNAT-2010, Protección y Manejo Ambiental de Especies Nativas de México de Flora y Fauna Silvestres, Categoría de Riesgo y Especificaciones Para su Inclusión, Exclusión o Cambio (NOM-059-SEMARNAT-2010). Secretaría de Medio Ambiente y Recursos Naturales. 2010. Available online: https://www.gob.mx/profepa/documentos/norma-oficial-mexicana-nom-059-semarnat-2010 (accessed on 20 January 2025).
- Solari, S.; Baker, R.J. Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference; Wilson, D.E., Reeder, D.M., Eds.; Johns Hopkins University Press: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2005; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Gates, C.; Ellison, K.; Gates, C.C. Numerical and geographic status. In American Bison: Status Survey and Conservation Guidelines; International Union for Conservation of Nature: Gland, Switzerland, 2010; pp. 55–62. [Google Scholar]
- Vázquez-Mantecón, M.C. El Bisonte de América. Historia, Polémica, Leyenda; Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México: Ciudad de México, Mexico, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Weese, J.S.; Shury, T.; Jelinski, M.D. The fecal microbiota of semi-free-ranging wood bison (Bison bison athabascae). BMC Vet. Res. 2014, 10, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergmann, G.T. Microbial community composition along the digestive tract in forage- and grain-fed bison. BMC Vet. Res. 2017, 13, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, G.T.; Craine, J.M.; Robeson, M.S., II; Fierer, N. Seasonal shifts in diet and gut microbiota of the American bison (Bison bison). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.T.M.; Badhan, A.K.; Reid, I.D.; Ribeiro, G.; Gruninger, R.; Tsang, A.; Guan, L.L.; McAllister, T. Comparative analysis of functional diversity of rumen microbiome in bison and beef heifers. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2023, 89, e0132023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fresno-Rueda, A.F.; Griffith, J.E.; Kruse, C.; St-Pierre, B. Effects of grain-based diets on the rumen and fecal bacterial communities of the North American bison (Bison bison). Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1163423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- List, R.; Pacheco, J.; Ponce, E.; Sierra-Corona, R.; Ceballos, G.; Sierra, R. The Janos Biosphere Reserve, Northern Mexico. Int. J. Wilderness 2010, 16, 35–41. [Google Scholar]
- Zambrano, L.J.; Díaz, S. Comité de Bioética. Guía Para la Correcta Toma de Sangre en Bovinos: A Partir de la Vena Coccígea y la Vena Yugular Externa; Universidad Nacional de Colombia: Bogotá, Colombia, 2014; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; Mcmurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S.P. Exact sequence variants should replace operational taxonomic units in marker-gene data analysis. ISME J. 2017, 11, 2639–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, D.; Jiang, Y.; Balaban, M.; Cantrell, K.; Zhu, Q.; Gonzalez, A.; Morton, J.T.; Nicolaou, G.; Parks, D.H.; Karst, S.M.; et al. Greengenes2 unifies microbial data in a single reference tree. Nat. Biotechnol. 2023, 42, 715–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaccard, P. The distribution of the flora in the alpine zone. New Phytol. 1912, 11, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, J.R.; Curtis, J.T. An ordination of the upland forest communities of Southern Wisconsin. Ecol. Monogr. 1957, 27, 325–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozupone, C.; Knight, R. UniFrac: A New Phylogenetic Method for Comparing Microbial Communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 8228–8235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Baeza, Y.; Pirrung, M.; Gonzalez, A.; Knight, R. EMPeror: A tool for visualizing high-throughput microbial community data. GigaScience. 2013, 2, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khomich, M.; Måge, I.; Rud, I.; Berget, I. Analysing microbiome intervention design studies: Comparison of alternative multivariate statistical methods. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0259973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metsalu, T.; Vilo, J. Clustvis: A web tool for visualizing clustering of multivariate data using Principal Component Analysis and heatmap. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W566–W570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarsella, E.; Zecconi, A.; Cintio, M.; Stefanon, B. Characterization of microbiome on feces, blood and milk in dairy cows with different milk leucocyte patterns. Animals. 2021, 11, 1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudi, K.; Moen, B.; Sekelja, M.; Frisli, T.; Lee, M.R. An eight-year investigation of bovine livestock fecal microbiota. Vet. Microbiol. 2012, 160, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glendinning, L.; Genç, B.; Wallace, R.J.; Watson, M. Metagenomic analysis of the cow, sheep, reindeer and red deer rumen. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruninger, R.J.; Sensen, C.W.; McAllister, T.A.; Forster, R.J. Diversity of rumen bacteria in Canadian cervids. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Xu, Q.; Yan, T.; Xue, B. Evaluation of composition and individual variability of rumen microbiota in yaks by 16S rRNA high-throughput sequencing technology. Anaerobe 2015, 34, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koringa, P.G.; Thakkar, J.R.; Pandit, R.J.; Hinsu, A.T.; Parekh, M.J.; Shah, R.K.; Jakhesara, S.J.; Joshi, C.G. Metagenomic characterisation of ruminal bacterial diversity in buffaloes from birth to adulthood using 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2019, 19, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giger-Reverdin, S.; Domange, C.; Broudiscou, L.P.; Sauvant, D.; Berthelot, V. Rumen function in goats, an example of adaptive capacity. J. Dairy Res. 2020, 87, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabee, A.E.; Kewan, K.Z.; Sabra, E.A.; El Shaer, H.M.; Lamara, M. Rumen bacterial community profile and fermentation in Barki sheep fed olive cake and date palm byproducts. PeerJ 2021, 9, e12447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, S.J.; Cunha, F.; Vieira-Neto, A.; Bicalho, R.C.; Lima, S.; Bicalho, M.L.; Galvão, K.N. Blood as a route of transmission of uterine pathogens from the gut to the uterus in cows. Microbiome 2017, 5, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oren, A. A plea for linguistic accuracy–also for Candidatus taxa. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 1085–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razin, S.; Hayflick, L. Highlights of mycoplasma research—An historical perspective. Biologicals 2010, 38, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, D.R.; May, M.; Bradbury, J.M.; Balish, M.F.; Calcutt, M.J.; Glass, J.I.; Tasker, S.; Messick, J.B.; Johansson, K.E.; Neimark, H. Mycoplasma. In Bergey’s Manual of Systematics of Archaea and Bacteria; Whitman, W.B., Kämpfer, P., Trujillo, M., Chun, J., DeVos, P., Hedlund, B., Dedysh, S., Eds.; Springer Science and Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 1–78. [Google Scholar]
- Paul, B.T.; Jesse, F.F.A.; Chung, E.L.T.; Che-Amat, A.; Lila, M.A.M.; Hashi, H.A.; Norsidin, M.J. Review of clinical aspects, epidemiology and diagnosis of haemotropic Mycoplasma ovis in small ruminants: Current status and future perspectives in tropics focusing on Malaysia. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2020, 52, 2829–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tagawa, M.; Matsumoto, K.; Inokuma, H. Molecular detection of Mycoplasma wenyonii and ‘Candidatus Mycoplasma haemobos’ in cattle in Hokkaido, Japan. Vet. Microbiol. 2008, 132, 177–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girotto, A.; Zangirolamo, A.F.; Bogado, A.L.G.; Souza, A.S.L.E.; da Silva, G.C.F.; Garcia, J.L.; Vilas Boas, L.A.; Biondo, A.W.; Vidotto, O. Molecular detection and occurrence of “Candidatus Mycoplasma haemobos” in dairy cattle of Southern Brazil. Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Vet. 2012, 21, 342–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Hu, Y.; Leng, C.; Shi, H.; Jiao, Z.; Chen, X.; Peng, Y.; Yang, H.; Kan, Y.; Yao, L. Molecular investigation of “Candidatus Mycoplasma haemobos” in goats and sheep in central China. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2019, 66, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz-Sánchez, A.A.; Corona-González, B.; Meli, M.L.; Álvarez, D.O.; Cañizares, E.V.; Rodríguez, O.F.; Rivero, E.L.; Hofmann-Lehmann, R. First molecular evidence of bovine hemoplasma species (Mycoplasma spp.) in water buffalo and dairy cattle herds in Cuba. Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nouvel, L.X.; Hygonenq, M.-C.; Catays, G.; Martinelli, E.; Le Page, P.; Collin, É.; Inokuma, H.; Schelcher, F.; Citti, C.; Maillard, R. First detection of Mycoplasma wenyonii in France: Identification, evaluation of the clinical impact and development of a new specific detection assay. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 63, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schambow, R.; Poulsen, K.; Bolin, S.; Krahn, D.; Norby, B.; Sockett, D.; Ruegg, P. Apparent prevalence of Mycoplasma wenyonii, “Candidatus Mycoplasma haemobos”, and bovine leukemia virus in Wisconsin and Michigan dairy cattle herds. JDS Commun. 2021, 2, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Ocampo, F.; Rodríguez-Camarillo, S.D.; Amaro-Estrada, I.; Quiroz-Castañeda, R.E. Draft Genome Sequence of “Candidatus Mycoplasma haemobos”, a Hemotropic Mycoplasma Identified in Cattle in Mexico. Genome Announc. 2016, 4, e00656-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiroz-Castañeda, R.E.; Martínez-Ocampo, F.; Dantán-González, E. Draft genome sequence of Mycoplasma wenyonii, a second hemotropic Mycoplasma species identified in Mexican bovine cattle. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2018, 7, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaimes-Martínez, C.A.; Quiroz-Castañeda, R.E.; Preciado-de la Torre, J.F.; Amaro-Estrada, I. Detección molecular del hemoplasma Candidatus Mycoplasma haemobos en ganado bovino de México. Acta Agrícola y Pecuaria. 2018, 4, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre, D.H.; Thompson, C.; Neumann, R.D.; Salatin, A.O.; Gaido, A.B.; Torioni de Echaide, S. Brote de micoplasmosis clínica por Mycoplasma ovis en ovinos de Salta, Argentina. Diagnóstico clínico, microbiológico y molecular. Rev. Argent. Microbiol. 2009, 41, 212–214. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Grazziotin, A.L.; Santos, A.P.; Guimaraes, A.M.S.; Mohamed, A.; Cubas, Z.S.; de Oliveira, M.J.; dos Santos, L.C.; de Moraes, W.; Vieira, R.F.d.C.; Donatti, L.; et al. Mycoplasma ovis in captive cervids: Prevalence, molecular characterization and phylogeny. Vet. Microbiol. 2011, 152, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, C.A.; Vidotto, O.; Conrado, F.O.; Santos, N.J.; Valente, J.D.; Barbosa, I.C.; Trindade, P.W.; Garcia, J.L.; Biondo, A.W.; Vieira, T.S. Mycoplasma ovis infection in goat farms from northeastern Brazil. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2017, 55, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Hernández, J.M.; Ballados-González, G.G.; Fernández-Bandala, D.; Martínez-Soto, S.; Velázquez-Osorio, V.; Martínez-Rodríguez, P.B.; Cruz-Romero, A.; Grostieta, E.; Lozano-Sardaneta, Y.; Salas, P.C.; et al. Molecular detection of Mycoplasma ovis in an outbreak of hemolytic anemia in sheep from Veracruz, Mexico. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2019, 51, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arendt, M.; Stadler, J.; Ritzmann, M.; Ade, J.; Hoelzle, K.; Hoelzle, L.E. Hemotrophic Mycoplasmas—Vector Transmission in Livestock. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornok, S.; Micsutka, A.; Meli, M.L.; Lutz, H.; Hofmann-Lehmann, R. Molecular investigation of transplacental and vector-borne transmission of bovine haemoplasmas. Vet. Microbiol. 2011, 152, 411–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaoka, F.; Suzuki, J.; Hirata, T.-I.; Ichijo, T.; Furuhama, K.; Harasawa, R.; Satoh, H. Vertical transmission of Mycoplasma wenyonii in cattle, supported by analysis of the ribonuclease P RNA gene. Acta Vet. Hung. 2015, 63, 271–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Register, K.B.; Jones, L.C.; Boatwright, W.D.; Shury, T.K.; Woodbury, M.; Hamilton, R.G.; Treanor, J.; Dyer, N.; Nol, P. Prevalence of Mycoplasma spp. in the Respiratory Tract of Healthy North American Bison (Bison bison) and Comparison with Serum Antibody Status. J. Wildl. Dis. 2021, 57, 683–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez, R.; Cohen, L.; Morick, D.; Mumcuoglu, K.Y.; Harrus, S.; Gottlieb, Y. Identification of Different Bartonella Species in the Cattle Tail Louse (Haematopinus quadripertusus) and in Cattle Blood. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 5477–5483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizrahi, I.; Jami, E. Review: The compositional variation of the rumen microbiome and its effect on host performance and methane emission. Animal 2018, 12, s220–s232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacífico, C.; Petri, R.M.; Ricci, S.; Mickdam, E.; Wetzels, S.U.; Neubauer, V.; Zebeli, Q. Unveiling the Bovine Epimural Microbiota Composition and Putative Function. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Zhao, B.; Yan, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Li, Z.; Han, L.; Sun, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Xia, Y. Comamonas-dominant microbial community in carbon poor aquitard sediments revealed by metagenomic-based growth rate investigation. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 169203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega-Morales, A.I.; Nava-Reyna, E.; Ávila-Rodríguez, V.; González-Álvarez, V.H.; Castillo-Martínez, A.; Siller-Rodríguez, Q.K.; Cabezas-Cruz, A.; Dantas-Torres, F.; Almazán, C. Detection of Rickettsia spp. in Rhipicephalus sanguineus (sensu lato) collected from free-roaming dogs in Coahuila state, northern Mexico. Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- la Peña, C.G.-D.; Zamudio-López, A.; Barraza-Guerrero, S.I.; Martínez-Aranda, E.; De la Cruz-Ramos, J.M.; Acosta-Ayala, A.; Siller-Rodríguez, Q.K.; Torres-Delgado, M.G.; Ávila-Rodríguez, V.; Vásquez-Arroyo, J.; et al. Bacterial Microbiota of the Brown Dog Tick (Rhipicephalus sanguineus), a Broad Starting Point to Establish Potential Pathogens in Northern Mexico. Microbiol Res. 2024, 15, 2507–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beristain-Ruiz, D.M.; Vital-García, C.; Figueroa-Millán, J.V.; Lira-Amaya, J.J.; Garza-Hernández, J.A.; Sánchez-Ayala, J.R.; Flores-Ceballos, S.; Rodríguez-Alarcón, C.A.; Olivas-Sánchez, M.P.; Pons-Monarrez, G. Molecular Detection of Tick-Borne Pathogens in American Bison (Bison bison) at El Uno Ecological Reserve, Janos, Chihuahua, Mexico. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Du, M.; Ahmad, A.A.; Wang, S.; Zheng, J.; Salekdeh, G.H.; Yan, P.; Han, J.; Tong, B.; et al. Age-dependent changes of hindgut microbiota succession and metabolic function of Mongolian cattle in the semi-arid rangelands. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 957341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jami, E.; Israel, A.; Kotser, A.; Mizrahi, I. Exploring the bovine rumen bacterial community from birth to adulthood. ISME J. 2013, 7, 1069–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.Y.; Ji, S.K.; Yan, H.; Wang, Y.J.; Liu, J.J.; Cao, Z.J.; Yang, H.J.; Zhang, W.J.; Li, S.L. Dynamic change of the gastrointestinal bacterial ecology in cows from birth to adulthood. MicrobiologyOpen 2020, 9, e1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodruff, K.L.; Hummel, G.L.; Austin, K.J.; Lake, S.L.; Cunningham-Hollinger, H.C. Calf rumen microbiome from birth to weaning and shared microbial properties to the maternal rumen microbiome. J. Anim. Sci. 2022, 100, skac264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Jiao, C.; Diao, Q.; Tu, Y. Effect of Dietary and Age Changes on Ruminal Microbial Diversity in Holstein Calves. Microorganisms 2023, 12, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, X.; Ji, S.; Duan, C.; Tian, P.; Ju, S.; Yan, H.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y. Age-Related Changes in the Ruminal Microbiota and Their Relationship with Rumen Fermentation in Lambs. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 679135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Zhang, K.; Li, C.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Y. Characterization and comparison of microbiota in the gastrointestinal tracts of the goat (Capra hircus) during preweaning development. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, T.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; Liu, J.; Shi, H. Rumen and fecal microbiota profiles associated with immunity of young and adult goats. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 978402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aune, K.; Gates, C.C.; Boyd, D.; Elkin, B.T.; Hugh-Jones, M.; Joly, D.O.; Nishi, J. Reportable or Notifiable Diseases. In American Bison: Status Survey and Conservation Guidelines 2010 (Revised June 2011); Gates, C.C., Freese, C.H., Gogan, P.J., Kotzman, M., Eds.; International Union for Conservation of Nature: Gland, Switzerland, 2010; pp. 27–37. [Google Scholar]
- Mackintosh, C.; Haigh, J.; Griffin, F. Bacterial diseases of farmed deer and bison. Rev. Sci. Tech. 2002, 21, 249–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyer, N.; Hansen-Lardy, L.; Krogh, D.; Schaan, L.; Schamber, E. An outbreak of chronic pneumonia and polyarthritis syndrome caused by Mycoplasma bovis in feedlot bison (Bison bison). J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2008, 20, 369–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janardhan, K.S.; Hays, M.; Dyer, N.; Oberst, R.D.; DeBey, B.M. Mycoplasma bovis outbreak in a herd of North American Bison (Bison bison). J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2010, 22, 797–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genova, S.G.; Streeter, R.N.; E Velguth, K.; A Snider, T.; Kocan, K.M.; Simpson, K.M. Severe anemia associated with Mycoplasma wenyonii infection in a mature cow. Can. Vet. J. 2011, 52, 1018–1021. [Google Scholar]
- Gladden, N.; Haining, H.; Henderson, L.; Marchesi, F.; Graham, L.; McDonald, M.; Murdoch, F.R.; Sala, A.B.; Orr, J.; Ellis, K. A case report of Mycoplasma wenyonii associated immune-mediated haemolytic anaemia in a dairy cow. Ir. Vet. J. 2015, 69, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strugnell, B.; McAuliffe, L. Mycoplasma wenyonii infection in cattle. In Pract. 2012, 34, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meli, M.L.; Willi, B.; Dreher, U.M.; Cattori, V.; Knubben-Schweizer, G.; Nuss, K.; Braun, U.; Lutz, H.; Hofmann-Lehmann, R. Identification, molecular characterization, and occurrence of two bovine hemoplasma species in Swiss cattle and development of real-time TaqMan quantitative PCR assays for diagnosis of bovine hemoplasma infections. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 3563–3568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boothby, J.T.; Jasper, D.E.; Zinkl, J.G.; Thomas, C.B.; Dellinger, J.D. Prevalence of mycoplasmas and immune responses to Mycoplasma bovis in feedlot calves. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1983, 44, 831–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ontiveros-Chacón, J.C.; García-De La Peña, C.; Domínguez-Viveros, J.; Aguilar-Palma, G.N.; Ávila-Rodríguez, V.; Estrada-Arellano, J.R.; Siller-Rodríguez, Q.K.; Valenzuela-Núñez, L.M.; Vásquez-Arroyo, J.; Herrera-Salazar, J.C.; et al. Blood Bacterial Microbiota of the American Bison (Bison bison) in Northern Mexico: A Reference for Health and Conservation. Ruminants 2025, 5, 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/ruminants5010010
Ontiveros-Chacón JC, García-De La Peña C, Domínguez-Viveros J, Aguilar-Palma GN, Ávila-Rodríguez V, Estrada-Arellano JR, Siller-Rodríguez QK, Valenzuela-Núñez LM, Vásquez-Arroyo J, Herrera-Salazar JC, et al. Blood Bacterial Microbiota of the American Bison (Bison bison) in Northern Mexico: A Reference for Health and Conservation. Ruminants. 2025; 5(1):10. https://doi.org/10.3390/ruminants5010010
Chicago/Turabian StyleOntiveros-Chacón, Juan Carlos, Cristina García-De La Peña, Joel Domínguez-Viveros, Guadalupe Nelson Aguilar-Palma, Verónica Ávila-Rodríguez, Josué Raymundo Estrada-Arellano, Quetzaly Karmy Siller-Rodríguez, Luis Manuel Valenzuela-Núñez, Jesús Vásquez-Arroyo, Juan Carlos Herrera-Salazar, and et al. 2025. "Blood Bacterial Microbiota of the American Bison (Bison bison) in Northern Mexico: A Reference for Health and Conservation" Ruminants 5, no. 1: 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/ruminants5010010
APA StyleOntiveros-Chacón, J. C., García-De La Peña, C., Domínguez-Viveros, J., Aguilar-Palma, G. N., Ávila-Rodríguez, V., Estrada-Arellano, J. R., Siller-Rodríguez, Q. K., Valenzuela-Núñez, L. M., Vásquez-Arroyo, J., Herrera-Salazar, J. C., Zamudio-López, A., & Correa-Gómez, J. (2025). Blood Bacterial Microbiota of the American Bison (Bison bison) in Northern Mexico: A Reference for Health and Conservation. Ruminants, 5(1), 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/ruminants5010010





