Interactions between Fish and Invertebrates in the Lowland Area of the Sava River following Excessive Change in Hydrological Regime
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Hydrological Features
2.2. Measurement of Environmental Parameters
2.3. Biocenotical Analysis
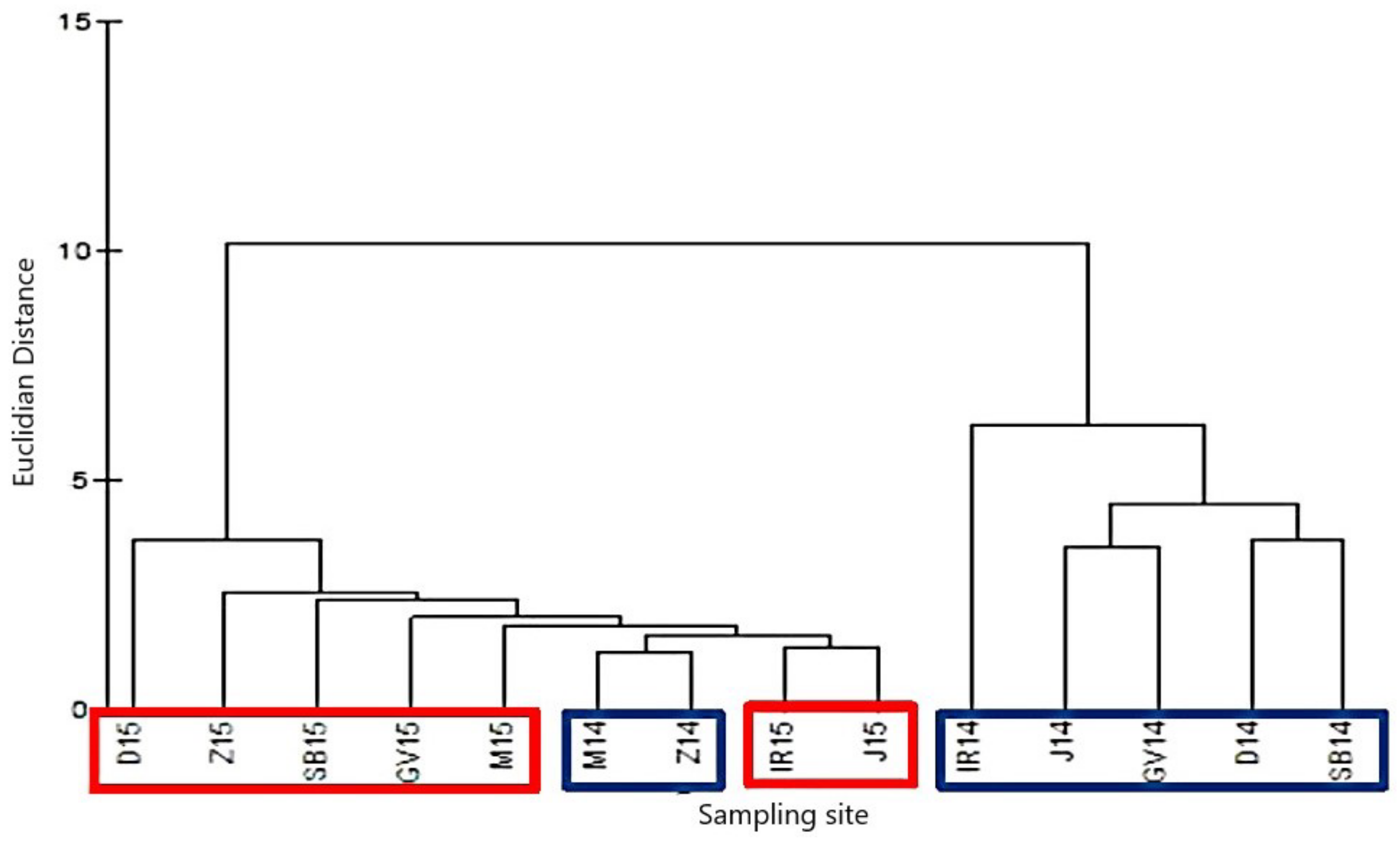
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Environmental Conditions
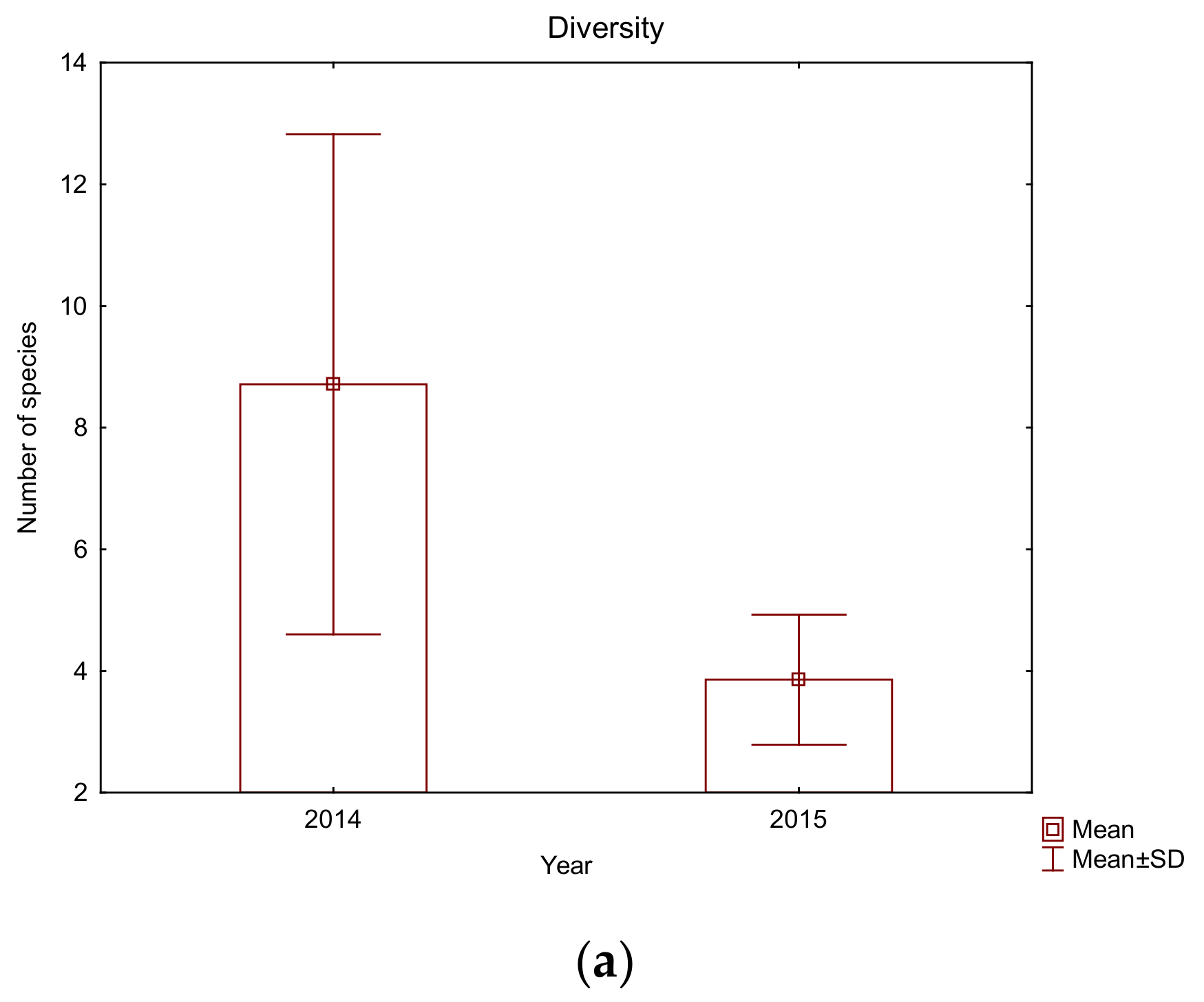
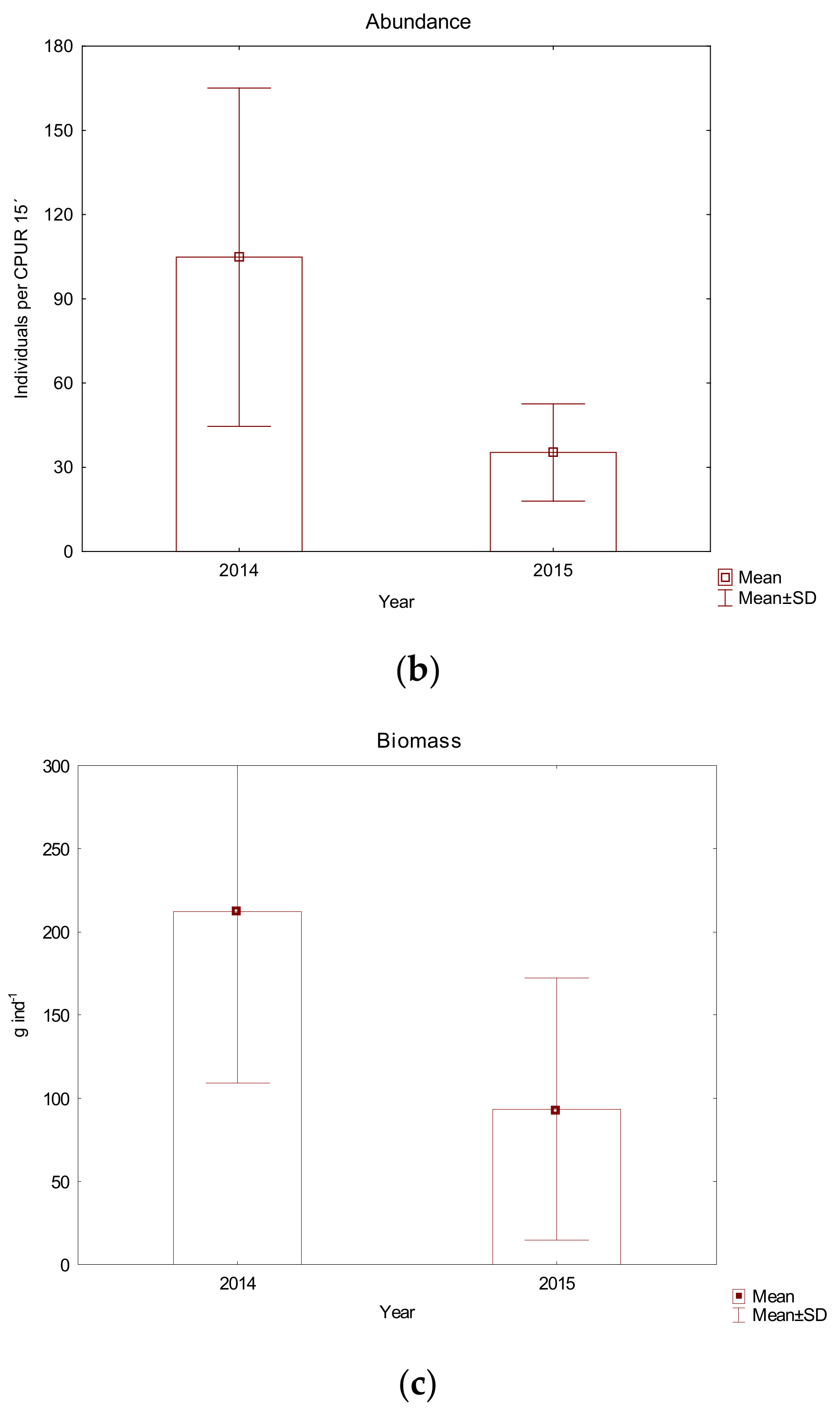
3.2. The Fish Community at the Studied Sites of the Sava River
3.3. Macrozoobenthos and Zooseston of the Riverine Littoral Zone
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shumilova, O.; Zak, D.; Datry, T.; Schiller, D.; Corti, R.; Foulquier, A.; Obrador, B.; Tockner, K.; Allan, D.C.; Altermatt, F. Simulating rewetting events in intermittent rivers and ephemeral streams: A global analysis of leached nutrients and organic matter. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2019, 25, 1591–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiegs, S.D.; Miliša, M.; Zwart, J.A. Global patterns and drivers of ecosystem functioning in rivers and riparian zones. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaav0486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lytle, D.A.; Poff, N.L. Adaptation to natural flow regimes. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2004, 19, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saigo, M.; Ruffener, L.; Scarabotti, P.; Marchese, M. Food chain length in a large floodplain river: Planktonic or benthic reliance as a limiting factor. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2017, 68, 1336–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abo-Taleb, H. Importance of Plankton to Fish Community. In Biological Research in Aquatic Science; Bozkurt, Y., Ed.; IntechOpen Limited: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanal, S.; Lutz, A.F.; Kraaijenbrink, P.D.; van den Hurk, B.; Yao, T.; Immerzeel, W.W. Variable 21st century climate change response for rivers in High Mountain Asia at seasonal to decadal time scales. Water Resour. Res. 2021, 57, e2020WR029266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burenina, T.A.; Prysov, D.A.; Musokhranova, A.V. The Effects of Climate Change on the Hydrological Regime of Northern Rivers in Krasnoyarsk Krai. Geogr. Nat. Resour. 2021, 42, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frau, D.; Medrano, J.; Calvi, C.; Giorgi, A. Water quality assessment of a neotropical pampean lowland stream using a phytoplankton functional trait approach. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaparro, G.; O’Farrell, I.; Hein, T. Multi-scale analysis of functional plankton diversity in floodplain wetlands: Effects of river regulation. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 667, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galir Balkić, A.; Ternjej, I.; Špoljar, M. Hydrology driven changes in the rotifer trophic structure and implications for food web interactions. Ecohydrology 2018, 11, e1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuczyńska-Kippen, N. Response of zooplankton indices to anthropogenic pressure in the catchment of field ponds. Water 2020, 12, 758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilgour, B.W.; Barton, D.R. Associations between stream fish and benthos across environmental gradients in southern Ontario, Canada. Freshw. Biol. 1999, 41, 553–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolter, C.; Freyhof, J. Diel fish movements in a temperate large lowland river. J. Fish Biol. 2004, 64, 632–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treer, T.; Piria, M.; Aničić, I.; Safner, R.; Tomljanović, T. Diet and growth of spirlin, Alburnoides bipunctatus in the barbel zone of the Sava River. Folia Zool. 2006, 55, 97–106. [Google Scholar]
- Piria, M.; Simonović, P.; Zanella, D.; Ćaleta, M.; Šprem, N.; Paunović, M.; Tomljanović, T.; Gavrilović, A.; Pecina, M.; Špelić, I.; et al. Long-term analysis of fish assemblage structure in the middle section of the Sava River—The impact of pollution, flood protection and dam construction. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adámek, Z.; Zahrádková, S.; Jurajda, P.; Bernardová, I.; Jurajdová, Z.; Janáč, M.; Němejcová, D. The response of benthic macroinvertebrate and fish assemblages to human impact along the lower stretch of the rivers Morava and Dyje Danube basin, Czech Republic. Croat. J. Fish. Ribar. 2013, 71, 93–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Marković, V.; Atanacković, A.; Tubić, B.; Vasiljević, B.; Simić, V.; Tomović, J.; Paunović, M. Indicative status assessment of the Velika Morava River based on aquatic macroinvertebrates. Water Resour. Manag. 2011, 1, 47–53. [Google Scholar]
- Dzhurtubayev, M.M.; Zamorov, V.V.; Dzhurtubayev, Y.M. Modern state of macrozoobenthos of the Danube River lakes of the Odessa Region. Hydrobiol. J. 2013, 49, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogbeibu, A.E.; Oribhabor, B.J. Ecological impact of river impoundment using benthic macro-invertebrates as indicators. Water Res. 2002, 36, 2427–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flessas, C.; Couillard, Y.; Pinel-Alloul, B.; St-Cyr, L.; Campbell, P.G. Metal concentrations in two freshwater gastropods (Mollusca) in the St. Lawrence River and relationships with environmental contamination. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2000, 57, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krings, W.; Kovalev, A.; Gorb, S.N. Influence of water content on mechanical behaviour of gastropod taenioglossan radulae. Proc. R. Soc. B 2021, 288, 20203173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wörner, U.; Zimmerman-Timm, H.; Kausch, H. Succession of protists on estuarine aggregates. Microb. Ecol. 2000, 40, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allan, J.D.; Castillo, M.M. Stream Ecology. Structure and Function of Running Waters; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2007; p. 379. [Google Scholar]
- Wallace, J.; Webster, J. The role of macroinvertebrates in stream ecosystem function. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1996, 41, 115–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breitig, G.; von Tümpling, W. Ausgewaehlte Methoden der Wasseruntersuchung, Band II. In Biologische Mikrobiologische und Toxikologische Methoden; Gustav Fischer Verlag: Jena, Germany, 1982; p. 579. [Google Scholar]
- Špoljar, M.; Primc-Habdija, B.; Habdija, I. The Influence of the lotic and lentic stretches on the zooseston flux through the Plitvice Lakes (Croatia). Ann. Limnol.-Int. J. Limnol. 2007, 43, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann-Timm, H.; Holst, H.; Kausch, H. Spatial dynamics of rotifers in a large lowland river, the Elbe, Germany: How important are retentive shoreline habitats for the plankton community? Hydrobiologia 2007, 593, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sertić Perić, M.; Miliša, M.; Matoničkin Kepčija, R.; Primc-Habdija, B.; Habdijas, I. Seasonal and fine-scale spatial drift patterns in a tufa-depositing barrage hydrosystem. Fund. Appl. Limnol. Arch. Hydrobiol. 2011, 178, 131–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Płaska, W.; Mieczan, T. Effects of water bugs on crustacean zooplankton in a shallow littoral zone. Knowl. Manag. Aquat. 2018, 419, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erős, T.; Tóth, B.; Sevcsik, A.; Schmera, D. Comparison of fish assemblage diversity in natural and artificial rip-rap habitats in the littoral zone of a large river (River Danube, Hungary). Int. Rev. Hydrobiol. 2008, 93, 88–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casatti, L.; Mendes, H.F.; Ferreira, K.M. Aquatic macrophytes as feeding site for small fishes in the Rosana Reservoir, Paranapanema River, Southeastern Brazil. Braz. J. Biol. 2003, 63, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Špoljar, M.; Fressl, J.; Dražina, T.; Meseljević, M.; Grčić, Z. Epiphytic metazoans on emergent macrophytes in oxbow lakes of the Krapina River, Croatia: Differences related to plant species and limnological conditions. Acta Bot. Croat. 2012, 71, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vono, V.; Barbosa, F.A. Habitats and littoral zone fish community structure of two natural lakes in southeast Brazil. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2021, 61, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossa, D.C.; Lansac-Tôha, F.A.; Bonecker, C.C.; Velho, L.F.M. Abundance of cladocerans in the littoral regions of two environments of the upper Paraná river floodplain, Mato Grosso do Sul, Brazil. Rev. Bras. Biol. 2001, 61, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Meerhoff, M.; Iglesias, C.; De Mello, F.T.; Clemente, J.M.; Jensen, E.; Lauridsen, T.L.; Jeppesen, E. Effects of habitat complexity on community structure and predator avoidance behaviour of littoral zooplankton in temperate versus subtropical shallow lakes. Freshw. Biol. 2007, 52, 1009–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brucet, S.; Boix, D.; Quintana, X.D.; Jensen, E.; Nathansen, L.W.; Trochine, C.; Meerhoff, M.; Gascon, S.; Jeppesena, E. Factors influencing zooplankton size structure at contrasting temperatures in coastal shallow lakes: Implications for effects of climate change. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2010, 55, 1697–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, M.C.; Bowen, Z.H.; Bovee, K.D.; Irwin, E.R. Flow and habitat effects on juvenile fish abundance in natural and altered flow regimes. Ecol. Appl. 2001, 11, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Chen, Q.; Tonina, D.; Cai, D. Effects of upstream reservoir regulation on the hydrological regime and fish habitats of the Lijiang River, China. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 76, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dražina, T.; Špoljar, M.; Primc, B.; Habdija, I. Small-scale patterns of meiofauna in a bryophyte covered tufa barrier (Plitvice Lakes, Croatia). Limnologica 2013, 43, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonović, P.; Piria, M.; Zuliani, T.; Ilić, M.; Marinković, N.; Kračun-Kolarević, M.; Paunović, M. Characterization of sections of the Sava River based on fish community structure. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 574, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heuvel, C.E.; Haffner, G.D.; Zhao, Y.; Colborne, S.F.; Despenic, A.; Fisk, A.T. The influence of body size and season on the feeding ecology of three freshwater fishes with different diets in Lake Erie. J. Great Lakes Res. 2019, 45, 795–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piniewski, M.; Prudhomme, C.; Acreman, M.C.; Tylec, L.; Oglęcki, P.; Okruszko, T. Responses of fish and invertebrates to floods and droughts in Europe. Ecohydrology 2017, 10, e1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aničić, I.; Treer, T.; Safner, R.; Piria, M.; Tomljanović, T.; Šprem, N.; Matulić, D. Final Report on the Implementation of the Program for Monitoring Freshwater Fisheries in 2014, Group (B) Sava Fishing Area; University of Zagreb: Zagreb, Croatia, 2014; p. 124. [Google Scholar]
- Nusch, E.A. Comparison of different methods for chlorophyll and phaeopigment determination. Arch. Hydrobiol. 1980, 14, 14–36. [Google Scholar]
- Bain, M.B.; Finn, J.T. Analysis of microhabitat use by fish: Investigator effect and investigator bias. Rivers 1991, 2, 57–65. [Google Scholar]
- Kottelat, M.; Freyhof, J. Handbook of European Freshwater Fishes; Cornol, K., Ed.; Switzerland and Freyhof: Berlin, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Froese, R.; Pauly, D. (Eds.) FishBase. 2010. Available online: http://www.fishbase.org (accessed on 15 October 2021).
- Zalewski, M. The estimate of fish density and biomass in rivers on the basis of relationship between specimen size and efficiency of electrofishing. Fish. Res. 1985, 3, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, K.R.; Gorley, R.N. Primer v6: User Manual/Tutorial (Plymouth Routines in Multivariate Ecological Research); PRIMER-E: Plymouth, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, K.R.; Warwick, R.M. Change in Marine Communities: An Approach to Statistical Analysis and Interpretation; PRIMER-E Ltd., Plymouth Marine Laboratory: Plymouth, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Ter Braak, C.J.F.; Šmilauer, P. Canoco Reference Manual and User’s Guide: Software for Ordination, Version 5.0; Microcomputer Power: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2012; p. 496. [Google Scholar]
- Allan, R.P.; Barlow, M.; Byrne, M.P.; Cherchi, A.; Douville, H.; Fowler, H.J.; Gan, T.Y.; Pendergrass, A.G.; Rosenfeld, D.; Swann, A.L.S.; et al. Advances in understanding large-scale responses of the water cycle to climate change. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2020, 1472, 49–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kundzewicz, Z.W. Climate change impacts on the hydrological cycle. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2008, 8, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, W.; Tang, C.; Zeng, F. Water level fluctuation under the impact of lake regulation and ecological implication in Huayang lakes, China. Water 2020, 12, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMillan, H.; Krueger, T.; Freer, J. Benchmarking observational uncertainties for hydrology: Rainfall, river discharge and water quality. Hydrol. Process. 2012, 26, 4078–4111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miró, J.J.; Estrela, M.J.; Olcina-Cantos, J.; Martin-Vide, J. Future Projection of Precipitation Changes in the Júcar and Segura River Basins (Iberian Peninsula) by CMIP5 GCMs Local Downscaling. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.R.; Kadlec, R.H.; Flaig, E.; Gale, P.M. Phosphorus retention in streams and wetlands: A review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 29, 83–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Wu, M.; Li, R. Distribution, sedimentation, and bioavailability of particulate phosphorus in the mainstream of the Three Gorges Reservoir. Water Res. 2018, 140, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Špoljar, M.; Primc-Habdija, B.; Habdija, I. Transport of seston in the karstic hydrosystem of the Plitvice Lakes (Croatia). Hydrobiologia 2007, 579, 199–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões, N.R.; Lansac-Tôha, F.A.; Velho, L.F.M.; Bonecker, C.C. Intra and inter-annual structure of zooplankton communities in floodplain lakes: A long-term ecological research study. Rev. Biol. Trop. 2012, 60, 1819–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevalainen, L.; Luoto, T.P. Relationship between cladoceran (Crustacea) functional diversity and lake trophic gradients. Funct. Ecol. 2017, 31, 488–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrend, R.D.L.; Fernandes, S.E.P.; Fujita, D.S.; Takeda, A.M. Eight years of monitoring aquatic Oligochaeta from the Baía and Ivinhema Rivers. Braz. J. Biol. Sci. 2009, 69, 559–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Simonović, P.; Povž, M.; Piria, M.; Treer, T.; Adrović, A.; Škrijelj, R.; Nikolić, V.; Simić, V. Ichthyofauna of the River Sava System, The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry. In The Sava River; Milačič, R., Ščančar, J., Paunović, M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; Volume 31, pp. 361–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piria, M.; Treer, T.; Aničić, I.; Safner, R.; Odak, T. The natural diet of five cyprinid fish species. Agric. Conspec. Sci. 2005, 70, 21–28. [Google Scholar]
- Treer, T.; Habeković, D.; Aničić, I.; Safner, R.; Kolak, A. Standard growth curve for chub (Leuciscus cephalus L. 1758) in Croatia. Croat. J. Fish. 1997, 55, 47–52. [Google Scholar]
- Treer, T.; Opačak, A.; Aničić, I.; Safner, R.; Piria, M.; Odak, T. Growth of bream, Abramis brama, in the Croatian section of the Danube. Czech J. Anim. Sci. 2003, 48, 251–256. [Google Scholar]
- Bartulović, V.; Dulčić, J.; Bogut, I.; Pavlicević, J.; Haskovic, E.; Glamuzina, B. First record of the freshwater bream, Abramis brama in the river Mala Neretva, Adriatic drainage system of Croatia. Cybium 2011, 35, 165–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulčić, J.; Tutman, P. Additional record of common bream Abramis brama (Cyprinidae) in the Adriatic drainage system (Norin river, Croatia). In Annales: Series Historia Naturalis; Scientific and Research Center of the Republic of Slovenia: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2015; p. 145. [Google Scholar]
- Razlutskij, V.; Mei, X.; Maisak, N.; Sysova, E.; Lukashanets, D.; Makaranka, A.; Jeppesen, E.; Zhang, X. Omnivorous carp (Carassius gibelio) increase eutrophication in part by preventing development of large-bodied zooplankton and submerged macrophytes. Water 2021, 13, 1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vagner, D.; Špoljar, M. Der Anteil der Oligochaeten in den Benthoszoenosen der Muendungen der Fluesse Una und Vrbas. In Proceedings of the 31. Konferenz der IAD, Baja, Hungary, 25–29 August 1996; pp. 565–569. [Google Scholar]
- Habdija, I.; Radanović, I.; Primc-Habdija, B.; Špoljar, M. Functional organization of macroinvertebrate benthic community on the gravel substrate in the river Sava. In Limnologische Berichte Donau, Wissenschaftliche Referate; Oesterreichisches Nationalkomitee fuer die Donauforschung der IAD: Vienna, Austria, 1997; pp. 297–300. [Google Scholar]
- Miracle, M.R.; Moss, B.; Vicente, E.; Romo, S.; Rueda, J.; Becares, E.; Fernandez-Alaez, C.; Fernandez-Alaez, M.; Hietala, J.; Kairesalo, T.; et al. Response of macroinvertebrates to nutrient and fish additions in European localities at different latitudes. Limnetica 2006, 25, 585–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuczynska-Kippen, N.; Pronin, M. Diversity and zooplankton species associated with certain hydroperiods and fish state in field ponds. Ecol. Ind. 2018, 90, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adámek, Z.; Maršálek, B. Bioturbation of sediments by benthic macroinvertebrates and fish and its implication for pond ecosystems: A review. Aquac. Int. 2012, 21, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biro, P.; Sadek, S.E.; Paulovits, G. The food of bream (Abramis brama L.) in 2 basins of lake Balaton of different trophic status. Hydrobiologia 1991, 209, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martyniak, A.; Jerzyk, M.S.; Adámek, Z. The food of bream Abramis brama in the Pierzchaly Reservoir Poland. Folia Zool. 1987, 36, 273–280. [Google Scholar]
- Naumenko, E.N. Effect of food availability in early ontogenesis on the rate of growth and numbers of bream Abramis brama L. in Kursh Bay of the Baltic Sea. Russ. J. Dev. Biol. 2011, 42, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakareko, T. The importance of benthic fauna in the diet of small common bream Abramis brama (L.), roach Rutilus rutilus (L.), pikeperch Sander lucioperca (L.) and ruffe Gymnocephalus cernuus (L.) in the Włocławek Reservoir. Fish. Aquat. Life 2002, 10, 221–231. [Google Scholar]
- Winfield, I.J.; Fletcher, J.M.; Ben James, J. Long-term changes in the diet of pike (Esox lucius), the top aquatic predator in a changing Windermere. Freshw. Biol. 2012, 57, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, C.M.; Borgstrøm, R. Shifts in density, habitat use, and diet of perch and roach: An effect of changed predation pressure after manipulation of pike. Fish. Res. 2008, 91, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raat, A.J.P. Synopsis of Biological Data on the Northern Pike Esox Lucius Linnaeus, 1758; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Bíró, P. First two-year growth of the bleak, Alburnus alburnus, in Lake Balaton. Aquac. Hung. 1980, 2, 168–180. [Google Scholar]
- Flinders, J.M.; Bonar, S.A. Growth, condition, diet, and consumption rates of northern pike in three Arizona reservoirs. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2008, 24, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazicioglu, O.; Polat, N.; Yilmaz, S. Feeding biology of pike, Esox lucius L., 1758 inhabiting Lake Ladik, Turkey. Turk. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2018, 18, 1215–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandlund, O.T.; Museth, J.; Øistad, S. Migration, growth patterns, and diet of pike (Esox lucius) in a river reservoir and its inflowing river. Fish. Res. 2016, 173, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
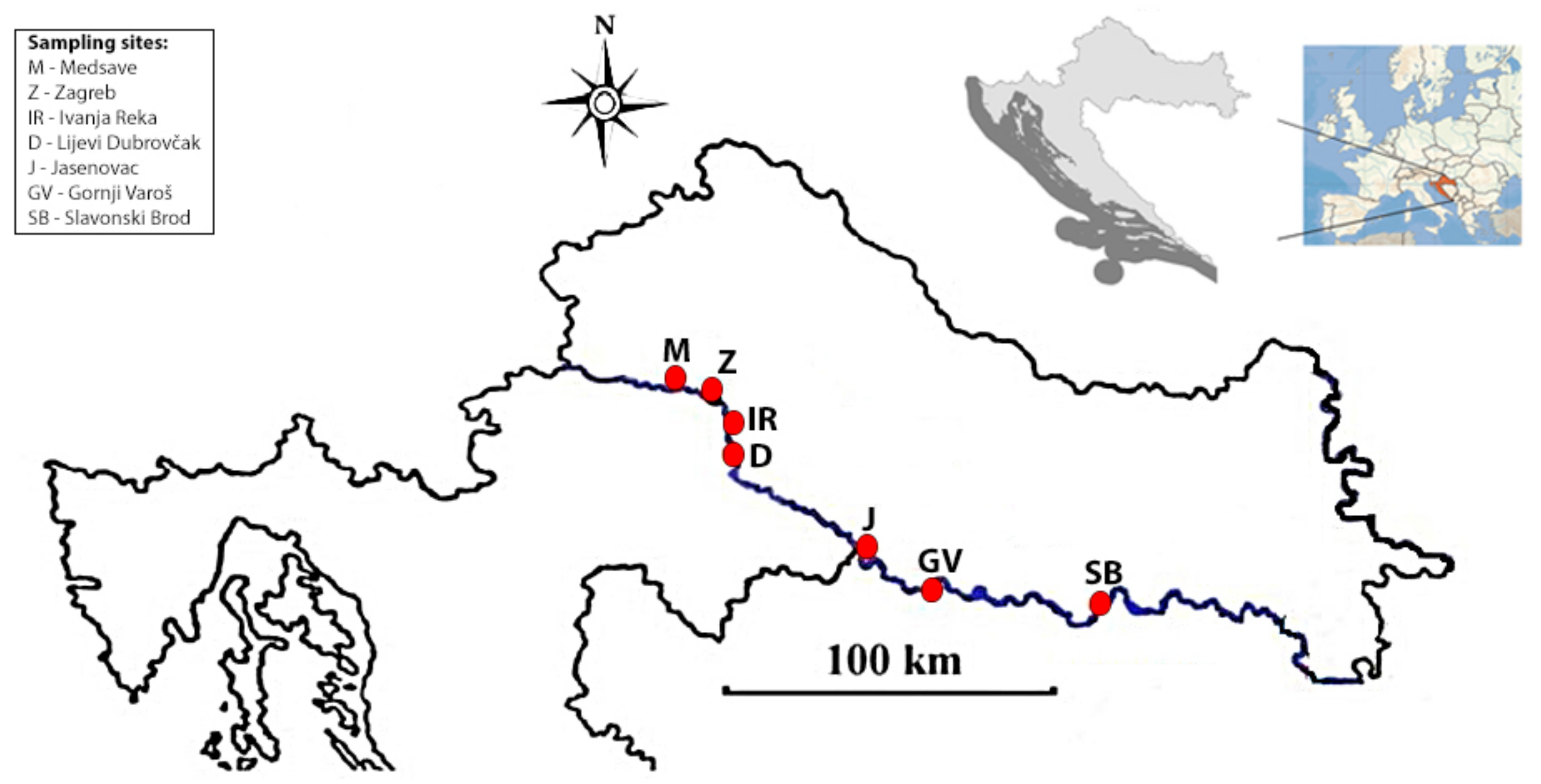
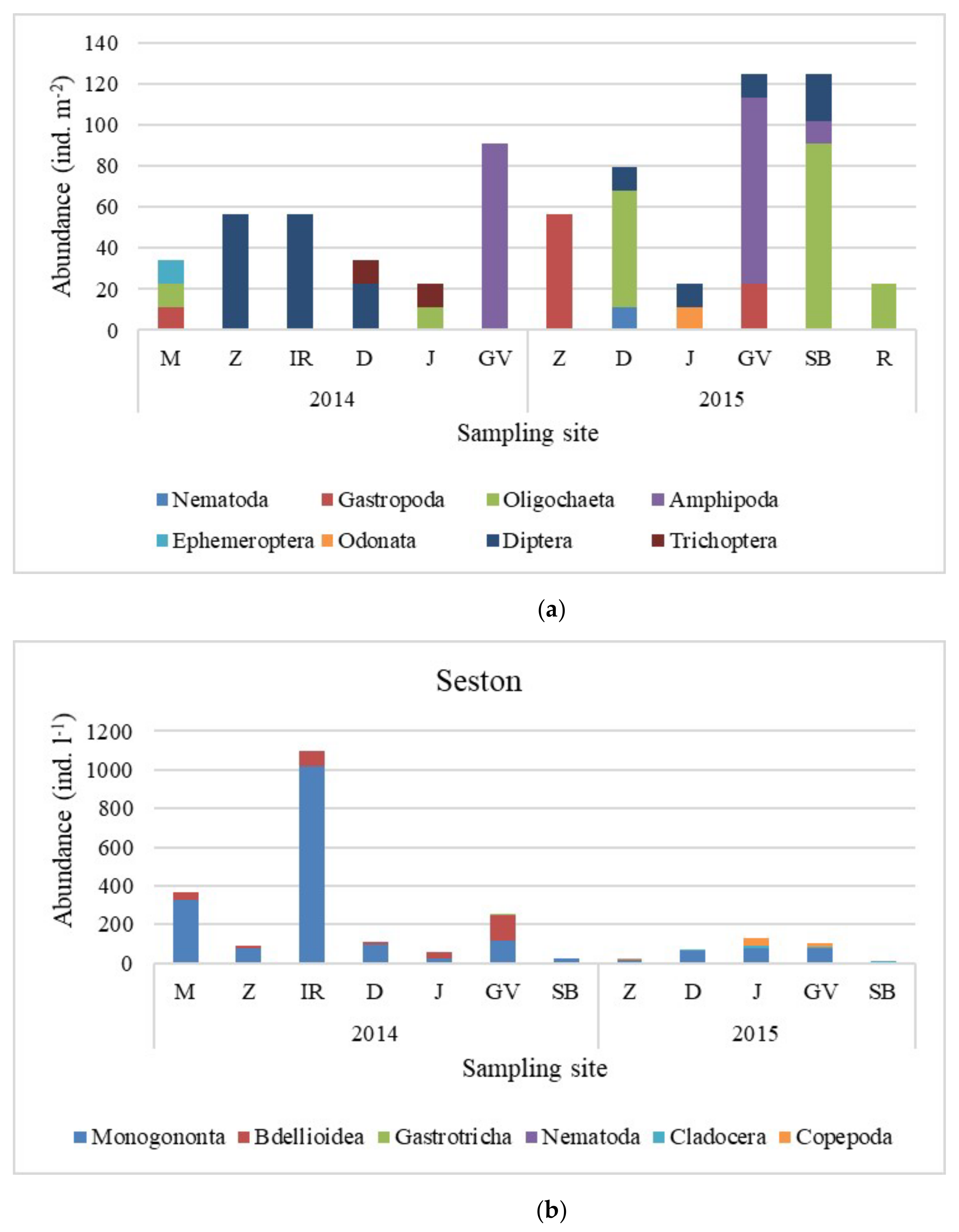
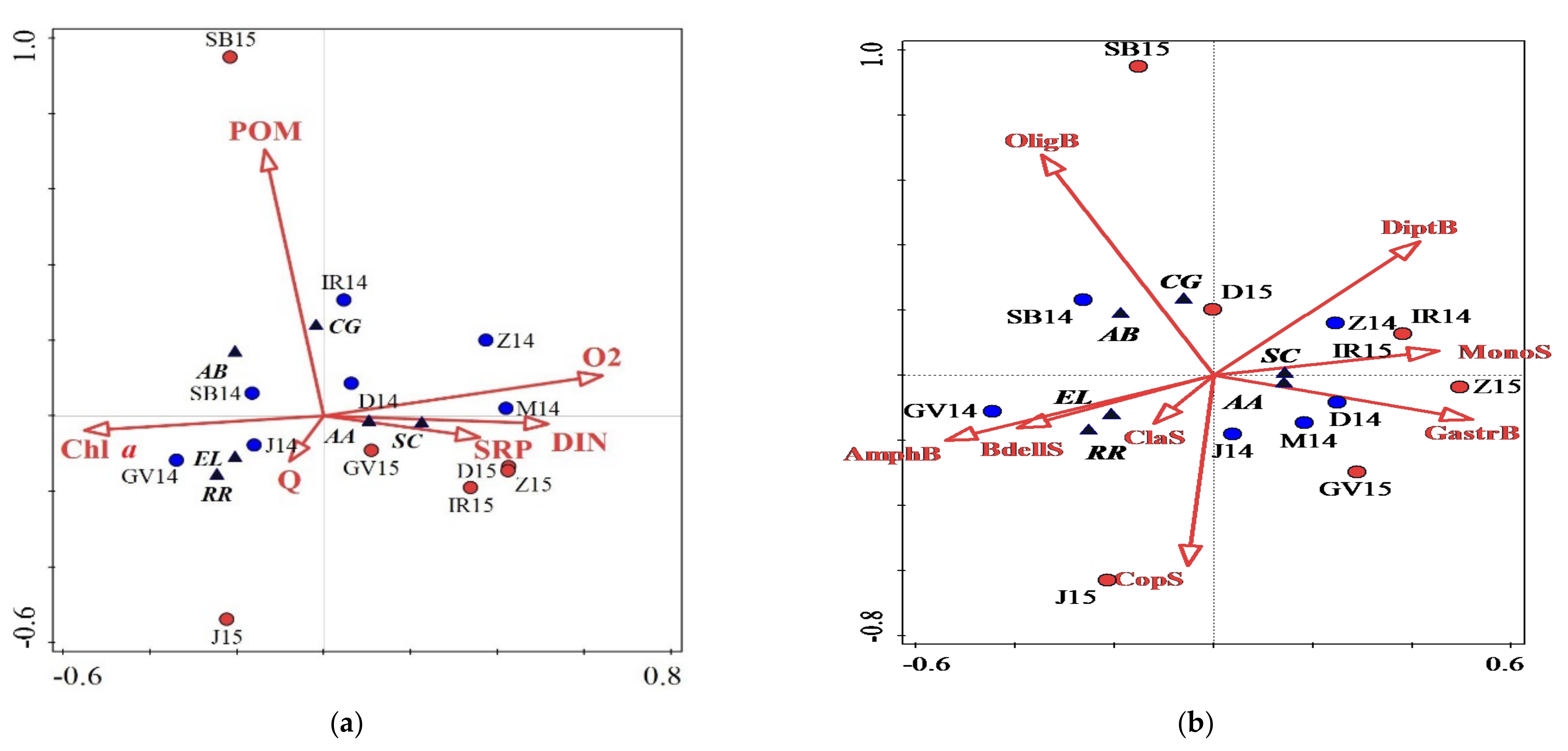
| Sampling Sites (Abbreviations) | Medsave (M) | Zagreb (Z) | Ivanja Reka (IR) | Lijevi Dubrovčak (D) | Jasenovac (J) | Gornji Varoš (GV) | Slavonski Brod (SB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coordinates | 45°50′03.77″ N, 15°46′29.01″ E | 45°47′14.24″ N, 15°59′25.46″ E | 45°46′48.62″ N, 16°08′13.94″ E | 45°38′49.62″ N, 16°20′24.44″ E | 45°16′05.68″ N, 16°54′49.40″ E | 45°08′51.27″ N, 17°14′10.53″ E | 45°08′58.62″ N, 18°00′22.21″ E |
| River (km) | 708 | 682 | 668 | 653 | 516 | 476 | 370 |
| Widthmax (m) | 80 | 85 | 85 | 86 | 112 | 164 | 245 |
| Depth (m) | 0.3–1.1 | 0.4–1.4 | 0.4–1.5 | 0.3–1.0 | 0.4–1.0 | 0.2–1.0 | 0.5–1.3 |
| Flow velocity (ms−1) | 7.00 | 1.50 | 1.50 | 0.6 | 2.70 | 1.00 | 3.00 |
| Tributary (upstream) | Gradna | Krapina | Trebež, Struga, Una | Lonja | Orljava | ||
| Habitat specification | Lotic | Lotic | Lotic | Lentic | Lentic | Lotic | Lentic |
| Anthropogenic impact | wastewater plant inflow | urbanisation, facilitate transport and industry | inflow of treated municipal water of Zagreb city | field leaching | field leaching | field leaching | industrial inflow |
| Bottom granulometry | rip-rap, rocks, gravel | rip-rap, sand | boulders, mud, debris | mud, sand | sand, mud, gravel | mud, rocks, boulders | mud, rocks |
| Macrophyte coverage (%) | None | None | None | None | None | 20% | 40% |
| Year | LQ 2014 | HQ 2015 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Mean ± SD | Min–Max | Mean ± SD | Min–Max |
| Water discharge (m3 s−1) | 341.87 ± 225.59 | 133.00–669.10 | 1217.27 ± 623.16 | 443.20–2166.00 |
| Flow velocity (m s−1) | 0.25 ± 0.25 | 0.06–0.79 | 2.41 ± 2.17 | 0.60–7.00 |
| Temperature (°C) | 21.07 ± 1.00 | 19.90–22.60 | 20.42 ± 3.19 | 16.40–23.30 |
| O2 (mg L−1) | 8.69 ± 3.33 | 5.75–13.42 | 6.47 ± 0.90 | 5.42–7.78 |
| pH | 7.94 ± 0.58 | 6.75–8.51 | 7.82 ± 1.03 | 5.50–8.38 |
| Conductivity (µS cm−1) | 467.71 ± 116.67 | 385.00–724.00 | 411.14 ± 31.07 | 366.00–465.00 |
| N–NH3 (mg L−1) | 0.477 ± 0.642 | 0.040–1.850 | 0.136 ± 0.098 | 0.000–0.260 |
| N–NO2− (mg L−1) | 0.162 ± 0.259 | 0.010–0.730 | 0.174 ± 0.202 | 0.070–0.630 |
| N–NO3− (mg L−1) | 1.265 ± 1.137 | 0.310–3.540 | 5.889 ± 6.976 | 0.010–19.600 |
| PO43− (mg L−1) | 0.260 ± 0.264 | 0.030–0.810 | 2.889 ± 5.227 | 0.280–14.600 |
| Chl a (µg L−1) | 7.442 ± 3.129 | 4.736–14.208 | 5.032 ± 2.257 | 2.101–7.696 |
| POM (mg AFDM L−1) | 153.428 ± 35.518 | 125.333–229.333 | 140.000 ± 44.127 | 100.00–229.333 |
| PIM (mg DM L−1) | 35.714 ± 9.946 | 26.000–56.666 | 77.714 ± 86.727 | 32.666–271.333 |
| Variable | NO3− | PO43− | CG | CE | Amphipoda |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AB | 0.561 | ||||
| EL | 0.606 | ||||
| Seston (ind. L−1) | |||||
| Bdelloidea | −0.727 | −0.573 | |||
| Monogononta | −0.641 | ||||
| Cladocera | 0.542 | 0.696 | |||
| Benthos (ind. m−2) | |||||
| Gastropoda | 0.561 | ||||
| Total invertebrates | 0.552 |
| Interactions | Axis 1 (%) | Axis 2 (%) | Variable | % | F | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fish abundance vs. Env | 52 | 21 | O2 | 23 | 3.3 | 0.03 |
| DIN | 19 | 3.2 | 0.012 | |||
| Chl a | 18 | 2.4 | 0.05 | |||
| POM | 12 | 2.3 | 0.1 | |||
| Q | 9 | 2 | 0.12 | |||
| Fish abundance vs. Invertebrates | 42 | 20 | AmphB | 18 | 2.7 | 0.05 |
| GastrB | 15 | 1.9 | 0.09 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tomljanović, T.; Špoljar, M.; Kattakulov, F.; Radočaj, T.; Matulić, D. Interactions between Fish and Invertebrates in the Lowland Area of the Sava River following Excessive Change in Hydrological Regime. Hydrobiology 2022, 1, 196-210. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrobiology1020015
Tomljanović T, Špoljar M, Kattakulov F, Radočaj T, Matulić D. Interactions between Fish and Invertebrates in the Lowland Area of the Sava River following Excessive Change in Hydrological Regime. Hydrobiology. 2022; 1(2):196-210. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrobiology1020015
Chicago/Turabian StyleTomljanović, Tea, Maria Špoljar, Farrukh Kattakulov, Tena Radočaj, and Daniel Matulić. 2022. "Interactions between Fish and Invertebrates in the Lowland Area of the Sava River following Excessive Change in Hydrological Regime" Hydrobiology 1, no. 2: 196-210. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrobiology1020015
APA StyleTomljanović, T., Špoljar, M., Kattakulov, F., Radočaj, T., & Matulić, D. (2022). Interactions between Fish and Invertebrates in the Lowland Area of the Sava River following Excessive Change in Hydrological Regime. Hydrobiology, 1(2), 196-210. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrobiology1020015







