Exploring the Roles of Chelating/Fuel Agents in Shaping the Properties of Copper Ferrites
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
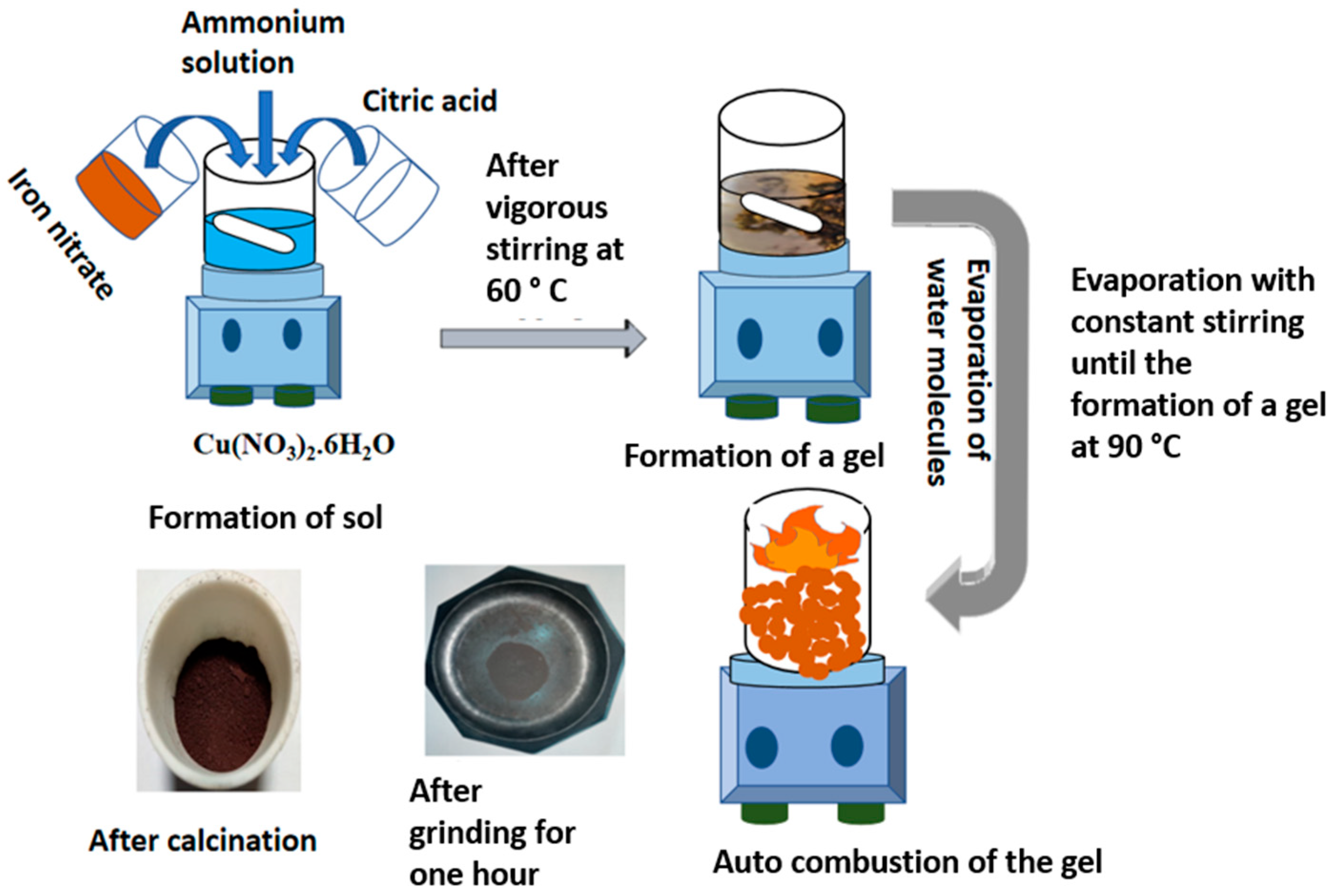
2.1. Method of Synthesis
2.2. Characterization Techniques
2.2.1. X-Ray Diffractometry (XRD)
2.2.2. Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy (FESEM)
2.2.3. High-Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy (HRTEM)
2.2.4. Ultraviolet–Visible Spectrophotometry
2.2.5. Vibrating Sample Magnetometer (VSM)
3. Results
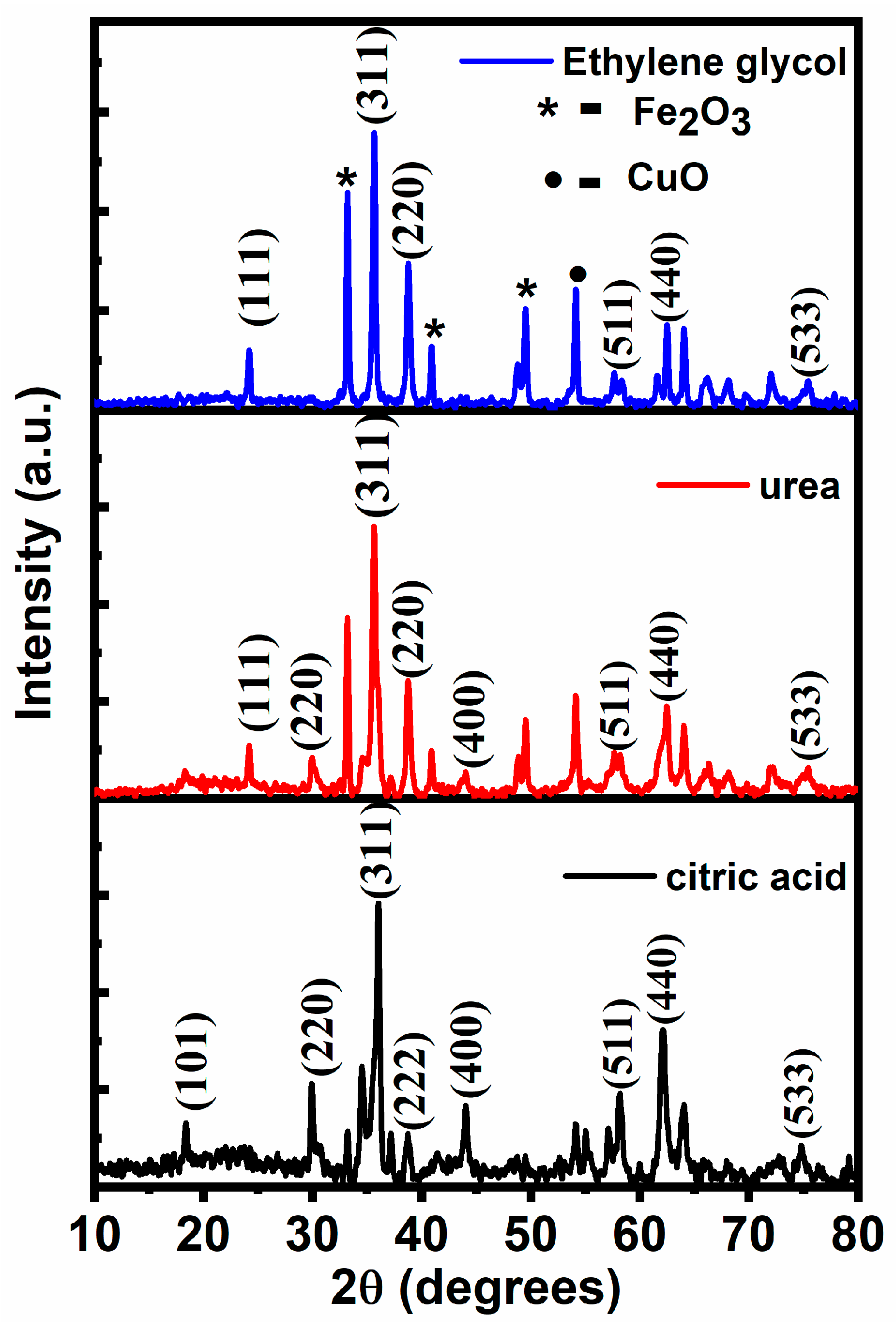
3.1. X-Ray Diffraction
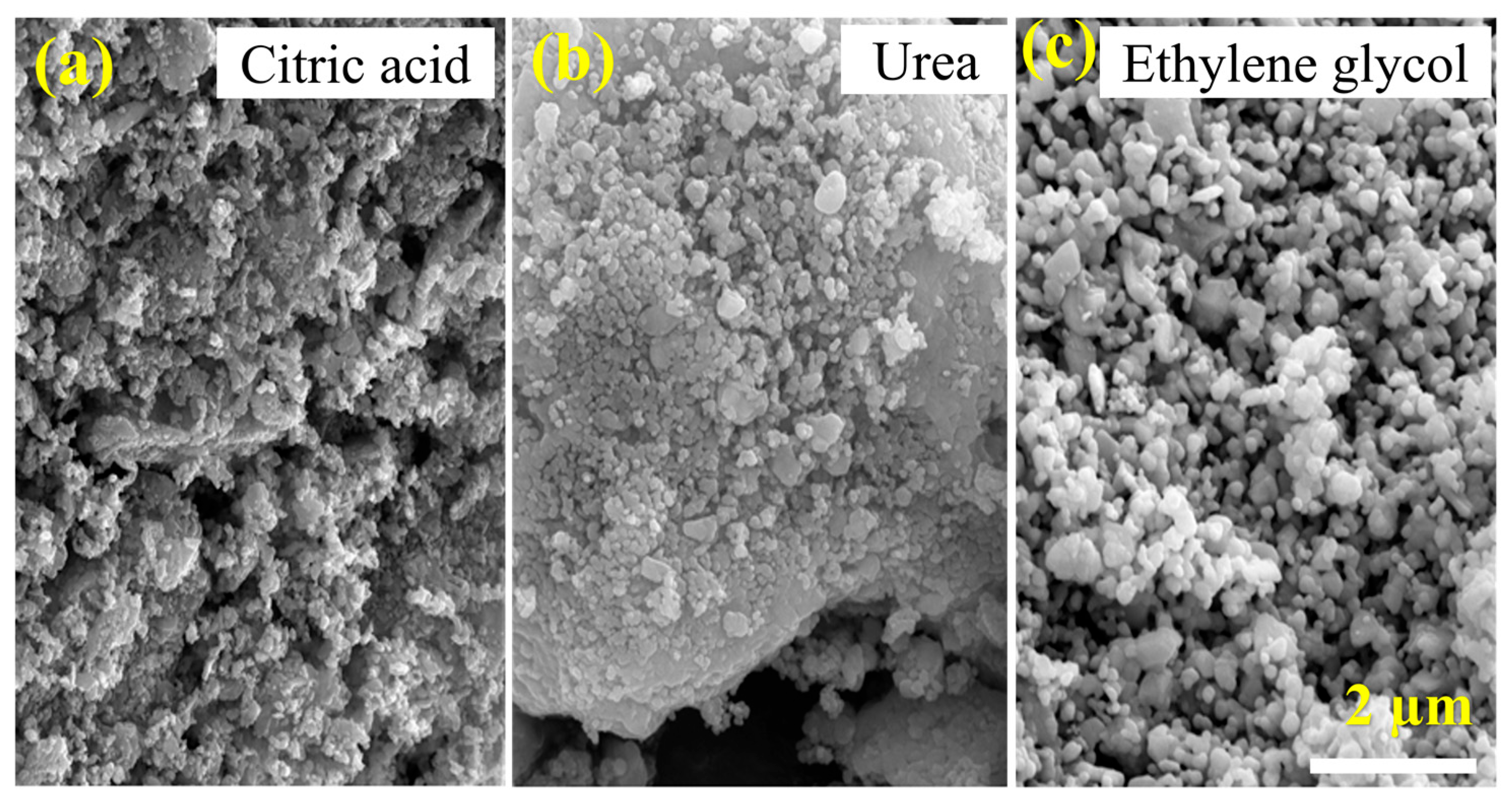
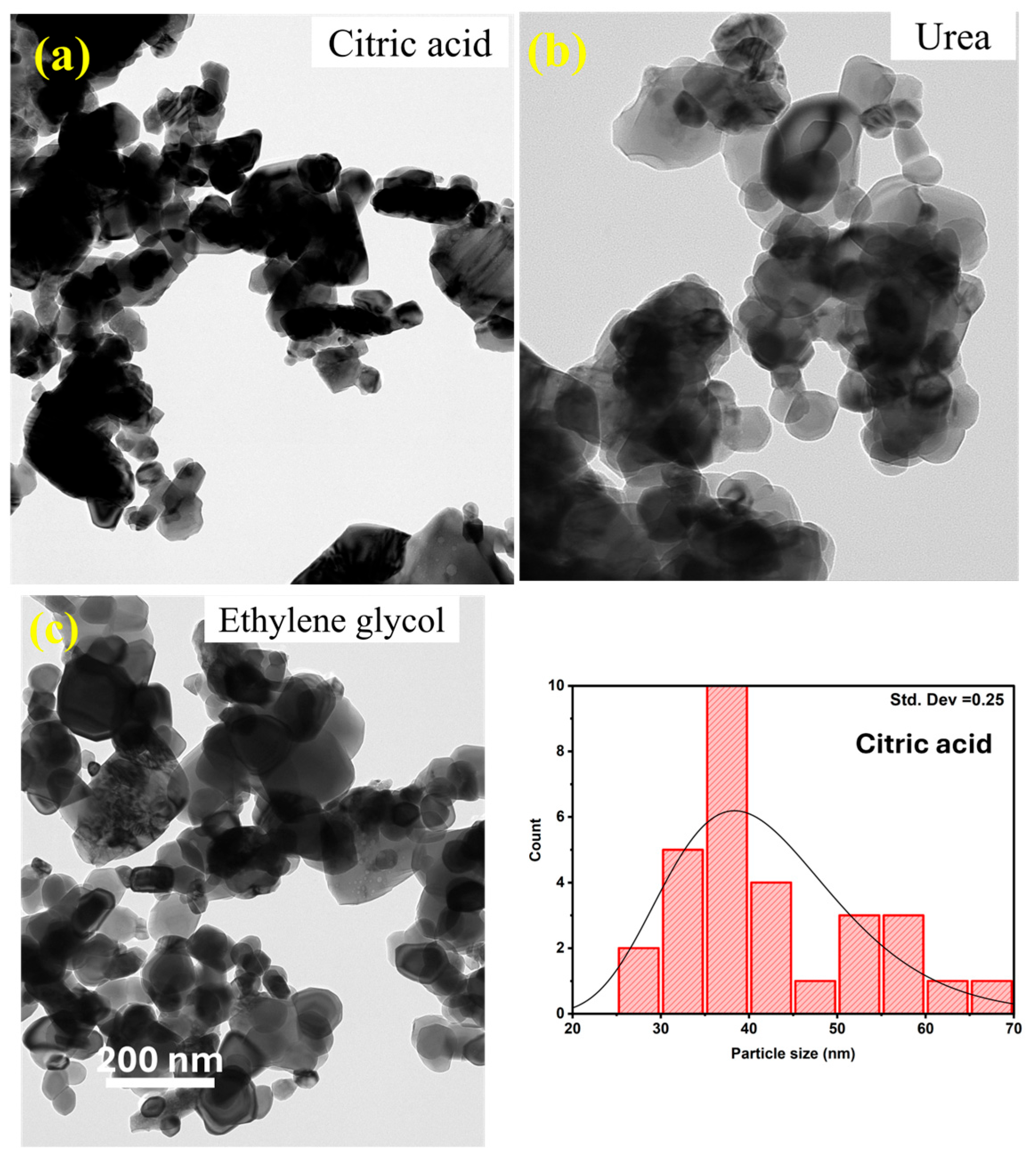
3.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
3.3. High-Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy (HRTEM)
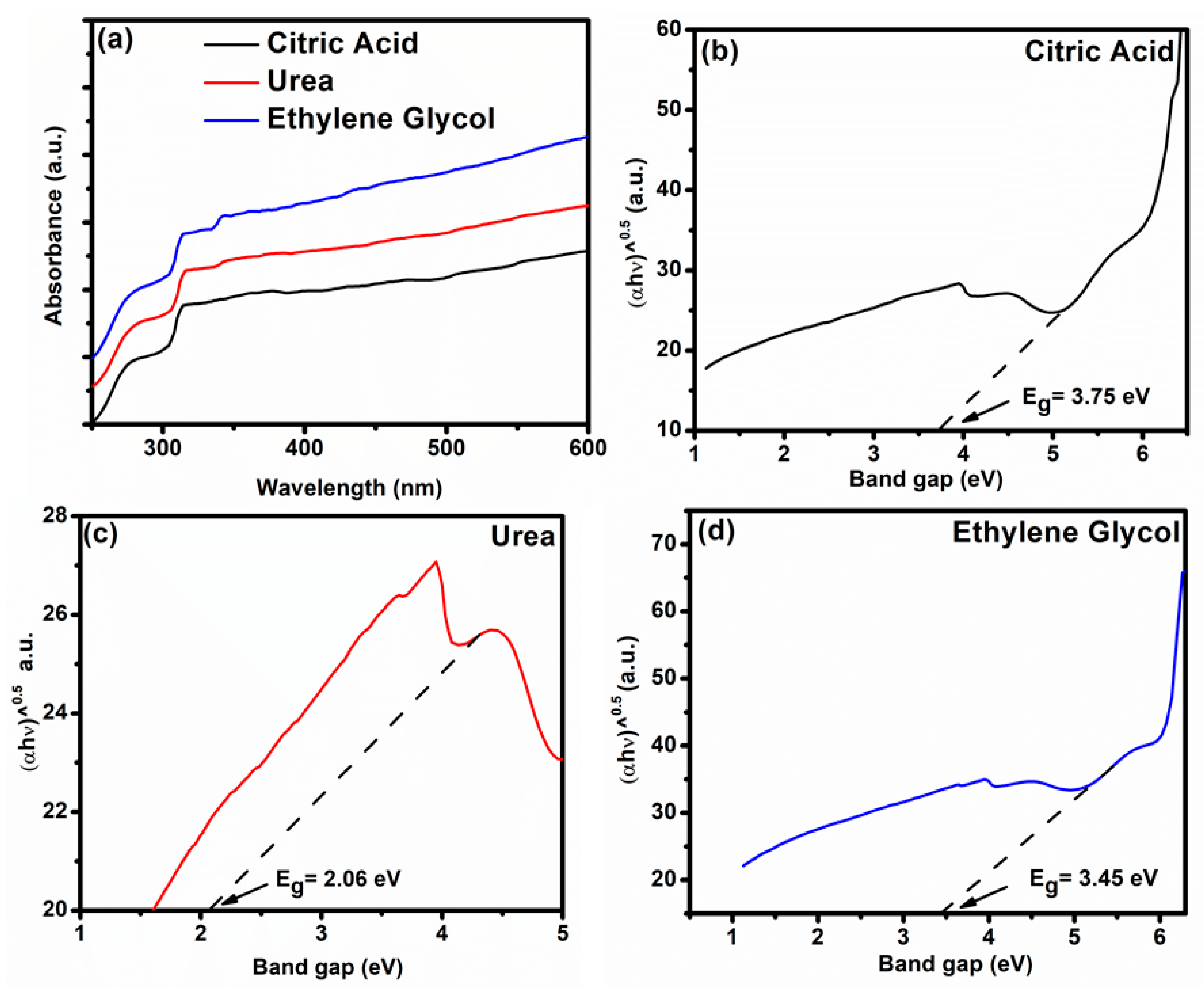
3.4. UV–Visible (UV-Vis) Spectroscopy
3.5. Vibrating Sample Magnetometer (VSM)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Majid, F.; Dildar, S.; Ata, S.; Bibi, I.; Mohsin, I.U.; Ali, A.; Almoneef, M.M.; Iqbal, M.; Irshad, S.; Nazir, A.; et al. Cobalt doping of nickel ferrites via sol gel approach: Effect of doping on the structural and dielectric properties. Z. Phys. Chem. 2021, 235, 1811–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ata, S.; Bano, S.; Bibi, I.; Alwadai, N.; Mohsin, I.U.; Al Huwayz, M.; Iqbal, M.; Nazir, A. Cationic distributions and dielectric properties of magnesium ferrites fabricated by sol-gel route and photocatalytic activity evaluation. Z. Phys. Chem. 2023, 237, 67–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; He, Y.; Xu, P.; Huang, D.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Tian, Q.; Wang, C. Spinel ferrites (MFe2O4): Synthesis, improvement and catalytic application in environment and energy field. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 294, 102486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Lievanos, K.R.; Stair, J.L.; Knowles, K.E. Cation distribution in spinel ferrite nanocrystals: Characterization, impact on their physical properties, and opportunities for synthetic control. Inorg. Chem. 2021, 60, 4291–4305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.; Kumar, S.; Mishra, A.; Sulania, I.; Tripathi, M.N.; Tripathi, A. Study of structural and electronic properties of few-layer MoS2 film. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 57, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Tripathi, M.N.; Tripathi, A. Strain-induced structural, elastic, and electronic properties of 1L-MoS2. J. Mater. Res. 2022, 37, 3340–3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alabada, R.; Aadil, M.; Mubarik, S.; Alsalmah, H.A.; Hassan, W.; Ahmad, Z.; Ibrahim, M.M.; Mersal, G.A. Wet-chemical synthesis of sponge-like porous Zn-doped copper oxide ceramic as an efficient solar-light triggered photocatalyst for multiple applications. Z. Phys. Chem. 2023, 237, 1713–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, M.; Salavati-Niasari, M.; Akbari, A. Magnetic nanocarriers: Evolution of spinel ferrites for medical applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 265, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talebniya, S.; Sharifi, I.; Saeri, M.R.; Doostmohammadi, A. Study of cation distribution and magnetic properties of MFe2O4 (M= Fe, Co, Zn, Mn, and Cu) nanoparticles. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 2022, 35, 899–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Kedia, S.K.; Mishra, A.; Avasthi, D.K.; Tripathi, A. Investigation of the annealing temperature for few-layer MoS2 and ion-beam induced athermal annealing/purification behaviour by in-situ XRD. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 639, 158106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salih, S.J.; Wali, M.M. Review on magnetic spinel ferrite (MFe2O4) nanoparticles: From synthesis to application. Heliyon 2023, 9, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dastjerdi, O.; Dehghani, H.S.; Mirshekari, S. A review of synthesis, characterization, and magnetic properties of soft spinel ferrites. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2023, 153, 110797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dippong, T.; Levei, E.A.; Cadar, O. Recent Advances in Synthesis and Applications of MFe2O4 (M = Co, Cu, Mn, Ni, Zn) Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2021, 6, 1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Şaşmaz Kuru, T. Effect of calcination temperature on structural, magnetic, and dielectric properties of Mg0.75Zn0.25Al0.2Fe1.8O4 ferrites. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2024, 35, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajivgandhi, G.N.; Ramachandran, G.; Kanisha, C.C.; Alharbi, N.S.; Kadaikunnan, S.; Khaled, J.M.; Alanzi, K.F.; Li, W.-J. Effect of Ti and Cu doping on the structural, optical, morphological and anti-bacterial properties of nickel ferrite nanoparticles. Res. Phys. 2021, 23, 104065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.; Choi, M.; Shin, H.-S.; Ju, B.-K.; Chun, M. Structural and magnetic properties of NiZn ferrite nanoparticles synthesized by a thermal decomposition method. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amadan, R.; El-Masry, M.M. Effect of (Co and Zn) doping on structural, characterization and the heavy metal removal efficiency of CuFe2O4 nanoparticles. J. Aust. Ceram. Soc. 2024, 60, 509–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masunga, N.; Mmelesi, O.K.; Kefeni, K.K.; Mamba, B.B. Recent advances in copper ferrite nanoparticles and nanocomposites synthesis, magnetic properties and application in water treatment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Singh, A.K.; Siddiqui, A.M. Synthesis and structural analysis of copper ferrite nanoparticles. In Proceedings of the AIP Conference Proceedings, Jodhpur, India, 18–22 December 2019; Volume 2265, p. 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo-de la Rosa, J.; Segarra Rubí, M. Influence of the synthesis route in obtaining the cubic or tetragonal copper ferrite phases. Inorg. Chem. 2020, 59, 8775–8788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshman, M. Recent developments in coupling reactions catalyzed by copper ferrite nanoparticles (CuFe2O4 NPs). J. Synth. Chem. 2023, 1, 148–154. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, D.; Lu, G.; Yao, J.; Zhou, C.; Liu, F.; Liu, J. Adsorption and catalytic electro-peroxone degradation of fluconazole by magnetic copper ferrite/carbon nanotubes. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 370, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Liu, Z.; Wu, W.; Li, Z.; Han, B.; Huang, Y. Preparation of single-crystal copper ferrite nanorods and nanodisks. Mater. Res. Bull. 2005, 40, 928–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponhan, W.; Maensiri, S. Fabrication and magnetic properties of electrospun copper ferrite (CuFe2O4) nanofibers. Solid State Sci. 2009, 11, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Lasluisa, J.X.; Salinas-Torres, D.; López-Ramón, M.V.; Álvarez, M.A.; Moreno-Castilla, C.; Cazorla-Amorós, D.; Morallón, E. Copper ferrite nanospheres composites mixed with carbon black to boost the oxygen reduction reaction. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 613, 126060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Meena, R.; Avasthi, D.K.; Tripathi, A. Study of Ion Velocity Effect on the Band Gap of CVD-Grown Few-Layer MoS2. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 46540–46547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reitz, C.; Suchomski, C.; Haetge, J.; Leichtweiss, T.; Jagličić, Z.; Djerdj, I.; Brezesinski, T. Soft-templating synthesis of mesoporous magnetic CuFe2O4 thin films with ordered 3D honeycomb structure and partially inverted nanocrystalline spinel domains. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 4471–4473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsov, M.V.; Morozov, Y.G.; Belousova, O.V. Synthesis of copper ferritenanoparticles. Inorganicmaterials 2013, 49, 606–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolahalam, L.A.; Viswanath, I.K.; Diwakar, B.S.; Govindh, B.; Reddy, V.; Murthy, Y.L.N. Review on nanomaterials: Synthesis and applications. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 18, 2182–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurian, M.; Nair, D.S. Effect of preparation conditions on nickel zinc ferrite nanoparticles: A comparison between sol–gel auto combustion and co-precipitation methods. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2016, 20, S517–S522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parauha, Y.R.; Sahu, V.; Dhoble, S.J. Prospective of combustion method for preparation of nanomaterials: A challenge. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2021, 267, 115054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandhasamy, S.; Pandey, A.; Minakshi, M. Polyvinylpyrrolidone assisted sol–gel route LiCo1/3Mn1/3Ni1/3PO4 composite cathode for aqueous rechargeable battery. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 60, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutka, A.; Mezinskis, G. Sol-gel auto-combustion synthesis of spinel-type ferrite nanomaterials. Front. Mater. Sci. 2012, 6, 128–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varma, A.; Mukasyan, A.S.; Rogachev, A.S.; Manukyan, K.V. Solution combustion synthesis of nanoscale materials. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 14493–14586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Z.; Deng, Z.; Zhang, L.; Chen, J.; Wang, G.; Wu, Z. The structure of copper ferrite prepared by five methods and its catalytic activity on lignin oxidative degradation. Mater. Res. Express 2020, 7, 035007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo-de la Rosa, J.; Segarra, M. Optimization of the synthesis of copper ferrite nanoparticles by a polymer-assisted sol–gel method. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 18289–18298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junaid, M.; Khan, M.A.; Abubshait, S.A.; Akhtar, M.N.; Kattan, N.A.; Laref, A.; Javed, H.M.A. Structural, spectral, dielectric and magnetic properties of indium substituted copper spinel ferrites synthesized via sol gel technique. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 27410–27418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, T.P.; Rodrigues, S.F.; Marques, G.N.; Viana Costa, R.C.; Garçone Lopes, C.G.; Aranas, C., Jr.; Rojas, A.; Gomes Rangel, J.H.; Oliveira, M.M. Synthesis, characterization, and photocatalytic investigation of CuFe2O4 for the degradation of dyes under visible light. Catalysts 2022, 12, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astaraki, H.; Masoudpanah, S.M.; Alamolhoda, S. Effects of ethylene glycol contents on phase formation, magnetic properties and photocatalytic activity of CuFe2O4/Cu2O/Cu nanocomposite powders synthesized by solvothermal method. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 14, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahba, M.A. Unveiling significant changes in optical, magnetic, and visible-light photocatalytic performance of CuFe2O4 nanocompositions through chelating agent modulation. Ceram. Int. 2025, 51, 4329–4342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandhasamy, S.; Singh, P.; Thurgate, S.; Ionescu, M.; Appadoo, D.; Minakshi, M. Olivine-type cathode for rechargeable batteries: Role of chelating agents. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 82, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soufi, A.; Hajjaoui, H.; Elmoubarki, R.; Abdennouri, M.; Barka, N. Sol-gel auto-combustion synthesis of Cu1-xMgxFe2O4 nanoparticles and their heterogenous Fenton-like activity towards tartrazine. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2022, 142, 109717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandyopadhyay, R.; Selbo, J.; Amidon, G.E.; Hawley, M. Application of powder X-ray diffraction in studying the compaction behavior of bulk pharmaceutical powders. J. Pharm. Sci. 2005, 94, 2520–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basak, M.; Rahman, M.L.; Ahmed, M.F.; Biswas, B.; Sharmin, N. The use of X-ray diffraction peak profile analysis to determine the structural parameters of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles using Debye-Scherrer, Williamson-Hall, Halder-Wagner and Size-strain plot: Different precipitating agent approach. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 895, 162694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deraz, N.M. Size and crystallinity-dependent magnetic properties of copper ferrite nano-particles. J. Alloys Compd. 2010, 501, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumitrescu, A.M.; Borhan, A.I.; Iordan, A.R.; Dumitru, I.; Palamaru, M.N. Influence of chelating/fuel agents on the structural features, magnetic and dielectric properties of Ni ferrite. Powder Technol. 2014, 268, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhiwahar, A.T.; Sundararajan, M.; Sakthivel, P.; Dash, C.S.; Yuvaraj, S. Microwave-assisted combustion synthesis of pure and zinc-doped copper ferrite nanoparticles: Structural, morphological, optical, vibrational, and magnetic behavior. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2020, 138, 109257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, D.R.; Chougule, B.K. Effect of copper substitution on electrical and magnetic properties of NiFe2O4 ferrite. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2009, 117, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Sharma, G.; Tyagi, N.; Siddiqui, A.M.; Khanuja, M. Advanced photocatalytic degradation of textile dyes and removal of heavy metal ions from MFe2O4 using photo-Fenton mechanism. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2024, 35, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathi, H.; Masoudpanah, S.M.; Alamolhoda, S.; Parnianfar, H. Effect of fuel type on the microstructure and magnetic properties of solution combusted Fe3O4 powders. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 7448–7453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavithradevi, S.; Suriyanarayanan, N.; Boobalan, T. Synthesis, structural, dielectric and magnetic properties of polyol assisted copper ferrite nano particles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 426, 37–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siriwipa, P.; Kamwanna, T.; Amornkitbamrung, V. Effect of fabrication method on the structural and the magnetic properties of copper ferrite. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 2016, 68, 697–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vara Prasad, B.B.V.S.; Ramesh, K.V.; Srinivas, A. Structural and magnetic studies of nano-crystalline ferrites MFe2O4 (M= Zn, Ni, Cu, and Co) synthesized via citrate gel autocombustion method. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 2017, 30, 3523–3535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghumare, A.B.; Mane, M.L.; Shirsath, S.E.; Lohar, K.S. Role of pH and sintering temperature on the properties of tetragonal–cubic phases composed copper ferrite nanoparticles. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2018, 28, 2612–2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padampalle, A.S.; Suryawanshi, A.D.; Navarkhele, V.M.; Birajdar, D.S. Structural and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline copper ferrites synthesized by sol-gel autocombustion method. Int. J. Rec. Technol. Eng. 2013, 2, 2277–3878. [Google Scholar]
- Sivakumar, A.; Dhas, S.S.J.; Almansour, A.I.; Kumar, R.S.; Arumugam, N.; Dhas, S.M.B. Assessment of crystallographic and magnetic phase stabilities of cubic copper ferrite at shocked conditions. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2021, 32, 2732–12742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tehrani-Bagha, A.R.; Gharagozlou, M.; Emami, F. Catalytic wet peroxide oxidation of a reactive dye by magnetic copper ferrite nanoparticles. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 1530–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Citric Acid | Urea | Ethylene Glycol | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S.N | 2θ (Degree) | FWHM (Degree) | D (nm) | 2θ (Degree) | FWHM (Degree) | D (nm) | 2θ (Degree) | FWHM (Degree) | D (nm) |
| 1 | 18.38724 | 0.40907 | 19.66542 | 24.17847 | 0.32129 | 25.27718 | 33.20684 | 0.26075 | 31.78027 |
| 2 | 29.94531 | 0.35739 | 23.00087 | 33.19765 | 0.28718 | 28.85475 | 35.63465 | 0.33955 | 24.56565 |
| 3 | 35.54951 | 0.385793 | 21.61594 | 35.65902 | 0.34187 | 24.40062 | 38.23839 | 0.42178 | 19.927 |
| 4 | 38.73603 | 0.4387 | 19.18751 | 38.77504 | 0.29921 | 28.13599 | 40.6133 | 0.24868 | 34.04962 |
| 5 | 44.02732 | 0.5668 | 15.11235 | 49.51476 | 0.24166 | 36.187 | 49.50369 | 0.32143 | 27.20518 |
| 6 | 58.16171 | 0.5019 | 18.10463 | 54.12291 | 0.30698 | 29.04909 | 54.12041 | 0.30891 | 28.86728 |
| 7 | 62.12348 | 0.5459 | 16.98199 | 62.30654 | 0.30893 | 30.03726 | 62.48548 | 0.31858 | 29.15497 |
| Fuel | Average Crystallite Size (D), nm | d-Spacing (311), Å | Lattice Constant (a), Å |
|---|---|---|---|
| Citric acid | 19 ± 0.18 | 1.40 | 8.66 |
| Urea | 29 ± 0.56 | 1.42 | 8.70 |
| Ethylene glycol | 27 ± 0.32 | 1.42 | 8.71 |
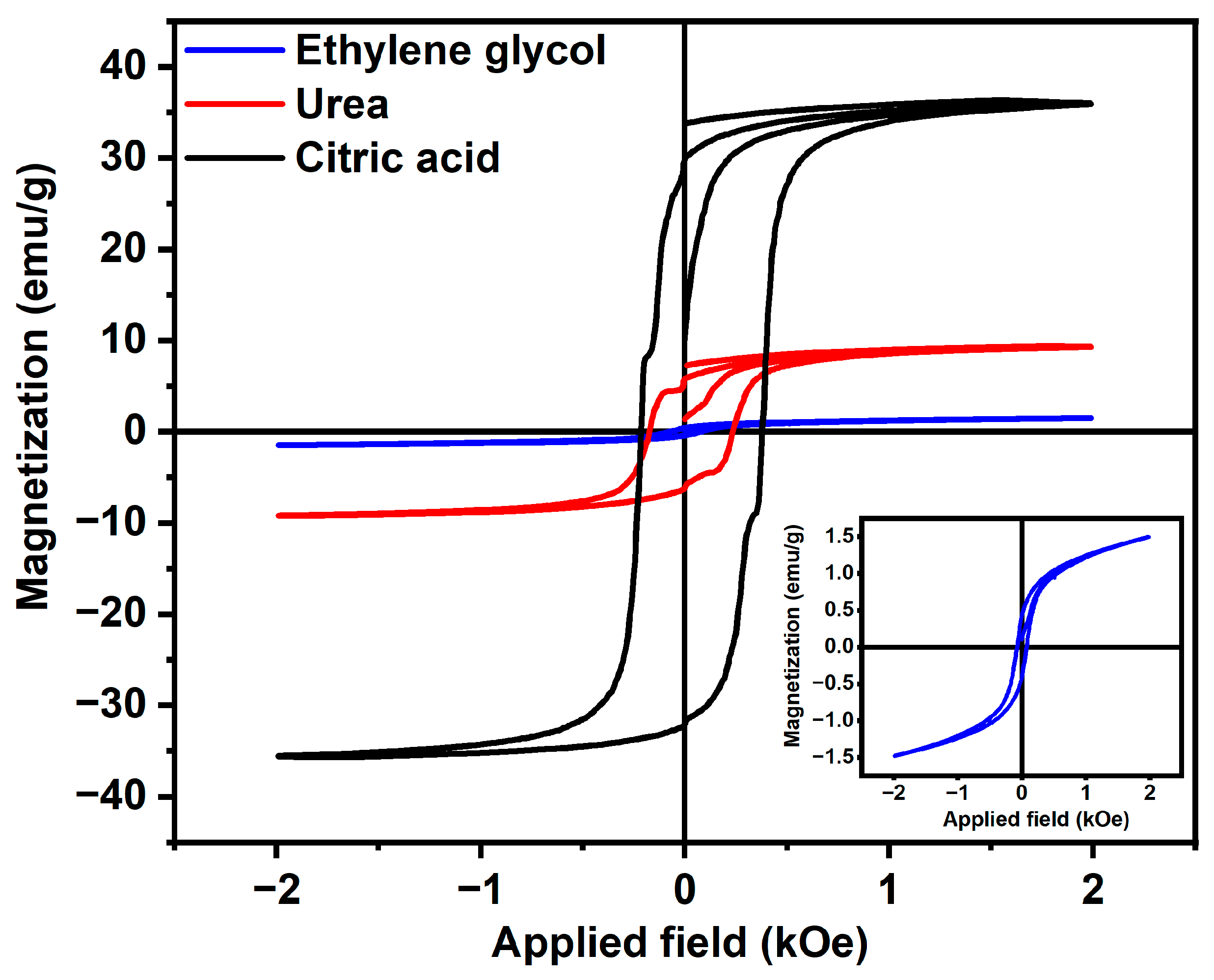
| Samples | Magnetic Saturation (MS), emu/gm | Remanence (MR), emu/gm | Coercivity (-HC), kOe | MR/MS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CuFe2O4 (CA) | 35.88 ± 0.317 | 31.60 | 0.28 | 0.88 |
| CuFe2O4 (Urea) | 9.34 ± 0.0685 | 4.77 | 0.09 | 0.51 |
| CuFe2O4 (EG) | 1.59 ± 0.0721 | 0.47 | 0.08 | 0.29 |
| S.n. | Methods | Fuel | Size (nm) | Ms(emu/gm) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Self-combustion with different temperatures from 773 to 1173 °C | Urea | 26.2–40.3 | 43.3–34.9 | [52] |
| Glycine | 36.3–38.6 | 31.3–24.7 | |||
| 2. | Citrate gel auto-combustion method | Citric acid | 18.4 | 24 | [53] |
| 3. | Sol-gel auto-combustion method with a ratio of metal nitrates to citric acid of 1:3 at different calcination temperatures of 600, 800, and 1000 °C and different pH values | Citric acid | 17.97, 25.20, 32.36, 34.39 | 9.26, 15.25, 19.26, 25.15 | [54] |
| 4. | Solution combustion method with different calcination temperatures ranging from 400 to 1100 °C | Urea | 8.2–49.8 | NA | [38] |
| 5. | Sol-gel auto-combustion method with a ratio of metal nitrates to citric acid of 1:3 at different calcination temperatures of 350, 550, 750, 950, and 1050 °C for 5 h | Citric acid | 22, 45, 66, 85 | 9.50, 9.91, 11, 21.34 | [55] |
| 6. | Sol-gel with different shock conditions | Urea | 35.46–35.56 | 35.35–35.75 | [56] |
| 7. | Polymeric precursor method | Citric acid and Ethylene glycol | 29 | 6.5 | [57] |
| 8. | Sol-gel auto-combustion | Citric acid | 19 ± 0.18 | 35.88 | Present work |
| Urea | 29 ± 0.56 | 9.34 | |||
| Ethylene glycol | 27 ± 0.32 | 1.59 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sharma, M.; Khan, M.; Khanuja, M.; Mishra, N. Exploring the Roles of Chelating/Fuel Agents in Shaping the Properties of Copper Ferrites. AppliedChem 2025, 5, 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem5020009
Sharma M, Khan M, Khanuja M, Mishra N. Exploring the Roles of Chelating/Fuel Agents in Shaping the Properties of Copper Ferrites. AppliedChem. 2025; 5(2):9. https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem5020009
Chicago/Turabian StyleSharma, Menka, Mayur Khan, Manika Khanuja, and Neeraj Mishra. 2025. "Exploring the Roles of Chelating/Fuel Agents in Shaping the Properties of Copper Ferrites" AppliedChem 5, no. 2: 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem5020009
APA StyleSharma, M., Khan, M., Khanuja, M., & Mishra, N. (2025). Exploring the Roles of Chelating/Fuel Agents in Shaping the Properties of Copper Ferrites. AppliedChem, 5(2), 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem5020009







